Submitted:
15 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Expanding Bands Method for Multi-spectral Images
- Second-order correlated bands include the auto-correlated bands () and the cross-correlated bands ().
- Nonlinear correlated bands include the bands stretched out by the square root () and those stretched out by the logarithmic function ().
2.2. Markov Chain Clustering in Wavelet Feature Space
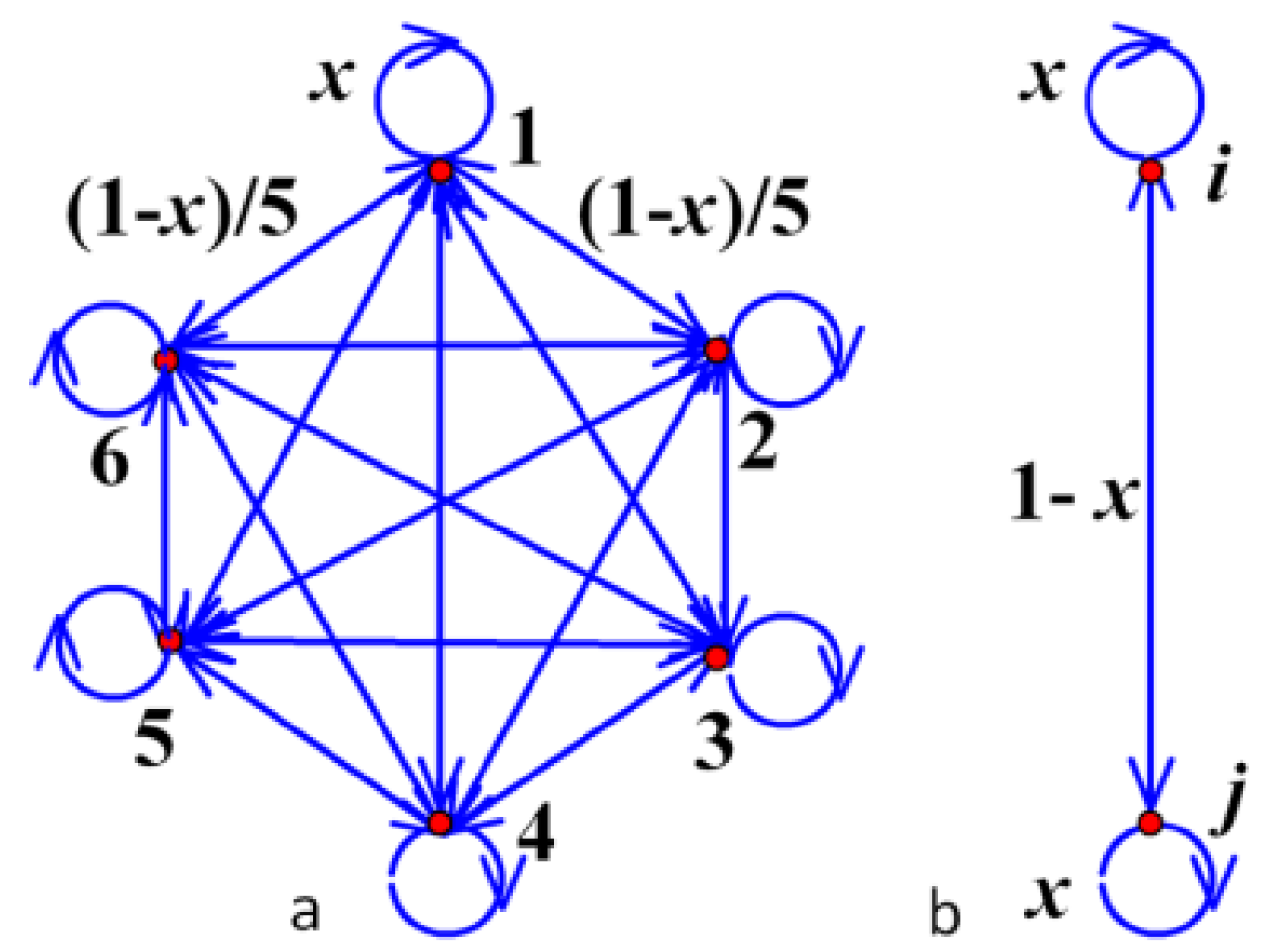
- Any two states in Ch are communicated.
