1. Introduction
Metals and alloys are multidisciplinary materials that can serve for a broad list of applications, such as biomedical, structural, catalytic, daily, optoelectronics, aeronautic, automotive, etc. One of the best examples is stainless steel, which can be found in low-to-high mechanically challenging applications such as jewelry and aircraft [
1]. However, modern technology and current societal challenges require materials with non-conventional combinations of properties or materials that conserve similar properties under extreme environments. For example, extreme temperature requirements have surpassed the operating limits of Ni-based superalloys [
2,
3]. Another example is the use of Ti-6Al-4V for biomedical implants which has been pointed out as highly toxic for these applications [
4,
5]. However, they are still the most widely used materials for nuclear and medical implants [
2,
3,
6]. Therefore, it is of great importance to develop better and safer materials to meet the needs of modern society.
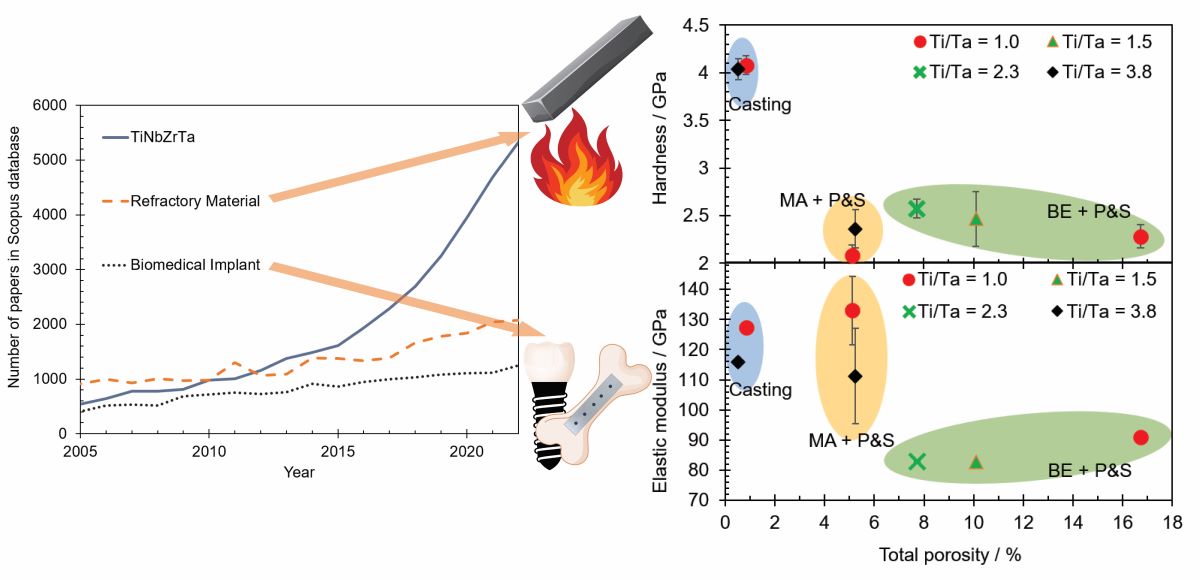
The high-entropy TiNbZrTa (TNZT) alloy is garnering significant attention for its exceptional thermal stability at elevated temperatures and remarkable biocompatibility [
2,
7], attributed to the low cytotoxicity of its constituent elements, Ti, Nb, Zr, and Ta [
8]. As a result, this alloy stands out as a promising material for applications in refractory and biomedical fields. Both applications converge on the principle of mechanical adequacy to secure their correct functionality. Hardness should be high enough to avoid shear failure during biomedical or refractory performance. Stiffness, i.e., elastic modulus, should be as close as possible to that of the human bone to avoid stress shielding during biomedical performance [
9,
10] but high enough to resist deformation during refractory applications.
The chemical composition and porosity are major parameters which affect stiffness and hardness. Different attempts towards tunning mechanical properties by minority alloying additions to the highly concentrated TNZT alloys have been reported, e.g., Fe [
11,
12,
13], Si [
11,
12], O [
11], Ag [
13], Sn [
13], etc. Variations of the base elements have also been studied, e.g., the Ti/Ta ratio [
14,
15]. So far, no systematic study of the effect of porosity on the mechanical properties of TNZT alloys has been reported. Similarly, the effect of chemical composition on their hardness and elastic modulus has not been well established.
Recently, multitude of paradoxes of conventional metallic materials have been challenged when applied to high-entropy alloys (HEAs) [
16]. This is mainly because of the effect of multiple principal elements in equiatomic or near equiatomic amount in HEAs, as opposed to single principal element in conventional alloys [
17]. The lattice distortion in HEAs because of multiple elements with different atomic radii in a solid solution may influence the interatomic bonding strength.
