Submitted:
15 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants and Milk Sampling
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Prospective Study
3.2. Relationship between HMO Profiles and Weight Growth Indicators of Infants Aged 0–4 Months
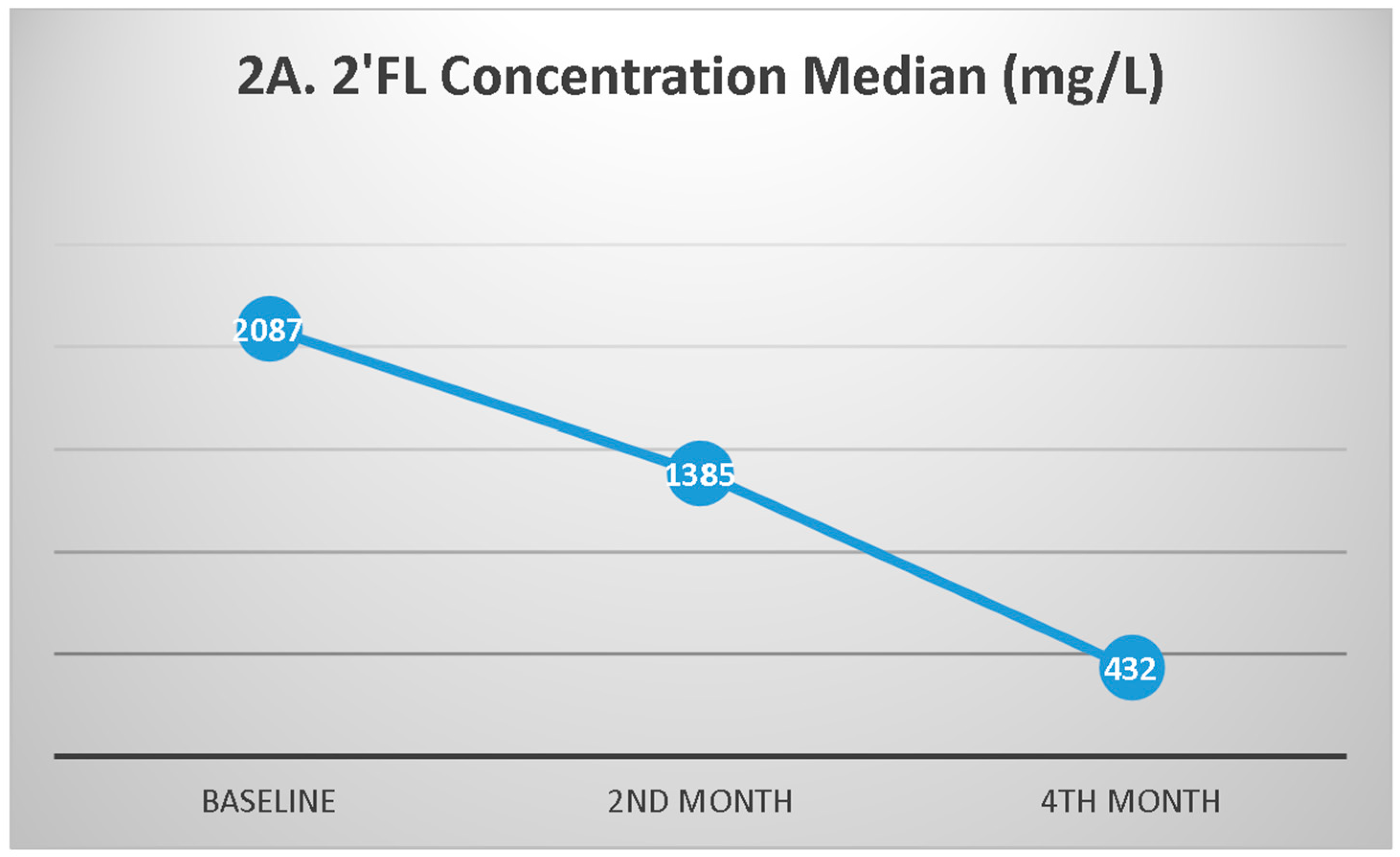
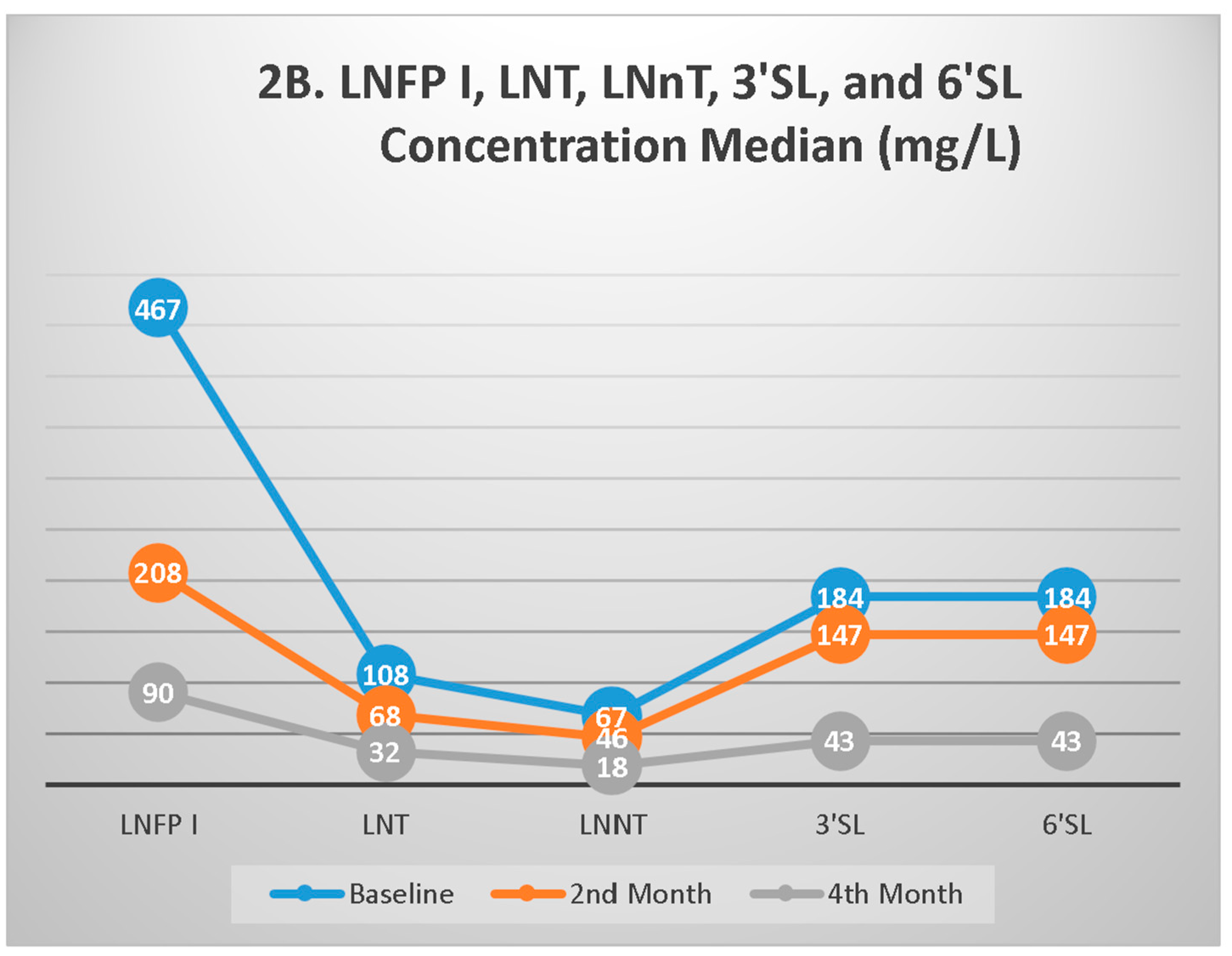
3.3. HMO Profiles During Follow-up
3.4. The Difference in HMO Profiles between Secretor Status
4. Discussion
4.1. Secretor Status
4.2. Relationship between HMO Profiles and Weight Growth Indicators in Infants Aged 0–4 Months
4.3. The Changes in HMOs During Follow-Up
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, C.; Ling, P.R.; Blackburn. G. Review of Infant Feeding: Key Features of Breast Milk and Infant Formula. Nutrients 2016, 118(5), 279. [CrossRef]
- Bode, L. Human milk oligosaccharides: Every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology 2012, 1;22(9), 1147–62. [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, O.; Zampini, L.; Galeazzi, T; Padella, L.; Santoro, L.; Peila, C. et al. Preterm Milk Oligosaccharides During the First Month of Lactation. PEDIATRICS 2011, 1; 128(6), e1520–31. [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; De Castro, C.; Bénet, T.; Hou, Y.; Sun, H.; Thakkar, S. et al. Temporal Change of the Content of 10 Oligosaccharides in the Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers. Nutrients 2016, 8;8(6), 346. [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.W.; Lind, M.V.; Laursen, R.P.; Yonemitsu, C.; Larnkjær, A.; Mølgaard, C. et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Composition Is Associated With Excessive Weight Gain During Exclusive Breastfeeding—An Explorative Study. Front Pediatr, 2019, 18;7, 297. [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C.C.; Lewis, Z.T.; Krishnan, S.; Bernstein, R.M, Moore, S.E.; Prentice, A.M. et al. Growth and Morbidity of Gambian Infants are Influenced by Maternal Milk Oligosaccharides and Infant Gut Microbiota. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1), 40466. [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, N.; Lee, L.Y.; De Castro, C.A.; Steenhout, P.; Thakkar, S.K. Longitudinal change of selected human milk oligosaccharides and association to infants’ growth, an observatory, single center, longitudinal cohort study. PLOS ONE, 2017, 9;12(2), e0171814. [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, N.; Odenwald, H.; Kukkonen, A.K.; Kuitunen, M.; Savilahti, E.; Kunz, C. FUT2-dependent breast milk oligosaccharides and allergy at 2 and 5 years of age in infants with high hereditary allergy risk. Eur J Nutr, 2017, 56(3), 1293–301. [CrossRef]