2.3. Adjustment of Clustering Centers
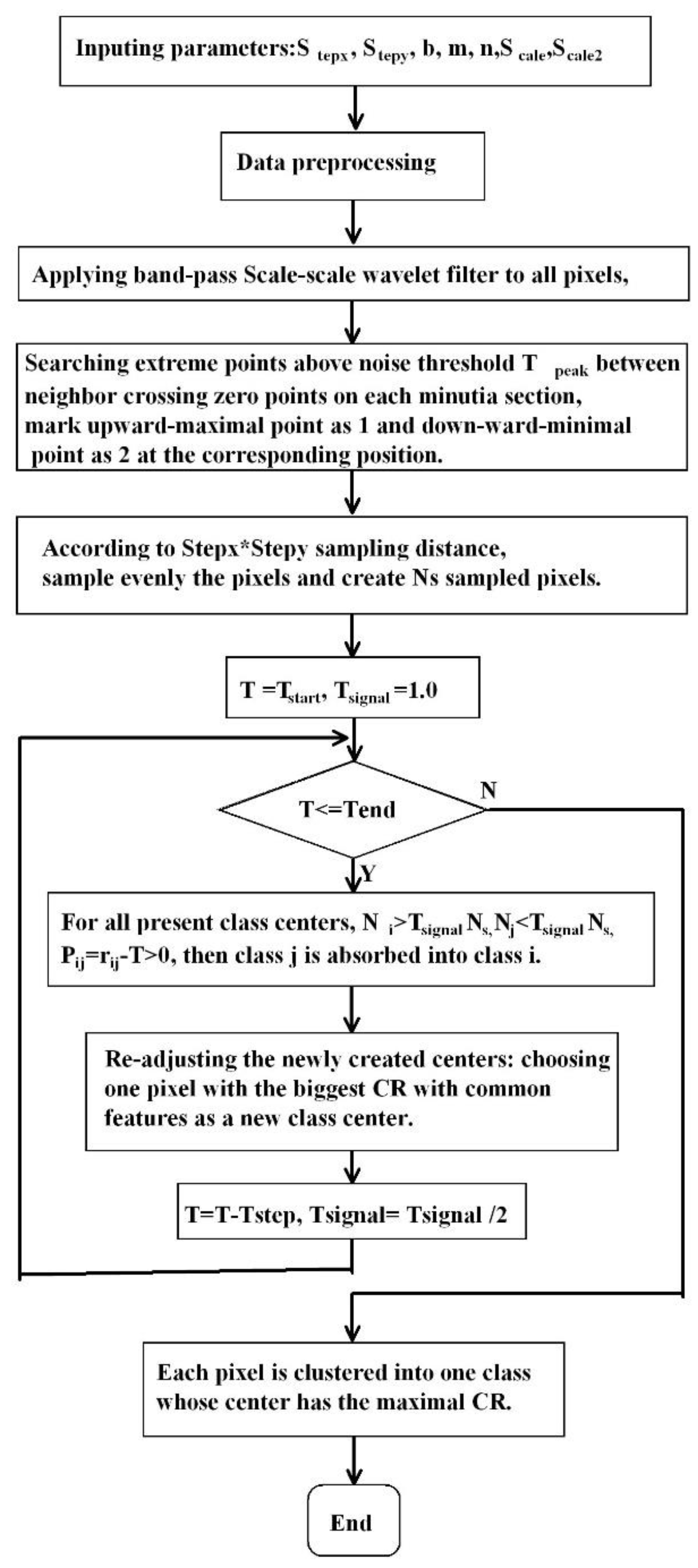
2.4. Wavelet-Feature Markov Clustering Algorithm
- Input parameters:
- 2
- Data preprocessing. Delete bands primarily affected by noise and atmosphere, such as the 1-6th, 33rd, 107-114th,153-168th, and 222-224th bands of AVIRIS. Multi-spectral images need to expand bands.