From the above, the understanding of elastic modulus and hardness in HEAs has also been challenged. The elastic moduli of HEAs, which is highly dependent on the bonding strength, may vary from the conventional alloys. As different pairs of atoms may be found at similar separation distances in HEAs, multiple bond strength values are expected [
18]. In addition to the unconventional behavior triggered by lattice distortion in the TNZT alloy, porosity is another factor that can also affect stiffness [
18,
19]. Regarding hardness, it is empirically correlated to the yield strength in conventional metallic materials. However, low plasticity as well as low strain hardening rate has been reported for TNZT-based alloys [
7,
15]. As strain hardening rate determines the difference between yield strength and ultimate tensile strength, its tendency cannot be accurately characterized from the tensile test of TNZT alloys with low-plasticity. The correlation of the tensile yield strength to hardness should be applied with caution [
20,
21]. Previous reports have shown that this conventional relationship is much higher than fracture strength in weak strain hardened HEAs because of their premature fracture under uniaxial loading [
21]. Besides the above, chemical composition changes and the introduction of 3D defects, such as pores, may also affect the hardness of TNZT alloys.
In this work, we report comparative correlations to describe the effect of chemical composition and porosity on the hardness and elastic modulus of different TNZT alloys. Different powder metallurgy (PM) techniques and arc melting were used to produce materials with different porosities. This study will serve as a foundation for future design of TNZT-based components for refractory and biomedical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of TNZT Alloys
The properties of powder materials used to produce the TNZT alloys are shown in
Table 1. All of them were provided by Alfa Aesar. The chemical compositions of TNZT alloys explored in this study are given in
Table 2.
2.1.1. Powder Metallurgy by Blend Element Technique.
The alloys produced by blend element (BE) and posterior press & sintering (P&S) are hereinafter referred as BE + P&S samples. The chemical composition of alloys produced by BE + P&S method are shown in
Table 2. The powders with desired compositions were mixed by a blender (Bioengineering Inversine 2L) in a closed vial for 30 min at 54 rpm. Blend elements were used before sintering to enhance the surface contact between elemental powders and secure their homogeneous mixing. Thus, it avoids excessive welding and limits particle growth. Approximately 8 g of powders were compacted at 1000 MPa through a rectangular die with dimensions 32 mm × 12 mm × 6 mm. The specimens were sintered in a high-vacuum tubular furnace (Carbolite HVT 15/75/450) at a pressure between 0.01 to 0.1 Pa. A two-steps sintering process was performed as follows: 1) increasing temperature at a speed of 5 °C min
-1 until 800°C and maintaining for two hours, and 2) increasing temperature up to 1400°C and maintaining the temperature for three hours. The sintering was carried out under Ar atmosphere to avoid oxidation. Posteriorly, the samples were furnace-cooled at 10 °C min
-1.
2.1.2. Powder Metallurgy by Mechanical Alloying.
The alloys produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and posterior P&S are hereinafter referred as MA + P&S samples. The chemical composition of alloys produced by this method are shown in
Table 2. MA was done in a planetary ball mill (Retsch model PM 400/2) at 350 rpm for 40 h divided in work stages of 8 minutes on and 10 minutes off to improve the homogenization of the TNZT alloy after press and sintering (P&S). Standard stainless steel jars and chromium steel balls with a ball to powder weight ratio of 10:1 were used for milling. 1 wt.% of stearic acid (C18H36O2) was used as debinding agent to avoid powder agglomeration. The powders were then compacted using a hydraulic press (Metallkraft model WPP 50 M) and a floating die of 1.8 cm3 at 1000 MPa for 10 seconds. The specimens were sintered in a high-vacuum tubular furnace (Carbolite HVT 15/75/450) at a pressure between 0.01 to 0.1 Pa with Ar atmosphere. Sintering was performed in three steps: 1) temperature increment at 5 °C min
-1 until 800°C and hold for one hour, 2) temperature increment up to 1400°C and holding for three hours, and 3) furnace-cooling at 10 °C min
-1 to room temperature.
2.1.3. Arc Melting and Casting.
The alloys produced by arc melting are hereinafter referred as casting or cast samples. The chemical composition of alloys produced by this method are shown in
Table 2. Arc melting was carried out at an Edmund Bühler GmbH MA M-1 under vacuum to minimize the formation of oxides. The alloys were remelted six times to ensure homogeneity.
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
Cross-sections of the HEAs were subjected to standard metallographic preparation, i.e., griding with SiC papers and polishing with an OP-S NonDry suspension of 0.04 μm particle size diluted in 20% H2O2. Porosity observations were carried out by optical Microscopy using a Nikon Eclipse LV100. Porosity was estimated by the Archimedes method according to ASTM B962-17. At least five measurements were averaged for each sample.
2.3. Mechanical Properties Evaluation
Microhardness was measured on the polished HEAs according to the ASTM: E384 using a Shimadzu Vickers HMV-2 microdurometer by applying 3 N for 15 s. At least 5 measurements were obtained per sample. The elastic modulus was measured by impulse excitation technique (IET, ATCP-Sonelastic). The software ATCP Sonelastic 3.0 was used to analyze the data.
