Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
03 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
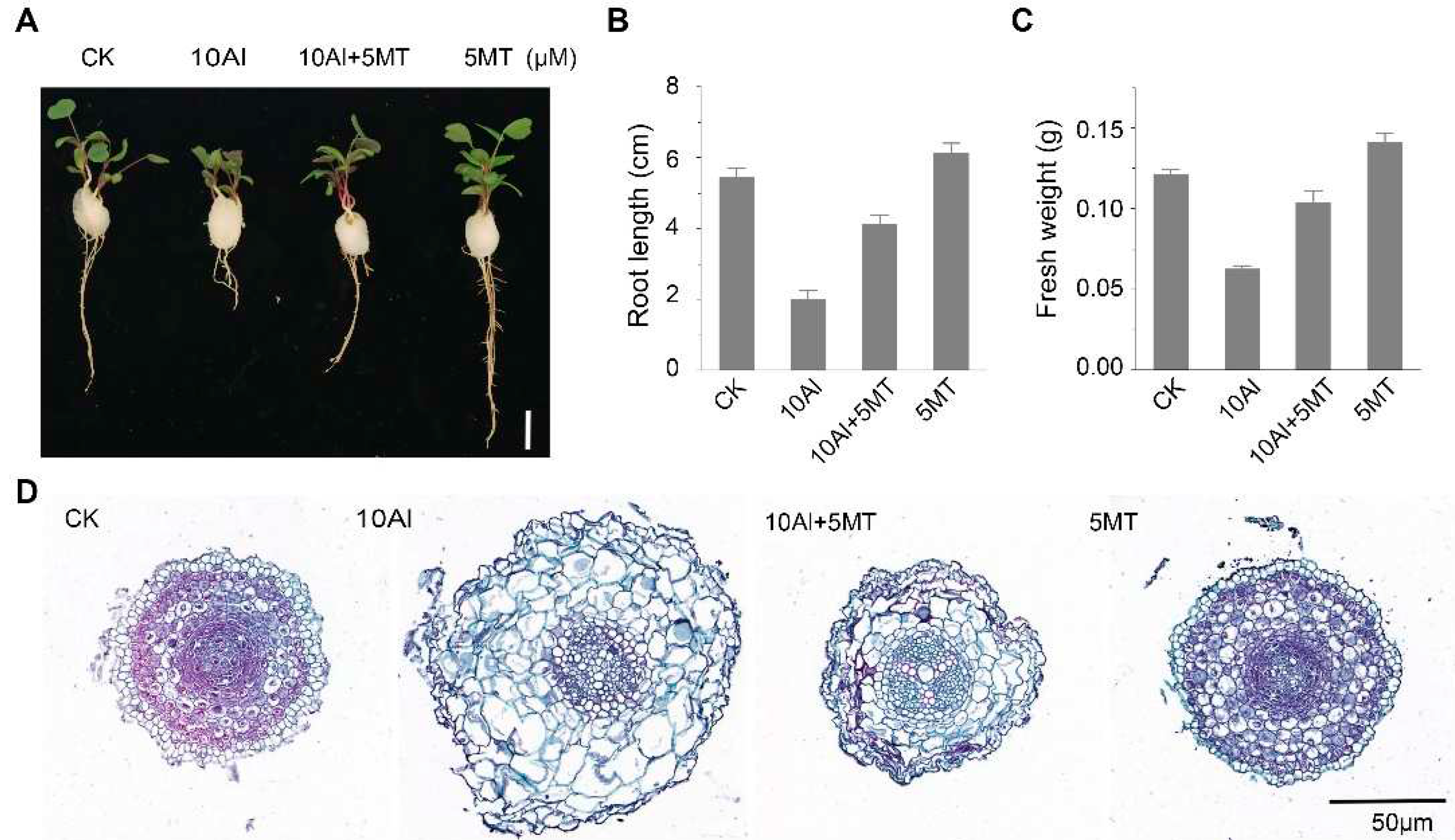
2.1. Melatonin applications significantly alleviate Al-induced growth inhibition in alfalfa
