Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
26 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. A Family of Polynomial Dynamical Systems
2.1. Matrix Representation of Polynomial Dynamical Systems
2.2. Discriminant Criterion and Matrix Representation of 3D Polynomial Dynamical Systems
2.3. Symmetry Relations on the Sets of Coefficient Matrices and D-Vectors

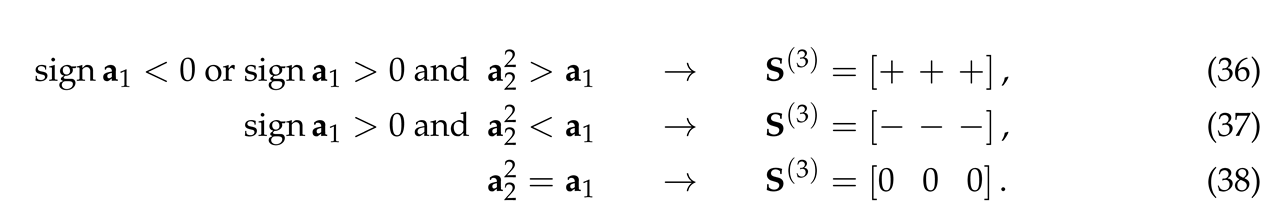
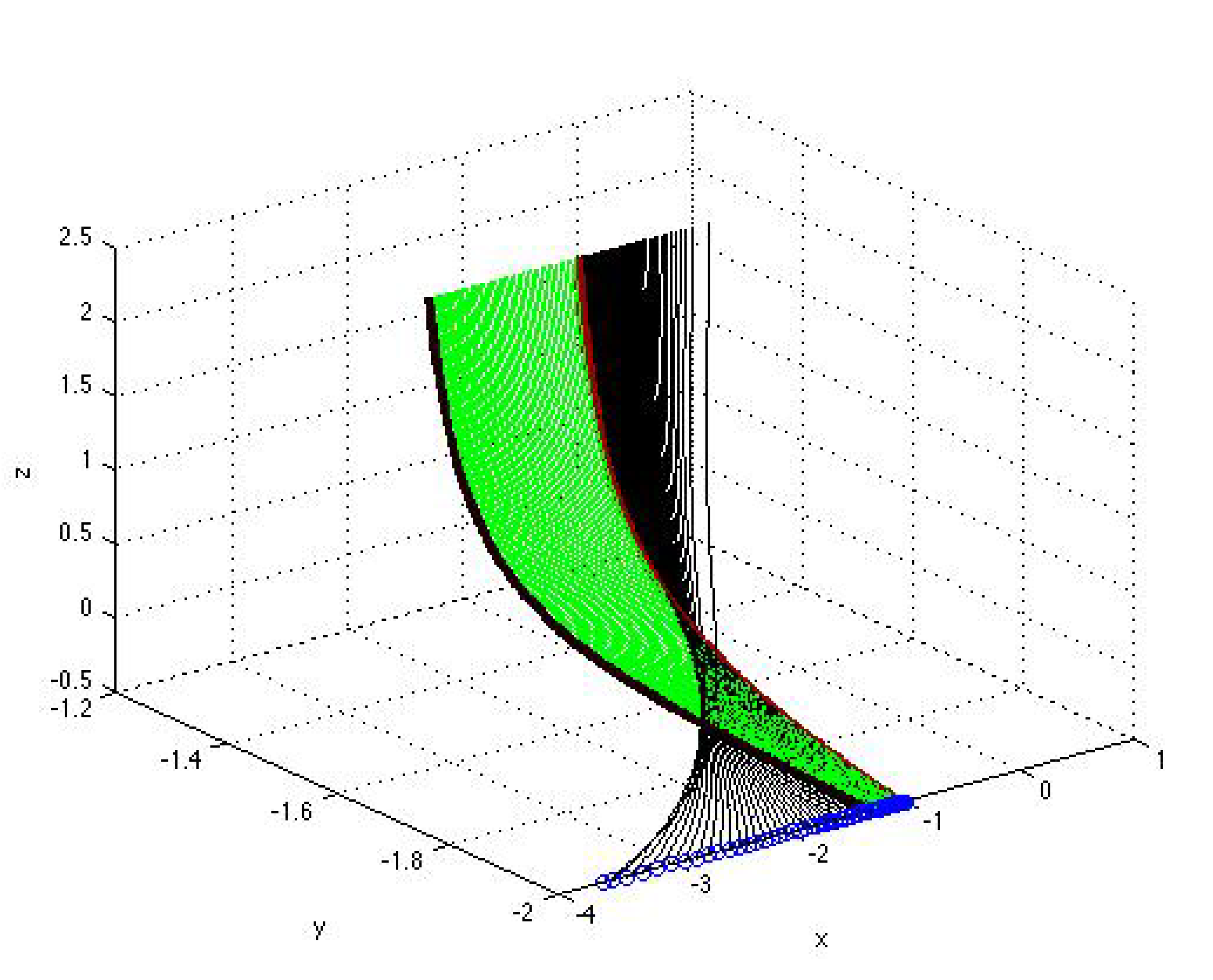
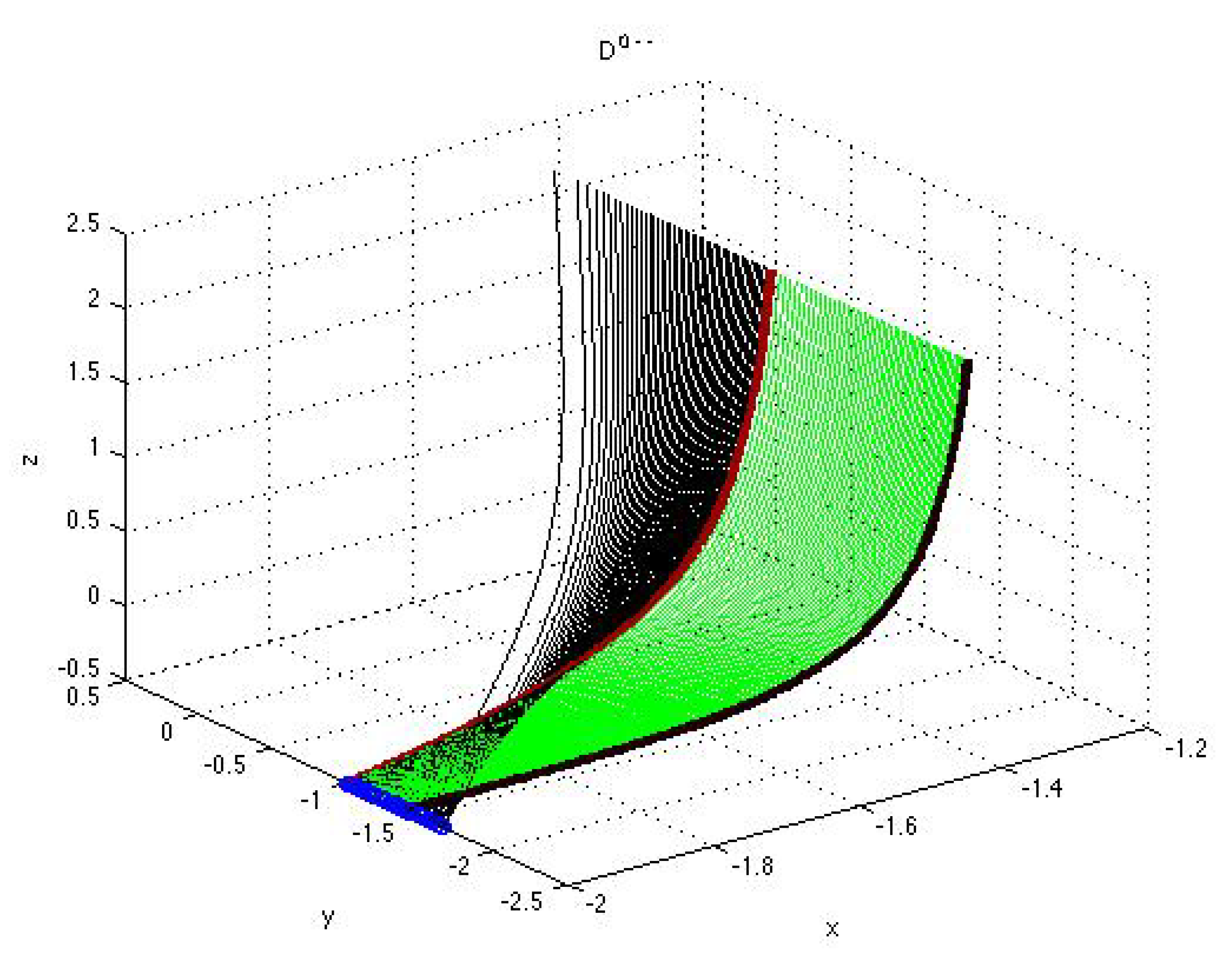
3. Classification of Solutions to Autonomous Polynomial Equations
3.1. Representations of Autonomous and Integrable Polynomial Dynamical Systems
3.2. General Solutions to Autonomous Second-Order Polynomial Equations
-
(a); is a first-order linear equation with constant coefficients and its solutions are differentiable monotone functions on the whole line.In what follows we will consider the equations with
-
(b)D> 0; there are three families of the general solutionof the equation :Family U, : solutions are unstable, since they(i) have a “movable” singularity with ,(ii) are monotonically increasing functions on the whole line for since for C> 0,(iii) satisfy the condition and(iv) have two horizontal asymptotes ; these solutions are not bounded on the whole line (the latter means instability).Family S, : solutions are stable since they have no singularities, are monotonically decreasing and bounded functions on the whole line, satisfying the condition , and have two asymptotes (the last condition written in the form of limits (A1) means stability).Family T, : and are stationary solutions of the equation satisfying the initial conditions and the first corresponds to in .Stationary solutions and are ’nonisolated’, so that in every neighborhood of each of these solutions there are infinitely many ’non-singular’ solutions or from families U or S:and an arbitrarily small change of the parameter in the initial condition or translates the stationary solution or to one of the stable or unstable solutions from the families S or U.
- (c), : all solutionsare unstable since they have a “moving” singularity at are monotonically increasing or decreasing (depending on the sign of a) functions for are not bounded on the whole line (the latter means instability) and have the asymptote . Stationary solutions are special in the sense that in any neighborhood there are infinitely many ’non-singular’ solutions .
