Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
24 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
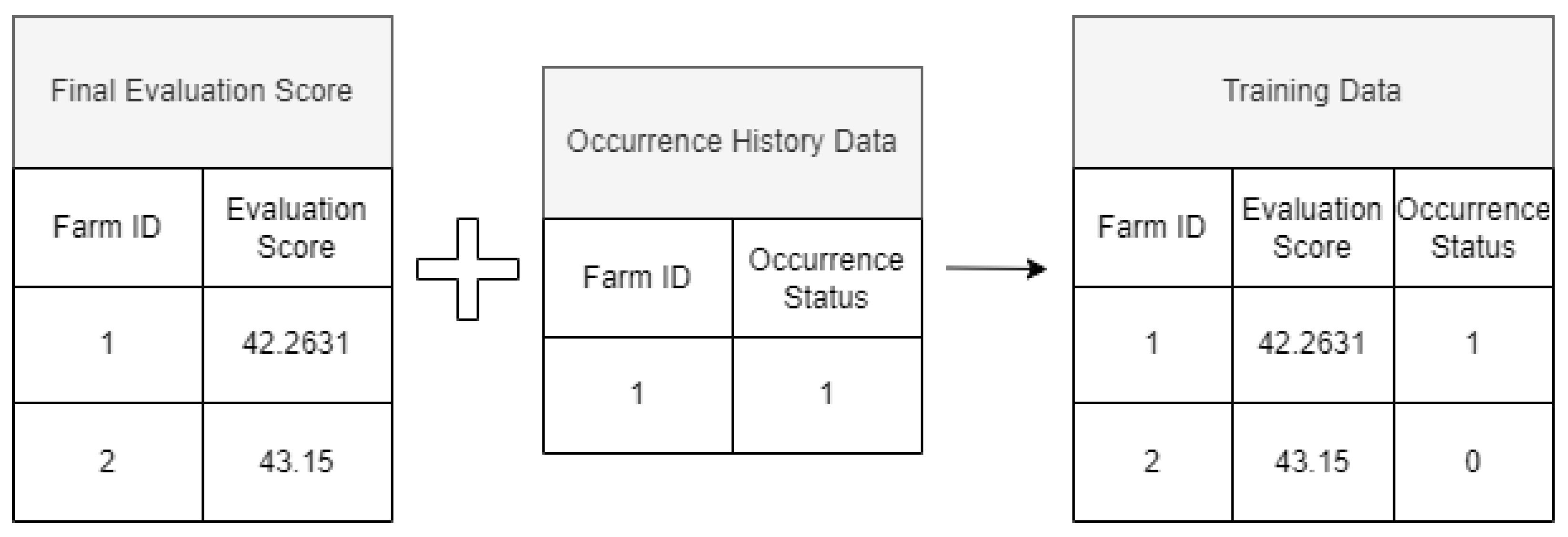
2.1. Data Preparation and Organization
2.2. Rule-Based Scoring
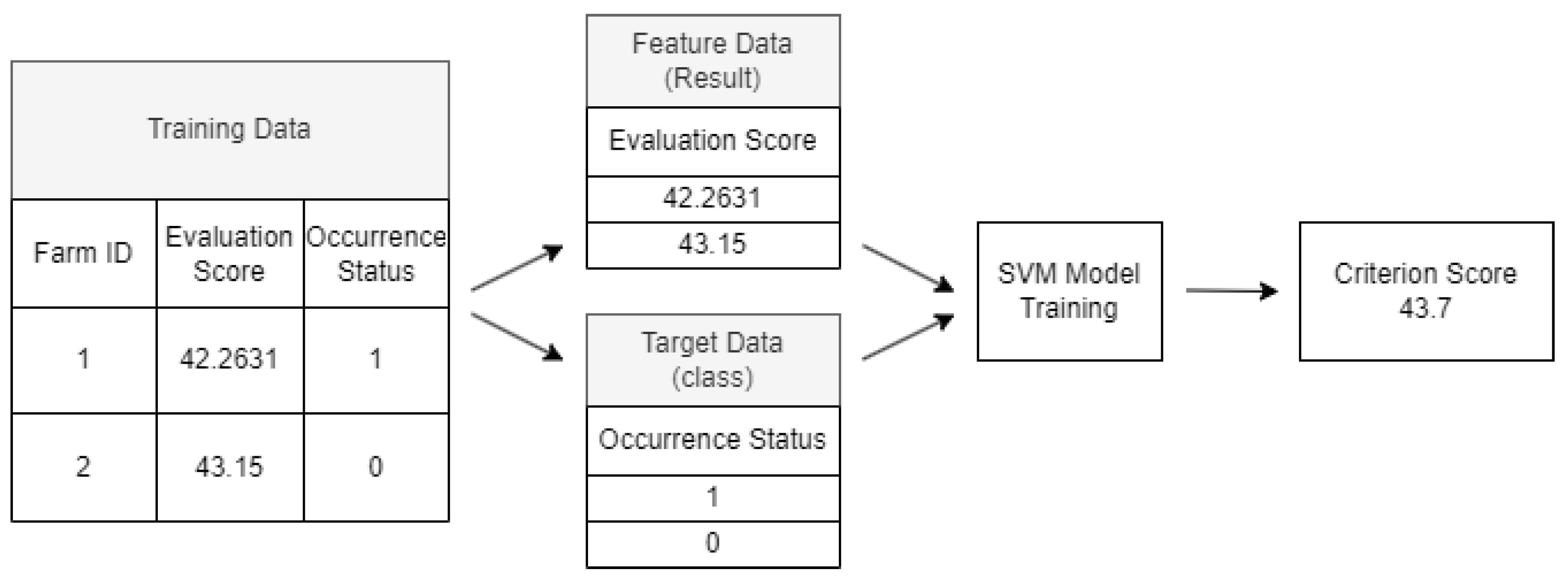
2.3. Decision Model
2.4. Experiment Setup
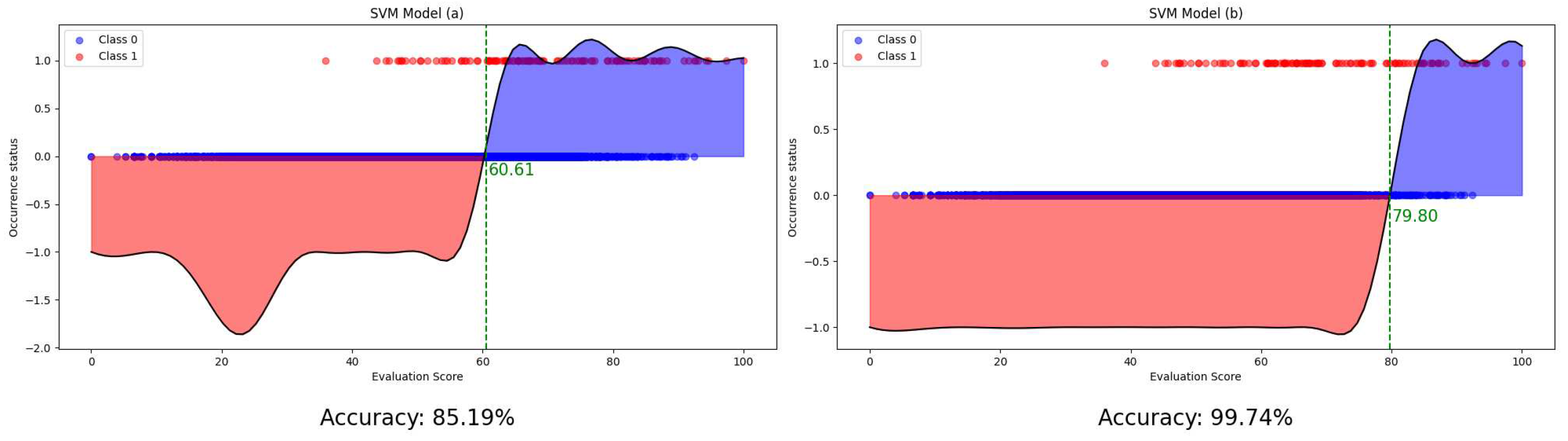
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, Sébastien and Bauzile, Billy and Mugnier, Amélie and Durand, Benoit and Vergne, Timothée and Paul, Mathilde C. A systematic review of mechanistic models used to study avian influenza virus transmission and control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.00394, . [CrossRef]
- Lucido, Abel G and Smith, Robert J and Lao, Angelyn R. Periodic culling outperforms isolation and vaccination strategies in controlling Influenza A H5N6 outbreaks in the Philippines. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.10130.