- 3
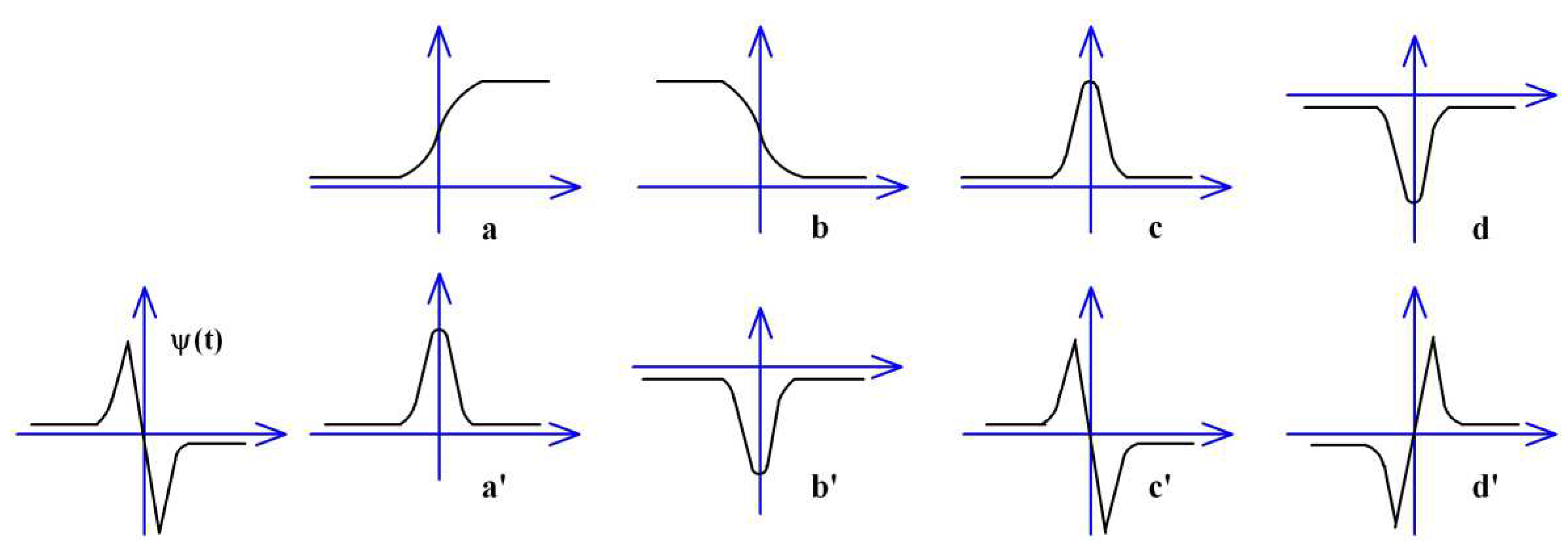
- Apply band-pass Scale-scale wavelet filter (for example, Equation 6, [25,26]) to all pixels, search extreme points above noise threshold Tpeak between neighbor crossing zero points on each minutia section, and mark upward-maximal point as 1 and downward-minimal point as 2 at the corresponding position.
- 4
- According to Stepx*Stepy sampling distance, sample the pixels and create Ns sampled pixels evenly.
- 5
- Apply simulated annealing Markov state decomposition clustering to Scale-Scale2~Scale scale minutia sections of sampled data.