- Saboor, M.; Ullah, A.; Qamar, K.; Mir, A.; and Moinuddin. Frequency of ABH secretors and non secretors: A cross sectional study in Karachi. Pak J Med Sci, 2014, 30(1), 189–93. [CrossRef]
- Bode, L. The functional biology of human milk oligosaccharides. Early Hum Dev, 2015, 91(11), 619–22. [CrossRef]
- Castanys-Muñoz, E.; Martin, M.J.; Prieto, P.A. 2’-fucosyllactose: an abundant, genetically determined soluble glycan present in human milk. Nutr Rev, 2013, 71(12), 773–89. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Infant and young child feeding [Internet]. [cited 2019 Nov 2]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding.
- Fewtrell, M.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fidler Mis, N. et al. Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2017, 64(1), 119–32. [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Gregory, J.W. Physiology of normal growth. Paediatr Child Health, 2009, 19(5), 236–40. [CrossRef]
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards: Methods and Development. Length/height-for-age, weightfor-age, weight-for-length, weight-for-height and body mass index-for age: methods and development. [Internet]. Available from: http://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/technical_report/en/index.html.
- Lewis, Z.T.; Totten, S.M.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Popovic, M.; Parker, E.; Lemay, D.G. et al. Maternal fucosyltransferase 2 status affects the gut bifidobacterial communities of breastfed infants. Microbiome, 2015, 3(1), 13. [CrossRef]
- Hoeflinger, J.L.; Davis, S.R.; Chow, J.; Miller, M.J. In Vitro Impact of Human Milk Oligosaccharides on Enterobacteriaceae Growth. J Agric Food Chem, 2015, 63(12), 3295–302. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; van’t Land, B.; Engen, P.A.; Naqib, A.; Green, S.J.; Nato, A. et al. Human milk oligosaccharides protect against the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD-mice. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1), 3829. [CrossRef]
- Sudarma, V.; Sunardi, D.; Marzuki, N.S.; Munasir, Z.; Asmarinah.; Hidayat, A.; Hegar, B. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Profiles and the Secretor and Lewis Gene Status of Indonesian Lactating Mothers. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr, 2023, 26(5), 266-276. [CrossRef]