- Seymour, Rowland G and Kypraios, Theodore and O’Neill, Philip D and Hagenaars, Thomas J. A Bayesian nonparametric analysis of the 2003 outbreak of highly pathogenic avian influenza in the Netherlands. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series C: Applied Statistics 2021, 70.5, 1323–1343, . [CrossRef]
- Choi, Woo Yong and Song, Kyu Ye and Lee, Chan Woo. AI4AI: Quantitative Methods for Classifying Host Species from Avian Influenza DNA Sequence. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.09197.
- Valdez, Lucas Daniel and Vassallo, Lautaro and Braunstein, Lidia Adriana. Epidemic control in networks with cliques. Physical Review E 2023, 107.5, 054304, . [CrossRef]
- Singh, Sarabjeet and Schneider, David J and Myers, Christopher R. The structure of infectious disease outbreaks across the animal-human interface. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1307.4628.
- Kojaku, Sadamori and Hébert-Dufresne, Laurent and Mones, Enys and Lehmann, Sune and Ahn, Yong-Yeol. The effectiveness of backward contact tracing in networks. Nature physics 2021, 17.5, 652–658, . [CrossRef]
- Niu, Shuai and Yin, Qing and Song, Yunya and Guo, Yike and Yang, Xian. Label dependent attention model for disease risk prediction using multimodal electronic health records. In 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM); pp. 449–458.
- Mesinovic, Munib and Watkinson, Peter and Zhu, Tingting. Explainable AI for clinical risk prediction: A survey of concepts, methods, and modalities. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.08407.
- Rapp, Michael and Kulessa, Moritz and Loza Mencía, Eneldo and Fürnkranz, Johannes. Correlation-based discovery of disease patterns for syndromic surveillance. Front. Big Data 2022, 4, 784159, . [CrossRef]
- Cooney, Philip and White, Arthur. Utilizing Expert Opinion to inform Extrapolation of Survival Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.02288.
- Rusek, Janusz and Tajduś, Krzysztof and Firek, Karol and Jędrzejczyk, Adrian. Bayesian networks and Support Vector Classifier in damage risk assessment of RC prefabricated building structures in mining areas. In 2020 5th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech); pp. 1–8.
- Ahmad, Saleem and Koh, Kyeyoung and Yoo, Daesung and Suh, Gukhyun and Lee, Jaeil and Lee, Chang-Min. Impact of inland waters on highly pathogenic avian influenza outbreaks in neighboring poultry farms in South Korea. Journal of Veterinary Science 2022, 23.3, . [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Dae-sung and Chun, Byung Chul and Hong, Kwan and Kim, Jeehyun. Risk Prediction of Three Different Subtypes of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Outbreaks in Poultry Farms: Based on Spatial Characteristics of Infected Premises in South Korea. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 897763, . [CrossRef]
- EOM, Chi-Ho and PAK, Sun-Il and BAE, Sun-Hak. Analysis of Potential Infection Site by Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Using Model Patterns of Avian Influenza Outbreak Area in Republic of Korea. Journal of the Korean Association of Geographic Information Studies 2017, 20.2, 60–74.
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. (2022). “AI Emergency Action Guidelines (SOP)”. Available online: https://www.mafra.go.kr/sn3hcv_v2023/skin/doc.html?fn=AD2F803A-4839-AD0A-53D4-46957505D0B3.hwp&rs=/sn3hcv_v2023/atchmnfl/bbs/202310 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Seo, I-H and Lee, I-B. CFD application for estimation of airborne spread of HPAI (highly pathogenic avian influenza). In Ist International Symposium on CFD Applications in Agriculture 1008; pp. 57–62, . [CrossRef]
- Korea National Spatial Data Infrastructure Portal. (2023). Available online: http://www.nsdi.go.kr/lxportal/?menuno=2679 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Korea Public Data Portal. (2023). Available online: https://www.data.go.kr/ (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Korea Meteorological Administration. (2023). Real-time weather conditions [Data file retrieved from KMA Weather Data API]. Available online: https://apihub.kma.go.kr/ (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Jeonnam Provincial Office of Animal Disease Control. (2023). Data on Farm basic information in Jeonnam. Jeonnam Provincial Government.
- Zheng, Shuai and Ding, Chris. Minimal support vector machine. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02370.
- Morales, Iván Ramírez and Cebrián, Daniel Rivero and Blanco, Enrique Fernández and Sierra, Alejandro Pazos. Early warning in egg production curves from commercial hens: A SVM approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 169–179, . [CrossRef]
- Pal, Mahesh. Support vector machines/relevance vector machine for remote sensing classification: A review. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1101.2987.
