Submitted:
14 November 2023
Posted:
15 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Human post-mortem midbrain samples
3.2. RNA isolation from human midbrain samples
3.3. RNA Sequencing and Functional Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quik, M. Smoking, Nicotine and Parkinson’s Disease. Trends Neurosci 2004, 27, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.E.; Obeso, J.A. Time to Move beyond Nigrostriatal Dopamine Deficiency in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann Neurol 2004, 55, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Stamelou, M.; Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Lang, A.E.; Weintraub, D.; Burn, D.; Halliday, G.M.; Bezard, E.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Past, Present, and Future of Parkinson’s Disease: A Special Essay on the 200th Anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov Disord 2017, 32, 1264–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figorilli, M.; Lanza, G.; Congiu, P.; Lecca, R.; Casaglia, E.; Mogavero, M.P.; Puligheddu, M.; Ferri, R. Neurophysiological Aspects of REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD): A Narrative Review. Brain Sci 2021, 11, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joza, S.; Hu, M.T.; Jung, K.-Y.; Kunz, D.; Stefani, A.; Dušek, P.; Terzaghi, M.; Arnaldi, D.; Videnovic, A.; Schiess, M.C.; et al. Progression of Clinical Markers in Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Multicentre Study. Brain 2023, 146, 3258–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.E. A Critical Appraisal of the Premotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease: Potential Usefulness in Early Diagnosis and Design of Neuroprotective Trials. Mov Disord 2011, 26, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Ulane, C.M.; Burke, R.E. Clinical Progression in Parkinson Disease and the Neurobiology of Axons. Ann Neurol 2010, 67, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.E.; O’Malley, K. Axon Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Exp Neurol 2013, 246, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Sandmann-Keil, D.; Gai, W.; Braak, E. Extensive Axonal Lewy Neurites in Parkinson’s Disease: A Novel Pathological Feature Revealed by Alpha-Synuclein Immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 1999, 265, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.I.; Jansen Steur, E.N.H.