- Thurl, S.; Munzert, M.; Henker, J.; Boehm, G.; Müller-Werner, B.; Jelinek, J. et al. Variation of human milk oligosaccharides in relation to milk groups and lactational periods. Br J Nutr, 2010, 14;104(9), 1261–71. [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Kunz, C.; Rudloff, S.; García-Mantrana, I.; Crehuá-Gaudiza, E. Martínez-Costa, C. et al. Association of Maternal Secretor Status and Human Milk Oligosaccharides With Milk Microbiota: An Observational Pilot Study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 68(2), 256–63. [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; De Castro, C.A.; Sprenger, N.; Binia, A.; Affolter, M.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.L. et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharides in the Milk of Mothers Delivering Term versus Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 2019, 5;11(6), 1282. [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Robertson, B.; Atakora, F.; Becker, A.B.; Subbarao, P.; Moraes, T.J. et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Concentrations Are Associated with Multiple Fixed and Modifiable Maternal Characteristics, Environmental Factors, and Feeding Practices. J Nutr, 2018, 1;148(11), 1733–42. [CrossRef]
- Günaydın, G.; Nordgren, J.; Sharma, S.; Hammarström, L. Association of elevated rotavirus-specific antibody titers with HBGA secretor status in Swedish individuals: The FUT2 gene as a putative susceptibility determinant for infection. Virus Res, 2016, 211, 64–8. [CrossRef]
- Paganini, D.; Uyoga, M.A.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Boekhorst, J.; Schneeberger, S.; Karanja, S. et al. Maternal Human Milk Oligosaccharide Profile Modulates the Impact of an Intervention with Iron and Galacto-Oligosaccharides in Kenyan Infants. Nutrients, 2019, 29;11(11), 2596. [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Berger, B.; Carnielli, V.; Ksiazyk, J.; Lagström, H.; Sanchez Luna, M. et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: 2′-Fucosyllactose (2′-FL) and Lacto-N-Neotetraose (LNnT) in Infant Formula. Nutrients, 2018, 24;10(9), 1161. [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.K.; Meehan, C.L.; McGuire, M.A.; Brooker, S.L.; Kamau-Mbuthia, E.W. et al. Key genetic variants associated with variation of milk oligosaccharides from diverse human populations. Genomics, 2021, 113(4), 1867–75. [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.; Carvalho, A.S.; Guillon, P.; Seixas, S.; Azevedo, M.; Almeida, R. et al. Infection-associated FUT2 (Fucosyltransferase 2) genetic variation and impact on functionality assessed by in vivo studies. Glycoconj J, 2010, 27(1), 61–8. [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, N.; Tytgat, H.L.P.; Binia, A.; Austin, S.; Singhal, A. Biology of human milk oligosaccharides: From basic science to clinical evidence. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2022, 35(2), 280–99. [CrossRef]
