1. Introduction
Computer vision tasks can be divided into four categories, namely image classification, object location, object detection, and semantic segmentation. Among them, semantic segmentation is more advanced than the others. To improve the accuracy of segmentation, it must maximize the efficiency of an encoder to obtain relevant features and understand the context contained in an image. In semantic segmentation, the ultimate goal is to classify all the marked pixels in the image.
In the past, to improve the performance of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for semantic segmentation, pre-trained classification networks were usually used as backbones, such as VGG [
1], ResNet [
2], and DenseNet [
3] trained on ImageNet. Later, to enable the network to have a larger receptive field and also to restore small objects in an image, dilated convolution was proposed by Yu and Koltun [
4], and then was used in the subsequent research [
5,
6,
7]. To segment larger objects and solve existing multi-scale objects in an image, some techniques such as Pyramid Pooling Module in PSPNet [
8], Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling Module in DeepLabv2 [
9], and Hierarchical Feature Fusion Module in ESPNet [
10], were proposed. Later, feature fusions between encoders and decoders were proposed in recent literatures [
11,
12]. Finally, to enable computers to learn human viewing behaviors, an attention mechanism was derived, such as Squeeze-and-Excitation Block in SENet [
13] and Convolutional Block Attention Module [
14].
In the paper, we proposed an image semantic segmentation model called Dual-Pyramid Wide Residual Network (DPWRN) to solve the segmentation for cross-style datasets, which is suitable for diverse segmentation applications. In addition to an encoder and decoder frequently used in semantic segmentation, the model also consists of two extra modules to improve the accuracy of segmentation; i.e., Pyramid of Kernel paralleled with Dilation (PKD) and Multi-Feature Fusion (MFF), so-called Dual-Pyramid. Besides, in the previous work, most semantic segmentation models conducted experiments on datasets with only one style. In the paper, to evaluate the generalization of the DPWRN and its superiority over most state-of-the-art models, three datasets with completely different styles are tested in the experiments; i.e., Cambridge-driving Labeled Video Database (CamVid) [
15], Digital Retinal Images for Vessel Extraction (DRIVE) [
16], and eBDtheque [
17]. As a result, the DPWRN verified its generalization and also showed its superiority over most state-of-the-art models. In summary, we identify the novelty and contributions of this paper as follows:
A model called the DPWRN was proposed to solve image semantic segmentation, which integrated PKD and MFF to improve the accuracy of segmentation.
Three cross-style datasets were used to evaluate the generalization of the DPWRN, in contrast to only one-style dataset tested in existing semantic segmentation models.
The DPWRN achieved very good results, as compared with the state-of-the-art models; i.e., ranking second (mIoU 75.95%) on CamVid, ranking first (F1-score 83.6%) on DRIVE, and ranking the first (F1-score 86.87%) on eBDtheque.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, the previous research related to image semantic segmentation is described. In
Section 3, an image semantic segmentation model is proposed to solve the segmentation for cross-style datasets, which is suitable for diverse segmentation applications. In
Section 4, to evaluate the generalization of the proposed model and its superiority over most state-of-the-art models, three datasets with completely different styles are tested in the experiments. Finally, we make conclusions and give future work in
Section 5.
2. Related Work
The earliest deep learning network for image semantic segmentation was the Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs) proposed by Long et al. [
11], which is an end-to-end network structure for the image classification on each pixel. To improve the network performance for image semantic segmentation, pre-trained image classification networks were usually used as backbones, such as VGG [
1], ResNet [
2], and DenseNet [
3] trained on ImageNet. In the down-sampling process, using multiple pooling layers or stride convolutions, the dimensionality of an input image can be reduced, the amount of parameters is also reduced, and then a larger receptive field is obtained at the same time. Finally, the output stride of the feature map is 32. Next, in the up-sampling process, the image is restored for classification prediction.
However, output stride 32 is not beneficial to image semantic segmentation when an object size in an image is less than 32×32 since the object cannot be restored. To enable the network to have a larger receptive field and also to restore small objects in the image, dilated convolution was proposed by Yu and Koltun [
4]. In the down-sampling process, the original convolution layers in the later stages are replaced with dilated convolution layers to obtain the final high-resolution feature map. Later, Chen et al. [
5], Yamashita et al. [
6], and Liu et al. [
7] began to use dilated convolution to increase the receptive field.
In order to segment larger objects, it is important to increase the receptive field, but multi-scale objects could exist in an image. In PSPNet [
8], PPM (i.e., Pyramid Pooling Module) was proposed by Zhao et al., which uses multiple varying-size pooling kernels in parallel to obtain the features of different-scale objects. In DeepLabv2 [
9], the ASPP (i.e., Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling) module was proposed by Chen et al., which uses multiple varying-dilated-rate convolutions in parallel to obtain the features of different-scale objects. However, dilated convolution incurs gridding artifacts where adjacent pixels would lack dependence on each other. This results in local information loss, especially when too large dilated rates make the features obtained from a long distance with little correlation. To solve this problem, Mehta et al. proposed the HFF (i.e., Hierarchical Feature Fusion) module in ESPNet [
10]. The HFF module applies parallel dilated convolution and serial residuals to effectively eliminate gridding artifacts.
The receptive field can be divided into low, medium, and high, determined by the depth of an encoder. A deeper-layer encoder produces higher-order features, whereas a shallower-layer encoder produces lower-order features. If only high-order features are used to restore an image in a decoder, segmentation results could be inaccurate. Thus, Feature fusions between encoders and decoders were proposed. Long et al. [
11] defined a skip architecture that combines semantic information from a deep, coarse layer with appearance information from a shallow, fine layer to produce accurate and detailed segmentations. Besides, Ronneberger et al. [
12] proposed U-Net where the feature map of the decoder is concatenated with the correspondingly cropped feature map from the encoder to produce more accurate segmentations.
When humans watch a scene, they observe each block in the scene carefully by means of local attention and find the most significant part so as to understand the content of all objects in the scene. For the so-called contexts in an image, if only adjacent pixels are considered for semantic segmentation, the results will be inaccurate, especially at the boundary between two different object types. To enable computers to learn human viewing behaviors, an attention mechanism was derived. Hu et al. proposed the SE (i.e., Squeeze-and-Excitation) block in SENet [
13], which uses the channel attention mechanism to let the neural network learn what to look at, but the contexts of an image are not fully utilized. To solve this problem, Woo et al. [
14] proposed CBAM (i.e., Convolutional Block Attention Module) which uses not only a channel attention mechanism but also a spatial attention mechanism, enabling the neural network to learn what to look at and which parts of an object to look at.
