Submitted:
05 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial identification via PCR
2.2. Phylogenetic tree based on pathogenic rpoD
2.3. Biochemical characteristics
2.4. Antibiotic susceptibility test
2.5. Comparison of the virulence of the isolated HJ-2023 strain and that of the controls
3. Discussion
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Sampling and polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
4.2. Phylogenetic analysis based on pathogenic rpoD
4.3. Biochemical tests
4.4. Antimicrobial susceptibility test
4.5. In vivo experiments to assess pathogenicity
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, J. E.; Lee, S. C.; Park, S. C.; Jeon, H. J.; Kim, K. Y.; Lee, Y. S.; Park, S.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, J. H.; Choi, S.-K. Molecular detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei and vibrio parahaemolyticus-associated acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in southeast Asian penaeus vannamei shrimp imported into Korea. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734812. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H. J.; Song, J. W.; Lee, C.; Kim, B.; Park, S. Y.; Kim, J. H.; Han, J. E.; Park, J. H. Antibacterial activity of bacillus strains against acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing vibrio campbellii in Pacific white leg shrimp. Fishes 2022, 7, 287. [CrossRef]
- Rattanadilog Na Phuket, T.; Charoensapsri, W.; Amparyup, P.; Imjongjirak, C. Antibacterial activity and immunomodulatory role of a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide sppr-amp1 against vibrio campbellii infection in Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2023, 132, 108479.
- Yu, L. H.; Teh, C. S.; Yap, K. P.; Thong, K. L. Diagnostic approaches and contribution of next-generation sequencing technologies in genomic investigation of vibrio parahaemolyticus that caused acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquaculture International 2020, 28, 2547–2559. [CrossRef]
- Santos, H. M.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Maquiling, K. R.; Tayo, L. L.; Mariatulqabtiah, A. R.; Lee, C.-W.; Chuang, K. P. Diagnosis and potential treatments for acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND): A Review. Aquaculture International 2019, 28, 169–185. [CrossRef]
- Fao, A. Report of the FAO/MARD technical workshop on early mortality syndrome (EMS) or acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome (AHPNS) of cultured shrimp (under TCP/VIE/3304). FAO, Rome, 2013, 54.
- de la Peña, L.; Cabillon, N.; Catedral, D.; Amar, E.; Usero, R.; Monotilla, W.; Calpe, A.; Fernandez, D.; Saloma, C. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) outbreaks in penaeus vannamei and P. Monodon cultured in the Philippines. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2015, 116, 251–254. [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Piamsomboon, P.; Aranguren Caro, L.; Kanrar, S.; Adami, R.; Juan, Y. First report of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) occurring in the USA. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2019, 132, 241–247. [CrossRef]
- Nunan, L.; Lightner, D.; Pantoja, C.; Gomez-Jimenez, S. Detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2014, 111, 81–86. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-B.; Choi, J.-H.; Kang, J.-C.; Kim, H. J.; Kim, J.-H. Shrimp bacterial and parasitic disease listed in the OIE: A Review. Microbial Pathogenesis 2022, 166, 105545.
- Tran, L.; Nunan, L.; Redman, R.; Mohney, L.; Pantoja, C.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Lightner, D. Determination of the infectious nature of the agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome affecting penaeid shrimp. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2013, 105, 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Nguyen, D. V.; Baruah, K.; Bossier, P. Probing the mechanism of VPAHPND extracellular proteins toxicity purified from vibrio parahaemolyticus AHPND strain in germ-free artemia test system. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 414–419. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V., Roy, S., Behera, B., Bossier, P., Das, B. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (Ahpnd): Virulence, pathogenesis and mitigation strategies in shrimp aquaculture. Toxins 2021, 13(8), 1-28. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Chen, I.-T.; Yang, Y.-T.; Ko, T.-P.; Huang, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-Y.; Huang, M.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-S.; Lightner, D. V.; Wang, H.-C.; Wang, A. H.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Hor, L.-I.; Lo, C.-F. The opportunistic marine pathogen vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [CrossRef]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S. A.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Ramos-Clamont Montfort, G.; Zenteno, E.; Sánchez-Salgado, J. L.; Vibanco-Pérez, N.; Aguilar Rendón, K. G. New insights into the mechanism of action of Pirab from vibrio parahaemolyticus. Toxins 2022, 14, 243. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Xia, X.; Dai, X.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. A vibrio owensii strain as the causative agent of AHPND in cultured shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 2018, 153, 156–164. [CrossRef]
- OIE. Chapter 2.2. 1. Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease. World Organisation for Animal Health, Paris, France, 2019.
