1. Introduction
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is one of the most economically important infectious diseases of livestock in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) due to its impact on livestock productivity and its effect on imposing international trade restrictions on live animals and livestock products. The causative agent, FMD virus (FMDV) is contagious and antigenically diverse, with six currently circulating serotypes that do not cross-protect.
There has been an escalation in FMD outbreaks in the past decade in southern Africa [
1,
2] with Zambia and Namibia reporting novel serotype O incursions due to the O/EA-2 topotype [
3,
4]. Before 2018, FMD was confined to three FMD high-risk areas of Zambia [
4,
5,
6] but in 2018, an FMDV serotype O outbreak was reported in the Chisamba District of Central Zambia [
4]. The disease spread to all the provinces in Zambia except the Luapula Province. A subsequent spillover of this outbreak to the Zambezi Region of Namibia during June – July 2021 was also recorded [
3]. Further spread of this lineage into Malawi and northern Mozambique was reported in 2022 [
7].
Vaccination campaigns together with stringent control measures have been used to eradicate FMD from Europe and most of South America [
8,
9,
10] whilst in endemic regions, vaccination especially
with good quality FMD vaccines is an important means of FMD control
and can help prevent losses in stock production and reduce the overall incidence of the disease[
11]
. Post Vaccination Monitoring (PVM) guidelines have been published to advise countries on the principles and suggested procedures for monitoring various aspects of FMD vaccination including post vaccination monitoring [
12]. In Southern Africa, FMD vaccination has targeted livestock mainly for prophylaxis and to prevent the spread of the disease using tri-valent vaccines containing Southern African Territories serotypes (SAT-1, SAT-2, SAT-3) antigens. The introduction of serotype O into the region means that new vaccines are needed to control outbreaks due to this serotype. As there is no empirical data available to show the appropriateness of serotype O vaccines in Zambia, this study was conducted using the principles of the PVM guidelines to assess the immunogenicity of an imported serotype O vaccine in Zambia.
The specific objectives of this study were to evaluate FMDV-specific antibody responses after a single dose and a second booster dose in vaccinated cattle and to compare results obtained by the virus neutralisation test (VNT) and a commercial solid-phase competitive ELISA kit (SPCE).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
Field studies were conducted in commercial cattle (Study A) and in subsistence cattle (Study B) to assess the immunogenicity of an imported serotype O vaccine using either a one or two-dose primary vaccination protocol. Study A animals were Friesian cattle from a commercial dairy farm in the Momboshi area of the Chisamba District, Zambia whilst Study B animals were mixed breeds in herds from different subsistence farmers (multiple sublocations) in the Rufunsa District, Zambia. There was no previous history of any FMD vaccination in either of these areas and there was no history of FMD outbreaks in the previous two years. Selected animals were six to twelve months old at vaccination and included both males and females. All animals were individually identified by ear tags to ensure accurate follow-up. Consent was obtained from the farmers to use their animals in the study and owners were advised not to move their animals out of the farms during the study. This project was approved under research ethics committee number REC 061-19 from the University of Pretoria, South Africa.
The protocol followed the Food and Agriculture Organization and World Organisation for Animal Health (FAO-WOAH) PVM guidelines Section 3.3 [
12]. In Study A, 69 animals were recruited including ten unvaccinated controls to act as sentinels for FMDV exposure, whilst in Study B, 55 animals were recruited including five unvaccinated controls. Sera from 32 cattle were randomly selected and tested for antibodies to FMDV for each of the five time points (0 - 168 days after the first vaccination; dpv).
Of the vaccinated animals in both studies, ten were given a second dose 28 days post-vaccination (dpv). A second dose is recommended by the vaccine manufacturer and previous research in immunologically naïve animals (i.e., with no previous FMDV exposure or vaccination) [
13]. Blood samples were collected in plain Vacutainer® tubes (Becton Dickinson USA) at first vaccination (0 dpv), 28 dpv (time of second vaccination), 56 dpv, 112 dpv and 168 dpv.
