1. Introduction
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), characterized by the progressive degeneration of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), retina, and choriocapillaris, is the leading cause of blindness in older individuals worldwide [
1,
2]. AMD is classified as early, intermediate, or advanced. Extracellular deposits, such as drusen and subretinal drusenoid deposits, and focal hypopigmentation/hyperpigmentation are typical characteristics of early and intermediate AMD. Advanced/late AMD with choroidal neovascularization (CNV) or geographic atrophy is characterized as neovascular AMD (nAMD). As the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key pathogenic factor in the development of nAMD [
3], intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF agents is currently the only established treatment for nAMD. However, anti-VEGF treatment has several limitations [
4].
The exact pathogenic mechanism of AMD remains unclear; however, a genome-wide association study revealed that immunological disturbances, including complement abnormalities, are partially responsible for the development and progression of AMD [
5]. Chemokines are chemotactic agents classified into four main subgroups: CXC, CC, C, and CX3C [
6]. Chemokines have various biological functions; some perform proinflammatory activities, whereas others regulate cellular homeostasis and cell migration; accordingly, they have potential roles in the development or progression of neuroinflammatory diseases [
7]. In particular, CXC chemokines play multiple roles, including chemotaxis of immune cells as well as regulation of angiogenesis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition [
8]. However, the pathogenic roles of chemokines in AMD remain unexplored. Fujimura et al. recently showed that intravitreal injection of a CXCR3 antibody into a laser-induced CNV mouse model enhanced angiogenesis [
9]. CXCR3 binds to ligands such as CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 [
8]. Increased levels of aqueous CXCL10 have been reported in patients with AMD [
10,
11]. However, the role of CXCR3 in nAMD has not been clarified.
Tyrosine residues in the N-terminal of chemokine receptors are post-translationally sulfated. These sulfated tyrosine residues modulate the binding to chemokine ligands that induce intracellular signaling pathways. Studies have also shown that the sulfated peptides of chemokine receptors increase the binding affinity of peptides to their cognate ligands [
12,
13]. In this study, we aimed to construct a sulfated-CXCR3 trap and demonstrate its in vivo effect in preventing CNV and chemotaxis.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
An automated 96-well parallel-array oligonucleotide synthesizer was used to prepare oligo primers (
Table S1). Wild-type mouse CXCR3 (mCXCR3-WT) and mCXCR3-2S nucleotides as well as wild-type human CXCR3 (hCXCR3-WT) and hCXCR3-2S nucleotides were synthesized through oligo shuffling [
14]. The EcoRV, BamHI, and XhoI restriction sites were introduced in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products, as shown within parentheses in the sequences listed in
Table S1. The synthesized double-stranded oligonucleotide was inserted into the EcoRV-, BamHI-, and XhoI-digested pET-41a vector (Novagen, Madison, WI, USA), containing an N-terminal GST, a polyhistidine (6×His) tag, and a C-terminal polyhistidine for purification.
2.2. Protein Purification
The mCXCR3-WT pET-41a, mouse sulfated CXCR3 peptide trap (mCXCR3-S2) pET-41a, hCXCR3-WT pET-41a, human sulfated CXCR3 peptide trap (hCXCR3-S2) pET-41a, and pSUPAR6-L3-3SY constructs were separately transformed into
Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) [
15]. The mCXCR3-WT and hCXCR3-WT transformants were induced with 0.1 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG, final concentration) at 37°C for 5 h. The mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 transformants were inoculated in 250 mL of Luria–Bertani medium containing 10 mM sulfotyrosine (Bachem, Bubendorf, Switzerland) and cultured until OD
600 = 1. For the overexpression of the fusion proteins, 1 mM IPTG was added and cultures were incubated for 20 h at 25°C. After centrifugation of the cultures at 10,000×
g for 10 min at 4°C, the bacterial pellets were resuspended in 10 mL of binding buffer (5 mM imidazole, 0.5 M NaCl, and 20 mM Tris-HCl; pH 7.9) and sonicated. The supernatant was loaded onto a pre-equilibrated Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with distilled water and binding buffer and allowed to flow by gravity. The column was washed thrice with 10 volumes of binding and elution (100 mM imidazole, 0.5 M NaCl, and 20 mM Tris-HCl; pH 7.9) buffer to eliminate any residual imidazole before dialysis (20 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, and 0.5 mM β-mer; pH 7.5) for 1 h. The dialyzed fusion proteins were resolved using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE). The gels were stained with Coomassie Blue R-250 and destained with 30% methanol and 10% acetic acid in distilled water.
