1. Introduction
Intracranial Aneurysms (IA) are present in an estimated 3.2% of the adult population and while the annual risk of rupture is moderate (2.2%) they carry a considerable burden for patients, physicians and the healthcare system [
1,
2]. To prevent ruptures, much effort is put into the early diagnosis, growth prediction and treatment of IA. Non-invasive imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) have steadily been improved making regular preventive screenings more and more feasible. Uncovering IA in an early stage gives neuroradiologists the chance to waging between treatment or continued surveillance of the aneurysm’s evolution. In this decision process, physicians rely on the geometrical and topological characterization of the IA together with other patient records. Scoring methods based on statistics, such as the PHASES score, may also contribute towards a final decision but have been shown to be an overall weak predictor [
3].
In place of statistics, Computational Fluid Mechanics (CFD) is proposed as a promising complementary tool. The goal hereby is simulating the haemodynamics of IA and extracting risk indicators to assess the severity of the case and possibly predict a rupture site. Despite substantial progress in this field, [
4,
5], there is still a latent dissent in the research community, not less emphasized during multitudinous CFD challenges [
6,
7,
8,
9]. It was confirmed that due to various modelling strategies, participating teams obtained dissimilar results that in some cases could point towards different interpretations. It is clear, that for a consolidated use of CFD in IA research it is imperative to tackle open modelling questions in advance.
Outflow Boundary Conditions (BCs) are one recurrent source of uncertainty in vascular fluid dynamics. Reliable measurements are difficult to obtain and are therefore rarely employed [
10]. Instead, the Principle of Minimum Work can be used to prescribe the flow split among the distal ends of the simulated network based on the relationship of their cross-section areas. This heuristic, which stems from the pursuit of minimizing the energy spent on the transport and storage of blood, has been confirmed through ex-vivo analysis by analyzing the regularity of the arterial branching patterns [
11]. The Law of Minimum Work (also referred to as Murray’s law), apart from being more realistic than plain stress-free outflows [
12,
13], bears the benefit with respect to the latter that it solely depends on geometrical features of the network. This is thus far an advantage as it makes boundary conditions reproducible across varying modelling assumptions, like rheology laws, solver schemes or boundary extrusions.
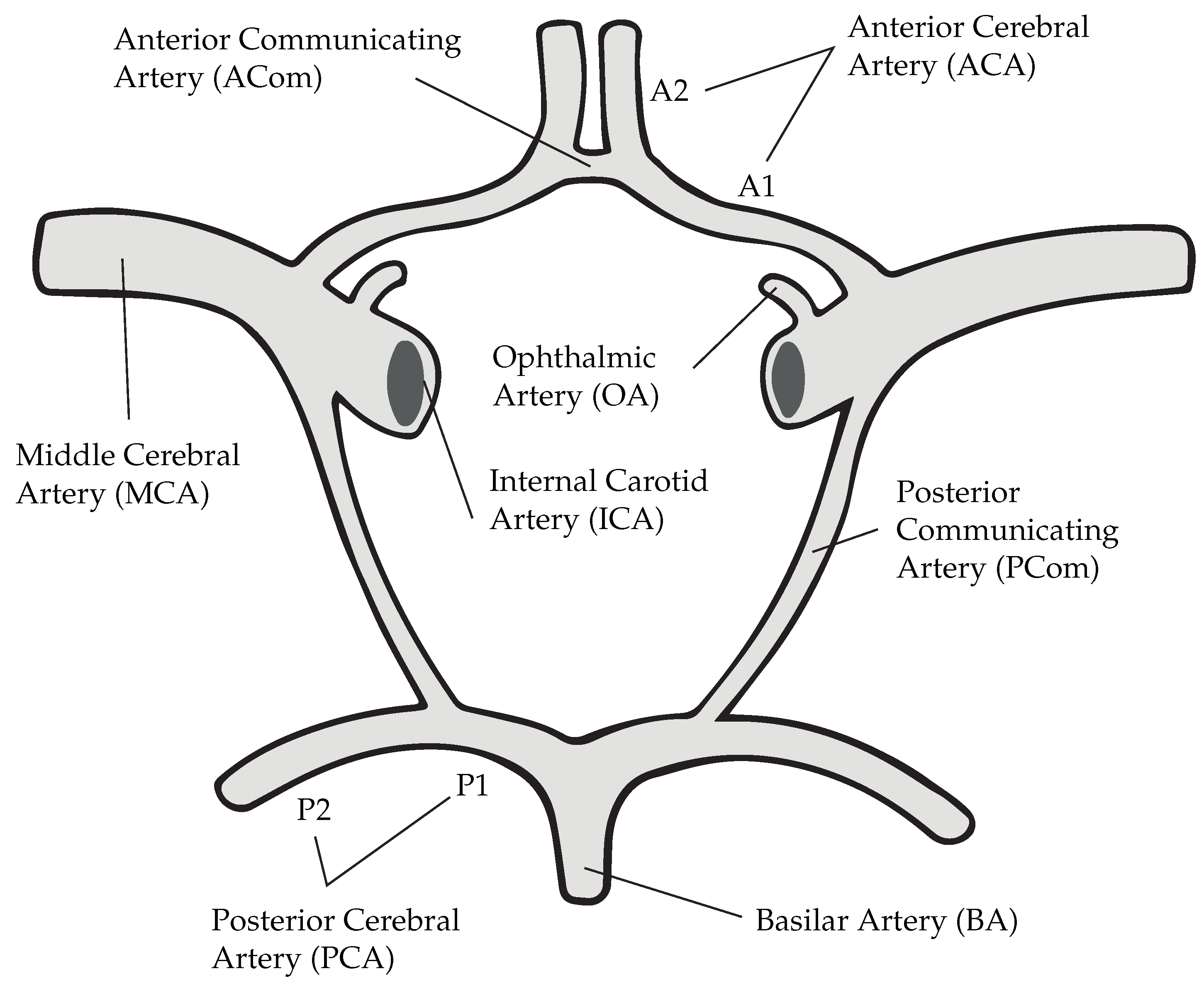
Nevertheless, Murray’s law has an undefined character when considering communicating arteries in the Circle of Willis, a loop of arteries found at the base of the brain (see
Figure 1). From an anatomical point of view, these vessels serve the purpose of linking anterior and posterior circulations, thereby providing alternative pathways for the blood in case of ischemia [
14]. Frequently, the PCom carries a lesser net flow from the ICA to the PCA, albeit different CoW configurations may perturb this rule [
15,
16,
17]. The majority of CFD studies that examine IA at the carotid arteries only consider one part of the anterior circulation, thereby defining the PCom as a regular system outlet [
12,
18] or neglecting it [
19,
20]. These two strategies pose two extreme cases and therefore inevitably raise the question, of whether they lead to physiological conditions or not.
Confronted with this bothersome question, we set the goal of this study to assess the significance of the changes in haemodynamics when using these said strategies. To do so, full 3D simulations of three patient-specific CoW with ICA-PCom bifurcation aneurysms will be thoroughly analyzed and used as reference cases. The core of the comparison will be the intra-aneurysmal flow and the exposure of the lumen to shear stresses.
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Medical Imaging and Segmentation
The angiography images were obtained using time-of-flight angiography on 1.5T and 3T MRI scanners with isotropic imaging and 0.6mm slice thickness. The lumen was segmented using 3DSlicer (
https://www.slicer.org/) under the supervision of neuroradiologists of the cooperating medical institution. Patient A has a complete CoW with one aneurysm of diameter 7.5 mm at the left ICA-PCom bifurcation. Patient B has a bilateral P1 hypoplasia and is therefore missing a connection of the basilar artery with both anterior circulations. The PComs are defined in this case as fetal since their size is larger than usual and they are in fact the main supplier of blood to the PCA [
21]. The aneurysm of the latter is located on the right side (
d = 5 mm) and features a pronounced lateral daughter sack. The complex geometry of this formation was later confirmed with image recordings during the operation procedure. Lastly, patient C too has an incomplete CoW due to an absent right PCom. In this case, two IA can be found, one at the left ICA-PCom bifurcation and one at the right MCA bifurcation. The former, being the only one considered during analysis, is classified as bilobular, due to the presence of two rounded sacks.