Not all samples were tested for the presence of FMDV antibodies because the budget for this study was limited. From Chisamba, samples from nine single-dose and nine double-dose cattle were tested as well as samples from four unvaccinated controls. From Rufunsa, samples from three single-dose, five double-dose and two unvaccinated control cattle were tested.
2.2. Vaccine
The animals were vaccinated with a monovalent FMDV serotype O Manisa vaccine of at least three PD50 from the Botswana Vaccine Institute containing purified inactivated FMDV antigen and aluminium hydroxide with saponin as an adjuvant. This aqueous adjuvanted vaccine is indicated for use in cattle, buffalo, sheep and goats. Each dose (1 ml) was given according to the recommendations from the vaccine manufacturer. In a primary course of vaccination, two injections three to four weeks apart are recommended, whilst a booster dose is advisable every four to six months depending on the risk and following local practice.
2.3. Serological Testing
All samples were shipped on ice to the Central Veterinary Research Institute (CVRI), Zambia and on arrival, sera were separated and then stored at -20°C until testing. All samples were tested with an FMDV non-structural protein (NSP) ELISA kit (IDEXX, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions at the CVRI to evaluate if natural exposure to FMDV had occurred during the study period. Antibodies to viral NSPs are considered a reliable indicator of evidence of previous or current viral replication in the host, irrespective of vaccination status [
14,
15,
16]. Test results for the NSP ELISA are expressed as a percentage positivity relative to the strong positive control [(optical density of test or control wells/optical density of strong positive control) × 100] [
17]. Values < 20% are considered negative, values ≥ 20% and < 30% are considered suspect and values ≥ 30% are considered positive.
Samples were also tested using a solid phase competitive ELISA (SPCE) or antibodies specific to FMDV serotype O structural proteins (IZSLER Biotechnology Laboratory, Brescia, Italy). This test detects antibodies elicited by vaccination and natural infection. A percentage inhibition for this test is calculated for each well (100 – [optical density of each test or control value/mean optical density of the 0% competition] × 100%), representing the competition between the test sera and a specific murine monoclonal antibody for the FMDV antigen on the ELISA plate. Using the semi-quantitative method applied in this test, sera are considered positive when there is inhibition ≥ 70% and negative when inhibition is < 70% at 1:10 dilution. A second dilution (1:30) of strongly positive sera samples (≥ 80% inhibition at 1:10 dilution) indicates the level of antibodies with strongly positive sera showing ≥ 80% inhibition at both 1:10 and 1:30 dilutions.
Samples were shipped on dry ice to the FAO World Reference Laboratory for FMD (WRLFMD), Pirbright, UK for testing by VNT as described previously [
18]. A representative Zambian field isolate from the O/EA-2 topotype (O/ZAM/7/2021) was used in the VNT to derive field strain-specific (heterologous) titres. Earlier comparison of the neutralisation of O Manisa and O/ZAM/7/2021 viruses by O Manisa post-vaccination sera had shown an antigenic similarity score (r
1 matching value) of 0.47, where 1.0 is a perfect match and values greater than or equal to 0.3 are considered indicative of an acceptable match for field vaccination (
https://www.wrlfmd.org/sites/world/files/quick_media/WRLFMD-2021-00008-ZAM-VMR-O-multiple_001.pdf). The post-vaccination VNT titres to heterologous viruses associated with post-vaccination cross-protection have been evaluated. Using VNT, an indicator of likely heterologous cross-protection is considered to be a log
10 reciprocal titre of 1.5 (1:32) after a single dose vaccination with serum collected 21 days later [
19,
20].
2.4. Data Analysis
Microsoft Office Excel 2016 (Microsoft Corporation, USA) and SPSS Statistics v29 (IBM, USA) were used to analyze the data.
3. Results
During the study, one animal died in Study A and five cattle died or went missing in Study B. Their deaths were attributed to tick-borne diseases.