3. Results and Discussion
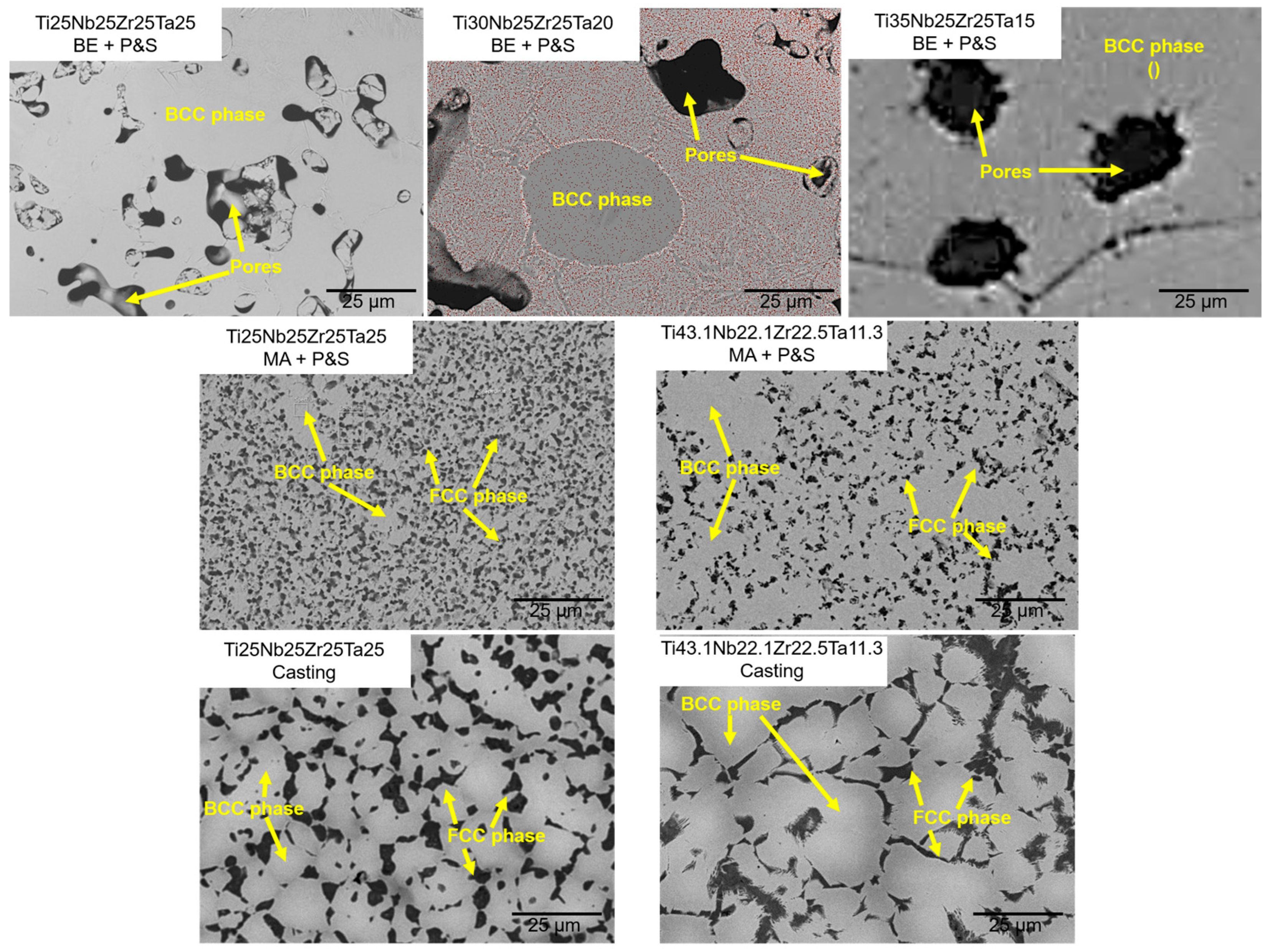
Figure 1 displays representative optical micrographs of the studied TNZT samples that allow observing the present phases, as well as morphology and size of pores and phases. Larger pore size was produced by the BE + P&S method (3‒27 μm) compared to that by MA + P&S (0.5‒3 μm) and cast alloys (0.5‒1.0 μm). The difference in pore size is related to the processing parameters of each production route. The resulting larger powder size from BE agrees with the larger pore size after sintering. As casting involves melting of the powders, negligible porosity was expected. The pores generated from the three routes showed rounded morphologies.
