Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
24 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
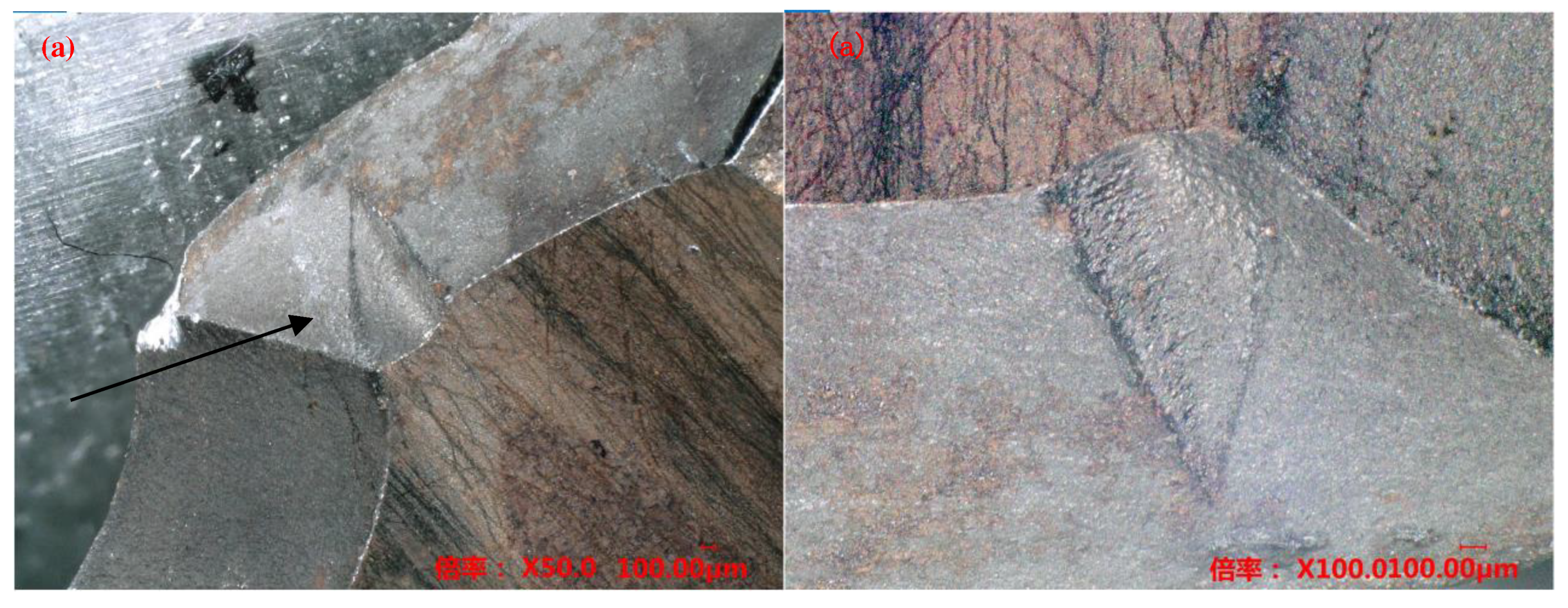
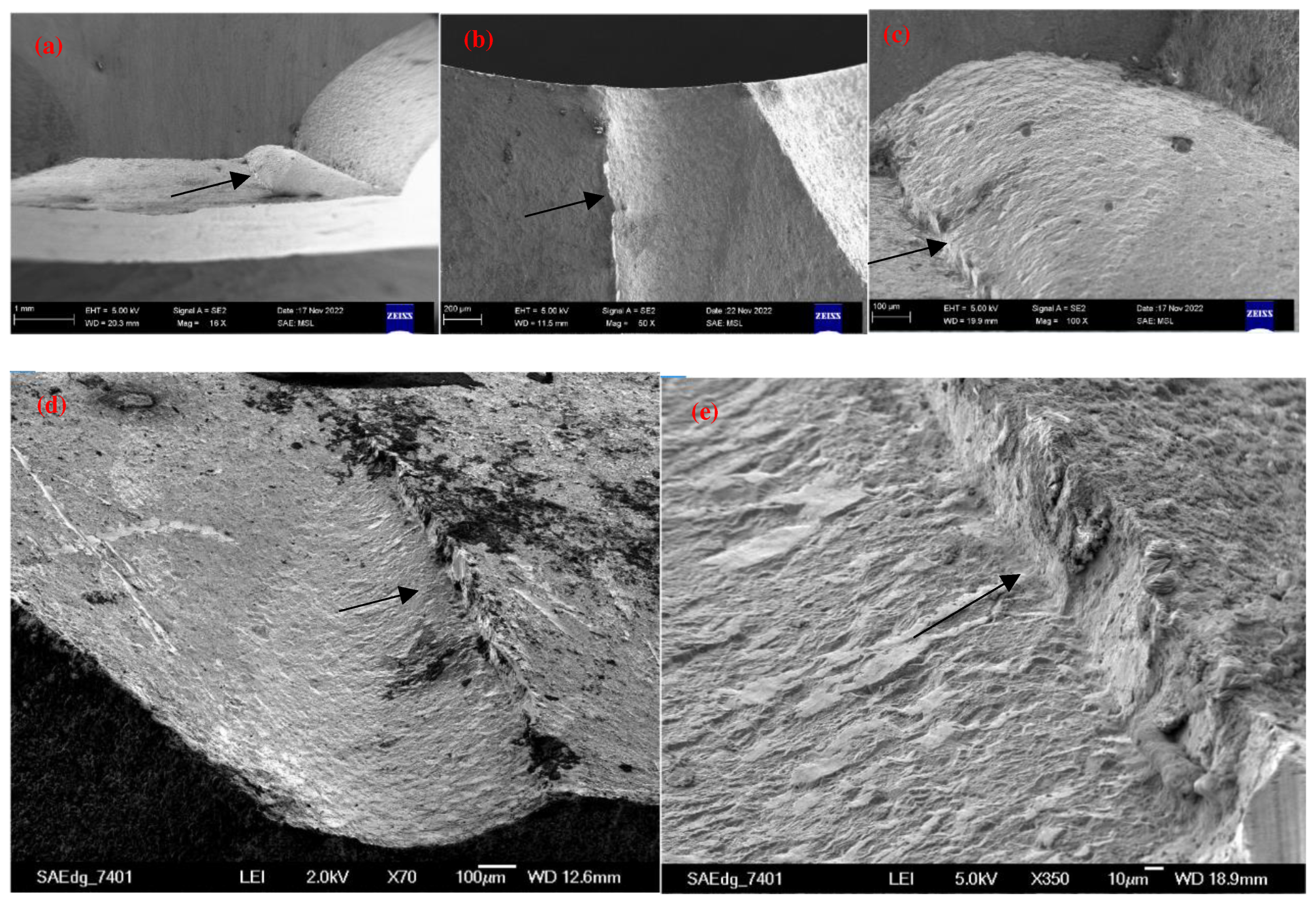
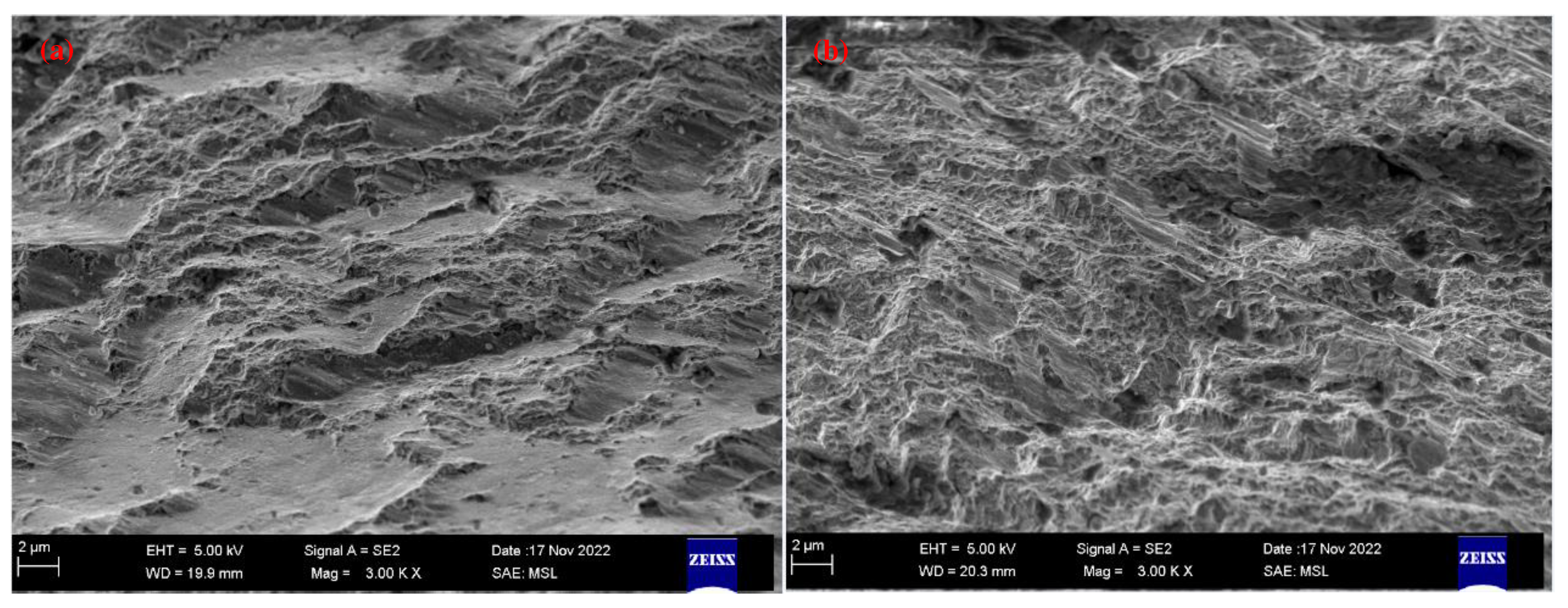
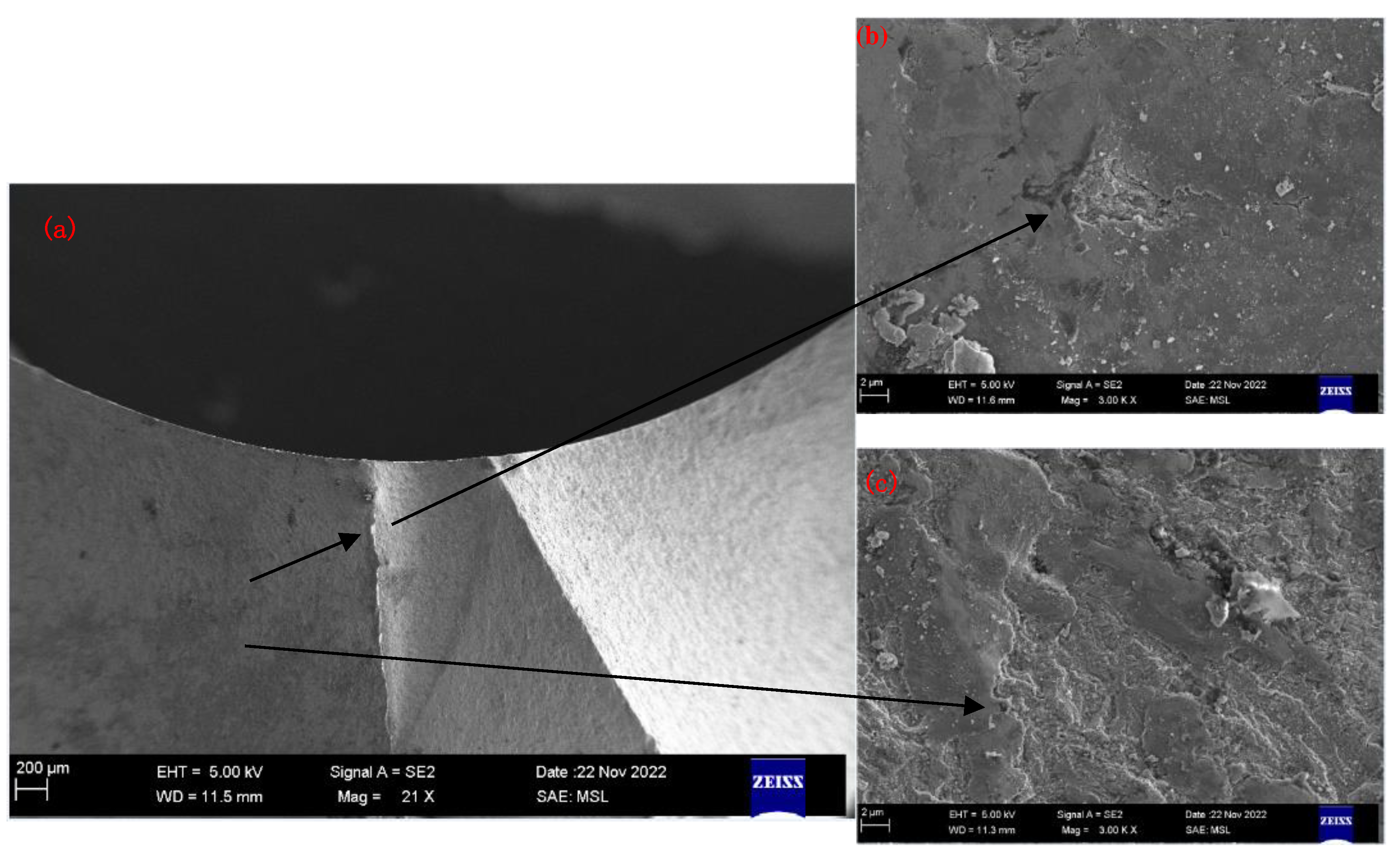
2.1. Detecting and analyzing the causes of mold fractures in parts
- (1)
- Material internal defects and stress concentration: The presence of different types and sizes of defects, such as inclusions, pores, slags, and internal cracks, could cause stress concentration and expand under stress, leading to brittle fracture. This type of stress concentration could cause brittle fracture of low-carbon steel molds.