Although three cattle tested weakly positive for NSP antibodies at single time points in the study (data not shown), all animals eventually tested negative for NSP antibodies and there was no evidence of clinical FMD in the study areas.
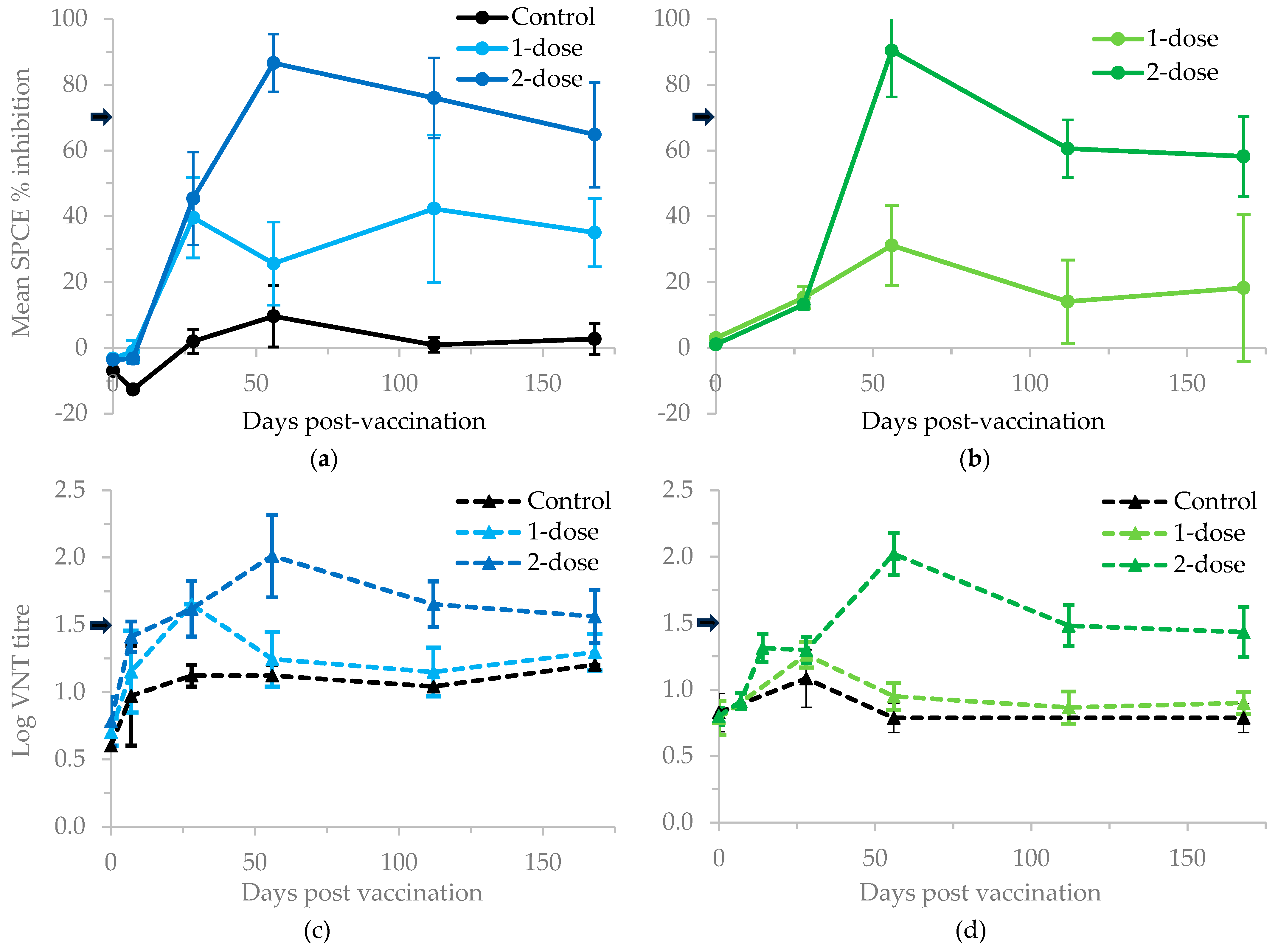
There were differences in the VNT titres between cattle receiving one and two doses of vaccine (
Table S1 and
Figure 1). The mean logs of the reciprocal VNT titres 56 dpv were 1.15 (standard error of the mean [SE] = 0.18, n = 3) and 1.65 (SE = 0.17, n = 5) for subsistence cattle receiving 1- and 2-doses of vaccine respectively, and 0.90 (SE = 0.08, n = 9) and 2.02 (SE = 0.16, n = 9) for commercial cattle receiving 1- and 2-doses of vaccine respectively. The mean titre obtained from the samples of unvaccinated animals was 1.01 log
10 (range 0.6 - 1.2). Only one subsistence animal (out of three) and no commercial animals (out of nine) that were vaccinated once developed protective titres by 56 dpv above the threshold value of 1.5 to be considered positive but three subsistence animals (out of five) and seven commercial animals (out of nine) that were vaccinated twice developed protective titres by 56 dpv to be considered positive. A one-sided independent samples T-test where equal variance was assumed showed a significant difference in titres at 56 dpv between commercial cattle given one- and two-doses of vaccine (p < 0.001). However, for subsistence cattle, no significant difference was observed (p = 0.064) but the sample size was small for the 1-dose group (n = 3).
