Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- (1)
- Identification of influential frequency domain pre-processing steps
- (2)
- Software products for frequency domain pre-processing
- (3)
- Rationales, algorithms, general comments, and suggestions for each pre-processing step
- (4)
- Summary and conclusions
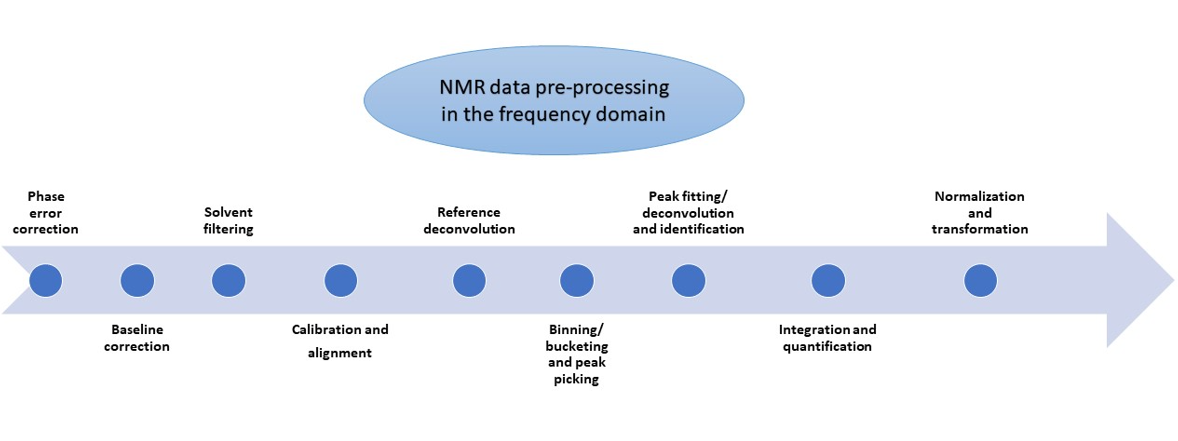
Brief overview of pre-processing steps in the NMR frequency domain