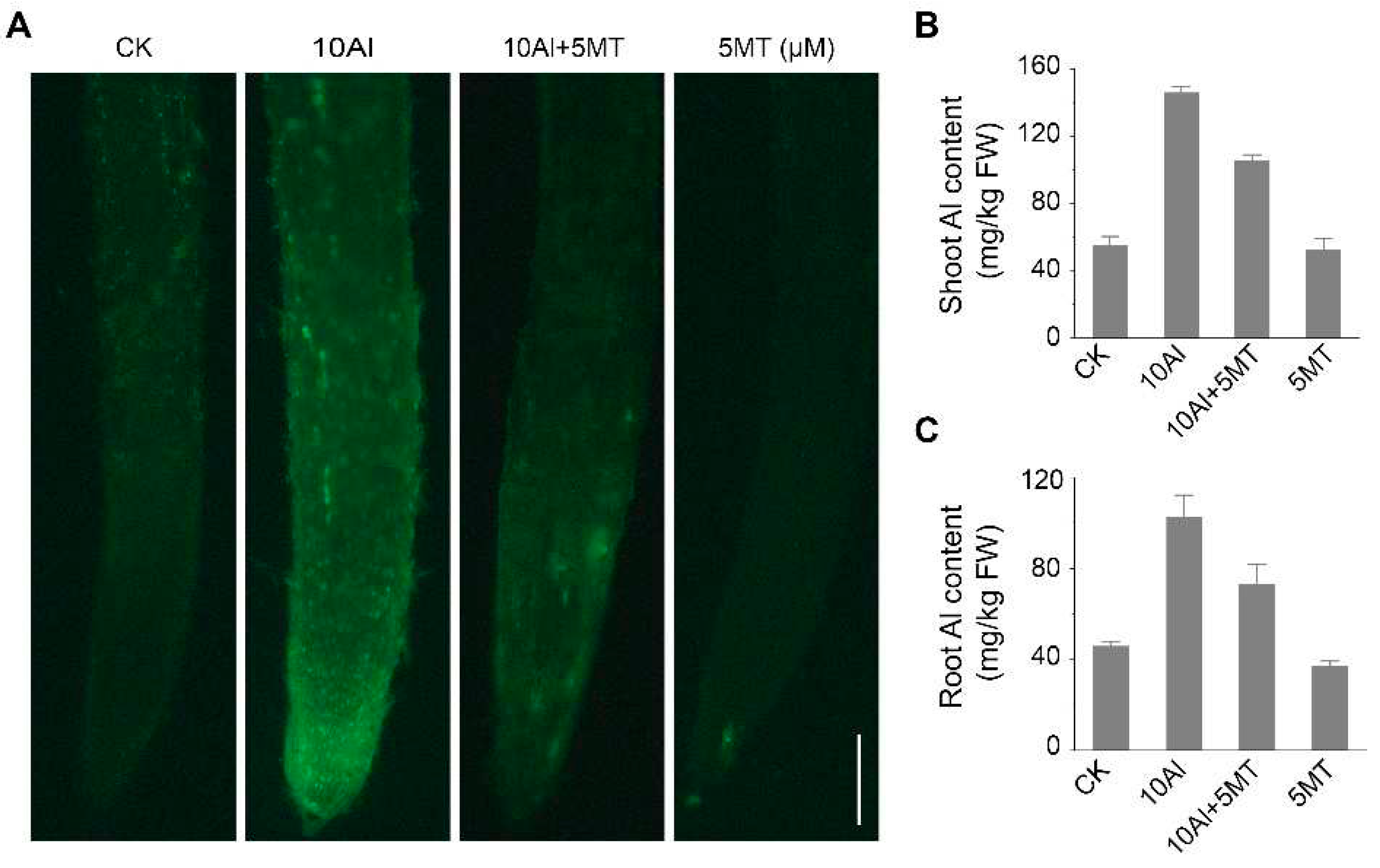
2.2. Melatonin could reduce the accumulation of Al in alfalfa roots under Al stress
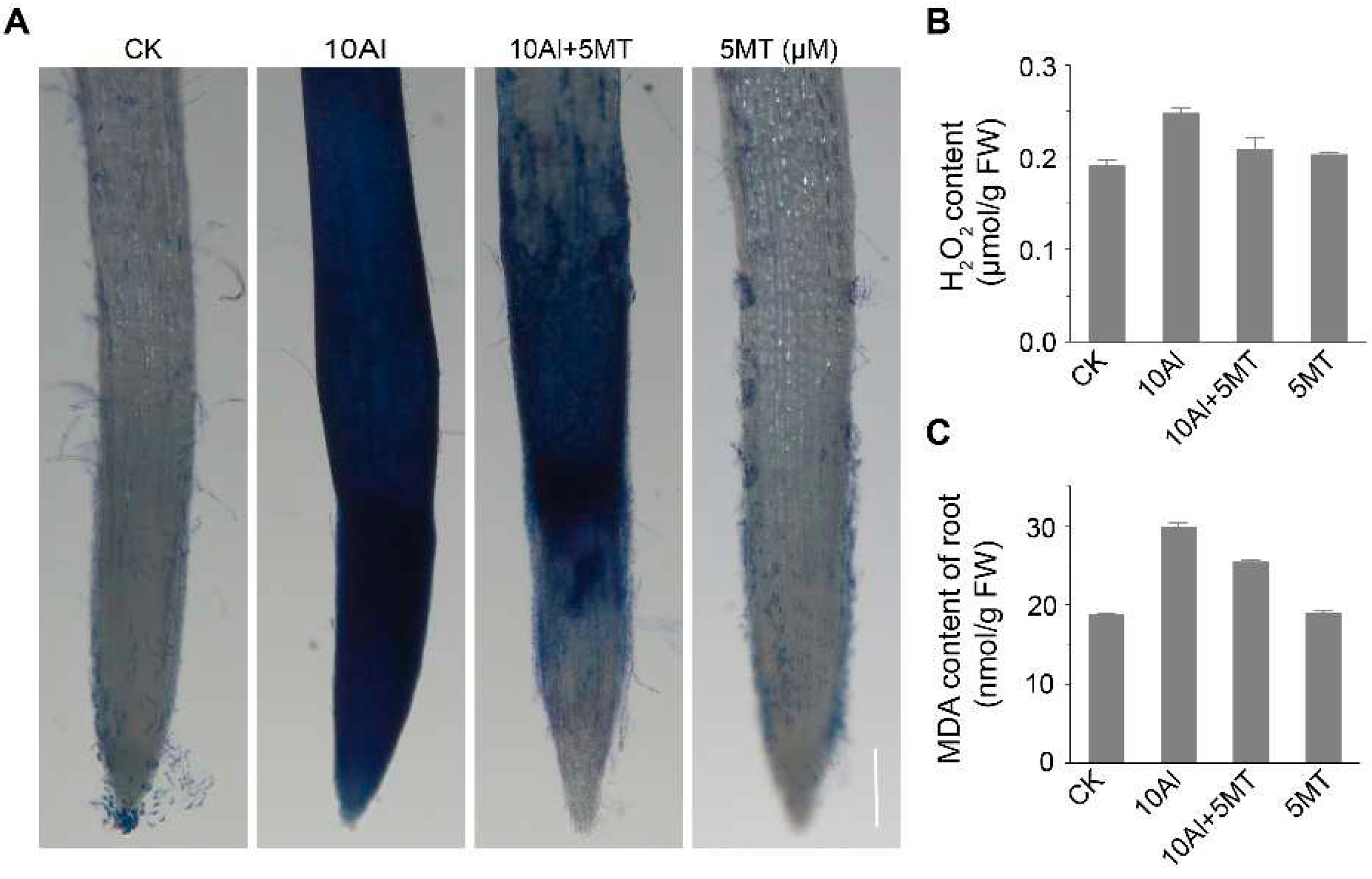
2.3. Melatonin could alleviate Al-induced oxidative damage in root apex cells
