1. Introduction
The oral cavity hosts various microorganisms and represents the habitat from which im-balances in the microbial flora can favor the onset of oral diseases such as caries, endodontic infections and periodontal diseases with possible systemic dissemination [
1,
2]. Therefore, the main goal of endodontic treatments is the prevention or repair of periapical pathology caused by these microorganisms [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. To achieve intracanal disinfection and to promote periapical healing, “chemo-mechanical preparation” of the tooth is performed by mechanical instrumentation of the root canal space and the simultaneous use of chemical agents [
8,
9]. Irrigation is complementary to instrumentation and facilitates the removal of pulp tissues and/or microorganisms [
10], above all in root canal system areas not achievable by mechanical instrumentation (isthmus, apical delta, accessory canals) [
11]. In addition to provide mechanical flushing action, microbicidal effects and dissolution of pulp tissue remnants, an ideal irrigant should be free of local and systemic ad-verse effects [
11]. The most used irrigants in endodontics are sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) and chlorhexidine (CHX), all of which are re-sponsible for harmful side effects [
12,
13,
14]. Among these, NaOCl is the unique irrigant solution with antimicrobial effects and ability to dissolve organic components (biofilm, pulp remnants). However, NaOCl reacts with the collagen in the dentine matrix, especially after prior exposure to a chelating agent, and this may alter the modulus of elasticity, the tensile and flexural strength and the microhardness of dentine [
15]. Moreover, is also caustic [
16], and its inadvertent extrusion towards the periapical tissues may result in type I and IV hypersensitivity responses [
16,
17] and NaOCl accident, such as facial skin bruising, emphysema, tissue necrosis and sometimes paresthesia [
18,
19,
20]. Because the efficacy of syringe irrigation depends on the proximity of the needles to the apical terminus of the root canal [
21,
22,
23] as well as on the apical enlargement [
24,
25], the risk of inadvertent apical extrusion is a complication that must be considered with use of NaOCl. Furthermore, it cannot be used in combination with other commonly used antimicrobial compounds such as CHX due to their chemical reaction forming a potentially toxic orange-brown precipitate [
26,
27,
28].
In recent years, the research for new intracanal irrigants and molecules with good biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity has increased. Pharmacological studies have recognized the value of medicinal plants as potential sources of bioactive compounds [
29] and since some natural plant extracts have antimicrobial and therapeutic properties, their potential use as endodontic irrigants or intracanal medicaments has been suggested [
30,
31,
32]. In addition to antimicrobial effects, plant irrigants are safer and less toxic to host tis-sues [
30].
Therefore, the trend to seek phyto therapeutic alternatives for endodontic treatment has re-emerged, recording a growing interest from researchers in the field of phytotherapy, both for its beneficial properties and reduced side effects, and for its ease of availability [
33]. The use of herbs in dentistry, known as “Phytotherapy or Phytomedicine or Ethnopharmacology,” has ancient origins and dates back to 1900, when Prinz [
34] conducted for the first time experimental tests supporting the use of essential oils (EOs) in dentistry as therapeutic agents for the treatment of the early stages of endodontic inflammation. Based on these data, the aim of this study was to evaluate the use of Thyme Essential Oil (TEO, Thymus vulgaris) alone or in combination with NaOCl to reduce the concentrations of NaOCl used for oral therapies, and to improve the antiseptic efficacy, reducing side effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thymus vulgaris EO
The pure EO of Thymus vulgaris (TEO) was provided by Specchiasol S.r.l. (Bussolengo, VR, Italy) and was stored in a brown glass bottle at a temperature of 0–4°C for the entire duration of the experiments. The concentration of TEO employed in the trial derived from previous studies [
35]. Starting from the concentration of the commercial packaging of TEO equal to 928mg/mL (weight/volume, w/v), TEO was diluted (1:10 volume/volume, v/v) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and subsequently in TSB (final dilution 1:100 v/v, corresponding to 9.28mg/mL w/v) [
36].
2.2. Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl)
A 6% sodium hypochlorite solution formula, CanalPro™ (Coltène Italia S.r.l), was used to prepare three different dilutions in sterile water, 6%, 3% and 1%, to test its anti-bacterial action against enroll bacterial strains.
2.3. Bacterial Strains
Two ATCC strains,
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 43300) and
Streptococcus mutans (ATCC 70061), were used as challenging microorganisms (Manassas, VA, USA). Further-more, some experimental trials were also performed using the following bacterial strains:
Citrobacter freundii, Enterococcus feciorum, Proteus mirabilis, Acinetobacter cioffi, Pseudomonas putrefaciens and
Klebsiella pneumoniae, belonging to the anaerobic bacteria species predominantly isolated from root canals [
37], isolated from skin lesion, blood, milk, eye, mucous membranes, and oral and pharyngeal swabs submitted to the laboratory of the Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Bari, Italy [
35]. All bacterial suspensions were prepared by inoculating 200µL of each microorganism in 3mL of Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) (Liofilchem, Teramo, Italy) and then incubated for 24h at 37°C. A-24h culture was used for each strain with a titer of 10
9CFU/mL, except for S. mutans for which a 24h-culture was used with a titer of 10
7CFU/mL.
2.4. TEO and NaOCl Cytotoxicity on Cell Cultures
The TEO maximum non-cytotoxic concentration was evaluated in vitro with the Toxicology Assay Kit as previously reported by Galgano et al., [
35] and was considered as the TEO concentration at which the viability of treated Madin Darby Bovine Kidney (MDBK) cells decreased by no more than 20% (CC20) with respect to the negative control.
Cytotoxicity was assessed by measuring the absorbance signal (optical density, OD), with a spectrophotometer and data were analyzed with a non-linear curve fitting procedure, and the goodness of fit was evaluated via a non-linear regression analysis of the dose–response curve. The maximum non-cytotoxic concentration was considered as the TEO concentration at which the viability of treated MDBK cells decreased by no more than 20% (CC20) with respect to the negative control. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
The same experiment was performed using NaOCl at different dilutions 6%, 3% and 1%.