Phase error correction
Baseline correction
Solvent filtering
Calibration and alignment
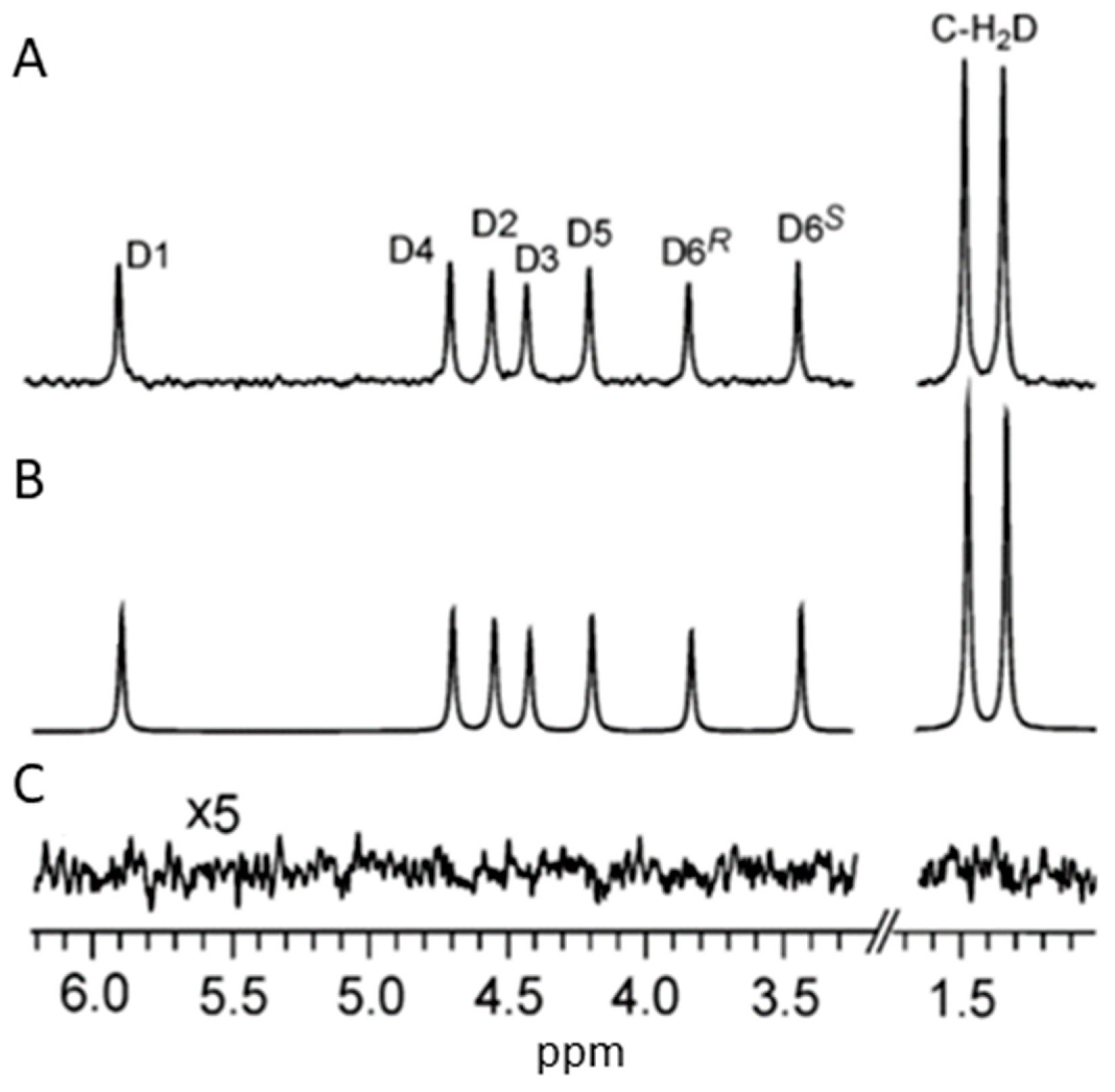
Reference deconvolution
Binning/bucketing and peak picking
Peak fitting/deconvolution and compound identification
Available frequency domain pre-processing choices in multiple software products
Understanding NMR pre-processing steps in the frequency domain