- Chang, Y.-H.; Kuo, W.-C.; Wang, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-M. Biocontrol of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp using a microalgal-bacterial consortium. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 734990. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ng, T. H.; Wang, H. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in penaeid shrimp. Reviews in Aquaculture 2020, 12, 1867–1880. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Bi, D.; Wang, H.; Zou, P.; Xie, G.; Wan, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, M.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Huang, J. PIRABVP-bearing vibrio parahaemolyticus and vibrio campbellii pathogens isolated from the same ahpnd-affected pond possess highly similar pathogenic plasmids. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, 8.
- Ahn, Y. S.; Piamsomboon, P.; Tang, K. F.; Han, J. E.; Kim, J. H. Complete genome sequence of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing vibrio campbellii LA16-V1, isolated from Penaeus Vannamei cultured in a Latin American country. Genome Announcements 2017, 5. [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Defoirdt, T.; Ina-Salwany, M. Y.; Yusoff, F. M.; Shariff, M.; Ismail, S. I.; Natrah, I. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and vibrio harveyi causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Penaeus Vannamei (Boone, 1931) isolated from Malaysian shrimp ponds. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734227. [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, L.; Bayot, B.; Arciniegas, S.; Bajaña, L.; Betancourt, I.; Panchana, F.; Reyes Muñoz, A. PIRVP genes causing AHPND identified in a new vibrio species (vibrio punensis) within the commensal orientalis clade. Scientific Reports 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Jang, G. I.; Park, J. I., Oh, E. G.; Kim, S. The relationship between acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and Vibrio parahaemolyticus Strains Isolated from shellfish and shrimp of the West Coast of Korea in 2019. Korean J Fish Aquat Sci 2020 53(5), 752–760.
- Cano-Gomez, A.; Høj, L.; Owens, L.; Andreakis, N. Multilocus sequence analysis provides basis for fast and reliable identification of vibrio harveyi-related species and reveals previous misidentification of important marine pathogens. Systematic and Applied Microbiology 2011, 34, 561–565. [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Macián, M. C.; Arahal, D. R.; Garay, E.; Pujalte, M. J. Multilocus sequence analysis of the central clade of the genus vibrio by using the 16S rrna, recA, pyrh, rpod, gyrb, rctb and toxr genes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2010, 60, 154–165. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Song, J.; Chen, J.; Bi, D.; Wang, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Tang, K. F.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Conjugative transfer of the PVA1-type plasmid carrying the PIRABVP genes results in the formation of new AHPND-causing vibrio. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Defoirdt, T.; Shariff, M.; M. Y, I.-S.; Yusoff, F. M.; Natrah, I. Horizontal gene transfer of thepirabgenes responsible for acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) turns a non-vibriostrain into an ahpnd-positive pathogen 2019.
- Tinwongger, S.; Nochiri, Y.; Thawonsuwan, J.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Awasthi, S. P.; Hinenoya, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Hirono, I. Virulence of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease Pir ab-like relies on secreted proteins not on gene copy number. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2016, 121, 1755–1765. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, G.; Zou, P.; Guo, C.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J. An isolate of vibrio campbellii carrying the PIR vp gene causes acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Emerging Microbes & Infections 2017, 6, 1–3.