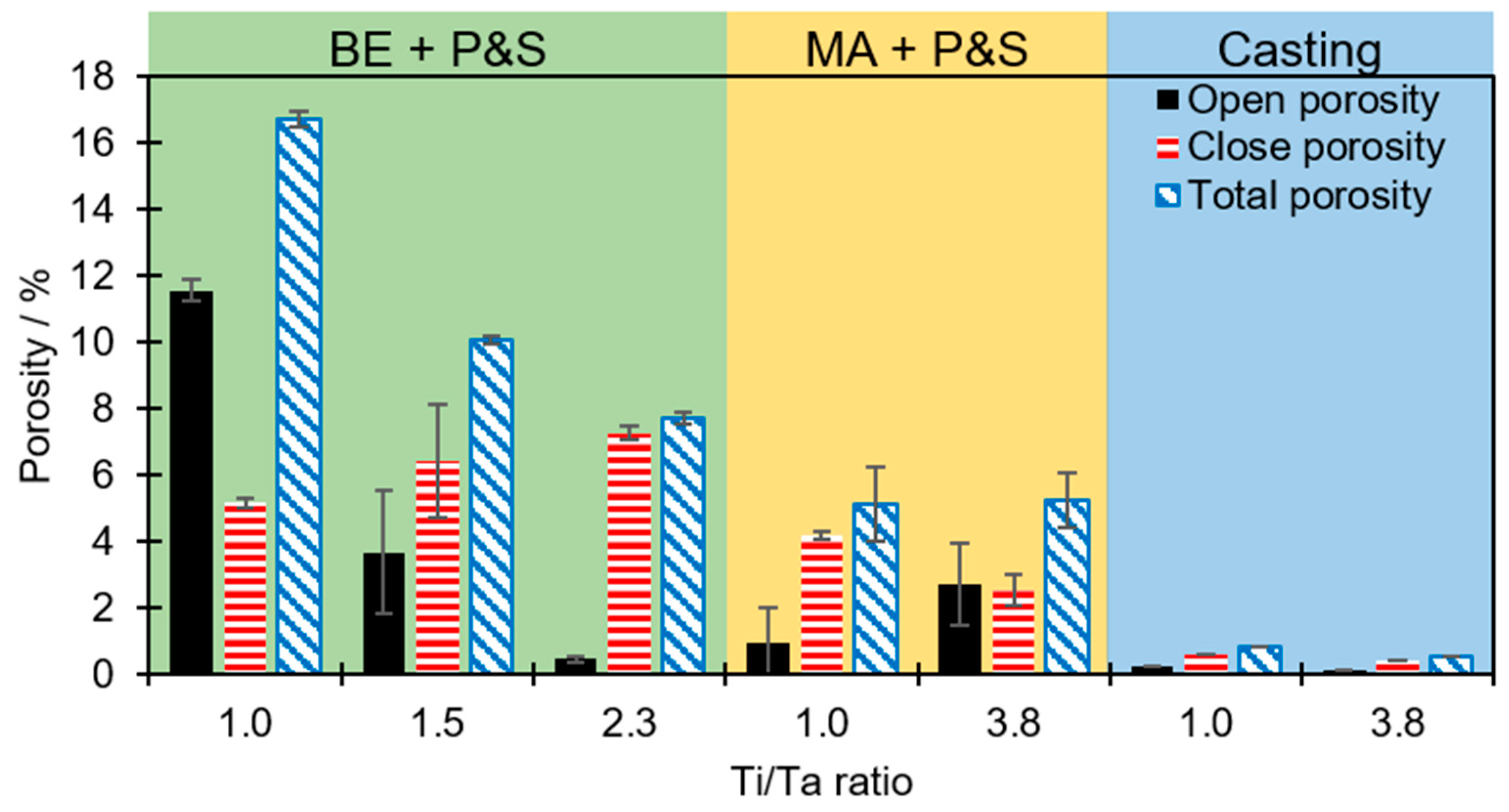
Figure 2 shows the open (interconnected), close and total porosity of the studied alloys for each technique. BE + P&S shows the highest level of porosity compared to MA + P&S and casting. The higher atomic diffusion generated by MA could be responsible for the higher density compared to BE. BE enhances powders mixing and surface contact but does not promote metallic bonding in the TNZT alloys [
15]. As expected, casting generated the most compacted alloys with lower porosity content, being a result of the full melting process with highly activated atomic diffusion compared to that of PM methods.
Porosity from BE + P&S increases while decreasing the Ti/Ta ratio. The Ti
25Nb
25Zr
25Ta
25, Ti
30Nb
25Zr
25Ta
20, and Ti
35Nb
25Zr
25Ta
15 samples showed total porosities of 16.7, 10.0 and 7.7 %, respectively. Thus, porosity increased 2.2 times by decreasing the Ti/Ta from 2.3 to 1.0. This phenomenon is explained by the highest melting point of Ta (3020 °C) compared to the other constituent elements (Ti: 1725 °C; Nb: 2477 °C; Zr: 1855 °C), which causes reduced atomic diffusion during sintering. Besides, the larger powder size from BE compared to MA reduces the surface contact of powders during sintering. These results are in agreement with the larger pore sizes produce by BE + P&S compared to the other two methods (Fig. 1). Reducing atomic diffusion could also affect the bonding formation and bonding energy. Reported BE + P&S TNZT alloys have shown elemental segregation. The lower the Ti/Ta ratio, the lower is the atomic diffusion and grain size [
15].