- Mishra, Swapnil and Berah, Tresnia and Mellan, Thomas A and Unwin, H Juliette T and Vollmer, Michaela A and Parag, Kris V and Gandy, Axel and Flaxman, Seth and Bhatt, Samir. On the derivation of the renewal equation from an age-dependent branching process: An epidemic modelling perspective. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.16487.
- Elsobky, Yumna and Nganwa, David and El Afandi, Gamal and Byomi, Ahmed and Reddy, Gopal and Abdalla, Ehsan. A quantitative risk assessment to evaluate the efficacy of mitigation strategies to reduce highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, subtype H5N1 (HPAI H5N1) in the Menoufia governorate, Egypt. BMC Veterinary Research 2021, 17.1, 210, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Xiaoni. Enterprise Supply Chain Risk Assessment Based on the Support Vector Machine Algorithm and Fuzzy Model. Secur. Commun. Networks 2022, 2022, . [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, Luca and De Leo, Giulio A. A cost analysis of alternative culling strategies for the eradication of classical swine fever in wildlife. Environment and Development Economics 2007, 12.5, 653–671.
| Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Farm Culling Criteria | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrain | Mountain range | In cases where there are mountain ranges or terrains with an altitude of 50m or higher blocking the direct path between the farm under analysis and the nearby farm. |
-10 |
| If the farm under analysis is located in the mountains or a mountain is within 100m proximity. |
+3 | ||
| River ratio | When the proportion of national rivers or local rivers within 3km of the farm under analysis is 3% or higher. |
+5 | |
| When the proportion of national rivers or local rivers within 3km of the farm under analysis is between 2% and 3%. |
+2 | ||
| When the proportion of national rivers or local rivers within 3km of the farm under analysis is between 1% and 2%. |
+1 | ||
| When the proportion of national rivers or local rivers within 3km of the farm under analysis is 1% or less. |
-2 | ||
| Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Farm Culling Criteria | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Status around the farm | Road proximity | In cases where the distance between the farm under analysis and the surrounding road (with 2 or more lanes) is within 1km. |
+5 |
| In cases where the distance between the farm under analysis and the surrounding road (with 2 or more lanes) is between 1km and 3km. |
+2 | ||
| In cases where the distance between the farm under analysis and the surrounding road (with 2 or more lanes) exceeds 3km. |
-3 | ||
| Population density | When the population density of the administrative area where the farm under analysis is located is 100 or more per 1 km2. |
+5 | |
| When the population density of the administrative area where the farm under analysis is located is 50 or more per 1 km2. |
+2 | ||
| When the population density of the administrative area where the farm under analysis is located is 30 or more per 1 km2. |
+1 | ||
| When the population density of the administrative area where the farm under analysis is located is 20 or fewer per 1 km2. |
-2 | ||
| Farm density | When the combined number of poultry and duck farms in the administrative area of the farm under analysis is 1 or more per 1 km2. |
+10 | |
| When the combined number of poultry and duck farms in the administrative area of the farm under analysis is between 0.5 and 0.1 per 1 km2. |