The pattern of structural proteins binding antibody responses largely mirrored those for neutralising antibodies. Peak responses in double-dose cattle were detected 56 days after the first vaccination. The mean SPCE percentage inhibitions 56 dpv were 25.7 (SE = 12.6, n = 3) and 86.6 (SE = 8.8, n = 5) for cattle from Rufunsa receiving 1- and 2-doses of vaccine respectively, and 14.1 (SE = 5.6, n = 9) and 60.6 (SE = 8.6, n = 9) for cattle from Chisamba receiving 1- and 2-doses of vaccine respectively. None of the animals from Rufunsa (out of three) and only one animal from Chisamba (out of nine) that were vaccinated once developed antibodies by 56 dpv above the threshold value of 70% inhibition to be considered positive but four animals from Rufunsa (out of five) and all animals from Chisamba (out of nine) that were vaccinated twice developed antibodies by 56 dpv to be considered positive (
Table S1,
Figure 1). A one-sided independent samples T-test where equal variance was assumed showed a significant difference in antibodies 56 dpv between cattle given one- and two-doses of vaccine (Rufunsa: p = 0.003, Chisamba: p < 0.001).
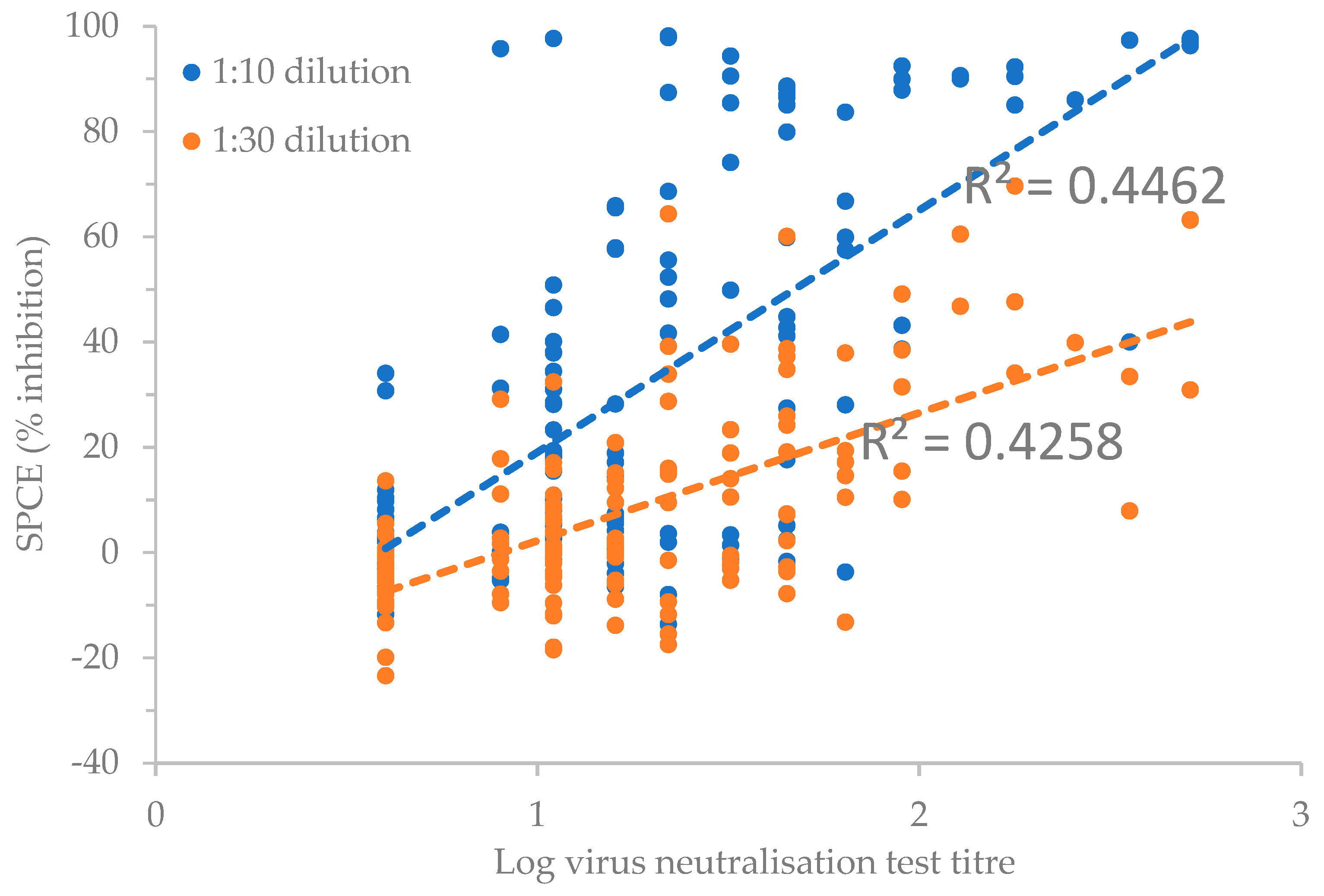
A Spearman's rank-order correlation determined the relationship between the log of the reciprocal of the virus neutralisation titres and the SPCE % inhibition results (
Figure 2). There was a positive correlation between the VNT and SPCE results, which was statistically significant (ρ = 0.598 for 1:10 dilution, and ρ = 0.562 for 1:30 dilution of SPCE % inhibition results, p < 0.001 for both dilutions).
The Cohen’s kappa coefficient was run to determine if there was an agreement between the two assays, using positive titre thresholds of ≥ 1:32 for the VNT and ≥ 70% inhibition for the SPCE. There was moderate agreement [
21,
22] between the two assays (κ = 0.516, 95% CI, 0.365 to 0.667, p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
In this study, the immunogenicity of an imported FMD vaccine was evaluated to determine its suitability for use in Zambia and other southern African countries. The evaluated vaccine is already widely used in sub-Saharan Africa and was an obvious candidate to control the FMDV serotype O outbreaks reported in the Southern African region [
3,
4]. FMDV-specific antibody responses were measured after one or two-dose primary courses of the vaccine. The study also compared results obtained by the VNT and a commercial SPCE kit to evaluate the use of simple-to-use tests to support PVM studies at a population level in settings where high-containment facilities are not available.