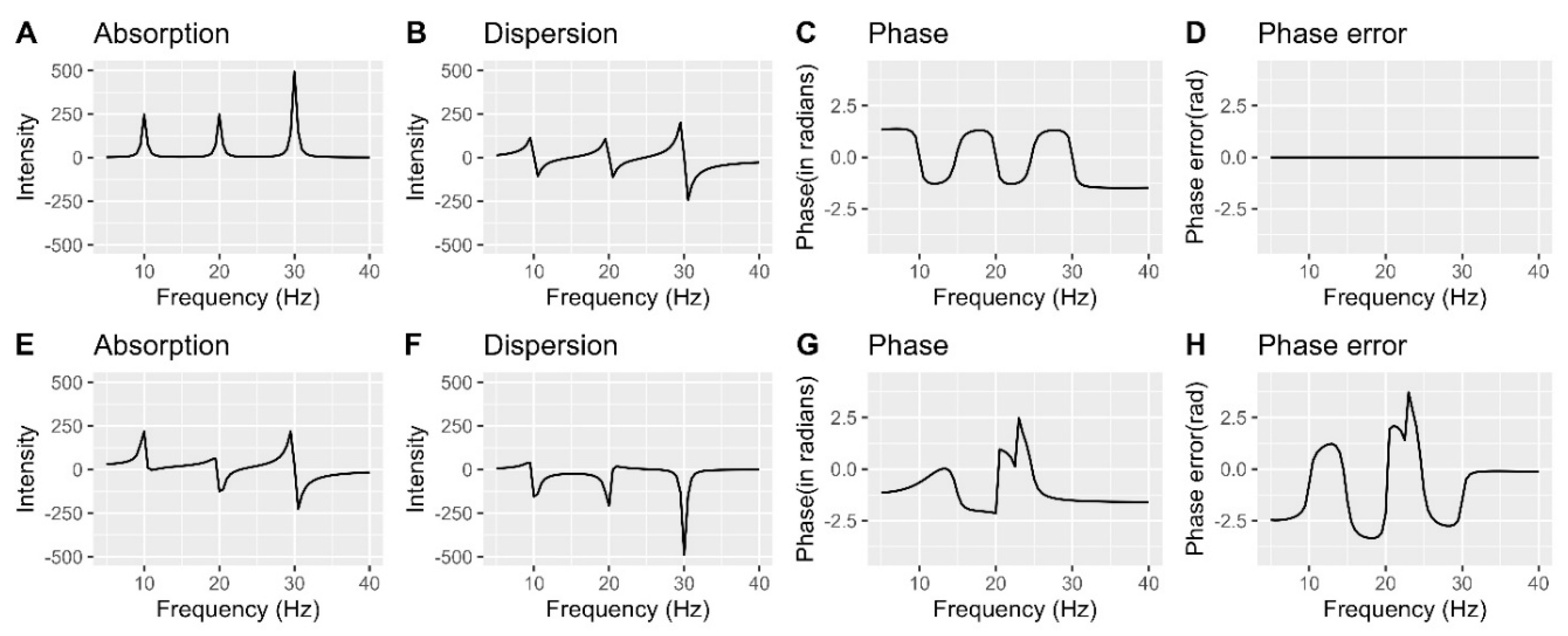
Understanding and correcting phase errors
Baseline correction techniques
Solvent filtering methods
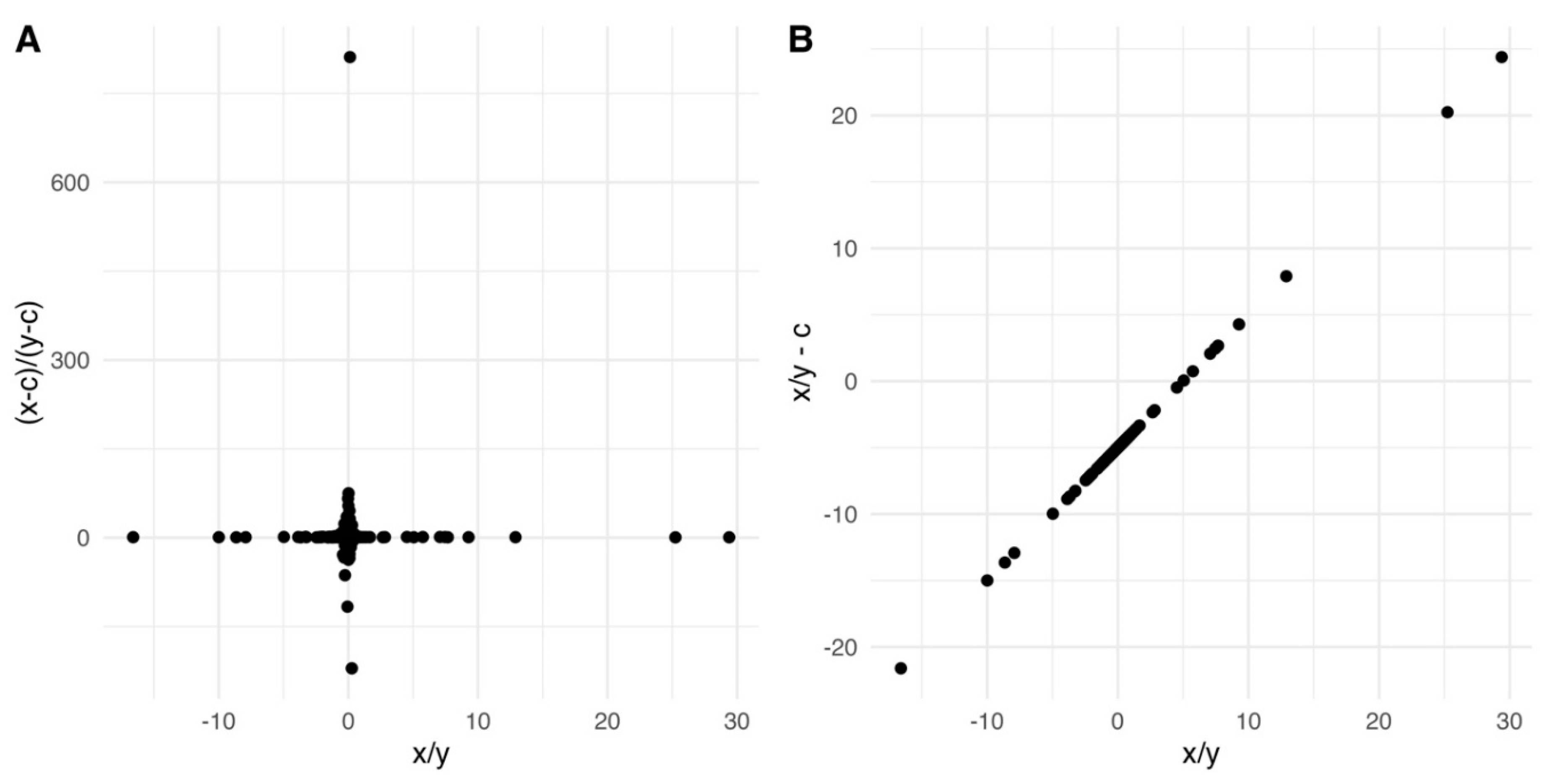
Methods and considerations for calibration and alignment
- (1)
- Select reference signal data points from a frequency spectrum and set the rest of the data points to 0, creating a reference-only spectrum (Aref).