2.2. Spatial Discretization
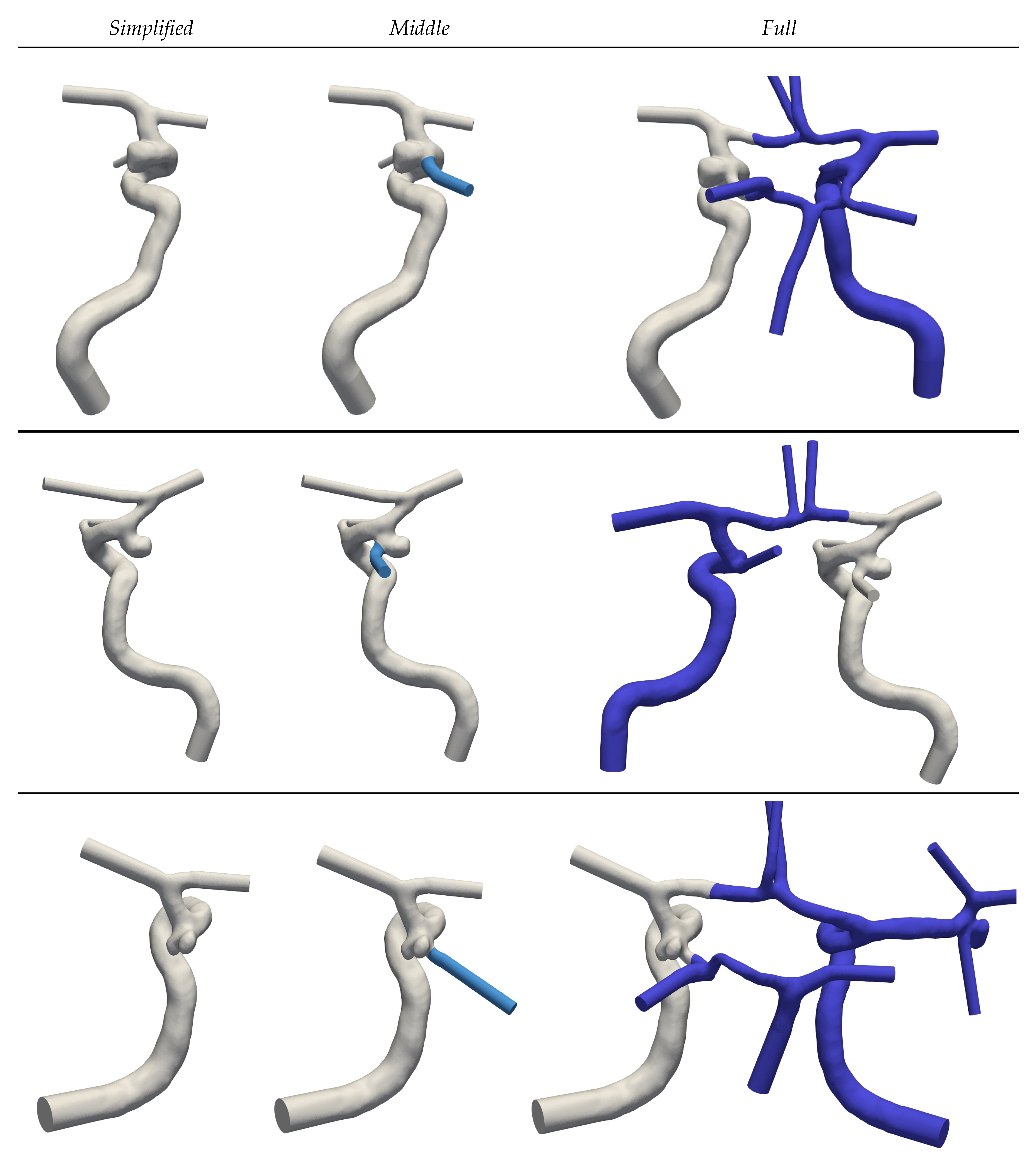
For each of the segmented geometries, three extensions of ascending complexity (see
Figure 2) are generated to assess the implications of Murray’s law on simulated haemodynamics. Geometries with the keyword
Simplified are constrained to the main supplying artery that leads to the IA. Communicating arteries and A2 segments (see
Figure 1) are in this case neglected.
Middle extends the prior
Simplified complexity by adding the PCom. Finally, the keyword
Full denotes the full CoW. To minimize perturbations caused by inlet and outlet models, extrusions have been made along these boundary patches [
10,
19]. Circular profiles are adapted by a least-square fit to the irregular vessel cross-sections and extended along the mean vessel direction using transfinite interpolations. This procedure additionally simplifies the imposition of circular inflow profiles and facilitates geometrical information required for the outflow boundary conditions.
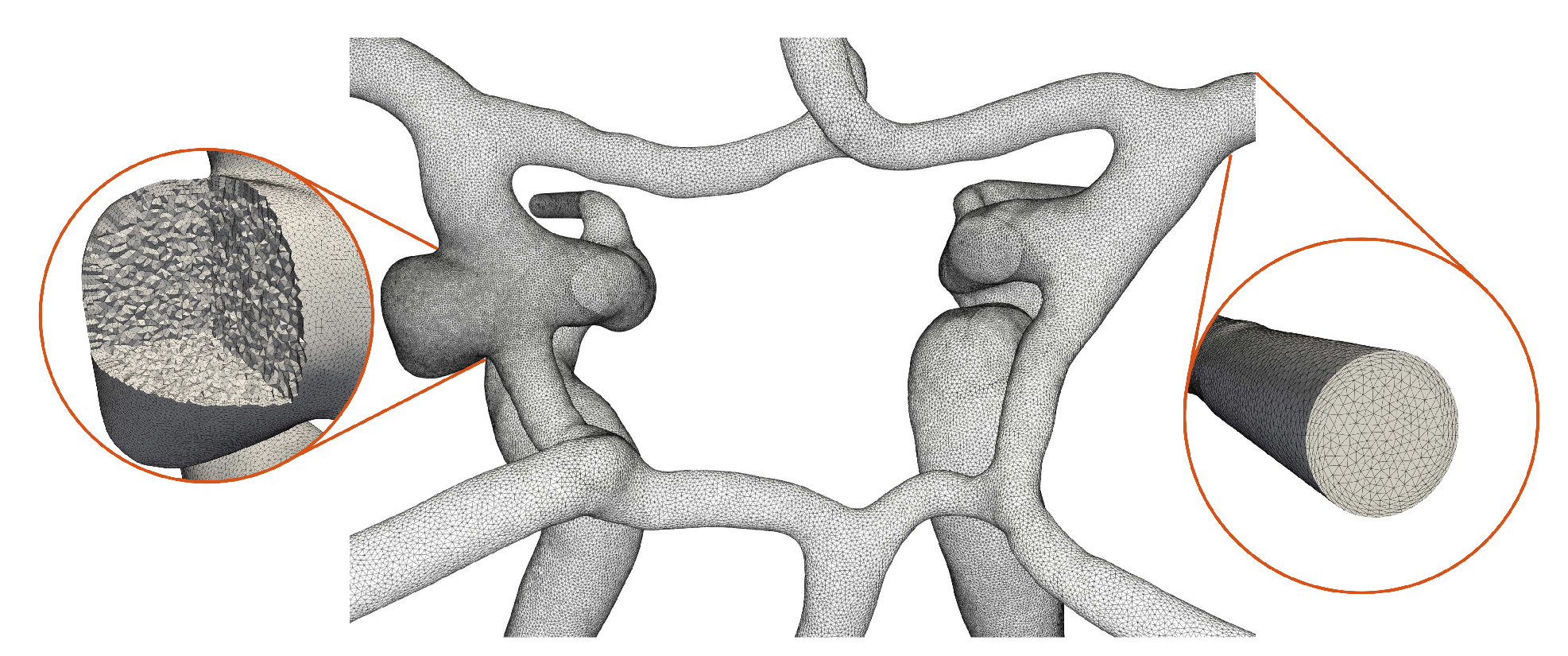
The open 2D surface meshes are parametrized using conformal maps, remeshed and extruded inwards to generate a set of boundary layers (growth factor 1.2) [
22]. The thickness is determined by the dimensionless wall distance of
= 1, an overestimated Reynolds number of
= 1000 and the averaged diameter of the ICAs. The interior is meshed with isotropic tetrahedral elements of mesh size
h =
mm which is progressively refined to
h =
mm at the aneurysm periphery (see
Figure 3).