- a)
- Set initial temperature T as Tstart, the clustering signal standard Tsignal (ratio of intra-class sampled pixel number over the number of total sampled pixels) is 1.0, and each pixel is one class center (beginning with Ns class centers). In the end, according to step b-e, apply Markov chain decomposition in state space to the wavelet features of sampled pixels by gradually depressing signal size.
- b)
- Make judgments to all present class centers. If class i is a significant signal in which the number of pixels is more prominent than , move to the next class. Otherwise, search forward one by one for another class j whose size is smaller than , and make clustering judgments between class j and i.
- c)
- According to Equation 8, if the CR between centers of two classes (i and j) meets the condition Pij=rij-T>0, then class j is absorbed into class i. Continuing this process b) until the last class is detected.
- d)
- According to Equations 4 and 5, re-adjust the newly created centers: among all the class centers merged into one new class at this iteration, choose one pixel with the biggest CR with common features as a new class center.
- e)
- Let T=T-Tstep decrease clustering temperature, and Tsignal= Tsignal /2 to reduce clustering size. Repeat steps a)-d) until T is reduced to the appointed small signal threshold Tend or set class number is reached.
- 6
- According to the clustering centers created by 5), each pixel is clustered into one class whose center has the maximal CR.
3. Results
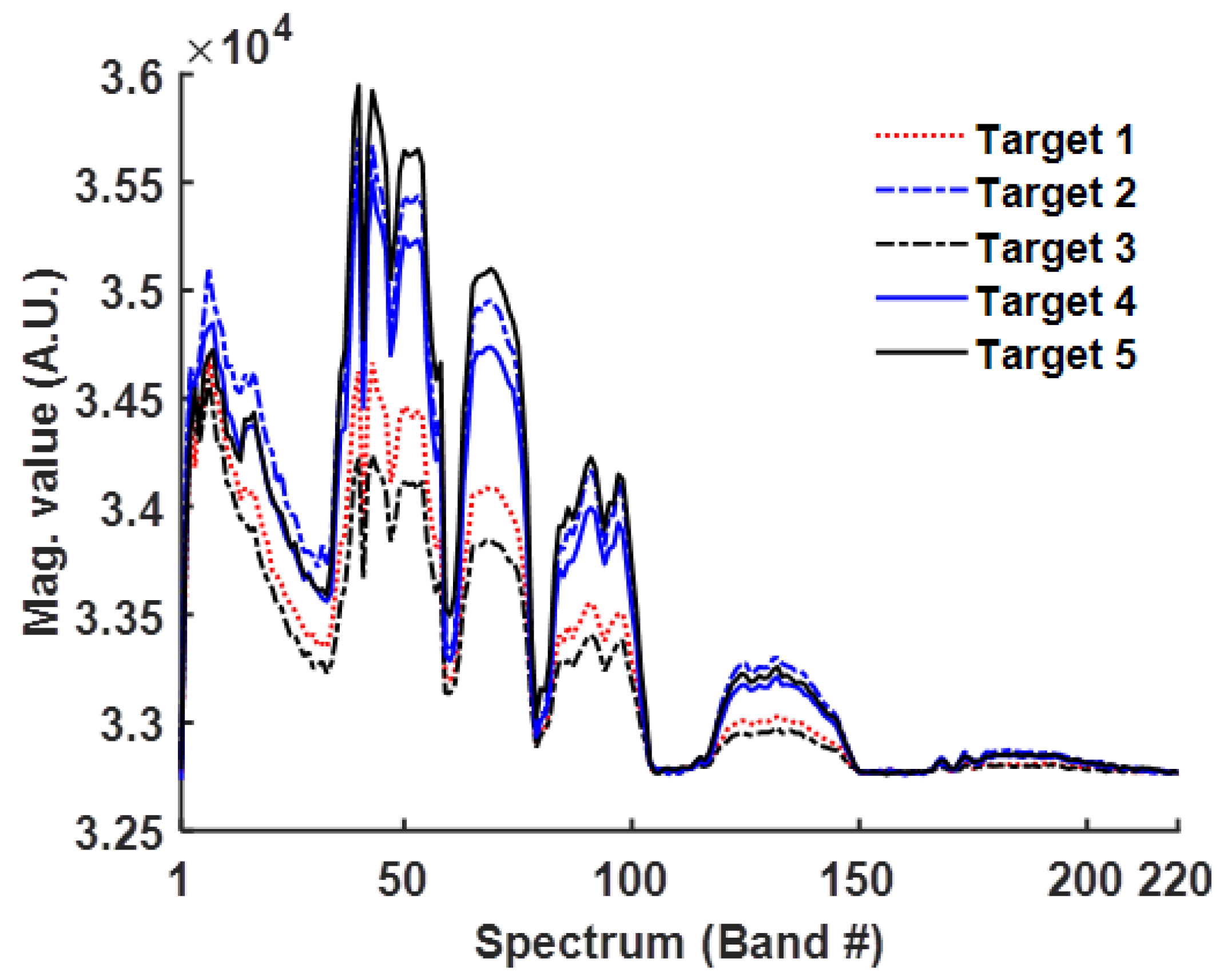
3.1. Multi-Spectral Data
3.2. Hyper-Spectral Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z. Fast multi-level clustering lossless compression algorithm for remotely sensed images, Journal of Image and Graphics 2003, 8(7), pp. 843-848.
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, P. Fast clustering lossless compression algorithm for hyperspectral images,” Journal of Remote Sensing 2003, 7(5), pp. 400-406.