3. Proposed Models
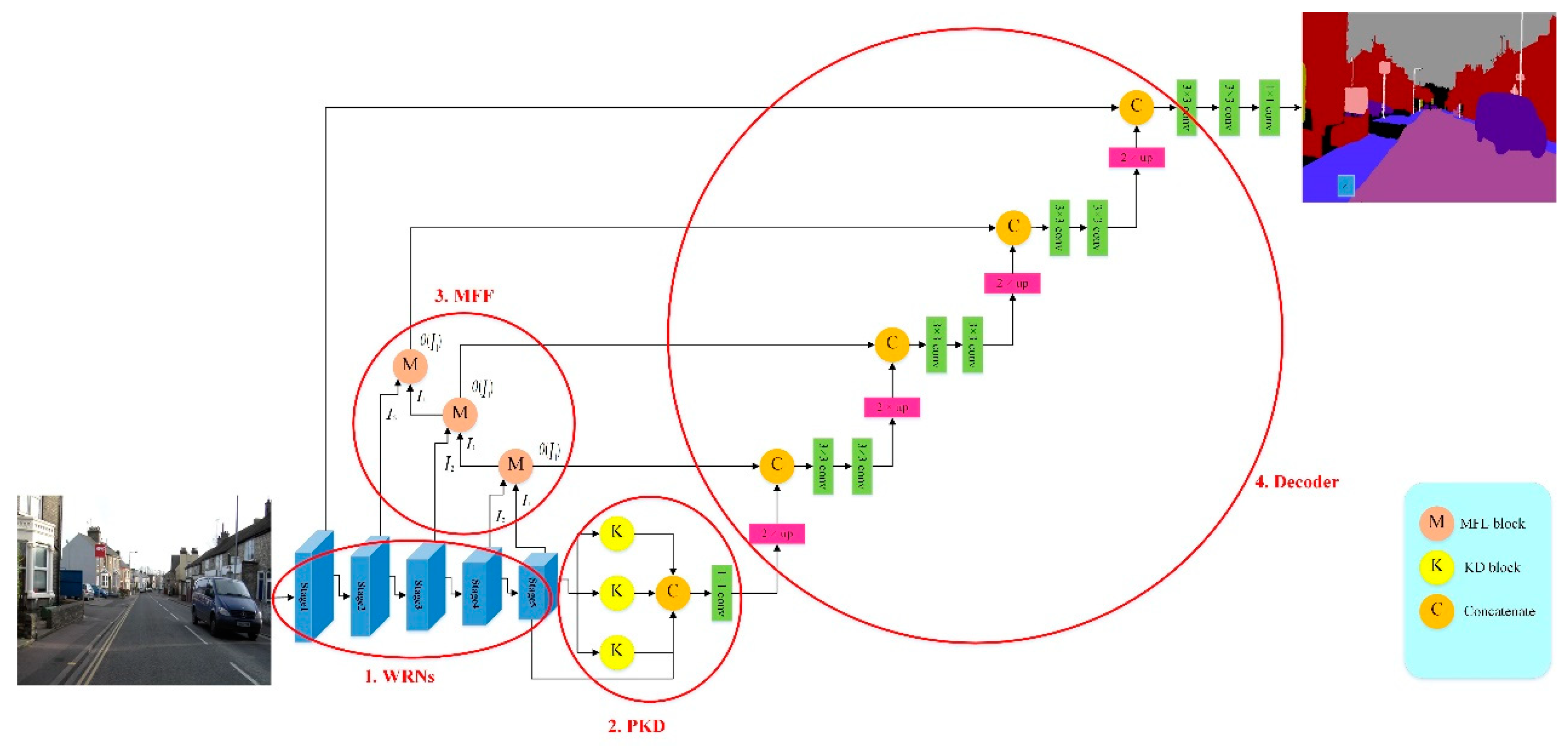
In this paper, we proposed an image semantic segmentation model called Dual-Pyramid Wide Residual Network (DPWRN) to solve the segmentation for cross-style datasets, which is suitable for diverse segmentation applications, as shown in
Figure 1. The whole architecture is composed of four modules; i.e., 1) encoder - Wide Residual Networks (WRNs), 2) Pyramid of Kernel paralleled with Dilation (PKD), 3) Multi-Feature Fusion (MFF), and 4) decoder.
The encoder uses a WRN as the backbone to extract the features of an image. Through 5 stages in the WRN, the high-level features of an image are extracted. However, if only the high-level features are used in the semantic segmentation, the segmentation is not good enough, because multi-scale objects and small objects in an image are not taken into account in the WRN. To make full use of all the features (i.e., high-level, mid-level, and low-level), the features should be further processed; i.e., processing them through the PKD module and processing them through the MFF blocks. The PKD module refines the high-level features from stage 5 using asymmetric convolution and dilated convolution, thereby solving multi-scale object problems. The MFF blocks fuse the high-level, mid-level, and low-level features from each stage, and effectively detect small objects. Finally, the results of the PKD module and the MFF blocks are concatenated together in the decoder to achieve the semantic segmentation of an image.
3.1. Wide Residual Networks
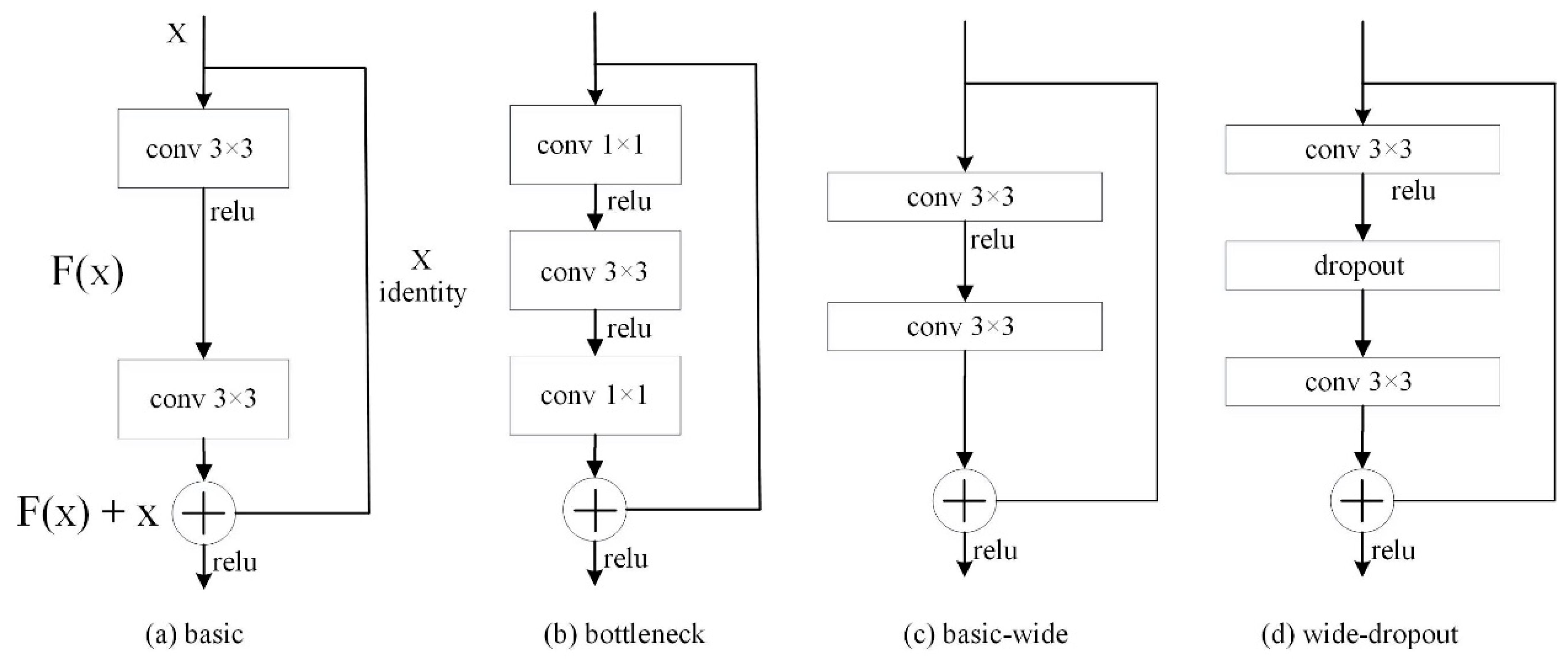
In general, for a deep learning network, the deeper the network is, the more it learns. However, as the network is too deep, network degradation can happen; in other words, the deeper the convolution is, the less likely the network learns effective features. Then, the classification accuracy of the network will decrease and be even worse than that of a shallow network. Thus, He et al. [
2] proposed deep residual neural networks for image recognition. By stacking residual blocks as shown in
Figure 2a,b, the deep residual neural network performs identify mapping which makes better features learned in shallow convolutional layers to map to deeper convolutional layers, thereby avoiding network degradation when it is too deep. However, there is no guarantee that each convolutional layer can learn effective weights. Later, Zagoruyk and Komodakis [
18] proposed a wide residual network which is a shallower and wider network, and the used residual blocks are shown in
Figure 2c,d.
