Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The high-frequency mixed current signals were decomposed using LSTM-DAE. This paper accurately acquired current signals of each load by exploiting the high sensitivity of LSTM to temporal signal features and the ability of DAE to transform load decomposition problems into denoising problems, which were then utilized as the fundamental data for load recognition.
- (2)
- Colored VI trajectories were generated by plotting VI trajectories obtained from multi-cycle voltage and current data. The R channel represented the normal multi-cycle VI trajectory, the G channel represented the current variation slope between adjacent sampling points, and the B channel represented the rate of power changes. Additionally, the VI trajectory background was color processed based on the difference in current amplitude to obtain a multi-cycle color-encoded VI trajectory feature library with filled background colors.
- (3)
- The VI trajectory feature library was transformed into an n×n image format and input into the AlexNet network for training. Since the traditional AlexNet network was not suitable for load recognition tasks, the BOA algorithm was employed to optimize the network parameters, thus achieving better recognition performance.
- (4)
- The PLAID dataset was utilized in the experiments, and the results demonstrated that the selected six load decomposition accuracies all exceeded 94.
2. Related works
3. LSTM-DAE based load decomposition
3.1. Load decomposition
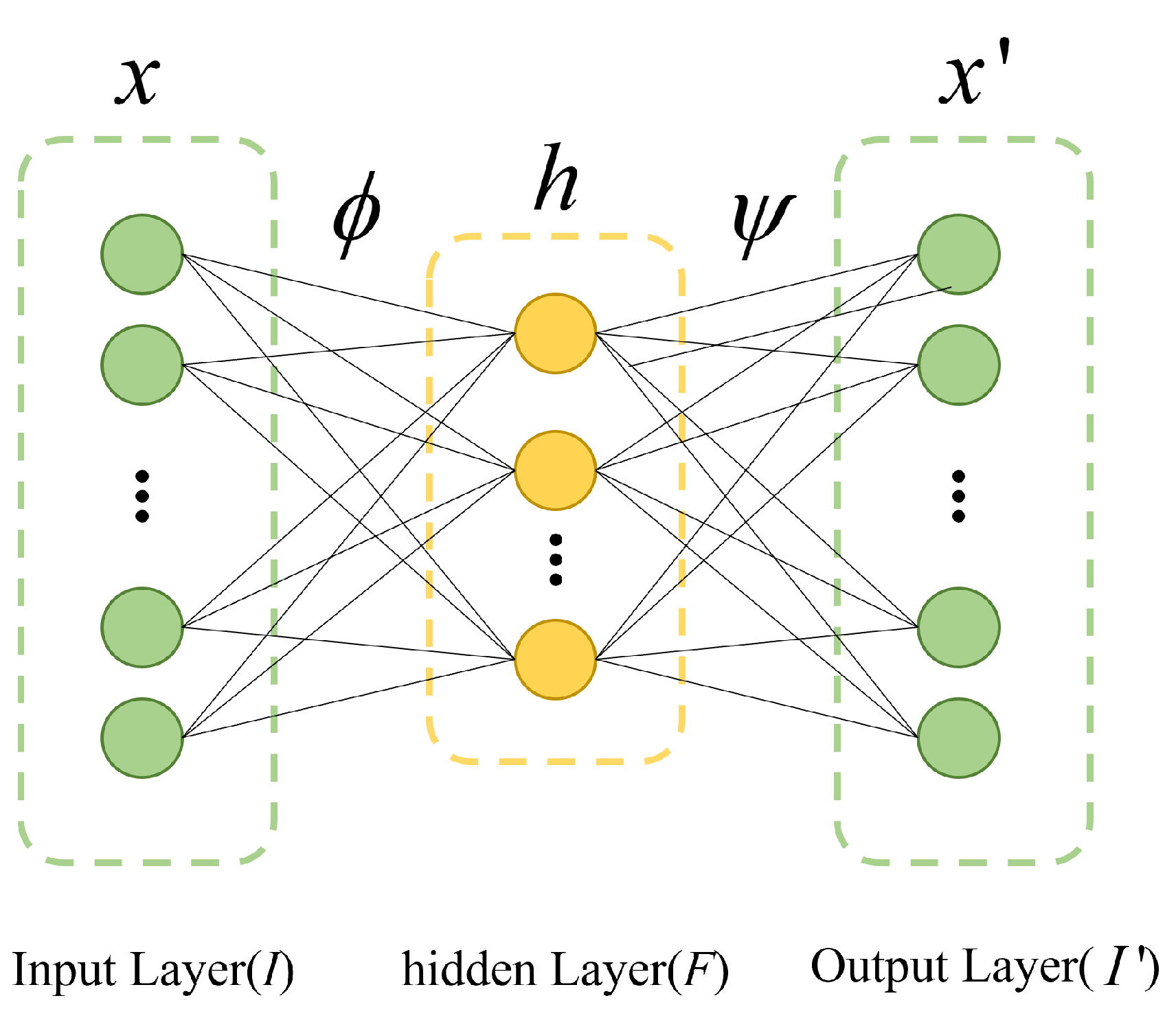
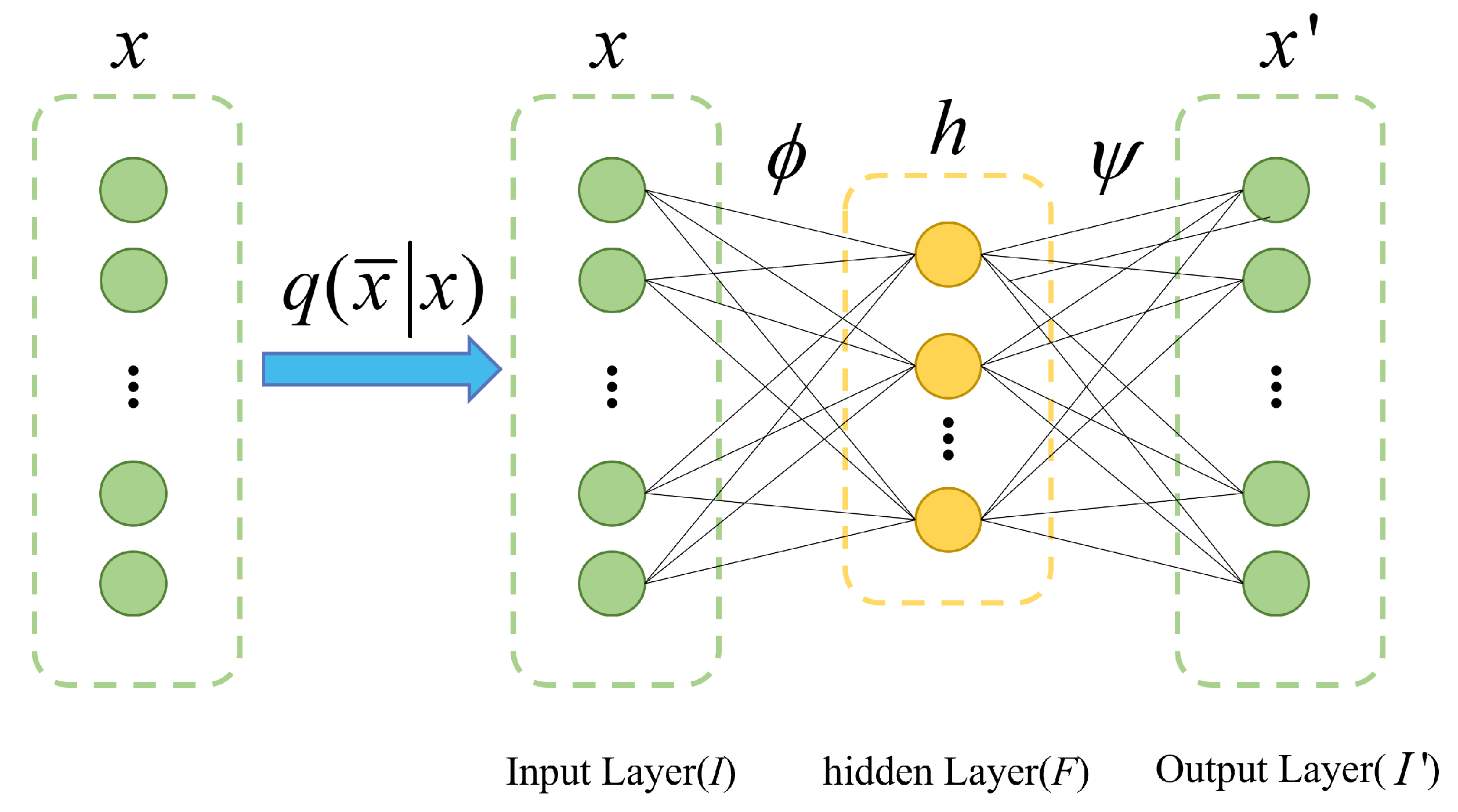
3.2. Denoising Autoencoder
- (1)
- Obtaining corrupted data by adding noise to normal data or randomly discarding parts of normal data was obtained.
- (2)
- Mapping the corrupted data to the low-dimensional hidden feature space by the self-encoder coding process .
- (3)
- The decoder decoded the corrupted data’s mapping in the hidden feature space using Equation 6 and obtained the reconstructed data.
- (4)
- The minimization problem of Equation 7 was solved using the backpropagation algorithm.
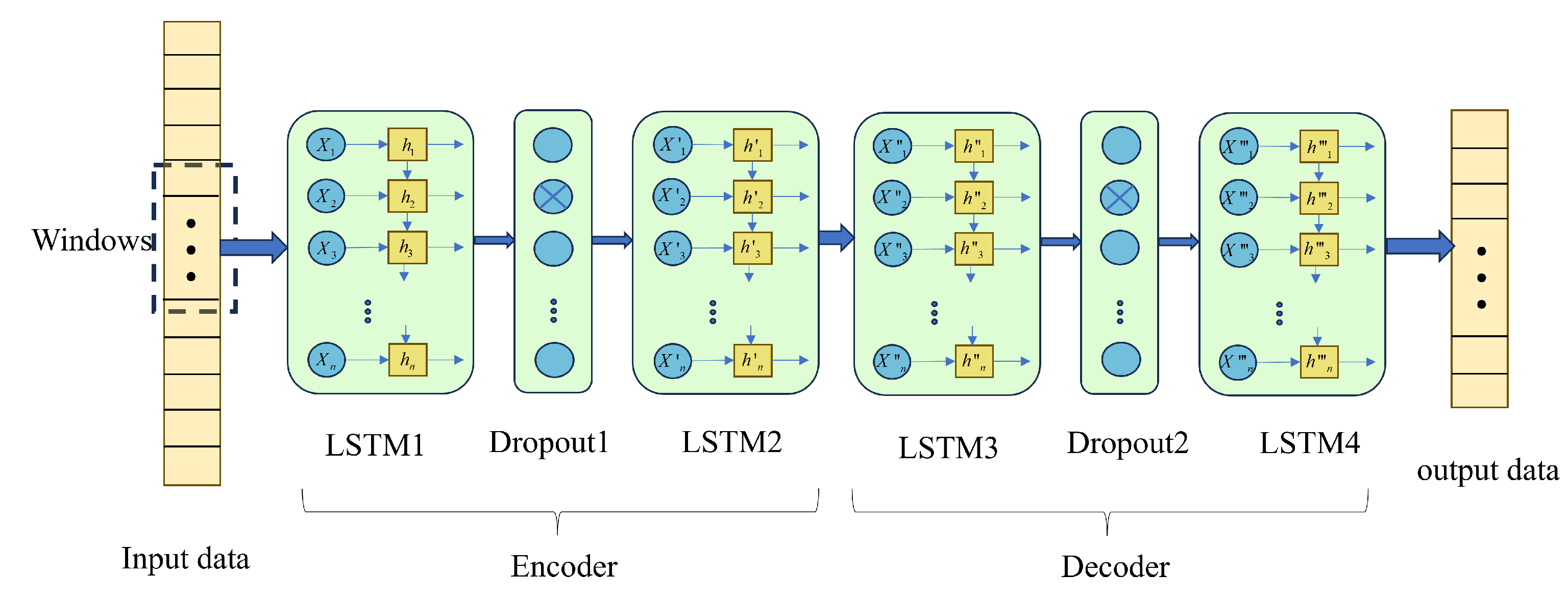
3.3. Decomposition model based on LSTM-DAE
4. Load recognition of VI traces based on background color coding
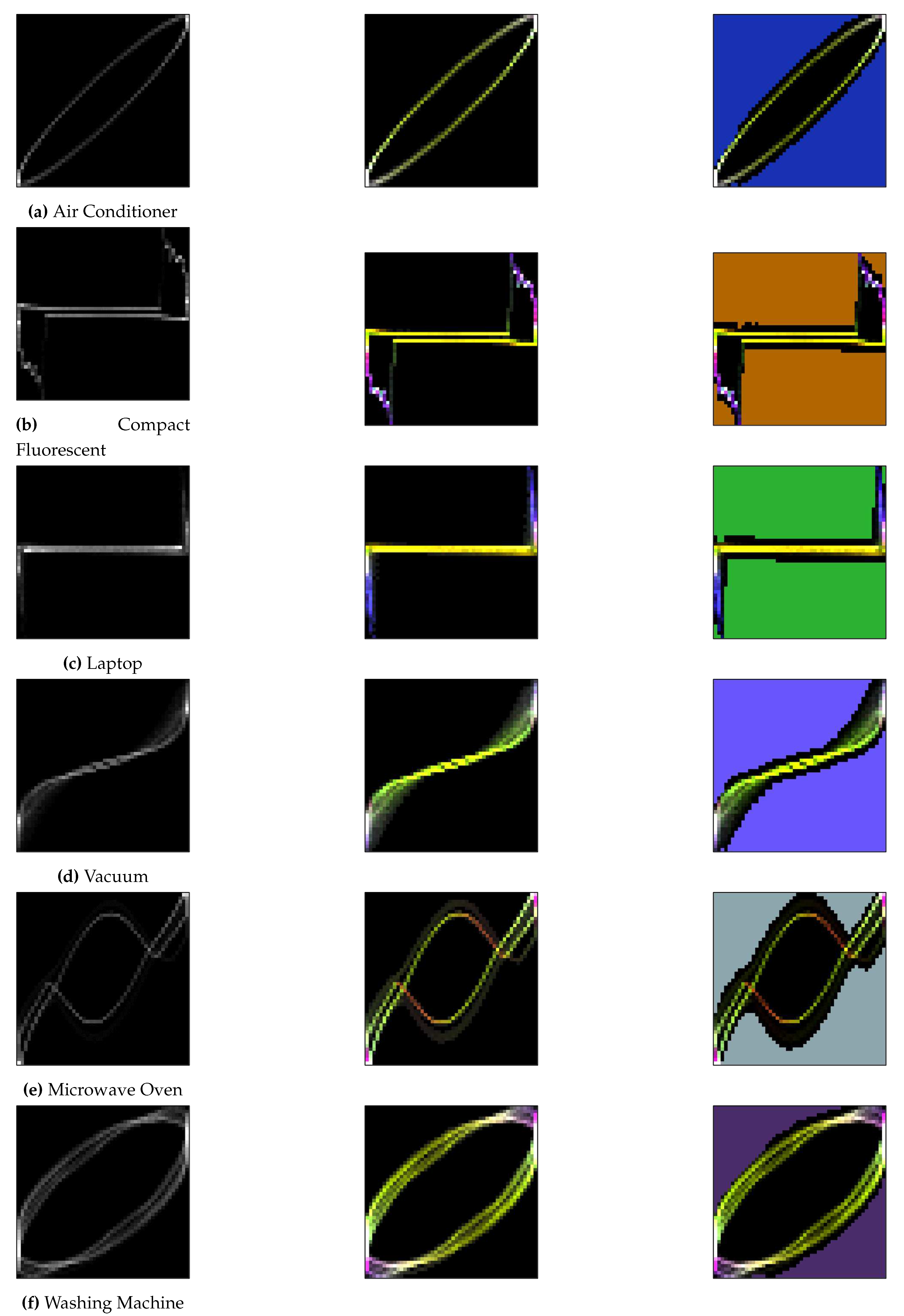
4.1. Construction of VI trajectory pixelization
- (1)
- Conventional VI traces typically analyzed changes in a single cycle, which failed to capture the characteristic changes of the load across different operating cycles. Therefore, the paper proposed to utilize 20 consecutive cycles of current-voltage signals to generate VI traces, aiming to provide a more comprehensive reflection of the changes across different cycles.
- (2)
- Color coding the VI trajectory: the multi-cycle VI trajectory was represented in red (R channel), the slope of the straight line segment between adjacent sampling points of the VI trajectory was represented in green (G channel), and the instantaneous power value was represented in blue (B channel), thereby generating a VI trajectory image with colored tracks.
- (3)
- Due to the significant differences in current amplitude between certain loads while having similar VI trajectories, and considering that current amplitude is an important load characteristic, this paper proposed assigning different colors to the background of VI trajectories based on the varying current amplitudes in order to highlight the differences in current amplitude.
- (1)
- Standardized the voltage and current values, and used the standardized voltage and current data to plot the standardized VI trajectory. The standardization formula was as follows:where was the maximum value of voltage in the steady state sequence and max was the maximum value of current in the steady state sequence. , were the voltage and current values of the mth sampling point in the sequence, and , were the voltage and current values of the mth sampling point after normalization.
- (2)
- Created the VI trajectory using normalized data, and used the created VI trajectory as the R channel of the colored VI trajectory.
- (3)
- Created the G channel by mapping the slope of the straight line segments to the (0,1) range using the function.where was the slope of the jth straight line segment and was the G-channel depth value of the jth straight line segment. The was mapped to the VI trajectory to obtain the corresponding G-channel depth value for each grid, which was then normalized to obtain the G-channel value for each grid point.
- (4)
-
The B channel was created with the following instantaneous power values:After the multi-cycle power values were computed and mesh stacked, they were normalized again.where was the instantaneous power value, was the power superimposed on each grid in the grid, max P was the maximum value of power in all the grids, and the resulting was the value of the B channel.
- (5)
- For the addition of the background color, the average of the RMS values of the current energy of the 25 adjacent cycles was obtained and matched with the set background color to determine the background color.
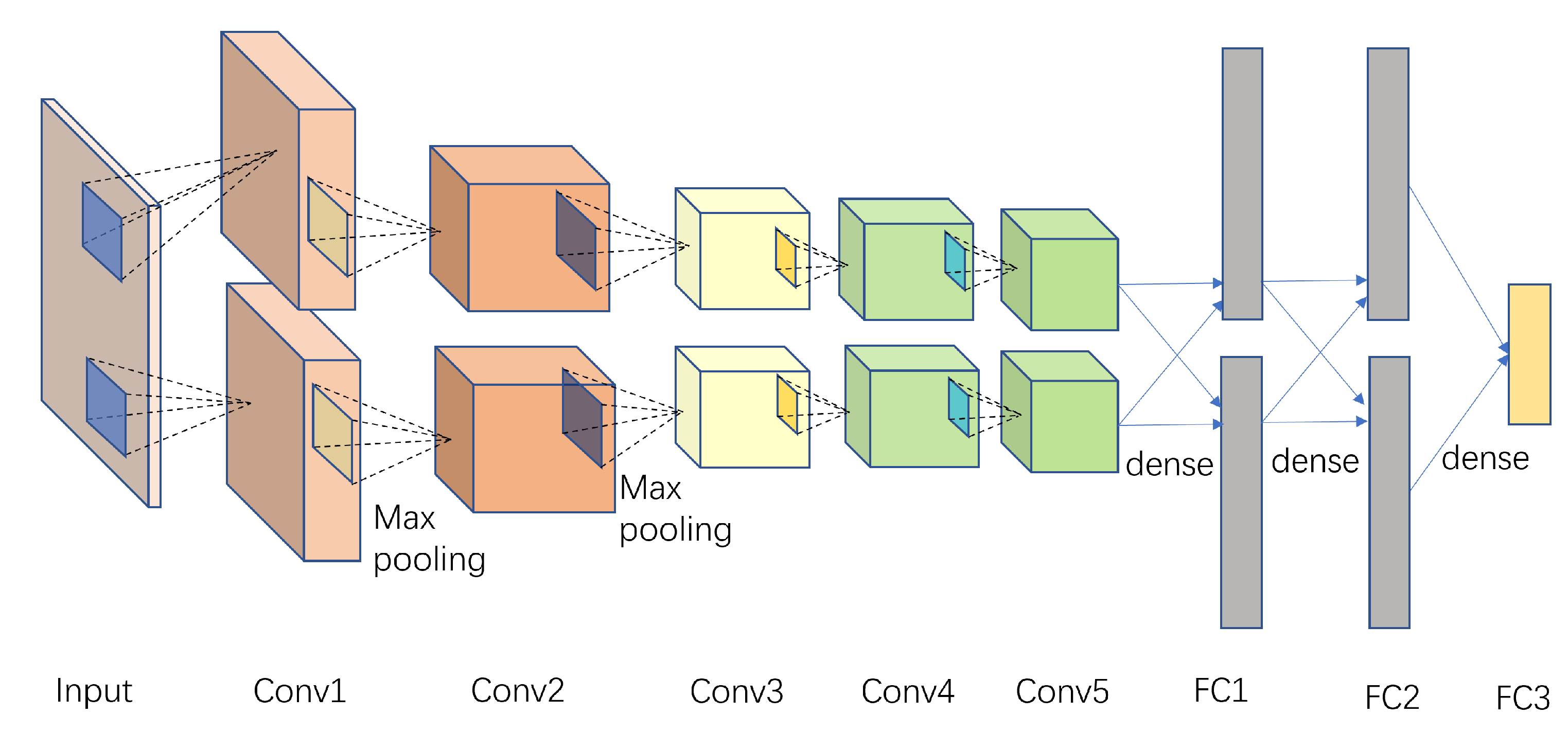
4.2. Construction of convolutional neural network
4.3. Bayesian optimization algorithm
5. Experimental analysis
5.1. Data set and evaluation criteria
5.2. Assessment of indicators
5.2.1. Evaluation indexes of decomposition process
5.2.2. Evaluation metrics for load recognition process
5.3. Example analysis
5.3.1. Load decomposition
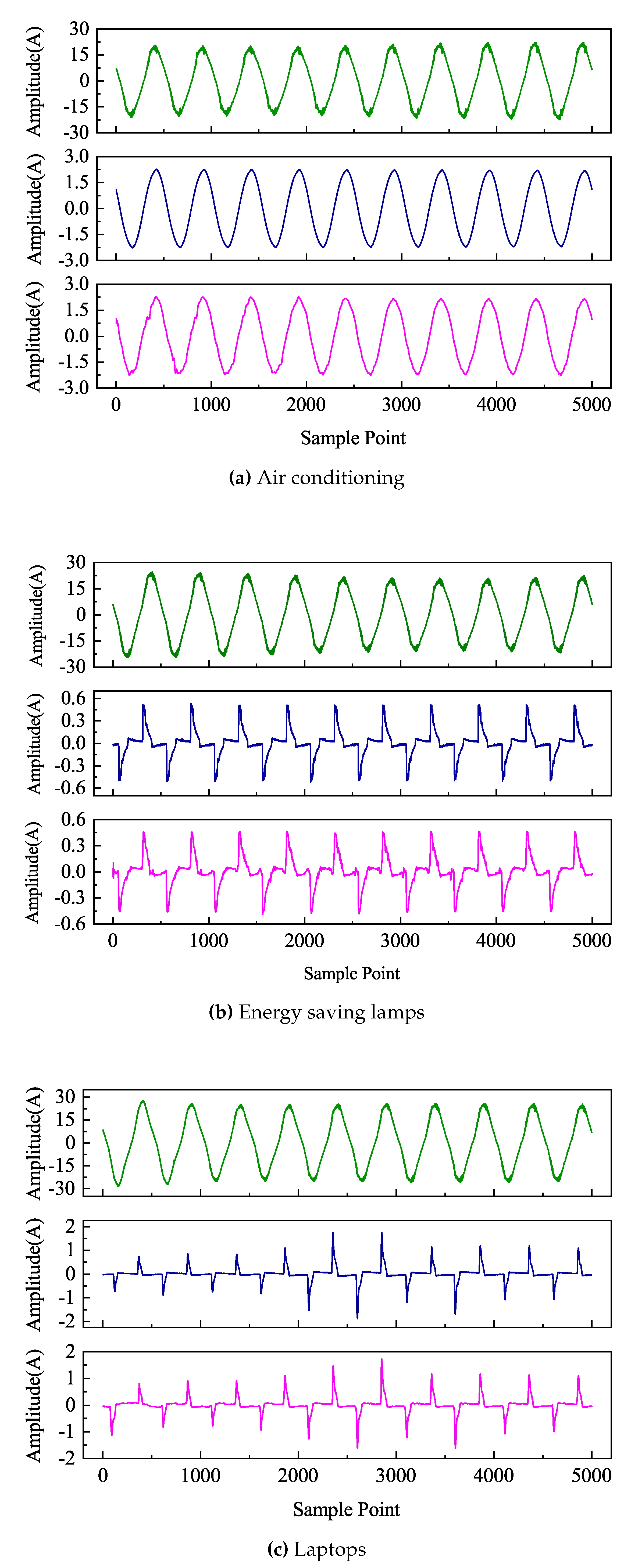
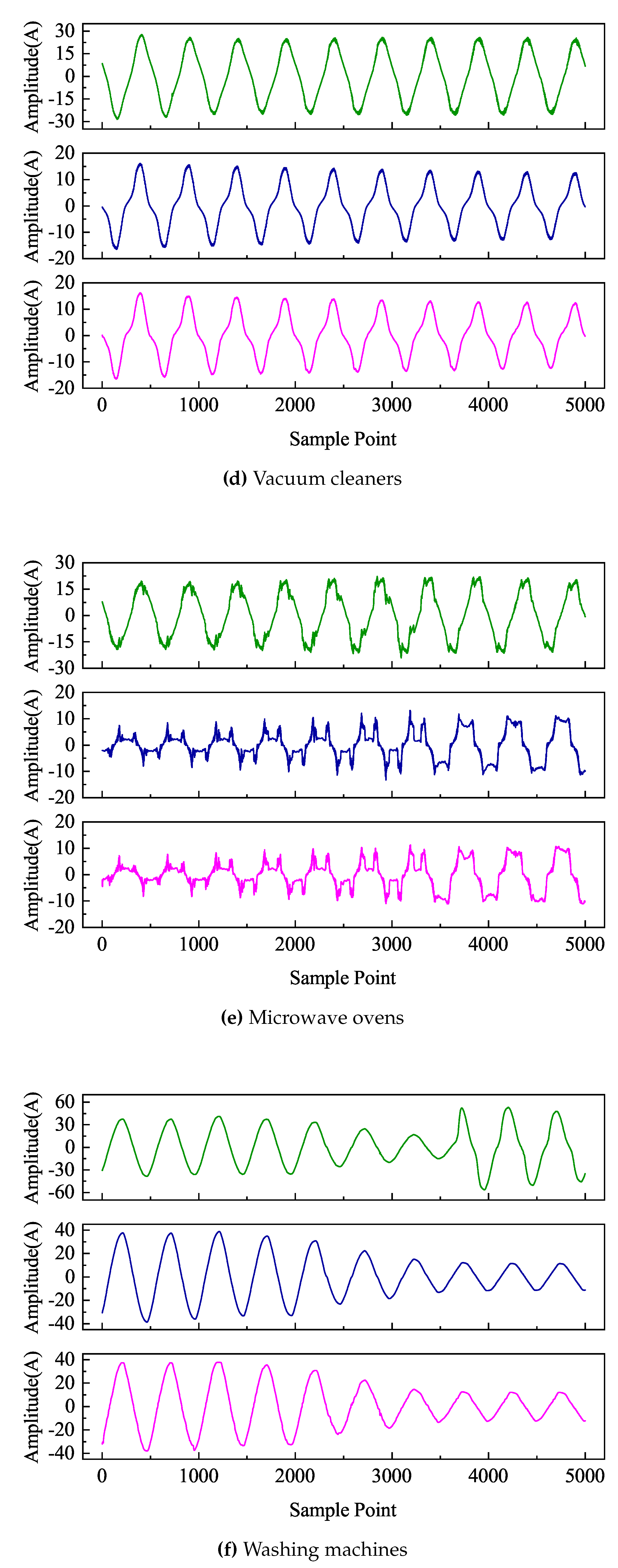
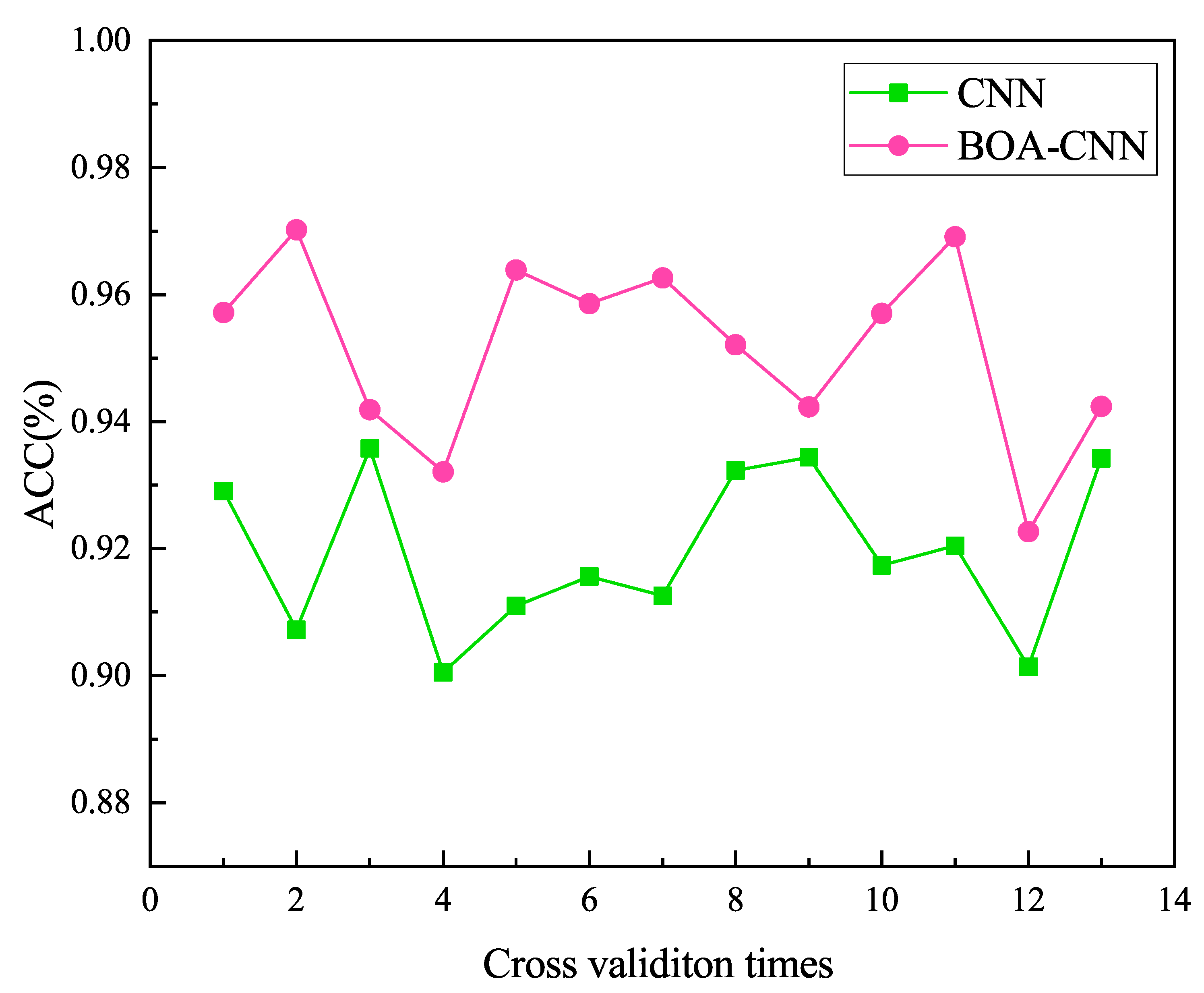
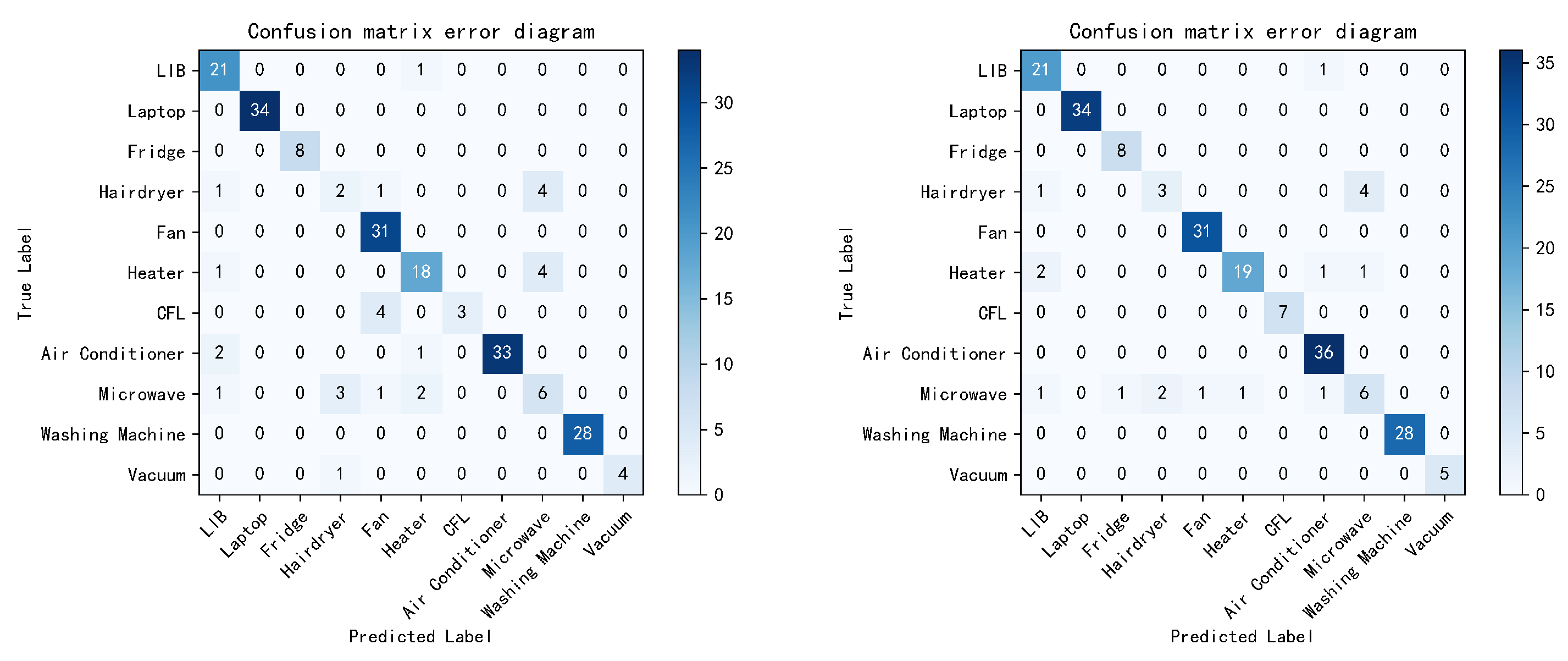
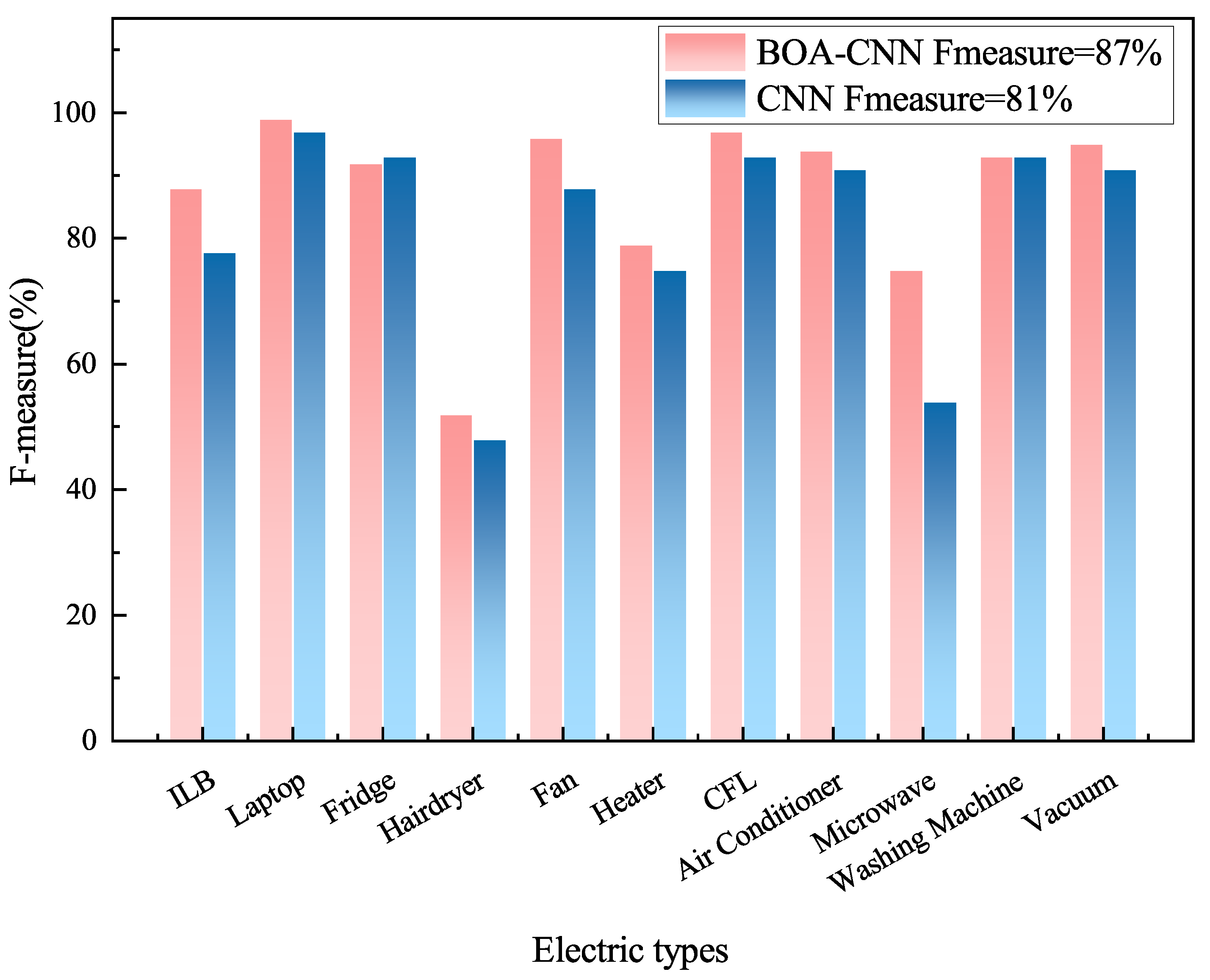
5.3.2. Load Recognition
6. Summarize
References
- Yang, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, G. Survey ondemand response mechanism and modeling in smart grid. Power System Technology 2016 , 40, 220–226.
- Qi, B.; Liu, L.; Han, L.; et al. Home appliance load identification algorithm based on system model. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation2018 , 55, 23–30.
- Zhang, G.; Wei, Q.; et al. A survey on the non-intrusive load monitoring. Acta Automatica Sinica2022 , 48, 644–663.
- Li, P. Non-intrusive method for power load disaggregation and monitoring. Master, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2009.
- Liu, Y .; Qiu, J.; Ma, J. SAMNet: Toward Latency-Free Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring via Multi-Task Deep Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid2022 , 13, 2412–2424. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Marwah, M.; Arlitt, M.; et al. Unsupervised Disaggregation of Low Frequency Power Measurements. Proceedings of the 2011 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, SIAM, 2011.
- Kolter, Z.; Jaakkola, T.; Kolter, J. Z. Approximate Inference in Additive Factorial HMMs with Application to Energy Disaggregation. Journal of Machine Learning Research2012 , 22, 1472–1482.
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; et. al. Transfer learning for multi-objective non-intrusive load monitoring in smart building. Applied Energy2023 , 329, 1472–1482. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Marwah, M.; Arlitt, M.; et.al. Neural NILM: Deep Neural Networks Applied to Energy Disaggregation. ACM International Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy Efficient Built Environments BuildSys, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, November 4, 2015.
- Roberto, B.; Felicetti, A.; Principi, E. Denoising Autoencoders for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring: Improvements and Comparative Evaluation. Energy and Buildings2018 , 158, 1461–1474.
- Odysseas, K.; Christoforos, N.; Dimitris, V. Sliding Window Approach for Online Energy Disaggregation Using Artificial Neural Networks. 10th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Patras, Greece, July 9, 2018.
- Zhang, C.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.; et.al. Sequence-To-Point Learning with Neural Networks for non-intrusive Load Monitoring. non-intrusive, non-intrusive, July 9, 2018, February 2, 2018.
- Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Cui, K. Non-intrusive load decomposition algorithm based on convolution block attention model. Power System Technology2021 , 45, 3700–3705.
- Piccialli, V,; Sudoso, A. Improving Non-Intrusive Load Disaggregation through an Attention-Based Deep Neural Network. Energies2021 , 41.
- Piccialli, V,; Sudoso, A.A nonintrusive recognition method of household load behavior based on DTW algorithm. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation2019 , 56, 17–22.
- Zhu, H.; Cao, N,; Lu, H.; et al. Non-intrusive load identification method based on feature weighted KNN. Electronic Measurement Technology2022 , 56, 70–75.
- Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xue, T.; et al. Non-intrusive load monitoring algorithm based on attention mechanism combined with global and sliding window. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation2021, 1–8.
- Yu, D.; Liu, M. A non-invasive load decomposiontion method base on deep circular convolutional model. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation2020, 57, 47–53.
- Lam, H.Y.; Fung, G.S.K.; Lee, W.K. A novel method to construct taxonomy electrical appliances based on load signatures. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics2007, 53, 653–660. [CrossRef]
- Bates, L. D.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; et al. Automated classification of appliances using elliptical fourier descriptors. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Dresden, Germany, October 23, 2017.
- Hassan, T.; Javed, F.; Arshad, N. An Empirical Investigation of VI Trajectory Based Load Signatures for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid2014, 5, 870–878. [CrossRef]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; et al. A Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, July 5, 2008.
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Bayesian-based novel deep learning hyperparameter optimization. Data Communications2019, 2, 35–38.
- Jones, D.; Schonlau, M.; Welch, W. Bayesian-based novel deep learning hyperparameter optimization. Journal of Global Optimization1998, 13, 455–492. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; et al. MagConv: Mask-Guided Convolution for Image Inpainting.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing2023, 32, 4716–4727. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, H.; Luo, X. A supervised event based non-intrusive load monitoring for non-linear appliances.Sustainability2018, 10. [CrossRef]
- De Baters, L.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; et al. Automated classification of appliances using elliptical fourier descriptors. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Dresden, Germany, October 23, 2017.
- Gao, J.; Kara, E.; Giri, S.; et al. A feasibility study of automated plug-load identification from high-frequency measurements. IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Orlando, FL, United states, December 13, 2015.
- Cui, H. Non-intrusive load monitoring and decomposition technology based on deep learning and application of typical scenarios. Master, Northeast Electric Power University, Dalian, China, 2023.
| Layers | Hyperparameters | Dynamic range |
|---|---|---|
| Number of convolution kernels | 30 ∼ 135 | |
| Conv | Convolution kernels size | 2 ∼ 6 |
| Convolution kernels step | 1 ∼ 3 | |
| Pool | Pool core size | 2 ∼ 6 |
| Pool nucleation step size | 1 ∼ 3 | |
| Dropout | Dropout rate | 0 ∼ 1 |
| Layers | Hyperparameters |
|---|---|
| a1,a2,a3,a4,a5 | The number of convolution kernels in five convolutional layers |
| b1,b2,b3,b4,b5 | Convolutional kernel size for five convolutional layers |
| c1,c2,c3,c4,c5 | Convolutional kernel step size for five convolution layers |
| d1,d2,d3 | The number of pooling kernels in the three pooling layers |
| e1,e2,e3 | Step size of pooling kernels in three pooling layers |
| f1,f2 | Dropout rate of the two layers |
| Load Type | RMSE | MAE | Phase Error | Correlation Coefficient(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air conditioner | 0.109 | 0.081 | 0.068 | 99.8 |
| Energy-saving lamps | 0.033 | 0.020 | 0.196 | 98.1 |
| Notebook | 0.097 | 0.040 | 0.332 | 94.5 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 0.295 | 0.220 | 0.035 | 99.9 |
| Microwave Oven | 0.668 | 0.456 | 0.129 | 99.2 |
| Washing Machines | 0.866 | 0.551 | 0.046 | 99.9 |
| Catagory | CNN | BOA-CNN |
|---|---|---|
| Conv1 | 3×3/48/1 | 4×4/60/1 |
| Pool1 | 3×3/2 | 2×2/1 |
| Conv2 | 5×5/128/2 | 4×4/121/1 |
| Pool2 | 3×3/2 | 2×2/1 |
| Conv3 | 3×3/192/1 | 4×4/126/1 |
| Conv4 | 3×3/192/1 | 3×3/55/1 |
| Conv5 | 3×3/192/1 | 3×3/125/1 |
| Droout1 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Droout1 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





