Submitted:
25 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starter culture, probiotic, and reagents
2.2. Preparation of yogurt
2.3. Preparation of YIC
2.4. Analysis of the Physicochemical properties of YIC mix and YIC
2.4.1. Fat particle size of YIC mix
2.4.2. Dynamic oscillatory characteristics of YIC mix
2.4.3. Total acidity and pH of YIC
2.4.4. Overrun of YIC
2.4.5. Hardness of YIC
2.4.6. Melting rate of YIC
2.5. Microstructure of YIC
2.6. Sensory evaluation of YIC
2.7. Number of survival B. longum in YIC
2.8. Survival of B. longum in simulated digestive system
2.9. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical properties of YIC
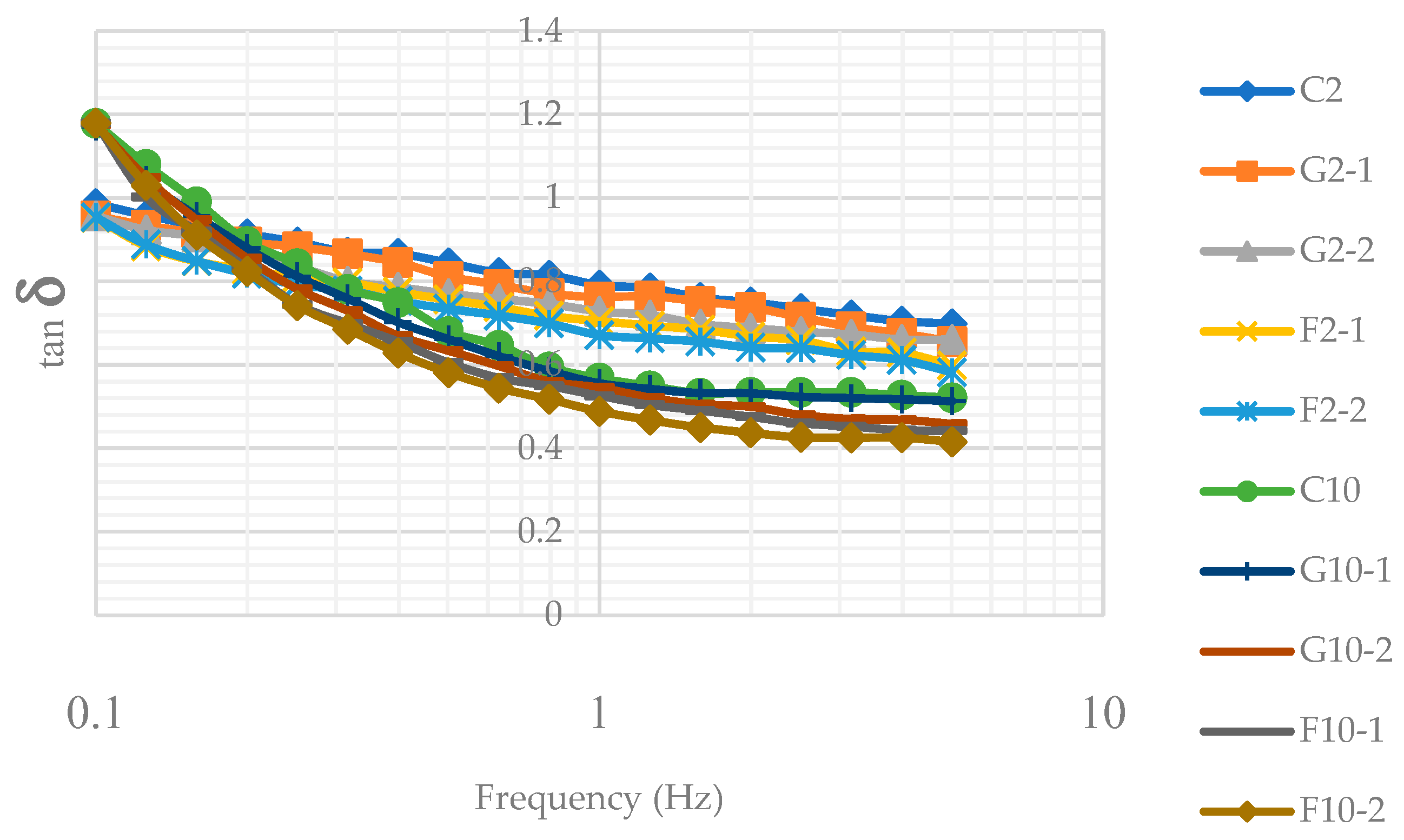
3.2. Oscillatory property of YIC mix
3.3. Hardness of YIC