- Wang, Z. Residual Clustering Based Lossless Compression for Remotely Sensed Images, 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Louisville, KY, USA, 2018, pp. 536-539. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Entropy Analysis for Clustering Based Lossless Compression of Remotely Sensed Images," 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Orlando, FL, USA, 2021, pp. 4220-4223. [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, S.; Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumba, K. Pattern Recognition, 4th ed; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 741-745.
- Ikotun, A. M.; Ezugwu, A. E.; Abualigah, L.; Abuhaija, B.; Heming, J. K-means Clustering Algorithms: A Comprehensive Review, Variants Analysis, and Advances in the Era of Big Data. Information Sciences 2023, 622, pp. 178-210. [CrossRef]
- Soto de la Cruz, R.; Castro-Espinoza, F. A.; Soto, L. Isodata-Based Method for Clustering Surveys Responses with Mixed Data: The 2021 StackOverflow Developer Survey. Computación y Sistemas 2023, 27(1), pp. 173-182. [CrossRef]
- Arai, K. Improved ISODATA Clustering Method with Parameter Estimation based on Genetic Algorithm. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2022, 13(5), pp. 187-193. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J. J.; McIntre, T. J.; Sienko, M. An Improved Hybrid Clustering Algorithm for Natural Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2000, 38(2), pp.1016-1032. [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Bretschneider, T. D-ISMC: A distributed unsupervised classification algorithm for optical satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, (July 2003), Vol. 6, pp. 3413-3419.
- Ren, H.; Chang, C.-I. A Generalized Orthogonal Subspace Projection Approach to Unsupervised Multi-spectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2000, 38(6), pp.2515-2528.
- Ifarraguerri, A.; Chang, C.-I. Unsupervised Hyperspectral Image Analysis with Projection Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2000, 38(6), pp.2529-2538. [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Schwarz, G.; Datcu, M. Remote sensing image classification: No features, no clustering. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2015, 8(11), pp. 5158-5170.