2.5. TEO and NaOCl Antibacterial Activity on ATCC bacterial strains
The antibacterial activities of TEO and NaOCl, used alone or in combination, were carried out on S. aureus (strain ATCC 43300) and S. mutans (strain ATCC 70061) in three different experimental tests. For the first experiments, final 1:100 (v/v) TEO dilutions were tested with the established S. aureus and S. mutans inoculum in TSB (109CFU/mL and 107CFU/mL, respectively) for 1min, 3min, 5min at room temperature (RT). The second experiment for the evaluation of NaOCl antibacterial activity, NaOCl solutions were pre-pared at concentrations of 1%, 3%, and 6% (v/v) in bacterial suspensions (S. aureus and S. mutans, with a titer of 109 CFU/mL and 107 CFU/mL, respectively) and then incubated at room temperature for 1min, 3min, 5min. Finally, the antibacterial activity of TEO, diluted 1:100, associated with NaOCl, at the concentration of 1%, was evaluated for the same bacterial strains and under the same conditions described above.
Then, 1mL aliquots of each suspension of the three tests, were diluted (ten-fold dilutions starting from 10−1 to 10−9) in TSB and cultured into Plate Count Agar (PCA) plates (Liofilchem, Teramo, Italy). The positive control (bacterial suspension without NaOCl) was contextually diluted and plated as above. All cultured plates were incubated at 37°C for 24h and 48h. All tests were performed in triplicate.
Bactericidal activity was evaluated after 24h and 48h of incubation at 37°C, as de-scribed above. The tests conducted on S. mutans were carried out by incubating the strain at 37°C in an atmosphere with 5% CO2. All the tests were performed in triplicate.
2.6. Antibacterial activity of TEO and NaOCl in the presence of sheep erythrocytes
The antibacterial activity of TEO and NaOCl was evaluated in the presence of organic components (i.e., sheep erythrocytes) to simulate the presence of organic residues such as in the infected root canal system that could alter the antimicrobial activity of two com-pounds. An aliquot of the suspensions composed of cultures of all the tested bacteria, 2 ATCC and 6 field strains, and TEO diluted at 1:100 (v/v) supplemented with NaOCl 1%, were tested for antimicrobial activity in the presence of 6% erythrocytes. After 1 min of contact at RT, 1mL aliquot of each mixture was diluted from 10−1 to 10−9 in TSB, cultured into PCA plates and incubated for 24h and 48h at 37°C. Each test was performed in tripli-cate. The tests conducted on S. mutans were carried out by incubating the strain at 37°C in an atmosphere with 5% CO2.
2.7. Data Analyses
The assessment of normality in the distribution was conducted using the Shapiro-Wilk test. For independent samples, a One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s HSD test as a post hoc analysis. A significance level of p < 0.05 was chosen to determine statistical significance. The statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism v8.1.2 (Dotmatics, Boston, USA). The normality of the distribution was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk normality test (W = 0.85584, p-value = 0.008262).
3. Results
3.1. TEO Cytotoxicity on Cell Cultures
The CC20 value of TEO was assessed at a 1:100 dilution (v/v), corresponding to a concentration of 9.28 mg/mL (weight/volume, w/v) and calculated as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three experiments. In all the experiments, the DMSO did not show any effect on MDBK cells. All NaOCl solutions showed higher cytotoxicity than TEO 1:100 (data not shown).
3.2. TEO and NaOCl Antibacterial Activity
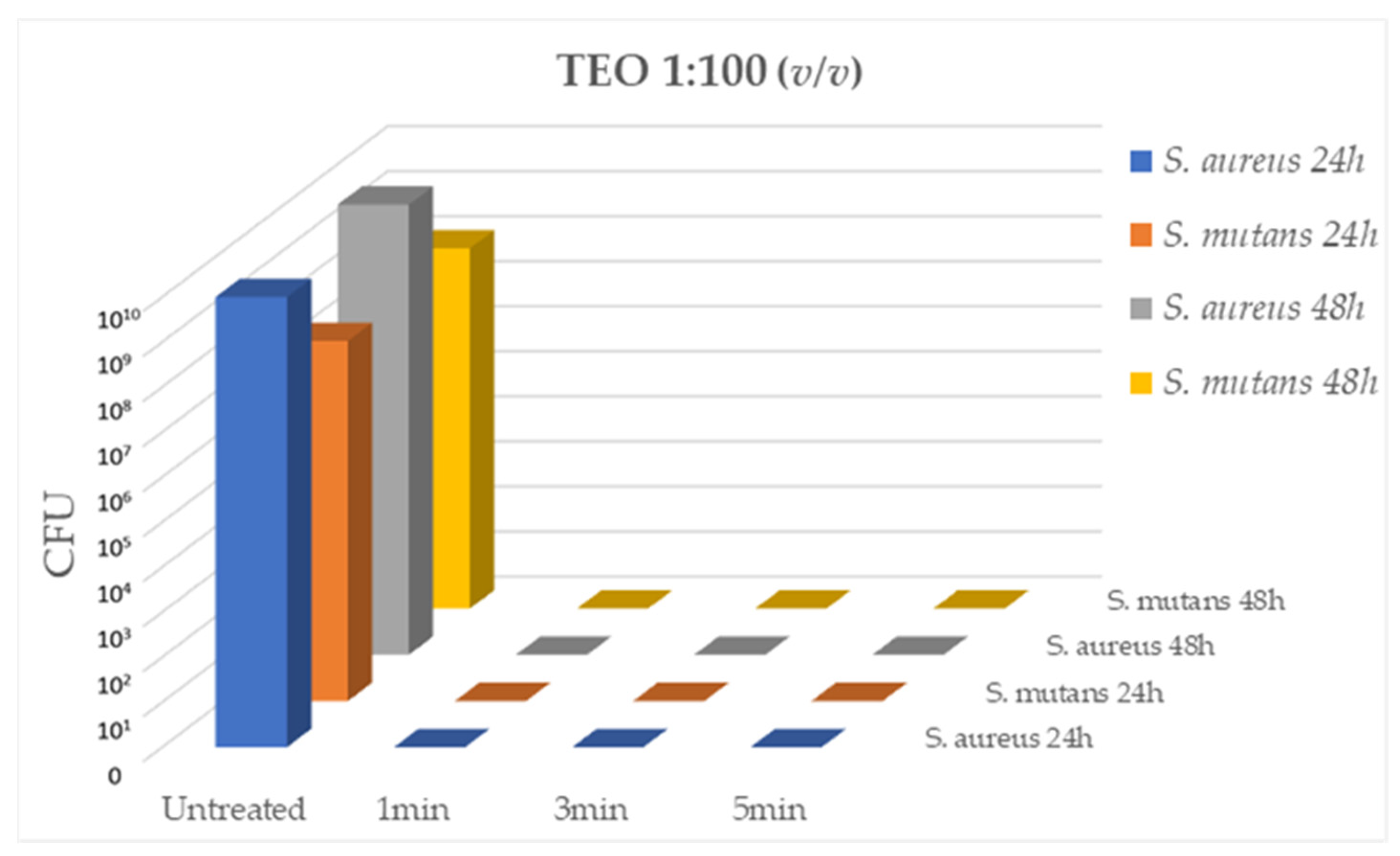
The antibacterial activity of TEO diluted 1:100 (v/v) on
S. aureus (strain ATCC 43300) and
S. mutans (strain ATCC 70061) cultures, was evaluated after 1min, 3min and 5min of contact at RT. As reported in
Figure 1, TEO diluted 1:100 demonstrated a strong bactericidal activity in the absence of cytotoxicity, at all contact times, with total inhibition of bacterial growth (CFU= 0.00 for all tested strains, p < 0.05).