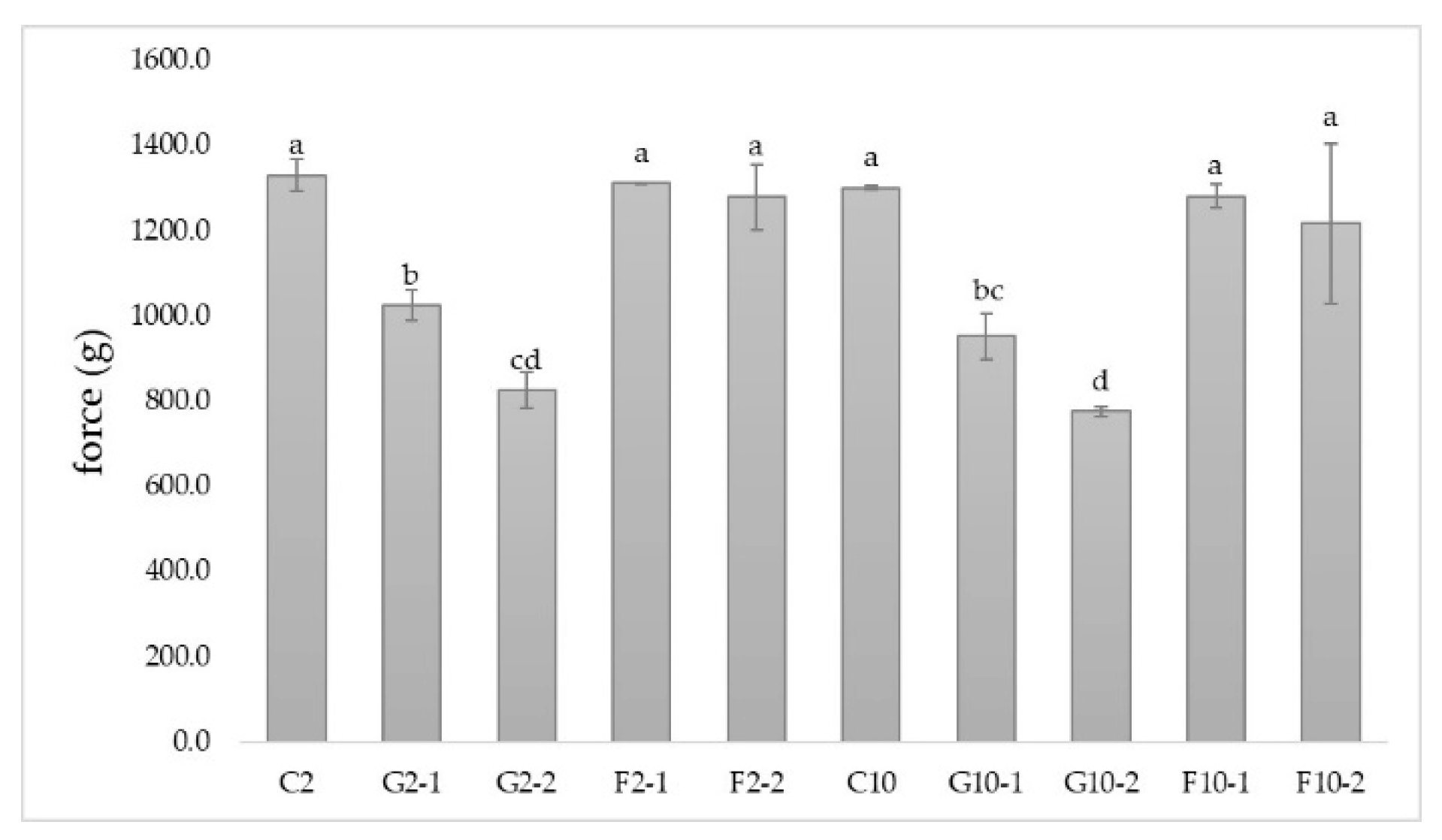
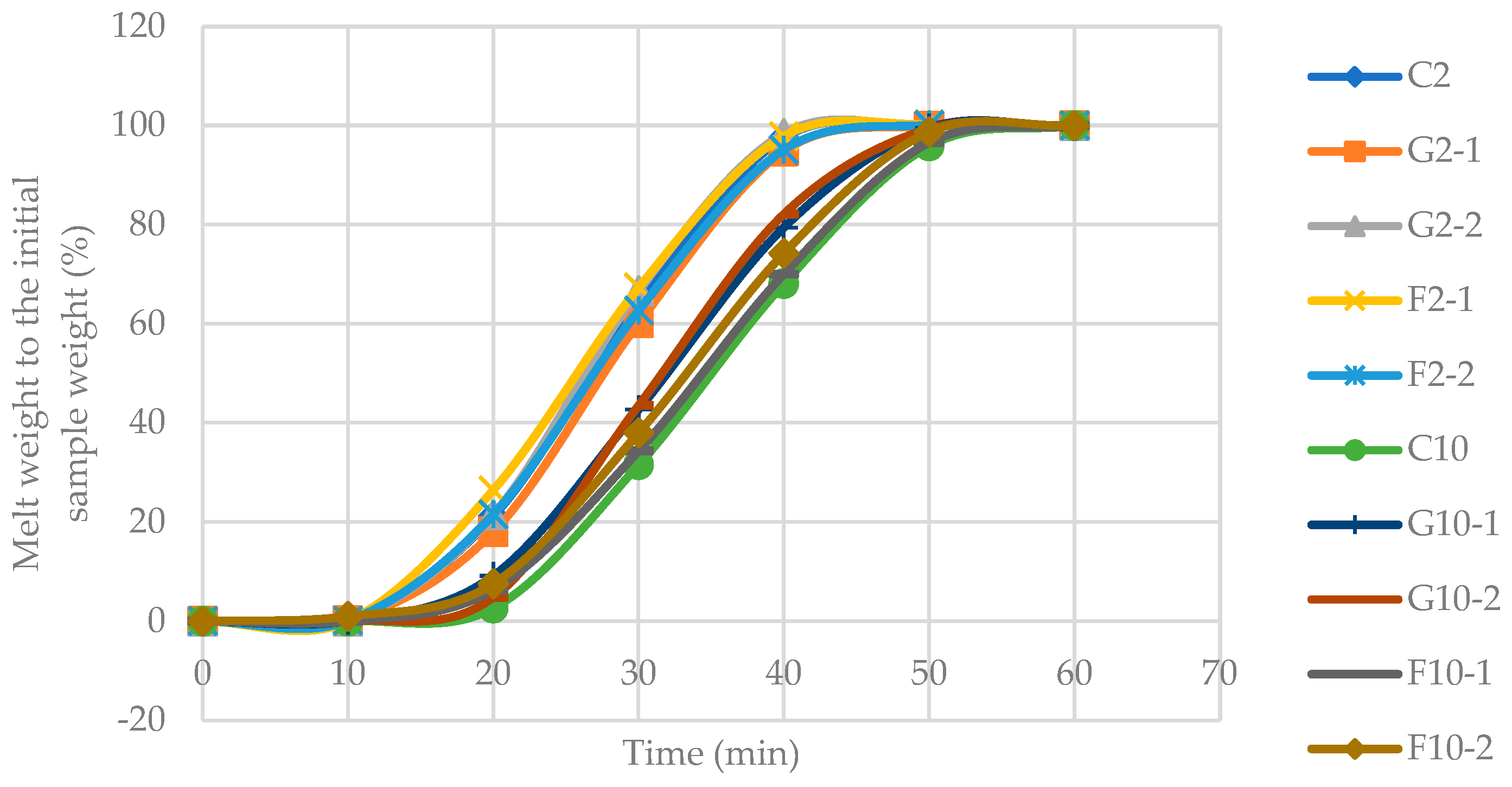
3.4. Melting rate of YIC
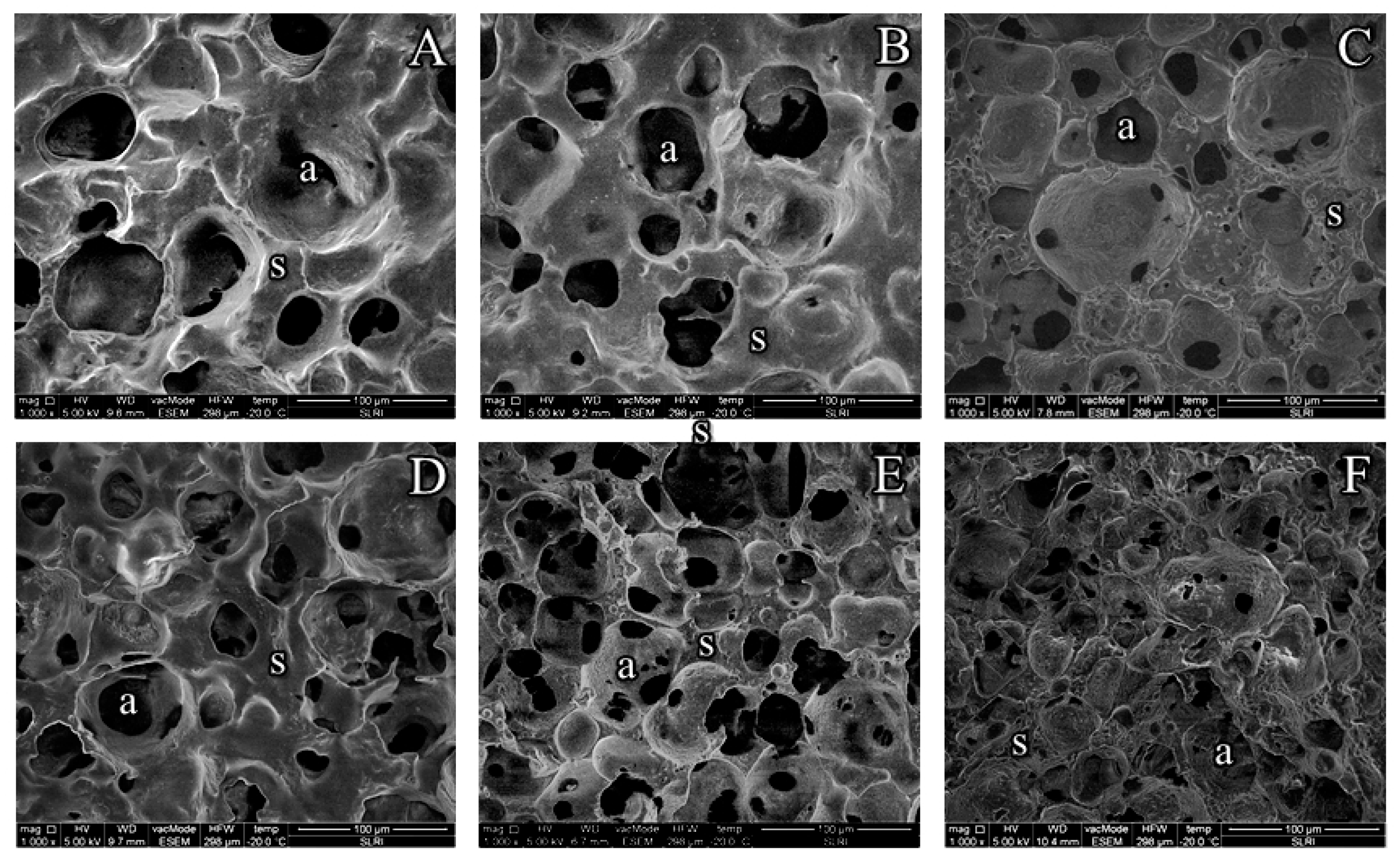
3.5. Microstructure of YIC
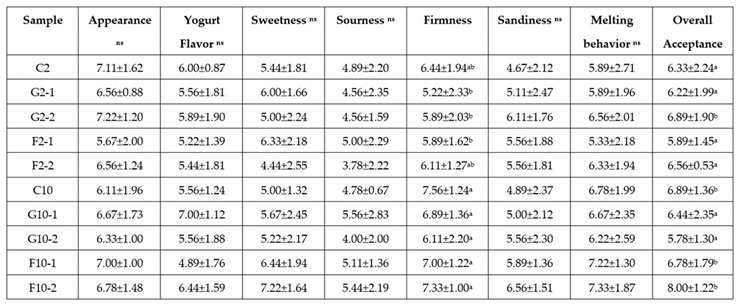
3.6. Sensory evaluation of YIC
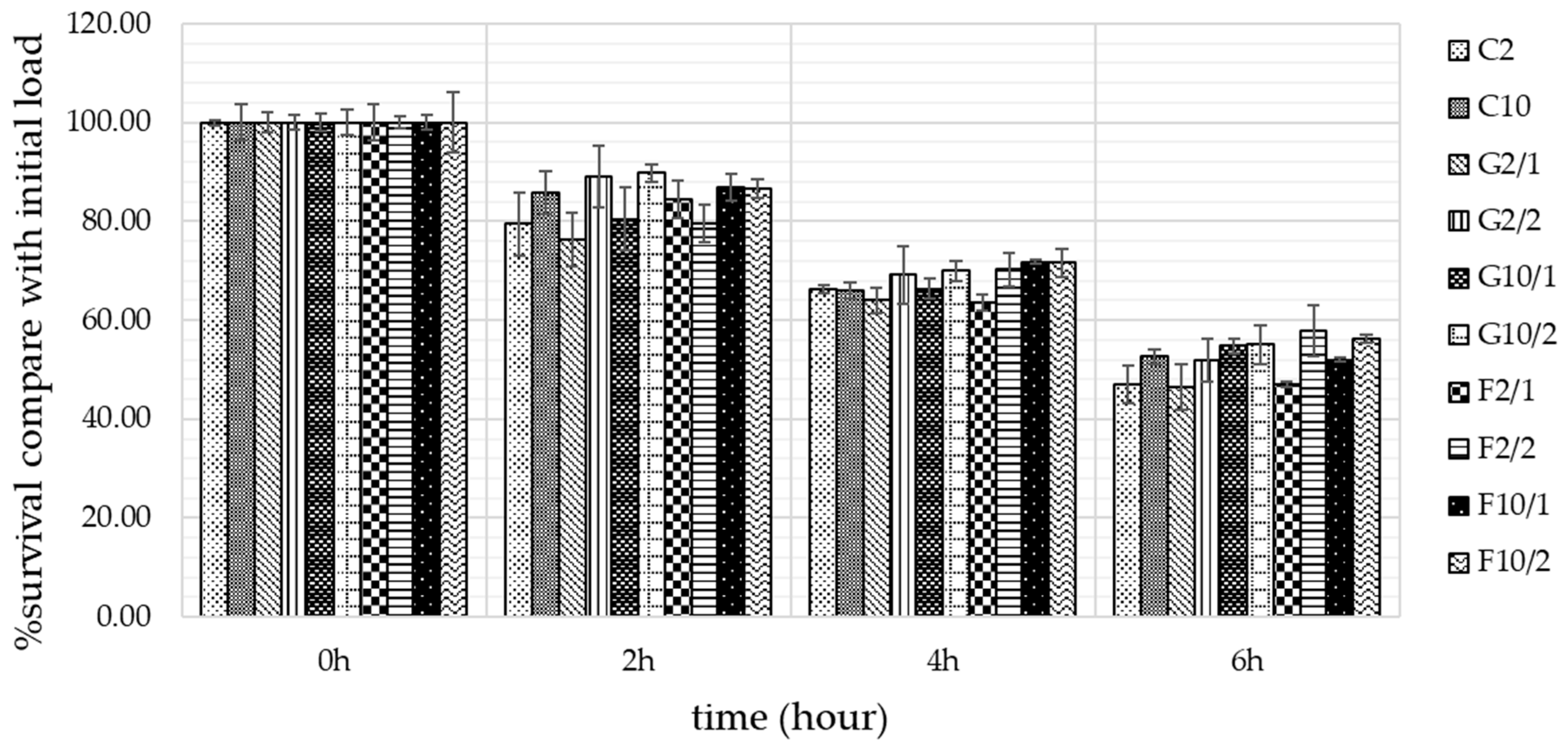
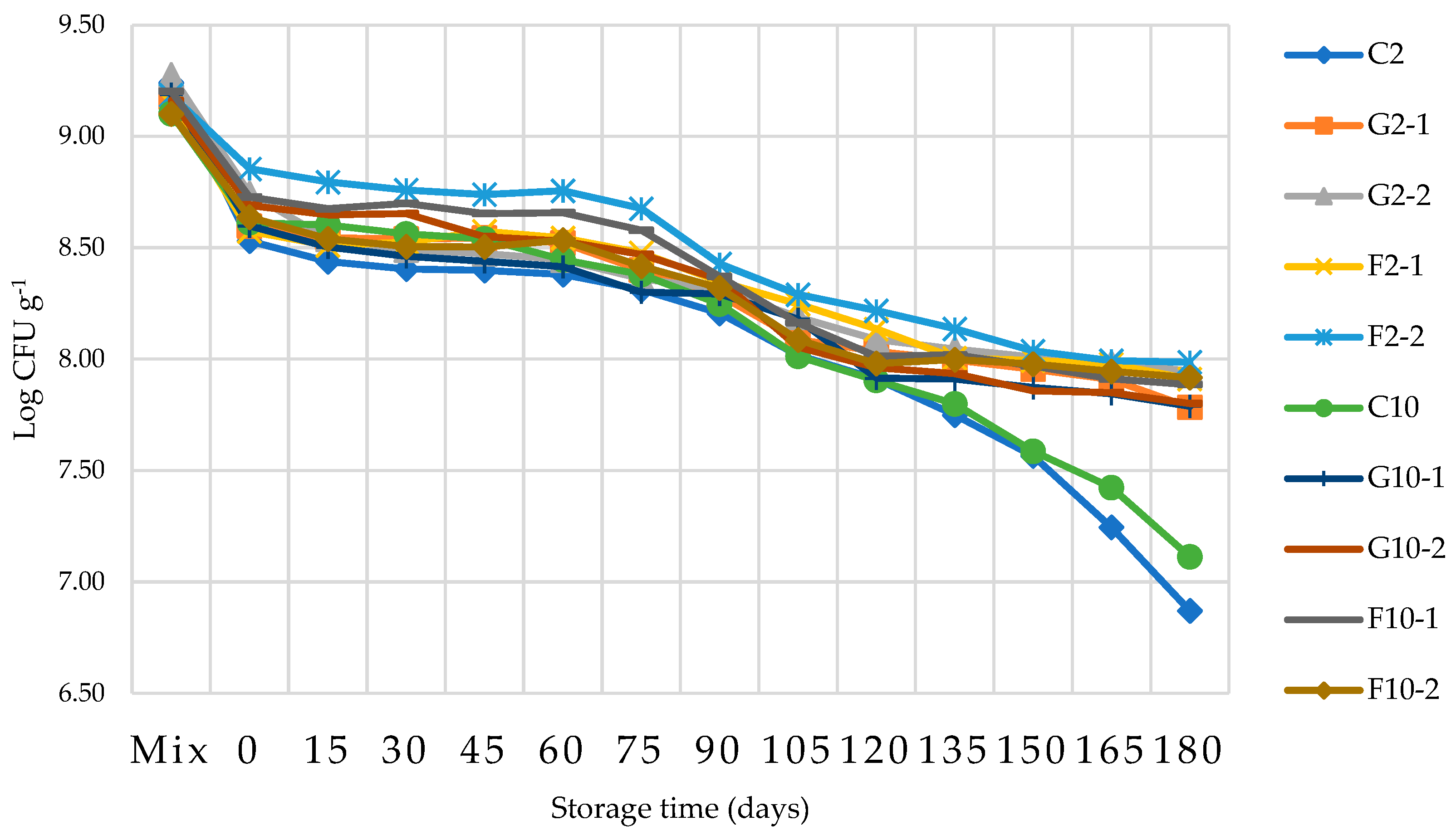
3.7. Survival of B. longum in YIC during storage
3.7. Survival of B. longum in a simulated GI tract
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institute Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- F. Clydesdale, "FOOD TECHNOLOGY MAGAZINE," 1 December 2004. [Online]. Available: https://www.ift.org/news-and-publications/food-technology-magazine/issues/2004/december/features/functional-foods-opportunities-and-challenges.
- N. M. Khair, N. A. A. Rahman, . A. S. Baharuddin, H. . S. Hafid and M. Wakisaka, "Capturing the impact of nanobubble liquid in enhancing the physical quality of ice cream," Journal of Agricultural and Food Engineering 2, pp. 1-4, 2020.
- Y.-K. Lee and S. Salminen, "The coming of age of probiotics," Trends in Food Science & Technology, pp. 241-245, 1995. [CrossRef]
- D. J. O’Sullivan, "Primary sources of probiotic cultures," in Probiotics in Food Safety and Human Health, Oxfordshire, Taylor & Francis Group, 2005, pp. 91-108.
- G. R. Gibson, "Fibre and effects on probiotics (the prebiotic concept)," Clinical Nutrition Supplements, pp. 25-31, 2004. [CrossRef]
- T. R. Marshall, H. D. Goff and R. W. Hartel, Ice cream, New York: Springer, 2003.