- (2)
- Material quality issues: If the material had uneven quality or inclusions, it could decrease the strength and toughness of the steel, making it increasingly susceptible to fracture under stress. In addition, cracks and corrosion on the surface of the steel could be responsible for static load fracture.
- (3)
- Mold electroplating quality: The quality of the electroplating coating on the mold surface could lead to mold fracture issues. Possible electroplating issues included the following:
- (a)
- Uneven thickness of the electroplating coating, which could cause uneven stress distribution on the mold surface, leading to cracks or plastic deformation and affecting the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the mold.
- (b)
- The problematic coating structure could affect the strength and toughness of the coating, making it prone to cracks and breakage during mold operation.
- (c)
- A high number of nonmetallic inclusions in the coating could affect the density of the coating and cause its toughness to decrease, leading to cracking or breakage.
- (d)
- The poor quality and surface roughness of the coating, which could attract small impurities, such as air and dust, further affecting its appearance and function. The presence of coating bubbles, delamination, or looseness could reduce the corrosion and protection functions, reducing the service life of the mold.
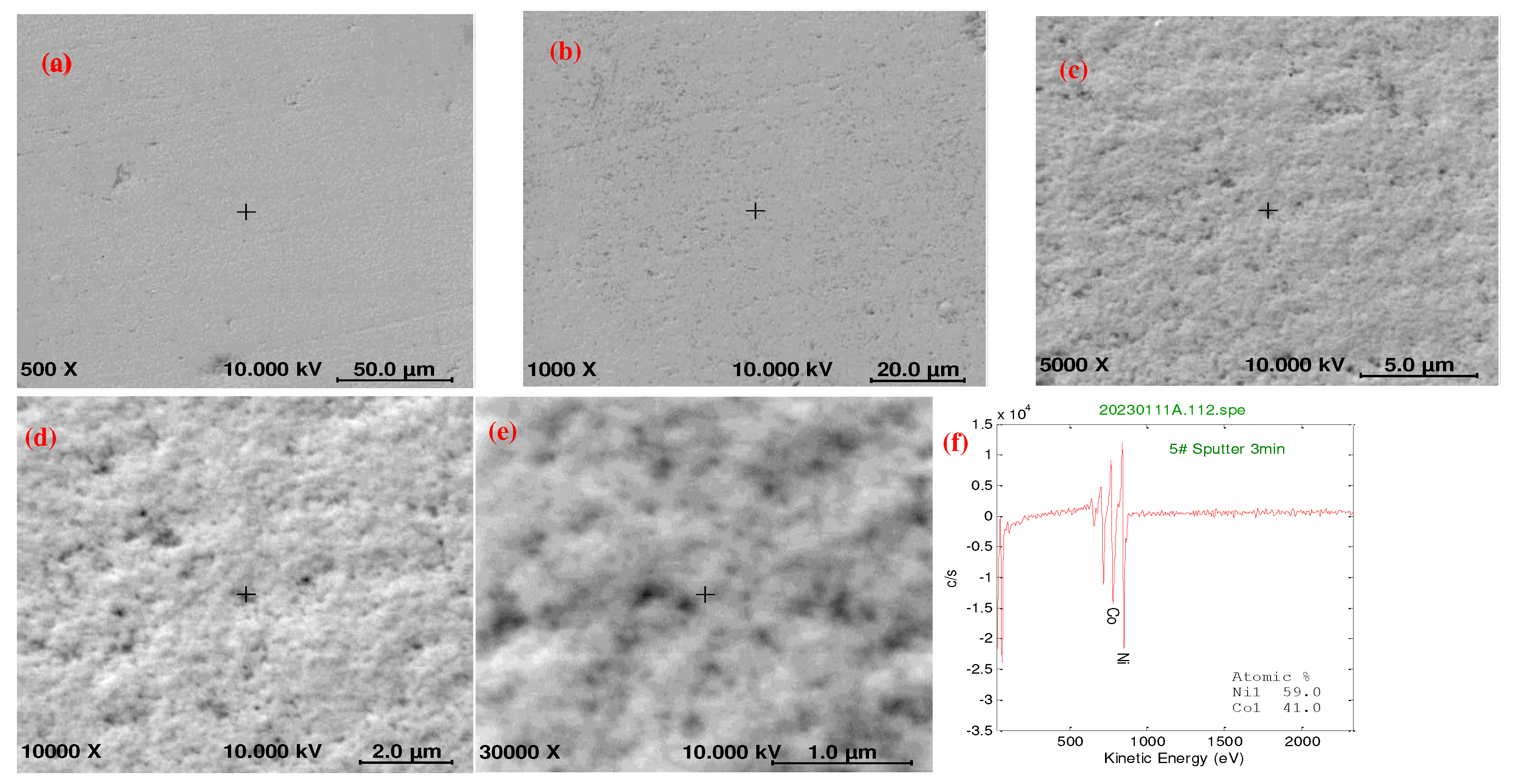
2.2. Using a double-pulse electrodeposition method for preparing NiCo coatings
- Uniform coating: The double-pulse power supply ensured highly uniform electroplating deposition, avoiding the formation of thick films and stacking on the workpiece surface.
- Dense coating: Positive and reverse pulses were used to deposit and redisperse ions in the plating solution. The double-pulse power supply generated additional reverse pulses, resulting in a uniform distribution of ions and a dense coating to prevent defects.
- Reduced coating looseness and holes: The stability provided by the double-pulse power supply reduced the probability of defects, such as loose coatings and holes.
- Reduced environmental impact: By reducing the amount of electrolyte needed, the double-pulse power supply minimized the losses of metal ions into sewage and its impact on the environment.