The production processes with higher atomic diffusion, i.e., MA + P&S and casting generated similar porosity regardless of the Ti/Ta ratio. The Ti25Nb25Zr25Ta25 and Ti43.1Nb22.1Zr22.5Ta11.3 produced by MA + P&S showed total porosities of 5.1 and 5.2 %, respectively. While the cast Ti25Nb25Zr25Ta25 and Ti43.1Nb22.1Zr22.5Ta11.3 samples have total porosities of 0.8 and 0.5 %, respectively. Considering that the P&S processes were realized at the same conditions, it is assumed that the difference in porosity is related to the lower atomic diffusion during the earlier stages of BE and MA. The elemental bonding generated by MA decreased the susceptibility of this route to Ti/Ta ratio compared to the BE. This agrees with the 3.2 times lower porosity in the Ti25Nb25Zr25Ta25 sample produced by MA + P&S than by BE + P&S. Thus, fabrication routes that promote more atomic diffusion are less susceptible to the density of the constituent elements. Therefore, the independence of the processing method to the alloy density can be ordered in the following sequence: casting > MA + P&S > BE + P&S.
The abovementioned effect of atomic diffusion on bonding formation is expected to influence the elastic modulus.
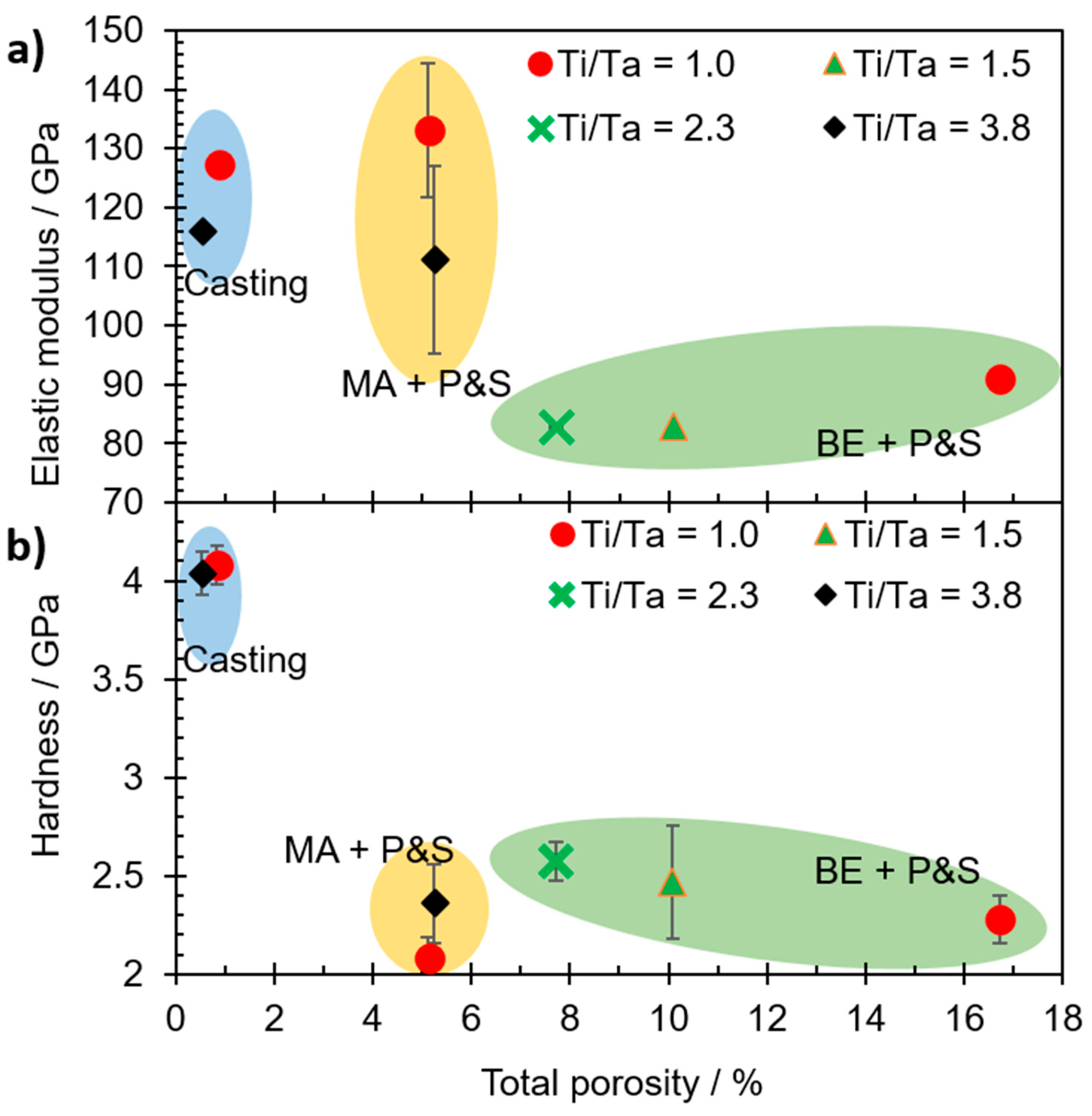
Figure 3a shows the elastic modulus as a function of the total porosity of alloys. It can be seen that the lower porosity generated higher elastic modulus, i.e., elastic modulus followed an inverse relationship with the total porosity. BE + P&S samples showed the lowest Young’s moduli values (82.7 to 91.0 GPa), followed by the MA + P&S (111.2 to 133.0 GPa) and then cast samples (115.9 to 127.3 GPa).