- H. D. Goff, Ice Cream and Frozen Desserts, New Jersey : Wiley, 2015.
- G. Cruz, A. E. Antunes, A. L. Sousa, . J. A. Faria and S. M. Saad, "Ice-cream as a probiotic food carrier," Food Research International, pp. 1233-1239, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Haynes and M. J. Playne, "Survival of probiotic cultures in low-fat ice-cream," Australian Journal of Dairy Technology, pp. 10-14, 2002.
- S. Adapa, H. Dingeldein, K. Schmidt and T. Herald, "Rheological Properties of Ice Cream Mixes and Frozen Ice Creams Containing Fat and Fat Replacers," Journal of Dairy Science, pp. 2224-2229, 2000. [CrossRef]
- M. Akin, M. Akin and Z. Kirmaci, "Effects of inulin and sugar levels on the viability of yogurt and," Food Chemistry , pp. 93-99, 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. Thaiudom "Effect of ratio of milk fat to soy bean oil and whipping time on qualities of milk ice cream," Songklannakarin Journal of Science and Technology, (in Thai), vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 191-204, 2007.
- F. Javidi, S. M. A. Razavi, F. Behrouzian and A. Alghooneh, "The influence of basil seed gum, guar gum and their blend on the rheological, physical and sensory properties of low fat ice cream," Food Hydrocolloids, pp. 625-633, 2016. [CrossRef]
- H. Goff, E. Verespej and A. Smith, "A study of fat and air structures in ice cream," International Dairy Journal, pp. 817-829, 1999. [CrossRef]
- L. Abadía-García, A. Cardador, S. T. Martín del Campo, S. M. Arvízu, E. Castaño-Tostado, C. Regalado-González, B. García-Almendarez and S. L. Amaya-Llano, "Influence of probiotic strains added to cottage cheese on generation of potentially antioxidant peptides, anti-listerial activity, and survival of probiotic microorganisms in simulated gastrointestinal conditions," International Dairy Journal, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 191-197, 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Abo-srea, E. Emara and T. H. EL-Sawah, "Impact of Konjac Glucomannan on Ice Cream-like Properties," International Journal of Dairy Science, pp. 177-183, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Tyl and G. D. Sadler, "pH and Titratable Acidity," in Food Analysis, Berlin, Springer, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E. Milani, A. Madadlou, S. A. Mortazavi, R. R. Mokarram and D. Salarbashi, "Synbiotic yogurt-ice cream produced via incorporation of microencapsulated lactobacillus acidophilus (la-5) and fructooligosaccharide," Journal of Food Science and Technology, vol. 51, pp. 1568-1574, 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Rolon, A. J. Bakke, J. N. Coupland, J. E. Hayes and R. F. Roberts, "Effect of fat content on the physical properties and consumer acceptability of vanilla ice cream," Journal of Dairy Science, pp. 5217-5227, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Floury, A. Desrumaux and J. Lardières, "Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distributions and rheological properties of model oil-in-water emulsions," Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, pp. 127-134, 2000. [CrossRef]
- C. Balthazara, H. L. Silva, A. Vieira, R. Neto, L. Cappato, P. Coimbra, J. Moraes, M. Andrade, V. Calado, D. Granato, M. Freitas, M. Tavares, R. Raices, M. Silva and A. Cruze, "Assessing the effects of different prebiotic dietary oligosaccharides in sheep milk ice cream," Food Research International, pp. 38-46, 2017. [CrossRef]
- U. Isik, D. Boyacioglu, E. Capanoglu and D. N. Erdil, "Frozen yogurt with added inulin and isomalt," Journal of Dairy Science, pp. 1647-1656, 2011. [CrossRef]
- G. R. Gibson, "Fibre and effects on probiotics (the prebiotic concept)," Clinical Nutrition Supplements, pp. 25-31, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Akalin and D. Erisir, "Effects of Inulin and Oligofructose on the Rheological Characteristics and Probiotic Culture Survival in Low-Fat Probiotic Ice Cream," Journal of Food Science, pp. 184-188, 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Muse and R. Hartel, "Ice Cream Structural Elements that Affect Melting Rate and Hardness," Journal of Dairy Science, pp. 1-10, 2004. [CrossRef]
- X. Guinard, C. Zoumas-Morse, L. Mori, V. Uatoni, D. Panyam and A. Kilara, "Sugar and fat effects on sensory properties of ice cream," Journal Of Food Science, pp. 1087-1094, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M. H. Eskandari, M. Niakosari and A. Bedeltavana, "The effect of inulin on the physicochemical properties and sensory attributes of low-fat ice cream," International Dairy Journal, pp. 52-55, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Wlibey and T. Cooke, "Effects of solute concentration, overrun and storage on the hardness of ice cream," International Dairy Federation, pp. 186-187, 1998.