2.3. Wound Healing Assay
SKOV3 human ovarian and MDM-MB-231 human breast cancer cell lines were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea) and seeded in 24-well plates (SKOV3, 2 × 10⁵ cells/well; MDM-MB-231, 3 × 10⁵ cells/well). When the cells reached 100% confluence, cell monolayers were scratched with a 200-μL sterile pipette tip to create a vertical wound. To avoid any influence on the cell growth rate, the cell culture medium was changed from RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum to serum-free RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The cells were incubated with or without 100 ng/mL CXCL10 (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and 10 μg/mL hCXCR3 WT or hCXCR3-S2. Phase-contrast images were captured after scratching and after 24 h of incubation at 37°C using a DP70 microscope (Olympus, Shinjuku, Japan) (
Figure S1).
2.4. Invasion Assay
The invasion assay was conducted using an 8-μm-pore 24-well Transwell plate (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) coated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and containing 25 μg Matrigel (Sigma Aldrich) and 0.1% gelatin (Sigma Aldrich). The cells were grown to 80% confluence in a growth medium, synchronized by starvation in serum-free RPMI-1640 medium for 24 h, and then seeded (2 × 10⁵ cells/mL) in the top chamber [
16]. The bottom chamber contained serum-free medium with or without 200 ng/mL CXCL10 and with or without 10 μg/mL hCXCR3 WT or hCXCR3-S2. The cells were fixed in 100% methanol for 10 min and stained with 0.1% crystal violet (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 10 min. The cells remaining on top of the filter were removed using a cotton swab, whereas those that had migrated to the underside of the filter were micrographed using a DP70 microscope (Olympus). Three fields per sample were captured at 10× magnification (
Figure S2).
2.5. Experimental Animals
Eight-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories Japan (Yokohama, Japan). All mice were housed in microisolator cages under specific pathogen-free conditions and maintained under a 12-:12-h dark/light cycle in a humidity- and temperature-controlled facility with ad libitum access to food and water.
2.6. Laser-Induced CNV Mouse Models
C57BL/6J mice were anesthetized with a mixture of Zoletil (Virbac, Carros Cedex, France)/xylazine (Bayer Healthcare, Leverkusen, Germany) (4:1) and topical 0.5% proparacaine (Alcaine; Alcon, Geneva, Switzerland). Tropherine eye drops (0.5% tropicamide and 0.5% phenylephrine hydrochloric acid; Hanmi Pharm, Seoul, South Korea) were dropped into the eyes for local anesthesia and pupil dilation. A slit-lamp delivery system (SL-1800; NIDEK, Tokyo, Japan) with a green laser photocoagulator (GYC-500; NIDEK) (532-nm laser, 50-μm spot size, 0.1-s duration, 200 mW) was used to generate three laser spots in each eye using 12-mm-diameter microscope cover glasses (Paul Marienfeld GmbH, Lauda-Königshofen, Germany) as contact lenses while protecting the optic nerve with a lubricant (hypromellose; SAMIL, Seoul, South Korea). Gaseous bubbles confirmed the disruption of Bruch’s membrane, and only laser spots produced by bubbling were included in the study. Intravitreal injection of mCXCR3-GST, mCXCR3-WT (5.2 µg/µL), mCXCR3-S2 (4.8 µg/µL), or aflibercept (EYLEA, 2 µg/µL; Bayer Healthcare) was performed immediately after the laser treatment.
2.7. Quantitation of CNV in the Mouse Model of Laser-Induced CNV
FITC-dextran (Sigma Aldrich) was intravenously injected into mice for fluorescent labeling. After 3 min, the mice were euthanized with CO2 gas, and their eyes were extracted. The anterior segments of the eyeball and neural retina were immediately detached from the RPE/choroid tissue. The RPE/choroid tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min and washed thrice with PBS. The RPE/choroid tissues were cut using four relaxing radial incisions, and then flat-mounted on an Aqua Poly/Mount (Polysciences, Inc., Warrington, PA, USA). Z-section images were captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope (FluoView 1000; Olympus). The Z-section images were reconstructed and quantified using image analysis software (Metamorph; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
The RPE/choroid tissues were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at 25℃ and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 min. After blocking with 1% bovine serum albumin in PBS for 1 h, the fixed tissues were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies against F4/80 (1:200; eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA). The stained tissues were washed with PBS for 5 min and incubated for 2 h at room 25°C with Alexa Fluor 555-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:1000; Thermo Fisher Scientific) secondary antibody.
After incubation with the secondary antibody, the tissues were stained with the nuclear dye 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (1:3000; Thermo Fisher Scientific) in PBS for 10 min at room temperature. The tissues were then mounted using a mounting medium (Agilent Dako, Danvers, MA, USA). The stained tissues were observed under a super-resolution confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM 800; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) and the stained cells were observed under an inverted microscope (#DMi1; Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All experimental data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical significance (p-value) was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test followed by Fisher’s least significant difference post-hoc test or Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Purification of mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2
To produce mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 proteins, we PCR-amplified the
mCXCR3-S2 and
hCXCR3-S2 using oligo shuffling. To overexpress and purify the mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 proteins, we constructed mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 expression vectors containing the GST domain and respective cDNA sequences. In addition, we constructed mCXCR3-WT and hCXCR3-WT expression vectors containing the GST protein domain and respective wilt-type cDNA sequences (
Figure S1a). We used the pSUPAR6-L3-3SY plasmid to express both mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 (
Figure S1b). Each recombinant protein contained a six-histidine residue tag.