The experimental elastic moduli can be compared with the theoretical ones by using the lineal equation (Eq. 1) that Fryxell and Chandler proved on materials with pores fractions from 0.02 to 0.17 [
22],
where
is the elastic modulus of the porous material,
is the elastic modulus of the dense material,
is a constant related to the Poisson’s ratio of the matrix and here a value of 1.9 is assumed [
23], and
is the pores fraction. The
was taken from the cast Ti
25Nb
25Zr
25Ta
25 sample (127.3 GPa) where porosity effect can be considered negligible for the mechanical properties. Thus, the theoretical elastic modulus of the Ti
25Nb
25Zr
25Ta
25 EB + P&S and MA + P&S samples is of 86.8 and 114.9 GPa, respectively. Theoretical values are 4.8 and 15.7 % lower than the experimental values of the EB + P&S and MA + P&S Ti
25Nb
25Zr
25Ta
25 samples (91.0 and 133.0 GPa, respectively). Despite bonding energy is recognized as the main factor influencing the elastic modulus, the difference between theoretical and experimental values may be related to other secondary microstructural factors [
24], such as the previously discussed lower atomic diffusion and possible elemental heterogeneous distribution from the PM methods compared to casting, which may also result in different phase percentage, or possible preferred crystallographic orientation (texture).
The lower Ti/Ta ratio promoted higher elastic modulus values. The elastic modulus in the BE + P&S samples increased 9.9% with increasing the Ti/Ta ratio from 1.0 to 2.3. An increment of elastic modulus of 19.6% was observed when decreasing the Ti/Ta ratio from 3.8 to 1.0 in the MA + P&S samples. Samples produced by casting also showed an increment of elastic modulus of 9.7% when decreasing the Ti/Ta ratio from 3.8 to 1.0. This implies that Ti/Ta ratio does not restricts the bonding strength, which is the main factor influencing the elastic modulus. Wolverton [
25] has reported a direct correlation between the atomic radius of alloying elements and the bonding energy in Al alloys. Therefore, the main effect of lowering the Ti/Ta ratio, i.e., increasing high-density Ta, was increasing the density of the alloys, limiting the atomic diffusion during their processing. This is in good agreement with the highest porosity of the samples with the lowest Ti/Ta ratio (
Figure 2).
The highest hardness was observed in the dense cast alloys (4.0 GPa) compared to the porous ones (2.0 to 2.6 GPa) which were produced by PM methods (i.e., BE + P&S and MA + P&S). However, porosity percentage and pore size did not show a clear trend regarding the hardness of the PM-processed TNZT alloys (
Figure 3b). Both PM methods obtained similar hardness values (2.0 to 2.6 GPa) notwithstanding of their different total porosity (5.1 to 16.7 %). Hence, the different pore size between MA + P&S (0.5‒3 μm) and BE + P&S (3‒27 μm) samples (
Figure 1) did not have an apparent effect on hardness.
Despite the widely reported local lattice strain discrepancy between neighboring cells due to large atomic size mismatch in HEAs [
16], Ti/Ta ratio did not show an obvious effect on hardness of the studied TNZT alloys. Hardness decreased to 13.2 and 11.4 % with Ti/Ta ratio decrement of 2.8 and 1.3 in the MA + P&S and BE + P&S samples, respectively. However, hardness increased 1.0 % in the cast sample with Ti/Ta ratio increment from 1.0 to 3.8. Considering that hardness depends mainly on microstructural features, the unclear tendencies of porosity and Ti/Ta ratio on hardness may be related to other microstructural features. Examples of the above are grain size, phase percentage, elemental distribution or preferred crystallographic orientation. Some materials with low porosity, similar to the ones studied here, have reported a negligible effect of porosity on hardness [
26].