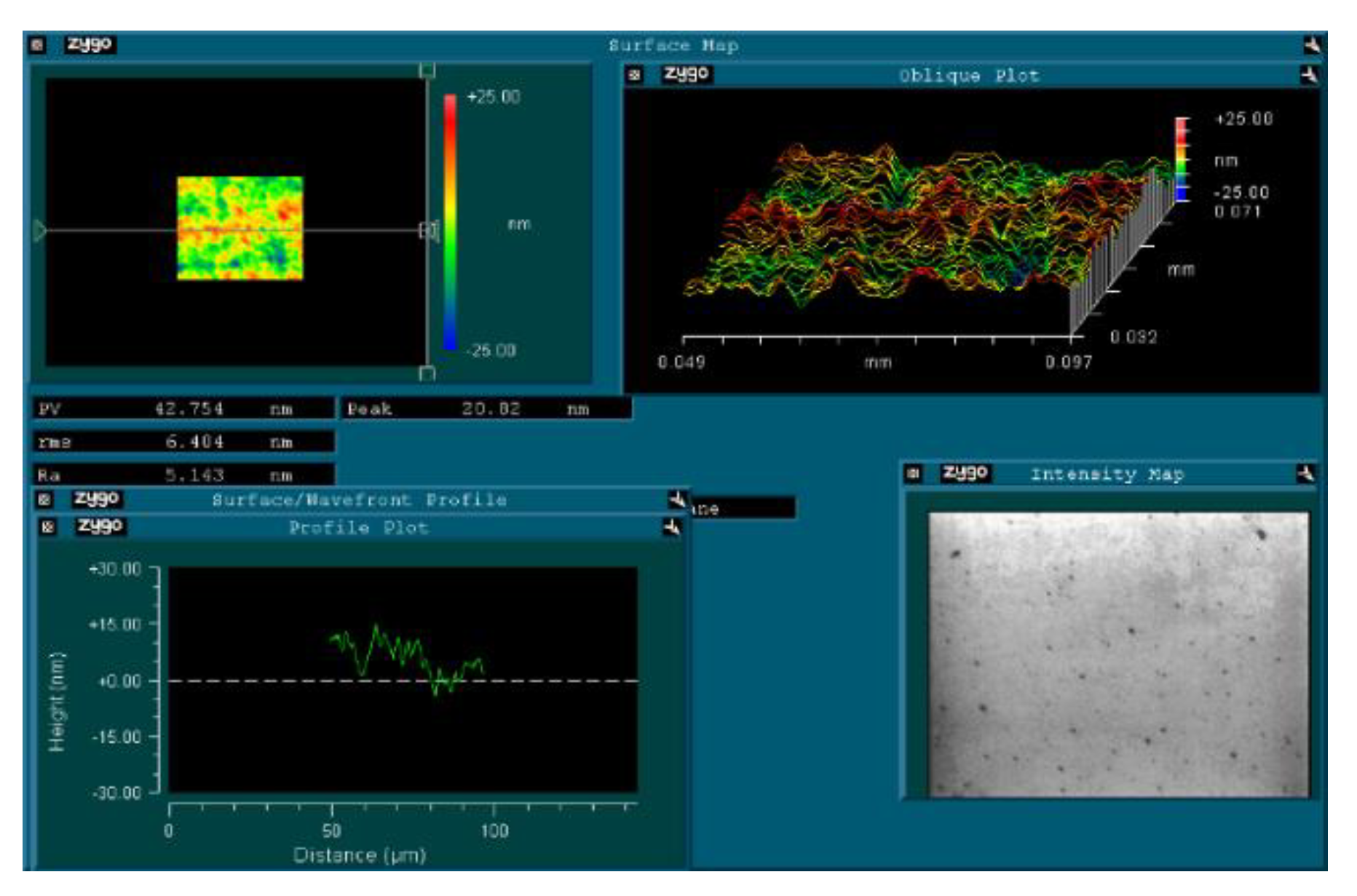
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L. Failure analysis of a plastic injection mold core plate. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 94, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wu, G.; Gong, J.; Zhang, F. Fracture analysis of an aluminum die casting mold. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2020, 43, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.; Jia, R.; Zhou, L. Evaluation of the failure of a die casting mold base. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 4015–4015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, F.; Zhu, X. Damage and lifecycle of ultra-precision machining mold. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 973–981. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Han, R.; Zeng, Z. Fracture analysis of a plastic injection mold slider. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 771, 138556. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Luo, R.; Du, W.; Cai, X.; Ding, Y. Microstructure characterization and failure analysis of a high strength steel die casting mold. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 745, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Han, R.; Zeng, Z.; He, G. Structural failure analysis of a thermosetting plastic mold. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2019, 19, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Meng, X. The study of multi-scale numerical simulation methodology for mold fatigue failure. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 95, 3835–3850. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Cao, J.; Yang, K. Progress of research on die casting mold failure. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 869–880. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, F.; Lu, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Failure analysis and evaluation of a high-speed steel cold heading die. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 3503–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Q. Fracture analysis of an injection mold steel made from a powder metallurgy technique. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Han, R.; Shao, Y.; Zeng, Z. Failure of plastic injection molds: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Wei, B.; Song, C.; Liu, H.; Fu, C. Failure analysis of a titanium alloy die casting mold. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. Fatigue failure analysis of hot work tool steel dies for forging processes. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108126. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Li, S.; Miao, H.; Li, M. Investigation of failures in cold forging die steel by FE simulation and metallography analysis. Mater. Des. 2020, 188, 108419. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Shen, D.; Qin, P. Severe plastic deformation of a die-material surface for prevention of stress corrosion cracking failure of stainless steel dies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 308–318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, M.; Lu, Q.; Yan, C. Fatigue fracture characteristics and crack initiation of hot work die steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Tost, M.; Kiefer, C.; Vollmer, M.; Klocke, F. Impact of heat treatment on wear, toughness, and failure mechanisms of high speed steel dies. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, T.; Tang, C.; You, X.; Fang, F. Improvement of the quality of TIN/TICN multilayer coatings through negative pulse modulation bipolar intermediate-frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 371, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X. Analysis of the Failure of High-Speed Steel Milling Cutter Coated by TiAlN. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L. Study on the Corrosion Resistance and Adhesion of CrN, 2017, TiAlN, and CrAlN Coatings on Dental Burs. Scanning 2017, 7364729. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. D.; Yue, T. M.; Lee, W. B.; Man, H.C. Influence of coating surface morphology on the delamination behavior of coating/substrate interfaces in multilayer coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 994–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, Y. Influence of coating parameters on wear and fracture of TiAlN coated cemented carbide cutting tools. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 372, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Wang, X.; Du, L.; Song, C. Effects of CrN coating thickness on wear resistance and fracture toughness of coated cemented carbides. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of TiN coating on the adhesion strength of diamond coatings. Thin Solid Film. 2017, 638, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Improving the adhesion strength of diamond coatings by the interface modification between TiN and Si substrates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 207, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Experimental and numerical investigation of influence of coating morphology on thermal shock resistance of TiAlN coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 734–743. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, K. Improvement of fracture resistance for ceramic cutting tools by friction stir processing. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 76, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Enhancement of wear resistance on a CrN coating by surface modification with a C plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Zhai, L.; Sun, J.; Li, X. Microstructural analysis of a TiAlN coating on an Al2O3 ceramic substrate. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4753–4759. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Chen, P. Improving surface quality of BK7 windows in a complex system through high-speed milling with coated tools. Precis. Eng. 2020, 62, 343–351. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Study on friction and wear behavior of cutting tools coated with tailored diamond-like carbon films under diesel oil lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2019, 132, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Kang, S.; Jeon, Y. Enhancing the adhesion strength of SiO2 by HfO2 intermediate layer in thin film coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 331, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, M.; Zhu, W.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Influence of sputtering parameters on the mechanical and tribological properties of Cr-AIN coated ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
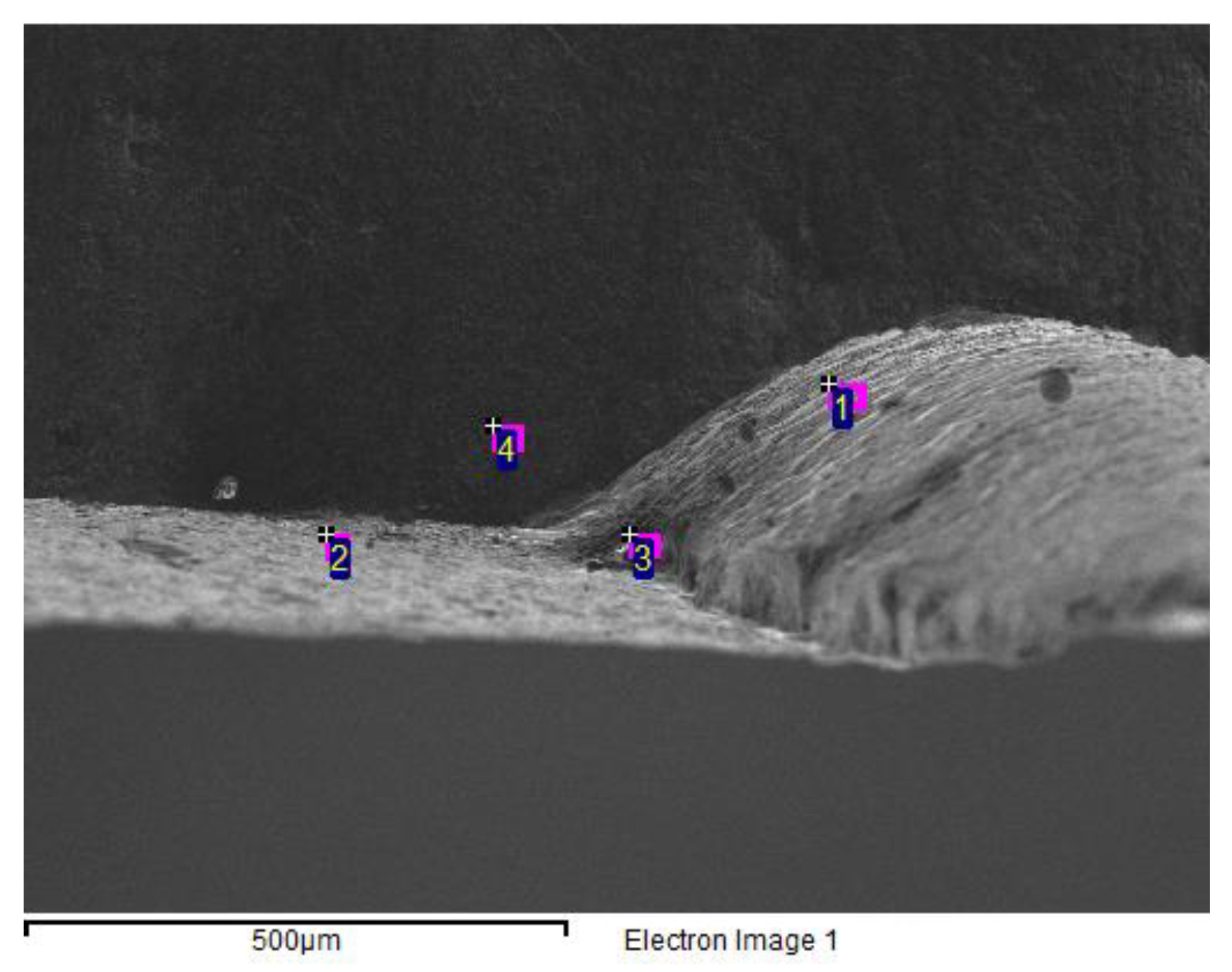