2.3. Haemodynamics Simulations
2.3.1. Navier-Stokes
The simulations have been carried out by numerically solving the transient, incompressible Navier-Stokes equations with an in-house Finite Element (FE) solver. The discrete system is set up by linear elements for both pressure and velocity and is consequently stabilized by a residual-based Variational Multiscale-type method [
23]. The weak formulation (see Equations (
1) and (
2)) is enriched with the residuals of the continuity
and residuals of momentum
. For details on the stabilization parameters,
and
we refer to [
24] and therein.
The time derivative is discretized with an implicit Euler scheme using a timestep
=
[
24]. To wash out the initial transient, all simulations are carried out for three complete cardiac cycles (
T =
), from which only the last one is considered for postprocessing.
2.3.2. Rheology
The shear-thinning rheology is modelled through the Carreau model describing its behaviour [
25] as in Equation (
3). The constants
=
,
=
,
=
,
=
,
n =
and the shear rate
were employed [
26].
2.3.3. Boundary Conditions
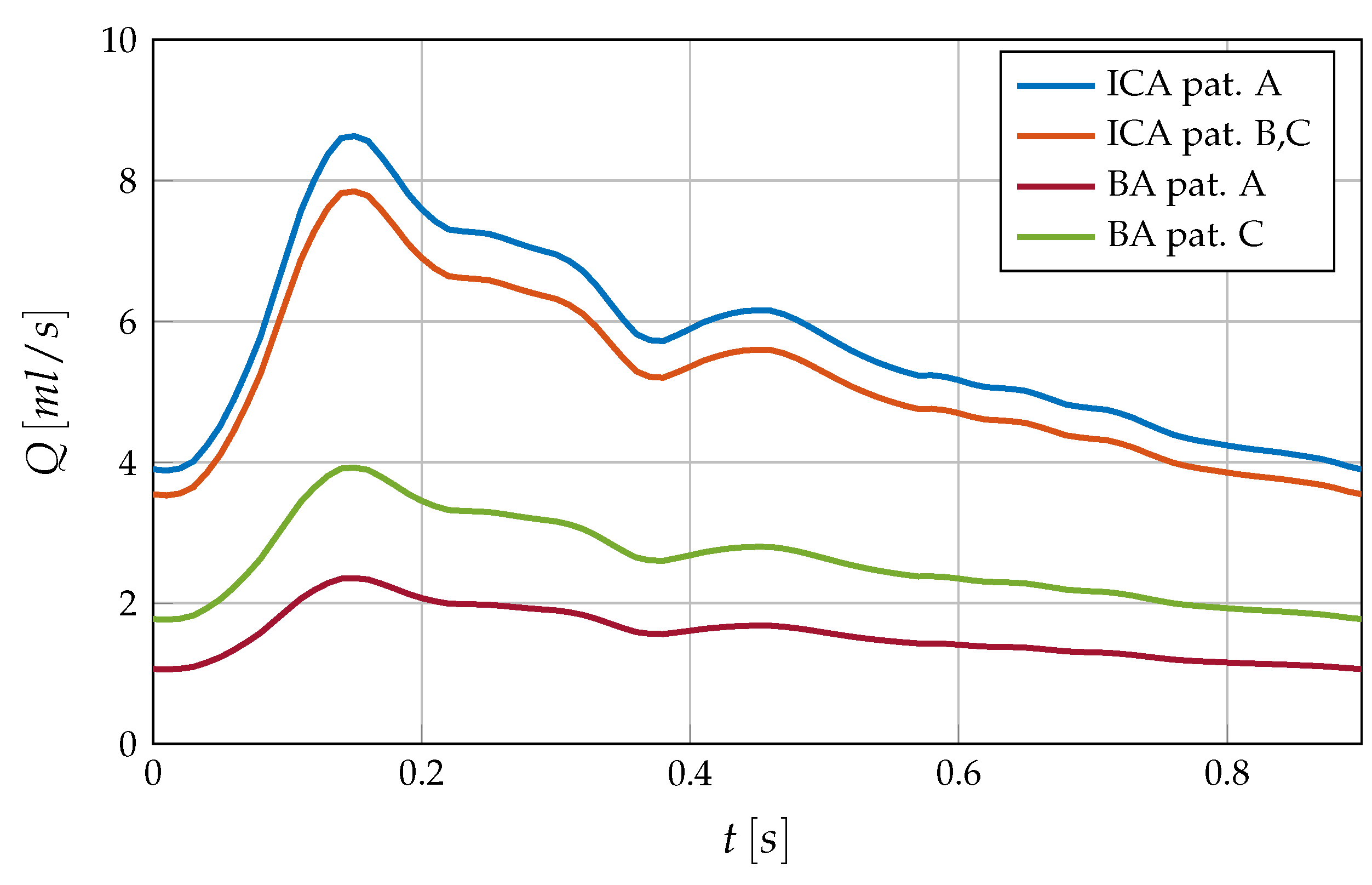
Inflow conditions are described with the help of a generalized volumetric flow curve which has been scaled and split among the supplying arteries (see
Figure 4). More precisely, in case A each ICA contributes 44% of the total volumetric flow while the BA carries only 12% due to its small size [
27]. Cases B and C follow a split of 40%-20% between each ICA and the BA. The flow rate
Q is imposed via parabolic velocity profiles at the base of the arterial system. The walls are considered fully rigid and are thus set through no-slip conditions.
The outflow of the system has been set following the Law of Minimum Work, also referred to as Murray’s law. It has been implemented as shown in Equation (
4) with index 3 for the mean cross-section area that the outlet extrusions provide [
12,
13]. The cube law has been chosen in this case based on Poiseulle assumptions for the long-term cost of blood transport in brain arteries.
The mass flow that Murray’s law dictates is weakly imposed through pressure conditions following the linear relationship
P =
[
28]. The required resistances
R have been iteratively adjusted for each outlet.
2.4. Haemodynamic Descriptors
The influence of the different domain extensions is measured through the WSS, OSI and velocity profiles. The velocity, as a primal variable, is intrinsically linked to any alterations in the system dynamics and is therefore considered for a first assessment. The former two quantities belong to a set of indicators related to vascular remodelling and therefore are regarded as risk factors in aneurysm formation [
29,
30]. Following the work of Meng et al. [
31], the destructive remodelling phenomena of arterial walls can be split into two groups, first, the mural-cell-mediated ones caused by abnormally high WSS and second the inflammatory remodelling induced by low WSS and high OSI. However, no consensus is found in the literature on threshold values for WSS and OSI. These quantities are calculated from the velocity fields through the stress tensor
as shown in Equations (
5) and (6) respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Simulations
The introduced cases have been each run in parallel on 64 computing cores using a message parsing interface. For the solution, the fully coupled system of pressure and velocity was solved using the ILU(4) block preconditioned Stabilized Bi-Conjugate Gradient method. Computing times of each cardiac cycle can be extracted from
Table 1. The number of elements, likewise seen in
Table 1, is notably higher for case A due to its larger volume and aneurysm sack.