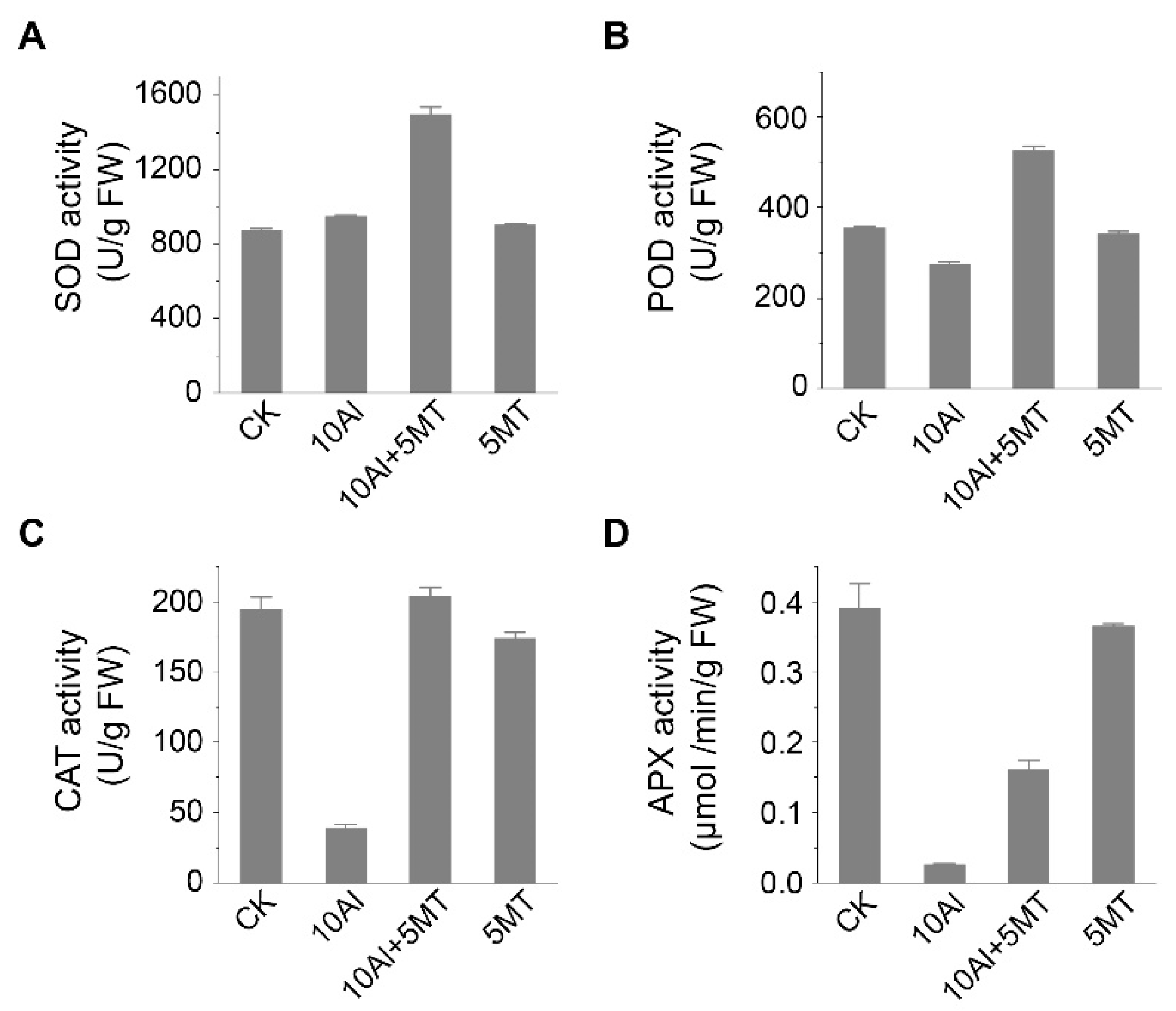
2.4. Melatonin may enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes
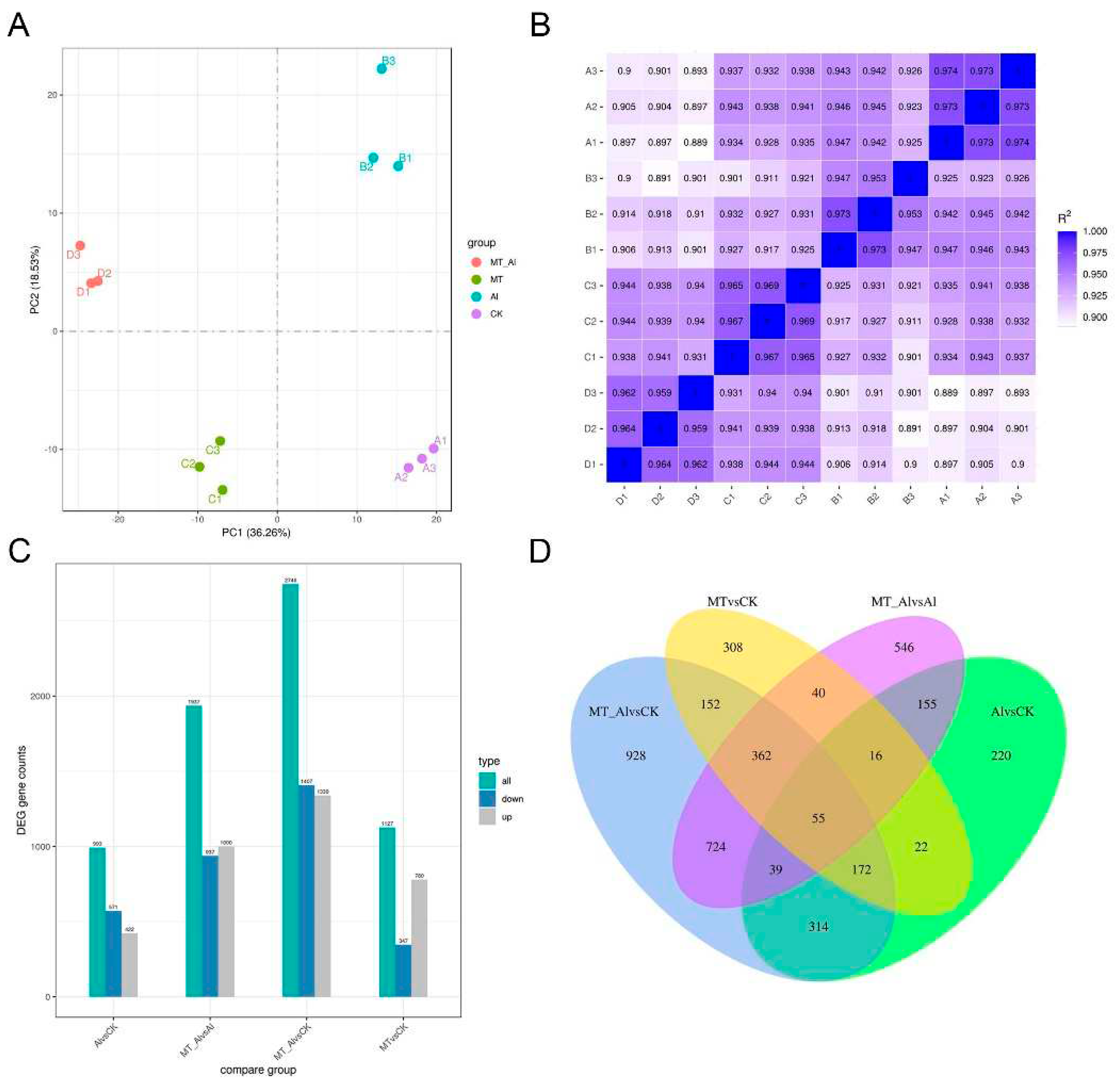
2.5. Treatments with Al and melatonin trigger transcriptome reprogramming in alfalfa roots