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnley, J.M.; Lees, A.J. Ageing and Parkinson’s Disease: Substantia Nigra Regional Selectivity. Brain 1991, 114 ( Pt 5), 2283–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, E.C.; Breidert, T.; Rousselet, E.; Hunot, S.; Hartmann, A.; Michel, P.P. The Role of Glial Reaction and Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003, 991, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.E.; Akther, M.; Jakaria, M.; Kim, I.-S.; Azam, S.; Choi, D.-K. Targeting the Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord 2020, 35, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Therapeutics Targeting the Inflammasome after Central Nervous System Injury. Transl Res 2016, 167, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Activation of Inflammatory Caspases and Processing of proIL-Beta. Mol Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of Assembly, Regulation and Signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Inflammasome Activation and Assembly at a Glance. J Cell Sci 2017, 130, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opdenbosch, N.; Lamkanfi, M. Caspases in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, B.S.; Bossaller, L.; De Nardo, D.; Ratter, J.M.; Stutz, A.; Engels, G.; Brenker, C.; Nordhoff, M.; Mirandola, S.R.; Al-Amoudi, A.; et al. The Adaptor ASC Has Extracellular and “prionoid” Activities That Propagate Inflammation. Nat Immunol 2014, 15, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera Ranaldi, E.D.L.R.M.; Nuytemans, K.; Martinez, A.; Luca, C.C.; Keane, R.W.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Proof-of-Principle Study of Inflammasome Signaling Proteins as Diagnostic Biomarkers of the Inflammatory Response in Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolo, G.; Plotegher, N.; Pozzobon, T.; Brucale, M.; Tessari, I.; Bubacco, L.; de Bernard, M. Triggering of Inflammasome by Aggregated α-Synuclein, an Inflammatory Response in Synucleinopathies. PLoS One 2013, 8, e553752013–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Activation and Regulation of Cellular Inflammasomes: Gaps in Our Knowledge for Central Nervous System Injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2014, 34, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funayama, M.; Nishioka, K.; Li, Y.; Hattori, N. Molecular Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease: Contributions and Global Trends. J Hum Genet 2023, 68, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, M.A.; Pankratz, N.; Lill, C.M.; Do, C.B.; Hernandez, D.G.; Saad, M.; DeStefano, A.L.; Kara, E.; Bras, J.; Sharma, M.; et al. Large-Scale Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Data Identifies Six New Risk Loci for Parkinson’s Disease. Nat Genet 2014, 46, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandres-Ciga, S.; Diez-Fairen, M.; Kim, J.J.; Singleton, A.B. Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease: An Introspection of Its Journey towards Precision Medicine. Neurobiol Dis 2020, 137, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulski, J.; Uitti, R.J.; Ross, O.A.; Wszolek, Z.K. Genetic Architecture of Parkinson’s Disease Subtypes - Review of the Literature. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 1023574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redenšek, S.; Dolžan, V.; Kunej, T. From Genomics to Omics Landscapes of Parkinson’s Disease: Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms. OMICS 2018, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunovic, F.; Yi, M.; Wang, Y.; Macey, L.; Brown, L.T.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Andersen, S.L.; Stephens, R.M.; Benes, F.M.; Sonntag, K.C. Gene Expression Profiling of Substantia Nigra Dopamine Neurons: Further Insights into Parkinson’s Disease Pathology. Brain 2009, 132, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Cosentino, F.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Giurato, G.; Borgione, E.; Marchese, G.; Santa Paola, S.; Lanuzza, B.; et al. MRNA Expression Profiling of Mitochondrial Subunits in Subjects with Parkinson’s Disease. Arch Med Sci 2023, 19, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Lanza, G.; Mogavero, M.P.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Borgione, E.; Iorio, R.; Ventola, G.M.; Marchese, G.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Ravo, M.; et al. A Transcriptome Analysis of MRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccaria, A.; Antinori, P.; Licker, V.; Kövari, E.; Lobrinus, J.A.; Burkhard, P.R. Multiomic Analyses of Dopaminergic Neurons Isolated from Human Substantia Nigra in Parkinson’s Disease: A Descriptive and Exploratory Study. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2022, 42, 2805–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Hou, W.