The elastic modulus showed a strong dependence on porosity while the hardness was just slightly impacted by porosity in TNZT alloys. This is related to the fact that elastic modulus is mainly dependent on the bonding energy, while hardness is mainly dependent on microstructural factors, such as grain size, phase content, grain boundary features, etc. [
27]. Regarding processing routes, the close values of bulk elastic moduli achieved by casting and MA+P&S samples indicate similar interatomic bonding strength. The difference in mechanical properties between the three studied processing routes is given by the difference in porosity or Ti/Ta ratio. The first effect is reflected in the properties associated with the microstructure (i.e., hardness), while the second effect in more significant in the properties related to the bonding energy (i.e., elastic modulus).
4. Conclusions
Three series of TiNbZrTa alloys with different Ti/Ta ratios were developed by blend element and posterior press and sintering (BE + P&S), mechanical alloying with press and sintering (MA + P&S), and casting methods. The effect of porosity and chemical composition on elastic modulus and hardness was compared among the samples produced by three different routes. The main findings can be summarized as follows:
The processing methods were influenced by the high-density Ta contents (lowering the Ti/Ta ratio) and produced total porosity in the following order: casting (0.5-0.8 %) < MA + P&S (5.1-5.2 %) < BE + P&S (7.7 – 16.7 %). Casting and MA + P&S were less affected than BE + P&S due to their higher atomic diffusion.
The main effect of lowering the Ti/Ta ratio was increasing the density of the alloys, limiting the atomic diffusion during their processing. The lower the Ti/Ta ratio, the higher the total porosity of the alloys.
Elastic modulus showed a low susceptibility to the Ti/Ta ratio. Thus, Ti/Ta ratio did not show a strong effect on the bonding energy. Elastic modulus was higher for the routes that promoted higher atomic diffusion (Casting:115.9-127.3 and MA + P&S: 111.0-133 GPa) than for the BE + P&S samples (82.8-91.0 GPa). The close values of bulk elastic moduli achieved by casting and MA+P&S samples indicate similar strength of interatomic bonds. The lower porosity generated higher elastic modulus.
Hardness was boosted in the dense cast alloys (4.0 GPa) compared to the porous ones (2.0 to 2.6 GPa). However, porosity and Ti/Ta ratio did not show a clear tendency on hardness among the porous alloys, which showed similar hardness values (2.0 to 2.6 GPa) despite their difference in total porosity (5.1 to 16.7%) and Ti/Ta ratio (1.0 to 3.8).
The effect of porosity is mainly reflected in the properties associated with the microstructure (i.e., hardness), while the effect of Ti/Ta ratio is more significant in the properties related to the bonding energy (i.e., elastic modulus).
Systematic studies evaluating the influence of other microstructural parameters on the hardness and elastic modulus of TiNbZrTa alloys, such as phase percentage, grain size, elemental distribution, pore distribution and morphology, and preferred crystallographic orientation are recommended for future research.
Author Contributions
C. González-Guillén: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization. G. Al Hawajreh: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization. E. Degalez-Duran: Data curation. E. Klyatskina: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing. M. Naeem: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing. L. Romero-Resendiz: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing-Original Draft. G. Gonzalez: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing - Review & Editing. V. Amigó: Conceptualization, Visualization, Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing - Review & Editing.
Funding
This research was funded by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades with grant number “RTI2018-097810-B-I00”, the European Commission via the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER), the UNAM-DGAPA-PASPA program (sabbatical year of G.G.), the Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigacion e Innovacion Tecnologica (PAPIIT)-UNAM under grant number IN102321, and the Programa de Apoyo a la Investigación y el Posgrado (PAIP) of the Facultad de Química of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México under grant number PAIP-50009223.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data related to this manuscript would be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Romero-Resendiz L, El-Tahawy M, Zhang T, Rossi MC, Marulanda-Cardona DM, Yang T, et al. Heterostructured stainless steel: Properties, current trends, and future perspectives. Mater Sci Eng R 2022;150:100691. [CrossRef]
- Xiong W, Guo AXY, Zhan S, Liu CT, Cao SC. Refractory high-entropy alloys: A focused review of preparation methods and properties. J Mater Sci Technol 2023;142:196–215. [CrossRef]