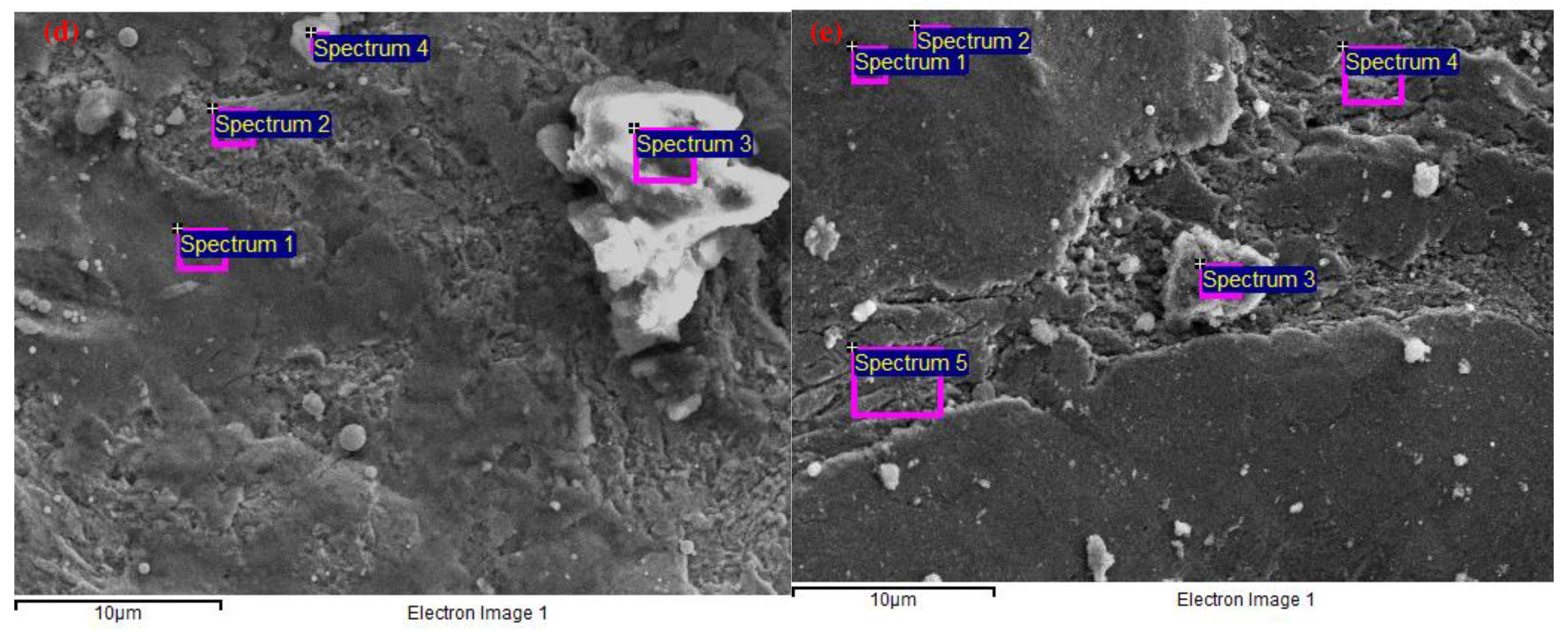


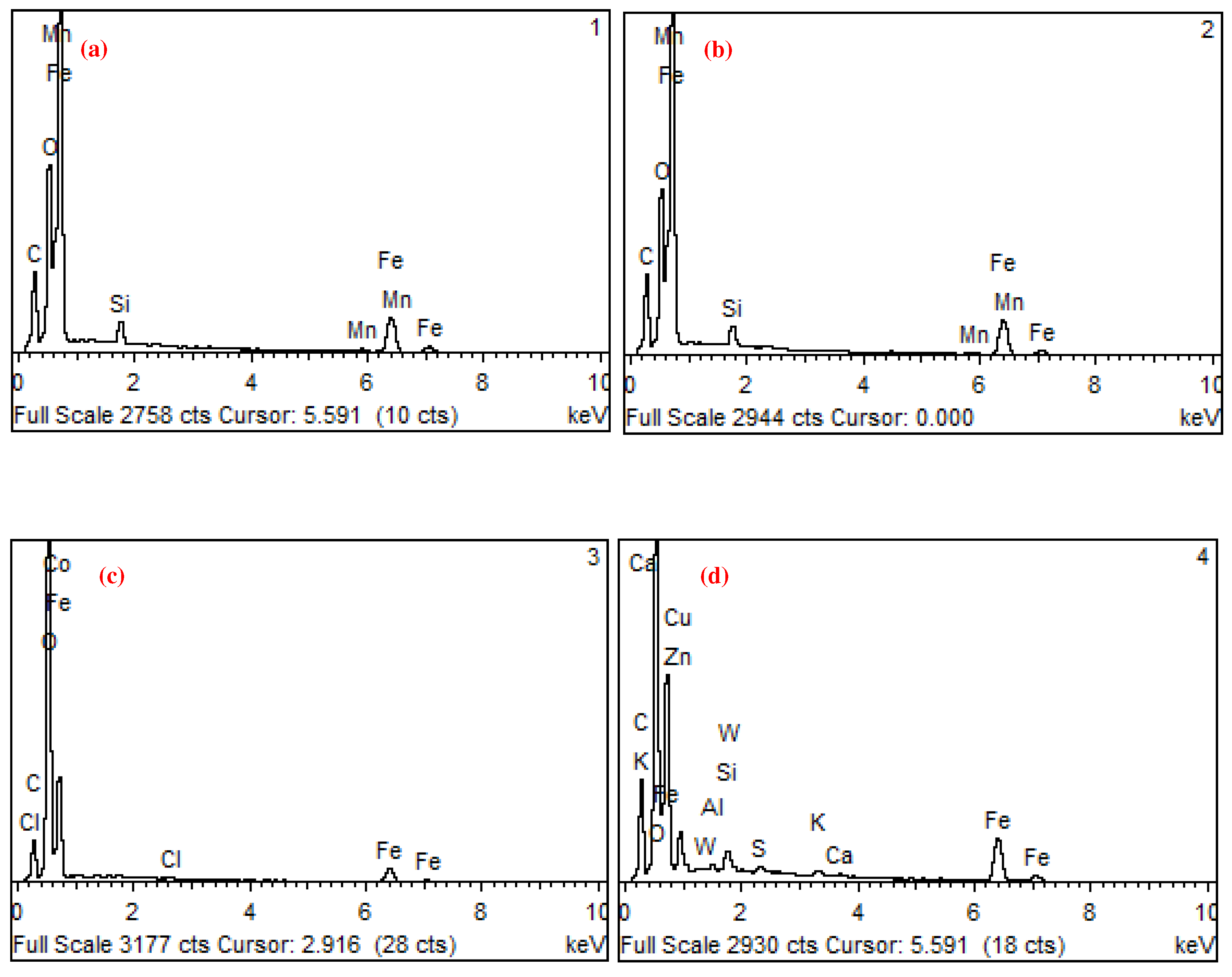

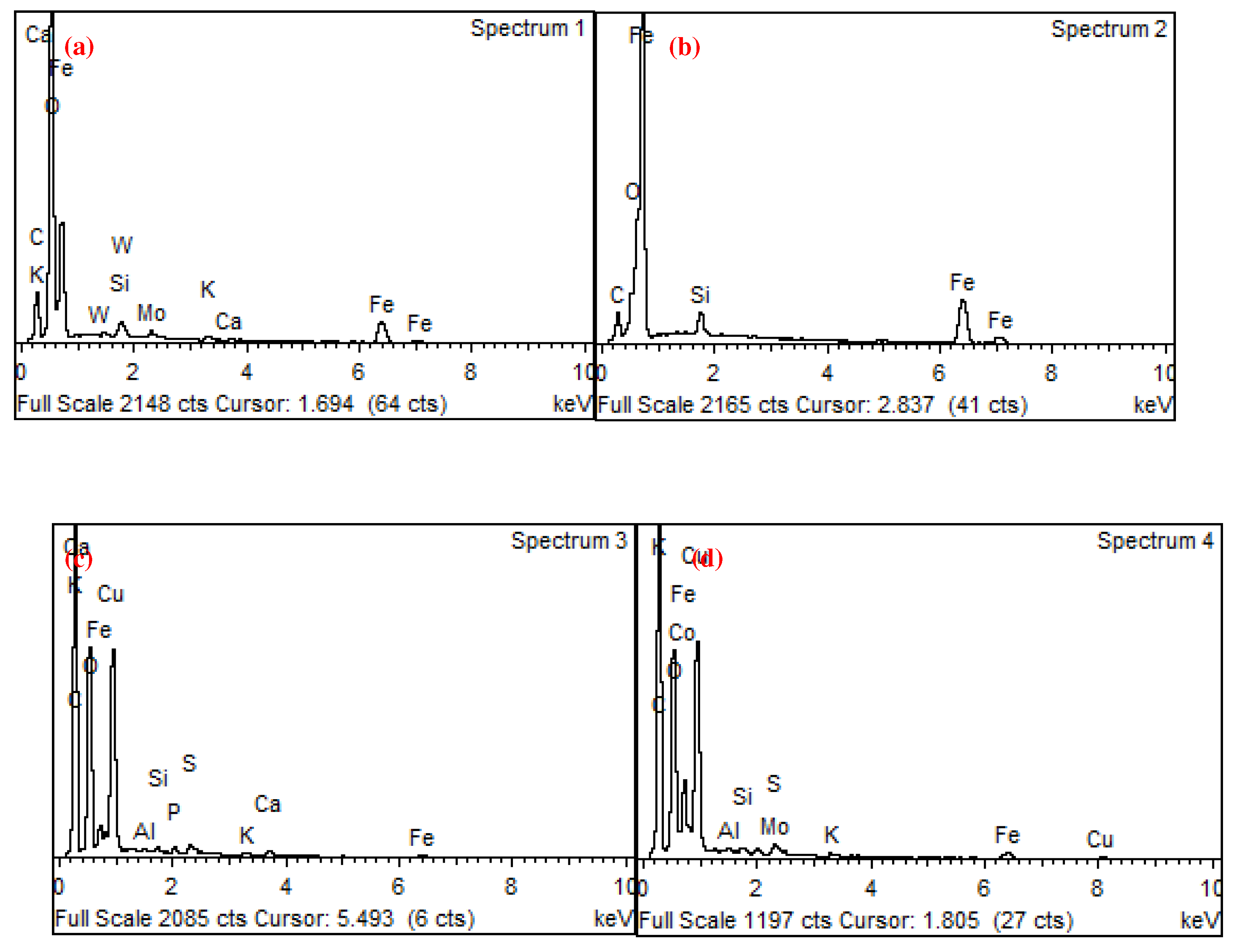
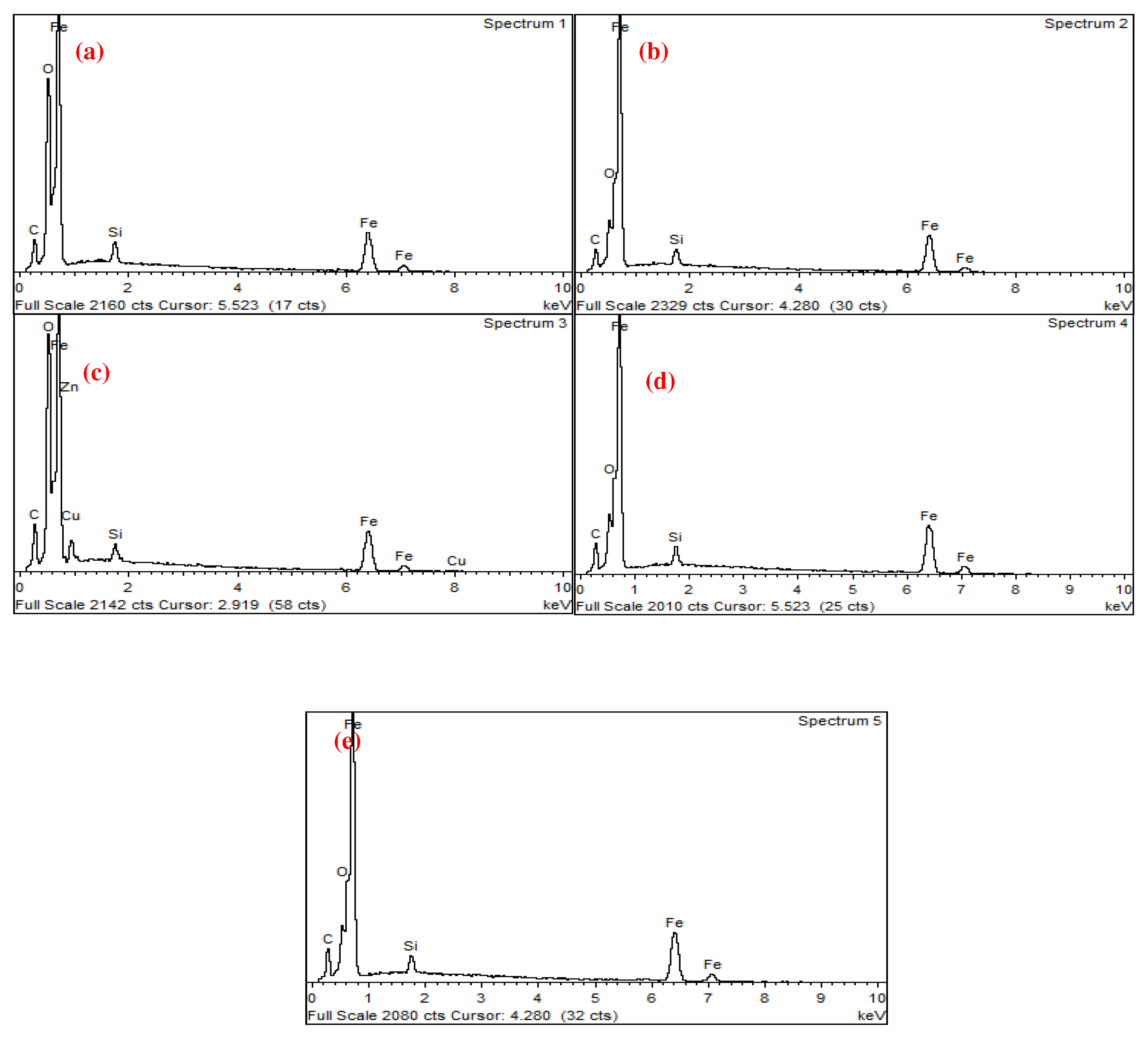
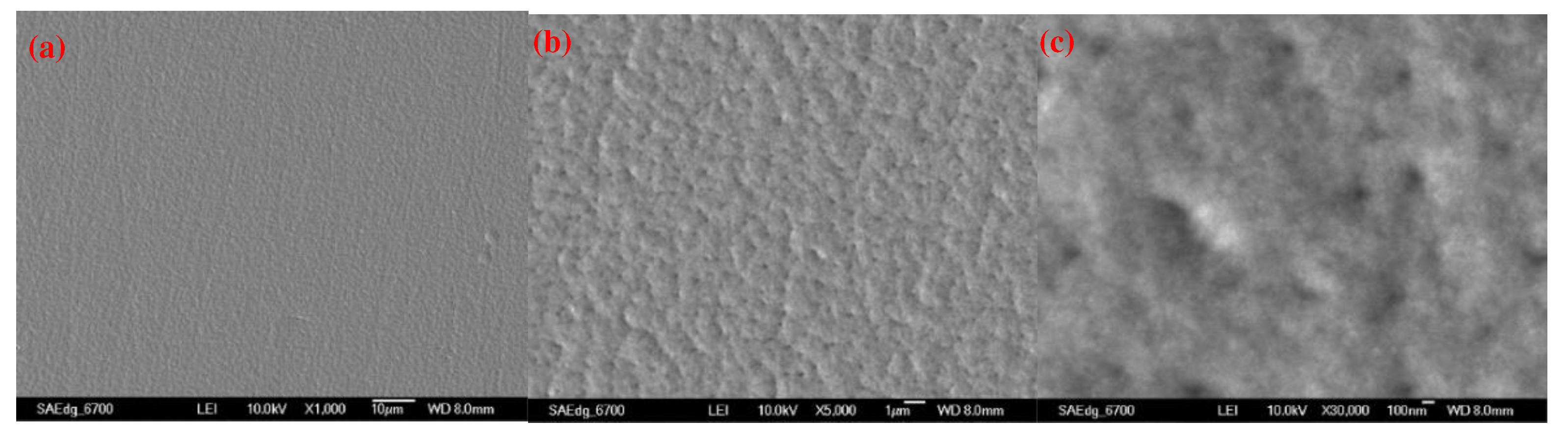
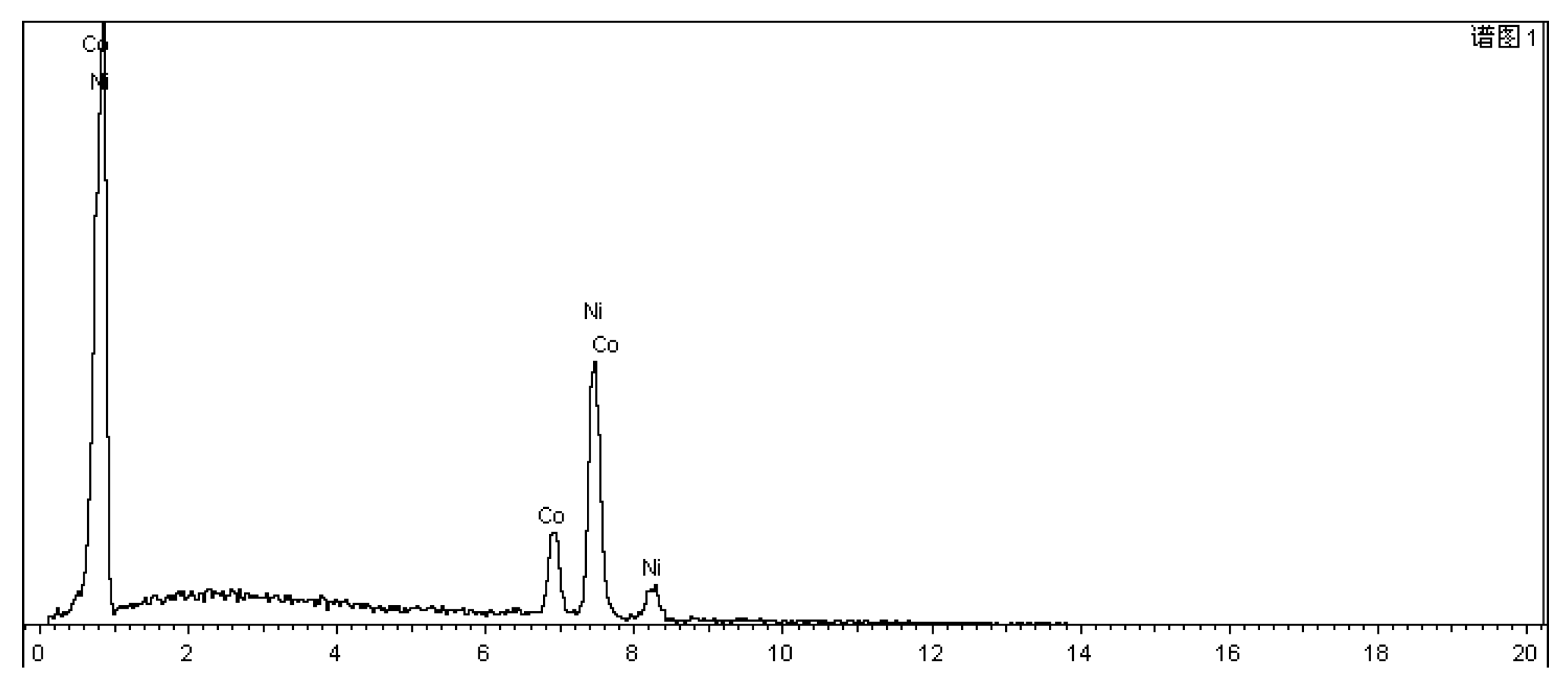

| Unit | Test item | |||||||
| Fe | Cu | Si | Mn | Cr | Co | Ni | ||
| Sample mold | (wt)% | 97.609 | 0.252 | 1.210 | 0.855 | 0.073 | NA | NA |
| wt.% | C | O | Al | Si | S | Cl | K | Ca | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zn | W |
| 1 | 9.06 | 10.2 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 79.7 | |||||||||
| 2 | 9.46 | 9.14 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 80.4 | |||||||||
| 3 | 7.67 | 32.6 | 0.4 | 57.3 | 2 | |||||||||
| 4 | 14.2 | 20.2 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 54.9 | 6.7 | 0.9 | 1 |
| wt.% | C | O | Al | Si | P | S | K | Ca | Fe | Co | Cu | Mo | W |
| 1 | 9.57 | 30.1 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 55.5 | 1.4 | 2 | |||||
| 2 | 4.47 | 2.67 | 1 | 91.8 | |||||||||
| 3 | 43.9 | 21.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 8.53 | 23.9 | |||
| 4 | 39.6 | 16.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 18.8 | 0.9 | 22.7 | 1.2 |
| C | O | Si | Fe | Cu | Zn | |
| 1 | 4.36 | 13.19 | 1.07 | 81.38 | ||
| 2 | 4.23 | 3.77 | 1.08 | 90.92 | ||
| 3 | 5.62 | 14.38 | 0.72 | 73.72 | 4.78 | 0.78 |
| 4 | 5.36 | 4.24 | 1.21 | 89.18 | ||
| 5 | 5.67 | 3.56 | 1.11 | 89.66 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | Plastic deformation (%) | Fracture strain (%) | |
| Raw materials of mold | 420 | 22 | 8 |
| Mold with special coating | 1738 | 25 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