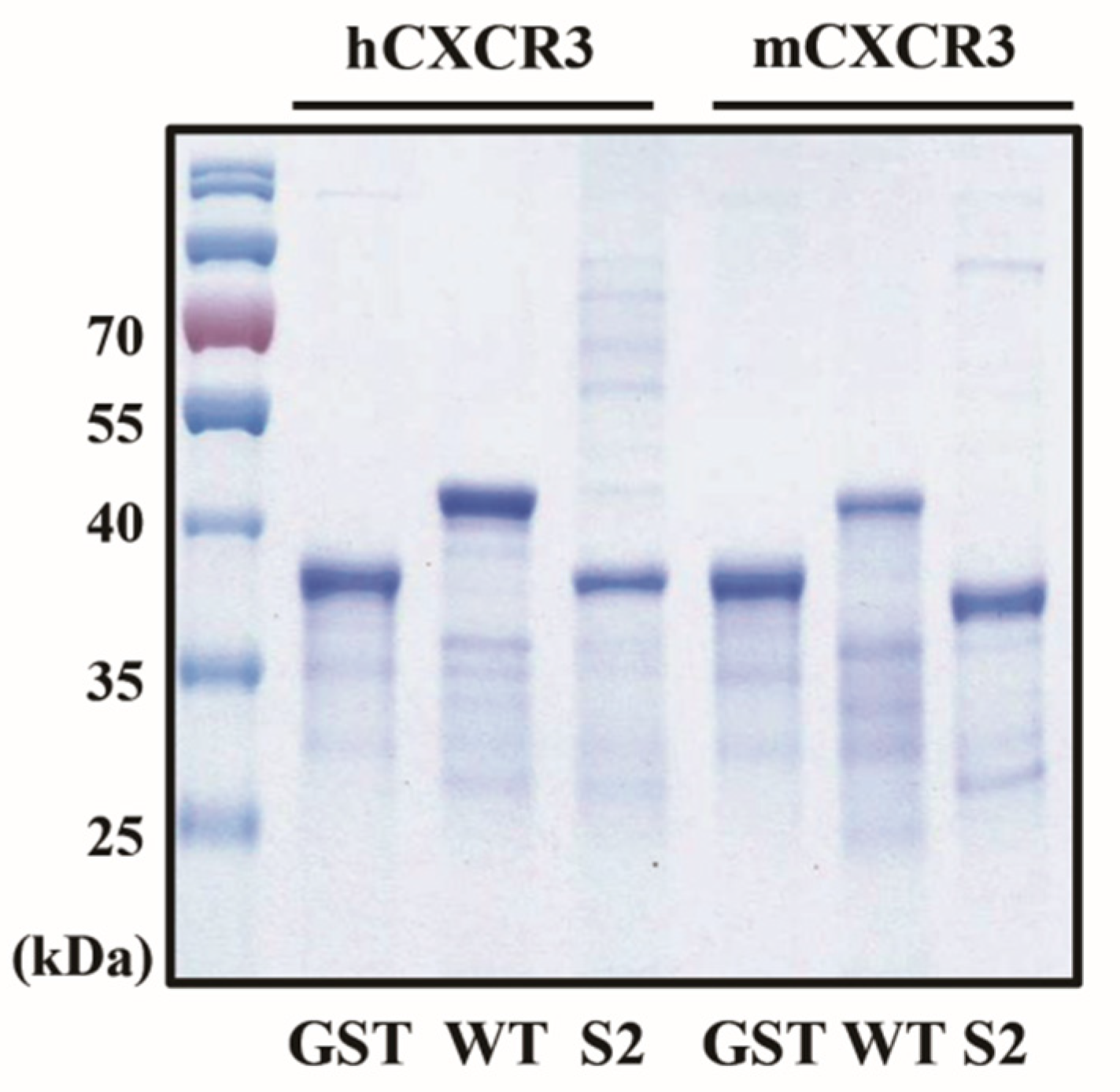
After overexpressing the fusion proteins in
E. coli BL21 (DE3), we purified the mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 proteins from the cell lysates using affinity chromatography and a metal-chelating matrix under urea-denaturing conditions. Both mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 were observed as single bands on SDS-PAGE. Notably, mCXCR3-S2 and hCXCR3-S2 could be distinguished from mCXCR3-WT and hCXCR3-WT by their reduced migration caused by the additional presence of sulfur moieties (
Figure 1) [
15].