The performance of an FMD vaccine can be assessed in vaccination-challenge studies according to the protocols defined in the WOAH Terrestrial Manual [
14]. However, due to several reasons including ethical considerations and costs,
in vitro studies are recommended [
23]. The relationship between serology and protection in FMD-vaccinated cattle has been previously studied by correlating the antibody titres at the point of challenge with the outcome, i.e. protected or not protected [
19,
24]. A correlation between neutralising antibody titre and protection against homologous challenge is well established [
25,
26]. The testing and analysis of day-of-challenge sera from vaccination-and-challenge cross-protection studies have long-established an association between
in vitro neutralising antibody titres to the challenge viruses and
in vivo clinical cross-protection [
24]. Cross-strain protection between different vaccines and challenge viruses also have similar relationships although much less data are available for these studies [
19,
24]. A recommended simple approach to assess cross-protection is to measure the amount of antibodies that vaccinated animals have against the field virus of concern [
24]. It’s against this background that this study examined day-of-challenge antibody titres to a heterologous challenge virus.
Apart from the three weakly positive samples observed at one time-point, neither seroconversion to FMDV NSP, nor clinical signs were observed throughout this study suggesting the FMDV-specific antibody titres detected were vaccine-induced. The observed mean reciprocal log virus neutralisation titre of 2.02 for commercial cattle from Chisamba and 1.65 for subsistence cattle from Rufunsa in second-dosed cattle (
Table S1 and
Figure 1), imply that the aqueous adjuvanted vaccine used in this study produced neutralisation titres likely to offer protection against the target lineages. However, the observed mean titres from single-dosed cattle from Chisamba (0.90) and Rufunsa (1.15) 56 days after the first vaccination suggest that the vaccine given in this way was not able to reach the recommended protective titres as described [
19,
20]. This emphasises the value of the second vaccine dose in this context, but its importance is likely to vary according to the potency of the vaccine and its antigenic match to the strain against which protection is required. After the primary course of vaccination, the manufacturer of this vaccine recommends a booster at 4-6 months, which also seems in line with the results obtained here on the duration of the antibody responses in VNT and ELISA. Apart from these general trends, care must be taken not to over-interpret the findings, as predicting protection from antibody titres cannot be done with precision due to several uncontrollable variables [
19]. Other studies [
26] have also shown that antibodies alone are not responsible for protection but are a correlate of the immune response in the animal.
Commercial ELISAs have been previously recommended for use for routine PVM at the population level [
12]. The correlation in results between the two test methods (i.e. VNT and SPCE) gives credence to the obtained results. Accordingly, the SPCE might be used in assessing the immunogenicity of vaccines where high-level biocontainment facilities are not available to conduct VNT.
5. Conclusions
This study confirms the value of PVM testing and shows that for this vaccine and field strain, a vaccination regime employing a two-dose primary course and revaccination after 4-6 months is likely to be appropriate, as recommended by the vaccine manufacturer. Countries, especially in sub-Saharan countries with a diversity of FMDV strains and inconsistent vaccine quality, are encouraged to implement PVM studies that can account for variations in vaccine potency and antigenic match.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: The solid-phase competitive ELISA (SPCE) % inhibition results at 1:10 dilution (results for 1:30 dilution not shown) and the log reciprocal of virus neutralisation test (VNT) titres in subsistence (Rufunsa) and commercial (Chisamba) cattle herds vaccinated with either one (day 0) or two doses (day 0 and 28) of an FMDV serotype O vaccine.