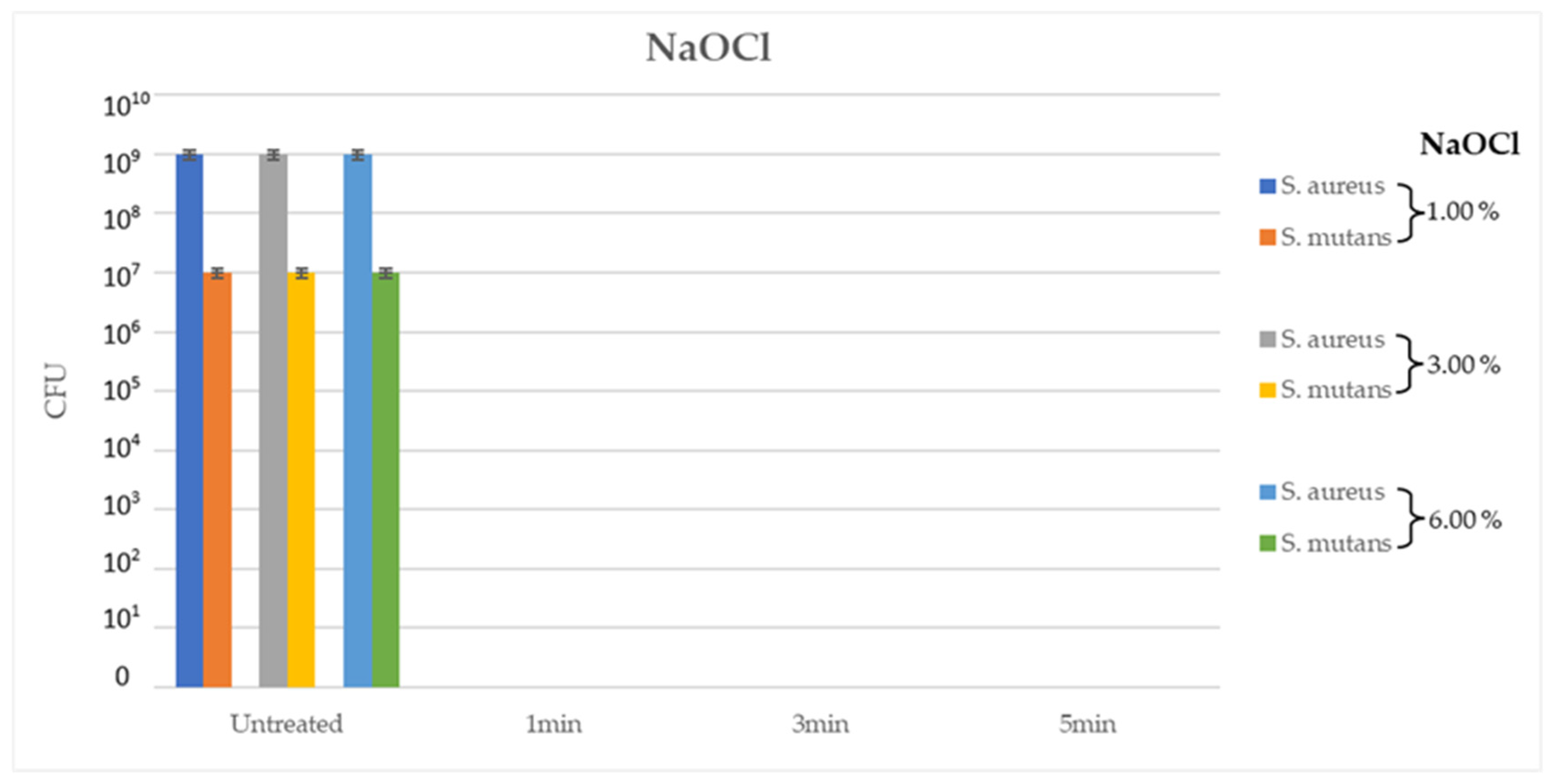
In the second experiment, NaOCl at different concentrations, 1%, 3% and 6%, yielded good results at every contact time (1min, 3min and 5min) on the ATCC tested bacterial strains, with a total inhibition of bacterial growth (CFU= 0.00 for all tested strains, p < 0.05). Interestingly, 1% NaOCl after 1min of contact at RT demonstrated the same antimi-crobial efficacy as 6% NaOCl solution after 5min of contact under the same conditions (
Figure 2).