- (d), : all solutionsare unstable since they have “movable” singularities for are monotonically increasing or decreasing (depending on the sign of parameter a) functions for because, for example,for , , and and are not bounded on the whole line (the latter means instability).
3.3. Equivalence Classes of D-Vectors and General Solutions to Autonomous Polynomial Equation Systems
3.4. Description of All Possible solution Combinations in Terms of Discriminants

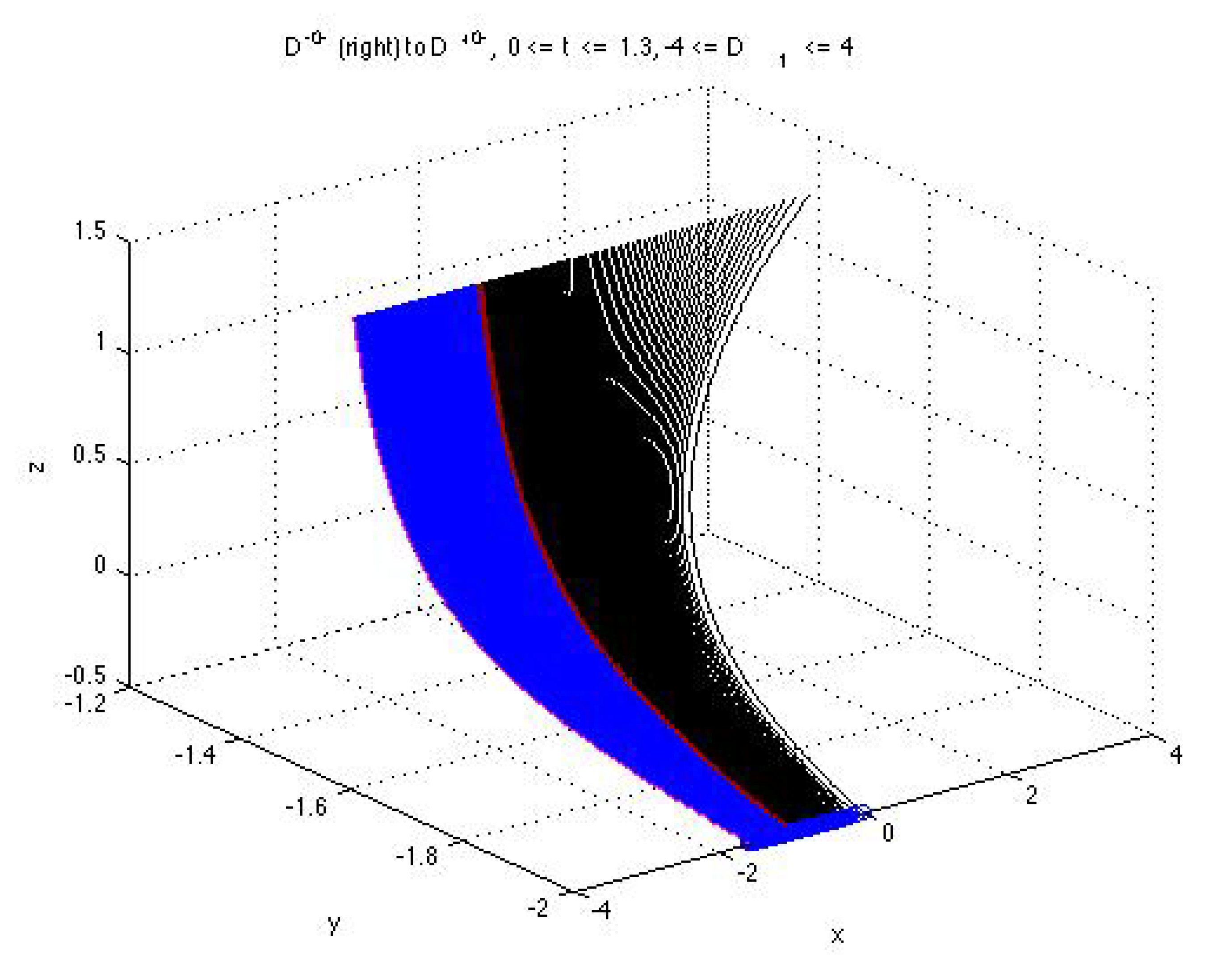
3.5. Analysis of Solutions to Cauchy Problems
4. Analysis of Bifurcations
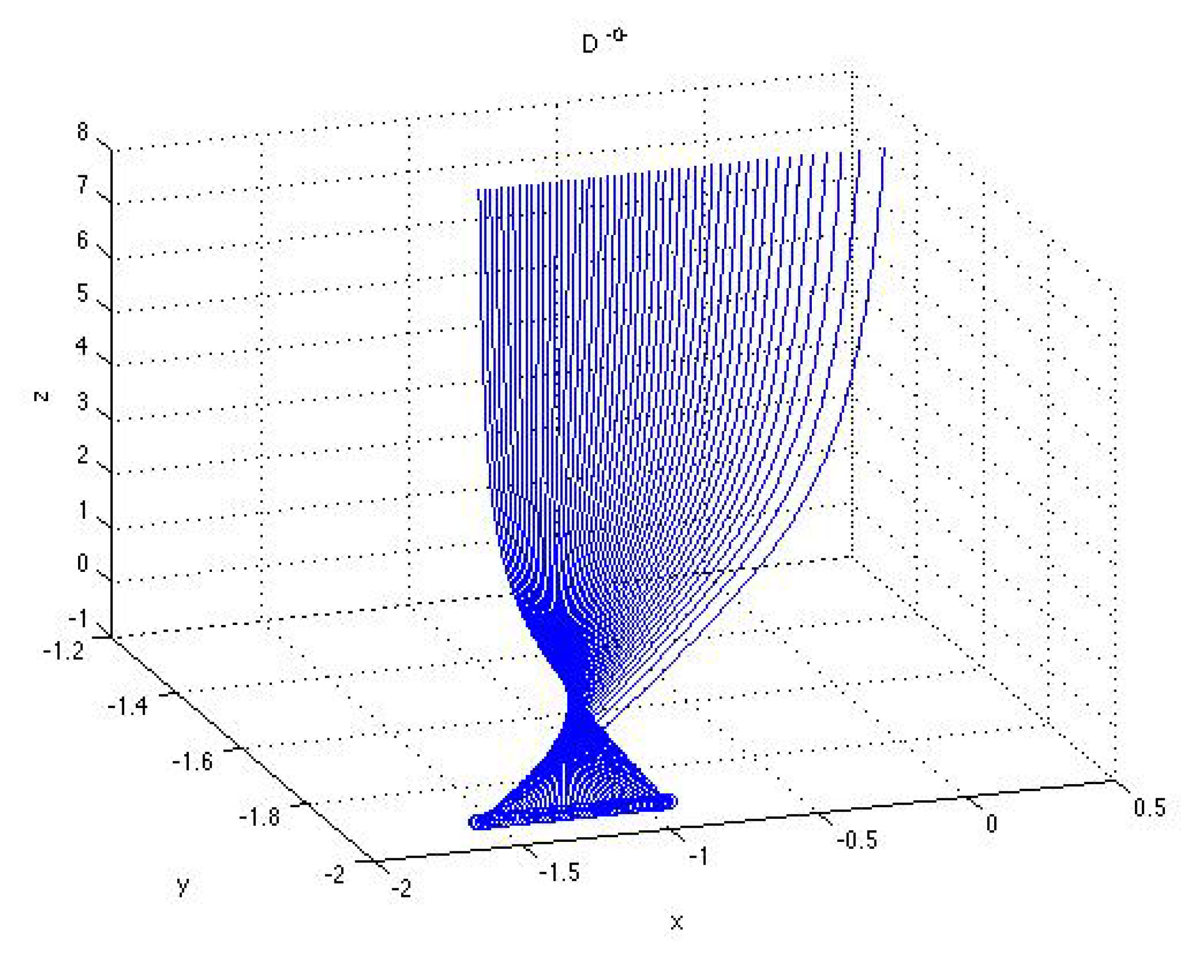
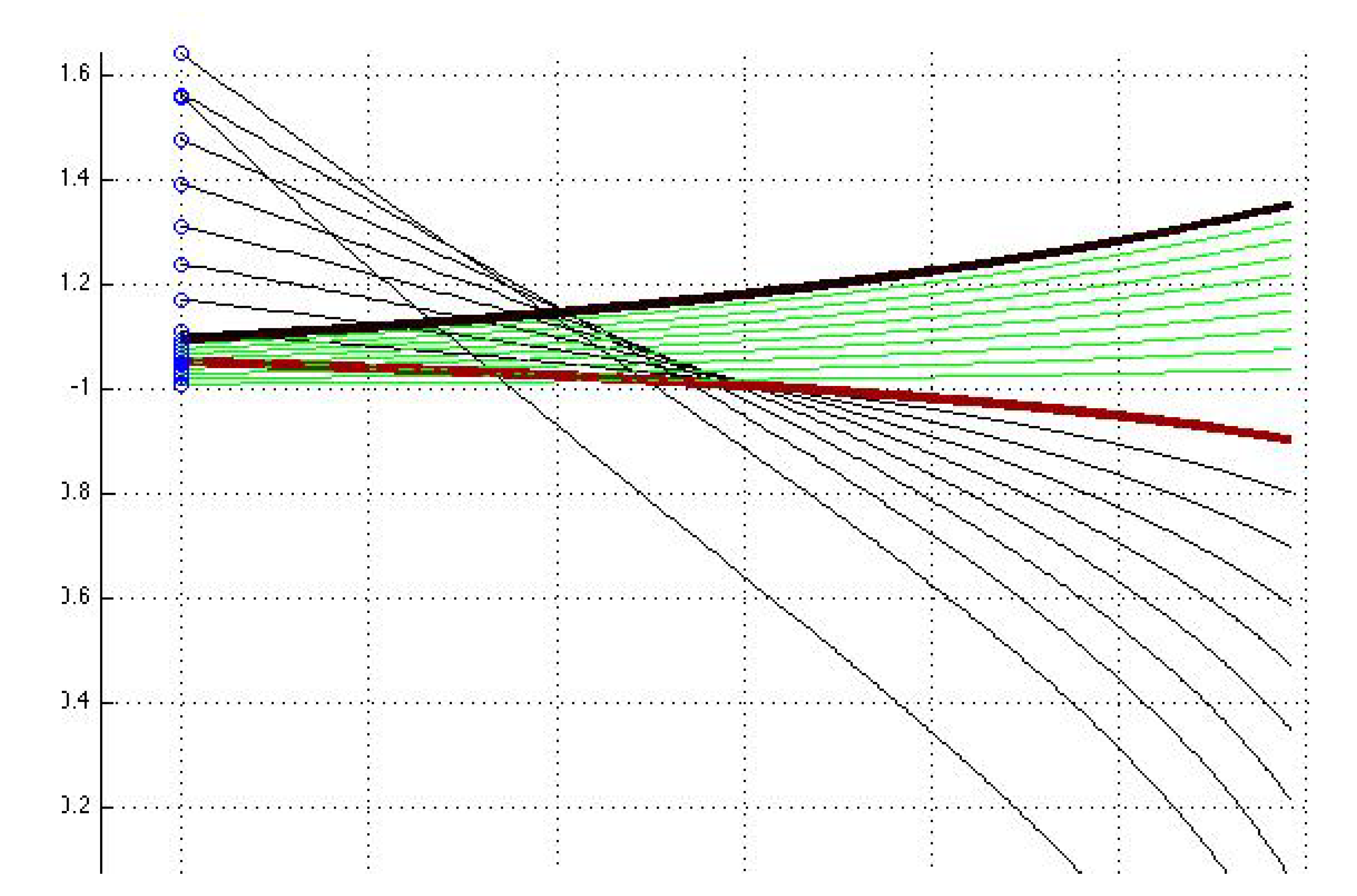
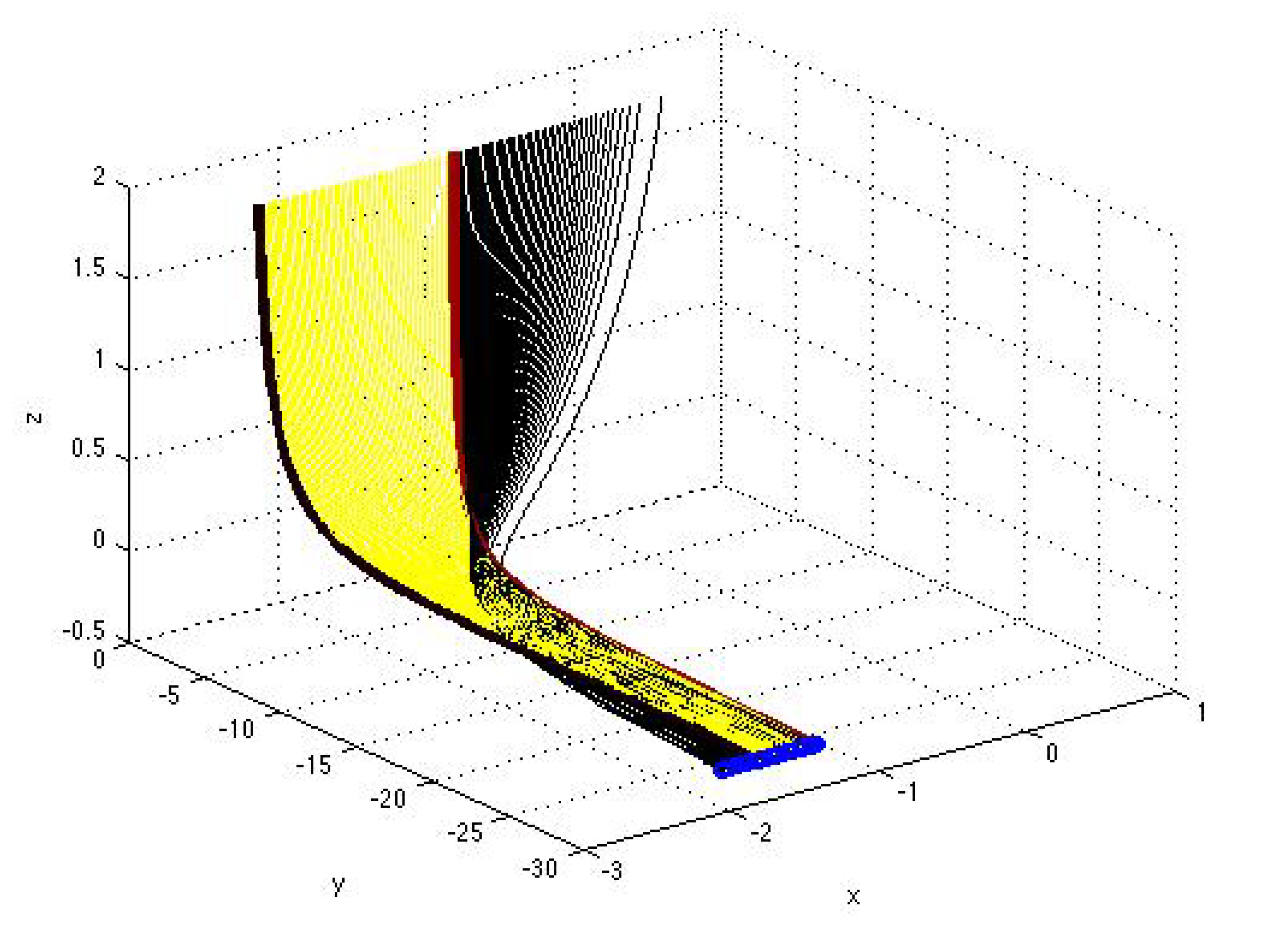
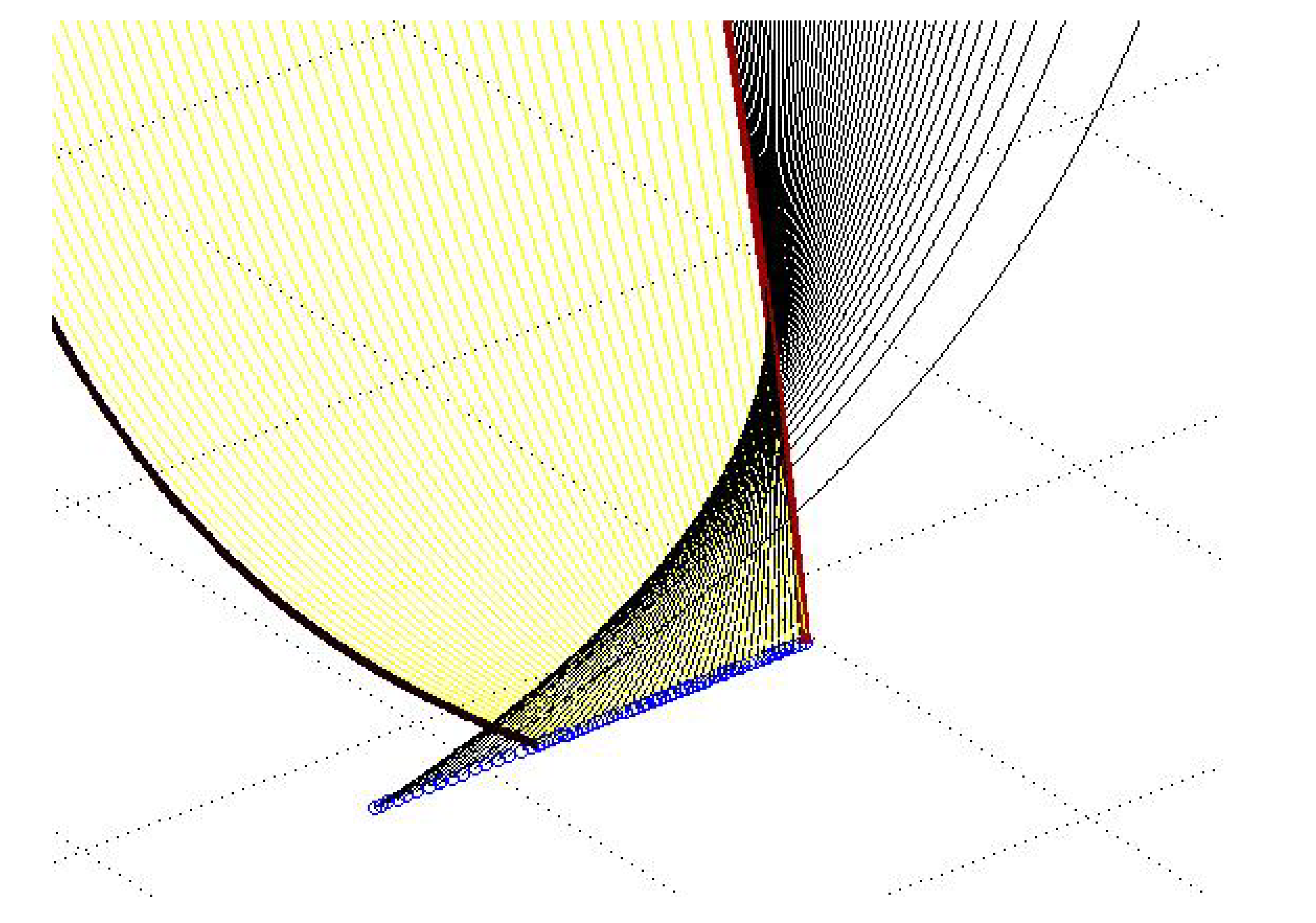
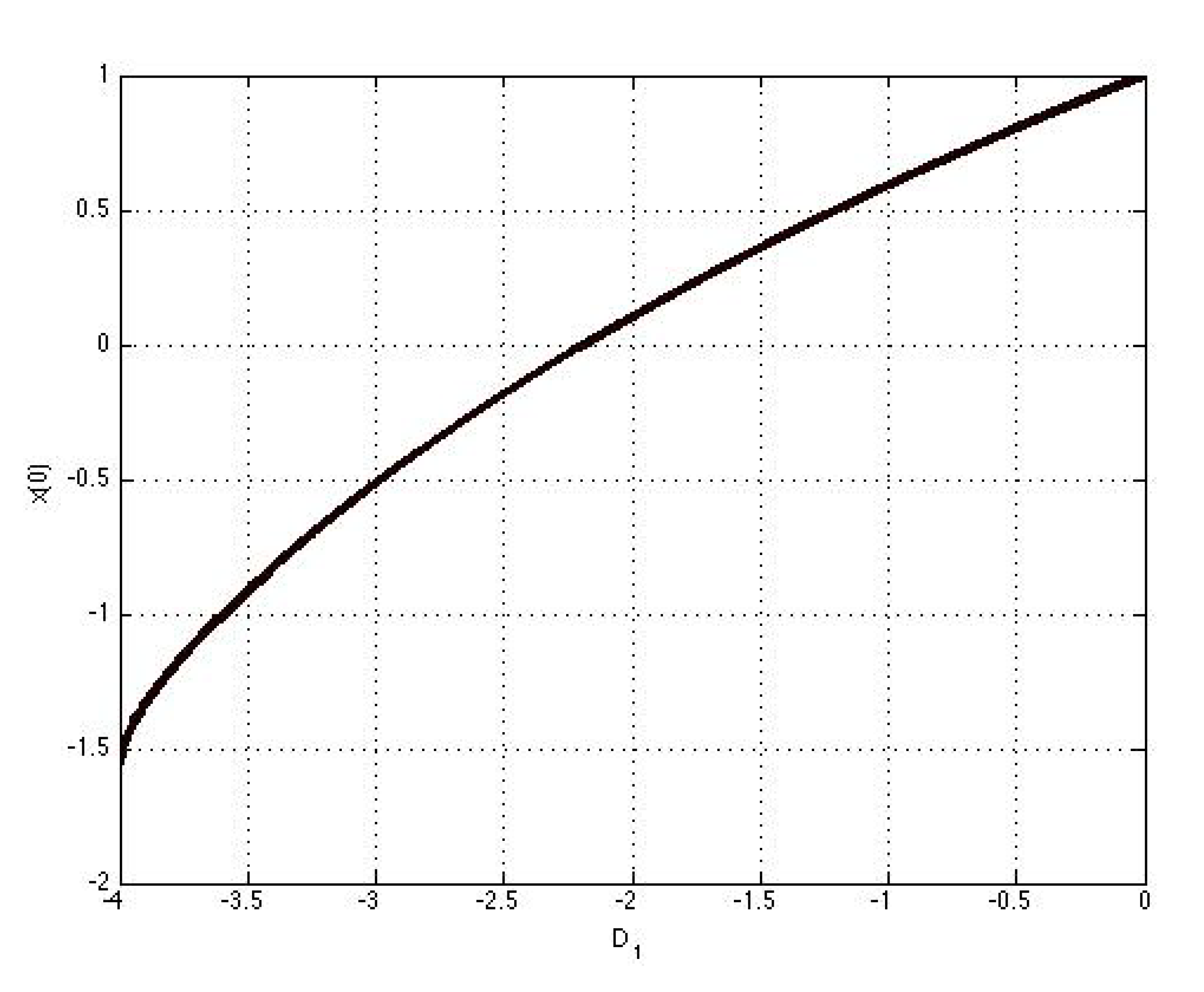
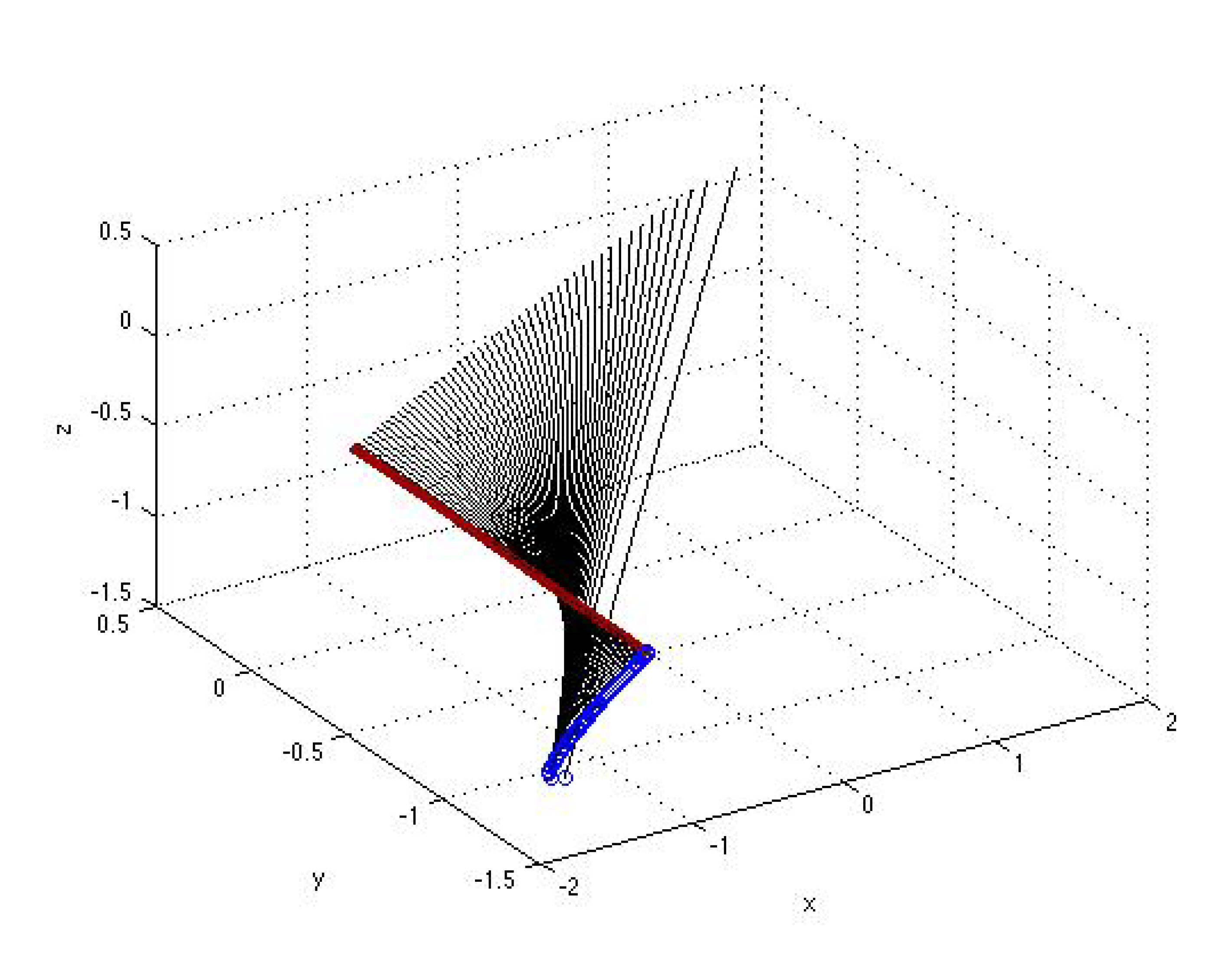
5. Conclusion