Author Contributions
F.B., A.B.L., G.M.M and P.F.; contributed to the study conception and design. C.B. and G.W. carried out the VNT testing, F.B., C.M., M.N., H.K. and L.M.; performed material preparation and data collection. D.J.P., D.P.K., F.B., M.Q and A.B.L.; data curation, F.B.; Original draft preparation, A.B.L., D.J.P., D.P.K., M.Q. and F.B.; Writing-review and editing, M.Q.; Supervision, G.M.M and P.F.; Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Government of Zambia through the Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Department of Veterinary.The work of the WRLFMD is supported by the Department for Environment, Food, and Rural Affairs (Defra; UK), and funding provided by the European Union (via a contract from EuFMD, Rome, Italy). The views expressed herein can in no way be taken to reflect the official opinion of the European Union. The Pirbright Institute receives grant-aided support from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council of the United Kingdom (projects BB/X011038/1, BB/X011046/1 and BBS/E/PI/23NB0004).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This project has been approved under research ethics committee number REC 061-19 from the University of Pretoria.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets produced and analyzed for this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance provided by farmers for allowing samples to be collected from their cattle. The Directorate of Veterinary Services at the Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock are thanked for the technical support. Special appreciation goes to the staff at CVRI and NALEIC who were involved in sample and data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chitray, M.; Grazioli, S.; Willems, T.; Tshabalala, T.; De Vleeschauwer, A.; Esterhuysen, J.J.; Brocchi, E.; De Clercq, K.; Maree, F.F. Development and validation of a foot-and-mouth disease virus SAT serotype-specific 3ABC assay to differentiate infected from vaccinated animals. Journal of Virological Methods 2018, 255, 44–51. [CrossRef]
- Thobokwe, G.; Matlho, O.; Fana, E.; Dibe, S. Resurgence of Foot and Mouth Disease in the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC) region In Proceedings of the The 9th annual congress of the Southern African Society For Veterinary Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine. , Farm Inn, Pretoria,Republic of South Africa., 2010.
- Banda, F.; Shilongo, A.; Hikufe, E.H.; Khaiseb, S.; Kabajani, J.; Shikongo, B.; Set, P.; Kapapero, J.K.; Shoombe, K.K.; Zaire, G. The first detection of a serotype O foot-and-mouth disease virus in Namibia. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2022,69, 1865-1674. [CrossRef]
- Banda, F.; Sinkala, Y.; Mataa, L.; Lebea, P.; Sikombe, T.; Kangwa, H.L.; Fana, E.M.; Mokopasetso, M.; Wadsworth, J.; Knowles, N.J.; et al. Characterization of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Viruses in Zambia-Implications for the Epidemiology of the Disease in Southern Africa. Viruses 2021, 13, 2195. [CrossRef]
- Banda, F.; Kasanga, C.J.; Sallu, R.; Sinkala, Y.; Sikombe, T.; Mulumba, M.; Rweyemamu, M.; Wambura, P. Investigation of Foot-and-Mouth Disease outbreaks in the Mbala and Kazungula districts of Zambia. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research 2014, 81. [CrossRef]
- Overby, E.; Zyambo, G.C.N. Foot and Mouth Disease outbreaks in Zambia. Review science technical. Office international Epizotics 1983, 2, 189–197. [CrossRef]
- WRLFMD. World Reference Laboratory for FMD Quarterly Report for April to June 2022. 2022, 12,25 and 26. https://www.wrlfmd.org/ref-lab-reports.
- Bergmann, I.E.; Malirat, V.; Neitzert, E.; Beck, E.; Panizzutti, N.; Sanchez, C.; Falczuk, A. Improvement of a serodiagnostic strategy for foot-and-mouth disease virus surveillance in cattle under systematic vaccination: a combined system of an indirect ELISA-3ABC with an enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot assay. Archives of Virology 2000, 145, 473–489. [CrossRef]
- Leforban, Y.; Gerbier, G. Review of the status of foot and mouth disease and approach to control/eradication in Europe and Central Asia. Review science technical. Office international Epizotics 2002, 21, 477–492. [CrossRef]
- Freimanis, G.; Di Nardo, A.; Bankowska, K.; King, D.; Wadsworth, J.; Knowles, N.; King, D. Genomics and outbreaks: Foot and Mouth Disease. Review science technical. Office international Epizotics 2016, 35, 175–189. [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P. Vaccination as a means of control of foot-and-mouth disease in sub-saharan Africa. Vaccine 1998, 16, 261–264. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Paton, D.; Duffy, S.; Bartels, C.; Knight-Jones, T. Foot and mouth disease vaccination and post-vaccination monitoring guidelines. 2016, doi:FAO ISBN: 978-92-5-109349-8 OIE ISBN: 978-92-95108-25-7. https://www.fao.org/3/i5975e/i5975e.pdf.