- San Luis, B. B.; Hedreyda, C. T. Analysis of a gene (VCH) encoding hemolysin isolated and sequenced from vibrio campbellii. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology 2006, 52, 303–313. [CrossRef]
- Wangman, P.; Longyant, S.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Senapin, S.; Sithigorngul, P.; Chaivisuthangkura, P. Pira & B toxins discovered in archived shrimp pathogenic vibrio campbellii isolated long before EMS/AHPND outbreaks. Aquaculture 2018, 497, 494–502. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J., Liu, L., Ke, Y., Li, X., Liu, Y., Pan, Y., & Wang, Y. Shrimp AHPND-causing plasmids encoding the PirAB toxins as mediated by pirAB-Tn903 are prevalent in various Vibrio species. Scientific reports 2017, 7(1), 42177. [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, C.; Cataletto, B.; Del Negro, P. Detection of pathogenic vibrio parahaemolyticus through biochemical and molecular-based methodologies in coastal waters of the Gulf of Trieste (North Adriatic Sea). FEMS Microbiology Letters 2010, 307, 158–164. [CrossRef]
- Elmahdi, S.; DaSilva, L. V.; Parveen, S. Antibiotic resistance of vibrio parahaemolyticus and vibrio vulnificus in various countries: A Review. Food Microbiology 2016, 57, 128–134. [CrossRef]
- Han, A.-R.; Yoon, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-W. Antibiotic resistance and plasmid profile of vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from Kyunggi-Incheon Coastal Area. The Korean Journal of Microbiology 2012, 48, 22–28. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Complete genome sequence of vibrio campbellii strain 20130629003s01 isolated from shrimp with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Gut Pathogens 2017, 9. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. B.; Okuda, J.; Matsumoto, C.