3.2. hCXCR3 Sulfation Attenuated CXCL10-Induced Cell Migration and Invasion
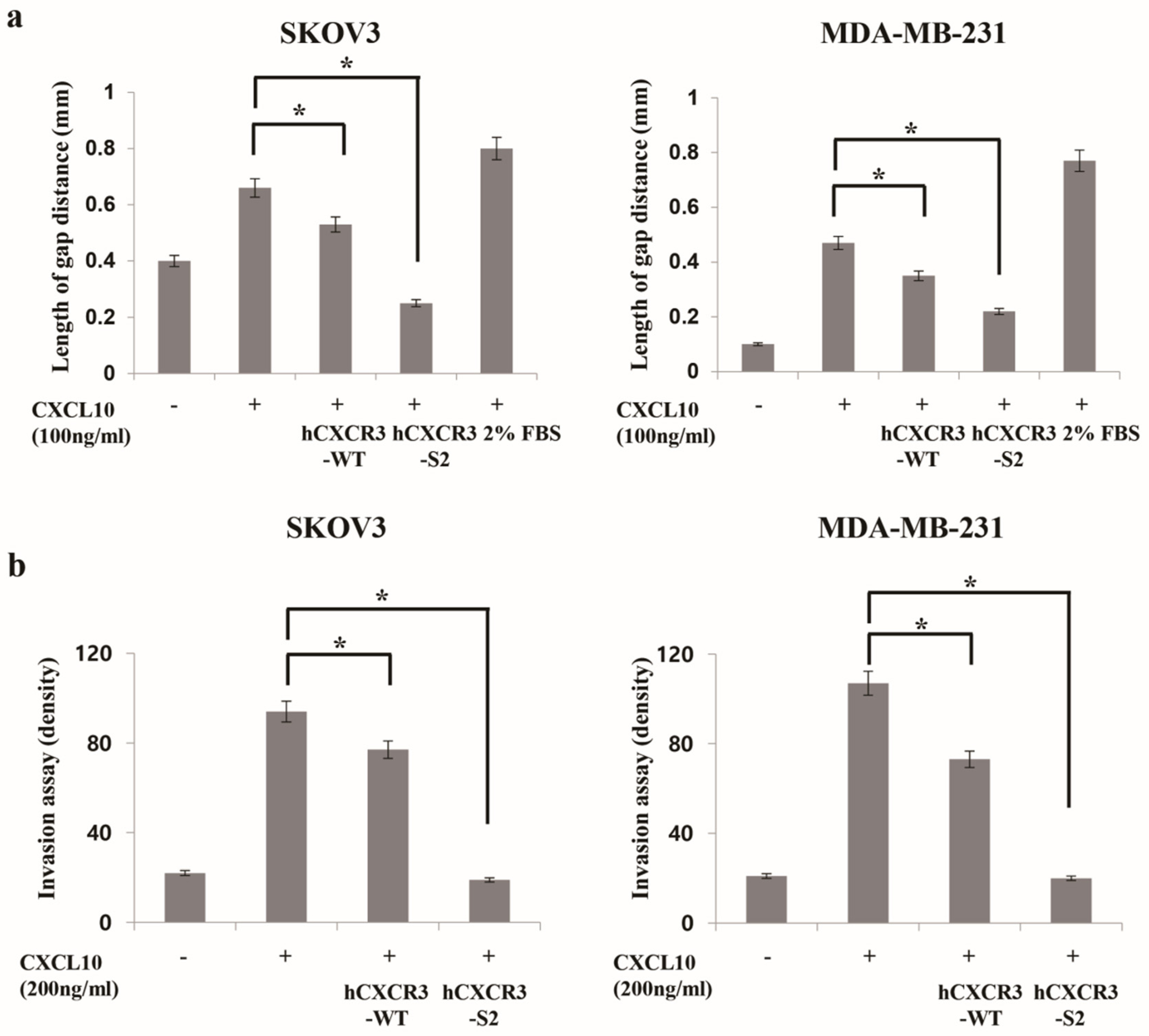
CXCR3 is highly expressed in metastatic cancer cells, and its binding with chemokine ligands, such as CXCL10, enhances the migration and invasive motility of cells [20,21,22]. To test the inhibitory effect of recombinant CXCR3-S2 and WT peptides on the interaction between CXCR3 and chemokines, we determined whether hCXCR3-S2 affected the CXCL10-induced migration and invasion of highly metastatic SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells using a scratch wound healing assay (
Figure 2a). After creating a scratch wound in the cell monolayer, the cells were treated with CXCL10, CXCL10, and hCXCR3-WT, or hCXCR3-S2. CXCL10 stimulation increased cell migration to the wound area after 24 h. However, treatment with hCXCR3-S2 inhibited the CXCL10-induced migration, suggesting that hCXCR3 sulfation suppressed the CXCL10-induced migration of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells.