In short, the residual blocks used in a residual network [
2] could be basic and bottleneck, as shown in
Figure 2a,b. For a deep network, a bottleneck residual block is a variant of the residual block, which utilizes 1×1 convolution to create a bottleneck reducing the number of parameters and matrix multiplications. The goal is to make residual blocks as thin as possible to increase depth and have fewer parameters. Then, it restores the dimensionality through another 1×1 convolution. Besides, the residual blocks used in a wide residual network [
18] could be basic-wide and wide-dropout, as shown in
Figure 2c,d. A basic-wide residual block using more filters is wider than a basic residual block, and a wide-dropout residual block uses dropout to avoid overfitting when more parameters are trained in a neural network.
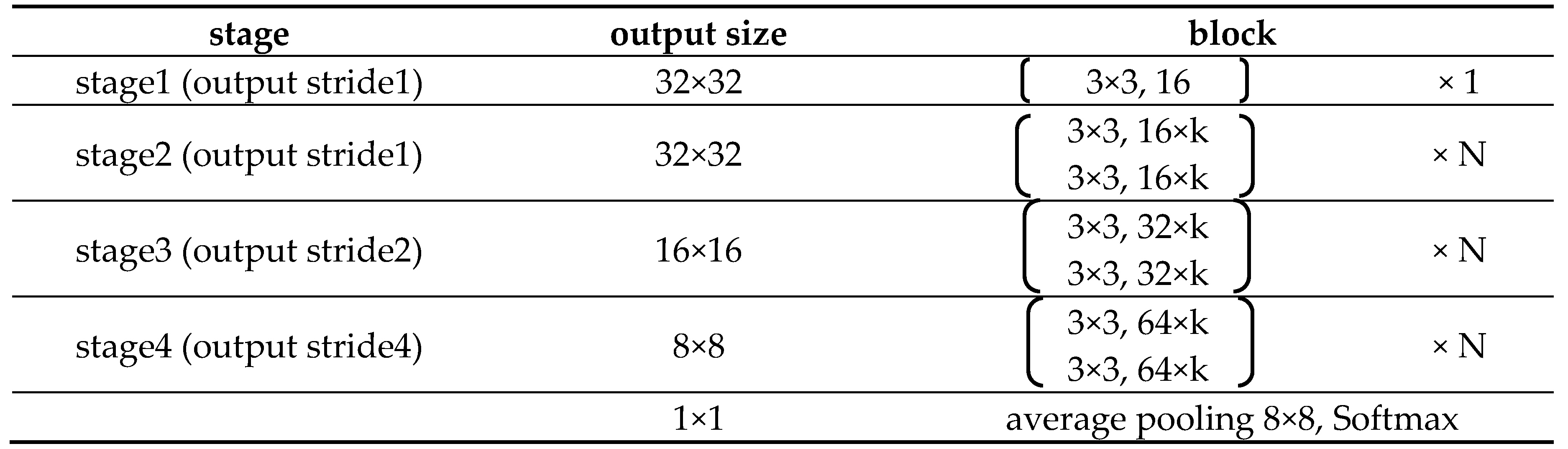
The architecture of the original WRN is shown in
Table 1 where two coefficients k and N are used to adjust the width and depth of the network, respectively. Coefficient k is the multiplier of the fixed filter number corresponding to the block in its stage and determines the width of the network. Coefficient N specifies how many blocks are needed in a stage and determines the depth of the network.
In the original WRN, Zagoruyk and Komodakis set coefficients k and N to a larger value in stage 1 and stage 2 (i.e., in output stride 1). This operation makes the network keep a fixed width and depth at the beginning of training. Although it can improve the network’s performance, the network is only suitable for small images, just as only the Cifar10 dataset was used as the subject in Zagoruyk and Komodakis’s experiments. As a result, the original WRN cannot be applied to larger images. Besides, since the wider and deeper network in the early stage incurs too many parameters to be trained, the graphics card memory cannot be sufficiently supported in general and the training would be disrupted.
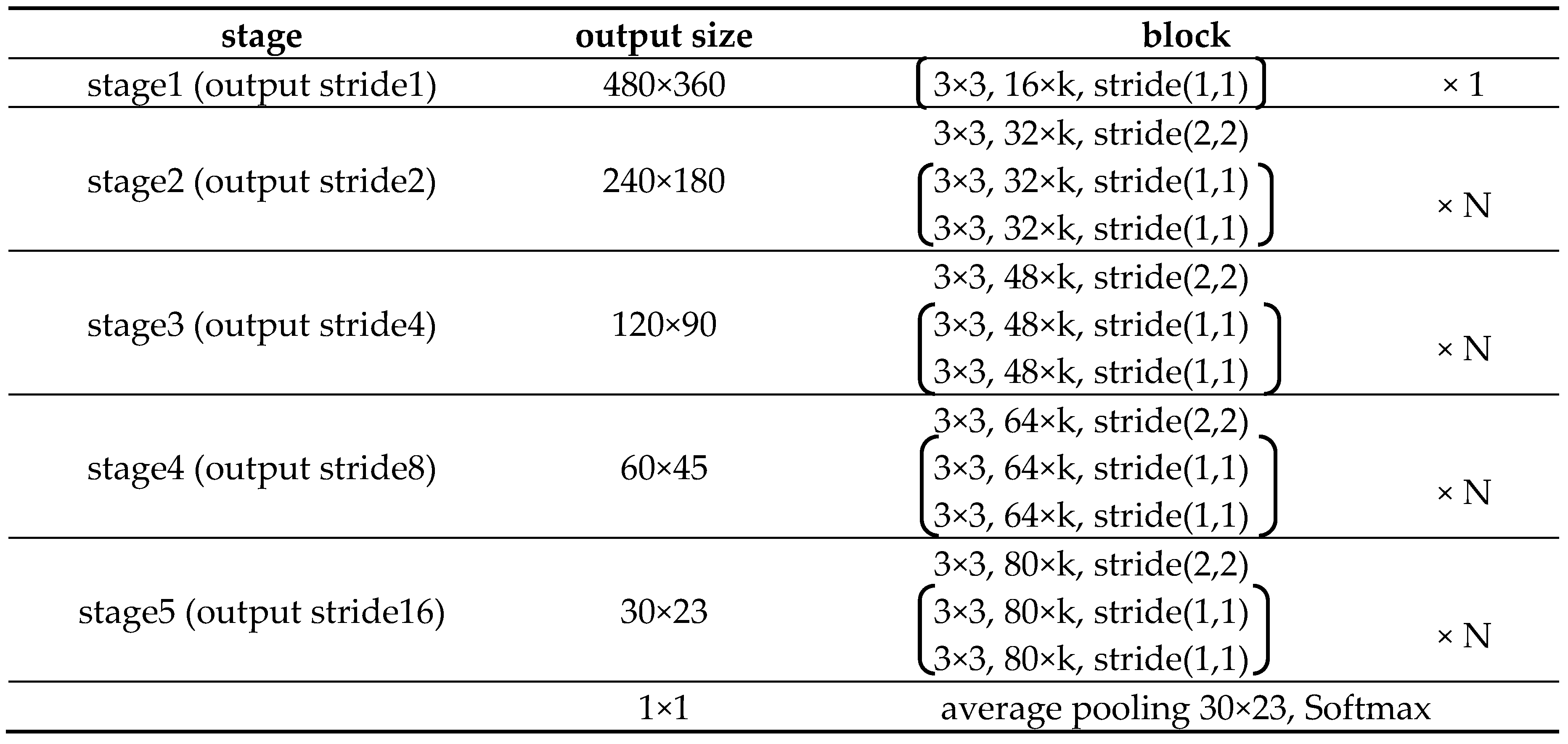
In our study, the WRN can be modified to achieve better performance than Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNN), based on keeping a balance between the width and depth of the network. For datasets with larger images, the modified WRN requires more stages (i.e., five stages) in the down-sampling path, and the output stride of stage 5 is changed into 16 to increase the receptive field; in other words, in contrast with the original WRN down-sampling performed by the first layers in stage 3 and stage 4, the modified WRN performs down-sampling in the first layers from stage 2 to stage 5. Besides, the stage 1 process in the original WRN is not used in the modified WRN. Finally, we redefine coefficient k corresponding to the blocks in all the stages. The architecture of the modified WRN is shown in
Table 2. The last average pooling layer is just used to pre-train the modified WRN and is not used in the proposed model.