- Chen, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, M. Bag-of-Visual-Words Scene Classifier for Remote Sensing Image Based on Region Covariance. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2022, 19, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yao, Y.; Lei, J.; Fang, L.; Huang, Q. Graph-Based Structural Deep Spectral-Spatial Clustering for Hyperspectral Image. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023 (accepted). [CrossRef]
- Firat, H.; Asker, M. E.; Bayindir, M. I.; Hanbay, D. 3D residual spatial–spectral convolution network for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Neural Computing and Applications 2023, 35(6), pp. 4479-4497. [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, M.; De, R. K.; Kundu, M. K. Segmentation of remotely sensed images using wavelet features and their evaluation in soft computing framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2003, 41(12), pp. 2900-2905.
- Anupong, W.; Jweeg, M. J.; Alani, S.; Al-Kharsan, I. H.; Alviz-Meza, A.; Cárdenas-Escrocia, Y. Comparison of Wavelet Artificial Neural Network, Wavelet Support Vector Machine, and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Methods in Estimating Total Solar Radiation in Iraq. Energies 2023, 16, 985. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, P. Greedy clustering algorithm and its application for the classification and compression of remotely sensed images, Jounal of University of Science and Technology of China 2003, 33(1), pp. 52-59.
- Wang, Z.; Zhou P. Fast clustering based on spectral wavelet features extraction and simulated annealing algorithm for multi-spectral Images, Journal of Image and Graphics. 2002, 7A(12), pp. 1257-1262.
- Haddad, S. A. P.; Serdijn, W. A. Ultra low-power Biomedical Signal Processing: An Analog Wavelet Filter Approach for Pacemakers, Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 34-50.
- Mallat, S.G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, pp.674–693. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods in Quantum Field Theories: A Modern Primer. Springer Nature, 2020; pp. 29-35.
- Bittelli, M.; Olmi, R.; Rosa, R. Random Process Analysis With R; Oxford University Press, 2022; pp. 25-31.
- Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.-N. Detection of Ventricular Fibrillation by Support Vector Machine Algorithm. IEEE International Asia Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics 2009, pp. 287-290.
- Swelends, W. The Lifting Scheme: A Custom-design Construction of Biorthogonal Wavelet. Journal of Appl. And Comput. Harmonic Analysis 1996, 3(2), pp. 186-220.
- Kulkarni, A.; McCaslin, S. Knowledge Discovery from Multi-spectral Satellite Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1(4), pp. 246-250,.
- Goodenough, D. G.; Bhogal, A. S.; Dyk, A.; Niemann, O.; Han, T.; Chen, H.; West, C.; Schmidt, C. Calibration of Forest Chemistry for Hyperspectral Analysis. In IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 2001, 1, pp. 52-56.
- Goodenough, D. G.; Dyk, A.; Niemann, K. O.; Pearlman, J. S.; Chen, H.; Han, T.; Murdoch, M.; West, C. Processing Hyperion and ALI for Forest Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2003, 41(6), pp. 1321-1331. [CrossRef]
- Candès, E. J.; Donoho, D. L. Ridgelets: A key to higher-dimensional intermittency? Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 1999, 357(1760), 2495-2509.