- (2)
- Transform Aref into the time domain to obtain the reference-only FID (FIDref).
- (3)
- Use simulation to deconvolve FIDref and obtain an ideal reference FID with a Lorentzian lineshape (FIDideal_ref).
- (4)
- Calculate a ratio variable for each time point in the time domain:
- (5)
- Multiply each time point of the original FID by the corresponding ratio variable to obtain the corrected whole FID:
- (6)
- Transform FIDcorrected back into the frequency domain to obtain a reference-deconvoluted whole spectrum with an ideal lineshape.
- (1)
- Signals can be split into multiple bins or combined into a single bin, resulting in non-meaningful bin summary data 32.
- (2)
- Fixed binning is not effective for handling overlapping peaks.
- (3)
- Bins are not comparable across spectra if alignment issues exist before binning 47.
Peak fitting/deconvolution, and compound identification
Integration and quantification
Normalization and transformation
Discussions and conclusion
References
- Lauterbur, P. C. Paul C. Lauterbur Notebook, 1971, Box 1. https://digital.sciencehistory.org/works/0c483j46q.
- LAUTERBUR, P. C. Image Formation by Induced Local Interactions: Examples Employing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Nature 1973, 242, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Miska, M.; Jung, A.; Weber, M.-A.; Saure, D.; Schmidmaier, G.; Weimer, A.; Moghaddam, A.; Doll, J. Posttraumatic Perfusion Analysis of Quadriceps, Patellar, and Achilles Tendon Regeneration With Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 2020, n/a (n/a). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddie, S.; Nagendran, A.; Cox, T.; Bomsztyk, J.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Brandner, S.; Manji, H.; Rees, J.; Ramsay, A.; Rossor, A.; D’Sa, S.; Reilly, M.; Carr, A.; Lunn, M. Peripheral Nerve Neurolymphomatosis: Clinical Features, Treatment and Outcomes. Muscle & Nerve 2020, n/a (n/a). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TopSpin | NMR Data Analysis | Bruker. https://www.bruker.com/en/products-and-solutions/mr/nmr-software/topspin.html (accessed 2021-06-22).
- NMR Webpage - SpinWorks. https://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~wolowiec/spinworks/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- Chemistry Software for Analytical and Chemical Knowledge Management. https://www.acdlabs.com/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- NMRPipe. https://spin.niddk.nih.gov/bax/software/NMRPipe/NMRPipe.html (accessed 2021-06-22).
- rNMR: Open Source Software for NMR Data Analysis. http://rnmr.nmrfam.wisc.edu/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- mestrelab. Mestrelab Research S.L. - Analytical Chemistry Software Solutions. Mestrelab. https://mestrelab.com/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- Chenomx Inc | Metabolite Discovery and Measurement. https://www.chenomx.com/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- mestrelab. Mnova. Mestrelab. https://mestrelab.com/software/mnova/ (accessed 2021-06-22).