3.2. Pyramid of Kernel Paralleled with Dilation
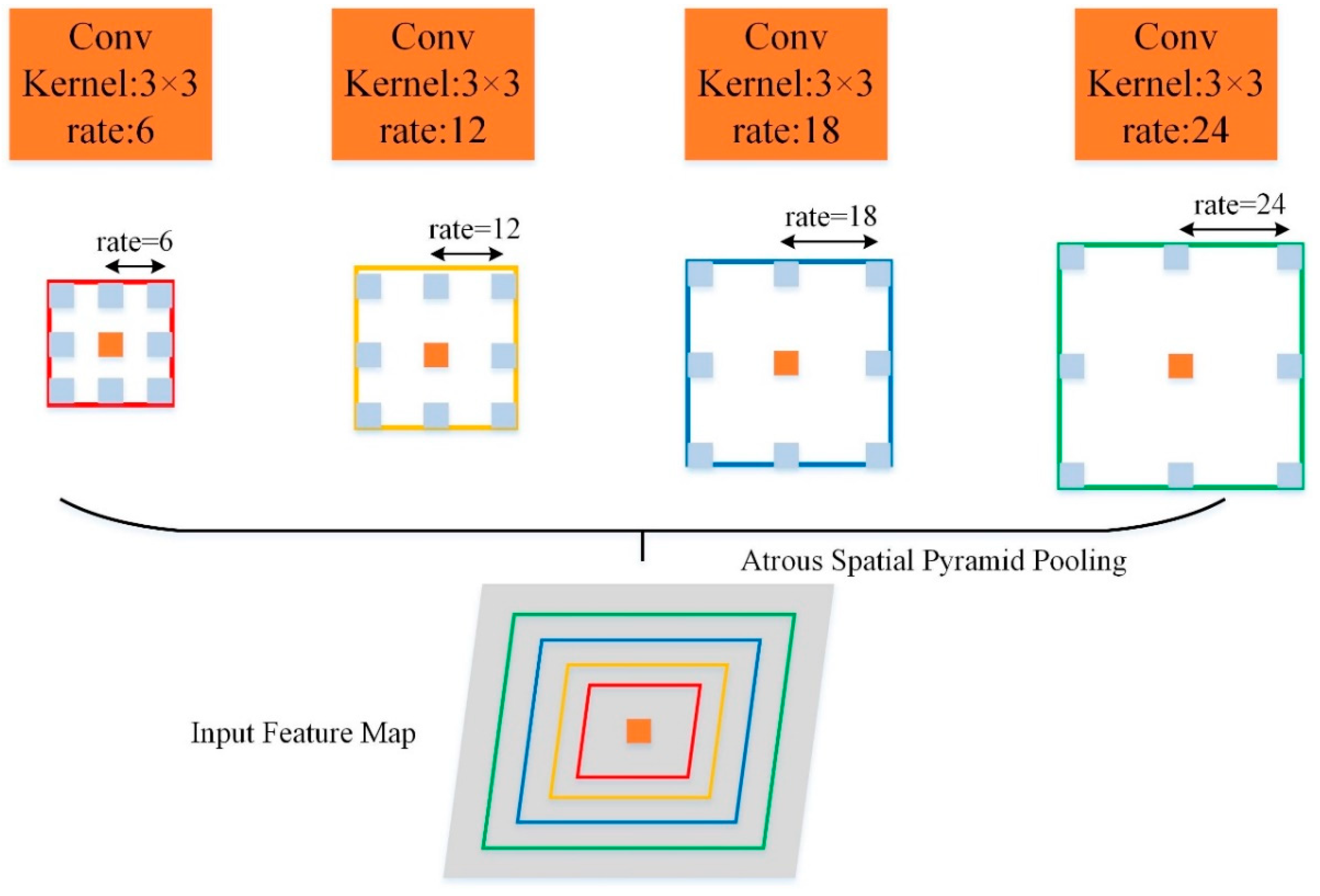
Objects in an image have multiple scales. Even objects of the same category have different scales due to the distance the image is taken from. Here, two methods are referred to and integrated together to solve this problem. One is the ASPP (i.e., Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling) module proposed by Chen et al. in DeepLabv2 [
9], which uses multiple varying-dilated-rate convolutions in parallel to obtain the features of different-scale objects, as shown in
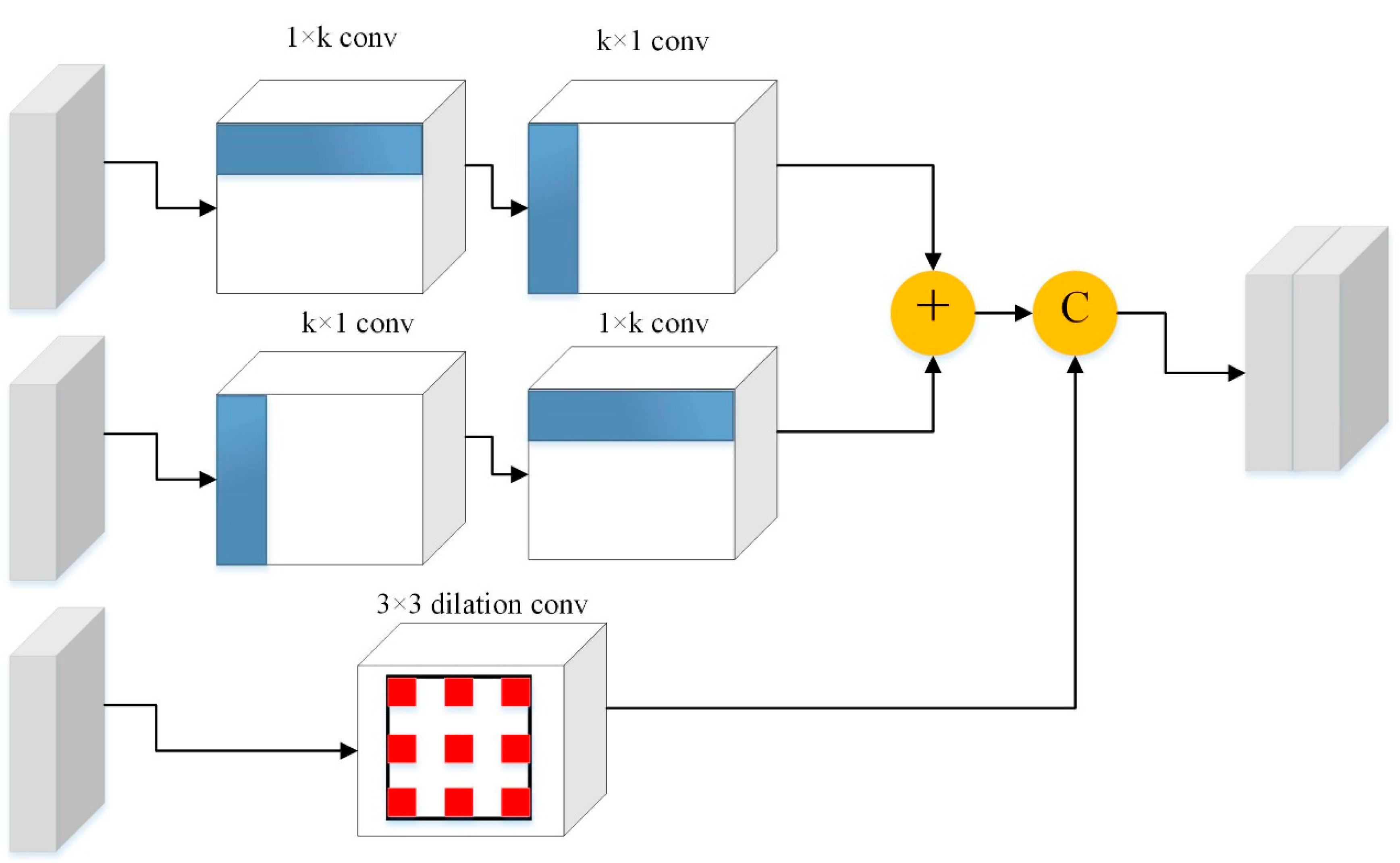
Figure 3. Another is the LKD (i.e., Large Kernel paralleled with Dilation) block proposed by Liu et al. [
7], as shown in
Figure 4, which uses the features from the dense kernels obtained by asymmetric convolution and the features from the sparse kernels of obtained by dilated convolution. The fusion of these two kinds of features effectively enhances the receptive field and solves the gridding artifacts caused by dilated convolution. In our model, three KD (i.e., Kernel paralleled with Dilation) blocks with coefficient k of asymmetric convolution set to 3 are used to obtain denser features, compared with original LKD blocks with larger coefficient k. Besides, the dilated convolution rate of these three KD blocks is set to 6, 12, and 18, respectively. By imitating the ASPP module, these three KD blocks are paralleled with different dilated rates. Finally, the feature maps output by these three KD blocks and the feature map output by stage 5 are concatenated together and then proceed to the next 1×1 convolution. Here, we call the integration PKD (i.e., Pyramid of Kernel paralleled with Dilation) module.
3.3. Multi-Feature Fusion
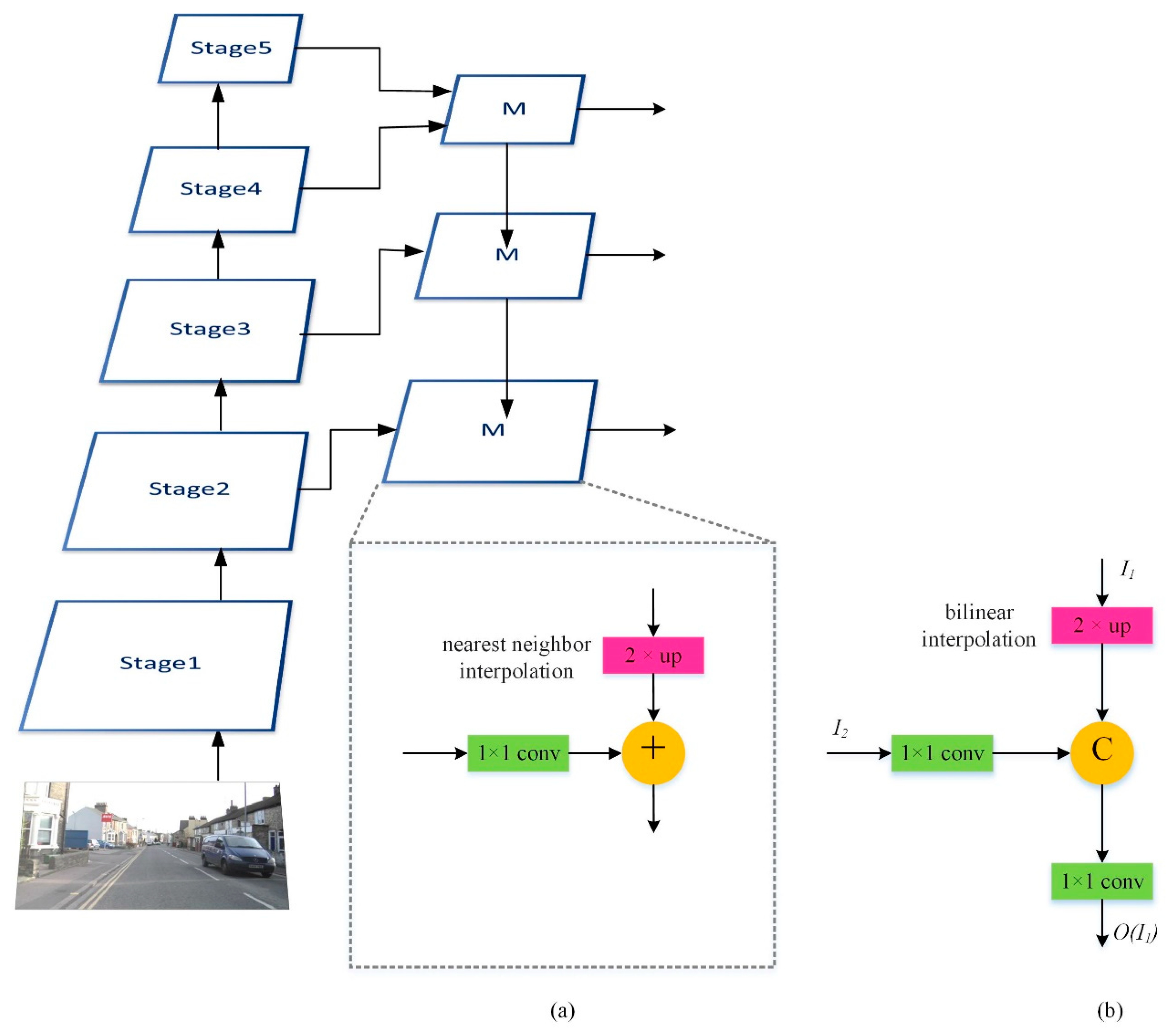