- Lagström, H.; Rautava, S.; Ollila, H.; Kaljonen, A.; Turta, O.; Mäkelä, J. et al. Associations between human milk oligosaccharides and growth in infancy and early childhood. Am J Clin Nutr, 2020, 1;111(4), 769–78. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Goodson, M.; Vang, W.; Kalanetra, K.; Barile, D.; Raybould, H. 2′-Fucosyllactose Supplementation Improves Gut-Brain Signaling and Diet-Induced Obese Phenotype and Changes the Gut Microbiota in High Fat-Fed Mice. Nutrients, 2020, 5;12(4), 1003. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, O.B. et al. Comparison of the gut microbiota profile in breast-fed and formula-fed Korean infants using pyrosequencing. Nutr Res Pract, 2015;9(3),242. [CrossRef]
- Soyyılmaz, B.; Mikš, M.H.; Röhrig, C.H.; Matwiejuk, M.; Meszaros-Matwiejuk, A.; Vigsnæs, L.K. The Mean of Milk: A Review of Human Milk Oligosaccharide Concentrations throughout Lactation. Nutrients, 2021, 9;13(8), 2737. [CrossRef]
- Samuel, T.M.; Binia, A.; de Castro, C.A.; Thakkar, S.K.; Billeaud, C.; Agosti, M. et al. Impact of maternal characteristics on human milk oligosaccharide composition over the first 4 months of lactation in a cohort of healthy European mothers. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1), 11767. [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Schols, H.A.; van den Heuvel, EGHM.; Voragen, A.G.J.; Gruppen, H. Occurrence of oligosaccharides in feces of breast-fed babies in their first six months of life and the corresponding breast milk. Carbohydr Res, 2011, 346(16), 2540–50. [CrossRef]
- Labbok, M.H.; Clark, D.; Goldman, A.S. Breastfeeding: maintaining an irreplaceable immunological resource. Nat Rev Immunol, 2004, 4(7), 565–72. [CrossRef]
- Kunz, C.; Rudloff, S.; Baier, W.; Klein, N.; Strobel, S. Oligosaccharides in human milk: structural, functional, and metabolic aspects. Annu Rev Nutr 2000, 20, 699–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayechu-Muruzabal, V.; van Stigt, A.H.; Mank, M.; Willemsen, L.E.M.; Stahl, B.; Garssen, J. et al. Diversity of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Effects on Early Life Immune Development. Front Pediatr, 2018, 10;6, 239. [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | n (%) |
| Maternal variables | |