The anatomical difference can also be seen in the maximum intensity projection of the velocity magnitude in
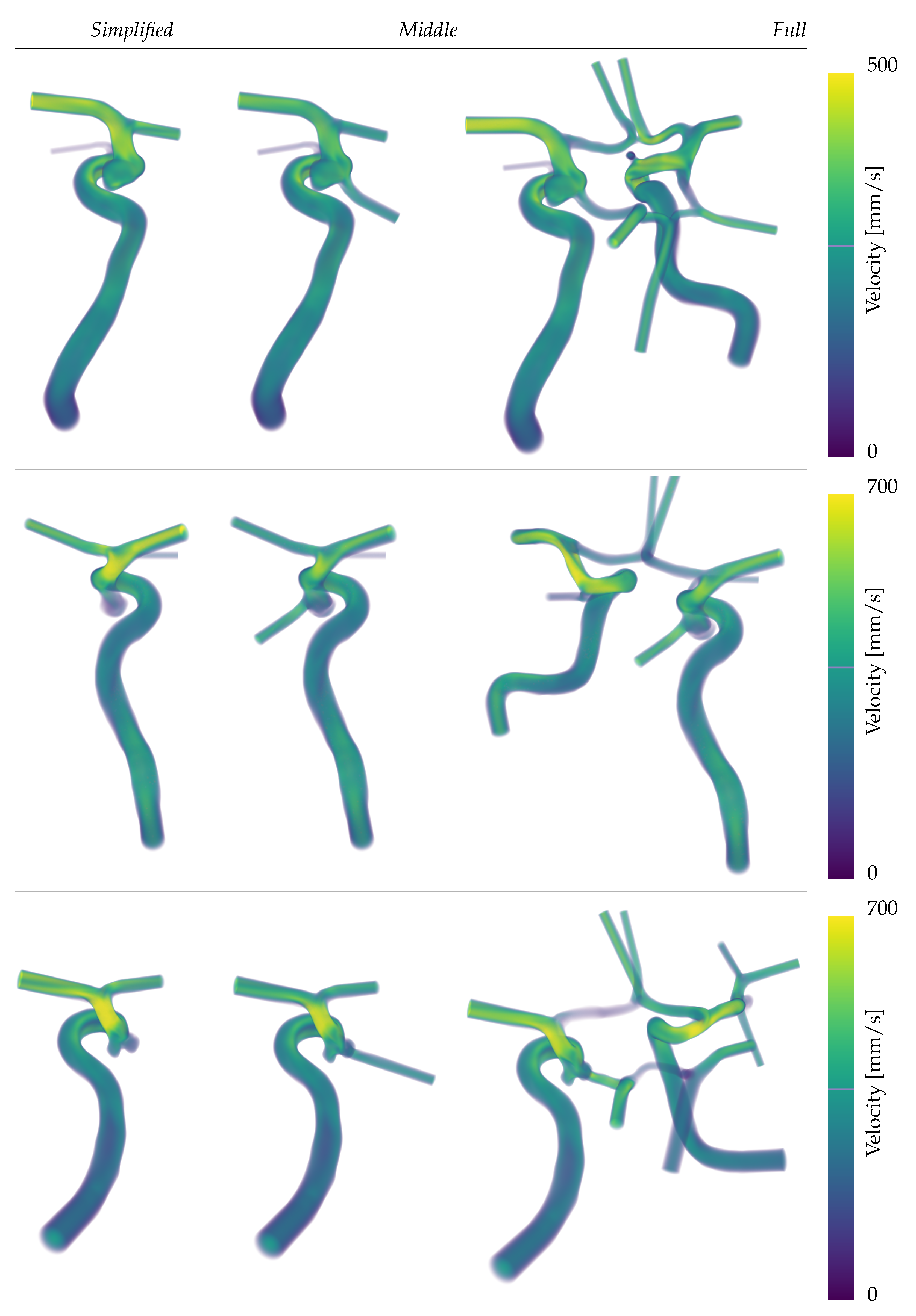
Figure 5. There slower flow velocities for patient A (first row) are seen despite similar tributary flows as in cases B and C. Further,
Figure 5 provides a first sketch of the direction and velocity of the main fluxes of each simulation. While more accurate quantifications of the flow split at the region of interest will be shown later in the results, it is noticeable here that the outlet profiles are strongly inertia driven (see any outlets in
Figure 5).
3.2. Intra-Aneurysmal Dynamics
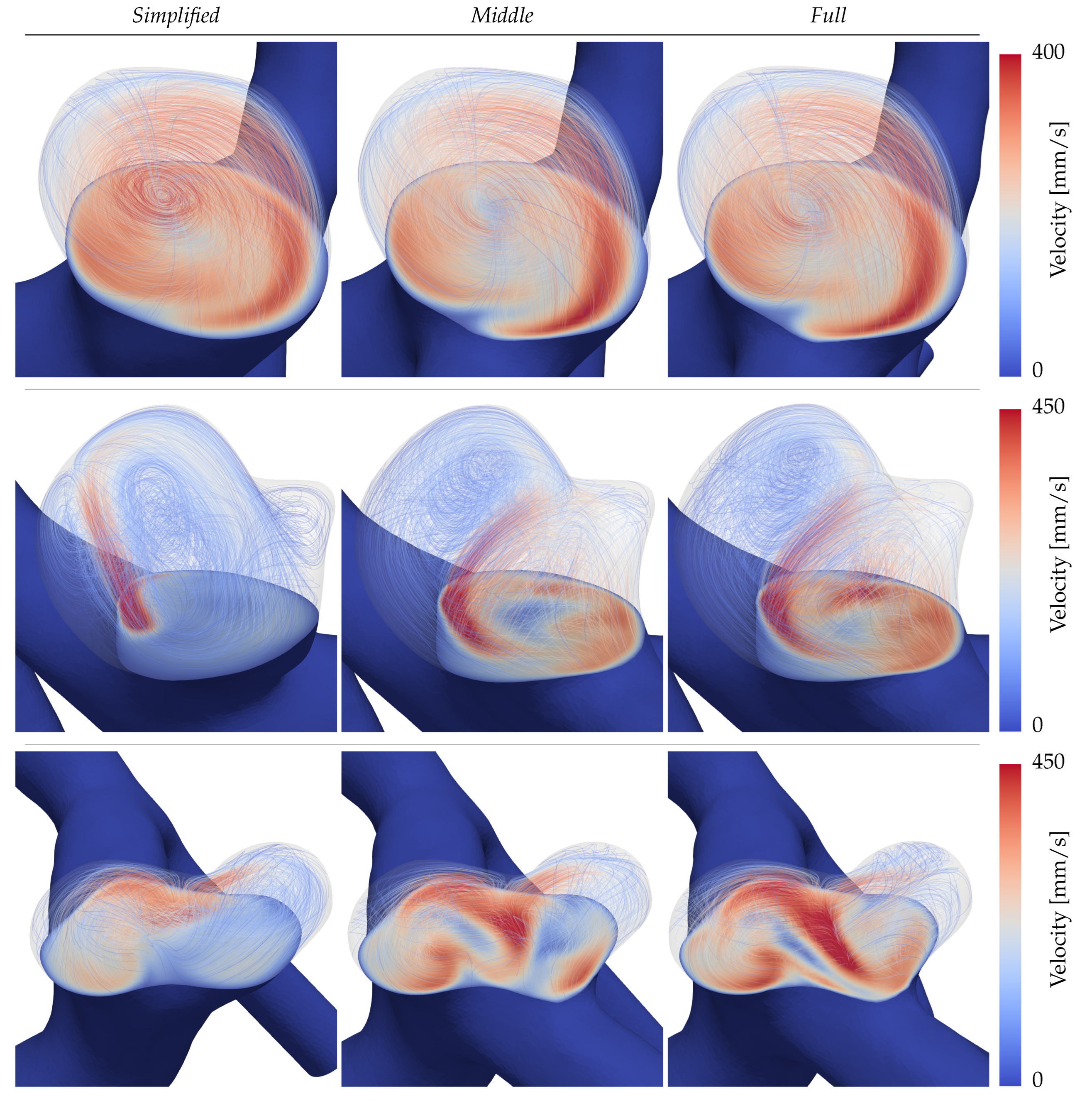
The flow structures in the domes are visualized in
Figure 6 for each patient and configuration. The aneurysms are cut with a plane around the neck height and velocity streamlines of the intra-aneurysmal flow are inscribed lightly to indicate the structure of the present vortices at peak diastolic time. For the inertial flow of aneurysm A (first row), all three configurations show a large, centred vortex traversing the dome that can be regarded as consistent across the three sizes. Per contrary, patients B and C in the second and third rows of
Figure 6 display clear discrepancies. Starting with the aneurysm B (second row) it is visible that in the simple configuration, the main inflow enters the dome focused as a small jet, later decaying into a stable weaker recirculation. For the
Middle and
Full extensions of the same case, the inflow hits the neck of the daughter sack, splitting its momentum among two vortices that traverse the main lobe and the daughter sack respectively. In the
Full simulation of B (second row, third column) the daughter sack’s recirculation is located farther up inside the dome leading to larger in-plane velocities. Lastly, patient C (third row of
Figure 6) presents the largest disparities on both quantitative and qualitative levels. On of the most noticeable differences in
Figure 6, is the inverted circulation of the right aneurysm dome in the
Full simulation with respect to the other two extensions.