We also performed Transwell invasion assays to evaluate the effect of hCXCR3 sulfation on the invasive abilities of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells (
Figure 2b). We observed that medium containing CXCL10, or CXCL10 and hCXCR2-WT, or hCXCR2-S2, in the bottom of the Transwell chamber efficiently induced the invasion of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells from the upper chamber. However, when hCXCR3-S2-containing medium was present in the bottom chamber, the CXCL10-induced invasion of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells was inhibited, indicating that hCXCR3 sulfation suppressed the CXCL10-induced motility of cells.
3.3. mCXCR3-S2 Prevented CNV and Macrophage Infiltration in the Laser-Induced CNV Mouse Model
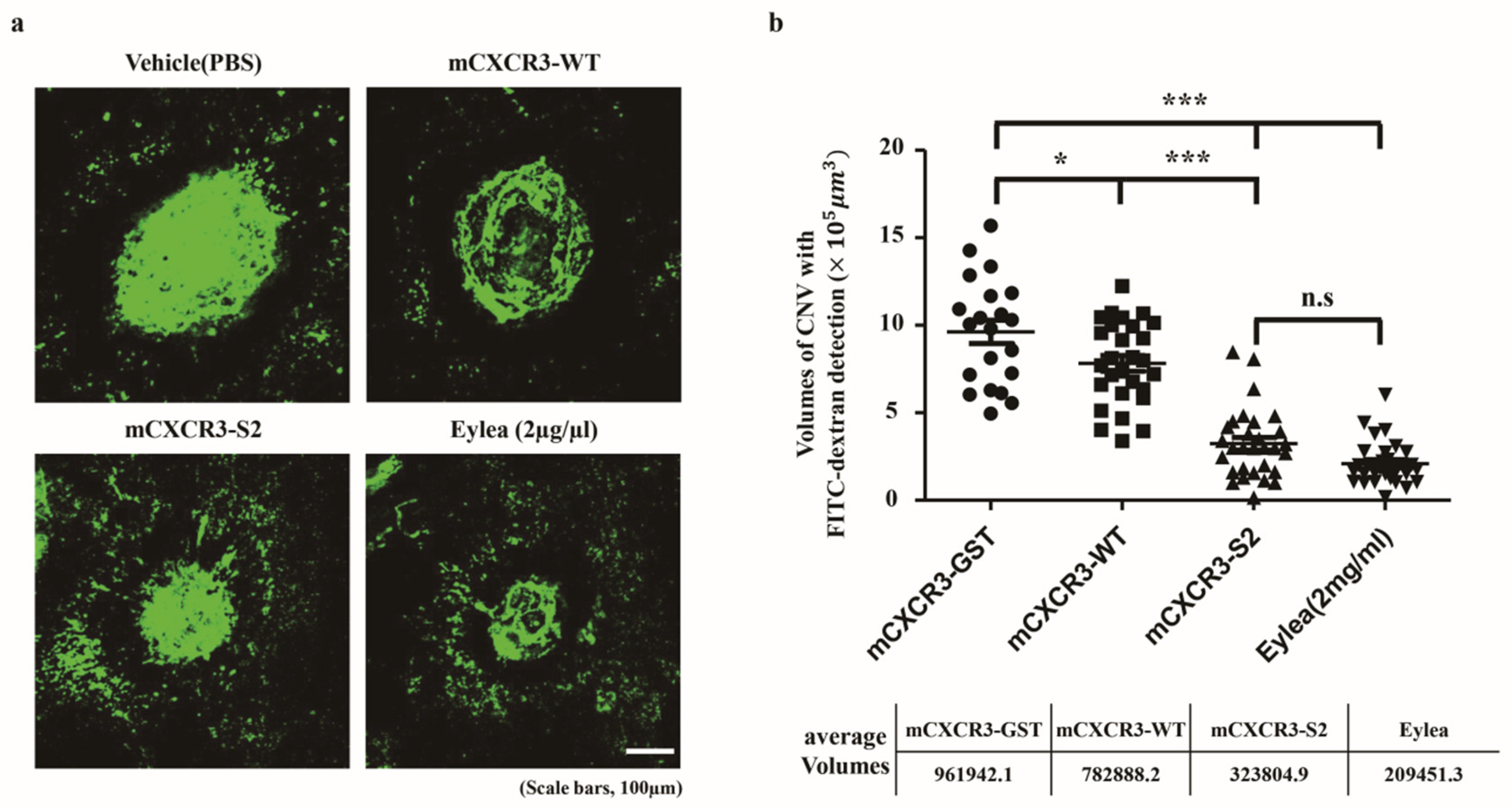
We intravitreally injected mCXCR3-GST, mCXCR3-WT, mCXCR3-S2, and EYLEA into laser-induced CNV mice. Seven days after the laser application and intravitreal treatment, 3D analyses of FITC-dextran-labeled flat-mounted RPE/choroid tissues demonstrated a marked decrease in CNV volume in the mCXCR3-S2-treated group compared with that in the mCXCR3-GST- and mCXCR3-WT-treated groups (
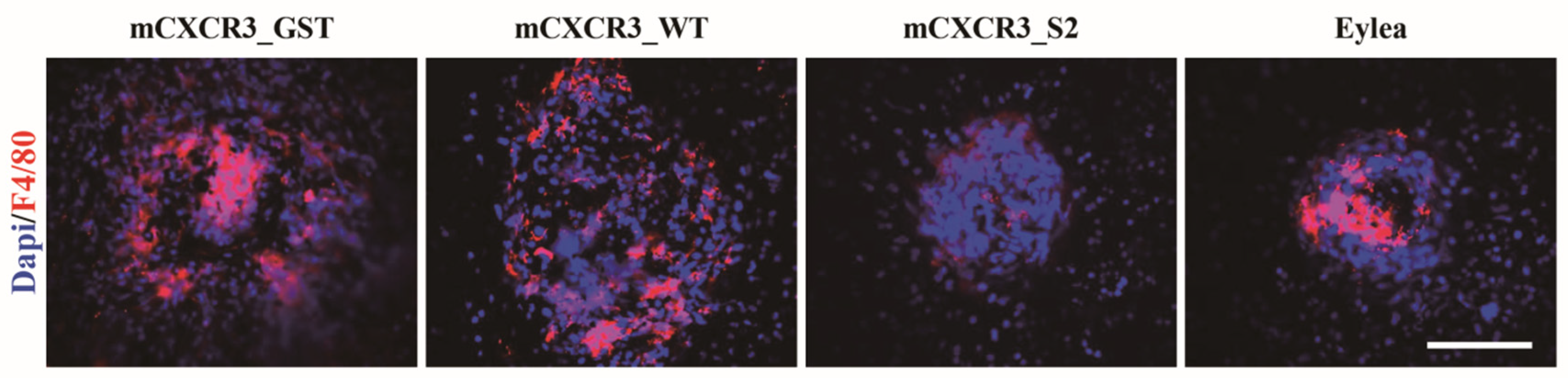
Figure 3). We further examined the infiltration of macrophages into the area of laser injury. Immunofluorescence staining for F4/80 showed that the number of F4/80-labeled cells was markedly reduced in the fibrovascular CNV lesions in the eyes treated with mCXCR3-S2 compared with that in the eyes treated with mCXCR3-GST or mCXCR3-WT (
Figure 4). This finding suggest that inhibition of macrophage infiltration at the injury site might be associated with the reduction in fibrovascular formation in the mCXCR3-S2-treated eyes.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we developed recombinant CXCR3-S2 peptide traps and found that compared with that in wild-type CXCR3 and GST control, intravitreal injection of these fusion proteins reduced CNV volume in a laser-induced CNV mouse model. The role of CXCR3 in nAMD remains largely unclear. Based on the findings of upregulated mRNA expression of CXCR3 and IP-10 in laser-induced mouse models and exacerbation of CNV with intravitreal injection of anti-CXCR3/anti-IP-10 neutralizing antibodies, Fujimura et al. suggested that CXCR3 plays an angiostatic role in CNV [