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Dou, K.; et al. N-Myc Downstream-Regulated Gene 2, a Novel Estrogen-Targeted Gene, Is Involved in the Regulation of Na+/K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 32289–32299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, N.; Kleiter, M.; Dietschi, E.; Leschnik, M.; Högler, S.; Wiedmer, M.; Dietrich, J.; Henke, D.; Steffen, F.; Schuller, S.; et al. A SINE Insertion in ATP1B2 in Belgian Shepherd Dogs Affected by Spongy Degeneration with Cerebellar Ataxia (SDCA2). G3 (Bethesda) 2017, 7, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Daniels, S.; Kim, Y.; Chu, H.-Y. Cell Type-Specific Decrease of the Intrinsic Excitability of Motor Cortical Pyramidal Neurons in Parkinsonism. J Neurosci 2021, 41, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Arias, P.; Einholm, A.P.; Mamsa, H.; Concheiro, C.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Romero, J.; Toustrup-Jensen, M.S.; Carracedo, A.; Jen, J.C.; Vilsen, B.; et al. A C-Terminal Mutation of ATP1A3 Underscores the Crucial Role of Sodium Affinity in the Pathophysiology of Rapid-Onset Dystonia-Parkinsonism. Hum Mol Genet 2009, 18, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardutz, H.; Singh, J.; Rehman, Z.; Bernat, P. Parkinson’s Disease and the Cardiac Cycle: A Rapid Literature Review and Case Series. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, M.B.E.; Keulers, T.G.; Vooijs, M.A.; Rouschop, K.M.A. LC3/GABARAP Family Proteins: Autophagy-(Un)Related Functions. FASEB J 2016, 30, 3961–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grand, J.N.; Bon, K.; Fraichard, A.; Zhang, J.; Jouvenot, M.; Risold, P.-Y.; Boyer-Guittaut, M.; Delage-Mourroux, R. Specific Distribution of the Autophagic Protein GABARAPL1/GEC1 in the Developing and Adult Mouse Brain and Identification of Neuronal Populations Expressing GABARAPL1/GEC1. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanji, K. [Multiple system atrophy and autophagy]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2014, 54, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haddad, S.; Serrano, A.; Moal, F.; Normand, T.; Robin, C.; Charpentier, S.; Valery, A.; Brulé-Morabito, F.; Auzou, P.; Mollet, L.; et al. Disturbed Expression of Autophagy Genes in Blood of Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Gene 2020, 738, 144454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.