Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Design of the framework
2.1. Advances of geospatial models
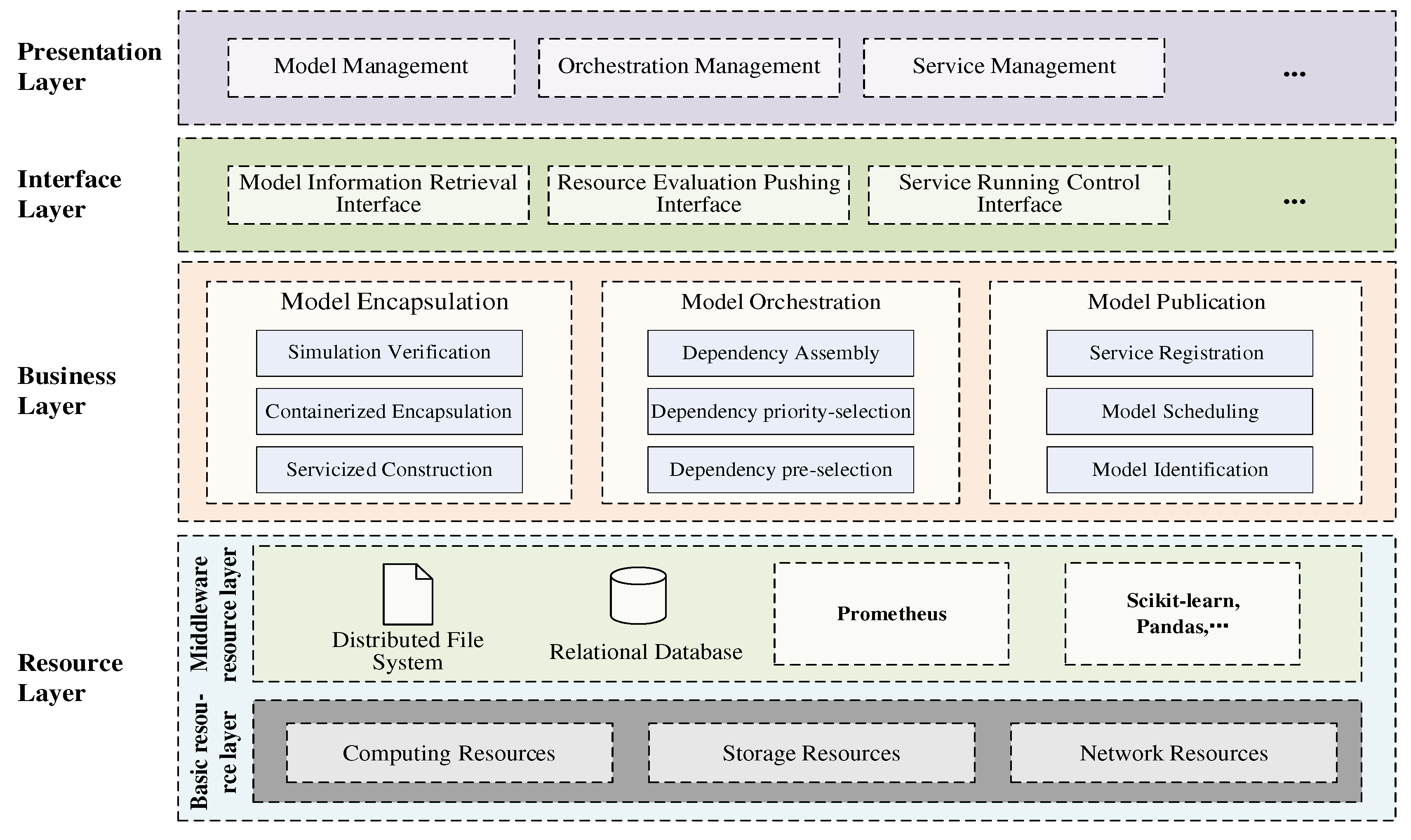
2.2. Containerized service-based integration framework
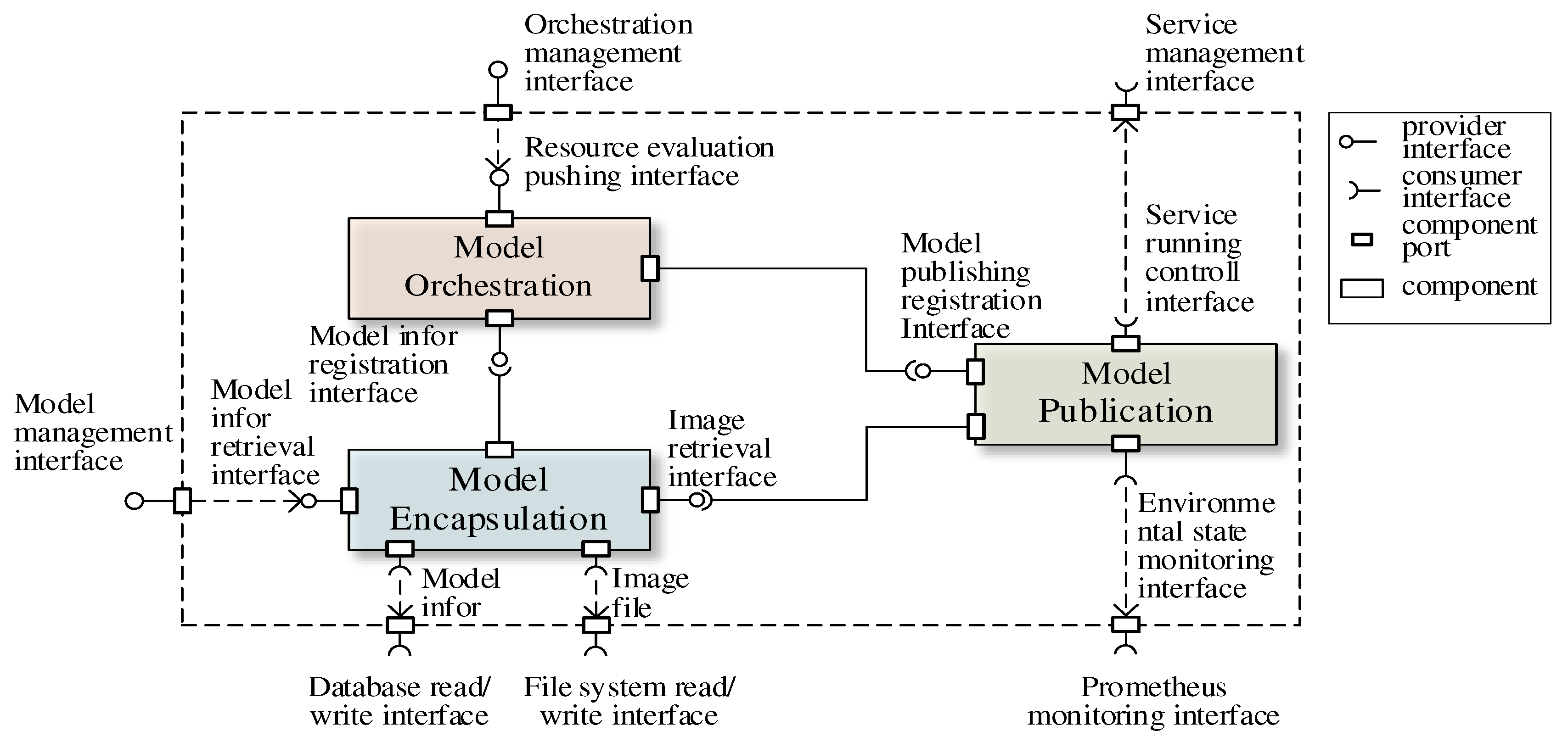
3. Design of the component
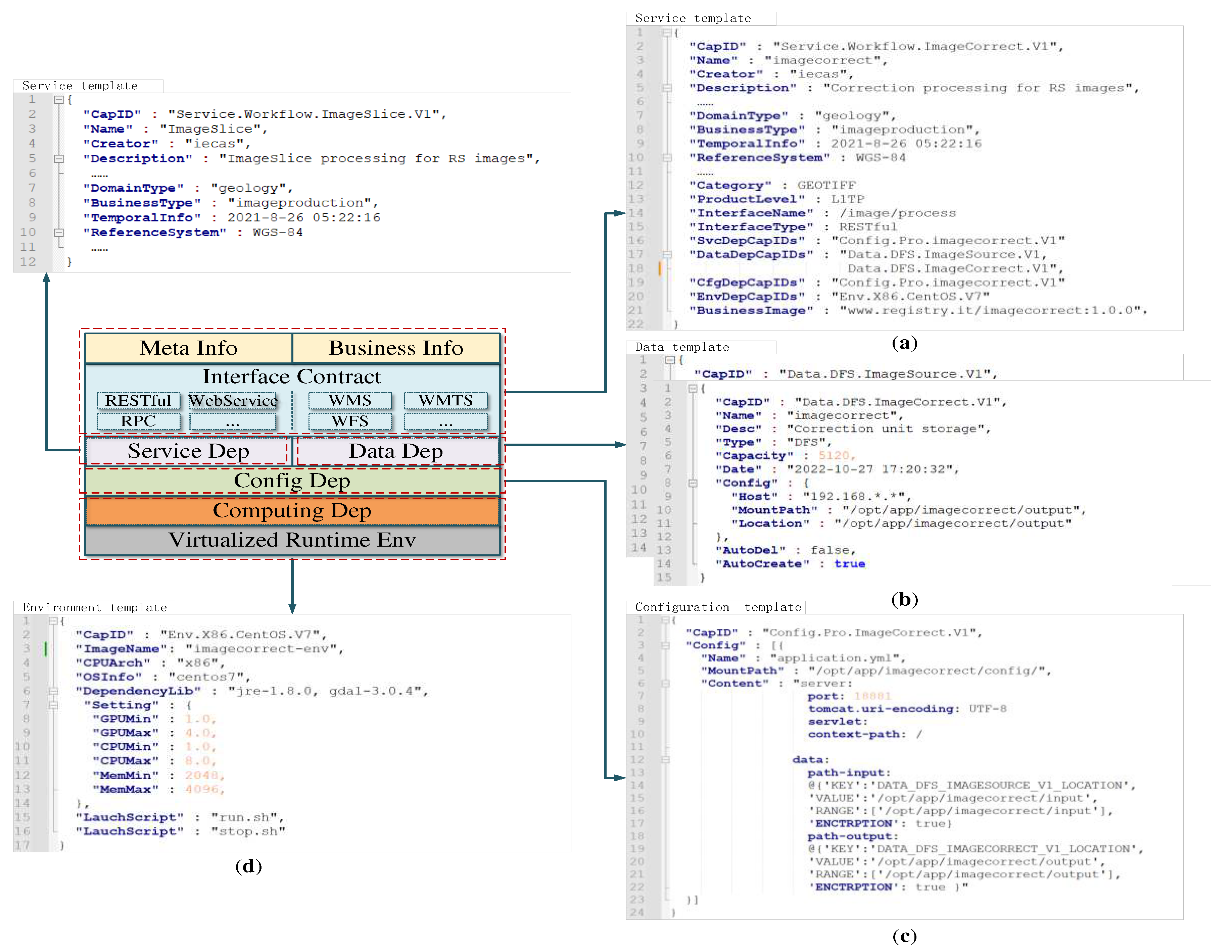
3.1. Servicized encapsulation of geospatial models
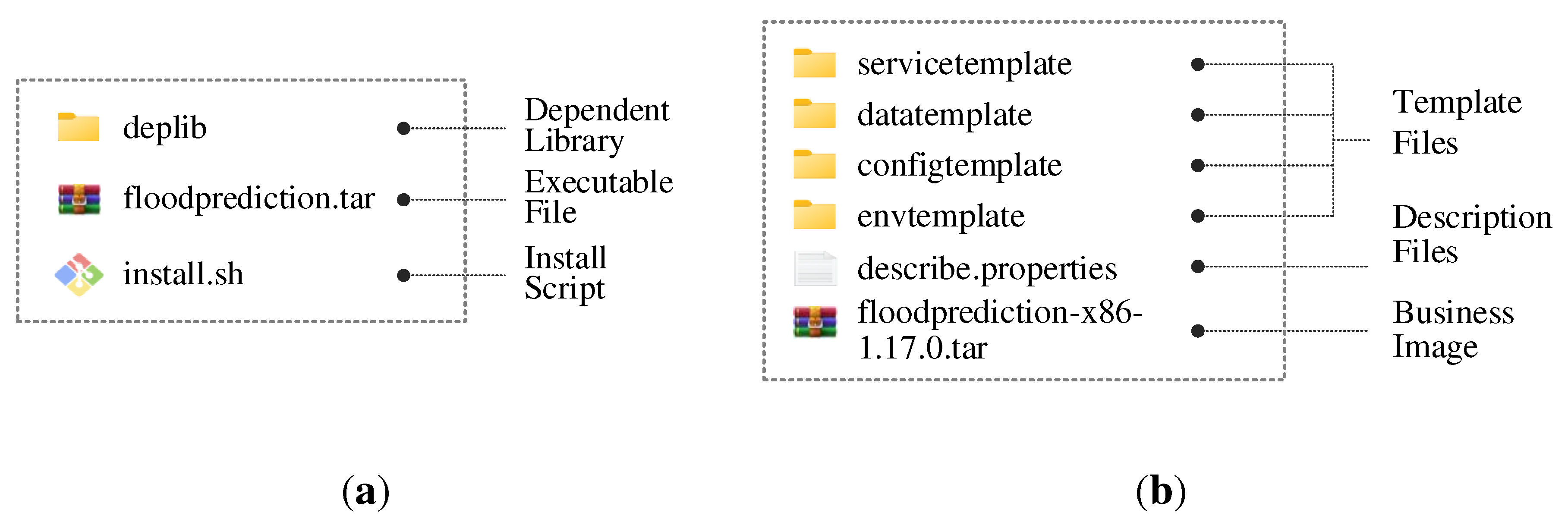
3.1.1. Servicized declaration of geospatial models
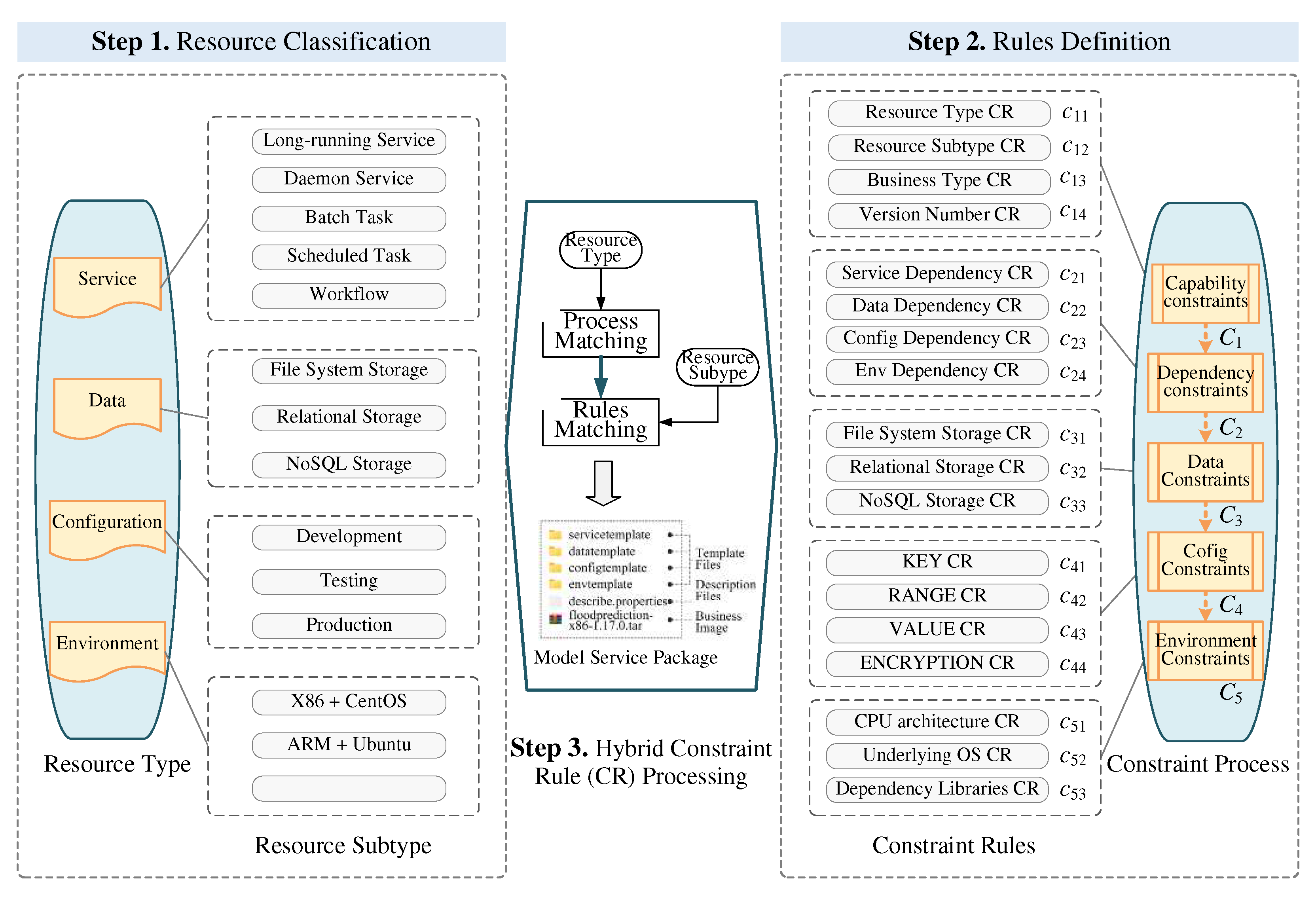
3.1.2. Standardized constraints of model services
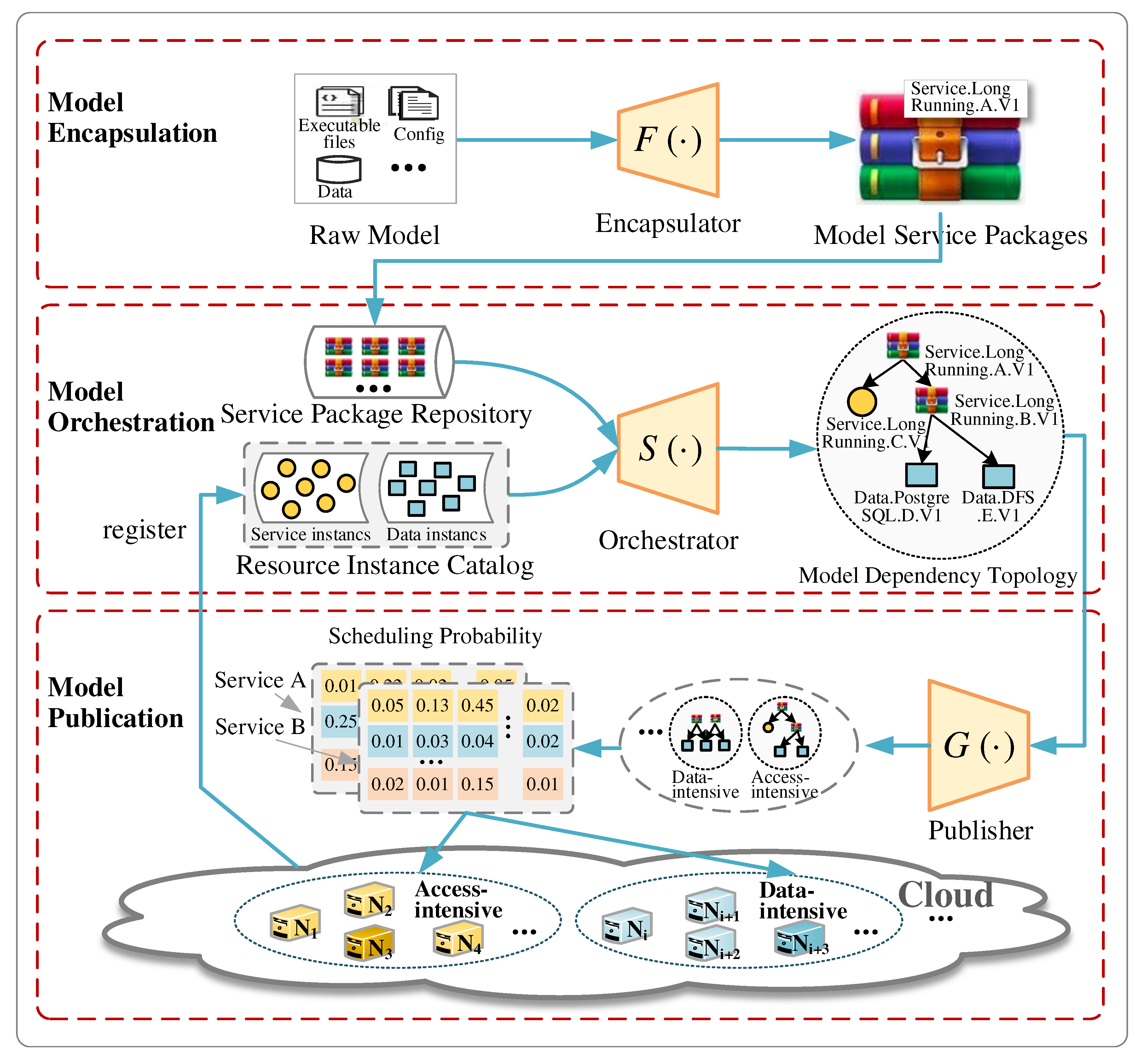
3.2. Prioritization-based orchestration of geospatial models
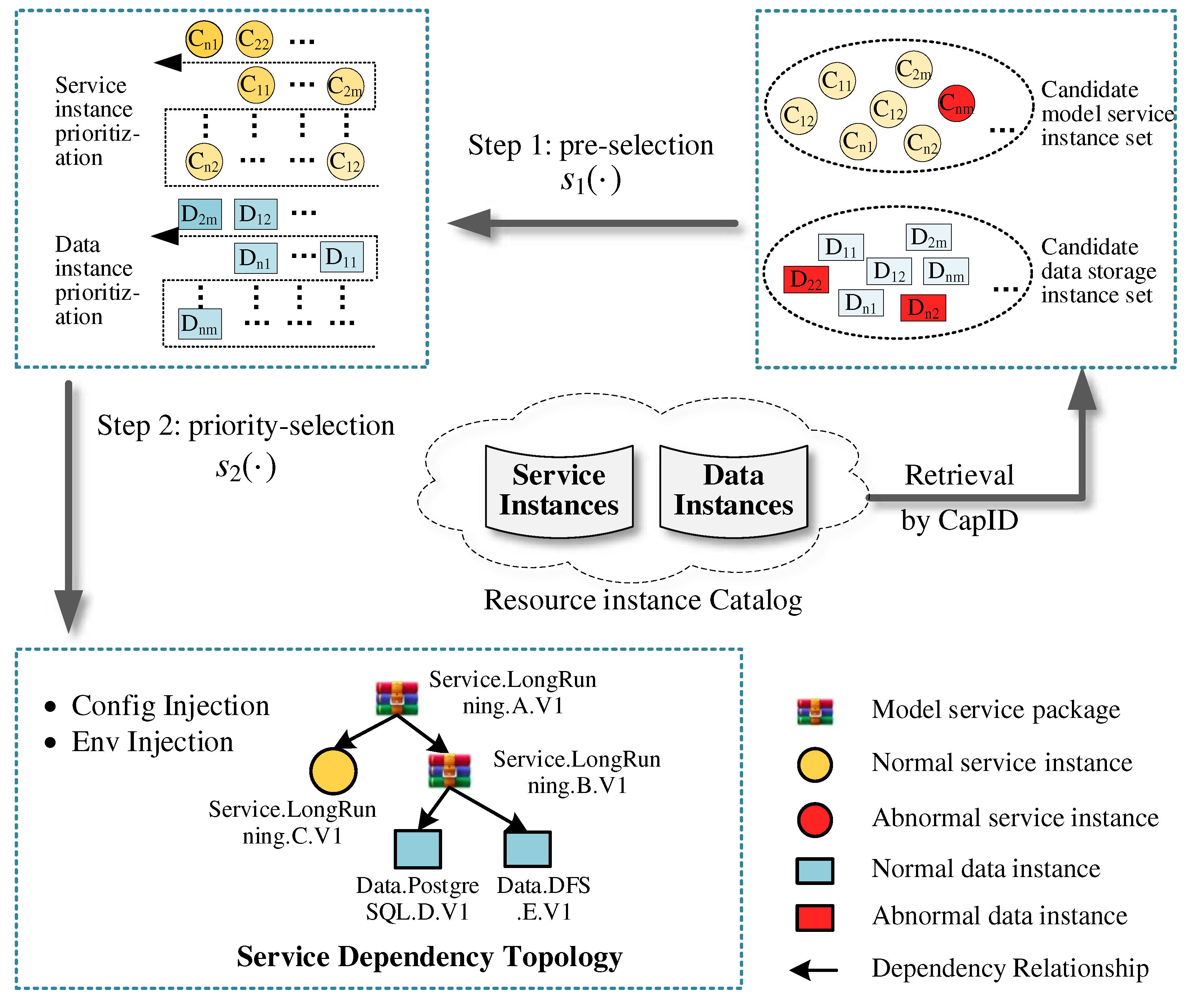
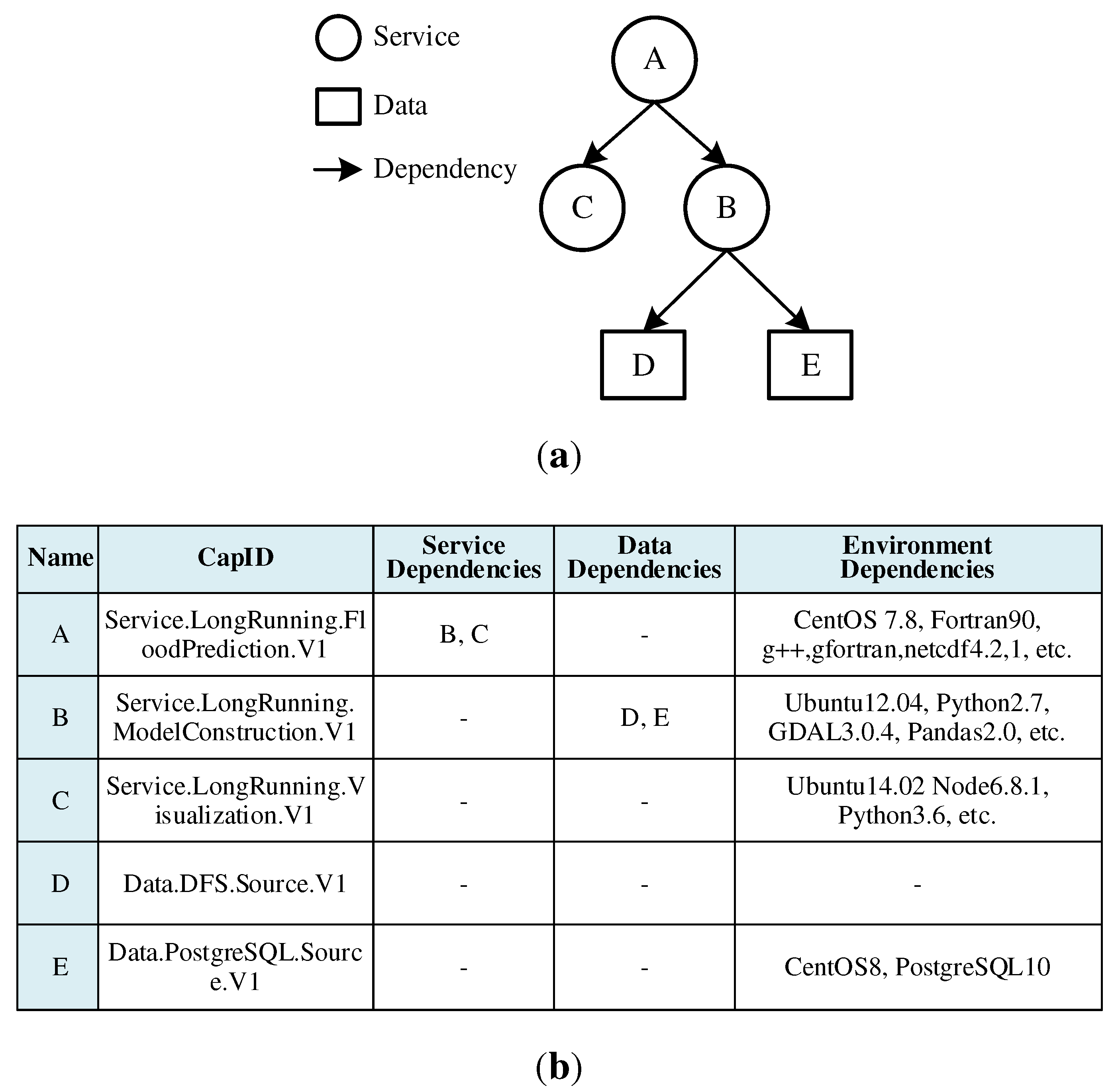
3.2.1. Priority-selection of dependent resources
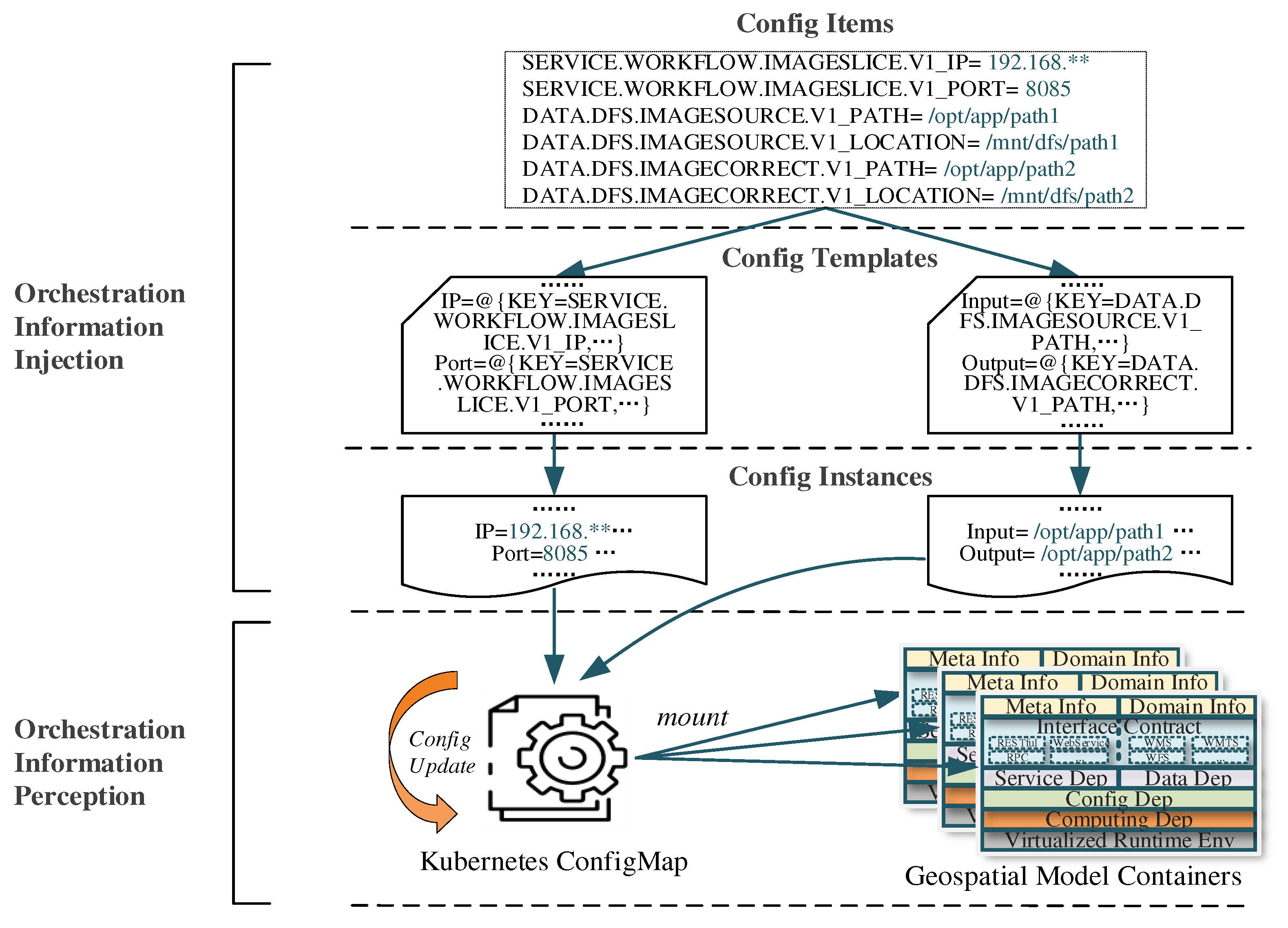
3.2.2. Implementation of dependency orchestration
3.3. Adaptive publication of geospatial models