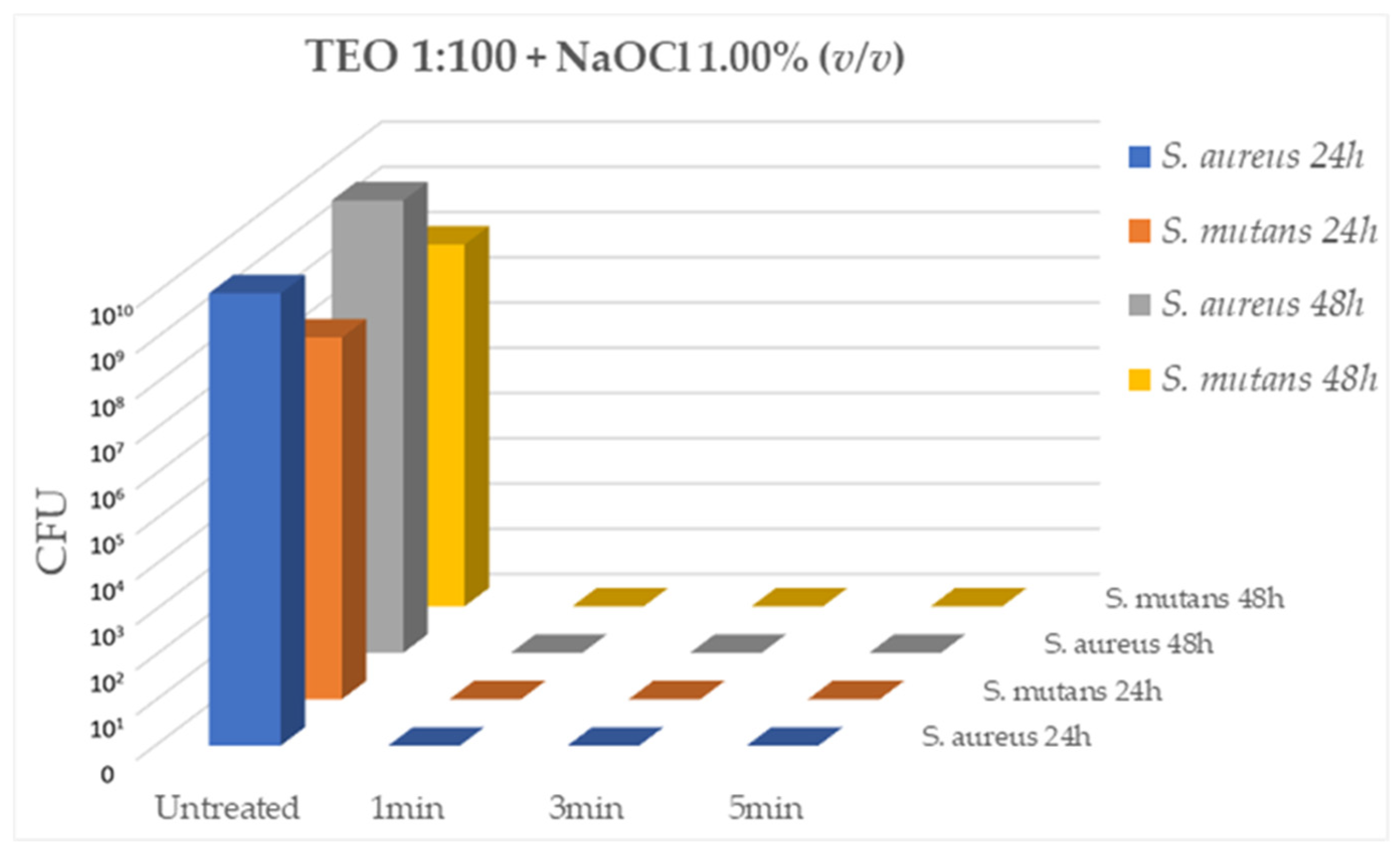
Having identified the 1:100 dilution of TEO and the concentration of 1% NaOCl as the solutions with effective antibacterial activity, the bactericidal activity of the two com-ponents used in association (TEO 1:100 and NaOCl 1%) was evaluated on the same ATCC bacterial strains,
S. aureus and
S. mutans, after 5min, 3min and 1min of contact at RT. As shown in
Figure 3, the association of the two compounds has a strong bactericidal activity against the two ATCC strains comparable to that demonstrated individually by the two compounds at all contact times evaluated (CFU= 0.00 for all tested strains, p < 0.05).
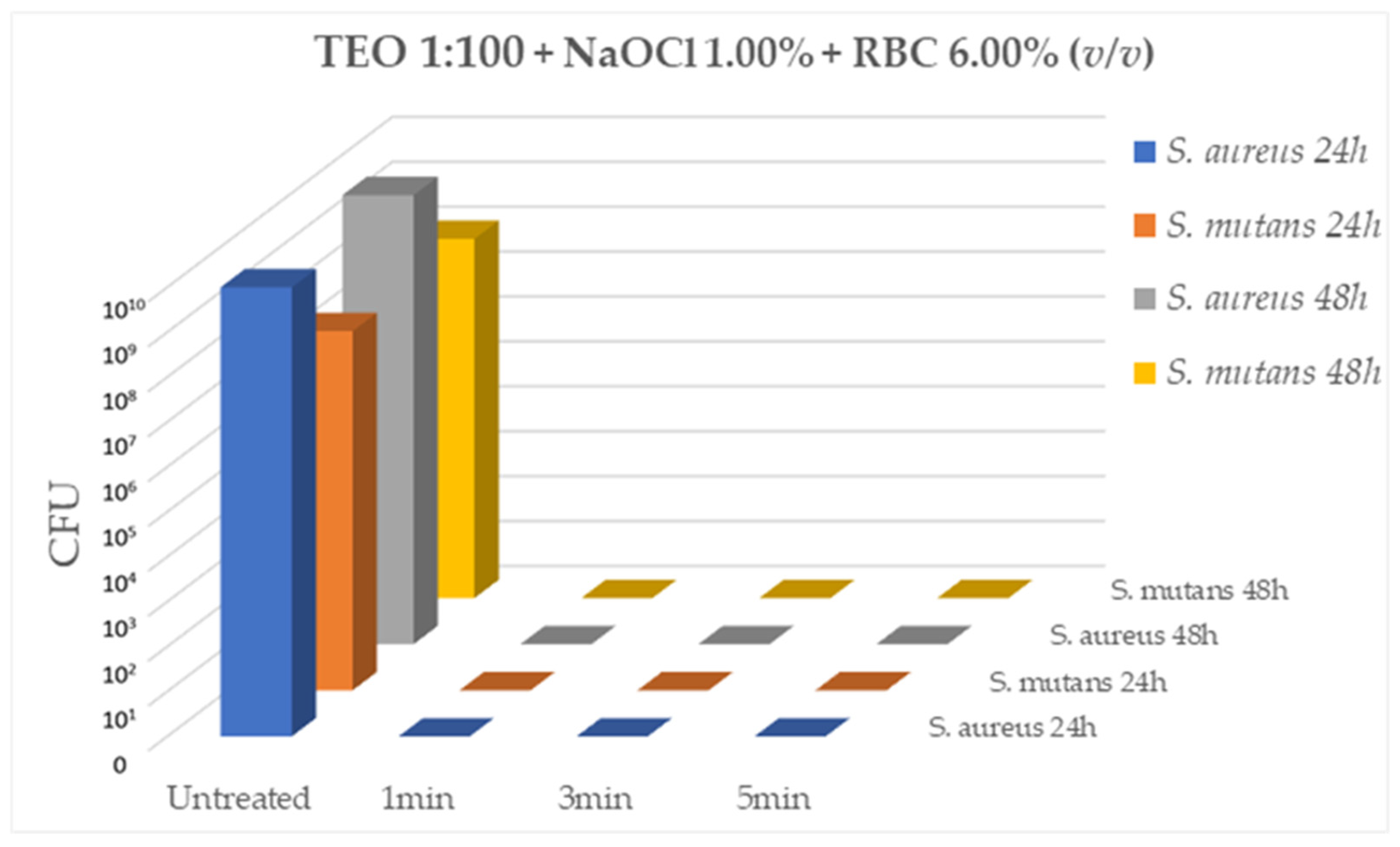
Lastly, testing TEO diluted 1:100 (v/v) in association of 1% NaOCl and in the presence of 6% of sheep erythrocytes, the mixed solution was able to effectively inhibit bacterial growth of both ATCC strains,
S. aureus (10
9CFU/mL) and
S. mutans (10
7CFU/mL), after 1min, 3min and 5min of contact at RT (CFU= 0.00 for all tested strains, p < 0.05) (
Figure 4).
Comparable results were obtained after evaluating the antibacterial activity of NaOCl at a concentration of 1% in the presence of a 6% erythrocyte suspension, on the 6 field strains (data not shown). The results obtained at 24 hours overlapped with those obtained at 48 hours for all tests performed.
4. Discussion
It is known that instruments are unable to reach a large part of the root canal system and that bacteria can also reside in fins extending laterally from the main canal, in isthmuses connecting adjacent root canals in the same root [
38,
39], in accessory canals, in apical ramifications and in patent dentinal tubules [
40,
41]. The importance of irrigation with the use of appropriate solution and medication able to reduce the number of microorganism-isms and increase chances for successful root-canal therapy, is crucial for a correct and effective debridement and disinfection of the root canal system [
42].
NaOCl is the most used irrigant used during instrumentation. It is a nonspecific proteolytic agent with wide-ranging activities against endodontic microorganisms [
11]. According to old laboratory studies, the desirable effects of NaOCl are a function of its con-centration [
43,
44,
45,
46,
47] but recent clinical studies have not detected a significant difference in the antimicrobial effect or healing of apical periodontitis between different concentrations of NaOCl [
48,
49]. Increasing the concentration may also amplify undesirable effects of the solution, such as the mechanical properties of dentine [
15]. Moreover, since NaOCl is also caustic [
16] its involuntary extrusion towards the periapical tissues may result in cytotoxic reactions and potential side effects, even accidental [
18,
19]. Other irrigants such as CHX have antimicrobial effects [
50,
51,
52] but have no dissolving action on tissues [
53,
54] and can reacts with residual NaOCl in the root canal to forms a potentially toxic orange-brown precipitate that can also cause discoloration [
26,
27,
28]. Use of toxic medications or irrigants can cause not only complications during root-canal treatment but may interfere with the repair process as well. Therefore, in choosing irrigants or medications during root-canal treatment, biocompatibility should be a major consideration. One way to select a medication or an irrigant with these two characteristics is to study the antibacterial and cytotoxic properties of available medications and irrigants at various dilutions, and then choose a medication or an irrigant that has both desirable properties [
55]. An ideal root-canal dis-infectant would be a substance with the least cytotoxicity and the strongest antimicrobial activity.
There is a recent increase in the search for new intracanal irrigants with good biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity to supplement and/or replace NaOCl. Among natural agents, EOs are potential germicides whose activity date back to 1900, when Prinz [
34] describe the first experiments of their use as germicidal agents for root canal treatments, root canal fillings or setting of crowns. Most of the antimicrobial activities of TEO appear to be associated with the phenolic compounds thymol, eugenol and carvacrol affecting the lipid ordering and stability of membrane bilayer and resulting in changes in permeability [
56,
57]. Moreover, EOs can interfere with bacterial enzymes, respiratory pathways, protein synthesis or transmembrane transportation activity [
58].
Previous studies have demonstrated the strong antibacterial activity of TEO against oral bacteria species [
35] and biofilm-producing bacteria [
59,
60]. Moreover, EOs act with the same effectiveness of NaOCl on antibiotic-sensitive and multidrug-resistant bacteria, even if organized in biofilms [
59].
Since the caustic action of NaOCl, resulting mainly from involuntary extrusion to-wards the periapical tissues, as well as its dose-dependent toxic effect are well-known, in the present study in order to reduce the concentration of NaOCl used while maintaining the chances of successful root canal therapy, we evaluated in vitro the maximum non-cytotoxic concentration of TEO, which was found to be equal to the 1:100 (v/v) dilution (9.28mg/mL w/v).
The antibacterial activity of TEO diluted 1:100 and of NaOCl at different concentrations (from 1% to 6%) evaluated after 1min of contact at RT with bacterial strains were found to be comparable, with complete inhibition of bacterial growth with both compounds. Bacterial strains such as Staphylococci and Streptococci are involved in endodontic pathologies [
6,
61,
62], and previous studies demonstrated the potential use of TEO as an intracanal drug as an alternative to conventional root canal irrigants [
63,
64]. However, one limit of TEO, as observed for CHX, is the lack of tissue-dissolving action and consequently, it should be used in combination to NaOCl as irrigant. Starting from this objection, in the present study TEO and NaOCl were tested together to evaluate their potential synergistic effect. Interesting, the two compounds were able to act in synergy without interference, completely inhibiting microbial growth after only 1min of contact, even in the presence of 6% (v/v) sheep erythrocyte that simulate the presence of organic remnants like pulp tissue which reproduce the infected environment of canal roots.
5. Conclusions
Our data confirm the efficacy of TEO as potential antimicrobial compound with possible applications as irrigant in endodontic treatments to counteract infection [
65,
66]. TEO demonstrated to be an effective microbicide with high biocompatibility and no interferences when mixed with NaOCl. Moreover, the association of TEO and NaOCl at low con-centrations inhibited totally microbial growth even in the presence of organic material. NaOCl remains the cornerstone (first choice) in root canal irrigation protocols, maintaining its antimicrobial properties even in lower concentrations. The antimicrobial efficacy in apical third depends on the proximity of the needles to the apical terminus of the root canal, therefore maintaining needle more coronal than working length to reduce the risk of inadvertent apical extrusion could determine a possible persistence of bacterial strains.
The combination with TEO could allow to reduce the concentrations of NaOCl, with the possibility for clinicians to increase safety in irrigation protocols for inadvertent extrusion of NaOCl towards the periapical tissues. Furthermore, the TEO irrigant could be used with greater safety near the apical terminus of the root canal for its better biocompatibility compared to NaOCl.
Whether the results of in vitro experiments can be applied in clinical practice remains to be investigated. There is evidence that in vitro tests adequately measure cytotoxicity and therefore can reasonably be used as a screening tool to evaluate the biocompatibility of test materials [
67,
68,
69].
Further studies, in vivo and in vitro, are therefore necessary to better investigate the potential of TEO as an irrigant, such as determining the interaction with inorganic debris, the penetration into the dentinal tubules, the effectiveness with different irrigation methods and the healing of the apical periodontitis.
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, M.G. and A.B. (Alessio Buonavoglia); methodology, M.G., L.D.B., L.C. and A.B. (Angelica Bianco); software, F.P. and A.H.O.; validation, A.P. (An-namaria Pratelli), and P.C.; formal analysis, F.P., A.B. (Alessio Buonavoglia), and A.H.O.; inves-tigation, M.G. and F.P.; resources, A.P. (Antonio Parisi); data curation, F.P. and A.I.; writ-ing—original draft preparation, M.G.; writ-ing—review and editing, A.P., F.P. and A.B. (Alessio Buonavoglia); visualization, A.P. (Antonio Parisi) and P.C.; supervision, A.P. (Annamaria Pratelli), M.G. and P.C.; project administration, A.P. (Annamaria Pratelli) and A.B. (Alessio Buonavoglia). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dzink, J.L.; Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D. The Predominant Cultivable Microbiota of Active and Inactive Lesions of Destructive Periodontal Diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1988, 15, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, M.; Polizzi, A.; Santonocito, S.; Romano, A.; Lombardi, T.; Isola, G. Impact of Oral Microbiome in Peri-odontal Health and Periodontitis: A Critical Review on Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakehashi, S.; Stanley, H.R.; Fitzgerald, R.J. The Effects of Surgical Exposures of Dental Pulps in Germ-Free and Conventional Laboratory Rats. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1965, 20, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundqvist, G. Bacteriological Studies of Necrotic Dental Pulps. In Umea University of Odontology Dissertation; University of Umea: Umea, Sweden, 1976; Vol. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Latronico, F.; Pirani, C.; Greco, M.F.; Corrente, M.; Prati, C. Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Api-cal Periodontitis Associated with Red Complex Bacteria: Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation. Odontology 2013, 101, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Zamparini, F.; Lanave, G.; Pellegrini, F.; Diakoudi, G.; Spinelli, A.; Lucente, M.S.; Camero, M.; Va-sinioti, V.I.; Gandolfi, M.G.; et al. Endodontic Microbial Communities in Apical Periodontitis. J. Endod. 2023, 49, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Lanave, G.; Diakoudi, G.; Lucente, M.S.; Zamparini, F.; Camero, M.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Martella, V.; Prati, C. Analysis of Oral Microbiota in Non-Vital Teeth and Clinically Intact External Surface from Patients with Severe Periodontitis Using Nanopore Sequencing: A Case Study. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Rôças, I.N.; Riche, F.N.S.J.; Provenzano, J.C. Clinical Outcome of the Endodontic Treatment of Teeth with Apical Periodontitis Using an Antimicrobial Protocol. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2008, 106, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, S.; Pisano, M.; Amato, A.; Abdellatif, D.; Iandolo, A. Modern Rotary Files in Minimally Invasive Endodon-tics: A Case Report. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2021, 13, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandolo, A.; Pisano, M.; Buonavoglia, A.; Giordano, F.; Amato, A.; Abdellatif, D. Traditional and Recent Root Canal Irrigation Methods and Their Effectiveness: A Review. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.D.; Woollard, G.W. Endodontic Irrigation. Gen. Dent. 2001, 49, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, D.R. Cultural History from the Vayupurana; 1st ed.; Motilal Banarsidass Publishers, 1973; Vol. 8120837231;
- Tewari, R.; Kapoor, B.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, A. Role of Herbs in Endodontics. Journal of Oral. Research and Review 2016, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppo, F.C.; Bergamaschi, C. de C.; Cogo, K.; Franz-Montan, M.; Motta, R.H.L.; Andrade, E.D. de Use of Phyto-therapy in Dentistry. Phytotherapy Research 2008, 22, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascon, F.M.; Kantovitz, K.R.; Sacramento, P.A.; Nobre-dos-Santos, M.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite on Dentine Mechanical Properties. A Review. J. Dent. 2009, 37, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashley, E.L.; Birdsong, N.L.; Bowman, K.; Pashley, D.H. Cytotoxic Effects of NaOCl on Vital Tissue. J. Endod. 1985, 11, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, A.Y.; Keila, S. Hypersensitivity to Sodium Hypochlorite. J. Endod. 1989, 15, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutsioukis, C.; Psimma, Z.; van der Sluis, L.W.M. Factors Affecting Irrigant Extrusion during Root Canal Irriga-tion: A Systematic Review. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guivarc’h, M.; Ordioni, U.; Ahmed, H.M.A.; Cohen, S.; Catherine, J.-H.; Bukiet, F. Sodium Hypochlorite Accident: A Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.; Venturi, G.; Bertoletti, P.; Francinelli, J.; Tonini, R.; Garo, M.L.; Salgarello, S. Sodium Hypochlorite Accident during Canal Treatment: Report of Four Cases Documented According to New Standards. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsioukis, C.; Verhaagen, B.; Versluis, M.; Kastrinakis, E.; van der Sluis, L.W.M. Irrigant Flow in the Root Canal: Experimental Validation of an Unsteady Computational Fluid Dynamics Model Using High-Speed Imaging. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsioukis, C.; Verhaagen, B.; Versluis, M.; Kastrinakis, E.; Wesselink, P.R.; van der Sluis, L.W.M. Evaluation of Irrigant Flow in the Root Canal Using Different Needle Types by an Unsteady Computational Fluid Dynamics Model. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.E.; Nurbakhsh, B.; Layton, G.; Bussmann, M.; Kishen, A. Irrigation Dynamics Associated with Positive Pressure, Apical Negative Pressure and Passive Ultrasonic Irrigations: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. Australian Endodontic Journal 2014, 40, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psimma, Z.; Boutsioukis, C.; Kastrinakis, E.; Vasiliadis, L. Effect of Needle Insertion Depth and Root Canal Curva-ture on Irrigant Extrusion Ex Vivo. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.B.; Adachi, J.D.; Beattie, K.A.; MacDermid, J.C. Development and Validation of a New Tool to Measure the Facilitators, Barriers and Preferences to Exercise in People with Osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basrani, B.R.; Manek, S.; Sodhi, R.N.S.; Fillery, E.; Manzur, A. Interaction between Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine Gluconate. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.; Santos Júnior, H.M.; Rezende, C.M.; Pinto, A.C.; Faria, R.B.; Simão, R.A.; Gomes, B.P.F.A. Interactions between Irrigants Commonly Used in Endodontic Practice: A Chemical Analysis. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Sarmast, N.D.; Terlier, T.; van der Hoeven, R.; Holland, J.N.; Parikh, N. Assessment of the Cytotoxic Ef-fects and Chemical Composition of the Insoluble Precipitate Formed from Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine Gluconate. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusti, A.; Mishra, S.R.; Sahoo, S.; Mishra, S.K. Antibacterial Activity of Some Indian Medicinal Plants. Ethnobo-tanical leaflet 2008, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Vinothkumar, T.; Rubin, M.; Balaji, L.; Kandaswamy, D. In Vitro Evaluation of Five Different Herbal Extracts as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant Using Real Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction. Journal of Conservative Dentistry 2013, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavizadeh, M.; Abbaszadegan, A.; Gholami, A.; Sheikhiani, R.; Shokouhi, M.; Shams, M.; Ghasemi, Y. Chemical Constituent and Antimicrobial Effect of Essential Oil from Myrtus Communis Leaves on Microorganisms Involved in Persistent Endodontic Infection Compared to Two Common Endodontic Irrigants: An in Vitro Study. Journal of Con-servative Dentistry 2014, 17, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadegan, A.; Sahebi, S.; Gholami, A.; Delroba, A.; Kiani, A.; Iraji, A.; Abbott, P.V. Time-dependent Antibacte-rial Effects of Aloe Vera and Zataria Multiflora Plant Essential Oils Compared to Calcium Hydroxide in Teeth Infected with Enterococcus Faecalis. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Gurtu, A.; Singhal, A.; Vinayak, V. Naturopathy and Endodontics–A Synergistic Approach. Journal of Dental Sciences & Oral. Rehabilitation 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prinz, H. The Essential Oils; Their Value and Use in Dentistry. The Dental register 1900, 54, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galgano, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Mrenoshki, D.; Capozza, P.; Omar, A.; Salvaggiulo, A.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Tempe-sta, M.; Pratelli, A.; et al. Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catella, C.; Camero, M.; Lucente, M.S.; Fracchiolla, G.; Sblano, S.; Tempesta, M.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, C.; La-nave, G. Virucidal and Antiviral Effects of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil on Feline Coronavirus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Lanave, G.; Camero, M.; Corrente, M.; Parisi, A.; Martella, V.; Prati, C. Next-Generation Sequenc-ing Analysis of Root Canal Microbiota Associated with a Severe Endodontic-Periodontal Lesion. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertucci, F.J. Root Canal Morphology and Its Relationship to Endodontic Procedures. Endod. Topics 2005, 10, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirani, C.; Buonavoglia, A.; Cirulli, P.P.; Baroni, C.; Chersoni, S. The Effect of the NRT Files Instrumentation on the Quality of the Surface of the Root Canal Wall. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2012, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulabivala, K.; Patel, B.; Evans, G.; Ng, Y.-L. Effects of Mechanical and Chemical Procedures on Root Canal Sur-faces. Endod Topics 2005, 10, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Loghin, S.; Siqueira, J.F. Exuberant Biofilm Infection in a Lateral Canal as the Cause of Short-Term En-dodontic Treatment Failure: Report of a Case. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Leone, P.; Solimando, A.G.; Fasano, R.; Malerba, E.; Prete, M.; Corrente, M.; Prati, C.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V. Antibiotics or No Antibiotics, That Is the Question: An Update on Efficient and Effective Use of Antibiotics in Dental Practice. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorer, W.R.; Wesselink, P.R. Factors Promoting the Tissue Dissolving Capability of Sodium Hypochlorite. Int. Endod. J. 1982, 15, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Moliz, M.T.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M.; Espigares-García, M.; Baca, P. Enterococcus Faecalis Biofilms Eradication by Root Canal Irrigants. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, R.G.; Wesselink, P.R.; Zaccheo, F.; Fanali, D.; Van Der Sluis, L.W.M. Reaction Rate of NaOCl in Contact with Bovine Dentine: Effect of Activation, Exposure Time, Concentration and PH. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojicic, S.; Zivkovic, S.; Qian, W.; Zhang, H.; Haapasalo, M. Tissue Dissolution by Sodium Hypochlorite: Effect of Concentration, Temperature, Agitation, and Surfactant. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, X.; Busanello, F.H.; So, M.V.R.; Dijkstra, R.J.B.; Sharma, P.K.; van der Sluis, L.W.M. Factors Affecting the Chemical Efficacy of 2% Sodium Hypochlorite against Oral Steady-state Dual-species Biofilms: Exposure Time and Volume Application. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulin, C.; Magunacelaya-Barria, M.; Dahlén, G.; Kvist, T. Immediate Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of the Effectiveness of 0.5% versus 3% Sodium Hypochlorite in Root Canal Treatment: A Quasi-randomized Controlled Trial. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Sangwan, P.; Tewari, S.; Duhan, J. Effect of Different Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite on Out-come of Primary Root Canal Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, B.P.F.A.; Ferraz, C.C.R.; ME, V.; Berber, V.B.; Teixeira, F.B.; Souza-Filho, F.J. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Several Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine Gluconate in the Elimination of Enterococcus Faecalis. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, R.; Bramante, C.M.; Letra, A.; Carvalho, V.G.G.; Garcia, R.B. Histologic Evaluation of Pulpotomies in Dog Using Two Types of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Regular and White Portland Cements as Wound Dressings. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2004, 98, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna, M.E.; Gomes, B.P.F.A.; Berber, V.B.; Zaia, A.A.; Ferraz, C.C.R.; de Souza-Filho, F.J. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Chlorhexidine and Sodium Hypochlorite. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology 2004, 97, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naenni, N.; Thoma, K.; Zehnder, M. Soft Tissue Dissolution Capacity of Currently Used and Potential Endodontic Irrigants. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, L.A.; Siqueira, E.L.; Santos, M.; Bombana, A.C.; Figueiredo, J.A.P. Dissolution of Pulp Tissue by Aqueous Solution of Chlorhexidine Digluconate and Chlorhexidine Digluconate Gel. Int. Endod. J. 2004, 37, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masillamoni, C.R.M.; Kettering, J.D.; Torabinejad, M. The Biocompatibility of Some Root Canal Medicaments and Irrigants. Int. Endod. J. 1981, 14, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, M.C.; Herrera, A.; Martínez, R.M.; Sotomayor, J.A.; Jordán, M.J. Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Compo-sition of Thymus Vulgaris, Thymus Zygis and Thymus Hyemalis Essential Oils. Food Control 2008, 19, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgano, M.; Capozza, P.; Pellegrini, F.; Cordisco, M.; Sposato, A.; Sblano, S.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Fracchiolla, G.; Corrente, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Evaluated In Vitro against Escherichia Coli and Staphylo-coccus Aureus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, N.; Dagli, R.; Mahmoud, R.; Baroudi, K. Essential Oils, Their Therapeutic Properties, and Implication in Dentistry: A Review. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2015, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, A.; Barreto, A.S.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T. Antimicrobial Effects of Essential Oils on Oral Microbiota Biofilms: The Toothbrush In Vitro Model. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgano, M.; Mrenoshki, D.; Pellegrini, F.; Capozzi, L.; Cordisco, M.; Del Sambro, L.; Trotta, A.; Camero, M.; Tem-pesta, M.; Buonavoglia, D.; et al. Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus Vulgaris L. Essen-tial Oil against Salmonella Spp. Isolates from Reptiles. Pathogens 2023, 12, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Latronico, F.; Greco, M.; D’Abramo, M.; Marinaro, M.; Mangini, F.; Corrente, M. Methicil-lin-Resistant Staphylococci Carriage in the Oral Cavity: A Study Conducted in Bari (Italy). Oral. Dis. 2010, 16, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Trotta, A.; Cordisco, M.; Zamparini, F.; Corrente, M.; Prati, C. Alveolar Osteitis Associated with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis. New Microbiol. 2022, 45, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abuidris, A.; Abdelaziz, S.; Roshdy, N.; Issa, M. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Two Herbals and Their Effect on Dentin Microhardness (A Comparative in Vitro Study). Egypt. Dent. J. 2020, 66, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy-Bota, M.C.; Man, A.; Santacroce, L.; Brinzaniuc, K.; Pap, Z.; Pacurar, M.; Pribac, M.; Ciurea, C.N.; Pin-tea-Simon, I.A.; Kovacs, M. Essential Oils as Alternatives for Root-Canal Treatment and Infection Control against Enter-ococcus Faecalis—A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Kohanteb, J. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil Against Major Oral Patho-gens. J. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 22, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.R. de; de Jesus Viegas, D.; Martins, A.P.R.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; Soares, C.P.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Jorge, A.O.C.; de Oliveira, L.D. Thymus Vulgaris L. Extract Has Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in the Absence of Cyto-toxicity and Genotoxicity. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2017, 82, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangberg, L.; Engström, B.; Langeland, K. Biologic Effects of Dental Materials. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology 1973, 36, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spångberg, L.S.W. Correlation of in Vivo and in Vitro Screening Tests. J. Endod. 1978, 4, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spångberg, L.; Rutberg, M.; Rydinge, E. Biologic Effects of Endodontic Antimicrobial Agents. J. Endod. 1979, 5, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).