The multi-scale features provided by the PKD module are only for larger objects since the PKD module uses the high-level features output from stage 5 in the WRN. In other words, the PKD module cannot yet provide precise features for smaller objects. Here, the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) proposed by Lin et al. [
19], as shown in
Figure 5a, is used for target detection. It is composed of a bottom-up pathway, a top-down pathway, and lateral connections. The bottom-up pathway is the encoder part used to obtain the features of different resolutions; i.e., the WRN in our model, whereas the top-down pathway uses feature fusion techniques. The feature maps of the upper layers have smaller resolutions but have richer high-level image information. On the other hand, the feature maps of lower layers have larger resolutions but have more low-level image information. For the feature fusion techniques, the deepest feature map of the encoder is passed to the top layer in the top-down pathway, and each layer in the top-down pathway up-samples the features from the previous layer by a factor of 2 (using nearest neighbor interpolation) and then merges them with the features (processed through 1×1 convolution) from the corresponding layer in the bottom-up pathway; i.e., adding them together. Since the FPN considers high-level, mid-level, and low-level features at the same time, it can effectively detect large and small objects. Here, we modify the feature fusion of the FPN and call it a Multi-Feature Fusion (MFF) block, as shown in
Figure 5b. The nearest neighbor interpolation in the up-sampling operations is replaced with the bilinear interpolation. Then, the original feature fusion operation is replaced with concatenation, and the 1×1 convolution is added to reduce the output dimensionality. The MFF block makes full use of the context in an image so that more accurate segmentation results can be achieved.