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Autonomous Polynomial Dynamical Systems Integrable in Elementary Functions
Appendix A.2. Examples with Bifurcations
References
- V. A. Gaiko, Global bifurcations and chaos in polynomial dynamical systems, 2003 International Conference Physics and Control. Proceedings, St. Petersburg, Russia, 2003, vol.2, pp.670–674. [CrossRef]
- Valery, A. Gaiko, Global Bifurcation Theory and Hilbert’s Sixteenth Problem, Book Series: Mathematics and its Applications, Vol. 562, Kluwer, Boston, 2003.
- Albert Luo, Polynomial Functional Dynamical Systems, E-book. Springer International Publishing, 2022.
- Bautin, N.N. , Leontovich, E.A.: Methods and Examples of the Qualitative Analysis of Dynamical Systems in a Plane. Nauka, Moscow (1990).
- V. A. Gaiko, On Global Bifurcation Theory of Polynomial Dynamical Systems and Its Applications, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Y. V. Shestopalov, A. Kh. Y. V. Shestopalov, A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, Qualitative theory of two-dimensional polynomial dynamical systems, Symmetry, 13:10 (2021), pp. 1884–1899. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev and Yu. V. Shestopalov, Qualitative analysis of quadratic polynomial dynamical systems associated with the modeling and monitoring of oil fields, Lobachevskii J. Math., 40:10 (2019), pp. 44-50. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh., Shakhverdiev. Some conceptual aspects of systematic optimization of oil field development. Oil Industry 2017, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- I. Buckley and M. C., Leverett. Mechanism of Fluid Displacement in Sands. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, System optimization of non-stationary flooding for the purpose of increasing oil recovery, Petroleum Engineering (2019), pp.44–49. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, S. V. A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, S. V. Arefiev, A. V. Denisov, R. R. Yunusov, Method for restoring the optimal mode of operation of the reservoir-well system, taking into account the instability of the displacement front, Oil Industry, 6 (2020), pp. 52–57. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, S. V. A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, S. V. Arefiev, The concept of monitoring and optimization of oil reservoirs waterflooding under the conditions of displacement front instability, Oil Industry, 11 (2021), pp. 104–109. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh., Shakhverdiev. Once again about oil recovery factor. Neftyanoe Khozyaystvo 2014, 1, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- J. M. T. Thomson, Instabilities and Catastrophes in Science and Engineering, J. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1982.
- L. Brenig and A., Goriely. Universal canonical forms for time-continuous dynamical systems. Phys. Rev. 1989, A40, 4119–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- <italic>V.M. Buchstaber, S. V.M. Buchstaber, S. Konstantinou-Rizos, A.V. Mikhailov Recent developments in integrable systems and related topics of mathematical physics, Springer Proc. Math. Stat., 273 (2018), Springer, Cham.
- William T. Bradley and William J., Cook. Two Proofs of the Existence and Uniqueness of the Partial Fraction Decomposition. International Mathematical Forum 2012, 7, 1517–1535. [Google Scholar]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, Y. V. A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, Y. V. Shestopalov, I. E. Mandrik, S. V. Arefiev, Alternative concept of monitoring and optimization water flooding of oil reservoirs in the conditions of instability of the displacement front, Petroleum Engineering, 12 (2019), pp. 118–123. [CrossRef]
- A. Kh. Shakhverdiev, System optimization of non-stationary water flooding for IOR/EOR. Oil industry 2019, 1, 44–50.
- F. Craig Forrest Jr., The Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Waterflooding Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME, New York, 1971.
- L.P. Dake, The practice of reservoir engineering - Shell Internationale Petroleum Maatschappij B.V., The Hague, The Netherlands, 2001.
- Dana Constantinescu, On the Bifurcations of a 3D Symmetric Dynamical System, Symmetry 15:4 ( 2023), pp. 923–935.
- Fenichel, N. Geometric Singular Perturbations Theory for Ordinary Differential Equations. J. Differ. Eq. 1979, 31, 53–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).