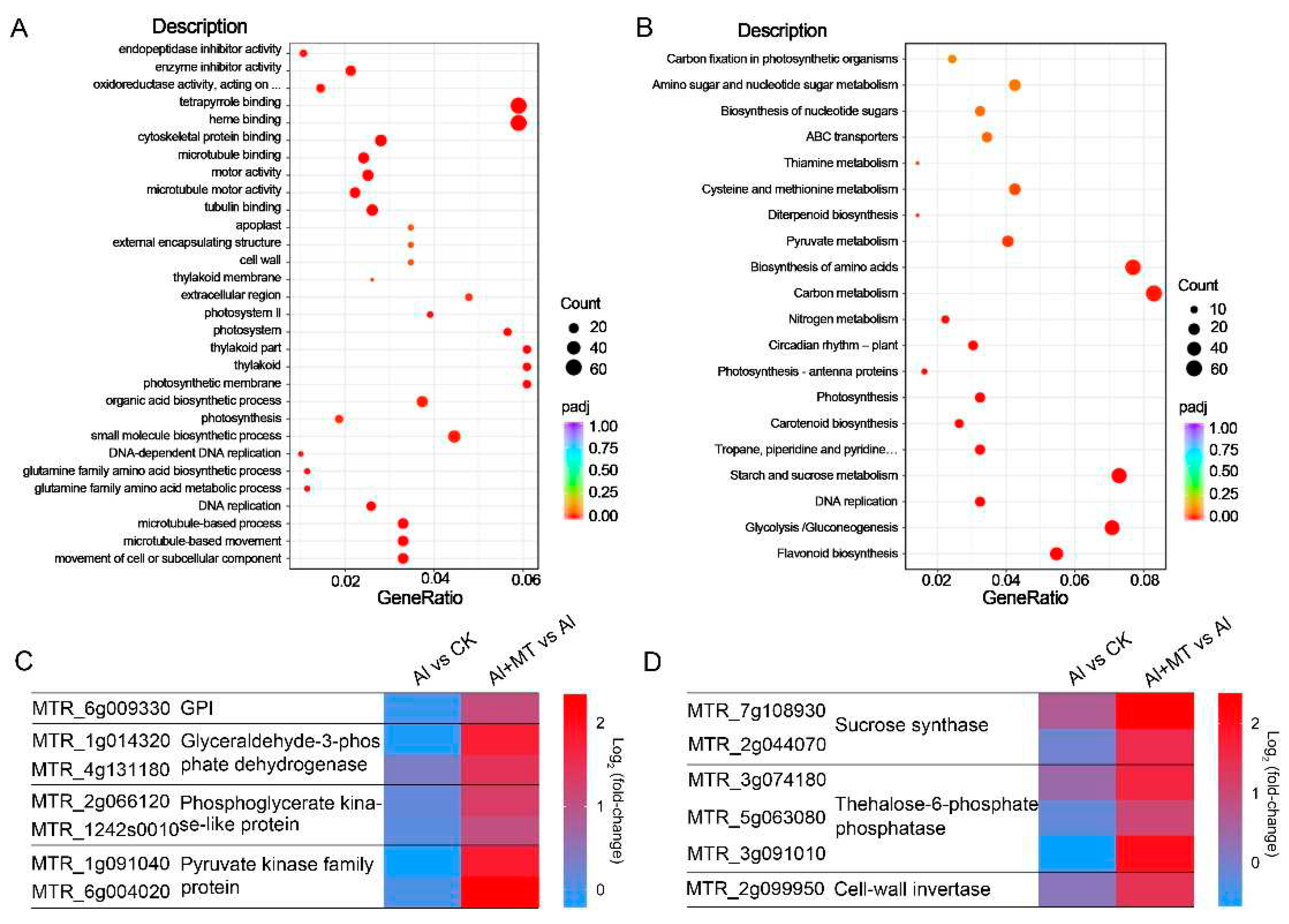
2.6. Gene Ontology (GO) classification and KEGG pathway analysis.
3. Discussion
3.1. Exogenous melatonin reduced Al concentration in both alfalfa roots and shoots.
3.2. Exogenous melatonin enhanced the antioxidant capacity in alfalfa.
3.3. Exogenous melatonin elevated C metabolism under Al stress in alfalfa.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant culture and measurements of Al treatments.