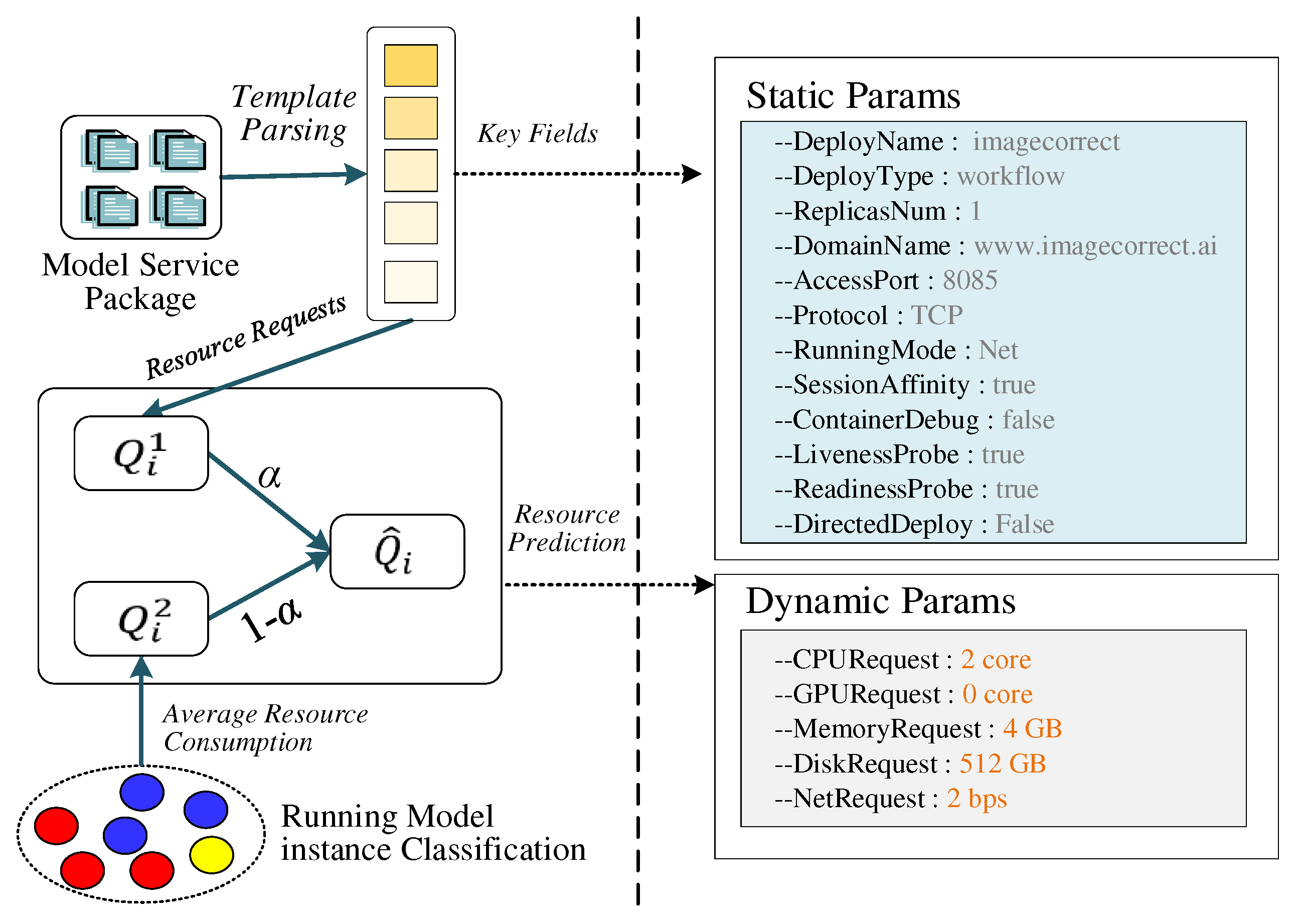
3.3.1. Model feature parameterization
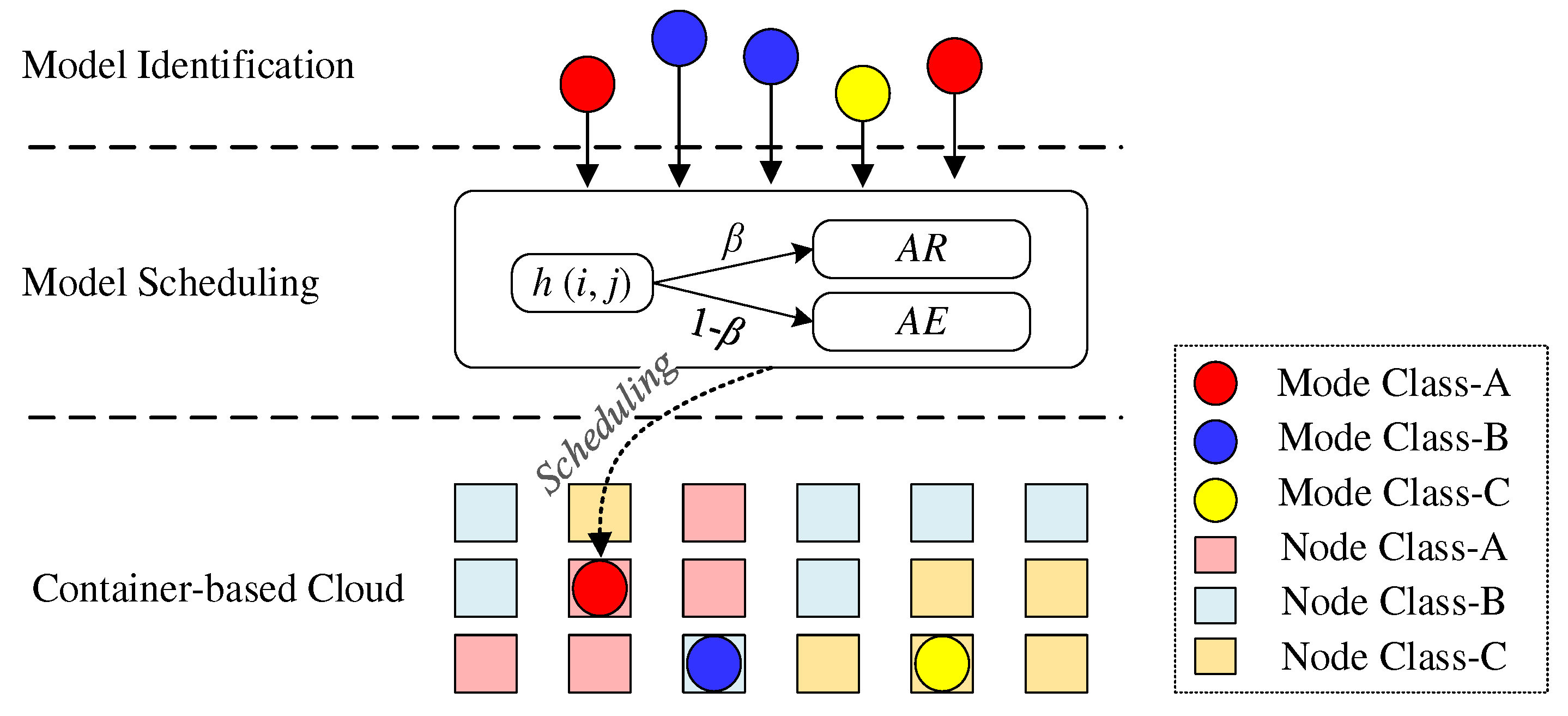
3.3.2. Heuristic model scheduling policies
4. Design of the system
4.1. System architecture and its component relationships
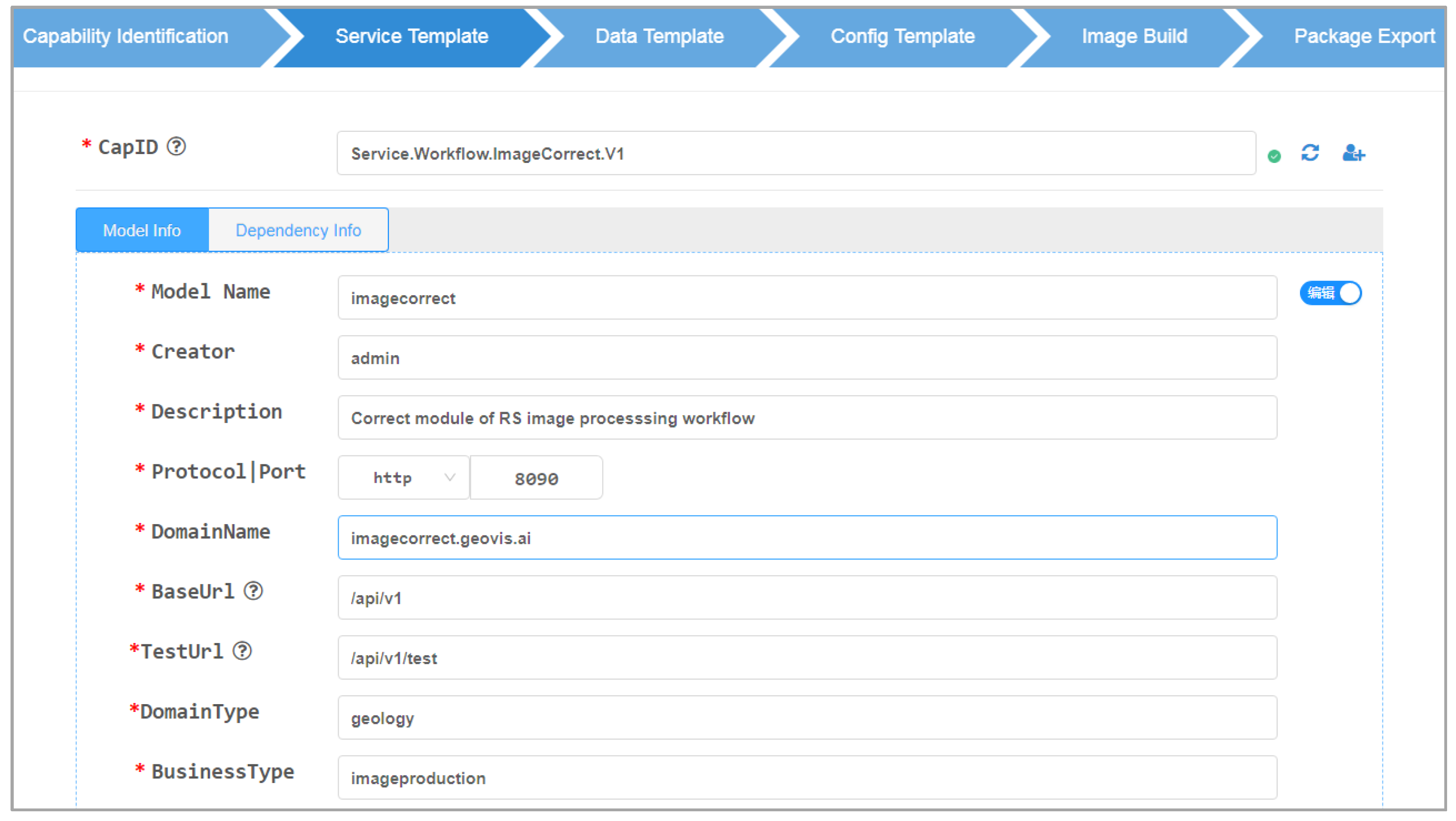
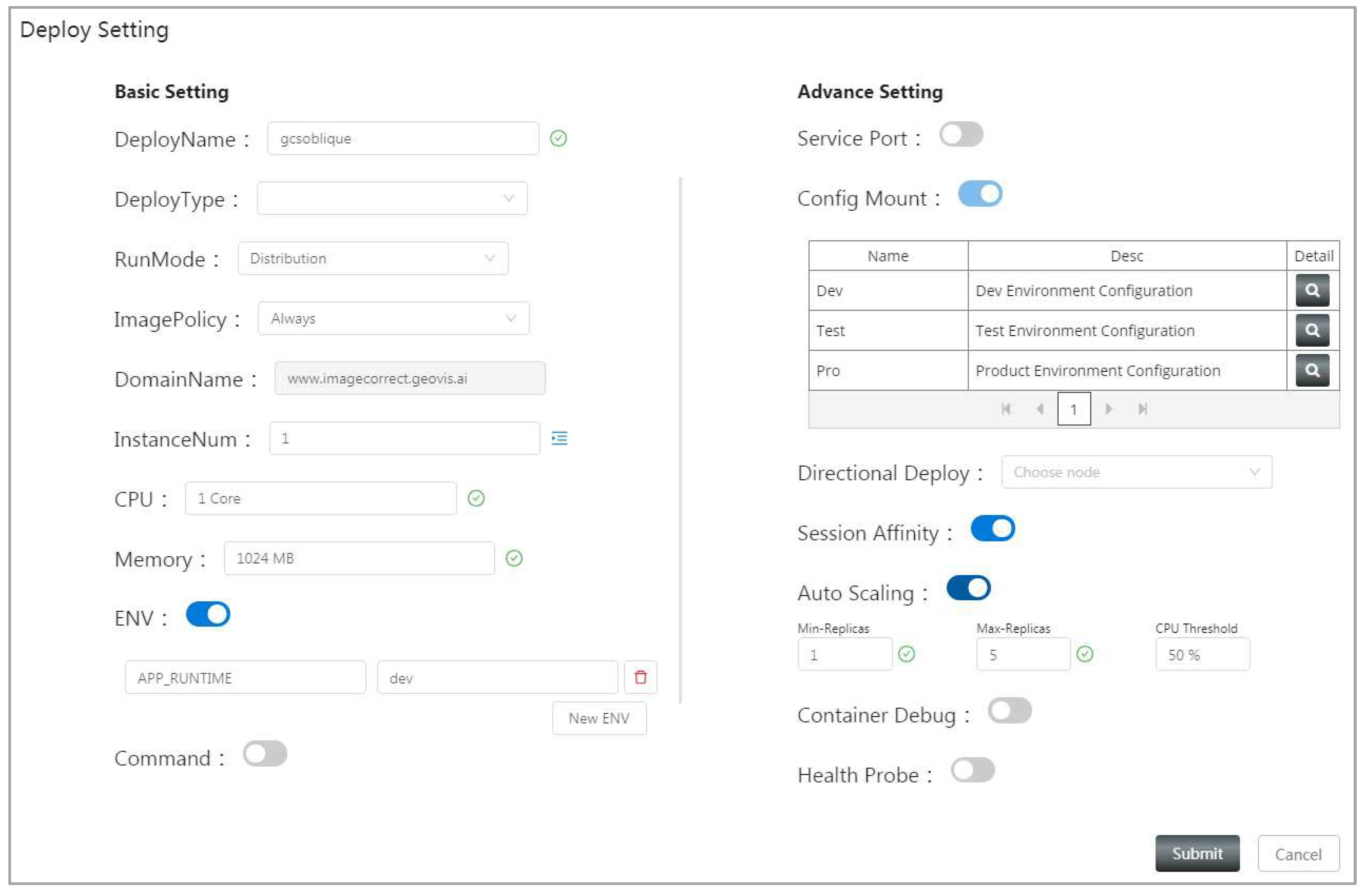
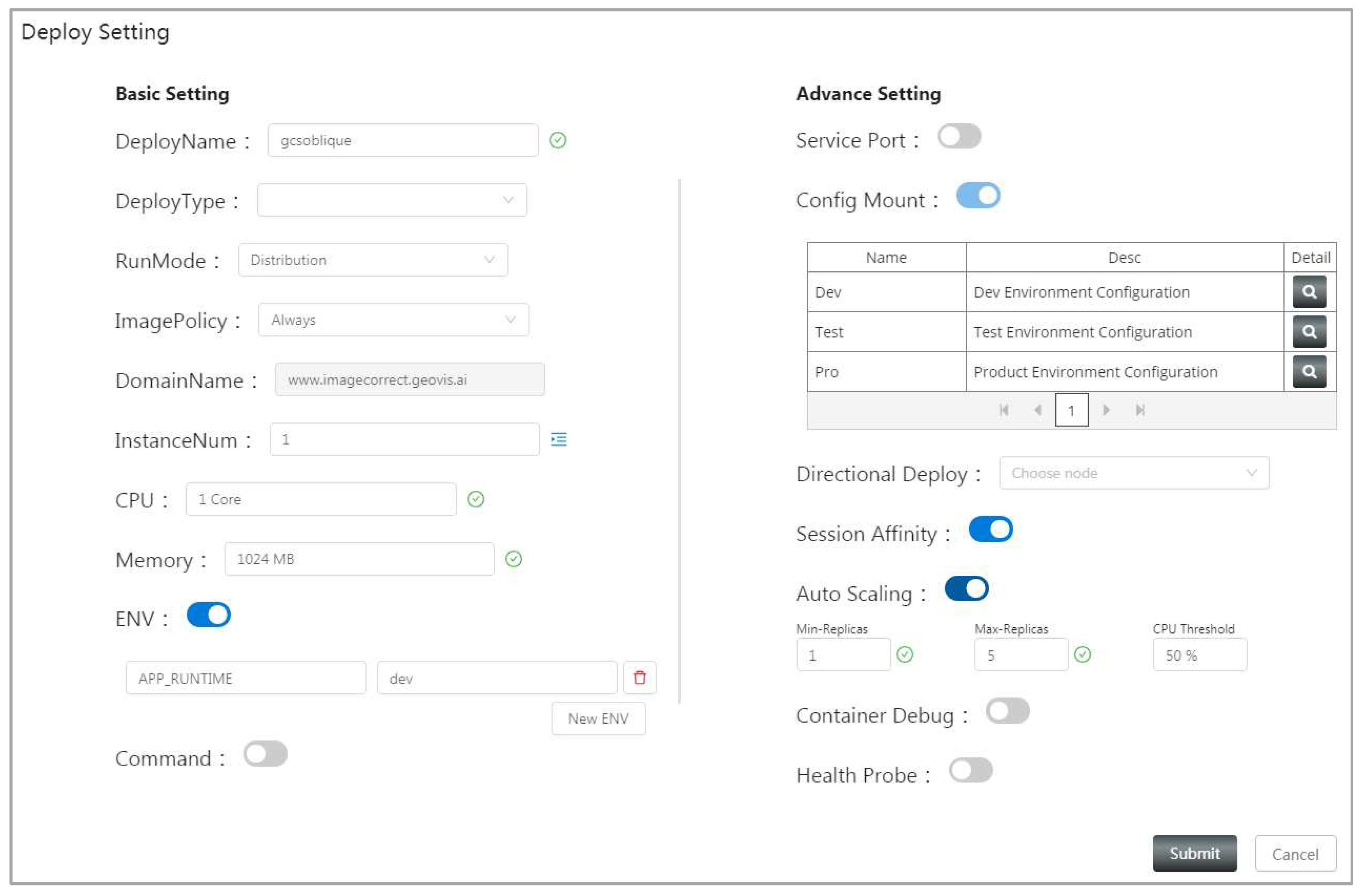
4.2. System implementation and function introduction
5. Case Studies
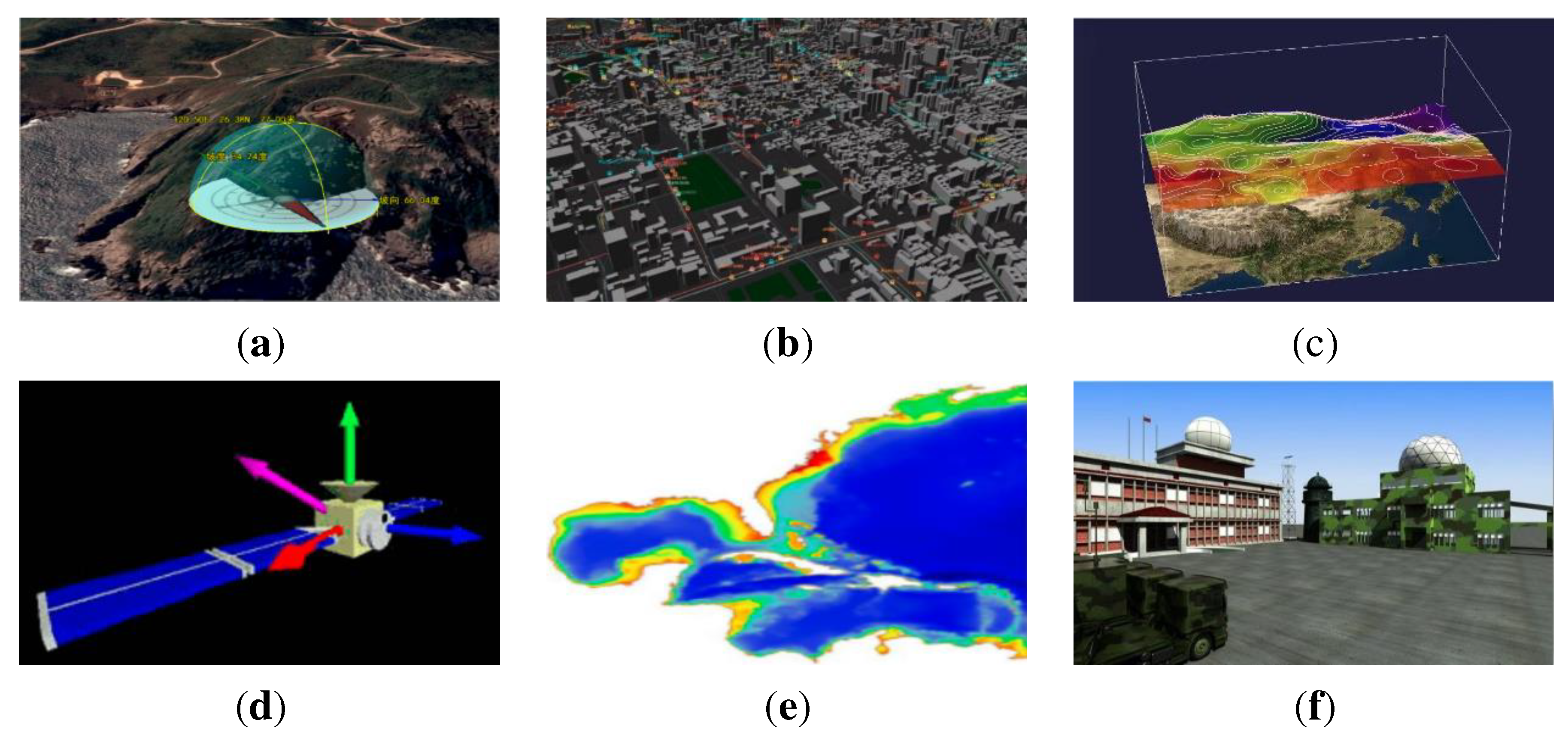
5.1. geospatial models for flood disaster prediction
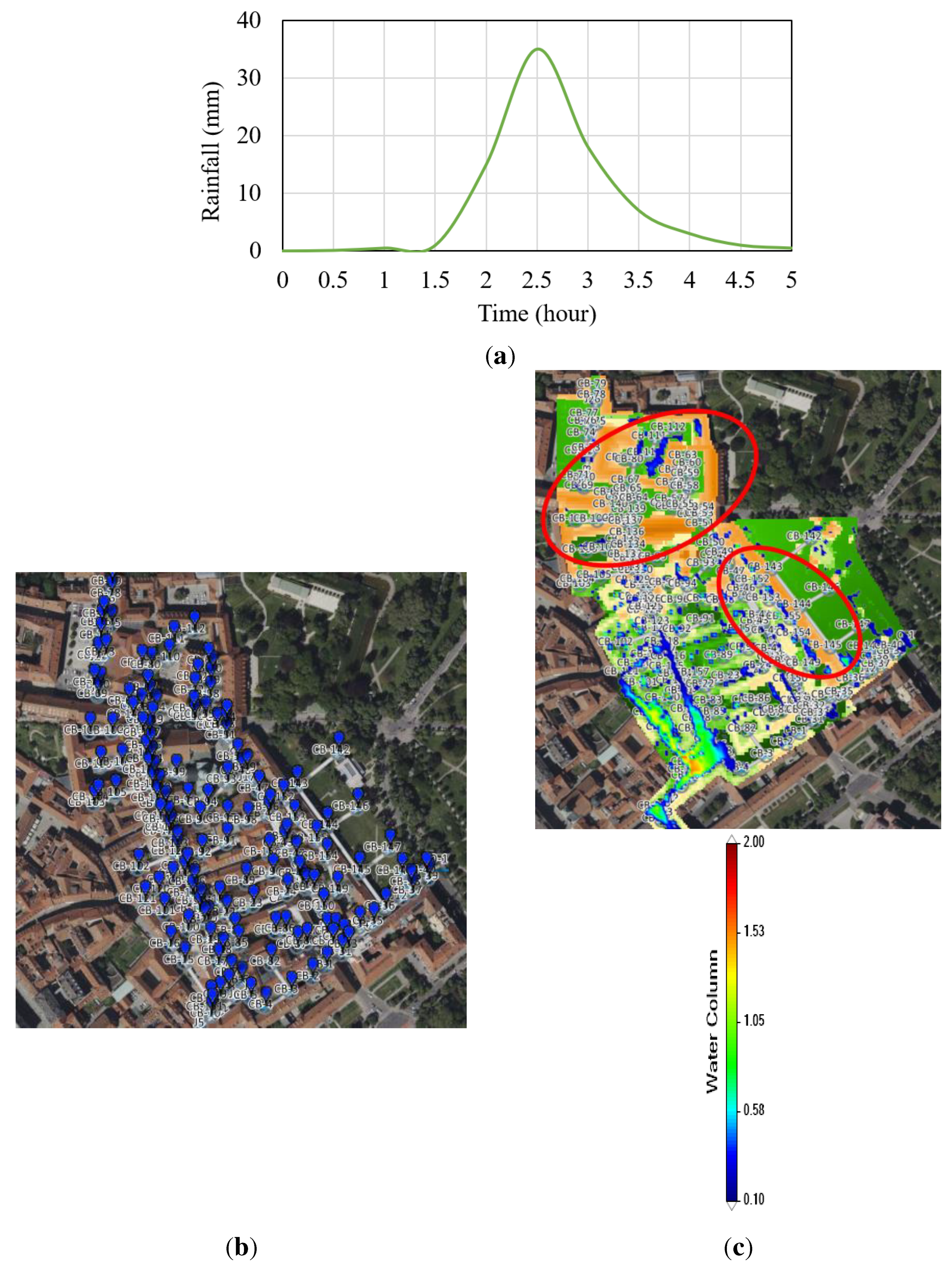
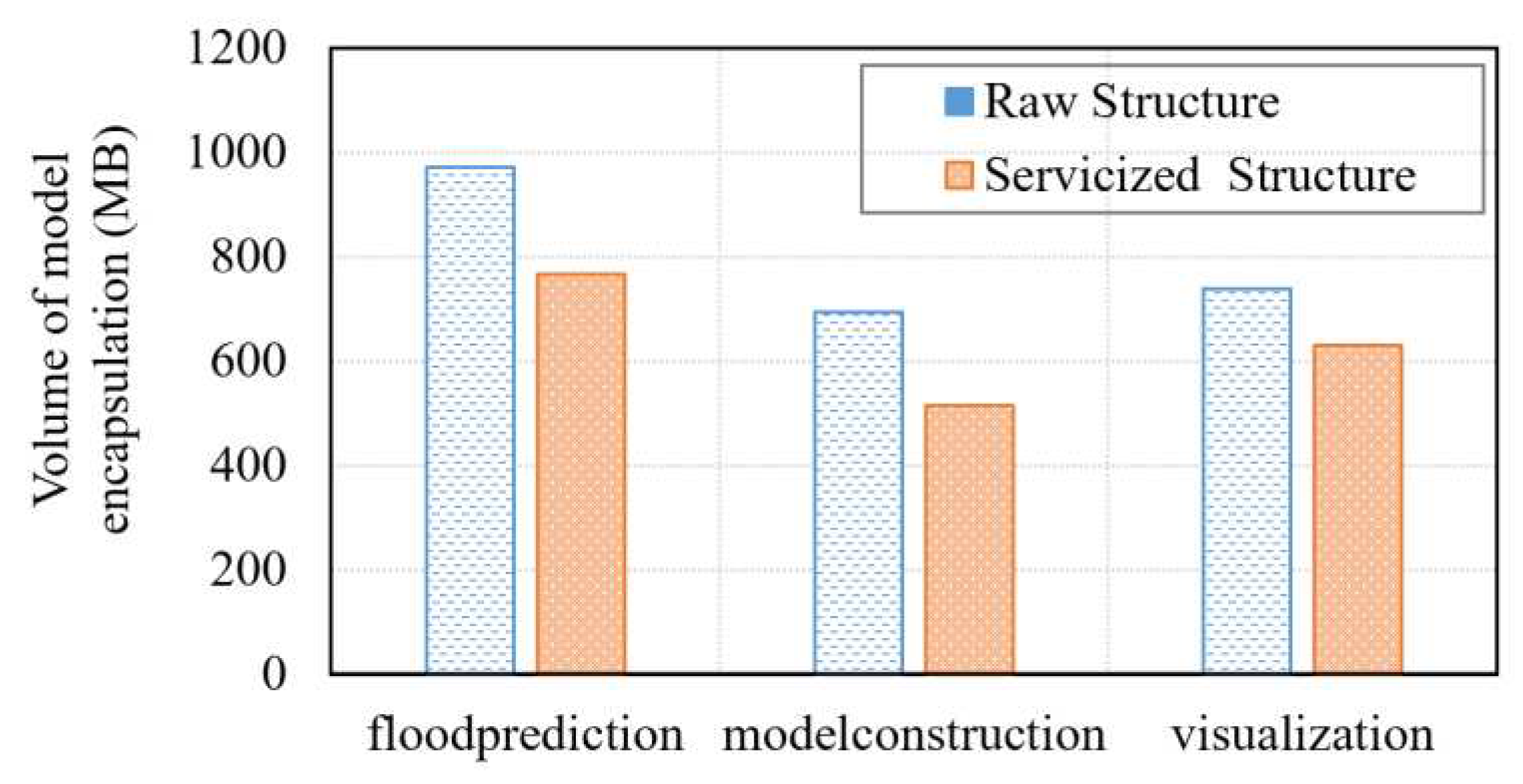
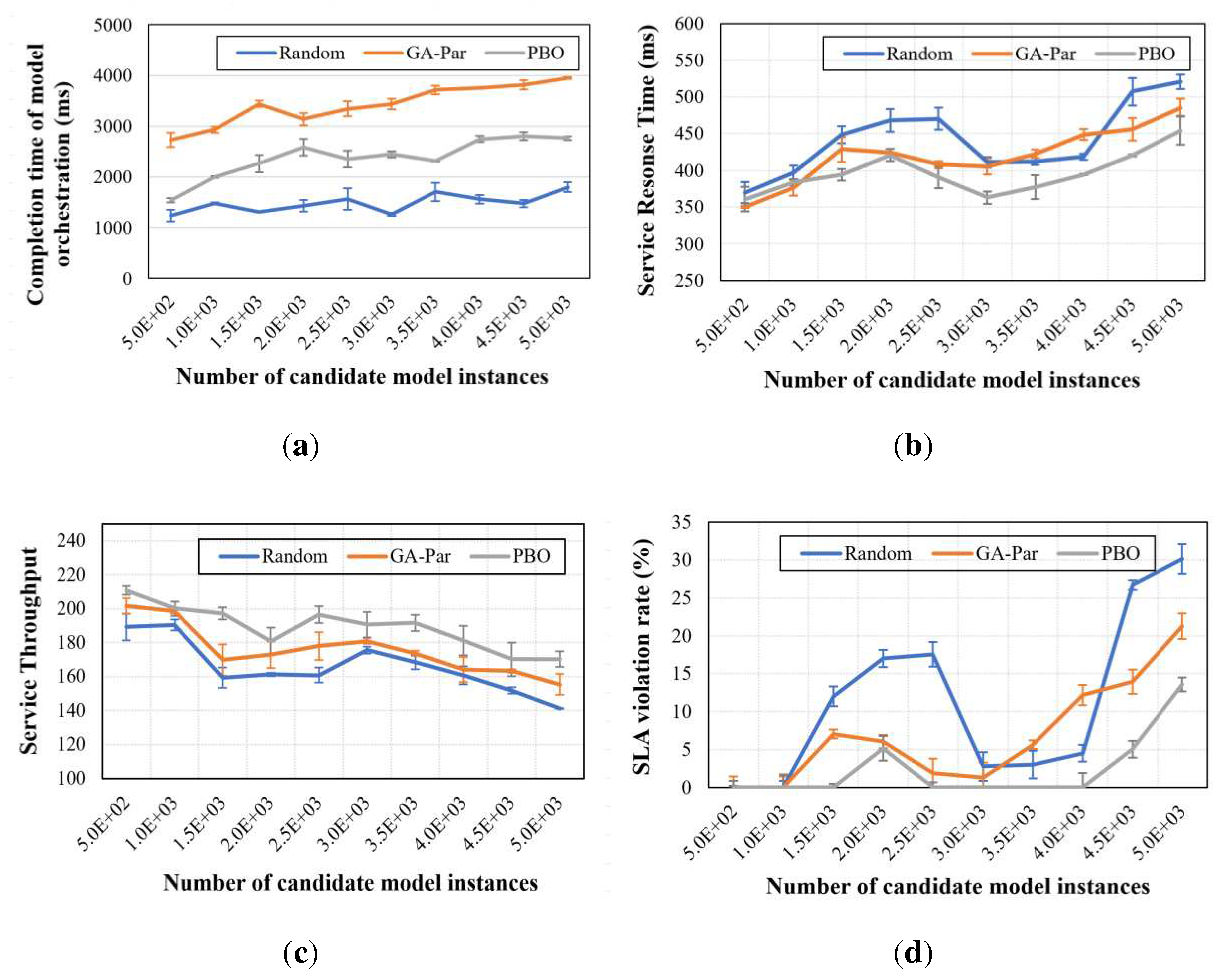
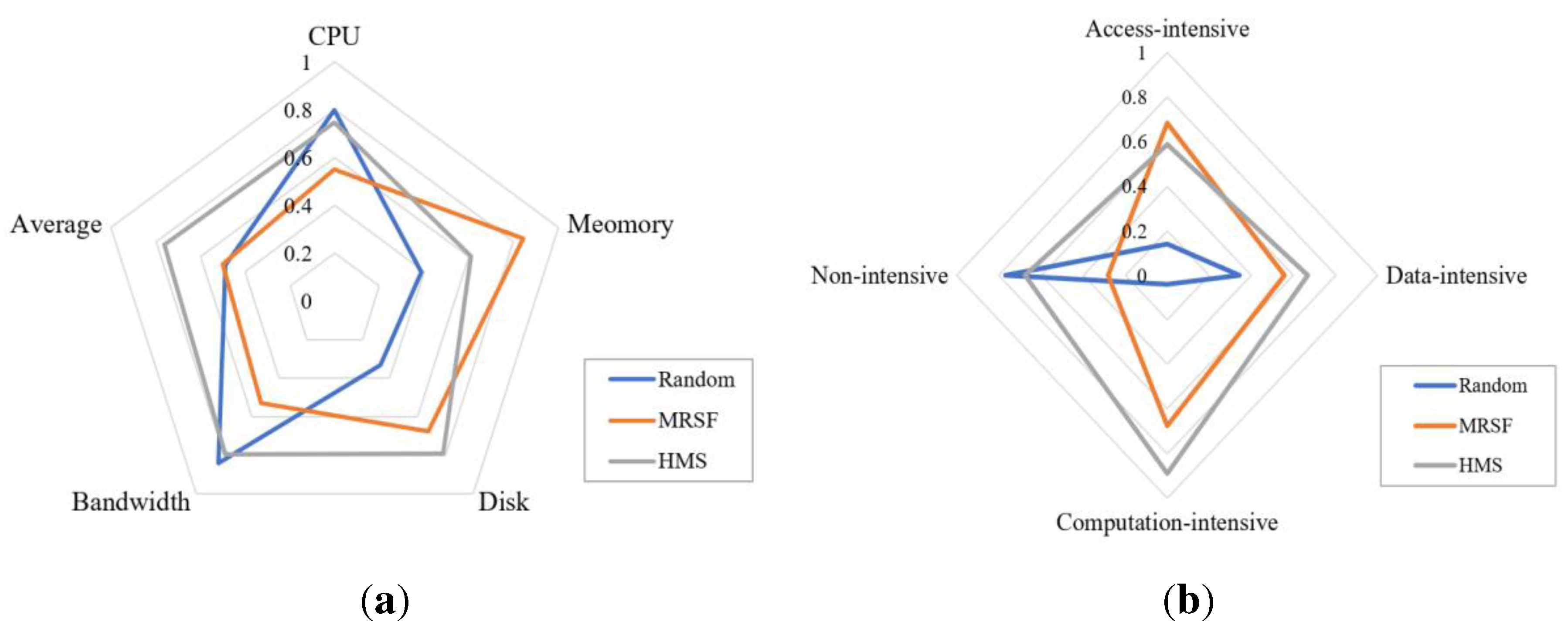
5.2. Practical verification of geospatial model integration
6. Conclusions and future work