-H.; Yao, Z.-W.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-M.; Li, Q.-Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.-Y.; Wei, X.-J.; Wan, G.-H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; et al. Nardosinone Regulates the Slc38a2 Gene to Alleviate Parkinson’s Symptoms in Rats through the GABAergic Synaptic and cAMP Pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 153, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Matsunaga, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshikawa, R.; Kawashima, K.; Ohizumi, Y. Nardosinone, a Novel Enhancer of Nerve Growth Factor in Neurite Outgrowth from PC12D Cells. Neurosci Lett 1999, 273, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezi, E.; Swerdlow, R.H. Mitochondria in Neurodegeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012, 942, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.H.T.; Barnes, O.L.; Chegini, F. Lewy Bodies and the Mechanisms of Neuronal Cell Death in Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Brain Pathol 2017, 27, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, W.D.; Boyson, S.J.; Parks, J.K. Abnormalities of the Electron Transport Chain in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Ann Neurol 1989, 26, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Jenner, P.; Clark, J.B.; Marsden, C.D. Mitochondrial Complex I Deficiency in Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 1989, 1, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindoff, L.A.; Birch-Machin, M.; Cartlidge, N.E.; Parker, W.D.; Turnbull, D.M. Mitochondrial Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 1989, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.D.; Parks, J.K.; Swerdlow, R.H. Complex I Deficiency in Parkinson’s Disease Frontal Cortex. Brain Res 2008, 1189, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshmand, M.; Kasraie, S.; Etemad Ahari, S.; Moin, M.; Bahar, M.; Zamani, A. Investigation of tRNA and ATPase 6/8 Gene Mutations in Iranian Ataxia Telangiectasia Patients. Arch Med Sci 2011, 7, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyano, F.; Okatsu, K.; Ishigaki, S.; Fujioka, Y.; Kimura, M.; Sobue, G.; Tanaka, K.; Matsuda, N. The Principal PINK1 and Parkin Cellular Events Triggered in Response to Dissipation of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Occur in Primary Neurons. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.K.; Cookson, M.R. Mitochondrial Quality Control and Dynamics in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2012, 16, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, K.-A.; Trapp, B.D. Axon-Glial Signaling and the Glial Support of Axon Function. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008, 31, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, A.; Rabin, E.E.; Flozak, A.S.; Chiarella, S.E.; Aillon, R.P.; Gottardi, C.J. Alpha-T-Catenin Is Expressed in Peripheral Nerves as a Constituent of Schwann Cell Adherens Junctions. Biol Open 2022, 11, bio059634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhan, J.; Cai, Q.; Xu, F.; Chai, R.; Lam, K.; Luan, Z.; Zhou, G.; Tsang, S.; Kipp, M.; et al. The Water Transport System in Astrocytes-Aquaporins. Cells 2022, 11, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.L.; Faridounnia, M.; Armao, D.; Snider, N.T. Stability Dynamics of Neurofilament and GFAP Networks and Protein Fragments. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2023, 85, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.R.; Ziemens, D.; Verkhratsky, A. On the Special Role of NCX in Astrocytes: Translating Na+-Transients into Intracellular Ca2+ Signals. Cell Calcium 2020, 86, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valori, C.F.; Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Astrocytes: Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Neurological Disorders. Trends Mol Med 2019, 25, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. cutPrimers: A New Tool for Accurate Cutting of Primers from Reads of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J Comput Biol 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex Heatmaps Reveal Patterns and Correlations in Multidimensional Genomic Data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J.; Tugendreich, S. Causal Analysis Approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
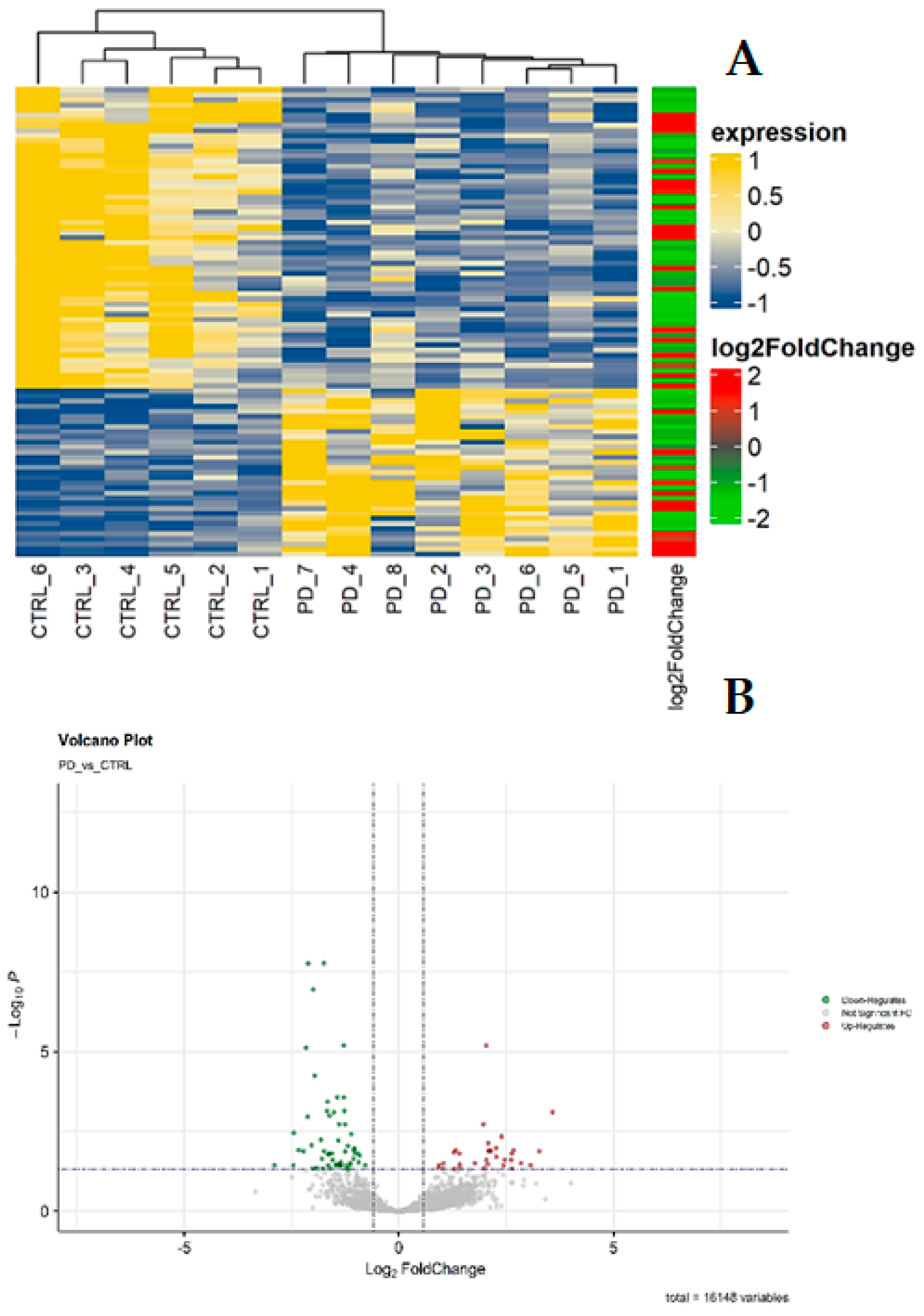
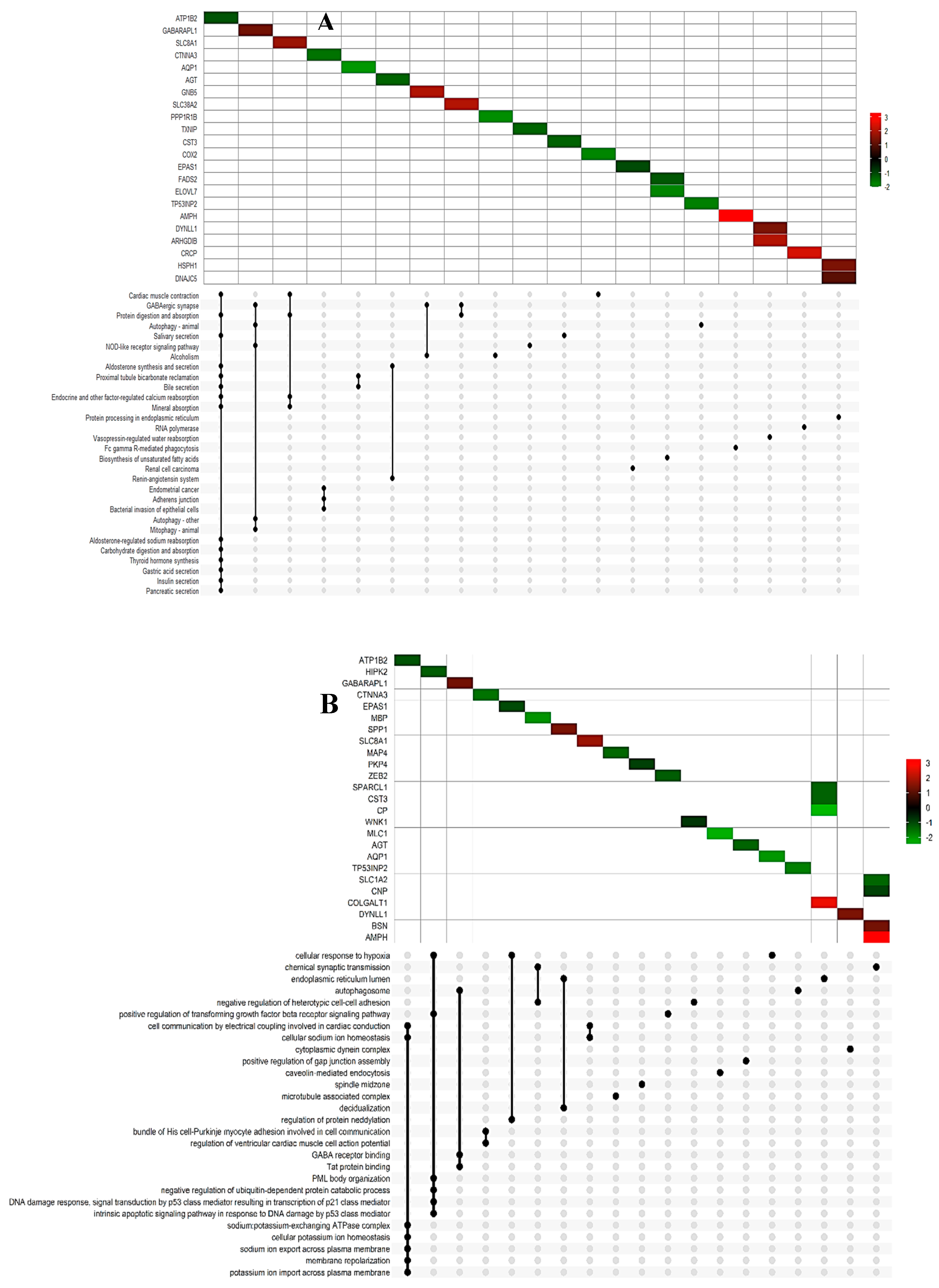
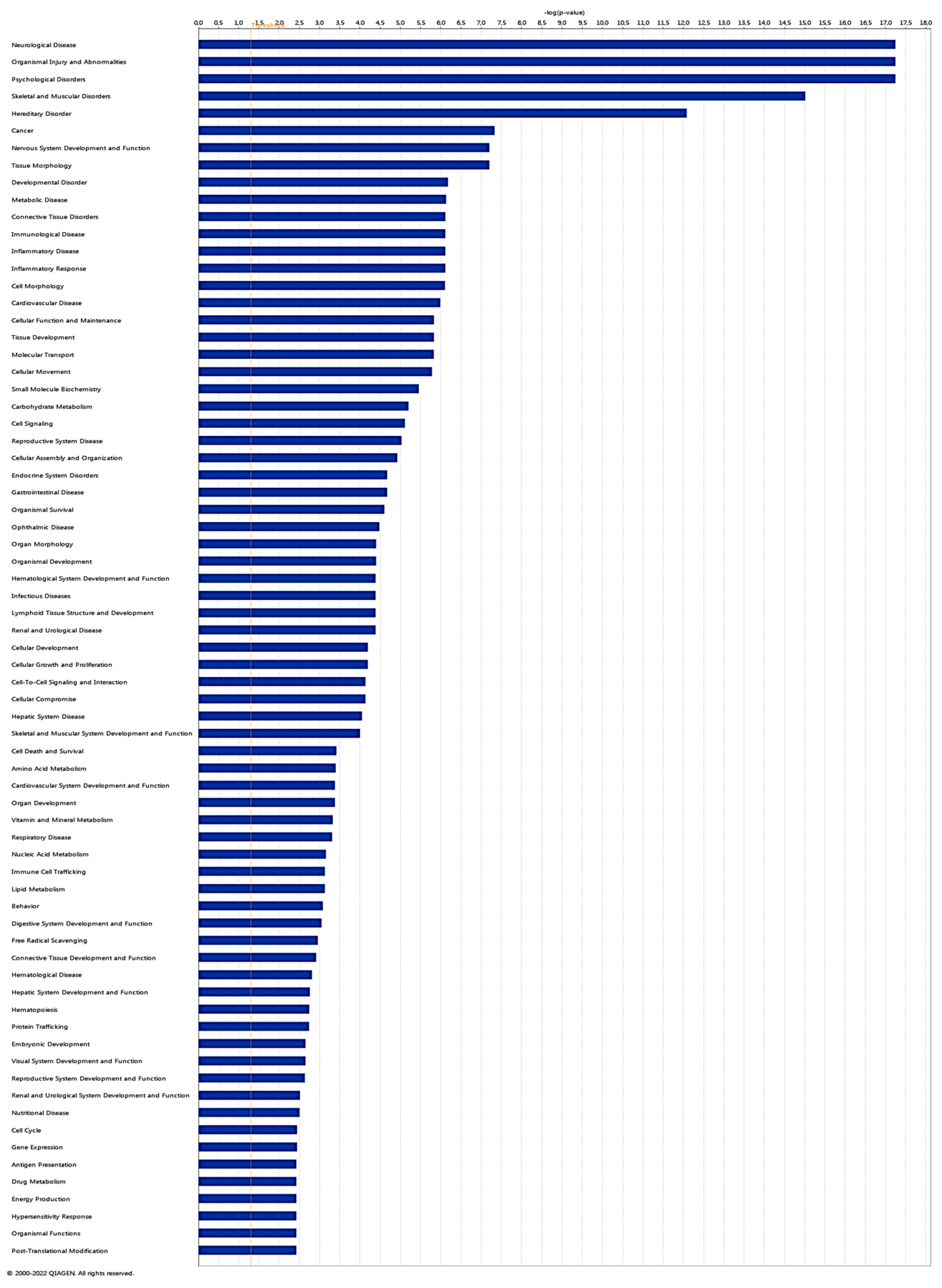
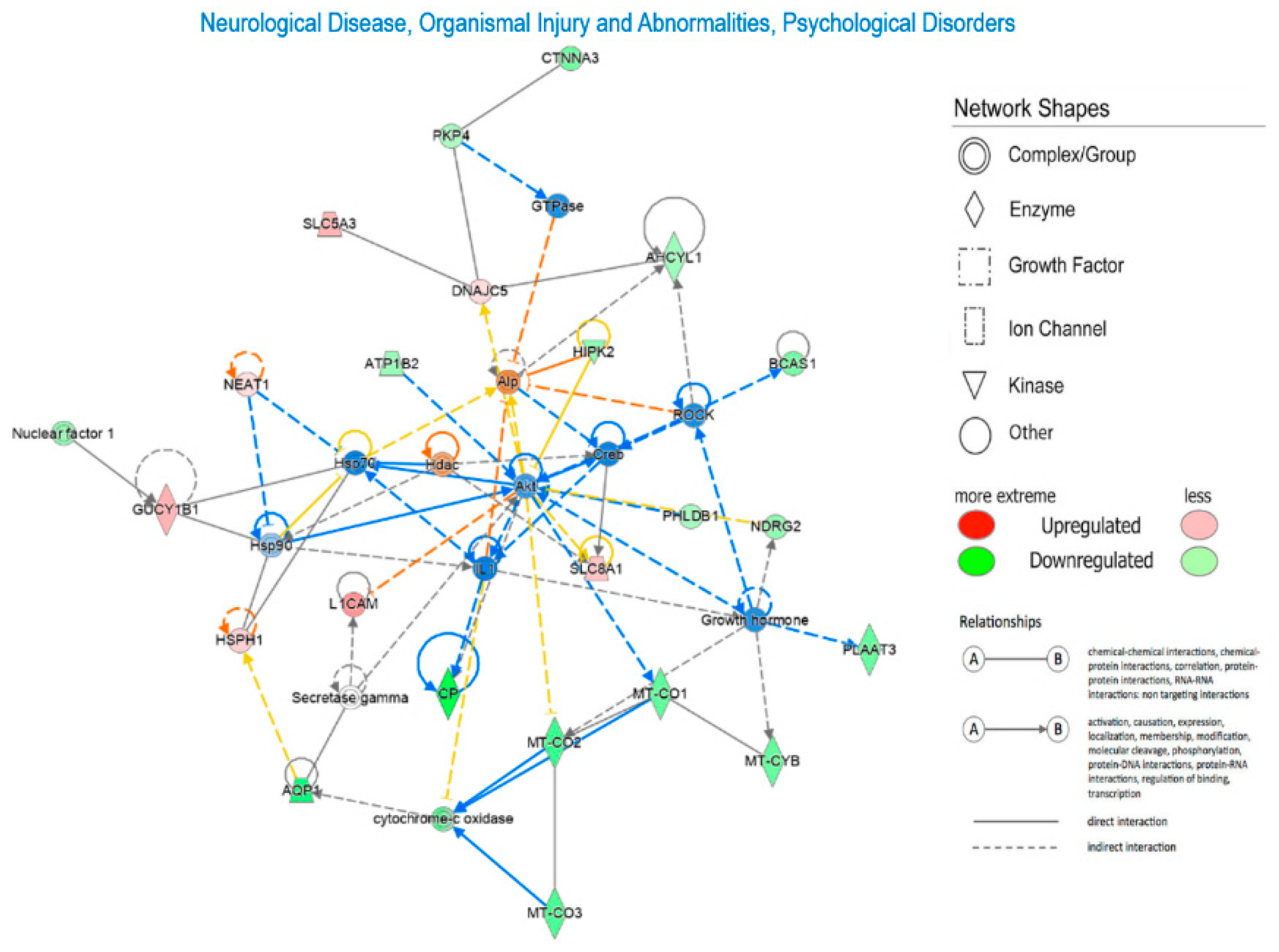
| Gene ID | Fold change | Gene ID | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETNPP1 | -7.435 | AC093330.1 | -2.718 |
| MIND4P12 | -5.475 | MAP4 | -2.693 |
| CP | -5.444 | S1C1A2 | -2.651 |
| M1C1 | -5.02 | TXNIP | -2.625 |