3.3. Wall Shear Stress
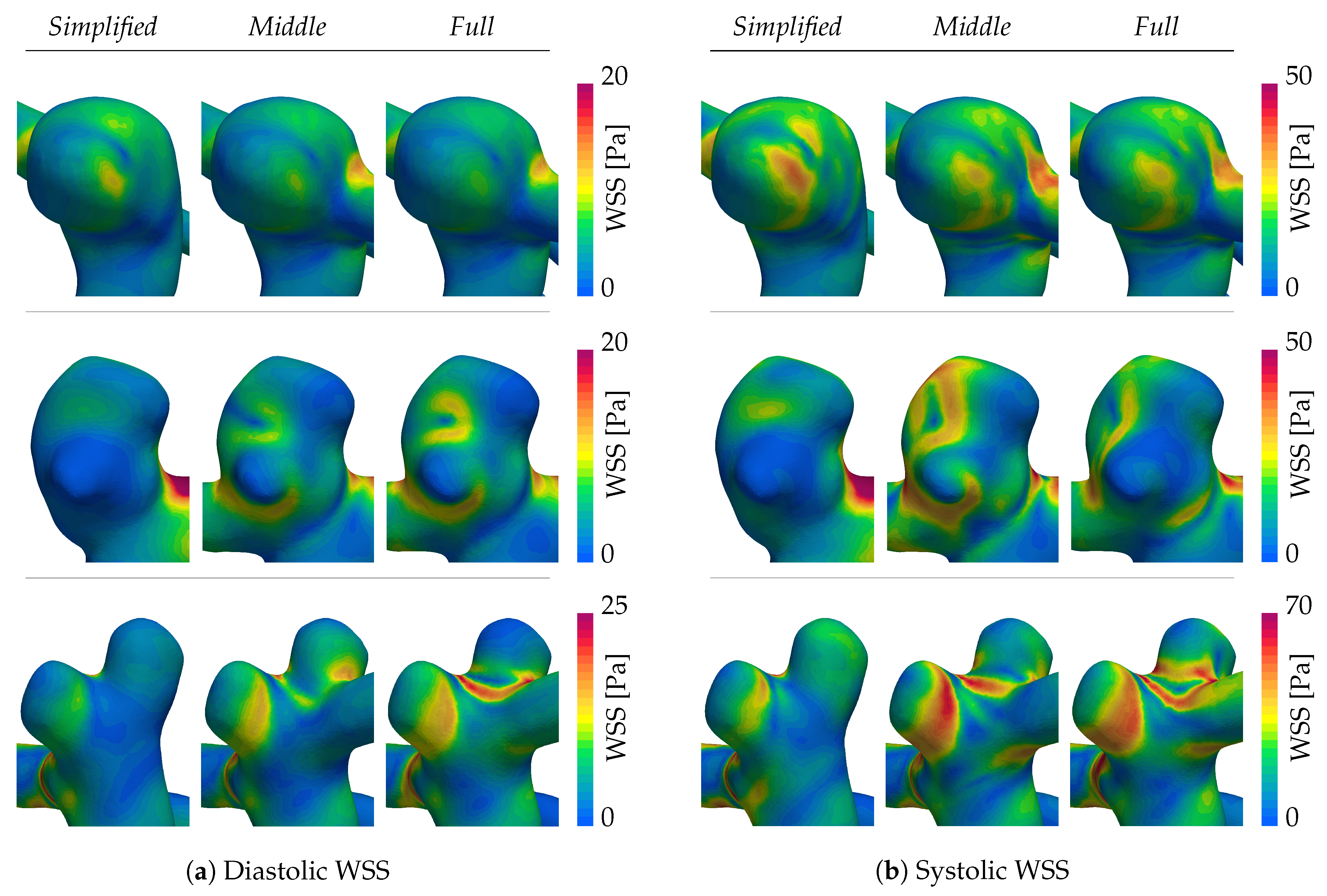
The WSS magnitude for peak diastole and systole are shown in
Figure 7a,b, respectively. Patient A (first row) is characterized by a stable, qualitatively similar WSS pattern across all extensions. Here, only the
Simplified case demonstrates smaller patches of higher shearing that are not present in the
Middle and
Full systems. Patients B and C instead exhibit persistently altered WSS patterns for all of the domain extensions. Setting the
Simplified system aside, one can observe shifts in patterns between the
Middle and
Full extensions in the second and third columns respectively. Most notable here is the daughter sack in patient B’s aneurysm (second row of
Figure 7). During diastole, the WSS is relatable between the
Middle and
Full systems. At systole, on the contrary, the shearing increases for the
Middle system, but remains low for the
Full system, leading to two distinct characterizations. Following the
Full system, the daughter sack could be identified as a risk factor due to low WSS exposure, whereas the
Middle simulation would not. Daughter sacks play hereby an important role since their appearance is linked to an augmented risk of rupture. The last patient case in the bottom row of
Figure 7a,b, again shows an inconsistent WSS among the different extensions, especially aggravated at the neck separating the two sacks.