- R. P. Sofjan and R. W. Hartel, "Effects of overrun on structural and physical characteristics of ice cream," International Dairy Journal, pp. 255-262, 2004. [CrossRef]
- C. Balthazar, H. A. Silva, A. Vieira, R. Neto, L. Cappato, P. Coimbra, J. Moraes, M. Andrade, V. Calado, D. Granato, M. Freitas, M. Tavares, R. Raices, M. Silva and A. C. Erdil, "Prebiotics addition in sheep milk ice cream: A rheological, microstructural and sensory study," Journal of Functional Foods, pp. 564-573, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Soukoulis, I. D. Fisk and T. Bohn, "Ice Cream as a Vehicle for Incorporating Health-Promoting Ingredients: Conceptualization and Overview of Quality and Storage Stability," Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, pp. 627-655, 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. Kailasapathy and K. Sultana, "Survival and beta-D-galactosidase activity of encapsulated and free Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis in ice-cream," Australian Journal of Dairy Technology, pp. 223-227, 2003.
- C. Alamprese, R. Foschino, M. Rossi and C. Pompei, "Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG addition in ice cream," International Journal of Dairy Technology, pp. 200-206, 2005. [CrossRef]
- E. Santos Leandro, E. A. Araújo, L. L. Conceição, C. A. Moraes and A. F. Carvalho, "Survival of Lactobacillus delbrueckii UFV H2b20 in ice cream produced with different fat levels and after submission to stress acid and bile salts," Journal of Functional Foods, pp. 503-507, 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. Shah, "Functional cultures and health benefits," International Dairy Journal, pp. 1262-1277, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Begley, C. G. Gahan and C. Hill, "The interaction between bacteria and bile," FEMS Microbiology Reviews, pp. 625-651, 2005. [CrossRef]
| Ice cream formulas |
code | SMP | sucrose | glucose | butter fat | S/E | FOS | GOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control with 2% fat | C2 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0.4 | - | - |
| Control with 10% fat | C10 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 0.4 | - | - |
| 2% fat + 1% FOS | F2-1 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0.4 | 1 | - |
| 2% fat + 2% FOS | F2-2 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0.4 | 2 | - |
| 10% fat + 1% FOS | F10-1 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 0.4 | 1 | - |
| 10% fat + 2% FOS | F10-2 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 0.4 | 2 | - |
| 2% fat + 1% GOS | G2-1 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0.4 | - | 1 |
| 2% fat + 2% GOS | G2-2 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 0.4 | - | 2 |
| 10% fat + 1% GOS | G10-1 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 0.4 | - | 1 |
| 10% fat + 2% GOS | G10-2 | 13 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 0.4 | - | 2 |
| Sample | pH | Total acidityns (%) |
Overrunns (%) |
Fat particle size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | 6.464±0.01b | 0.289±0.01 | 34.54±1.41 | 0.25736a |
| G2-1 | 6.447±0.00ab | 0.279±0.01 | 34.86±0.71 | 0.23105a |
| G2-2 | 6.449±0.00ab | 0.276±0.00 | 34.30±0.54 | 0.22300a |
| F2-1 | 6.454±0.00b | 0.265±0.00 | 34.42±1.69 | 0.22198a |
| F2-2 | 6.463±0.00b | 0.272±0.00 | 35.36±0.49 | 0.21595a |
| C10 | 6.433±0.00a | 0.273±0.02 | 34.27±1.29 | 1.09153d |
| G10-1 | 6.429±0.01a | 0.285±0.00 | 34.57±1.38 | 1.01056c |
| G10-2 | 6.433±0.00a | 0.279±0.00 | 35.30±1.46 | 1.00952c |
| F10-1 | 6.429±0.00a | 0.277±0.01 | 34.62±0.79 | 0.99850c |
| F10-2 | 6.432±0.02a | 0.272±0.02 | 34.74±1.47 | 0.92681b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