| PPDPF | -4.631 | AGf | -2.61 |
| PAQR6 | -4.469 | RHOBTB3 | -2.604 |
| ACBD7 | -4.345 | CST3 | -2.562 |
| MOBP | -4.315 | SPARC11 | -2.55 |
| AQP1 | -4.069 | MIND2P28 | -2.544 |
| TAG1N | -4.001 | HIPK2 | -2.427 |
| MBP | -3.977 | ZEB2 | -2.425 |
| PAJP2B | -3.892 | NDRG2 | -2.408 |
| PPP1R1B | -3.766 | MIURN | -2.382 |
| MTATP6P1 | -3.736 | DAAM2 | -2.381 |
| MT-C02 | -3.5 | NFIX | -2.343 |
| E1OV17 | -3.456 | FADS2 | -2.325 |
| SCARA3 | -3.419 | ATP1B2 | -2.268 |
| MT-C03 | -3.338 | HEPACAM | -2.263 |
| TP53INP2 | -3.336 | SHIN1 | -2.203 |
| FAM107A | -3.168 | FAR1 | -2.182 |
| SEPTIN4 | -3.158 | AHCYU | -2.157 |
| A1AD | -3.122 | EPAS1 | -2.075 |
| MT-CO1 | -3.116 | PH1DB1 | -2.058 |
| IRAG1 | -3.089 | GFAP | -2.043 |
| P1AAT3 | -3.056 | MAP4K4 | -2.041 |
| MT-CYB | -3.045 | PAD12 | -1.938 |
| CINNA3 | -2.949 | CNP | -1.916 |
| FAT3 | -2.906 | PKP4 | -1.874 |
| BCAS1 | -2.857 | WNK1 | -1.714 |
| TSC2204 | -2.767 |
| Gene ID | Fold change | Gene ID | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|
| I110RA | 12.026 | FYB1 | 4.204 |
| AMPH | 9.664 | ARHGDIB | 4.111 |
| HS6ST3 | 8.405 | S1C38A2 | 4.104 |
| VSN11 | 7.195 | GNB5 | 3.998 |
| CO1GA1T1 | 6.373 | NAA30 | 3.930 |
| PRDM11 | 6.234 | S1C8A1 | 3.409 |
| 11CAM | 6.208 | DYNLL1 | 2.680 |
| GPR34 | 6.141 | HSPH1 | 2.666 |
| ZNF618 | 5.543 | SPP1 | 2.660 |
| RCSD1 | 5.419 | BSN | 2.518 |
| CRCP | 5.257 | GABARAP11 | 2.471 |
| 1NA | 4.831 | YWHAG | 2.443 |
| PIPRT | 4.812 | QDPR | 2.060 |
| GUCY1B1 | 4.422 | DNAjC5 | 2.042 |
| S1CSA3 | 4.338 | NEAT1 | 1.926 |
| SRGN | 4.250 | TNPO1 | 1.890 |
| SCN8A | 4.236 |
| Molecules in network | Score | Focus molecules | Diseases and functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHCYL1, Akt, Alp, AQP1, ATP1B2, BCAS1, CP, Creb, CTNNA3, cytochrome-c oxidase, DNAJCS, Growth hormone, GTPase, GUCY1B1, Hdac, HIPK2, Hsp70, Hsp90, HSPH1, IL1, L1CAM, MT-C01, MTC02, MT-C03, MT-CYB, NDRG2, NEAT1, Nuclear factor M1, PHLDB1, PKP4, PLAAT3, ROCK, Secretase gamma, SLCSA3, SLC8A1 | 49 | 22 | Neurological Disease, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities, Psychological Disorders |
| 14-3-3, 20s proteasome, 26s Pro teasome, ALAD, BSN, Calmodulin, calpain, CG, CNP, COLGALT1, Collagen Alpha1, Collagen type I (complex), Collagen type IV, EPAS1, ERK1/2, FAR1, Focal adhesion kinase, GFAP, HEPACAM, IN A, insulin, MAP4, MBP, MLC1, PDGF BB, Pka, PP2A, SEPTIN4, SLC1A2, SRGN, TAGLN, Tgf beta, transglutaminase, VSNL1, WNK1 | 38 | 18 | Cellular Function and Maintenance, Nervous System Development and Function, Tissue Development |