3.4. Oscillatory Shearing
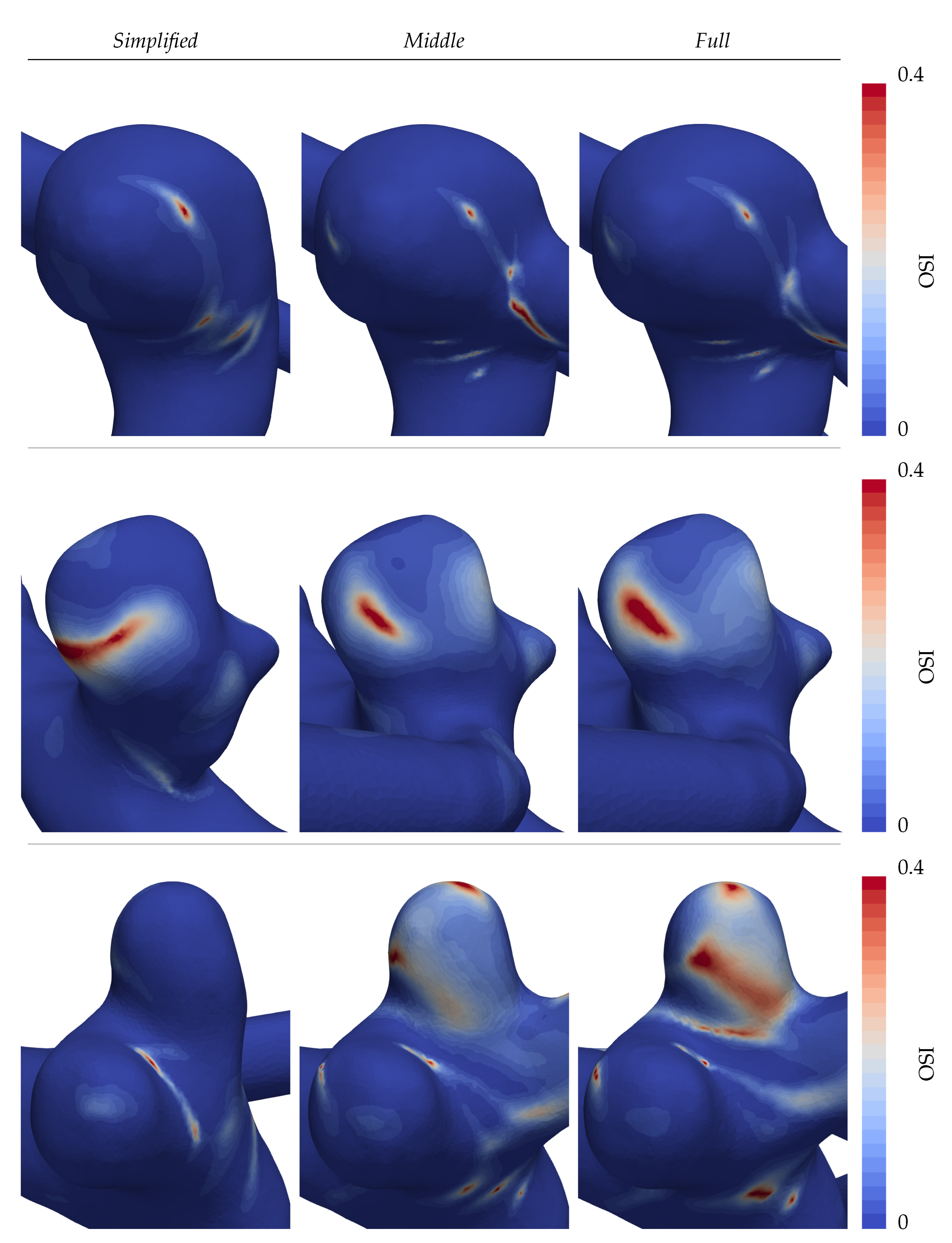
Following the same structure of
Figure 7a,b, the OSI is displayed in
Figure 8. The observed stable WSS profile of aneurysm A inevitably leads to a nearly absent oscillatory shearing with only small localized peaks (see the first row in
Figure 8). Large dissent of the OSI distributions is again found in patients B and C (second and third rows of
Figure 8), where especially the distal lobe of patient C points out. There, overall high values are found on the visible face in the
Full CoW simulation, in contrast to the other cases.
3.5. Volumetric Flow
The shifts in flow paths and volumes are arguably the cause for the previously described dissimilarities. On a general scale, the predominant portions of the flow enter the domain through the ICAs and are distributed with an affinity towards large calibre outlets, such as the MCAs. These, on average account for around half of the flow of one brain hemisphere alone in our computations. The BA, when present, supplies the posterior circulation of the brain without directly irrigating the anterior circulation. Therefore, the flux traversing the PCom is strictly unidirectional carrying blood away from the ICA towards the PCA, in accordance with the commonly observed flow direction [
16,
32].
For each simulation, the volumetric flow per cardiac cycle has been computed at the peripheral arteries of the aneurysm fundus.
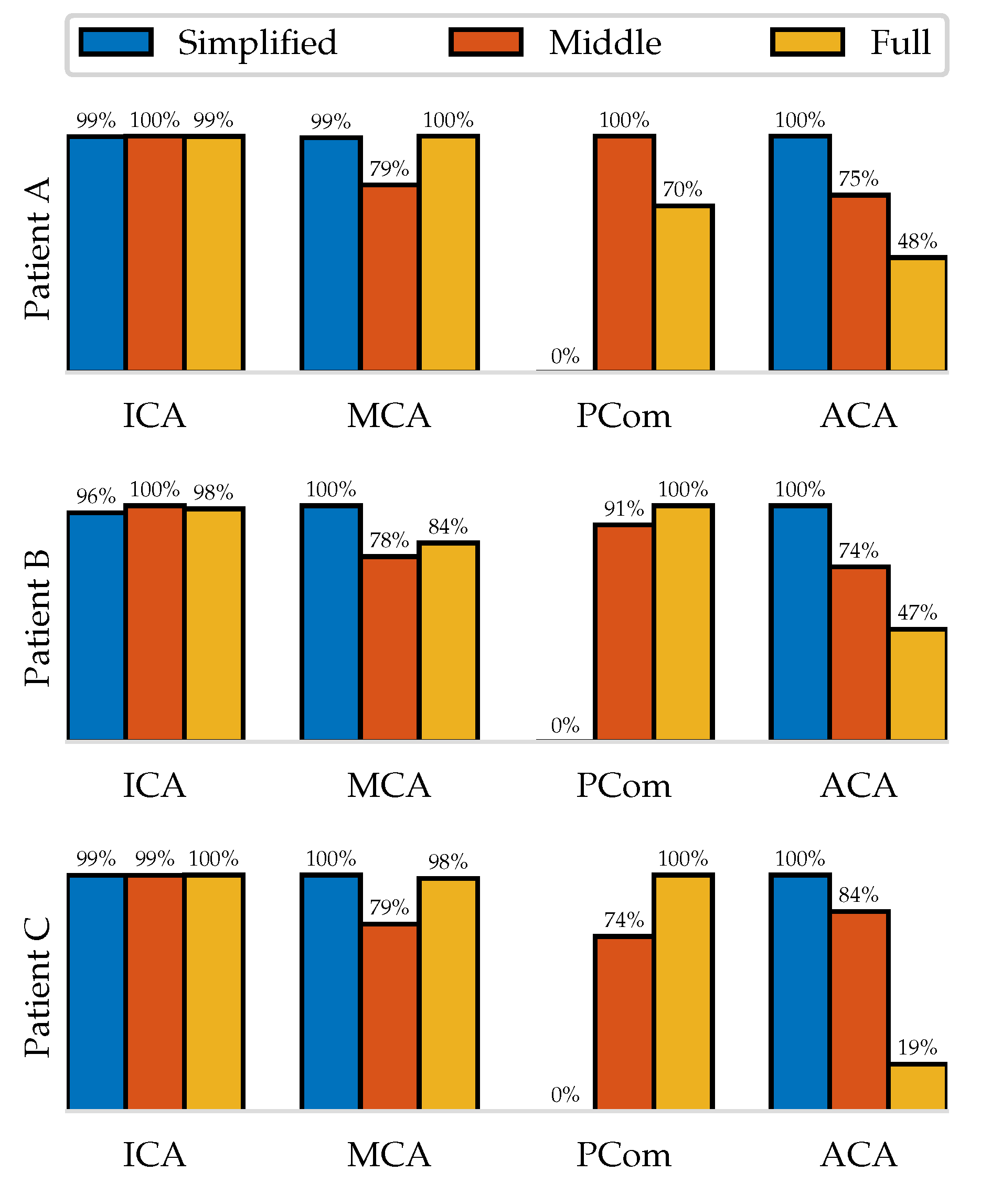
Figure 9 shows this quantity normalized with respect to the maximum mean flow of the three extensions. It can be seen that in the
Simplified simulations the flow that would leave through the PCom is distributed among the other outlets, causing their flow rates to be consistently higher. The
Middle distinguishes itself from the
Full through lower outflows through the MCA and larger ones through the ACA but exhibits no general trend on the PCom.