- Ebbels, T. M. D.; De Iorio, M. Statistical Data Analysis in Metabolomics. In Handbook of Statistical Systems Biology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2011; pp 163–180. [CrossRef]
- Ernst, R. R. Numerical Hilbert Transform and Automatic Phase Correction in Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1969, 1, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, F. G.; Phillips, P. S. Automatic Phase Correction in Magnetic Resonance Using DISPA. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1984, 59, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotak, C. H.; Dumoulin, C. L.; Newsham, M. D. Automatic Phase Correction of Fourier Transform NMR Spectra Based on the Dispersion versus Absorption (DISPA) Lineshape Analysis. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1984, 57, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, E. A.; Sidky, E. Y.; Farra, T. C. Calculation of Phase-Correction Constants Using the DISPA Phase-Angle Estimation Technique. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1989, 82, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. E.; Campbell, T. W.; Moore, R. N. Automated Phase Correction of FT NMR Spectra by Baseline Optimization. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1989, 85, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montigny, F.; Elbayed, K.; Brondeau, J.; Canet, D. Automatic Phase Correction of Fourier-Transform NMR Data and Estimation of Peak Area by Fitting to a Lorentzian Shape. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, A. A New Algorithm for Automatic Phase Correction by Symmetrizing Lines. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1991, 91, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R. E.; Delaglio, F.; Levy, G. C. Phase Correction of Two-Dimensional NMR Spectra Using DISPA. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1992, 98, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balacco, G. A New Criterion for Automatic Phase Correction of High-Resolution NMR-Spectra Which Does Not Require Isolated or Symmetrical Lines. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A 1994, 110, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džakula, Ž. Phase Angle Measurement from Peak Areas (PAMPAS). Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2000, 146, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Weng, Z.; Goh, L.; Garland, M. An Efficient Algorithm for Automatic Phase Correction of NMR Spectra Based on Entropy Minimization. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2002, 158, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larry Bretthorst, G. Automatic Phasing of MR Images. Part I: Linearly Varying Phase. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2008, 191, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brouwer, H. Evaluation of Algorithms for Automated Phase Correction of NMR Spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2009, 201, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, E. H.; Hoferer, J.; Mertens, D.; Kasper, G. Automated Phase Correction via Maximization of the Real Signal. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2009, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Liu, C. A Robust Automatic Phase Correction Method for Signal Dense Spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2013, 234, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motegi, H.; Tsuboi, Y.; Saga, A.; Kagami, T.; Inoue, M.; Toki, H.; Minowa, O.; Noda, T.; Kikuchi, J. Identification of Reliable Components in Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS): A Data-Driven Approach across Metabolic Processes. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 15710–15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corol, D. I.; Harflett, C.; Beale, M. H.; Ward, J. L. An Efficient High Throughput Metabotyping Platform for Screening of Biomass Willows. Metabolites 2014, 4, 946–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, G.; Zuriarrain, J.; Zuriarrain, A.; Berregi, I. Quantitative Determination of Carboxylic Acids, Amino Acids, Carbohydrates, Ethanol and Hydroxymethylfurfural in Honey by (1)H NMR. Food Chem 2016, 196, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolinska, A.; Blanchet, L.; Buydens, L. M. C.; Wijmenga, S. S. NMR and Pattern Recognition Methods in Metabolomics: From Data Acquisition to Biomarker Discovery: A Review. Analytica Chimica Acta 2012, 750, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuperlovic-Culf, M.; Cormier, K.; Touaibia, M.; Reyjal, J.; Robichaud, S.; Belbraouet, M.; Turcotte, S. (1)H NMR Metabolomics Analysis of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells: Effect of VHL Inactivation on Metabolism. Int J Cancer 2016, 138, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T. N.; Valkenborg, D.; Smets, K.; Verwaest, K. A.; Dommisse, R.; Lemière, F.; Verschoren, A.; Goethals, B.; Laukens, K. An Integrated Workflow for Robust Alignment and Simplified Quantitative Analysis of NMR Spectrometry Data. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zailer, E.; Diehl, B. W. K. Alternative Determination of Blood Alcohol Concentration by 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2016, 119, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiru, F. Introduction to Post-Processing Techniques. Eur J Radiol 2008, 67, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, U. L.; Ludwig, C.; Rüterjans, H. WAVEWAT-Improved Solvent Suppression in NMR Spectra Employing Wavelet Transforms. J Magn Reson 2002, 156, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savorani, F.; Tomasi, G.; Engelsen, S. B. Icoshift: A Versatile Tool for the Rapid Alignment of 1D NMR Spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2010, 202, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravdova, V.; Walczak, B.; Massart, D. L. A Comparison of Two Algorithms for Warping of Analytical Signals. Analytica Chimica Acta 2002, 456, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T. N.; Laukens, K. Getting Your Peaks in Line: A Review of Alignment Methods for NMR Spectral Data. Metabolites 2013, 3, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Daszykowski, M.; Walczak, B.; Sweatman, B. C.; Connor, S. C.; Haseldeo, J. N.; Crowther, D. J.; Gill, R. W.; Lutz, M. W. Peak Alignment of Urine NMR Spectra Using Fuzzy Warping. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2006, 46, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.; Morris, G. A.; Swanson, A. G.; Cowburn, D. Suppression of T1 Noise in 2D NMR Spectroscopy by Reference Deconvolution. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A 1993, 101, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G. A.; Barjat, H.; Home, T. J. Reference Deconvolution Methods. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 1997, 31, 197–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, K.; Lam, M.; Webb, A. Reference Deconvolution: A Simple and Effective Method for Resolution Enhancement in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance 2000, 12, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, H.; Melssen, W. J.; in ‘t Zandt, H. J. A.; van der Graaf, M.; Heerschap, A.; Buydens, L. M. C. Automatic Correction for Phase Shifts, Frequency Shifts, and Lineshape Distortions across a Series of Single Resonance Lines in Large Spectral Data Sets. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 2000, 144, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, R.; Wehrens, R.; Buydens, L. M. C. Improved DOSY NMR Data Processing by Data Enhancement and Combination of Multivariate Curve Resolution with Non-Linear Least Square Fitting. J Magn Reson 2004, 169, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbels, T. M. D.; Lindon, J. C.; Coen, M. Processing and Modeling of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Metabolic Profiles. Methods Mol Biol 2011, 708, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchades-Carrasco, L.; Palomino-Schätzlein, M.; Pérez-Rambla, C.; Pineda-Lucena, A. Bioinformatics Tools for the Analysis of NMR Metabolomics Studies Focused on the Identification of Clinically Relevant Biomarkers. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2016, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G. A. NMR Data Processing☆. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry (Third Edition); Lindon, J. C., Tranter, G. E., Koppenaal, D. W., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2017; pp. 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, T.; Sinnaeve, D.; Van Gasse, B.; Tsiporkova, E.; Rietzschel, E. R.; De Buyzere, M. L.; Gillebert, T. C.; Bekaert, S.; Martins, J. C.; Van Criekinge, W. NMR-Based Characterization of Metabolic Alterations in Hypertension Using an Adaptive, Intelligent Binning Algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Astle, W.; De Iorio, M.; Ebbels, T. M. D. BATMAN—an R Package for the Automated Quantification of Metabolites from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra Using a Bayesian Model. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, D.; Avizonis, D. Electronic Referencing in Quantitative NMR. In eMagRes; American Cancer Society, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Betson, T. R.; Augusti, A.; Schleucher, J. Quantification of Deuterium Isotopomers of Tree-Ring Cellulose Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8406–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, M.; Le Moyec, L.; Barrey, E.; Triba, M.; Bouchemal, N.; SAVARIN, P.; ROBERT, C. Energetics of Endurance Exercise in Young Horses Determined by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics. Frontiers in Physiology 2015, 6, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, S. M.; Klein, M. S.; Hochrein, J.; Oefner, P. J.; Spang, R.; Gronwald, W. State-of-the Art Data Normalization Methods Improve NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis. Metabolomics 2012, 8 (Suppl 1), 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Su, B.-N.; Ye, Q.; Palaniswamy, V. A.; Bolgar, M. S.; Raglione, T. V. Improving the Efficiency of Quantitative (1)H NMR: An Innovative External Standard-Internal Reference Approach. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2014, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Shi, L.; Luo, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Liang, P.; Li, K.; Mok, V. C. T.; Chu, W. C. W.; Wang, D. Histogram-Based Normalization Technique on Human Brain Magnetic Resonance Images from Different Acquisitions. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2015, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, C.; Jensen, L. J.; Jarmer, H.; Berka, R.; Gautier, L.; Nielser, H. B.; Saxild, H.-H.; Nielsen, C.; Brunak, S.; Knudsen, S. A New Non-Linear Normalization Method for Reducing Variability in DNA Microarray Experiments. Genome Biol 2002, 3, research0048–research0048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, R. A.; Hoefsloot, H. C.; Westerhuis, J. A.; Smilde, A. K.; van der Werf, M. J. Centering, Scaling, and Transformations: Improving the Biological Information Content of Metabolomics Data. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocke, D.; Lee, G. C.; Tillinghast, J.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Wu, S. LMGene Software for Data Transformation and Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Gene Expression Arrays, 2012. http://www.bioconductor.org/packages//2.7/bioc/html/LMGene.html (accessed 2021-06-28).