9]. In the present study, we clearly demonstrated the efficacy of locally administered recombinant CXCR3-S2 peptide traps in a laser-induced CNV model, thus validating the role of chemokine–chemokine receptor signaling in disease development. Interestingly, attenuation of both CNV and macrophage recruitment in vivo was significantly greater with the recombinant CXCR3-S2 peptide traps than with the wild-type CXCR3 proteins. These results were consistent with those of previous studies, which reported that sulfation of chemokine receptors plays a critical role in their signaling [17,18,19].
Several studies have shown that macrophage recruitment contributes to the development of CNV in AMD [1,23,24]. In our study, diminished recruitment of F4/80
+ cells was observed in sulfated CXCR3 antibody-injected mice. Whether macrophages play a protective or aggravating role in CNV remains unclear; however, macrophages trigger VEGF secretion in the angiogenic environment of the choroid [25,26]. We speculated that a sulfated CXCR3 antibody could capture CXCL10 before the latter could induce the chemotaxis of M1 macrophages [27] and therefore, could exert a protective effect against CNV. It should be noted that the incorporation of sulfotyrosine, an unnatural amino acid, has some drawbacks, such as low yield, low permeability, and leaky suppression [
15]. Further studies are warranted to overcome these limitations.
5. Conclusions
Intravitreal injection of recombinant CXCR3-S2 peptide traps attenuated CNV and macrophage recruitment in a mouse CNV model. Our results indicate that targeting CXCL10–CXCR3 signaling may be useful for treating patients with nAMD. Additional investigations of the use of recombinant CXCR3-S2 peptide traps as a novel treatment for patients with AMD as well as for those with CXCR3-related cancers are warranted.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Diagram of the control, CXCR3-WT, and CXCR3-S2 fusion proteins; Figure S2: hCXCR3-S2 inhibits the CXCL10-induced migration of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells; Figure S3: hCXCR3-S2 inhibits the CXCL10-induced invasion of SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells; Figure S4: Quantification of F4/80 fluorescence intensity. (** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). Scale bar = 100 µm; Table S1: CXCR3 primers used in oligo shuffling. In total, 10 oligos (39 nt in length) were synthesized.