- Doel, T.R. Optimisation of the immune response to foot-and-mouth disease vaccines. Vaccine 1999, 17, 1767–1771. [CrossRef]
- WOAH-Manual. Foot and Mouth Disease Chapter 3.1.8. 2022, doi:Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, twelfth edition 2021 WOAH (2021). Available online at: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (accessed June 30, 2021).
- Barnett, P.V.; Geale, D.W.; Clarke, G.; Davis, J.; Kasari, T.R. A Review of OIE Country Status Recovery Using Vaccinate-to-Live Versus Vaccinate-to-Die Foot-and-Mouth Disease Response Policies I: Benefits of Higher Potency Vaccines and Associated NSP DIVA Test Systems in Post-Outbreak Surveillance. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2015, 62, 367–387. [CrossRef]
- Colling, A.; Morrissy, C.; Barr, J.; Meehan, G.; Wright, L.; Goff, W.; Gleeson, L.J.; van der Heide, B.; Riddell, S.; Yu, M.; et al. Development and validation of a 3ABC antibody ELISA in Australia for foot and mouth disease. Australian Veterinary Journal 2014, 92, 192–199. [CrossRef]
- Bruderer, U.; Swam, H.; Haas, B.; Visser, N.; Brocchi, E.; Grazioli, S.; Esterhuysen, J.J.; Vosloo, W.; Forsyth, M.; Aggarwal, N.; et al. Differentiating infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth-disease: evaluation of an ELISA based on recombinant 3ABC. Veterinary Microbiology 2004, 101, 187–197. [CrossRef]
- Fishbourne, E.; Ludi, A.B.; Wilsden, G.; Hamblin, P.; Statham, B.; Bin-Tarif, A.; Brocchi, E.; Grazioli, S.; Dekker, A.; Eblé, P.; et al. Efficacy of a high potency O (1) Manisa foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in cattle against heterologous challenge with a field virus from the O/ME-SA/Ind-2001 lineage collected in North Africa. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2761–2765. [CrossRef]
- FAO-WRLFMD. Recommendation to AgResults on using serological indicators (“valency testing”) of cross-protection for FMDvaccines.2022. https://www.wrlfmd.org/sites/world/files/quick_media/Cross-neutralisation%20measure%20AgResults%20Final%20v2.1.pdf.
- Hammond, J.M.; Maulidi, B.; Henning, N. Targeted FMD Vaccines for Eastern Africa: The AgResults Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccine Challenge Project. Viruses 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33 1, 159-174. [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G. Statistics in the medical literature: 3. Stat Med 1999, 18, 487–490. [CrossRef]
- Maree, F.F.; Kasanga, C.J.; Scott, K.A.; Opperman, P.A.; Melanie, C.; Sangula, A.K.; Raphael, S.; Yona, S.; Wambura, P.N.; King, D.P.; et al. Challenges and prospects for the control of foot-and-mouth disease: an African perspective. Veterinary medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2014, 5, 119–138. [CrossRef]
- Gubbins, S.; Paton, D.J.; Dekker, A.; Ludi, A.B.; Wilsden, G.; Browning, C.F.J.; Eschbaumer, M.; Barnabei, J.; Duque, H.; Pauszek, L.L.; et al. Predicting cross-protection against foot-and-mouth disease virus strains by serology after vaccination. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Barnett, P.V.; Statham, R.J.; Vosloo, W.; Haydon, D.T.; Barnett, P.V.; Statham, R.J.; Vosloo, W.; Haydon, D.T. Foot-and-mouth disease vaccine potency testing: determination and statistical validation of a model using a serological approach. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3240–3248. [CrossRef]
- van Bekkum, J.G.; Fish, R.C.; Nathans, I. Immunologic responses in Dutch cattle vaccinated with foot-and-mouth disease vaccines under field conditions: neutralizing antibody responses and immunity to O, A, and C types. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1969, 30, 2125–2129. [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).