| Nutritional status | |
| BMI<25 kg/m2 | 79 (65.8) |
| BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 41 (34.2) |
| Economic status | |
| Low-middle income | 61 (50.8) |
| High-income | 59 (49.2) |
| All | Secretor Positive | Weak Secretor | ||||
| r | p-value | r | p-value | r | p-value | |
| WAZ Baseline | ||||||
| 2’FL | -0.145 | 0.113 | -0.205 | 0.089 | -0.029 | 0.840 |
| LNFP I | -0.068 | 0.459 | -0.971 | 0.558 | 0.021 | 0.883 |
| LNT | 0.048 | 0.601 | 0.098 | 0.419 | -0.010 | 0.944 |
| LNnT | 0.060 | 0.517 | 0.061 | 0.618 | 0.092 | 0.527 |
| 3’SL | 0.043 | 0.641 | 0.150 | 0.216 | -0.066 | 0.650 |
| 6’SL | 0.053 | 0.567 | 0.164 | 0.175 | -0.067 | 0.643 |
| WAZ 2nd month | ||||||
| 2’FL | -0.131 | 0.162 | -0.294 | 0.016* | 0.142 | 0.331 |
| LNFP I | -0.094 | 0.313 | -0.157 | 0.204 | -0.091 | 0.536 |
| LNT | 0.036 | 0.701 | 0.083 | 0.506 | -0.101 | 0.489 |
| LNnT | 0.016 | 0.865 | -0.005 | 0.968 | -0.061 | 0.680 |
| 3’SL | 0.018 | 0.850 | -0.071 | 0.570 | 0.105 | 0.471 |
| 6’SL | 0.014 | 0.879 | -0.074 | 0.550 | 0.104 | 0.478 |
| WAZ 4th month | ||||||
| 2’FL | 0.028 | 0.768 | -0.157 | 0.204 | 0.359 | 0.013* |
| LNFP I | -0.019 | 0.839 | 0.016 | 0.895 | -0.052 | 0.728 |
| LNT | -0.006 | 0.947 | 0.071 | 0.568 | -0.157 | 0.291 |
| LNnT | 0.030 | 0.751 | 0.003 | 0.978 | -0.043 | 0.774 |
| 3’SL | -0.089 | 0.344 | -0.063 | 0.613 | -0.113 | 0.450 |
| 6’SL | -0.080 | 0.400 | -0.061 | 0.623 | -0.089 | 0.552 |
| WLZ 0 month | ||||||
| 2’FL | -0.033 | 0.720 | -0.033 | 0.786 | 0.044 | 0.759 |
| LNFP I | -0.081 | 0.381 | -0.209 | 0.082 | 0.150 | 0.298 |
| LNT | 0.001 | 0.993 | -0.030 | 0.807 | 0.004 | 0.977 |
| LNnT | -0.032 | 0.726 | -0.067 | 0.579 | 0.047 | 0.745 |
| 3’SL | 0.038 | 0.676 | 0.064 | 0.596 | -0.029 | 0.842 |
| 6’SL | 0.034 | 0.712 | 0.059 | 0.629 | -0.025 | 0.863 |
| WLZ 2nd month | ||||||
| 2’FL | 0.002 | 0.984 | -0.229 | 0.063 | 0.338 | 0.018* |
| LNFP I | -0.002 | 0.819 | 0.273 | 0.437 | -0.171 | 0.240 |
| LNT | 0.105 | 0.262 | 0.131 | 0.025* | -0.080 | 0.587 |
| LNnT | 0.044 | 0.636 | 0.096 | 0.289 | -0.070 | 0.631 |
| 3’SL | 0.043 | 0.684 | 0.115 | 0.352 | 0.022 | 0.879 |
| 6’SL | 0.031 | 0.742 | 0.101 | 0.416 | 0.020 | 0.894 |
| WLZ 4th month | ||||||
| 2’FL | 0.040 | 0.672 | -0.127 | 0.306 | 0.292 | 0.046* |
| LNFP I | 0.072 | 0.449 | 0.163 | 0.188 | -0.054 | 0.718 |
| LNT | 0.069 | 0.468 | 0.198 | 0.107 | -0.148 | 0.321 |
| LNnT | 0.118 | 0.210 | 0.216 | 0.079 | -0.004 | 0.981 |
| 3’SL | 0.062 | 0.511 | 0.108 | 0.386 | -0.004 | 0.979 |
| 6’SL | 0.053 | 0.574 | 0.108 | 0.384 | -0.029 | 0.844 |