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, C.Q.; Shi, W.Z. Spatial analysis modelling and principle; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y. System modelling and simulation; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bennie, J.; Huntley, B.; Wiltshire, A.; Hill, M. O. Baxter, R. Slope, aspect and climate: Spatially explicit and implicit models of topographic microclimate in chalk grassland. Ecological Modelling 2008, 216, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.; Kim, J. Participatory sensing, and digital twin city: Updating virtual city models for enhanced risk-informed decision-making. Journal of Management in Engineering 2020, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M. A.; Tvoroshenko, I.; Baker, J. H.; Kochura, L.; Lyashenko, V. Interactive geoinformation three-dimensional model of a landscape park using geoinformatics tools. International Journal on Advanced Science Engineering Information Technology 2020, 10, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkiewicz, J.; Sochacki, M.; Zakrzewski, B. Generic model of a satellite attitude control system. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Su, F.Z.; Du, J.X.; Feng, P.F.; Zhang, S.X. Tidal flat extraction and change analysis based on the RF-W model: A case study of Jiaozhou bay, east China. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 1436–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.J.; Xu, B.L.; Jing, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.R.; Wang, L.H. Three-dimensional visual perception technology and simulation of individual soldier in combat. In Proceedings of the 2021 28th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Nanchang, China, 3-5 Nov. 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Ren, Z.G.; Cao, Y.B. Research on seamless integration of spatial analysis model and GIS. Geospatial Information 2014, 12, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.N.; Chen, M.; Lu, G.N.; Lin, H.; He, L.; Yue, S.S. Prototyping an open environment for sharing geospatial analysis models on cloud computing platform. International Journal of Digital Earth 2013, 6, 356–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.Y.; Ames, D.P.; Chen, M.; Nelson, E. J.; Khattar, R. A container-based approach for sharing environmental models as web services. International Journal of Digital Earth 2021, 14, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.N.; Chen, M.; Yue, S.S.; Zheng, P.B.; Peng, G.Q.; Lu, G.N. A model-service deployment strategy for collaboratively sharing geo-analysis models in an open web environment. International Journal of Digital Earth 2017, 10, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.S.; Chen, M.; Wen, Y.N.; Lu, G.N. Service-oriented model-encapsulation strategy for sharing and integrating heterogeneous geo-analysis models in an open web environment. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2016, 114, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenov, L.; Stanimirovi, A.; Djordjevi, S.; Kajan. Realization of component-based GIS application framework. 7th AGILE Conference on Geographic Information Science 2004, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Liu, L.P.; Yu, H.L. XML based GIS application model definition and description language GBMDL. China Management Informationization 2009, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.L.; Wang, R.J.; Cui, C.Y.; Xie, C.J. GIS application model based on cloud computing. Network Computing and Information Security: Second International Conference. 2012, 130-136.
- Ou, S. J. Research and application of geographic information system development based on component architecture. PhD diss., Jilin University, Jilin, 2003.