4.2. Anatomical observation of root tip cells
4.3. Moring staining
4.4. Determination of Al content
4.5. Determination of H2O2 content
4.6. Analysis of oxidative damage
4.7. Determination of antioxidant enzyme activity
4.8. RNA extraction and transcriptome sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochian, L.V.; Piñeros, M.A.; Liu, J.; Magalhaes, J. V Plant Adaptation to Acid Soils: The Molecular Basis for Crop Aluminum Resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, H.; Meriga, B.; Surapu, V.; Gadi, J.; Sunita, M.S.L.; Suravajhala, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Toxicity and Tolerance of Aluminum in Plants: Tailoring Plants to Suit to Acid Soils. Biometals 2016, 29, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschenrieder, C.; Gunsé, B.; Corrales, I.; Barceló, J. A Glance into Aluminum Toxicity and Resistance in Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, X.; Han, X.; Tang, R.; Chu, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, F.; Fu, A.; Luan, S.; et al. A Defective Vacuolar Proton Pump Enhances Aluminum Tolerance by Reducing Vacuole Sequestration of Organic Acids. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofoe, R.; Thomas, R.H.; Asiedu, S.K.; Wang-Pruski, G.; Fofana, B. Abbey, Lord Aluminum in Plant: Benefits, Toxicity and Tolerance Mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1085998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.B.; Horst, W.J. Aluminum-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth: Roles of Cell Wall Assembly, Structure, and Function. 2015, 253-274.
- Zhu, X.F.; Wan, J.X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, X.S.; Zheng, S.J.; Shen, R.F. PARVUS Affects Aluminum Sensitivity by Modulating the Structure of Glucuronoxylan in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant. Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Cao, X.C.; Zhu, L.F.; Hu, W.J.; Hu, A.Y.; Abliz, B.; Bai, Z.G.; Huang, J.; Liang, Q.D.; Sajid, H.; et al. Boron Reduces Cell Wall Aluminum Content in Rice (Oryza Sativa) Roots by Decreasing H2O2 Accumulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, X.Z.; Jing, H.K.; Shen, R.F.; Zhu, X.F. The MYB Transcription Factor MYB103 Acts Upstream of TRICHOME BIREFRINGENCE-LIKE27 in Regulating Aluminum Sensitivity by Modulating the O-Acetylation Level of Cell Wall Xyloglucan in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant, J. 2022, 111, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, S.; Lanzoni, M.; Adriana, R.; Martinelli, P.; Antunes, R. Aluminum-Induced Stress Differently Modifies Urochloa Genotypes Responses on Growth and Regrowth: Root-to-Shoot Al-Translocation and Oxidative Stress. 2018, 141-152.
- Huang, W.; Yang, X.; Yao, S.; LwinOo, T.; He, H.; Wang, A.; Li, C.; He, L. Reactive Oxygen Species Burst Induced by Aluminum Stress Triggers Mitochondria-Dependent Programmed Cell Death in Peanut Root Tip Cells. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 82, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y. Aluminum Toxicity in Plant Cells: Mechanisms of Cell Death and Inhibition of Cell Elongation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, J.P.; Saha, B.; Panigrahi, J.; Yanase, E.; Koyama, H.; Panda, S.K. Redox Balance, Metabolic Fingerprint and Physiological Characterization in Contrasting North East Indian Rice for Aluminum Stress Tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.S.; Yang, Z.M. Nitric Oxide Reduces Aluminum Toxicity by Preventing Oxidative Stress in the Roots of Cassia Tora, L. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Huang, Y.; Qu, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; He, W.; Ding, J.; Liu, C.; et al. A Maize ZmAT6 Gene Confers Aluminum Tolerance via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maejima, E.; Osaki, M.; Wagatsuma, T.; Watanabe, T. Contribution of Constitutive Characteristics of Lipids and Phenolics in Roots of Tree Species in Myrtales to Aluminum Tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 160, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, F.; Borgo, L.; Rabêlo, F.H.S.; Rossi, M.L.; Linhares, F.S.; Martinelli, A.P.; Azevedo, R.A.; Lavres, J. Aluminum-Induced Toxicity in Urochloa Brizantha Genotypes: A First Glance into Root Al-Apoplastic and -Symplastic Compartmentation, Al-Translocation and Antioxidant Performance. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojórquez-Quintal, E.; Escalante-Magaña, C.; Echevarría-Machado, I.; Martínez-Estévez, M. Aluminum, a Friend or Foe of Higher Plants in Acid Soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Su, Q.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Bao, J.; Li, J.; Tu, H.; Zeng, C.; Fu, J.; He, H. Genome-Wide Characterization of MATE Gene Family and Expression Profiles in Response to Abiotic Stresses in Rice (Oryza Sativa). BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Ryan, P.R.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Yan, W.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Luo, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. ZmMATE6 from Maize Encodes a Citrate Transporter That Enhances Aluminum Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 111016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kichigina, N.E.; Puhalsky, J.V.; Shaposhnikov, A.I.; Azarova, T.S.; Makarova, N.M.; Loskutov, S.I.; Safronova, V.I.; Tikhonovich, I.A.; Vishnyakova, M.A.; Semenova, E.V.; et al. Aluminum Exclusion from Root Zone and Maintenance of Nutrient Uptake Are Principal Mechanisms of Al Tolerance in Pisum Sativum, L. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2017, 23, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligaba, A.; Katsuhara, M.; Ryan, P.R.; Shibasaka, M.; Matsumoto, H. The BnALMT1 and BnALMT2 Genes from Rape Encode Aluminum-Activated Malate Transporters That Enhance the Aluminum Resistance of Plant Cells. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, J.O.; Martins, L.G.C.; Barros, B.A.; Pimenta, M.R.; Lana, U.G.P.; Duarte, C.E.M.; Pastina, M.M.; Guimaraes, C.T.; Schaffert, R.E.; Kochian, L. V.; et al. Repeat Variants for the SbMATE Transporter Protect Sorghum Roots from Aluminum Toxicity by Transcriptional Interplay in Cis and Trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019, 116, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Magalhaes, J.V.; Shaff, J.; Kochian, L. V Aluminum-Activated Citrate and Malate Transporters from the MATE and ALMT Families Function Independently to Confer Arabidopsis Aluminum Tolerance. Plant, J. 2009, 57, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gai, J.; Li, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of MATE Transporters and Expression Patterns of a Subgroup of MATE Genes in Response to Aluminum Toxicity in Soybean. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, B.D.; Ryan, P.R.; Richardson, A.E.; Tyerman, S.D.; Ramesh, S.; Hebb, D.M.; Howitt, S.M.; Delhaize, E. HvALMT1 from Barley Is Involved in the Transport of Organic Anions. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Lv, A.; Wen, W.; Fan, N.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Zhou, P.; An, Y. MsMYB741 Is Involved in Alfalfa Resistance to Aluminum Stress by Regulating Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Plant, J. 2022, 112, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbels, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Klenke, E.; Goebel, A.; Schnakenberg, E.; Ehlers, C.; Schiwara, H.W.; Schloot, W. Melatonin in Edible Plants Identified by Radioimmunoassay and by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Pineal Res. 1995, 18, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin as a Regulatory Hub of Plant Hormone Levels and Action in Stress Situations. Plant Biol. (Stuttg). 2021, 23 Suppl 1, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MB, A.; J, H.R. Protective Effect of Melatonin against Chlorophyll Degradation during the Senescence of Barley Leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin in Flowering, Fruit Set and Fruit Ripening. Plant Reprod. 2020, 33, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; David, A.; Yadav, S.; Baluška, F.; Bhatla, S.C. Salt Stress-Induced Seedling Growth Inhibition Coincides with Differential Distribution of Serotonin and Melatonin in Sunflower Seedling Roots and Cotyledons. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, X.; Wei, H.; Li, G. Exogenous Melatonin Alleviates Salt Stress by Improving Leaf Photosynthesis in Rice Seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cui, J. Melatonin Alleviates Cadmium Toxicity by Reducing Nitric Oxide Accumulation and IRT1 Expression in Chinese Cabbage Seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 15394–15405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Lin, X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, X.; Ke, Q. Melatonin Alleviates Chromium Toxicity in Maize by Modulation of Cell Wall Polysaccharides Biosynthesis, Glutathione Metabolism, and Antioxidant Capacity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Qi, C.D.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.D. Melatonin Alleviates Copper Toxicity via Improving Copper Sequestration and ROS Scavenging in Cucumber. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, B.; Mao, Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Rengel, Z.; Chen, Q. Melatonin Alleviates Aluminum Toxicity through Modulating Antioxidative Enzymes and Enhancing Organic Acid Anion Exudation in Soybean. Funct. Plant Biol. 2017, 44, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Lv, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Jin, C.; Lin, X. Melatonin Ameliorates Aluminum Toxicity through Enhancing Aluminum Exclusion and Reestablishing Redox Homeostasis in Roots of Wheat. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Feng, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J. Melatonin Alleviates Aluminum-Induced Growth Inhibition by Modulating Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism, and Reestablishing Redox Homeostasis in Zea Mays, L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, Y.E.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Ding, C.B.; Liao, J.Q.; Hu, C.; Zhou, L.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yuan, S.; Yuan, M. Exogenous Melatonin Alleviates Oxidative Damages and Protects Photosystem II in Maize Seedlings Under Drought Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Tan, J.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Wu, D.; Jia, J.; Yang, Z. Transcriptome Analysis of Response to Aluminum Stress in Pinus Massoniana. Forests 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Santos, T.M.; da Silva, R.G.; Kumar, P.; Kottapalli, P.; Crasto, C.; Kottapalli, K.R.; França, S.C.; Zingaretti, S.M. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Sugarcane Response to Aluminum Stress by Rna-Seq. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisel, N.; Zoller, S.; Künzli-Gontarczyk, M.; Lampart, T.; Münsterkötter, M.; Brunner, I.; Bovet, L.; Métraux, J.P.; Sperisen, C. Transcriptome Responses to Aluminum Stress in Roots of Aspen (Populus Tremula). BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, G.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Ashraf, U.; Qiao, J.; Li, X.; Wan, X.; Zheng, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Provides Insights into the Differential Effects of Aluminum on Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea, L.). Genes (Basel). 2022, 13, 1830. 13.