| AGT, AMPH, Ap1, ARHGDIB, Calcineurin protein(s), CD3, collagen type I (family), cytokine, ELOVL7, FYB1, GNBS, Gsk3, IKK (complex), IL12 (complex), integrin, integrin alpha L beta 2, Jnk, LDL, MAP4K4, Mek, MTURN, NFAT (complex), Nfat (family), NFIX, NFkB (complex), Nrlh, P38 MAPK, PAD12, Pkc(s), PPP1R1B, Rac, SPARCL1, SPP1, TCR, voltage-gated calcium channel Act in, AMPK, Ck2, C LEC9A, CST3, DYNLL1, | 25 | 13 | Cardiovascular Disease, Cell-To-Cell Signaling and Interaction, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities |
| Actin, AMPK, Ck2, C LEC9A, CST3, DYNLL1, ERK, F Actin, FADS2, FAM 107 A, GABARAPL1, G PR34 , hemoglobin, Histone h3, Histone h4, IgG, IL1ORA, IL12 (family), immunoglobulin, interferon alpha, Mapk, MHC Class II (complex), Notch, P13K (complex), RNA polymerase 11 , SHTN1, Siglech, SRC (family), trypsin, tubulin, TXNIP, Ubiquitin, Vegf, YWHAG, ZEB2 | 20 | 11 | Cell-To-Cell Signaling and Interaction, Infectious Diseases, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities |
| ACOD1, CARD16, CASP8, Cd24a, COL2A1, cytokine receptor, Dglucose, DAAM2, FAT3, GBPS, HCAR2, HEPACAM2, IFNG, ligp1, IL10RB, IL17RE, IL18BP, IL2RA, IRAGl , LGALS1, LTC4S, MLKL, NAA30, NLRCS, PARVG, PLAAT3, PRDM11, QDPR, REL, RHOBTB3, SCARA3, Tlr11, TNFRSF10B, TP531NP2, ZBP1 | 18 | 10 | Gastrointestinal Disease, Inflammatory Response, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities |
| CFB, CHADL, CNTLN, CSNK1A1, EP300, ETNPPL, FAM110D, FAM83G, FRMD4A, FRY, HDAC4, HDAC5, IKZF2, IL15RA, importin alpha, MECOM, miR-129-Sp (and other miRNAs w/seed UUUUUGC), MOBP, NRBP2, PAIP2B, PAQR6, PDCD1LG2, PPDPF, PRMT1, RCSD1, SCN8A, SMARCB 1, SNX22, SNX24, SOX2, SOX9, TNP01, TSC22D4, ZDBF2, ZNF 618 | 18 | 10 | Carbohydrate Metabolism, Cell Cycle, Cellular Assembly and Organization |
| ACBD7, betaestradiol, CA2, CALCRL, Clathrin, CRCP, DEFB116, DNPH1, DOCK3, ERBB, FMOS, HS6ST3, HTR4, INP P5F, L-histidine, L1CAM, Ly6a (includes others), MAL, NOS1, OGDHL, OGN, Pplc, PROTEASE, PTEN, PTPRT, PYGL, SEMA3A, sGC, SLC38A2, SLC02B1, SRC, sulfotransferase, SULT1C2, TBC1D24, Wap | 10 | 6 | Cellular Development, Connective Tissue Development and Function, Skeletal and Muscular System Development and Function |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