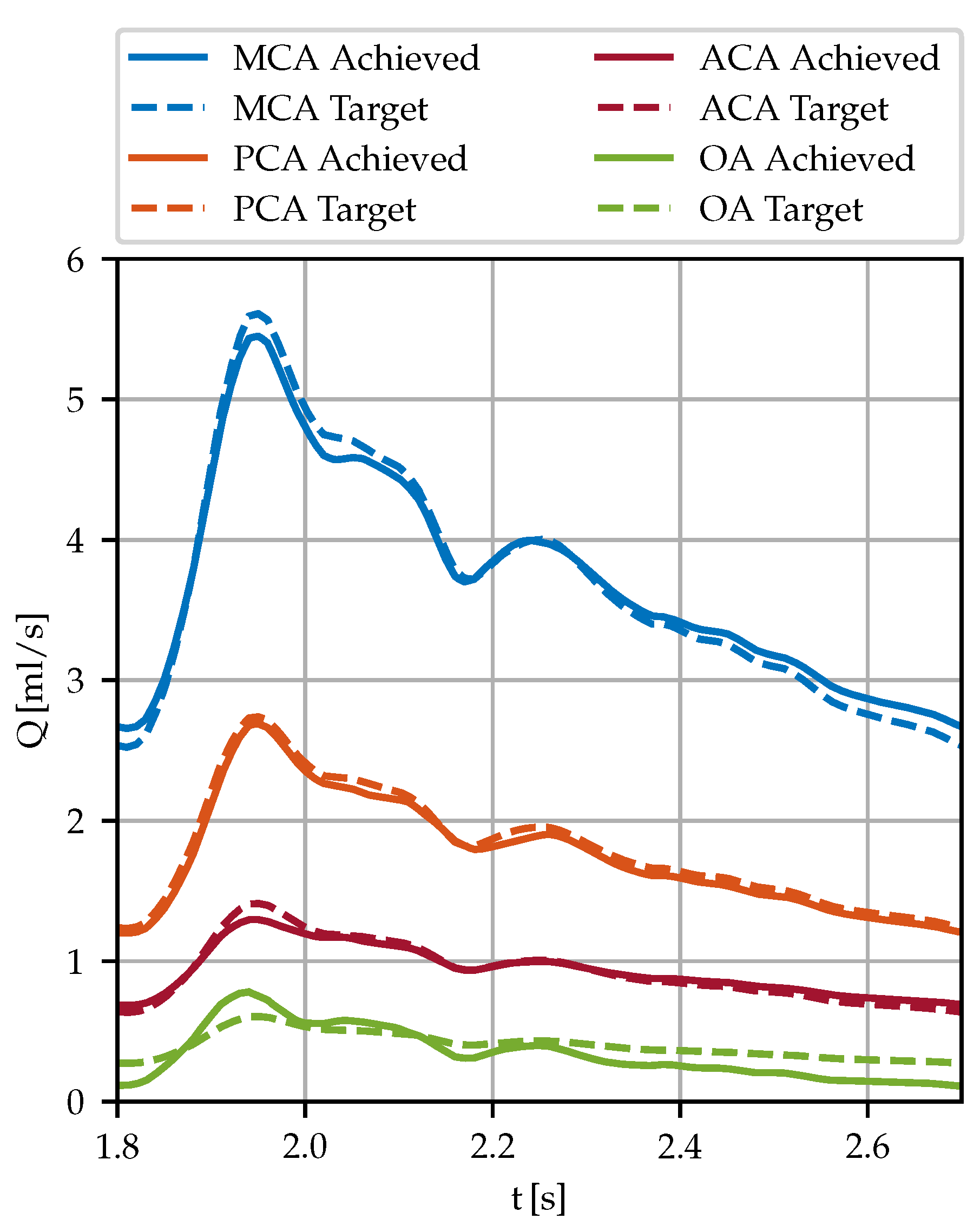
Lastly, the goodness of the boundary condition model is shown for which the resistances
have been fitted in an iterative process to minimize
error between the targeted flow and the achieved one. In
Figure 10 the volumetric flow of the left hemisphere’s outlets (aneurysm A) are shown together with the targeted curves as a representative example of the fitting performance. The linear law enables controlling the mass flow through pressure BCs within a relative error of 5% per cardiac cycle despite non-Newtonian and transient flows. The largest relative deviations have been observed at small vessels during peak systolic and peak diastolic times, as for instance the OA (green curves) in
Figure 10.
4. Discussion
The quantitative and qualitative differences induced by altering the computation domains exceed the expectations, reaching similar deviations as in the simulation challenges [
6,
7,
9]. To assess these changes, each of the complexity levels (
Simplified,
Middle and
Full) is going to be discussed with a special interest in the possible biases and their interactions with Murray’s law.
Starting with the Simplified strategy, the patient geometries shown in this study have clearly visible PComs, by which neglecting them and their influence on the closely located fundus is likely unreasoned. The simulations that have been run confirm that neglecting the Pcoms indeed changes drastically the results, thereby confirming the initial intuition. Without further dragging out the discussion around this strategy, we conclude that it is clearly unfit for the presented vasculatures.
The
Middle extension, being one of the most commonly found in literature, shows more resemblance with the
Full CoW simulations. Nevertheless, moderated alterations in the haemodynamics have sometimes been observed to cause a magnified change in WSS. It cannot be excluded that based on these observations different correlations between flow dynamics and aneurysm evolution might be drawn. The contributing factors to the differences are on one side, changed boundary flow rates and on the other one the lack of interactions with the opposing hemisphere and the posterior circulation. The boundary conditions for the
Middle extension split the stream entering through the ICA among the present outlets based on their cubed diameter proportions. Naturally, when additional outlets are added to the system, these proportions shift towards a more global system. In a similar fashion, additional suppliers, such as the neighbouring ICA and the BA, are participants in causing blood to traverse communicating vessels into other circulation segments. Although most of the interhemispheric flow was observed at the ACom, hence distal to the aneurysm fundus, the influence of the inflow streams cannot be generally disregarded from being important. In our study, equal flow rates for the ICAs were imposed following a popular choice shown in [
6] due to a lack of measurement data. As stated before, this is irrefutably one of the biases taken into consideration that could be lifted by measurements in follow-up work. The second agent that causes altering results between the
Full CoW and
Middle simulations is as stated the interaction between both anterior and posterior circulations. By not imposing a boundary midway in a PCom, more slack is left for the flow to unravel its natural properties. Examples of this, among others, are pressure drops at posterior arterial junctions and bifurcations that effectively alter upstream pressure distributions and are of notable relevance when using lower-order methods [
12,
33]. In the face of the recorded observations, the
Full CoW is likely to provide a more physiologically accurate haemodynamic profile than both other complexity levels while considering the influence of the used heuristics.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we conducted a detailed analysis to examine how different domain extensions and complexity levels affect haemodynamics in the CoW. Using patient-specific geometries and computational fluid dynamics, we simulated three models of increasing complexity for each patient. All these simulations considered non-Newtonian, pulsatile fluid flow, and outflow splits were determined using Murray’s law.
The obtained results showed significant variations in flow patterns throughout the arterial network, particularly in two out of the three cases. This highlights the importance of carefully analyzing topology to avoid modelling errors and conflicting results.
We conclude that studying the entire Circle of Willis or utilizing measurement data is essential to ensure physiological haemodynamics. To balance computational demands and accuracy, we suggest a two-step approach: a coarse large-scale simulation of the CoW to provide boundary conditions and a highly resolved local simulation focused on the region of interest, ensuring both reliability and high-fidelity haemodynamics. This approach can be applied to other vascular pathologies as well.