- Senkov ON, Miracle DB, Chaput KJ, Couzinie JP. Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys - A review. J Mater Res 2018;33:3092–128. [CrossRef]
- Karimi S, Alfantazi AM. Ion release and surface oxide composition of AISI 316L, Co-28Cr-6Mo, and Ti-6Al-4V alloys immersed in human serum albumin solutions. Mater Sci Eng C 2014;40:435–44. [CrossRef]
- Costa BC, Tokuhara CK, Rocha LA, Oliveira RC, Lisboa-Filho PN, Costa Pessoa J. Vanadium ionic species from degradation of Ti-6Al-4V metallic implants: In vitro cytotoxicity and speciation evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C 2019;96:730–9. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen HD, Pramanik A, Basak AK, Dong Y, Prakash C, Debnath S, et al. A critical review on additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J Mater Res Technol 2022;18:4641–61. [CrossRef]
- Nasibi S, Alimohammadi K, Bazli L, Eskandarinezhad S, Mohammadi A, Sheysi N. TZNT alloy for surgical implant applications: A systematic review. J Compos Compd TZNT 2020;2:62–8. [CrossRef]
- Sidhu SS, Singh H, Gepreel MAH. A review on alloy design, biological response, and strengthening of β-titanium alloys as biomaterials. Mater Sci Eng C 2021;121:111661. [CrossRef]
- Guo L, Ataollah Naghavi S, Wang Z, Nath Varma S, Han Z, Yao Z, et al. On the design evolution of hip implants: A review. Mater Des 2022;216:110552. [CrossRef]
- Cui YW, Chen LY, Chu YH, Zhang L, Li R, Lu S, et al. Metastable pitting corrosion behavior and characteristics of passive film of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti–6Al–4V in NaCl solutions with different concentrations. Corros Sci 2023;215:111017. [CrossRef]
- Raducanu D, Cojocaru VD, Nocivin A, Cinca I, Serban N, Cojocaru EM. Contributions to Mechanical Characteristics Improvement of Some Biomedical TNTZ Alloys by Adding Fe, Si, and O: A Comparative Study. Jom 2019;71:264–71. [CrossRef]
- Kopova I, Stráský J, Harcuba P, Landa M, Janeček M, Bačákova L. Newly developed Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta-Si-Fe biomedical beta titanium alloys with increased strength and enhanced biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C 2016;60:230–8. [CrossRef]
- Zareidoost A, Yousefpour M. A study on the mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of the new as-cast TZNT alloys for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 2020;110:110725. [CrossRef]
- Yang M, Shao L, Duan JM, Chen XT, Tang BY. Temperature dependence of mechanical and thermodynamic properties of Ti(25+x)Zr25Nb25Ta(25-x) (x ≤ 20) refractory high entropy alloys: Influences of substitution of Ti for Ta. Phys B Condens Matter 2021;606:412851. [CrossRef]
- Al Hawajreh G, Gonzalez G, Romero-Resendiz L, Vidilli A, Otani LB, Amigó V. Effect of the Ti/Ta ratio on the feasibility of porous Ti25+x-Nb25-Zr25-Ta25-x (X= 0, 5, and 10) alloys for biomedical applications. J Mater Res Technol 2023:109181. [CrossRef]
- George EP, Raabe D, Ritchie RO. High-entropy alloys. Nat Rev Mater 2019;4:515–34. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Zhao S, Ding J, Chong Y, Jia T, Ophus C, et al. Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nature 2020;581:283–7. [CrossRef]
- Ching WY, San S, Brechtl J, Sakidja R, Zhang M, Liaw PK. Fundamental electronic structure and multiatomic bonding in 13 biocompatible high-entropy alloys. Npj Comput Mater 2020;6:1–10. [CrossRef]
- Bram Dr M, Ebel Dr T, Wolff M, Cysne Barbosa Dr AP, Tuncer Dr N. Applications of powder metallurgy in biomaterials. Adv. Powder Metall., Woodhead Publishing; 2013, p. 520–54. [CrossRef]
- Keist JS, Palmer TA. Development of strength-hardness relationships in additively manufactured titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 2017;693:214–24. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Qu R, Zhang Z. Relation Between Strength and Hardness of High-Entropy Alloys. Acta Metall Sin (English Lett 2021;34:1461–82. [CrossRef]
- Fryxell RE, B. A. Chandler. Creep, Strength, Expansion, and Elastic Moduli of sintered BeO as a function of grain size, porosity and grain orientation. J Am Ceram Soc 1964;47:283–91. [CrossRef]
- Choren JA, Heinrich SM, Silver-Thorn MB. Young’s modulus and volume porosity relationships for additive manufacturing applications. J Mater Sci 2013;48:5103–12. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, MT. Beta Titanium Alloys: The Lowest Elastic Modulus for Biomedical Applications: A Review Surface processing and alloying View project Powder Metallurgy Titanium Alloys View project. Int J Mater Metall Eng 2014;8:822–7.
- Wolverton, C. Solute-vacancy binding in aluminum. ACTA Mater 2007;55:5867–72. [CrossRef]
- Romero-Resendiz L, Rossi MC, Segui-Esquembre C, Amigo-Borras V. Development of a porous Ti-35Nb-5In alloy with low elastic modulus for biomedical implants. J o f Mater Res Technol 2023;22:1151–64. [CrossRef]
- Furukawa M, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Valiev RZ, Langdon TG. Factors influencing the flow and hardness of materials with ultrafine grain sizes. Philos Mag A 1998;78:203–16. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).