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Nishibuchi, M. Identification of vibrio parahaemolyticus strains at the species level by PCR targeted to the toxr gene. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1999, 37, 1173–1177. [CrossRef]
- Sirikharin, R.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Sanguanrut, P.; Chi, T. D.; Mavichak, R.; Proespraiwong, P.; Nuangsaeng, B.; Thitamadee, S.; Flegel, T. W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Characterization and PCR detection of binary, pir-like toxins from vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. PLOS ONE 2015, 10. [CrossRef]
- Phiwsaiya, K.; Charoensapsri, W.; Taengphu, S.; Dong, H. T.; Sangsuriya, P.; Nguyen, G. T.; Pham, H. Q.; Amparyup, P.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Longyant, S.; Sithigorngul, P.; Senapin, S. A natural vibrio parahaemolyticus Δ pira vp pirb vp+ mutant kills shrimp but produces neither PIR vp toxins nor acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease lesions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2017, 83.
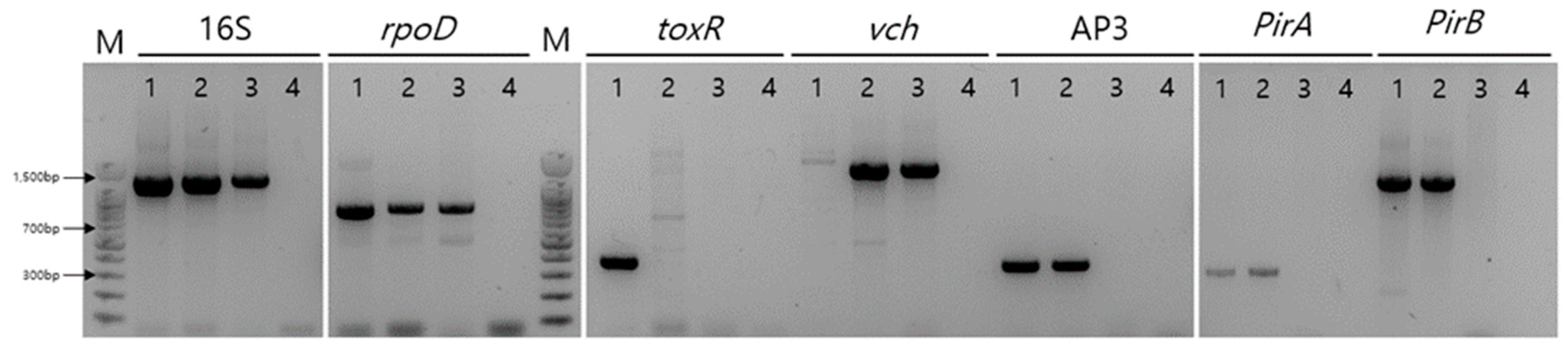
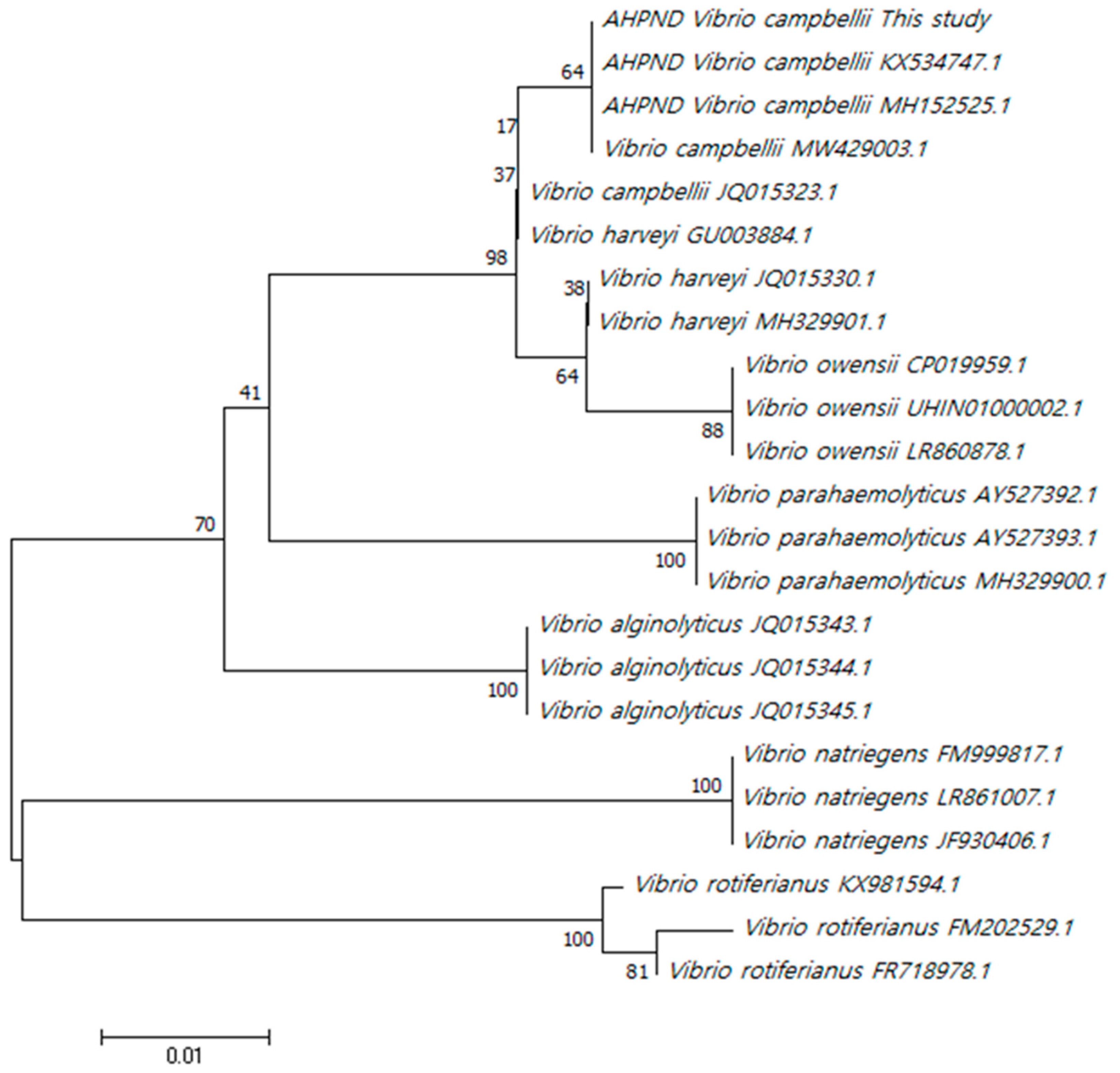
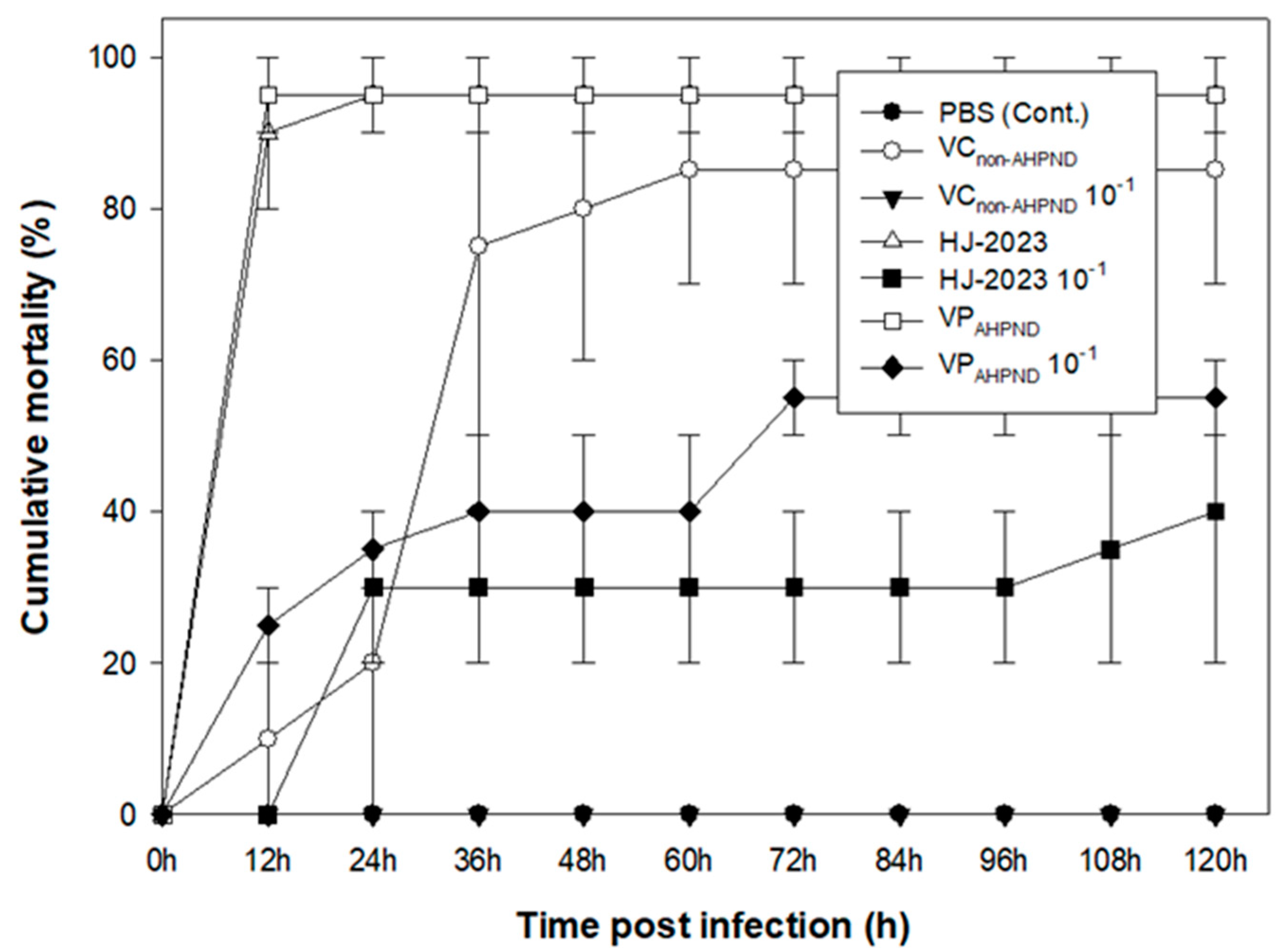
| Isolates | VPAHPND | HJ-2023 | VCNon-AHPND | |
| Biochemical test | Abbreviation | |||
| β-galactosidase | ONPG | - | + | - |
| Arginine dihydrolase | ADH | - | - | - |
| Lysine décarboxylase | LDC | + | + | + |
| Ornithine décarboxylase | ODC | - | + | + |
| Citrate utilization | CIT | - | - | - |
| H2S production | H2S | - | - | - |
| Urease production | URE | - | - | - |
| Tryptophane désaminase | TDA | - | - | - |
| Indole production | IND | + | + | + |
| Acétoïne production (Vogues–Proskawer reaction) | VP | - | - | - |