- Durbin, B. P.; Hardin, J. S.; Hawkins, D. M.; Rocke, D. M. A Variance-Stabilizing Transformation for Gene-Expression Microarray Data. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (suppl_1), S105–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, W.; von Heydebreck, A.; Sültmann, H.; Poustka, A.; Vingron, M. Variance Stabilization Applied to Microarray Data Calibration and to the Quantification of Differential Expression. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (suppl_1), S96–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J. W. Improving Your Data Transformations: Applying the Box-Cox Transformation. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation 2010, 15, 12. [Google Scholar]
| TopSpin | SpinWorks | ACD/LABS | NMRPipe | rNMR | Mnova | Chenomx | |
| Phase error correction | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Baseline correction | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Solvent filtering | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Calibration and alignment |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
| Reference deconvolution | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Binning/bucketing and peak picking |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
| Peak fitting/deconvolution and identification |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
| Integration and quantification |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
| Normalization and transformation |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
| Pre-processing | Purpose | Possible problems | Our recommendations |
| a). Phase error correction | Remove phase errors. | There might still be some obvious phase errors left. | Use a linear mixed model or multiple models to catch specific phase errors for individual signals. Derive desired spectra from phase error-free magnitude and power spectra |
| b). Baseline correction | Reset baseline. | We should be very careful when we use baseline corrected spectra for quantification. | Do baseline correction in the time domain (removal DC offsets), correct phase errors well, and skip this step. |
| c). Solvent filtering | Remove distorted solvent peaks. | Remove the solvent peaks might influence neighbour peaks. |
Do EC correction and phase correction well. If this step has to be processed, be aware of its neighbours. |
| d). Calibration and alignment | Adjust ppm values for a whole spectrum (calibration) and align each peak across spectra (alignment). | Alignment might affect peak areas and quantification. | Do calibration but not alignment. |
| e). Reference deconvolution | Use a reference signal to remove lineshape distortion. | Peaks are not necessarily distorted in the same way. Multiplets might not be distorted the same way as peaks. | Skip this step. |
| f). Binning/ bucketing and peak picking | Reduce high dimensions. | Fixed width bins might not contain complete peak information and cannot be used for compound identification and quantification. | Recommend peak picking or intelligent binning. |
| g). Peak fitting/ deconvolution and compound identification | Deconvolute signals and identify compounds. | Libraries might not be comparable to experimental spectra. | Find standard spectra from libraries with the closest conditions to an experimental condition. |
| h). Integration and quantification | Summarize spectrum data with compound lists and their concentrations. | Lorentzian fitted lines are good for identification but not quantification since it causes bias concentration estimation and variance under-estimation | Estimate compound concentrations from non-fit data. |
| i). Normalization, and transformation | Make data comparable, or suitable to assumptions needed for statistical analysis. | Spectrum-wise normalization might remove true differences between samples. Location-wise normalization removes true differences between signals and might even enlarge noise to the same levels of true signals. Analysis based on transformed data might not be easy to be transformed back. | Except internal reference area based spectrum-wise normalization, all other methods are not for molecules’ quantification but for further statistical analysis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