3.4. Decoder
The purpose of the decoder is to restore the image to the original size and to present the segmentation results, in contrast to the encoder which reduces the image resolution through multiple down-sampling operations to obtain the features. In the WRN, four down-sampling operations are used and the resolution of the final feature map becomes 1/16 of the original image size. To restore the image to the original size, the decoder requires four up-sampling operations. In the first three up-sampling operations, the results of the up-sampling operations are concatenated with the feature map from the MFF blocks for further processing. But, in the last up-sampling operation, the results of the up-sampling operation are concatenated with the feature map from stage 1 in the WRN. In the decoder, the up-sampling operations just use bilinear interpolation to enlarge the image resolution and are without any learning. Therefore, after each up-sampling operation, two 3×3 convolutional layers are needed to learn how to restore the image. After the feature map is restored to the original size, we need a 1×1 convolutional layer for prediction using the Softmax function, where the number of filters is the number of categories in the dataset.
4. Experiments
In this section, to evaluate the generalization of the proposed model and its superiority over most state-of-the-art models, three datasets with completely different styles are selected and tested in the experiments; i.e., Cambridge-driving Labeled Video Database (CamVid) [
15], Digital Retinal Images for Vessel Extraction (DRIVE) [
16], and eBDtheque [
17]. In the following subsections, we introduce the datasets used in the experiments, the experimental environments, and the evaluation indicators used to compare the proposed model with the state-of-the-art models. Finally, we present the experimental results of the model on CamVid, DRIVE, and eBDtheque, and validate its superiority over most state-of-the-art models.
4.1. Datasets
CamVid is the earliest urban street view dataset used for semantic segmentation. The videos in the dataset were taken by a car driving in Cambridge. It is composed of five video sequences, and each frame of the video is 960×720 pixels. In total, it provides 701 images with annotations where 367 images are for training, 101 images for validation, and 233 images for testing. Although 32 categories of objects are provided in Camvid, only the combined 11 categories were presented and used in most literature since some categories appear less frequently in the videos.
DRIVE is the retinal blood vessel segmentation dataset, and each image is with 584×565 pixels. It consists of 40 colored fundus images with annotations where 20 images are for training and 20 images for testing. Only 2 categories are provided in DRIVE; i.e., background and blood vessels.
eBDtheque is the dataset of comic collections, including America, Japan, and Europe. It is composed of 100 comic images with different sizes of pixels, and a total of 850 panels, 1092 balloons, 1550 comic characters, and 4691 lines of text.
4.2. Experimental Environments
The proposed model was implemented in TensorFlow 2.0 [
20] and trained on the platform NVIDIA Titan RTX 24GB. The optimizer used is Adam [
21] (learning rate 0.0001, beta1 0.9, beta2 0.999), and the loss function used is categorical cross-entropy. The batch size of these three datasets used to train the model is all set to 2. However, the numbers of epochs for training on these three datasets are not the same; i.e., 15 for CamVid, 15 for DRIVE, and 300 for eBDtheque. The hyper-parameters k and N of our encoder on CamVid and eBDtheque are set to 10 and 3, respectively, whereas the k and N on DRIVE are set to 8 and 4. Besides, to improve the experimental results on CamVid, two pre-training processes are required. First, the weights of the model were pre-trained on the Cifar100 dataset [
22]. Then, the weights of the model were further pre-trained on the Cityscapes dataset [
23], and finally, the weights of the model of the model were trained again on the target CamVid.
Here, we pre-processed the datasets for training the model. For CamVid, we resized the sizes of the images to 480×360 and expanded the original training set from 367 to 3000. The augmentation method is to conduct horizontal flips and rotations at random on the images. For DRIVE, we adopted the expanded training set (i.e., from the original 20 to 234) used in the SA-Unet [
24] and resized the sizes of the images to 480×480 for training. Finally, the images of eBDtheque were all resized to 480×480 for training.
4.3. Evaluation Indicators
To compare the proposed model with the state-of-the-art models, we use different evaluation indicators on these three datasets.
For CamVid, the standard mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) is used to evaluate the segmentation results as follows:
For DRIVE, Sensitivity (SE), Specificity (SP), Accuracy (ACC), Area under the Curve (AUC), and F1-Score are used to evaluate the segmentation results as follows:
For eBDtheque, since no test sets are supported, 5-fold cross-validation is used to evaluate the segmentation results, based on Precision, Recall, and F1-score.
4.4. Experimental Results on CamVid
In this subsection, the ablation experiments were conducted first to verify the benefits of considering the PKD module and MFF blocks in the proposed model. Then, to optimize the benefits of the PKD module and MFF blocks, we turned to refine the CamVid dataset and conducted progressive training. Finally, we present the comparisons among the state-of-the-art models on CamVid and the segmentation results of our model.
4.4.1. Ablation Study for the PKD Module and MFF Blocks
As mentioned in
Section 3, the PKD module and MFF blocks facilitate the encoder to grasp the context in an image, thereby achieving more accurate segmentation results. As shown in
Table 3, considering the PKD module and/or MFF blocks in the model significantly improves the segmentation results, especially the MFF blocks. In total, the mIoU increases by 2.12%, as compared with only using the encoder.
4.4.2. Progressive Training
To optimize the benefits of the PKD module and MFF blocks and then to further promote the mIoU (i.e., 75.83) of the model, we turned to refine the CamVid dataset. The refined datasets were used in a series of training called progressive training. As mentioned in
Section 4.2, we expanded the original training set of CamVid from 367 to 3000 by conducting horizontal flips and rotations randomly on the images. In the refining process, a total of 8 training sets called Data1~Data8 are expanded, and each one has the same 3000 images. The differences between these 8 datasets are 1) random horizontal flips and rotations on images and 2) dividing the length and width of images by equal proportions, then enlarging images, and finally random cropping. The division ratios of Data1~Data8 are 0.6 (i.e., enlarging most), 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.85, 0.9, and 1 (i.e., retaining the original size).