This study deals with the modelling challenge in IA research, which, if addressed comprehensively, could reduce discrepancies in computational fluid dynamics results, enhancing our understanding of IAs and their treatment principles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P. Jeken Rico. and A. Goetz.; methodology, P. Jeken Rico.; software, A. Larcher.; validation, P. Jeken Rico., P. Meliga. and A. Goetz.; formal analysis, P. Jeken Rico.; investigation, P. Jeken Rico.; resources, Y. Özpeynirci.; data curation, Y.Özpeynirci.; writing—original draft preparation, P. Jeken Rico.; writing—review and editing, A. Goetz.; P. Meliga.; visualization, A. Goetz.; supervision, E.Hachem.; project administration, E.Hachem; funding acquisition, E.Hachem. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Horizon ERC (European Union) grant number 101045042, Project CURE. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Research Council Executive Agency. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Informed Consent Statement
Specific patient consent was waived due to the retrospective study design.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IA |
Intracranial Aneurysm |
| CFD |
Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| ICA |
Internal Carotid Artery |
| PCom |
Posterior Communicating Artery |
| WSS |
Wall Shear Stress |
| OSI |
Oscillatory Shear Index |
References
- Wójtowicz, K.; Przepiorka, L.; Kujawski, S.; Marchel, A.; Kunert, P. Unruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms: Management Strategy and Results of a Single-Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvela, S. Outcome of Patients with Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Future Risk of Rupture of Unruptured Aneurysm. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagiola, I.; Mihalea, C.; Caroff, J.; Ikka, L.; Chalumeau, V.; Iacobucci, M.; Ozanne, A.; Gallas, S.; Marques, M.; Nalli, D.; Carrete, H.; Caldas, J.G.; Frudit, M.E.; Moret, J.; Spelle, L. The PHASES score: To treat or not to treat? Retrospective evaluation of the risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neuroradiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiga, G.; Berg, P.; Sugiyama, S.; Kono, K.; Steinman, D.A. The computational fluid dynamics rupture challenge 2013 - Phase I: Prediction of rupture status in intracranial aneurysms. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Roloff, C.; Beuing, O.; Voß, S.; Sugiyama, S.; Aristokleous, N.; Anayiotos, A.S.; Ashton, N.; Revell, A.; Bressloff, N.W.; et al. The Computational Fluid Dynamics Rupture Challenge 2013 - Phase II: Variability of Hemodynamic Simulations in Two Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valen-Sendstad, K.; Bergersen, A.W.; Shimogonya, Y.; Goubergrits, L.; Bruening, J.; Pallares, J.; Cito, S.; Piskin, S.; Pekkan, K.; Geers, A.J.; et al. Real-World Variability in the Prediction of Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Shear Stress: The 2015 International Aneurysm CFD Challenge. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, P.; Voß, S.; Saalfeld, S.; Janiga, G.; Bergersen, A.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Bruening, J.; Goubergrits, L.; Spuler, A.; Cancelliere, N.; et al. Multiple Aneurysms AnaTomy CHallenge 2018 (MATCH): Phase I: Segmentation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Janiga, G.; Berg, P. Multiple Aneurysms AnaTomy CHallenge 2018 (MATCH)-Phase Ib: Effect of morphology on hemodynamics. PLOS ONE 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Voß, S.; Janiga, G.; Saalfeld, S.; Bergersen, A.W.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Bruening, J.; Goubergrits, L.; Spuler, A.; Chiu, T.L.; et al. Multiple Aneurysms AnaTomy CHallenge 2018 (MATCH)—phase II: rupture risk assessment. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Janiga, G. A review on the reliability of hemodynamic modeling in intracranial aneurysms: Why computational fluid dynamics alone cannot solve the equation. Neurosurg. Focus. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helthuis, J.H.; van Doormaal, T.P.; Hillen, B.; Bleys, R.L.; Harteveld, A.A.; Hendrikse, J.; van der Toorn, A.; Brozici, M.; Zwanenburg, J.J.; van der Zwan, A. Branching Pattern of the Cerebral Arterial Tree. Anat. Rec. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chnafa, C.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Brina, O.; Pereira, V.M.; Steinman, D.A. Improved reduced-order modelling of cerebrovascular flow distribution by accounting for arterial bifurcation pressure drops. J. Biomech. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Preim, B.; Berg, P. Flow-splitting-based computation of outlet boundary conditions for improved cerebrovascular simulation in multiple intracranial aneurysms. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosner, J.; Reddy, V.; Lui, F. Neuroanatomy, Circle of Willis, 1 ed.; StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
- Devault, K.; Gremaud, P.A.; Novak, V.; Olufsen, M.S.; Vernières, G.; Peng, Z. Blood Flow in the Circle of Willis: Modelling and Calibration. PMC 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, J.; Birnefeld, J.; Zarrinkoob, L.; Wåhlin, A.; Eklund, A. Hemodynamic Disturbances in Posterior Circulation Stroke: 4D Flow Magnetic Resonance Imaging Added to Computed Tomography Angiography. Front. Neurosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindenes, L.B.; Håberg, A.K.; Johnsen, L.H.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Robben, D.; Vangberg, T.R. Variations in the circle of willis in a large population sample using 3D TOF angiography: The tromsø study. PLoS ONE 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chnafa, C.; Brina, O.; Pereira, V.M.; Steinman, D.A. Better Than Nothing: A Rational Approach for Minimizing the Impact of Outflow Strategy on Cerebrovascular Simulations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.; Putman, C.; Cebral, J. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Intracranial Aneurysms: Effects of Parent Artery Segmentation on Intra-Aneurysmal Hemodynamics. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2006, 27, 1703–1709, Available online: http://www.ajnr.org/content/27/8/1703.full.pdf (accessed on). [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, K.D.; Kallmes, D.F.; Dragomir-Daescu, D. Cerebral aneurysm blood flow simulations are sensitive to basic solver settings. J. Biomech. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, G.; Golshani, K.; Ferrell, A.; Zomorodi, A.; Smith, T. A review of the management of posterior communicating artery aneurysms in the modern era. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuzaine, C.; Remacle, J.F. Gmsh: A 3-D Finite Element Mesh Generator with built-in Pre- and Post-Processing Facilities. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, A.; Calderer, R. A variational multiscale method for incompressible turbulent flows : Bubble functions and fine scale fields. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, E.; Rivaux, B.; Kloczko, T.; Digonnet, H.; Coupez, T. Stabilized finite element method for incompressible flows with high Reynolds number. J. Comput. Phys. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, F.; Behr, M.; Heinkenschloss, M. Shape optimization in unsteady blood flow: A numerical study of non-Newtonian effects. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaruto, A.M.; Janela, J.; Moura, A.; Sequeira, A. Sensitivity of hemodynamics in a patient specific cerebral aneurysm to vascular geometry and blood rheology. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Fujita, N.; Enoki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Murase, K.; Nakamura, H. Relationship between Variations in the Circle of Willis and Flow Rates in Internal Carotid and Basilar Arteries Determined by Means of Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Semiautomated Lumen Segmentation: Reference Data from 125 Healthy Volunteers. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1770–1775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vignon-Clementel, I.E.; Alberto Figueroa, C.; Jansen, K.E.; Taylor, C.A. Outflow boundary conditions for three-dimensional finite element modeling of blood flow and pressure in arteries. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussel, L.; Rayz, V.L.; McCulloch, C.; Martin, A.; Acevedo-Bolton, G.; Lawton, M.; Higashida, R.; Smith, W.S.; Young, W.L.; Saloner, D. Aneurysm growth occurs at region of low wall shear stress: Patient-specific correlation of hemodynamics and growth in a longitudinal study. Stroke 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urschel, K.; Tauchi, M.; Achenbach, S.; Dietel, B. Investigation of wall shear stress in cardiovascular research and in clinical practice—from bench to bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Tutino, V.M.; Xiang, J.; Siddiqui, A. High WSS or Low WSS? Complex interactions of hemodynamics with intracranial aneurysm initiation, growth, and rupture: Toward a unifying hypothesis. AJNR 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen, J.C.; Franke, C.L.; Ramos, L.M.; Wilmink, J.T.; Van Gijn, J. Direction of Flow in Posterior Communicating Artery on Magnetic Resonance Angiography in Patients with Occipital Lobe Infarcts. Stroke 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynard, J.P.; Valen-Sendstad, K. A unified method for estimating pressure losses at vascular. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).