- Starck, J. L.; Candès, E. J.; Donoho, D. L. The curvelet transform for image denoising. IEEE Transactions on image processing 2002, 11(6), pp. 670-684. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
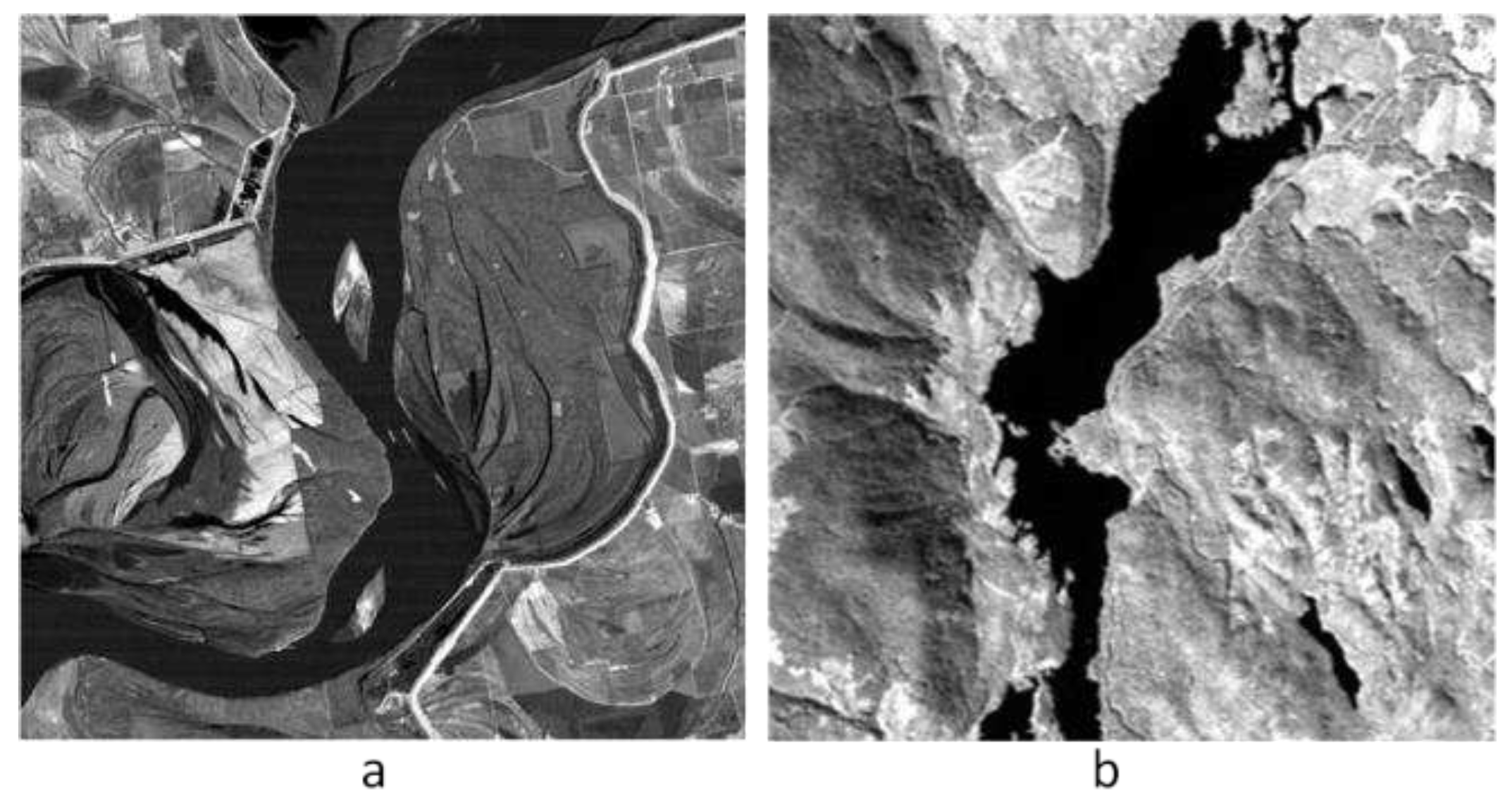
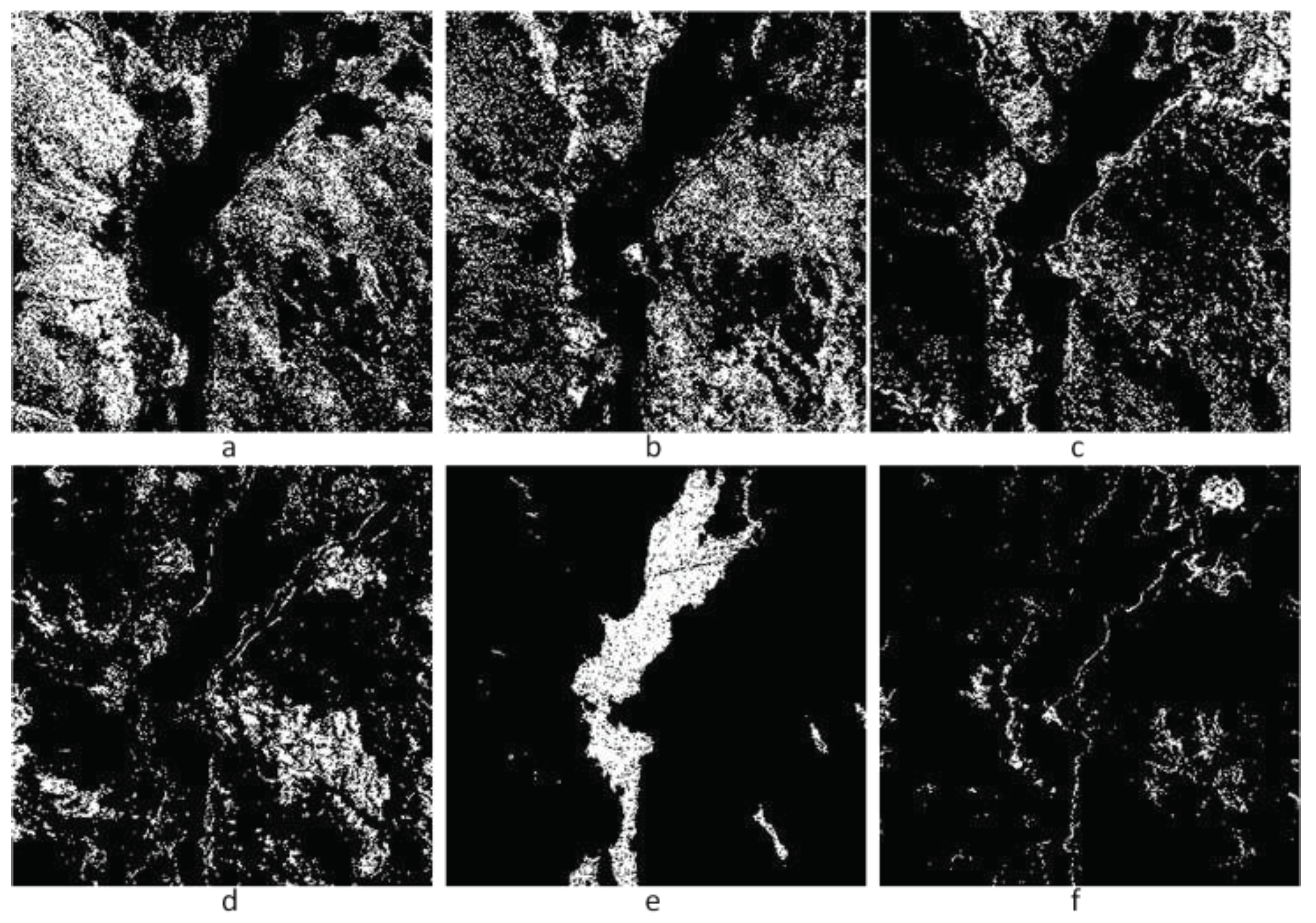
| Band number | Tcr1 | Tcr2 | Class number |
| 6(Scale=2) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 4 |
| 39 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 36 |
| Band no. | Tcr1 | Tcr2 | Scale2 | Class no. |
| 39 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 4 | 18 |
| Tpeak | Tend | Class number |
| 0 | 0.4 | 133 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 65 |
| 5 | 0.4 | 38 |
| 7 | 0.4 | 26 |
| 10 | 0.4 | 22 |
| 15 | 0.4 | 24 |
| Tend | Scale2 | Class number | Time/sec. |
| 0.4 | 2 | 8 | 13 |
| 0.4 | 3 | 17 | 21 |
| 0.4 | 4 | 38 | 51 |
| 0.6 | 4 | 85 | 52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