|
WV 2nd month (total g/2 mo) |
||||||
| 2’FL | -0.045 | 0.663 | -0.161 | 0.193 | 0.062 | 0.672 |
| LNFP I | -0.091 | 0.330 | -0.143 | 0.249 | -0.105 | 0.474 |
| LNT | -0.016 | 0.867 | 0.048 | 0.700 | -0.174 | 0.231 |
| LNnT | -0.020 | 0.833 | -0.011 | 0.929 | -0.156 | 0.285 |
| 3’SL | 0.111 | 0.233 | -0.001 | 0.991 | -0.016 | 0.914 |
| 6’SL | 0.101 | 0.281 | -0.005 | 0.968 | -0.012 | 0.933 |
| Se+Le+ | Se+Le- | |||
| r | p-value | r | p-value | |
| WAZ Baseline | ||||
| 2’FL | -0.083 | 0.406 | -0.525 | 0.025* |
| LNFP I | -0.098 | 0.328 | 1 | 0.693 |
| LNT | 0.023 | 0.822 | 0.188 | 0.456 |
| LNnT | 0.015 | 0.883 | 0.243 | 0.331 |
| 3’SL | 0.024 | 0.814 | 0.205 | 0.415 |
| 6’SL | 0.034 | 0.738 | 0.208 | 0.408 |
| WAZ 2nd month | ||||
| 2’FL | -0.134 | 0.187 | -0.213 | 0.411 |
| LNFP I | -0.060 | 0.557 | -0.309 | 0.228 |
| LNT | 0.040 | 0.693 | 0.066 | 0.801 |
| LNnT | -0.006 | 0.954 | 0.179 | 0.492 |
| 3’SL | 0.026 | 0.797 | -0.012 | 0.962 |
| 6’SL | 0.024 | 0.815 | -0.011 | 0.996 |
| WAZ 4th month | ||||
| 2’FL | -0.015 | 0.884 | -0.275 | 0.286 |
| LNFP I | -0.009 | 0.927 | -0.027 | 0.918 |
| LNT | 0.009 | 0.932 | -0.081 | 0.758 |
| LNnT | 0.030 | 0.770 | 0.042 | 0.874 |
| 3’SL | -0.113 | 0.272 | -0.015 | 0.995 |
| 6’SL | -0.099 | 0.336 | -0.017 | 0.948 |
| WLZ Baseline | ||||
| 2’FL | -0.040 | 0.690 | -0.007 | 0.977 |
| LNFP I | -0.159 | 0.111 | 0.478 | 0.045* |
| LNT | -0.026 | 0.793 | 0.170 | 0.500 |
| LNnT | -0.043 | 0.670 | -0.017 | 0.946 |
| 3’SL | 0.051 | 0.608 | -0.129 | 0.611 |
| 6’SL | 0.045 | 0.654 | -0.127 | 0.617 |
| WLZ 2nd month | ||||
| 2’FL | 0.018 | 0.860 | -0.255 | 0.323 |
| LNFP I | 0.042 | 0.680 | -0.438 | 0.079 |
| LNT | 0.186 | 0.066 | -0.140 | 0.593 |
| LNnT | 0.106 | 0.297 | -0.092 | 0.726 |
| 3’SL | 0.049 | 0.633 | -0.014 | 0.957 |
| 6’SL | 0.035 | 0.728 | -0.012 | 0.963 |
| WLZ 4th month | ||||
| 2’FL | 0.014 | 0.894 | 0.229 | 0.377 |
| LNFP I | 0.050 | 0.630 | 0.257 | 0.319 |
| LNT | 0.054 | 0.600 | 0.130 | 0.619 |
| LNnT | 0.089 | 0.386 | 0.350 | 0.168 |
| 3’SL | 0.033 | 0.748 | 0.221 | 0.395 |
| 6’SL | 0.025 | 0.804 | 0.223 | 0.390 |
| WV 2nd month (total g/2 mo) | ||||
| 2’FL | -0.062 | 0.540 | -0.037 | 0.888 |
| LNFP I | -0.066 | 0.516 | -0.314 | 0.220 |
| LNT | 0.004 | 0.971 | -0.118 | 0.653 |
| LNnT | 0.012 | 0.904 | -0.007 | 0.978 |
| 3’SL | 0.070 | 0.491 | 0.291 | 0.257 |
| 6’SL | 0.060 | 0.555 | 0.292 | 0.256 |
| HMOs profiles | Mean (CI 95%) | p-value | Mean difference (95% CI) | |
| WAZ | ||||
| 2nd month | 2’FL ≥med | -0.50 (-0.74 – 0.25) | 0.143 | -0.26 (-0.61 – 0.09) |