Funding
This research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, grant number 2022R1F1A1060081.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Konkuk University IACUC (protocol code KU18080 and date of approval) and were conducted in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or supplementary materialThe data presented in this study are available in [insert article or supplementary material here].
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Peter G. Schultz (Department of Chemistry and Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology, CA, USA) for providing the pSUPAR6-L3-3SY plasmid.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ambati, J.; Anand, A.; Fernandez, S.; Sakurai, E.; Lynn, B.C.; Kuziel, W.A.; Rollins, B.J.; Ambati, B.K. An animal model of age-related macular degeneration in senescent Ccl-2- or Ccr-2-deficient mice. Nat Med 2003, 11, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, J.; Atkinson, J.; Gelfand, G. Immunology of age-related macular degeneration. Nat Rev Immunol 2013, 13, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Liew, G.; Mitchell, P. Clinical update: New treatments for age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2007, 9583, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.S.; Schwartz, S.D.; Hubschman, J.P. Age-related macular degeneration: Current and novel therapies. Maturitas 2010, 1, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, L.G.; Igl, I.; Bailey, J.N.; Grassmann, F.; Sengupta, S.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Burdon, K.P.; Hebbring, S.J.; Wen, C.; Gorski, M.; Kim, I.K.; Cho, D.; Zack, D.; Souied, E.; Scholl, H.P.; Bala, E.; Lee, K.E.; Hunter, D.J.; Sardell, R.J.; Mitchell, P.; Merriam, J.E.; Cipriani, V.; Hoffman, J.D.; Schick, T.; Lechanteur, Y.T.; Guymer, R.H.; Johnson, M.P.; Jiang, Y.; Stanton, C.M.; Buitendijk, G.H.; Zhan, X.; Kwong, A.M.; Boleda, A.; Brooks, M.; Gieser, L.; Ratnapriya, R.; Branham, K.E.; Foerster, J.R.; Heckenlively, J.R.; Othman, M.I.; Vote, B.J.; Liang, H.H.; Souzeau, E.; McAllister, I.L.; Isaacs, T.; Hall, J.; Lake, S.; Mackey, D.A.; Constable, I.J.; Craig, J.E.; Kitchner, T.E.; Yang, Z.; Su, Z.; Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Ouyang, H.; Flagg, K.; Lin, D.; Mao, G.; Ferreyra, H.; Stark, K.; von Strachwitz, C.N.; Wolf, A.; Brandl, C.; Rudolph, G.; Olden, M.; Morrison, M.A.; Morgan, D.J.; Schu, M.; Ahn, J.; Silvestri, G.; Tsironi, E.E.; Park, K.H.; Farrer, L.A.; Orlin, A.; Brucker, A.; Li, M.; Curcio, C.A.; Mohand-Saïd, S.; Sahel, J.A.; Audo, I.; Benchaboune, M.; Cree, A.J.; Rennie, C.A.; Goverdhan, S.V.; Grunin, M.; Hagbi-Levi, S.; Campochiaro, P.; Katsanis, N.; Holz, F.G.; Blond, F.; Blanché, H.; Deleuze, J.F.; Igo, R.P.; Truitt, B.; Peachey, N.S.; Meuer, S.M.; Myers, C.E.; Moore, E.L.; Klein, R.; Hauser, M.A.; Postel, E.A.; Courtenay, M.D.; Schwartz, S.G.; Kovach, J.L.; Scott, W.K.; Liew, G.; Tan, A.G.; Gopinath, B.; Merriam, J.C.; Smith, R.T.; Khan, J.C.; Shahid, H.; Moore, A.T.; McGrath, J.A.; Laux, R.; Brantley, M.A.; Agarwal, A.; Ersoy, L.; Caramoy, A.; Langmann, T.; Saksens, N.T.; de Jong, E.K.; Hoyng, C.B.; Cain, M.S.; Richardson, A.J.; Martin, T.M.; Blangero, J.; Weeks, D.E.; Dhillon, B.; van Duijn, C.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Romm, J.; Klaver, C.C.; Hayward, C.; Gorin, M.B.; Klein, M.L.; Baird, P.N.; den Hollander, A.I.; Fauser, S.; Yates, J.R.; Allikmets, R.; Wang, J.J.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Klein, B.E.; Hagstrom, S.A.; Chowers, I.; Lotery, A.J.; Léveillard, T.; Zhang, K.; Brilliant, M.H.; Hewitt, A.W.; Swaroop, A.; Chew, E.Y.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; DeAngelis, M.; Stambolian, D.; Haines, J.L.; Iyengar, S.K.; Weber, B.H.; Abecasis, G.R.; Heid, I.M. A large genome-wide association study of age-related macular degeneration highlights contributions of rare and common variants. Nat Genet 2016, 2, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O. Chemokines: A new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 2000, 2, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webers, A.; Heneka, M.T.; Gleeson, P.A. The role of innate immune responses and neuroinflammation in amyloid accumulation and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol Cell Biol 2020, 1, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandercappellen, J.