Then, progressive training is used to test if the refined datasets can be used to promote the mIoU of the model. First, the model was trained using Data1, then trained using Data2, and so on until Data8 was used. During the progressing training, if any dataset cannot promote the mIoU, the dataset is discarded. As shown in
Table 4, the training using Data4, Data5, and Data 7 reduces the mIoU of the model, so they are not considered in the later training. Finally, the mIoU after the progressive training is promoted to 75.95%, as compared with the mIoU of 75.83% as shown in
Table 3.
4.4.3. Comparisons and Segmentation Results
As shown in
Table 5, the IoU of each category and/or the mIoU of all the models including ours are presented. Our model (full) is in the 2nd place and performs better than most state-of-the-art models. Although DeepLabV3Plus+SDCNetAug proposed by Zhu et al. [
25] has the best mIoU, the training dataset was augmented by the synthesized samples that led to significant improvements in accuracy; in other words, the images in the training dataset are not completely real. Besides, the segmentation results of our model on CamVid are visualized as shown in
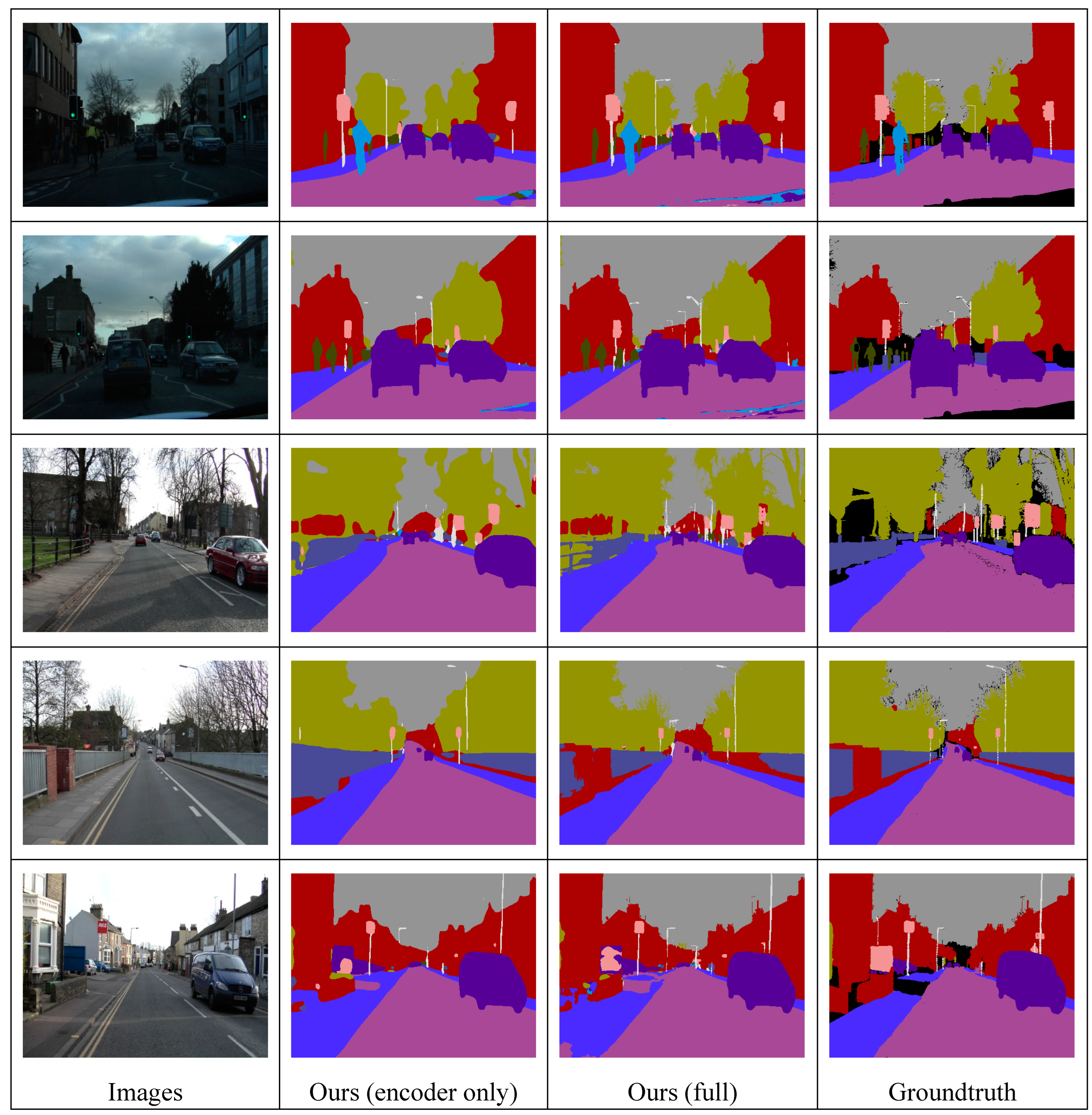
Figure 6. We can find that considering the PKD module and MFF blocks in the proposed model achieves more accurate segmentation results of small objects, especially Sign, Pedestrian, and Pole.
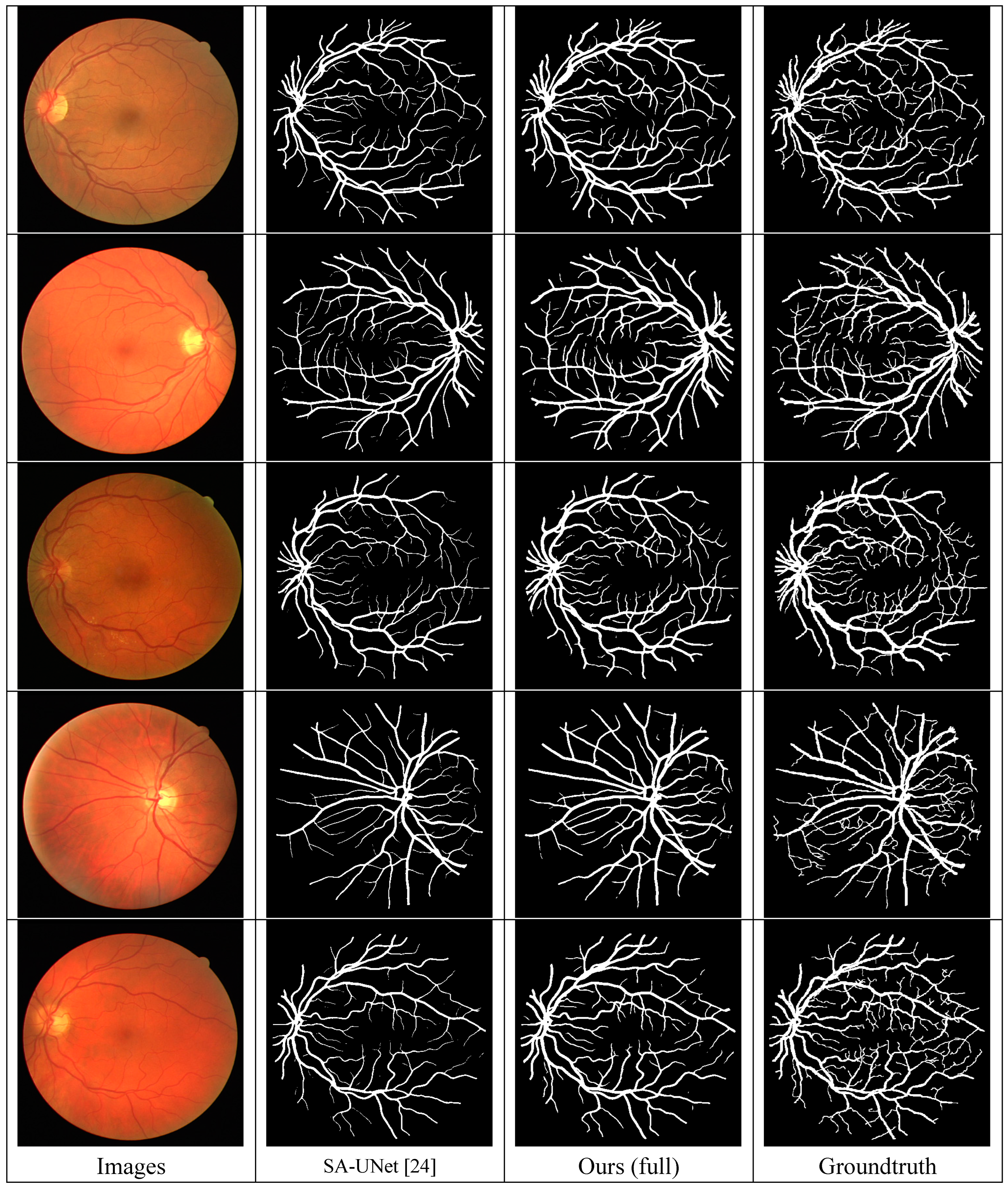
4.5. Experimental Results on DRIVE
To verify the generalization of the proposed model, we conducted experiments on DRIVE and compared it with the state-of-the-art models. As mentioned in
Section 4.2, we adopted the expanded training set used in the SA-Unet [
24] for training. As shown in
Table 6, our model (full) is in the 2nd place (83.07%) for SE and in the first place (83.60%) for F1-score, where F1-score increases by 0.97%, as compared with the SA-Unet [
24]. Besides, the segmentation results of SA-UNet [
24] and our model on DRIVE are visualized as shown in
Figure 7.