- Liu, W.; Xiong, C.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Candidate Genes Potentially Involved in Al Stress Response in Alfalfa. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Lal, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Chourasia, K.N.; Naga, K.C.; Kumar, D.; Das, S.K.; Zinta, G. Mechanistic Insights on Melatonin-Mediated Drought Stress Mitigation in Plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Stass, A.; Horst, W.J. Apoplastic Binding of Aluminum Is Involved in Silicon-Induced Amelioration of Aluminum Toxicity in Maize. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3762–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Wu, Y.R.; Wu, P.; Zheng, S.J. Cell Wall Polysaccharides Are Specifically Involved in the Exclusion of Aluminum from the Rice Root Apex. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, J.L.; He, L.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Zheng, S.J. Effect of Aluminum on Cell Wall, Plasma Membrane, Antioxidants and Root Elongation in Triticale. Biol. Plant. 2008, 52, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Shen, R.; Nagao, S.; Tanimoto, E. Aluminum Targets Elongating Cells by Reducing Cell Wall Extensibility in Wheat Roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Eticha, D.; Rao, I.M.; Horst, W.J. Alteration of Cell-Wall Porosity Is Involved in Osmotic Stress-Induced Enhancement of Aluminium Resistance in Common Bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris, L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3245–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Zhu, X.F.; Peng, Y.X.; Zheng, C.; Li, G.X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.Z.; Zheng, S.J. Cell Wall Hemicellulose Contributes Significantly to Aluminum Adsorption and Root Growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XF, Z.; YZ, S.; GJ, L.; SC, F.; BC, Z.; YH, Z.; J, B.; T, J.; XY, X.; CZ, M.; et al. XTH31, encoding an in Vitro XEH/XET-Active Enzyme, Regulates Aluminum Sensitivity by Modulating in Vivo XET Action, Cell Wall Xyloglucan Content, and Aluminum Binding Capacity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Sharma, R.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin Synthesis and Function: Evolutionary History in Animals and Plants. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2019, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Weeda, S.; Ren, S.; Guo, Y.D. Roles of Melatonin in Abiotic Stress Resistance in Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Ahmed, S.; Sehar, Z.; Gautam, H.; Gandhi, S.G.; Khan, N.A. Hydrogen Peroxide Modulates Activity and Expression of Antioxidant Enzymes and Protects Photosynthetic Activity from Arsenic Damage in Rice (Oryza Sativa, L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, B.; Ke, Q.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Melatonin Promotes Plant Growth by Increasing Nitrogen Uptake and Assimilation under Nitrogen Deficient Condition in Winter Wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Duan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, D. Foliar Spraying of Melatonin Confers Cadmium Tolerance in Nicotiana Tabacum, L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Feng, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J. Melatonin Alleviates Aluminum-Induced Growth Inhibition by Modulating Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism, and Reestablishing Redox Homeostasis in Zea Mays L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Pang, J.; Yong, J.W.H.; Chen, Y.; Bai, C.; Gille, C.; Shi, Q.; Wu, D.; Han, X.; et al. Supplementary Calcium Restores Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea) Growth and Photosynthetic Capacity Under Low Nocturnal Temperature. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R. Melatonin Enhances Drought Tolerance by Regulating Leaf Stomatal Behavior, Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism, and Related Gene Expression in Maize Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 779382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.F.; Chao, D.Y.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Gao, J.P.; Lin, H.X. Overexpression of the Trehalose-6-Phosphate Phosphatase Gene OsTPP1 Confers Stress Tolerance in Rice and Results in the Activation of Stress Responsive Genes. Planta 2008, 228, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, M.; Sun, M.; Jiang, X.; Qiao, F. Plant Hormone Signals Regulate Trehalose Accumulation against Osmotic Stress in Watermelon Cells. Protoplasma 2022, 259, 1351–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmas, S.A.; Argyrokastritis, A.; Loukas, M.G.; Eliopoulos, E.; Tsakas, S.; Kaltsikes, P.J. Isolation and Characterization of Drought-Related Trehalose 6-Phosphate-Synthase Gene from Cultivated Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum, L. ). Planta 2006, 223, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.; Yan, L.; Wu, X.; Hussain, S.; Aziz, O.; Wang, Y.; Imran, M.; Jiang, C. Boron Alleviates the Aluminum Toxicity in Trifoliate Orange by Regulating Antioxidant Defense System and Reducing Root Cell Injury. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 208, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. Silicon Mediated Redox Homeostasis in the Root-Apex Transition Zone of Rice Plays a Key Role in Aluminum Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Q.; Li, J. Phenolic Profiles, Antioxidant Activities, and Neuroprotective Properties of Mulberry (Morus Atropurpurea Roxb.) Fruit Extracts from Different Ripening Stages. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Lan, P.; Ding, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. A New Perspective on the Toxicity of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil: Tandem Mass Tag Proteomics and Metabolomics in Earthworms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