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer Lett 2008, 2, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, S.; Takahashi, H.; Yuda, K.; Ueta, T.; Iriyama, A.; Inoue, T.; Kaburaki, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Yanagi, Y. Angiostatic effect of CXCR3 expressed on choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2021, 4, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.M.; Proia, A.D.; Johnson, W.H.; Cyr, D.; Lashkari, K. Interferon gamma-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) and eotaxin as biomarkers in age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010, 8, 4226–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoneyama, S.; Mabuchi, F.; Gotoh, T.; Tateno, Y.; Sugiyama, A.; Kubota, T.; Iijima, H. Aqueous humor cytokine levels in patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Res 2015, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldkamp, C.T.; Seibert, C.; Peterson, F.C.; De la Cruz, N.B.; Haugner, J.C.; Basnet, H.; Sakmar, T.P.; Volkman, B.F. Structural basis of CXCR4 sulfotyrosine recognition by the chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12. Sci Signal 2008, 37, ra4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Z.; Millard, C.J.; Ludeman, J.P.; Simpson, L.S.; Clayton, D.J.; Payne, R.J.; Widlanski, T.S.; Stone, M.J. Tyrosine sulfation influences the chemokine binding selectivity of peptides derived from chemokine receptor CCR3. Biochemistry 2011, 9, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemmer, W.P.; Crameri, A.; Ha, K.D.; Brennan, T.M.; Heyneker, H.L. Single-step assembly of a gene and entire plasmid from large numbers of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Gene 1995, 164, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Cellitti, S.E.; Geierstanger, B.H.; Schultz, P.G. Efficient expression of tyrosine-sulfated proteins in E. coli using an expanded genetic code. Nat Protoc 2009, 12, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Ahn, S.S.; Lim, Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Shin, S.Y. Inhibitory effect of Alisma canaliculatum ethanolic extract on NF-Κb-dependent CXCR3 and CXCL10 expression in TNFα-exposed MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 9, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, R.A.; Campanella, G.S.; Manice, L.A.; Luster, A.D. CXCR3 requires tyrosine sulfation for ligand binding and a second extracellular loop arginine residue for ligand-induced chemotaxis. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 15, 5838–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludeman, J.P.; Stone, M.J. The structural role of receptor tyrosine sulfation in chemokine recognition. Br J Pharmacol 2014, 5, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, C.J.; Ludeman, J.P.; Canals, M.; Bridgford, J.L.; Hinds, M.G.; Clayton, D.J.; Christopoulos, A.; Payne, R.J.; Stone, M.J. Structural basis of receptor sulfotyrosine recognition by a CC chemokine: The N-terminal region of CCR3 bound to CCL11/eotaxin-1. Structure 2014, 11, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Han. X.; Yan, J.; Pan, Y.; Gong, J.; Di, J.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y. The prognostic significance of chemokine receptor CXCR3 expression in colorectal carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother 2012, 5, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmüller, C.; Zech, D.; Avril, S.; Boxberg, M.; Dawidek, T.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Schmitt, M.; Kiechle, M.; Bronger, H. CXCR3 mediates ascites-directed tumor cell migration and predicts poor outcome in ovarian cancer patients. Oncogenesis 2017, 5, e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Yuan, L. The role of CXCR3 and its ligands in cancer. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 1022688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Heidmann, D.G.; Suner, I.J.; Hernandez, E.P.; Monroy, D.; Csaky, K.G.; Cousins, S.W. Macrophage depletion diminishes lesion size and severity in experimental choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003, 8, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Tang, M.; Yuan, M.; Hu, A.; Zhan, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Lu, L. Macrophage polarization in experimental and clinical choroidal neovascularization. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 30933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Takagi, H.; Takagi, C.; Suzuma, K.; Otani, A.; Ishida, K.; Matsumura, M.; Ogura, Y.; Honda, Y. The potential angiogenic role of macrophages in the formation of choroidal neovascular membranes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999, 9, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Campos, M.; Abu-Asab, M.; Ortolan, D.; Hotaling, N.; Bharti, K.; Wong, W.T. Choroid-resident macrophages maintain local vasculature and RPE integrity and spontaneously regenerate following depletion. BioRxiv 2019, 9, e55564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Qu, Q.; Zheng, B.; Xiong, S.; Fan, G.H. The chemotaxis of M1 and M2 macrophages is regulated by different chemokines. J Leukoc Biol 2015, 1, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).