| Gelatinase production | GEL | - | + | + |
| Glucose production | GLU | + | + | + |
| Manitol acidification | MAN | + | + | + |
| Inositol acidification | INO | - | - | - |
| Sorbitol acidification | SOR | - | - | - |
| Rhamose acidification | RHA | - | - | - |
| Saccharose acidification | SAC | - | - | - |
| Melobiose acidification | MEL | - | - | - |
| Amygdalin acidification | AMY | + | + | - |
| Arabinose acidification | ARA | - | - | + |
| Nitrite metabolism | NO2 | + | + | + |
| Oxidase test | OXY | + | + | + |
| Isolates | VPAHPND | HJ-2023 | VCNon-AHPND | |
| Biochemical test | Abbreviation | |||
| Nitrate reduction | NO3 | + | + | + |
| Indole production | TRP | + | + | + |
| Glucose fermentation | GLU | + | + | + |
| Arginine Dihydrolase | ADH | - | - | - |
| Urease production | URE | - | - | - |
| Hydrolysis (β-glucosidase) (ESCulin) | ESC | - | + | - |
| Hydrolysis (protease) (GELatin) | GEL | - | + | + |
| β-galactosidase (Para-Nitrophenyl-βD-Galactopyanosidase) | PNPG | - | + | + |
| Glucose assimilation | GLU | - | - | + |
| Arabinose assimilation | ARA | - | - | + |
| Mannose assimilation | MNE | + | + | + |
| Mannitol assimilation | MAN | - | - | + |
| N-acetyl-glucosamine assimilation | NAG | - | - | + |
| Maltose assimilation | MAL | + | + | + |
| Potassium gluconate assimilation | GNT | - | + | + |
| Capric acid assimilation | CAP | - | - | - |
| Adipic acid assimilation | ADI | - | - | + |
| Malate assimilation | MLT | + | + | + |
| Trisodium citrate assimilation | CIT | - | - | + |
| Phenylacetic acid assimilation | PAC | - | - | - |
| Oxidase test | OXY | + | + | + |
| Antibiotics(Conc.) | HJ-2023 | VPAHPND | VCnon-AHPND |
| CIP (5 µg) | 18.8 ± 0.2 (I) | 16.5 ± 0.1 (I) | 23.0 ± 0.1 (S) |
| NoR (10 µg) | 20.3 ± 0.3 | 20.0 ± 0.0 | 17.5 ± 0.1 |