+5 | ||
| When the combined number of poultry and duck farms in the administrative area of the farm under analysis is between 0.3 and 0.5 per 1 km2. |
+2 | ||
| When the combined number of poultry and duck farms in the administrative area of the farm under analysis is 0.3 or fewer per 1 km2. |
-2 | ||
| Farmland ratio | When the proportion of farmland within 3km of the farm under analysis is 30% or more. |
+5 | |
| When the proportion of farmland within 3km of the farm under analysis is between 20% and 30%. |
+2 | ||
| When the proportion of farmland within 3km of the farm under analysis is between 10% and 20%. |
+1 | ||
| When the proportion of farmland within 3km of the farm under analysis is 10% or less. |
-2 | ||
| Traditional market | When the distance between the analysis target farm and the market is less than 1km. |
+5 | |
| When the distance between the analyzed farm and the market is more than 1km and less than 2km. |
+3 | ||
| When the distance between the analysis target farm and the market is more than 2km and less than 5km. |
+2 | ||
| When the distance between the analysis target farm and the market exceeds 5km. |
-1 | ||
| Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Farm Culling Criteria | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Breed | Breeding type | In the case where the farm under analysis raises breeding chickens. | +0 |
| In the case where the farm under analysis raises meat chickens. | +0 | ||
| In the case where the farm under analysis raises laying hens. | +5 | ||
| In the case where the farm under analysis raises breeding ducks. | +20 | ||
| In the case where the farm under analysis raises meat ducks. | +15 | ||
| Epidemic information | Analyzing nearby farm distances | If the distance between the farm under analysis and the nearby farm is within 500m. |
+30 |
| If the distance between the farm under analysis and the nearby farm is 500m 3km. |
+5 | ||
| If the distance between the farm under analysis and the nearby farm is 3km 10km. |
+2 | ||
| If the distance between the farm under analysis and the nearby farm exceeds 10km. |
-5 | ||
| Weather | Temperature | If the temperature on the day of analysis is below 0℃. | +7 |
| If the temperature on the day of analysis is 0℃ 15℃. | +5 | ||
| If the temperature on the day of analysis is 15℃ 20℃. | +3 | ||
| If the temperature on the day of analysis is 20℃ 30℃. | +0 | ||
| If the temperature on the day of analysis exceeds 30℃. | -10 | ||
| Wind direction | If the wind blows from the nearby farm under analysis towards the farm under analysis at an average speed of 3.3 m/s or more on the day of analysis. |
+5 | |
| Epidemiological history | Analysis farm occurrence history | In the case where the farm under analysis has had one occurrence of HPAI in the past 5 years. |
+10 |
| In the case where the farm under analysis has had two occurrences of HPAI in the past 5 years. |
+20 | ||
| In the case where the farm under analysis has had three occurrences of HPAI in the past 5 years. |
+40 | ||
| Ecological environment | Distance from migratory bird habitat | If the distance between the farm under analysis and the main migratory bird habitat is within 15km. |
+7 |
| If the distance between the farm under analysis and the main migratory bird habitat is 15 30km. |
+3 | ||
| If the distance between the farm under analysis and the main migratory bird habitat exceeds 30km. |
-3 | ||
| Farm Name | Evaluation Score | Final Evaluation Score |
|---|---|---|
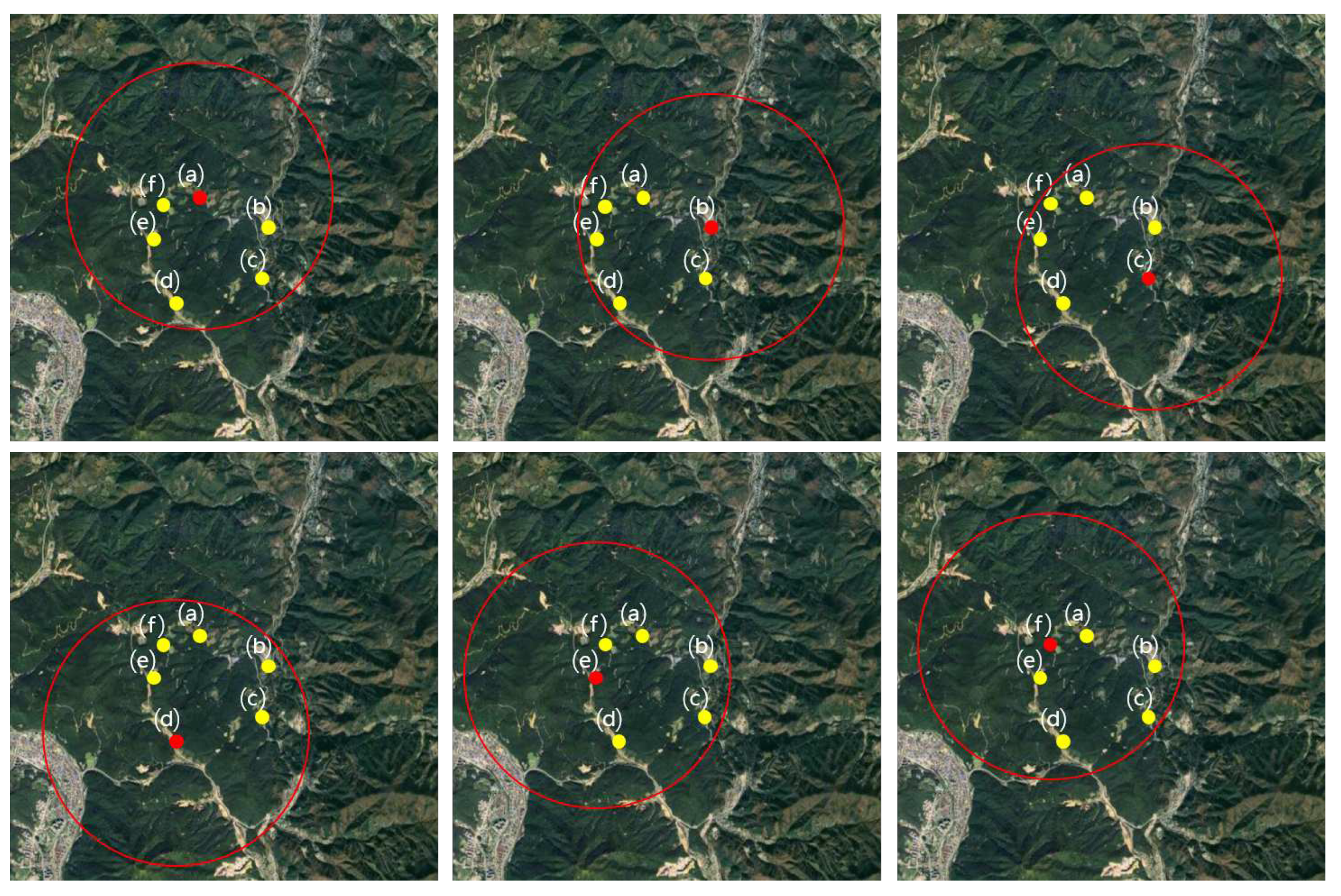
| (a) | =45, =30, =48, =32, =38 | |
| (b) | =50, =54, =55, =60, =58 | |
| (c) | =12, =16, =18, =20, =9 | |
| (d) | =50, =54, =55, =60, =58 | |
| (e) | =88, =76, =74, =79, =85 | |
| (f) | =33, =35, =50, =48, =39 |
| Experiment Method | Recall | Precision | Accuracy | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Method | 1 | 0.1037 | 0.1037 | 0.1817 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 0.7865 | 0.4252 | 0.8408 | 0.5046 |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 0.9851 | 0.1805 | 0.4537 | 0.2829 |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 0.839 | 0.489 | 0.8419 | 0.5619 |
| Year of Occurrence | Experiment Method | Recall | Precision | Accuracy | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ]4*2014 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.093023 | 0.093023 | 0.17 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 0.75 | 0.222222 | 0.732558 | 0.343 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.145455 | 0.453488 | 0.254 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 0.75 | 0.222222 | 0.732558 | 0.343 | |
| ]4*2015 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.134043 | 0.134043 | 0.236 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 0.952381 | 0.437956 | 0.829787 | 0.6 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.225806 | 0.540426 | 0.368 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 0.904762 | 0.431818 | 0.82766 | 0.585 | |
| ]4*2016 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.060241 | 0.060241 | 0.114 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 1 | 0.138889 | 0.626506 | 0.244 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.104167 | 0.481928 | 0.189 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 1 | 0.138889 | 0.626506 | 0.244 | |
| ]4*2017 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.054348 | 0.054348 | 0.103 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 1 | 0.714286 | 0.978261 | 0.833 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.076923 | 0.347826 | 0.143 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 1 | 0.714286 | 0.978261 | 0.833 | |
| ]4*2020 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.02381 | 0.02381 | 0.047 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 1 | 0.111111 | 0.809524 | 0.2 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.034483 | 0.333333 | 0.067 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 1 | 0.125 | 0.833333 | 0.222 | |
| ]4*2021 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.057143 | 0.057143 | 0.108 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 1 | 0.4 | 0.914286 | 0.571 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.090909 | 0.428571 | 0.167 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 1 | 0.4 | 0.914286 | 0.571 | |
| ]4*2022 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.097436 | 0.097436 | 0.178 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 0.368421 | 0.466667 | 0.897436 | 0.412 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 0.894737 | 0.114865 | 0.317949 | 0.204 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 0.631579 | 0.461538 | 0.892308 | 0.533 | |
| ]4*2023 | Conventional Method | 1 | 0.030303 | 0.030303 | 0.059 |
| Proposed Method (w=1) | 1 | 0.333333 | 0.939394 | 0.5 | |
| Proposed Method (w=485) | 1 | 0.037037 | 0.212121 | 0.071 | |
| Proposed Method (w=8.5) | 1 | 0.285714 | 0.924242 | 0.444 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