- Jia, J. Research on key technologies of geographic information system development. Construction & Design for Project 2022, 9, 142–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dontsov, A. A.; Sutorikhin, I. A. Development of a geographic information system for data collection and analysis based on microservice architecture. CEUR Workshop Proceedings 2021, 3006, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H. GIS functional component library and functional integration. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2001, 04, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, D.; Ying, X.X.; Gao, X.B.; Tao, W.D.; Cui, Y.J.; Hua, T.T. A WebGIS platform design and implementation based on open source GIS middleware. 24th International Conference on Geoinformatics. 2016, pp. 1-5.
- Wang, S.H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, E.Q. An integrated GIS platform architecture for spatiotemporal big data. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 94, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, B.; Grant, D.; Oppenheimer; Brewer, E.; Wilkes, J. Borg, Omega, and Kubernetes. Communications of the ACM 2016, 59, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.H. Isolation Forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15-19 Dec. 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, J.; Ploskas, N.; Papathanasiou, J.; Ploskas, N. Topsis. Multiple Criteria Decision Aid: Methods, Examples and Python Implementations 2018, 136, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.Y.; Lin, T.; Yang, R.Y.; Ji, S.L.; Ranjan, R.; Romanovsky, A.; Lin, C.T.; Xu, J. GA-Par: Dependable microservice orchestration framework for geo-distributed clouds. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 2020, 31, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