| GM (10 µg) | 12.3 ± 0.1 (I) | 11.2 ± 0.2 (R) | 11.5 ± 0.1 (R) |
| NA (30 µg) | 21.0 ± 0.2 (S) | 23.2 ± 0.2 (S) | 28.2 ± 0.2 (S) |
| C (30 µg) | 23.3 ± 0.2 (S) | 19.7 ± 0.1 (S) | 32.5 ± 0.2 (S) |
| T (30 µg) | 22.3 ± 0.3 (S) | 20.5 ± 0.3 (S) | 31.2 ± 0.1 (S) |
| S (10 µg) | 8.3 ± 0.1 (R) | 9.5 ± 0.1 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| TE (30 µg) | 23.3 ± 0.1 (S) | 19.5 ± 0.3 (S) | 21.0 ± 0.1 (S) |
| E (15 µg) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 9.5 ± 0.1 (R) | 11.0 ± 0.1 (R) |
| CF (30 µg) | 9.8 ± 0.1 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| K (30 µg) | 12.3 ± 0.1 (R) | 12.0 ± 0.2 (R) | 10.5 ± 0.1 (R) |
| VA (30 µg) | 11.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| AM (10 µg) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| CC (2 µg) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| L (2 µg) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) | 0.0 ± 0.0 (R) |
| Target | Primer | Sequences (5′-3′) | Product size (bp) | Reference |
| 16S rRNA | V16S-F | GGG GAT AAC CAT TGG AAA CGA T | 1,313 | This study |
| V16S-R | AAA CTA CCT ACT TCT TTT GCA GC | |||
| rpoD | VRpoD-F | ATT GAA GAA GGT ATT AAC CAA G | 755 | This study |
| VRpoD-R | GAC ATR CGA CGG CTG ATG TCT TT | |||
| toxR | toxR-F | AAC CCG CTT TCT TCA GAC TC | 399 | [38] |
| toxR-R | AAC GAG TCT TCT GCA TGG TG | |||
| Vch | VCH-F | ATT AGA TAT TTG ACT GAA TGG CG | 1,359 | [31] |
| VCH-R | CTT AGA ATG GAT GAT TCG AAA GT | |||
| AP3 | AP3-F | ATG AGT AAC AAT ATA AAA CAT GAA AC | 333 | [39] |
| AP3-R | GTG GTA ATA GAT TGT ACA GAA | |||
| PirA | VpPirA-F | ATG AGT AAC AAT ATA AAA C | 336 | [40] |
| VpPirA-R | TTA GTG GTA ATA GAT TG | |||
| PirB | VpPirB-F | ATG ACT AAC GAA TAC GT | 1,317 | |
| VpPirB-R | CTA CTT TTC TGT ACC AA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