| 2’FL <med | -0.24 (-0.49 – 0.01) | |||
| 4th month | 2’FL ≥med | -0.54 (-0.8 – 0.28) | 0.057 | -0.36 (-0.73 – 0.01) |
| 2’FL <med | -0.18 (-0.44 – 0.09 | |||
| 2nd month | LNFP I ≥med | -0.45 (-0.70 – 0.21) | 0.333 | -0.17 (-0.52 – 0.18) |
| LNFP I <med | -0.28 (-0.53 – 0.03) | |||
| 4th month | LNFP I ≥med | -0.49 (-0.76 – 0.23) | 0.145 | -0.28 (-0.65 – 0.10) |
| LNFP I <med | -0.22 (-0.48 – 0.05) | |||
| 2nd month | LNT ≥med | -0.39 (-0.64 – 0.15) | 0.793 | -0.05 (-0.40 – 0.30) |
| LNT <med | -0.35 (-0.59 – 0.10) | |||
| 4th month | LNT ≥med | -0.50 (-0.76 – 0.23) | 0.141 | -0.28 (-0.65 – 0.09) |
| LNT <med | -0.22 (-0.48 – 0.05) | |||
| 2nd month | LNnT ≥med | -0.42 (-0.67 – 0.17) | 0.583 | -0.10 (-0.45 – 0.25) |
| LNnT <med | -0.32 (-0.57 – 0.08) | |||
| 4th month | LNnT ≥med | -0.47 (-0.74 – 0.20) | 0.254 | -0.22 (-0.59 – 0.16) |
| LNnT <med | -0.25 (-0.51 – 0.01) | |||
| 2nd month | 3’SL ≥med | -0.36 (-0.61 – 0.11) | 0.914 | 0.02 (-0.33 – 0.37) |
| 3’SL <med | -0.38 (-0.63 – 0.13) | |||
| 4th month | 3’SL ≥med | -0.36 (-0.63 – 0.09) | 0.991 | -0.002 (-0.38 – 0.37) |
| 3’SL <med | -0.36 (-0.62 – 0.10) | |||
| 2nd month | 6’SL ≥med | -0.36 (-0.61 – 0.11) | 0.914 | 0.02 (-0.33 – 0.37) |
| 6’SL <med | -0.38 (-0.63 – 0.13) | |||
| 4th month | 6’SL ≥med | -0.36 (-0.63 – 0.09) | 0.991 | -0.002 (-0.38 – 0.37) |
| 6’SL <med | -0.36 (-0.62 – 0.09) | |||
| WLZ | ||||
| 2nd month | 2’FL ≥med | -0.29 (-0.58 – 0.01) | 0.687 | 0.08 (-0.33 – 0.50) |
| 2’FL <med | -0.38 (-0.67 – 0.08) | |||
| 4th month | 2’FL ≥med | -0.52 (-0.81 – 0.23) | 0.228 | -0.25 (-0.66 – 0.16) |
| 2’FL <med | -0.27 (-0.56 – 0.02) | |||
| 2nd month | LNFP I ≥med | -0.42 (-0.71 – 0.13) | 0.391 | -0.18 (-0.59 – 0.23) |
| LNFP I <med | -0.24 (-0.54 – 0.05) | |||
| 4th month | LNFP I ≥med | -0.58 (-0.86 – 0.29) | 0.078 | -0.37 (-0.77 – 0.04) |
| LNFP I <med | -0.21 (-0.50 – 0.08) | |||
| 2nd month | LNT ≥med | -0.28 (-0.57 – 0.02) | 0.581 | 0.12 (-0.30 – 0.53) |
| LNT <med | -0.39 (-0.68 – 0.1) | |||
| 4th month | LNT ≥med | -0.48 (-0.77 – 0.19) | 0.439 | -0.16 (-0.58 – 0.25) |
| LNT <med | -0.32 (-0.61 – 0.03) | |||
| 2nd month | LNnT ≥med | -0.36 (-0.65 – 0.06) | 0.824 | -0.05 (-0.46 – 0.37) |
| LNnT <med | -0.31 (-0.60 – 0.02) | |||
| 4th month | LNnT ≥med | -0.49 (-0.79 – 0.20) | 0.382 | -0.18 (-0.60 – 0.23) |
| LNnT <med | -0.31 (-0.60 – 0.02) | |||
| 2nd month | 3’SL ≥med | -0.31 (-0.60 – 0.2) | 0.826 | 0.05 (-0.37 – 0.46) |
| 3’SL <med | -0.36 (-0.65 – 0.06) | |||
| 4th month | 3’SL ≥med | -0.39 (-0.69 – 0.10) | 0.969 | 0.008 (-0.41 – 0.42) |
