Submitted:
27 October 2023
Posted:
02 November 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Data
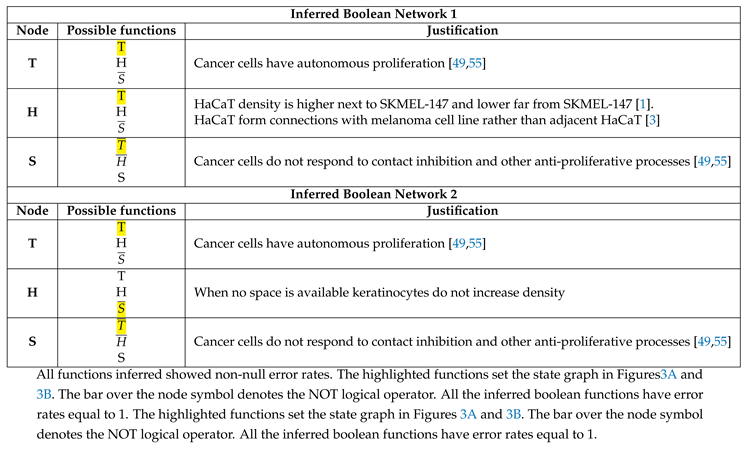
2.2. Boolean Network Inference
2.3. Estimating the Cellular Automata Dynamic Rules from BN Basins through Consensus of State Transition Comparison
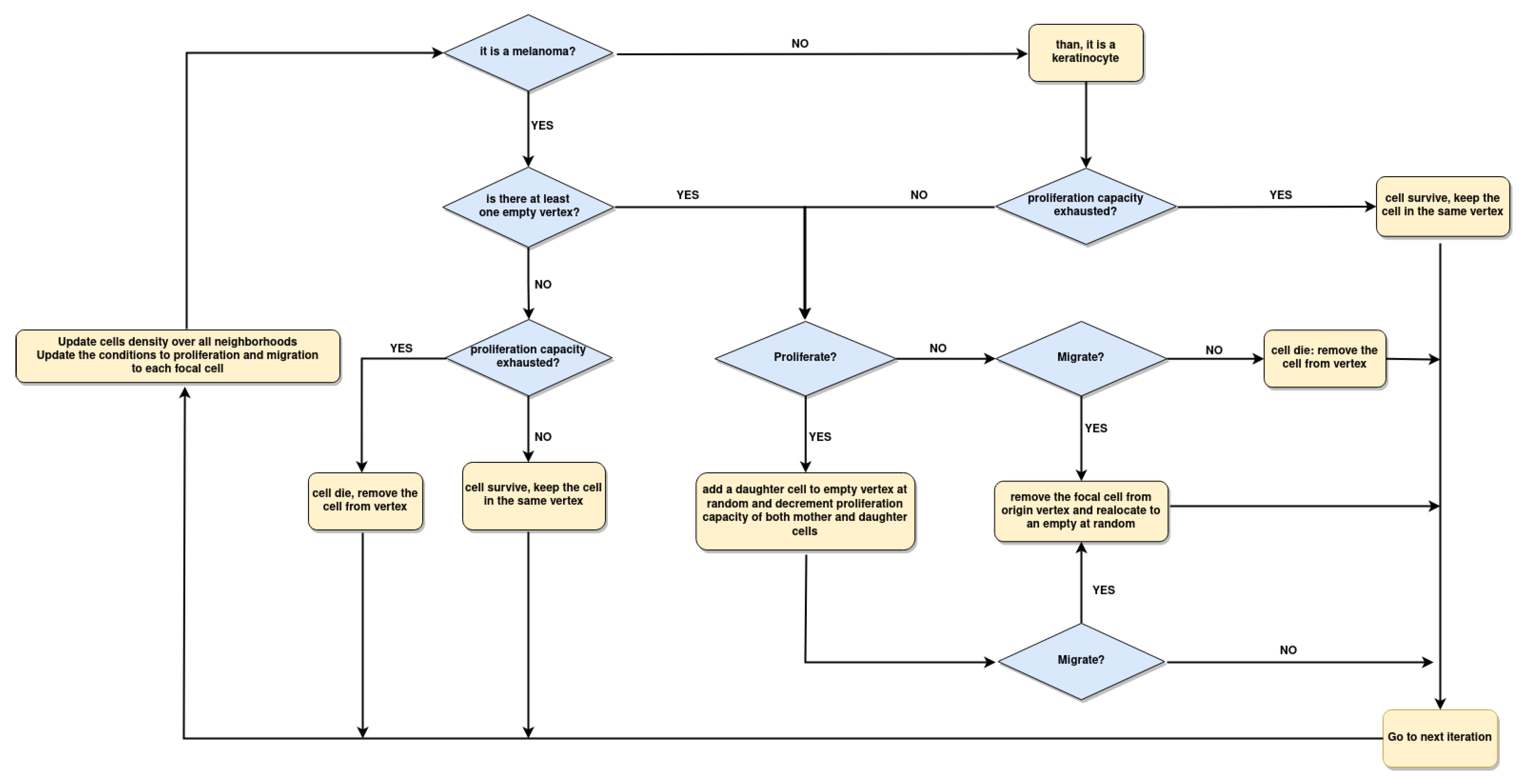
2.4. Implementation of Square-Lattice Cellular Automata
2.5. Spatial Configuration, Parameter Estimation, and Population Dynamics Process Probabilities
3. Results
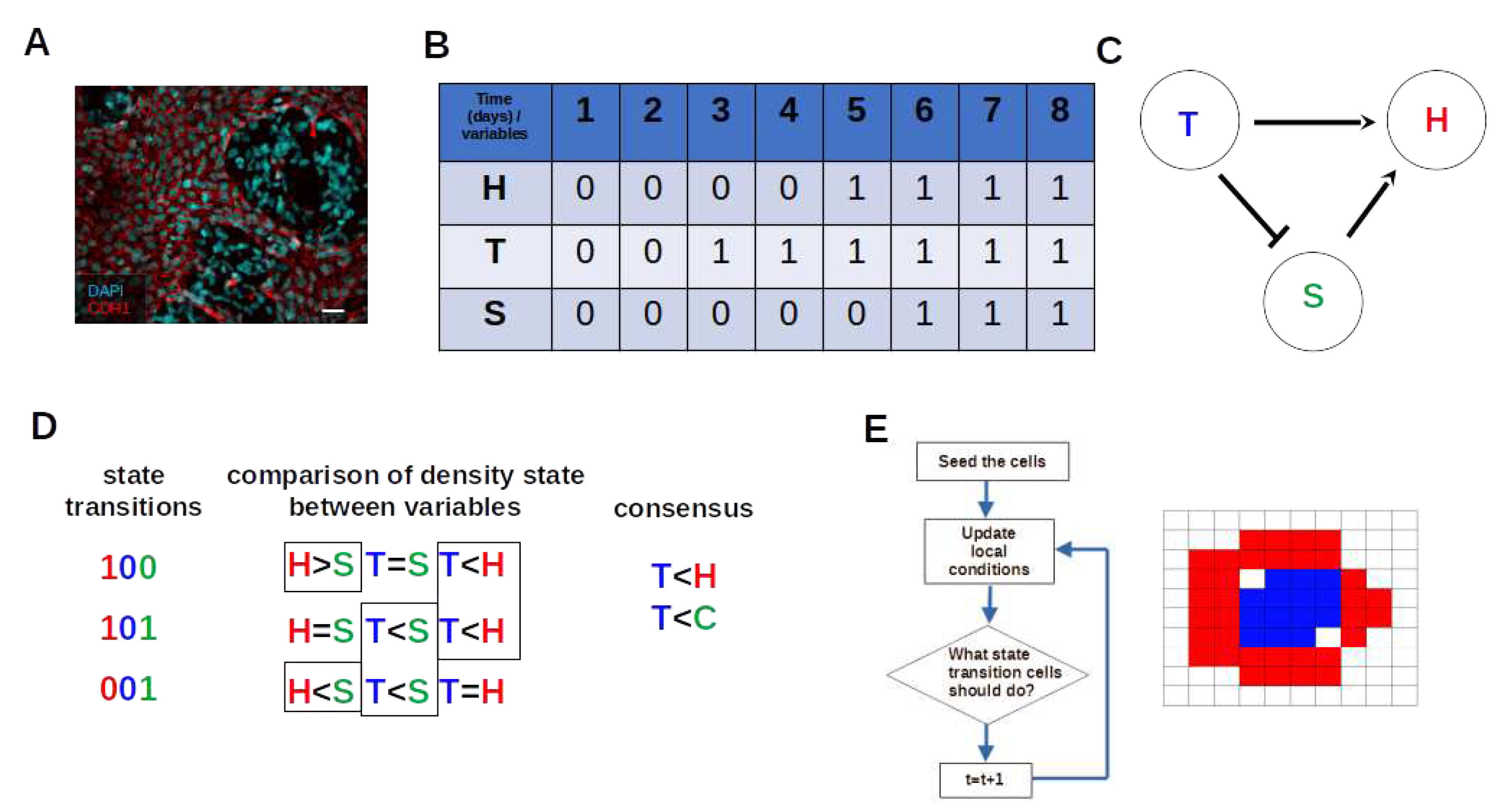
3.1. The Iterative k-Means Binarization Method Demonstrated That Both Populations Are in High Density after 4 Days
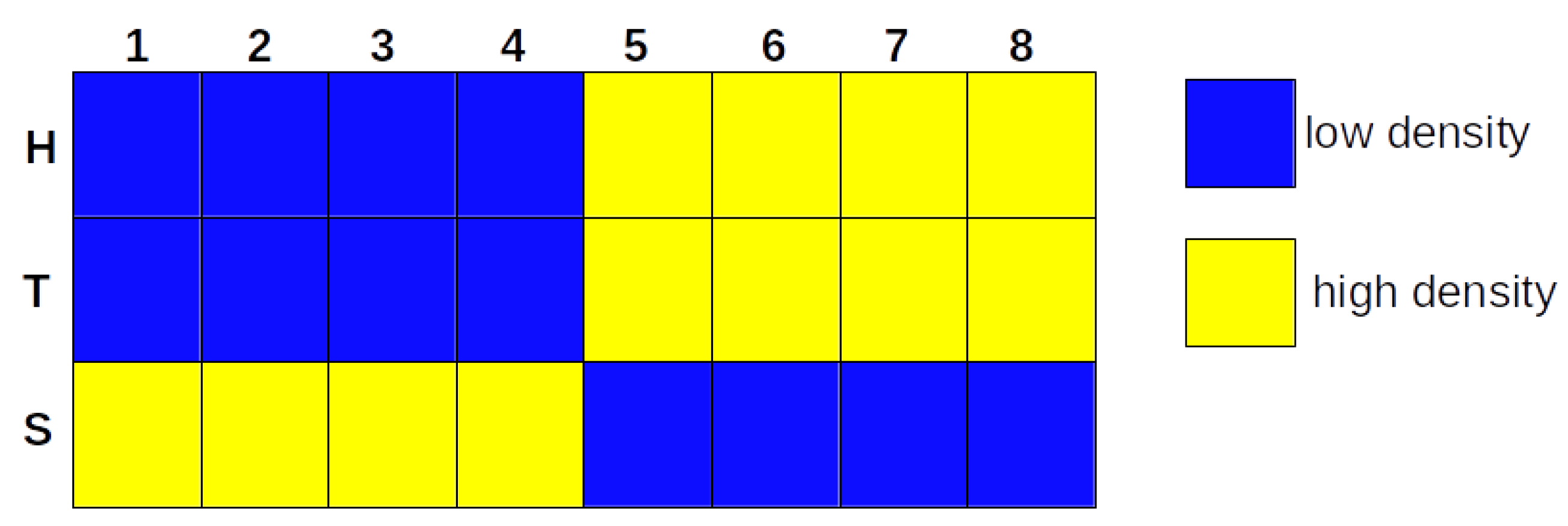
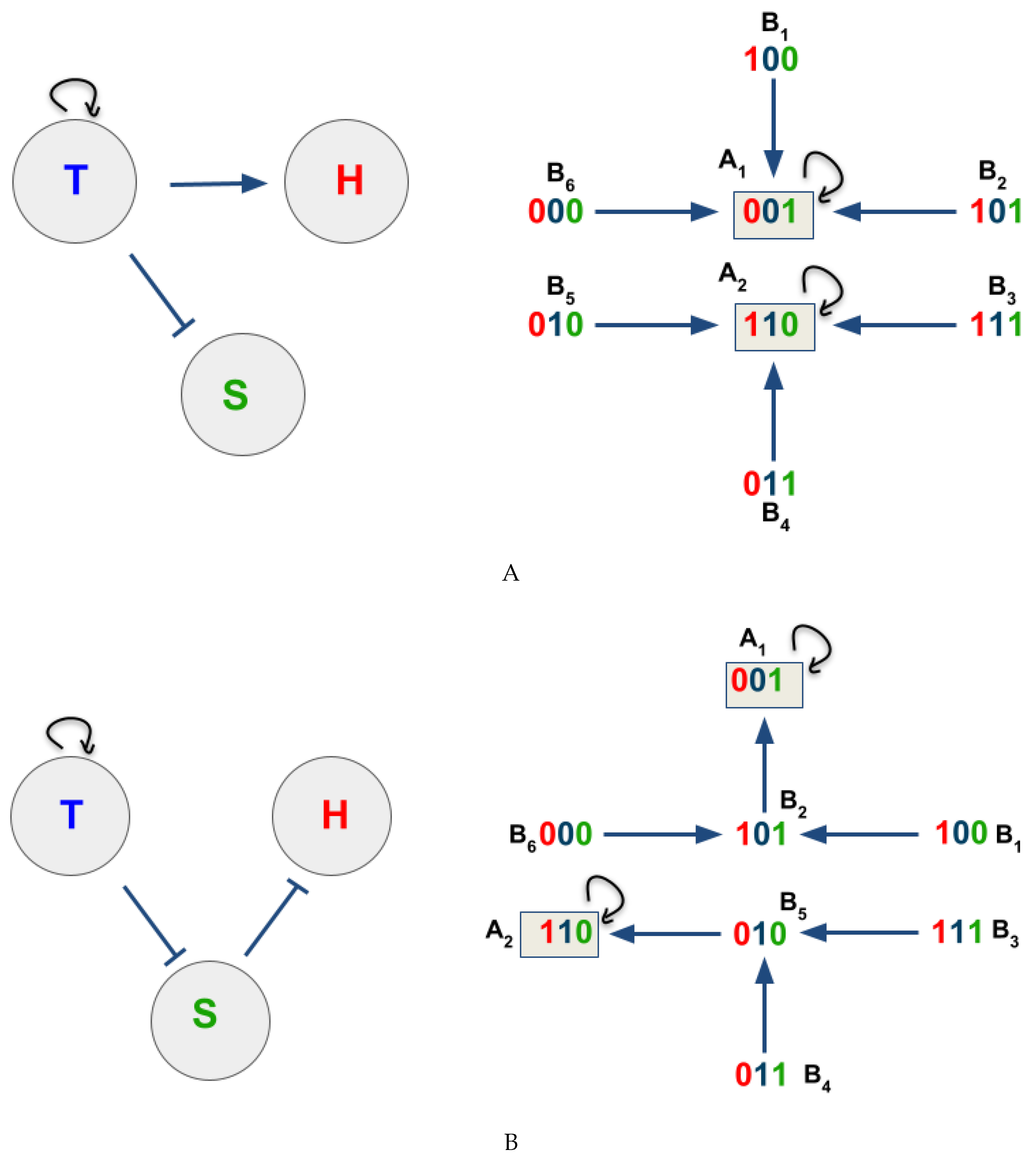
3.2. The Network Dynamics Exhibit Two Singleton Attractors
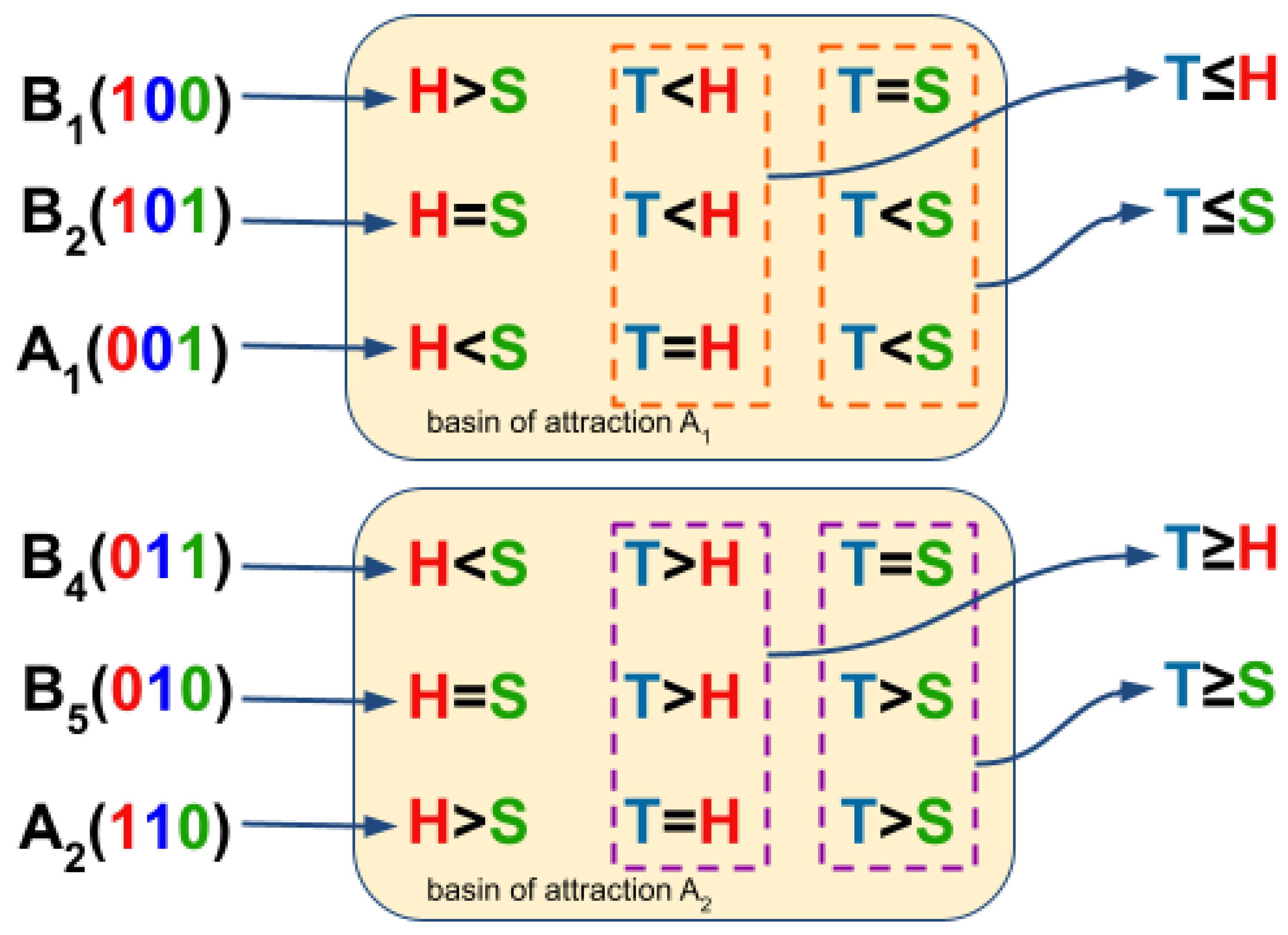
3.3. Boolean Network Basin Provide Cellular Automata Dynamic Rules for Proliferation and Migration
3.4. Data from Cell Lines and Growth Curves Allow Us to Propose a Simple Rule to Describe Survival and Death Dynamics
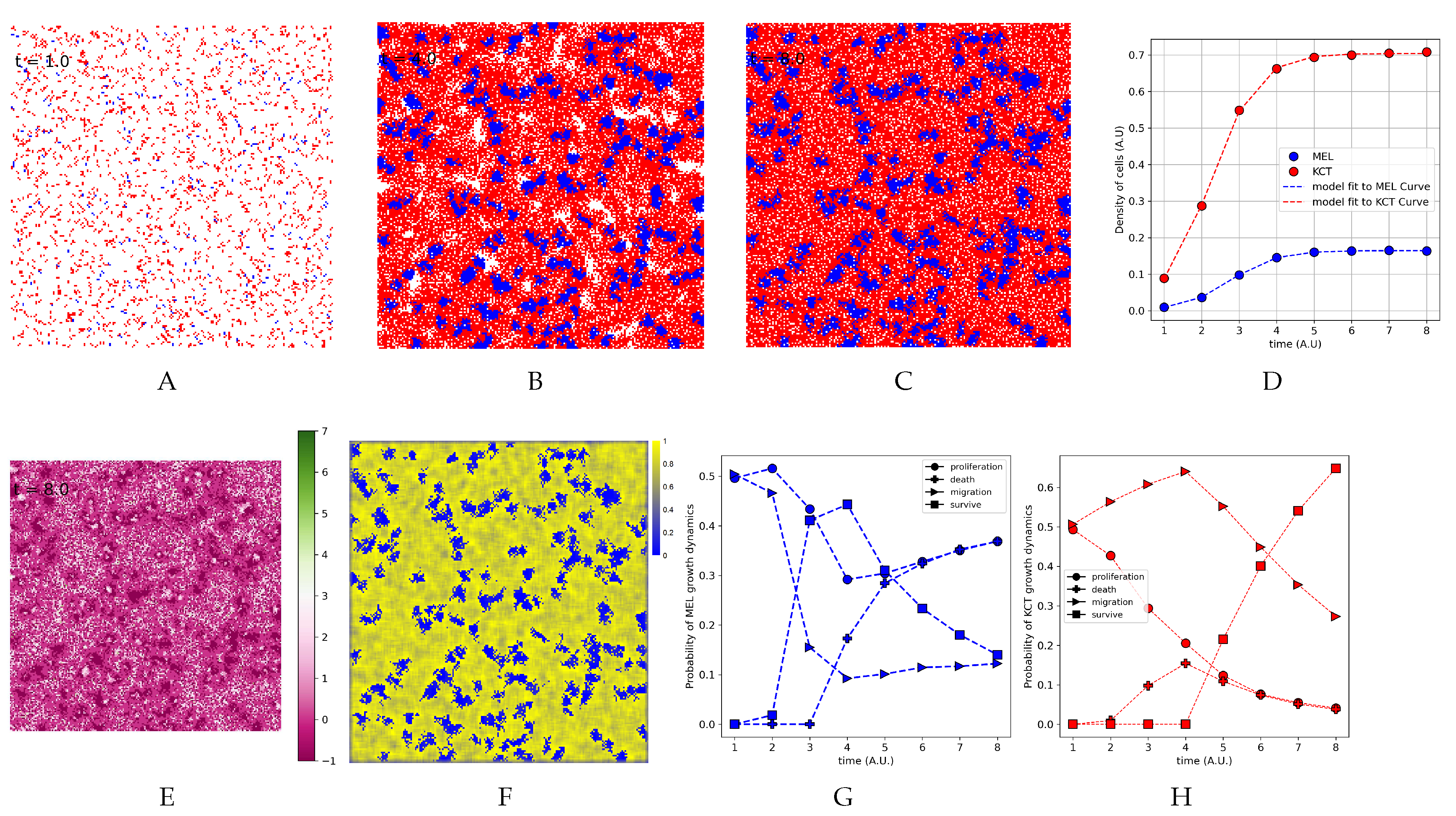
3.5. The Parameter Estimation Are in Agreement with Experimental Data
3.6. The Density of H Indeed is Higher Close to T Cluster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Morais MCC, Stuhl I, Sabino AU, Lautenschlager WW, Queiroga AS, Tortelli Jr TC, et al. Stochastic model of contact inhibition and the proliferation of melanoma in situ. Sci Rep. 2017; 7: 8026. [CrossRef]
- Kodet O, Lacina L, Krejčí E, Dvořánková B, Grim M, Štork J, et al. Melanoma cells influence the differentiation pattern of human epidermal keratinocytes. Mol Cancer. 2015; 14: 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz J, Simiczyjew A, Dratkiewicz E, Kot M, Pietraszek-Gremplewicz K, Wilk D, et al. Melanoma stimulates the proteolytic activity of HaCaT keratinocytes. Cell Commun Signal. 2022; 20: 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Neumann, JV. Theory of self-reproducing automata. Edited by Arthur W Burks. 1966.
- Wolfram, S. Statistical mechanics of cellular automata. Rev Mod Phys. 1983; 55: 601. [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, S. Homeostasis and differentiation in random genetic control networks. Nature. 1969; 224: 177-178. [CrossRef]
- Bornholdt, S. Boolean network models of cellular regulation: prospects and limitations. J R Soc Interface. 2008; 5: 85-94. [CrossRef]
- Dormann S, Deutsch A. Modeling of self-organized avascular tumor growth with a hybrid cellular automaton. In Silico Biol. 2002; 2: 393-406. [CrossRef]
- Spencer SL, Gerety RA, Pienta KJ, Forrest S. Modeling somatic evolution in tumorigenesis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006; 2: 108. [CrossRef]
- Enderling H, Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P. Migration rules: tumours are conglomerates of self-metastases. Br J Cancer. 2009; 100: 1917-1925. [CrossRef]
- Enderling H, Anderson AR, Chaplain MA, Beheshti A, Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P. Paradoxical dependencies of tumor dormancy and progression on basic cell kinetics. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 8814-8821. [CrossRef]
- Kansal A, Torquato S, Chiocca E, Deisboeck T. Emergence of a subpopulation in a computational model of tumor growth. J Theor Biol. 2000; 207: 431-441. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Strouthos CG, Wang Z, Deisboeck TS. Simulating brain tumor heterogeneity with a multiscale agent-based model: linking molecular signatures, phenotypes and expansion rate. Mathematical and computer modelling. 2009; 49: 307-319. [CrossRef]
- Wcisło R, Dzwinel W, Yuen DA, Dudek AZ. A 3-D model of tumor progression based on complex automata driven by particle dynamics. J Mol Mod 2009; 15: 1517-1539. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Deisboeck TS. Computational modeling of brain tumors: discrete, continuum or hybrid? Sci Mod Sim. 2009; 381–393. [CrossRef]
- Anderson AR, Rejniak KA, Gerlee P, Quaranta V. Microenvironment driven invasion: a multiscale multimodel investigation. J Math Biol. 2009; 58: 579-624. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Wang Z, Sagotsky JA, Deisboeck TS. Multiscale agent-based cancer modeling. J Math Biol. 2009; 58: 545–559. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, AR. A hybrid mathematical model of solid tumour invasion: the importance of cell adhesion. Math Med Biol. 2005; 22: 163-186. [CrossRef]
- Sottoriva A, Verhoeff JJ, Borovski T, McWeeney SK, Naumov L, Medema JP, et al. Cancer stem cell tumor model reveals invasive morphology and increased phenotypical heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2010; 70: 46-56. [CrossRef]
- Gatenby RA, Smallbone K, Maini PK, Rose F, Averill J, Nagle RB, et al. Cellular adaptations to hypoxia and acidosis during somatic evolution of breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007; 97: 646-653. [CrossRef]
- Gerlee P, Anderson A. Evolution of cell motility in an individual-based model of tumour growth. J Theor Biol. 2009; 259: 67-83. [CrossRef]
- Silva AS, Yunes JA, Gillies RJ, Gatenby RA. The potential role of systemic buffers in reducing intratumoral extracellular pH and acid-mediated invasion. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 2677-2684. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Chen LL, Deisboeck TS. Multi-scale, multi-resolution brain cancer modeling. