Submitted:
31 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material and Treatment
2.2. Determination of Astaxanthin in H. pluvialis
2.3. Metabolite Extraction and LC-MS/MS-based Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Data Process and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of NaCl Concentration on Astaxanthin Accumulation in H. pluvialis
3.2. Effect of NaNO3 Concentration on Astaxanthin Accumulation in H. pluvialis
3.3. Comparison of the Metabolic Characteristics in H. pluvialis under the Different Stress Conditions
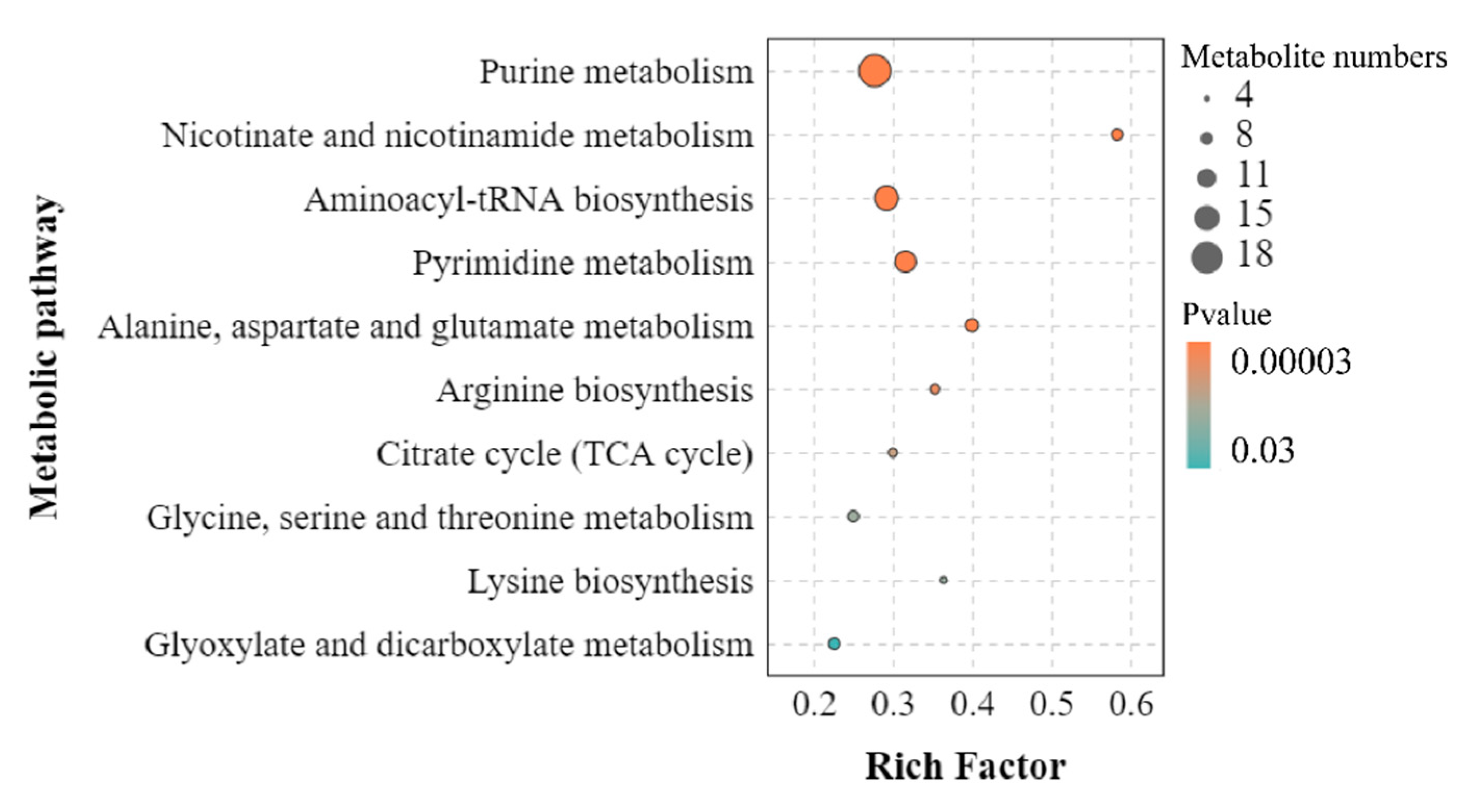
3.4. KEGG Pathway Analysis
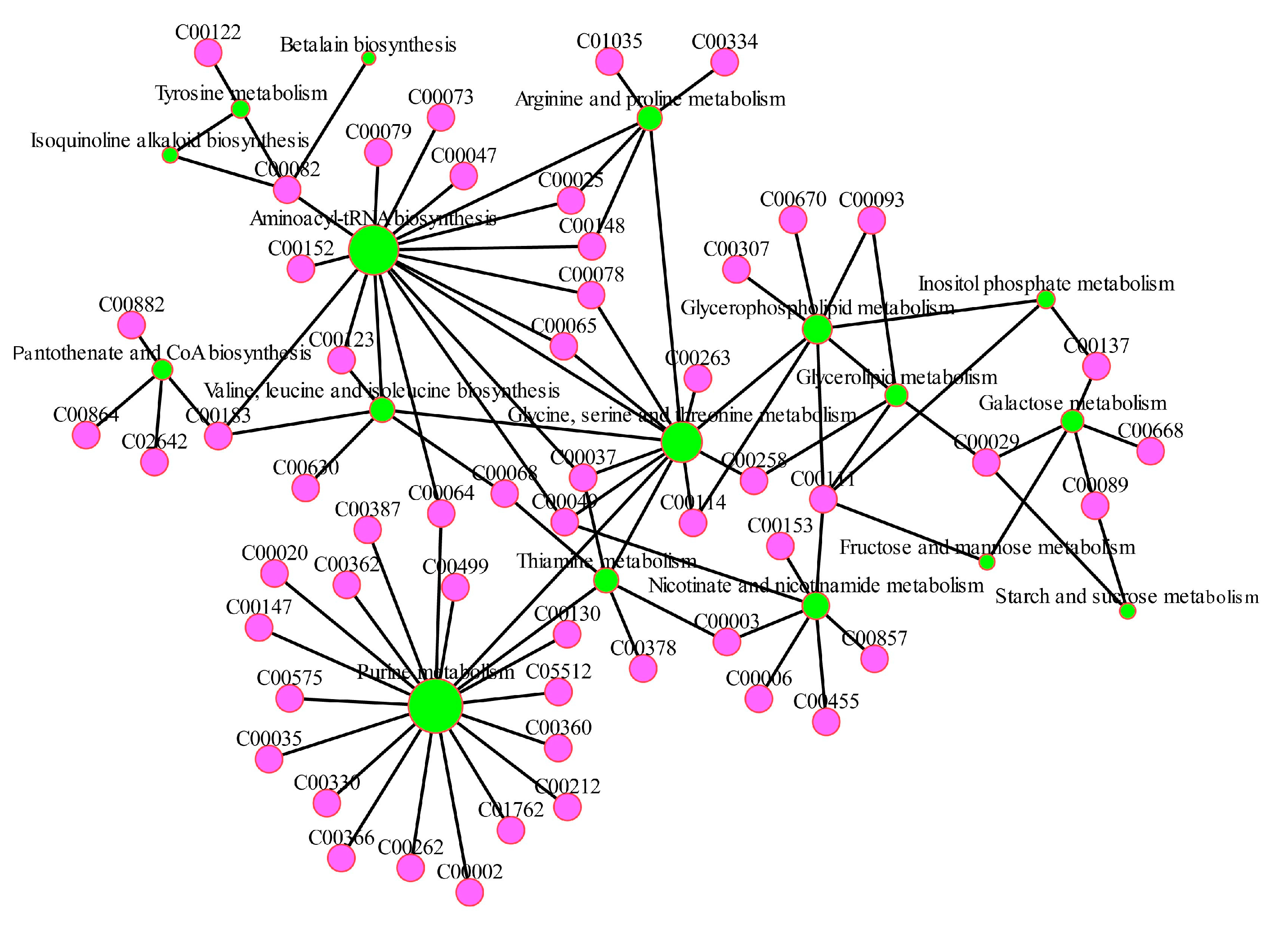
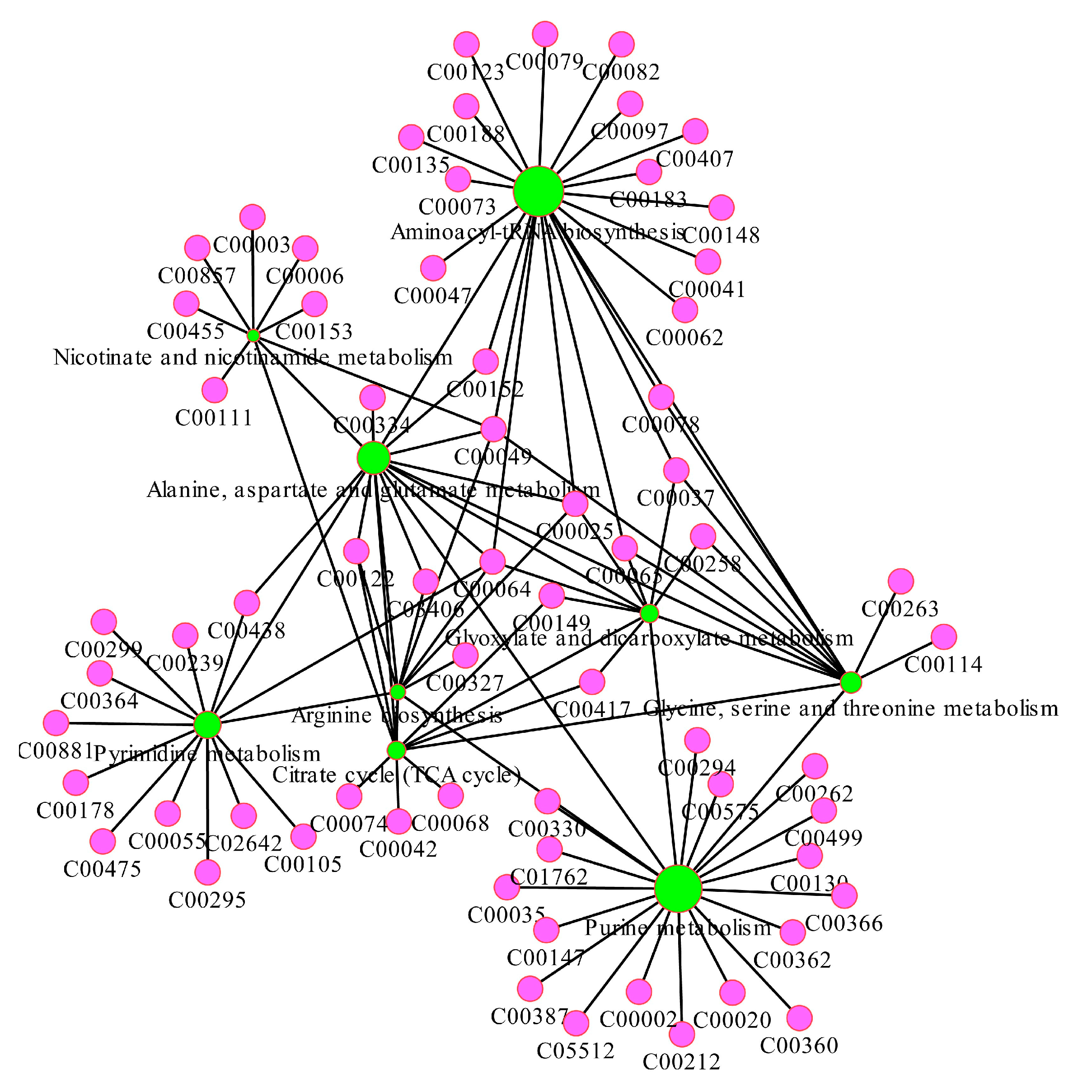
3.5. Metabolimic Network Construction and Analysis
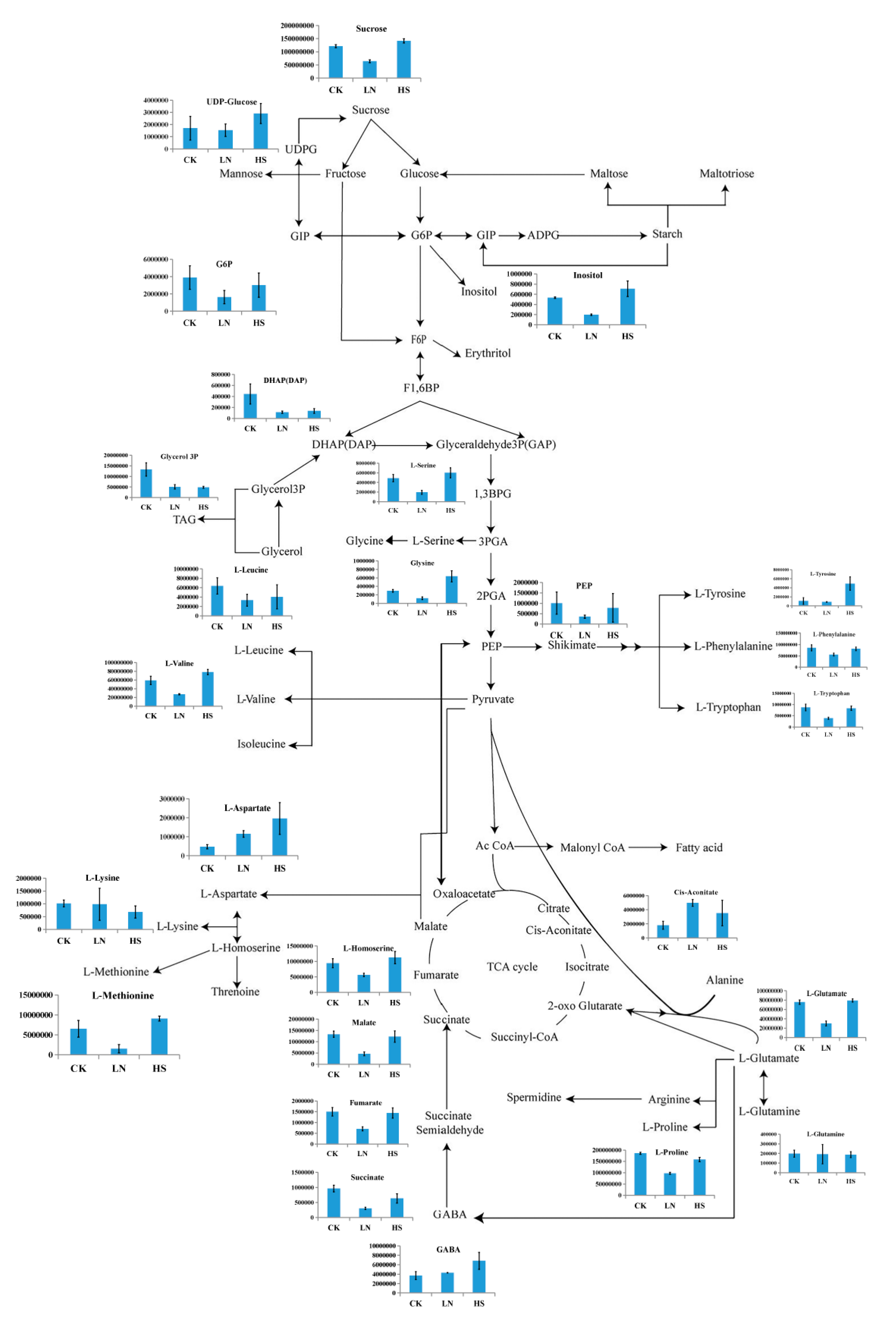
3.6. Major Carbon Metabolism and the Changes in Identified Metabolites Related to Astaxanthin Accumulation in H. pluvialis
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic Characteristics of Astaxanthin Accumulation in H. pluvialis under the High Salinity Stress
4.2. Metabolic Characteristics of Astaxanthin Accumulation in H. pluvialis under the Nitrogen-deficient Stress
4.3. Comparative Analysis of the major carbon metabolism in H. pluvialis under the different stress conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, K.C.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Kamarudin, M.S. Astaxanthin as feed supplement in aquatic animals. Rev Aquacult, 2018, 10, 738–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, Y. Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids. J Agr Food Chem, 2000, 48, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, N.; Wang, C.K.; Liu, X.F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, X.M.; Du, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zhang, H.B. De novo synthesis of astaxanthin: from organisms to genes. Trends Food Sci Tech, 2019, 92, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, L.M.; Potin, P.; Craigie, S.J.; Raven, A.J.; Merchant, S. Sabeeha.; Helliwell, E.K.; Alison, G.S.; Camire, E.M.; Brawley, H.S. Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: revisiting our understanding. J Appl Phycol, 2017, 29, 949–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatyana, A.K.; Min, S.K.; Jong, W.H.; Taizo, M.; Chikako, N.; Gwang, H. Kim. Cold-tolerant strain of Haematococcus pluvialis (Haematococcaceae, Chlorophyta) from Blomstrandhalvøya (Svalbard). Algae, 2013, 28, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.X.; Hou, L.L.; Zhang, F.; Cong, X.M.; Wang, Z.D.; Guo, Y.L.; Shi, J.W.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, X.C.; Zang, X.N. Ultrastructural changes of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyta) in process of astaxanthin accumulation and cell damage under condition of high light with acetate. Algae, 2020, 35, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, A.B.; Ashley, S.; Haley, J.; Richard, P.; Matthew, B.T. The description of Haematococcus privus sp. nov. (Chlorophyceae, Chlamydomonadales) from North America. Algae, 2023, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gannoru, K.S.H.N.; Vinoj, C.L.; Pemaththu, H.V.N.; Thilini, U.A.; Chang, J.S. Haematococcus pluvialis: A potential feedstock for multiple-product biorefining. J Clean Prod, 2022, 344, 131103. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Tao, M.; Huang, D.Q.; Wang, C.G.; Lou, S.L.; Li, H.; Shi, Q.; Hu, Z.L. A chromosome-level genome assembly for the astaxanthin producing microalga Haematococcus pluvialis. Sci Data, 2023, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, G.; Carreon, J.R. Commercial astaxanthin production derived by green alga Haematococcus pluvialis: a microalgae process model and a techno-economic assessment all through production line. Algal Res, 2016, 18, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.M.; Liang, Y.M.; Cheng, J.J.; Daroch, M. Astaxanthin-producing green microalga Haematococcus pluvialis: from single cell to high value commercial products. Front Plant Sci, 2016, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, L.T. Cell cycles and proliferation patterns in Haematococcus pluvialis. Chin J Oceanol Limn, 2017, 35, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, D.; Zhang, J.; Sawdon, J.A.; Peng, C.A. Enhanced astaxanthin accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis using high carbon dioxide concentration and light illumination. Bioresource Technol, 2018, 256, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Alimujiang, A.; Wang, X.; Luo, S.W.; Balamurugan, S.; Yang, W.D.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.Y. Ethanol induced jasmonate pathway promotes astaxanthin hyperaccumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis. Bioresource Technol, 2019, 289, 121720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.G.; Cui, D.D.; Zhuo, P.L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, N.J. A new approach to promote astaxanthin accumulation via Na2WO4 in Haematococcus pluvialis. J Oceanol Limnol, 2019, 37, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.H.; Li, L.M.; Qin, S.; Huang, Q. Transcriptomic and metabolic analysis of an astaxanthin-hyperproducing Haematococcus pluvialis mutant obtained by low-temperature plasma (LTP) mutagenesis under high light irradiation. Algal Res, 2020, 45, 101746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Wang, J.X.; Shi, M.L.; Niu, X.F.; Yu, X.H.; Gao, L.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.W. Metabolomic and network analysis of astaxanthin-producing Haematococcus pluvialis under various stress conditions. Bioresource Technol, 2014, 170, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recht, L.; Töpfer, N.; Batushansky, A.; Sikron, N.; Gibon, Y.; Fait, A.; Zarka, A. Metabolite profiling and integrative modeling reveal metabolic constraints for carbon partitioning under nitrogen starvation in the green algae Haematococcus pluvialis. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289, 30387–30403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.X.; Xia, F.; Liu, M.; Cui, X.G.; Wahid, F.; Jia, S.R. Metabolomic profiling of the astaxanthin accumulation process induced by high light in Haematococcus pluvialis. Algal Res, 2016, 20, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.L.; Bian, C.; Tao, M.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.H.; Lv, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.G.; You, X.X.; Jia, B.; Xu, J.M.; Li, J.C.; Li, Z.; Shi, Q.; Hu, Z.L. Genome and transcriptome sequencing of the astaxanthin-producing green microalga, Haematococcus pluvialis. Genome Biol Evol, 2019, 11, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Ellis, D.I. Metabolomics: current analytical platforms and methodologies. Trac-Trend Anal Chem, 2005, 24, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, M.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.W.; Zhao, P.; Li, T.; Yu, X. Enhanced astaxanthin production from Haematococcus pluvialis using butylated hydroxyanisole. J Biotechnol, 2016, 236, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokabi, K.; Gorelova, O.; Ismagulova, T.; Itkin, M.; Malitsky, S.; Boussiba, S.; Khozin-Goldberg, I. Metabolomic foundation for differential responses of lipid metabolism to nitrogen and phosphorus deprivation in an arachidonic acid-producing green microalga. Plant Sci, 2019, 283, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollywood, K.; Brison, D.R.; Goodacre, R. Metabolomics: current technologies and future trends. Proteomics, 2006, 6, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtin, K.; Kuehnle, M.; Rehbein, J.; Schuler, P.; Nicholson, G.; Albert, K. Determination of astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters in the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis by LC-(APCI) MS and characterization of predominant carotenoid isomers by NMR spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2009, 395, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.H.; Sun, H.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.J. Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. The Analyst, 2012, 137, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussiba, S.; Fan, L.; Vonshak, A. Enhancement and determination of astaxanthin accumulation in green-alge Haematococcus pluvialis. Method Enzymol, 1992, 213, 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Yamanishi, Y. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007, 36, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Huang, B.Q.; Zhang, H. Phosphorus deficiency affects multiple macromolecular biosynthesis pathways of Thalassiosira weissflog HL. Acta Oceanol Sin, 2014, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, B.; Işık, O.; Uslu, L.; Azgın, C. The effect of stress due to nitrogen limitation on lipid content of Phaeodactylum Tricornutum (Bohlin) cultured outdoor in photobioreactor. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci, 2015, 15, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, S.M.; Cokus, J.S.; Gallaher, D.S.; Walter, A.; Lopez, D.; Erickson, E.; Endelman, B.; Westcott, D.; Larabell, A.C.; Merchant, S.S.; Pellegrini, M.; Niyogi, K.K. Chromosome-level genome assembly and transcriptome of the green alga Chromochloris zofingiensis illuminates astaxanthin production. PNAS, 2017, 114, 4296–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Sakamoto, Y. Singlet oxygen quenching ability of astaxanthin esters from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol Lett, 1999, 21, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Wang, B.B.; Han, D.X.; Sommerfeld, M.; Lu, Y.H.; Chen, F.; Hu, Q. Molecular mechanisms of the coordination between astaxanthin and fatty acid biosynthesis in Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae). Plant J, 2015, 81, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A. Osmoregulation in Dunaliella, part HL: photosynthesis and starch contribute carbon for glycerol synthesis during a salt stress in Dunaliella tertiolecta. Plant Physiol Bioch, 2007, 45, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoys, C.; Romero-Losada, B.A.; Río, D.E.; Guerrero, G.M.; Romero-Campero, J.F.; García-Gonz´alez, M. Unveiling the underlying molecular basis of astaxanthin accumulation in Haematococcus through integrative metabolomic-transcriptomic analysis. Bioresource Technol, 2021, 332, 125150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Han, B.Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, P.; Xu, J.W.; Yu, X.Y. Enhancing Haematococcus pluvialis biomass and γ-aminobutyric acid accumulation by two-step cultivation and salt supplementation. Bioresource Technol, 2019, 285, 121334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiris, K.; Muylaert, K.; Fraeye, I.; Foubert, I.; Brabanter, J.; Cooman, L. Antioxidant potential of microalgae in relation to their phenolic and carotenoid content. J Appl Phycol, 2012, 24, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Li, Q.Q.; Han, B.Y.; Zhao, Y.T.; Geng, S.X.; Ning, D.L.; Ma, T.; Yu, X.Y. Comparative physiological and metabolomic analyses of the hyperaccumulation of astaxanthin and lipids in Haematococcus pluvialis upon treatment with butylated hydroxyanisole. Bioresource Technol, 2019, 292, 122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.J.; Zhang, L.T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.G. Enhancement of astaxanthin accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis by exogenous oxaloacetate combined with nitrogen deficiency. Bioresource Technol, 2022, 345, 126484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhan, J.; He, C.; Wang, Q. Comparative metabolic profiling of the lipid-producing green microalga Chlorella reveals that nitrogen and carbon metabolic pathways contribute to lipid metabolism. Biotechnol Biofuels, 2017, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, C.; Ding, W.; Li, T.; Xu, J.W.; Zhao, P.; Yu, X. Butylated hydroxytoluene induces astaxanthin and lipid production in Haematococcus pluvialis under high-light and nitrogen-deficiency conditions. Bioresource Technol, 2018, 266, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, W.L.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Nikoloski, Z.; Sweetlove, L.J.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolic control and regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in photosynthetic and heterotrophic plant tissues. Plant Cell Environ, 2012, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, P. Environmental and cultural stimulants in the production of carotenoids from microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biot, 2004, 63, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, S.J.; Durkin, C.A.; Berthiaume, C.T.; Morales, R.L.; Armbrust, E. Transcriptional responses of three model diatoms to nitrate limitation of growth. Front Mar Sci, 2014, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockin, N.L.; Mock, T.; Mulholland, F.; Kopriva, S.; Malin, G. The response of diatom central carbon metabolism to nitrogen starvation is different from that of green algae and higher plants. Plant Physiol, 2012, 158, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.K.; Lim, P.E.; Vello, V.; Sim, K.S.; Abdul, B.M.N.; Mustafa, E.M.; Nik, S.N.M.; Liew, K.E.; Chen, B.J.T.; Phang, S.M. Metabolic and physiological regulation of Chlorella sp. (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) under nitrogen deprivation. J Oceanol Limnol, 2019, 37, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M. Astaxanthin biosynthesis enhanced by reactive oxygen species in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol Bioproc, 2003, 8, 322. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Zhao, Y.T.; Ding, W.; Han, B.Y.; Geng, S. .; Ning, D.L.; Ma, T.; Yu, X.Y. Gamma-aminobutyric acid facilitates the simultaneous production of biomass, astaxanthin and lipids in Haematococcus pluvialis under salinity and high-light stress conditions. Bioresource Technol, 2021, 320, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
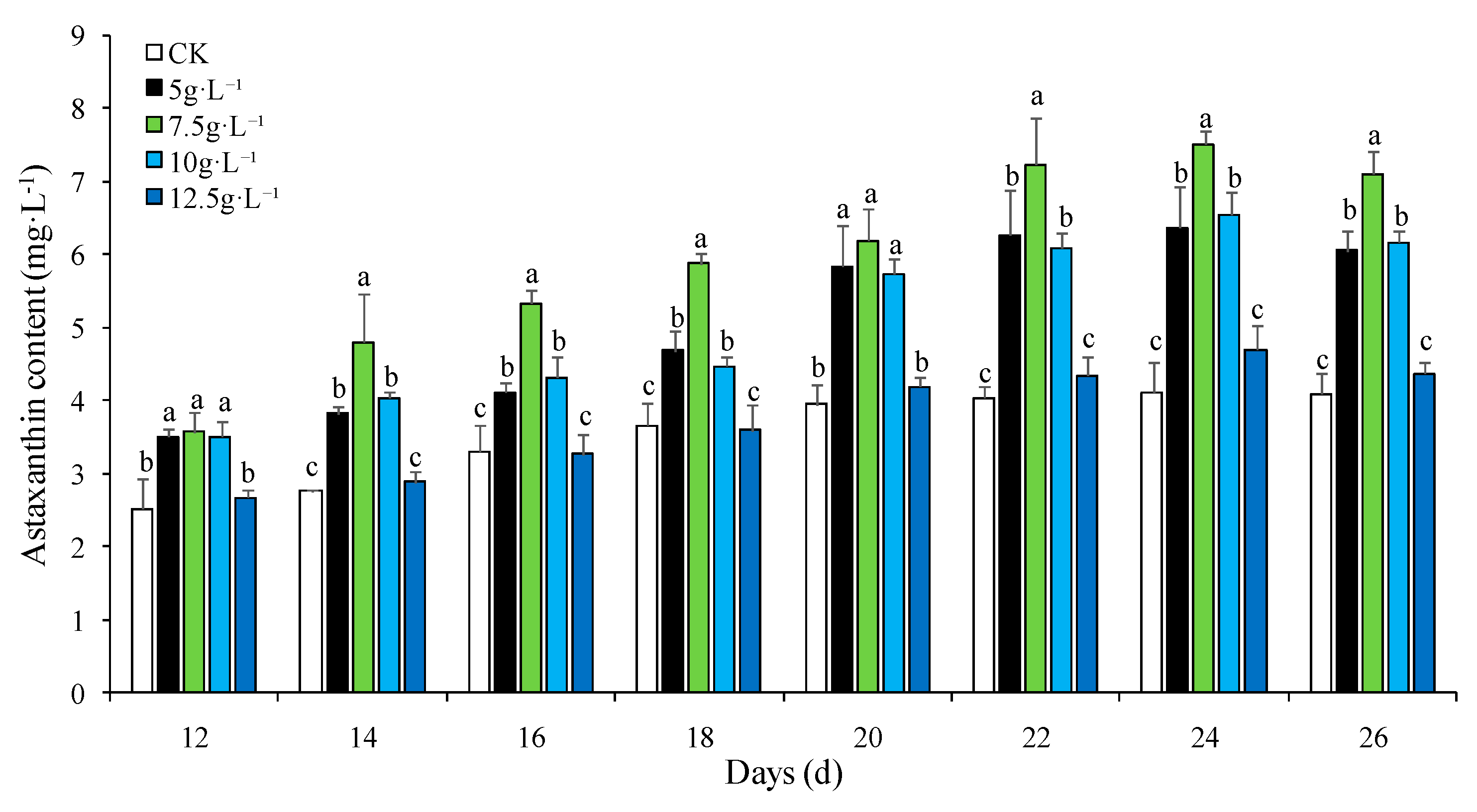
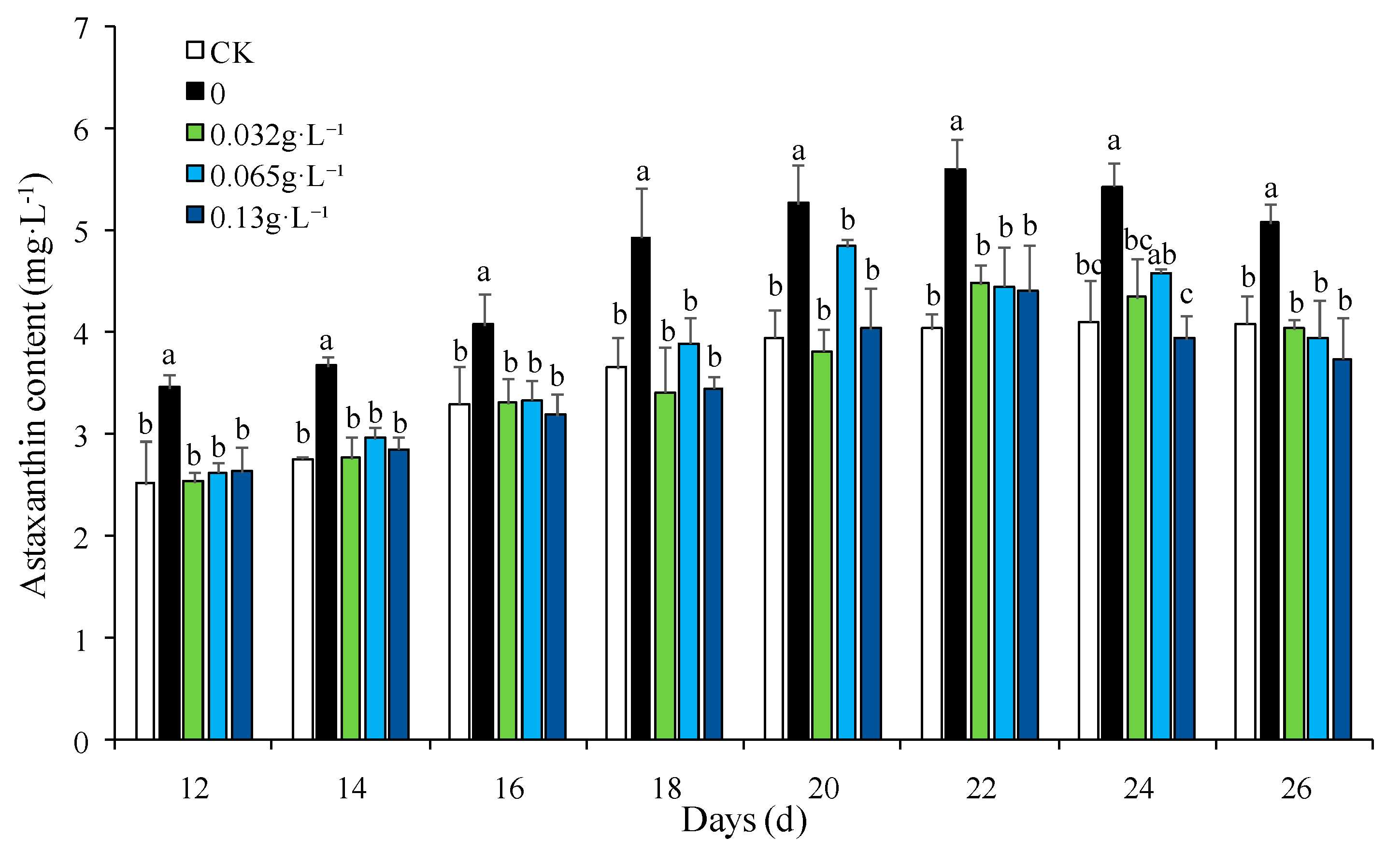
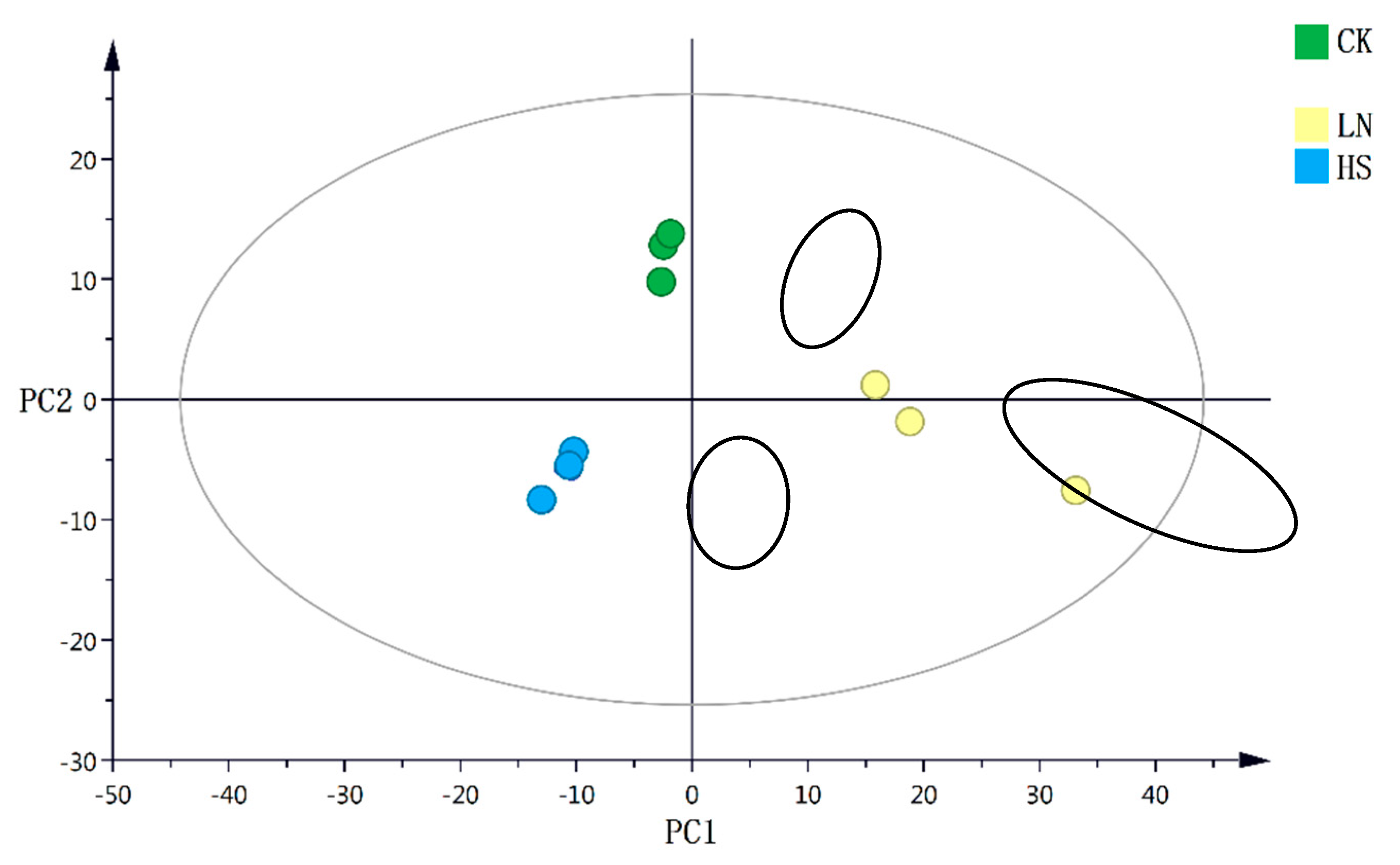
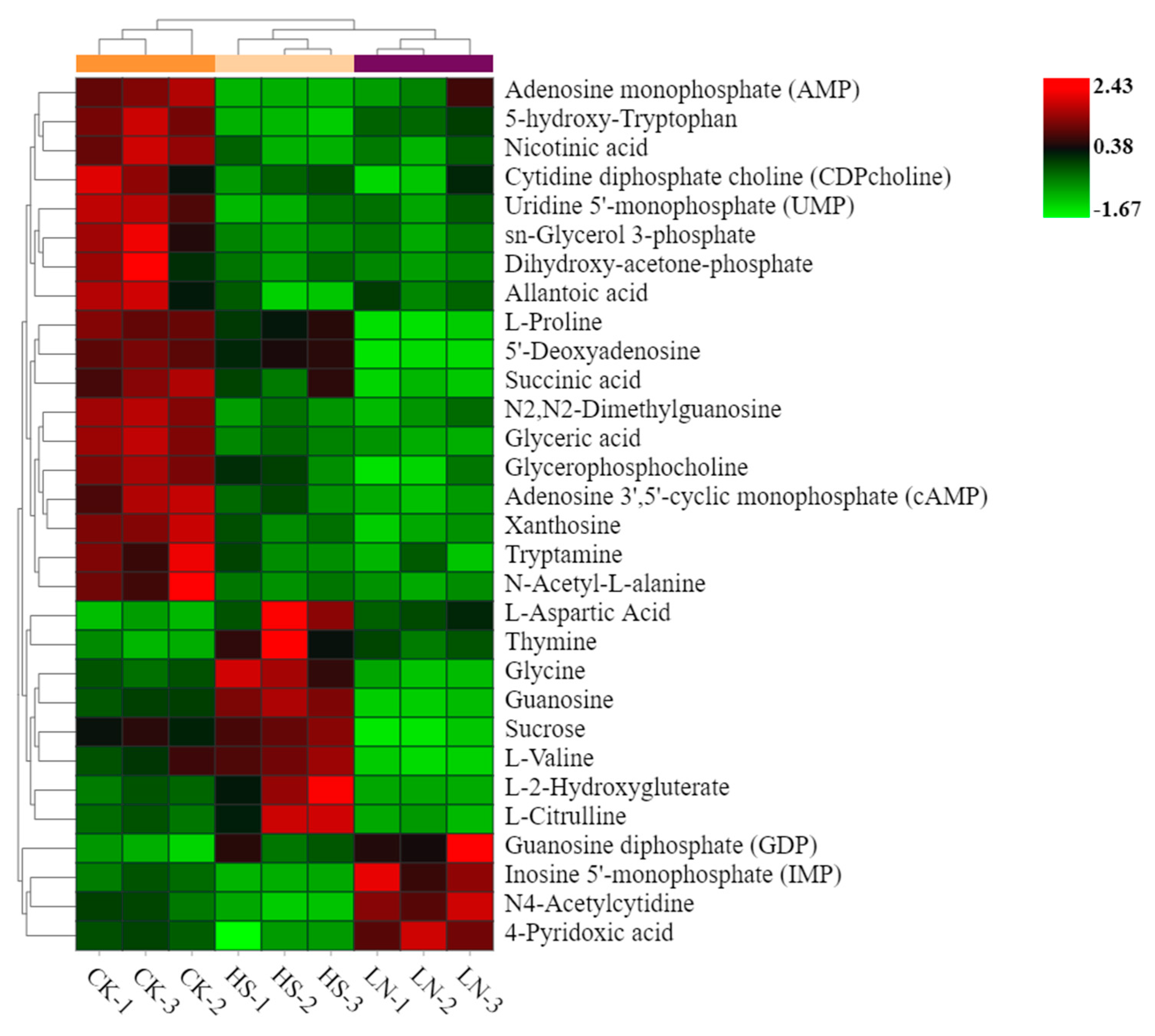

| Medium | NaCl gradient (g·L-1) | NaNO3 gradient (g·L-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BBM | 0.025 | 0.25 |
| High salinity | BBM | 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5 | 0.25 |
| Low nitrogen | nitrogen-deficient BBM | 0.025 | 0, 0.032, 0.065, 0.13 |
| Metabolite | KEGG code |
Fold change | Metabolite | KEGG code |
Fold change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS vs CK | LN vs CK | HS vs CK | LN vs CK | ||||
| N2,N2-Dimethylguanosine | NA | 0.35 | 0.33 | 6-Hydroxynicotinic acid | C01020 | 0.81 | 1.77 |
| AMP | C00020 | 0.19 | 0.47 | N6-Acetyl-L-lysine | C02727 | 0.72 | 0.42 |
| Glycerophosphocholine | C00670 | 0.73 | 0.57 | ATP | C00002 | 5.11 | 1.48 |
| Glyceric acid | C00258 | 0.35 | 0.23 | L-Lactic acid | C01432 | 0.85 | 0.47 |
| 5-hydroxy-Tryptophan | C01017 | 0.15 | 0.46 | NAD | C00003 | 1.32 | 0.36 |
| Nicotinic acid | C00253 | 0.43 | 0.48 | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine | C00140 | 0.97 | 0.49 |
| L-Aspartate | C00049 | 4.14 | 2.42 | NAAD | C00857 | 1.30 | 0.35 |
| L-Proline | C00148 | 0.85 | 0.52 | N-Acetylcadaverine | NA | 1.85 | 0.69 |
| Thymine | C00178 | 4.62 | 2.11 | dAMP | C00360 | 0.34 | 0.76 |
| L-Carnitine | C00318 | 0.39 | 0.84 | Malate | C00711 | 0.92 | 0.34 |
| UMP | C00105 | 0.31 | 0.41 | N-Carbamoyl-L-aspartic acid | C00438 | 1.99 | 0.63 |
| cAMP | C00575 | 0.40 | 0.21 | Guanosine | C00387 | 1.75 | 0.38 |
| ℽ-Glutamyl-L-methionine | NA | 3.09 | 1.17 | L-Asparagine | C00152 | 0.96 | 0.56 |
| GDP | C00035 | 1.99 | 3.12 | Cytidine | C00475 | 0.72 | 0.75 |
| Nicotinamide | C00153 | 1.80 | 1.53 | Arginine | C03406 | 0.57 | 0.25 |
| Dimethylglycine | C01026 | 0.53 | 0.97 | Sucrose | C00089 | 1.17 | 0.53 |
| 2'-O-methyladenosine | C04779 | 0.71 | 0.35 | Orotic acid | C00295 | 0.26 | 0.67 |
| ℽ -L-Glutamyl-L-phenylalanine | NA | 1.00 | 8.80 | Allantoic acid | C00499 | 0.31 | 0.50 |
| 5'-Deoxyadenosine | C05198 | 0.78 | 0.06 | L-Citrulline | C00327 | 2.35 | 0.52 |
| 5-Aminopentanoic acid | C00431 | 0.58 | 0.68 | Flavone | C15608 | 0.46 | 1.23 |
| L-Tyrosine | C00082 | 4.51 | 0.80 | 7-methylguanosine | NA | 1.13 | 0.39 |
| Pantothenic acid | C00864 | 0.88 | 0.44 | Riboflavin | C00255 | 0.72 | 1.12 |
| L-Pipecolic acid | C00408 | 2.92 | 1.44 | FAD | C00016 | 1.24 | 0.45 |
| Deoxycytidine | C00881 | 1.50 | 2.15 | cis-4-Hydroxy-D-proline | C03440 | 0.20 | 0.08 |
| N-Acetylglutamine | NA | 1.97 | 1.42 | NADP | C00006 | 4.32 | 0.54 |
| CMP | C00055 | 0.63 | 0.43 | Biopterin | C06313 | 0.36 | 1.29 |
| Tryptamine | C00398 | 0.51 | 0.42 | L-Glutamate | C00025 | 1.05 | 0.40 |
| Choline | C00114 | 0.50 | 1.03 | L-Homoserine | C00263 | 1.19 | 0.60 |
| CDPcholine | C00307 | 0.49 | 0.38 | Hypoxanthine | C00262 | 0.46 | 1.30 |
| Glycerol3P | C00093 | 0.37 | 0.38 | Pyridoxal | C00250 | 1.06 | 0.70 |
| cis-Aconitate | C00417 | 1.97 | 2.78 | 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | C00196 | 1.34 | 0.25 |
| Nicotinamide ribotide | C00455 | 3.47 | 3.62 | Cholesterol sulfate | C18043 | 1.39 | 1.56 |
| Adenine | C00147 | 0.99 | 3.87 | N-Formylmethionine | C03145 | 1.62 | 0.18 |
| N-Acetyl-L-alanine | NA | 0.38 | 0.31 | Glycyl-L-leucine | C02155 | 0.62 | 1.11 |
| Xanthosine | C01762 | 0.51 | 0.36 | L-Valine | C00183 | 1.32 | 0.46 |
| Deoxyguanosine | C00330 | 2.02 | 0.83 | 4-Guanidinobutyric acid | C01035 | 0.70 | 0.94 |
| D-Neopterin | C05926 | 2.44 | 0.37 | FMN | C00061 | 1.60 | 0.94 |
| Succinate | C00042 | 0.66 | 0.31 | Glutathione disulfide | C00127 | 1.85 | 0.66 |
| O-Succinyl-L-homoserine | C01118 | 0.58 | 0.09 | Urocanic acid | C00785 | 0.59 | 0.59 |
| Uric acid | C00366 | 1.18 | 1.41 | L-Methionine | C00073 | 1.39 | 0.23 |
| N6-methyladenosine | NA | 0.75 | 0.24 | 2-keto-D-Gluconic acid | C06473 | 1.33 | 0.29 |
| D-glucosamine 1-phosphate | C06156 | 0.48 | 0.32 | L-Homocysteic acid | C16511 | 1.18 | 0.64 |
| Isobutyryl-CoA | C00630 | 7.57 | 0.92 | dTMP | C00364 | 0.56 | 1.20 |
| DHAP | C00111 | 0.31 | 0.26 | Inosine | C00294 | 1.01 | 0.25 |
| Thiamine | C00378 | 14.25 | 101.38 | L-Serine | C00065 | 1.23 | 0.40 |
| GABA | C00334 | 1.84 | 1.16 | IMP | C00130 | 0.30 | 2.96 |
| GDP-L-fucose | C00325 | 0.50 | 0.28 | L-2-Aminoadipic acid | C00956 | 1.13 | 0.78 |
| Phenyllactic acid | C05607 | 3.24 | 0.62 | dGMP | C00362 | 0.42 | 2.51 |
| D-Glucose-6-phosphate | C00092 | 0.77 | 0.42 | S-Adenosylhomocysteine | C00021 | 1.09 | 0.11 |
| Glycine | C00037 | 2.16 | 0.41 | N4-Acetylcytidine | NA | 0.51 | 1.81 |
| Creatine | C00300 | 1.26 | 1.12 | UDP-D-Glucuronate | C00167 | 2.13 | 0.27 |
| 1-Methylxanthine | C16358 | 0.61 | 0.16 | UDP -Glucose | C00029 | 1.70 | 0.90 |
| Deoxyinosine | C05512 | 1.64 | 0.73 | L-Kynurenine | C00328 | 0.97 | 0.37 |
| Dephospho-CoA | C00882 | 22.19 | 1.84 | N-Acetyl-L-phenylalanine | C03519 | 1.44 | 0.35 |
| β-Hydroxybutyric acid | C01089 | 1.65 | 0.46 | L-Leucine | C00123 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| TPP | C00068 | 4.57 | 1.54 | L-Phenylalanine | C00079 | 0.95 | 0.65 |
| ℽ -L-Glutamyl-L-valine | NA | 0.82 | 2.99 | taurine | C00245 | 1.13 | 0.24 |
| Adenosine | C00212 | 1.13 | 0.33 | Acetyl-DL-Leucine | NA | 1.23 | 0.37 |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate | C00074 | 0.77 | 0.35 | dCMP | C00239 | 0.44 | 1.32 |
| L-2-Hydroxygluterate | C03196 | 3.10 | 0.27 | Pyridoxine | C00314 | 0.86 | 1.14 |
| Kynurenic acid | C01717 | 0.51 | 0.07 | L-Tryptophan | C00078 | 0.96 | 0.45 |
| L-Glutamine | C00064 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 4-Pyridoxic acid | C00847 | 0.52 | 1.71 |
| Pseudouridine | C02067 | 0.51 | 1.11 | Inositol | C00137 | 1.33 | 0.37 |
| L-Lysine | C00047 | 0.67 | 0.97 | Uridine | C00299 | 0.94 | 0.88 |
| Cytosine | C00380 | 0.57 | 0.79 | Ureidopropionic acid | C02642 | 0.76 | 0.15 |
| 5-Aminolevulinic acid | C00430 | 6.15 | 0.60 | Fumarate | C00122 | 0.96 | 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