| 3’SL <med | -0.40 (-0.69 – 0.11) | |||
| 2nd month | 6’SL ≥med | -0.31 (-0.60 – 0.02) | 0.826 | 0.05 (-0.37 – 0.46) |
| 6’SL <med | -0.36 (-0.65 – 0.06) | |||
| 4th month | 6’SL ≥med | -0.39 (-0.69 – 0.10) | 0.969 | 0.008 (-0.41 – 0.42) |
| 6’SL <med | -0.40 (-0.69 – 0.11) | |||
| 4th month | LNFP I ≥med | 3404 (3189 – 3618) | 0.202 | -198 (-504 – 108) |
| LNFP I <med | 3602 (3384 – 3820) | |||
| 2nd month | LNT ≥med | 2145 (1971 – 2319) | 0.826 | -27.3 (-274 – 219) |
| LNT <med | 2172 (1998 – 2347) | |||
| 4th month | LNT ≥med | 3401 (3185 – 3617) | 0.198 | -200 (-505 – 106) |
| LNT <med | 3601 (3385 – 3817) | |||
| 2nd month | LNnT ≥med | 2112 (1936 – 2287) | 0.459 | -92.3 (-338 – 154) |
| LNnT <med | 2204 (2032 – 2376) | |||
| 4th month | LNnT ≥med | 3384 (3167 – 3602) | 0.139 | -229 (-534 – 75) |
| LNnT <med | 3614 (3300 – 3827) | |||
| 2nd month | 3’SL ≥med | 2158 (1984 – 2332) | 0.992 | -1.19 (-248 – 245) |
| 3’SL <med | 2159 (1985 – 2334) | |||
| 4th month | 3’SL ≥med | 3498 (3280 - 3715) | 0.968 | -6.23 (-314 – 302) |
| 3’SL <med | 3504 (3286 – 3722) | |||
| 2nd month | 6’SL ≥med | 2158 (1984 – 2332) | 0.992 | -1.19 (-248 – 245) |
| 6’SL <med | 2159 (1985 – 2334) | |||
| 4th month | 6’SL ≥med | 3498 (3280 – 3715) | 0.968 | -6.23 (-314 – 302) |
| 6’SL <med | 3504 (3286 – 3722) |
| HMOs profiles | Secretor positive Median (IQR) |
Weak Secretor Median (IQR) |
p-value |
| 2’FL | |||
| Baseline | 2288 (764, 4316) | 1900 (48.6, 2670) | 0.014* |
| 2nd month | 1581 (215, 2710) | 870 (49, 2386) | 0.082 |
| 4th month | 554 (156, 759) | 207 (11.5, 540) | 0.013* |
| LNFP I | |||
| Baseline | 590 (164, 1401) | 410 (112, 1002) | 0.060 |
| 2nd month | 198 (131, 446) | 231 (155, 833) | 0.391 |
| 4th month | 96 (25.8, 488) | 60.4 (22.9, 288) | 0.523 |
| LNT | |||
| Baseline | 116 (50, 1808) | 107 (61.4, 223) | 0.484 |
| 2nd month | 63.2 (41.3, 98.1) | 89.7 (40.8, 140.9) | 0.064 |
| 4th month | 31.4 (16.5, 87.1) | 32.6 (21, 62.9) | 0.979 |
| LNnT | |||
| Baseline | 75.6 (36.1, 118.7) | 64.8 (36, 109) | 0.542 |
| 2nd month | 42.2 (30.4, 59.2) | 54.5 (30.2, 76.7) | 0.060 |
| 4th month | 20.3 (9.6, 50) | 15.7 (10.5, 29.1) | 0.392 |
| 3’SL | |||
| Baseline | 185 (132) | 184 (142, 225) | 0.435 |
| 2nd month | 139 (102, 179) | 153 (116, 191) | 0.365 |
| 4th month | 43.4 (39.3, 59.0) | 43.3 (38.6, 51.5) | 0.734 |
| 6’SL | |||
| Baseline | 185 (132, 260) | 184 (142, 223) | 0.546 |
| 2nd month | 139 (102, 178) | 152 (116, 191) | 0.346 |
| 4th month | 43.4 (39.4, 58.9) | 44.2 (38.9, 51.3) | 0.852 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