4.6. Experimental Results on eBDtheque
We also conducted experiments on eBDtheque to verify the generalization of our model and compared it with the state-of-the-art models. As shown in
Table 7, our model (full) is the best one (84.86%) for Recall and also the best one (86.87%) for F1-score. Besides, the segmentation results of Dubray and Laubrock [
43] and our model on eBDtheque are visualized as shown in
Figure 8. We can find that the segmentation results of Japanese-style comics are relatively poor, as shown in the second row, because most of the comics in eBDtheque are mainly European and American styles.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, we proposed an image semantic segmentation model called Dual-Pyramid Wide Residual Network (DPWRN) to solve the segmentation for cross-style datasets. First, it uses the WRN to extract the features of an image. Then, the features are further processed and fused through the PKD module and MFF blocks. This process makes full use of the context in the image and makes the segmentation more accurate. Finally, the image is restored through the decoder, and the pixels are classified. Next, we conducted the experiments on three datasets with completely different styles, including CamVid for urban street scenes, DRIVE for retinal blood vessels, and eBDtheque for comics, and then compared the proposed DPWRN with the state-of-the-art models. As a result, the DPWRN verified its generalization and also showed the superiority over most state-of-the-art models.
In the future, since an encoder architecture has strong influences on the results of semantic segmentation, we expect to extract the optimal features from the encoder. We will use the Self-adaptive Harmony Search Algorithm proposed by Wang and Huang [
49] to optimize coefficient k, coefficient N, and the number of filters multiplied by k in all the stages of the WRN, based on different datasets. so that the optimal features of an image can be obtained from the WRN.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Yin-Fu Huang; methodology, Yin-Fu Huang; software, Guan-Ting Shen; validation, Guan-Ting Shen; writing—original draft preparation, Guan-Ting Shen; writing—review and editing, Yin-Fu Huang; supervision, Yin-Fu Huang.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1409.1556v6 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27-30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 21-26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1511.07122v3 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1706.05587v3 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, T.; Furukawa, H.; Fujiyoshi, H. Multiple skip connections of dilated convolution network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Athens, Greece, 7-10 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Pang, Y.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S.; Shao, L. Filling the gaps in atrous convolution: semantic segmentation with a better context. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 34019–34028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 21-26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7-12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5-9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 12-18 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Staal, J.; Abramoff, M.D.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; van Ginneken, B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, C. et al. In eBDtheque: a representative database of comics. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 25-28 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Wide residual networks. arxiv, 2017; arXiv:1605.07146v4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 21-26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M. et al. In TensorFlow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Savannah, GA, USA, 2-4 Nov. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1412.6980v9. [Google Scholar]
- CIFAR-100. Available online: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html.
- Cordts, M. et al. In The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27-30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Yi, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Fan, C. SA-UNet: spatial attention u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Milan, Italy, 10-15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. et al. In Improving semantic segmentation via video propagation and label relaxation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15-20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Hsu, W.T.; Chiu, C.Y.; Wu, T.F.; Sun, M. Efficient uncertainty estimation for semantic segmentation in videos. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. BiSeNet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bilinski, P.; Prisacariu, V. Dense decoder shortcut connections for single-pass semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Couprie, C.; Kokkinos, I. Deep spatio-temporal random fields for efficient video segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.C.; Chiu, C.T.; Hsiao, S.C. Semantic segmentation via enhancing Context Information by fusing multiple high-level features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems, Coimbra, Portugal, 20-22 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Kamiya, T. WideSegNeXt: semantic image segmentation using wide residual network and next dilated unit. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 11427–11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Fully convolutional pyramidal networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 229132–229140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liskowski, P.; Krawiec, K. Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2016, 35, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, J.I.; Prokofyeva, E.; Blaschko, M.B. A discriminatively trained fully connected conditional random field model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2017, 64, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.T. Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2018, 65, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. Multiscale network followed network model for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 16-20 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, S.; He, H. Dual encoding U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13-17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Cai, W. Vessel-Net: retinal vessel segmentation under multi-path supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13-17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yang, M.; Tang, M.; Xu, Y. Attention guided network for retinal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13-17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Verma, M.; Nakashima, Y.; Nagahara, H.; Kawasaki, R. IterNet: retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1-5 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, H. Study group learning: improving retinal vessel segmentation trained with noisy labels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September– 1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dubray, D.; Laubrock, J. Deep CNN-based speech balloon detection and segmentation for comic books. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Sydney, Australia, 20-25 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.; Tolle, H. Method for real time text extraction of digital manga comic. International Journal of Image Processing 2011, 4, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, A.K.N.; Burie, J.; Ogier, J. Panel and speech balloon extraction from comic books. In Proceedings of the 10th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia, 27-29 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud, C.; Burie, J.; Ogier, J.; Karatzas, D.; van de Weijer, J. An active contour model for speech balloon detection in comics. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 25-28 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud, C.; Burie, J.; Ogier, J. Text-independent speech balloon segmentation for comics and manga. In Proceedings of the IAPR International Workshop on Graphics Recognition, Sousse, Tunisia, 20-21 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Rigaud, C.; Burie, J.C. Multi-task model for comic book image analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Thessaloniki, Greece, 8-11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.M.; Huang, Y.F. Self-adaptive harmony search algorithm for optimization. Expert Systems with Applications 2010, 37, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).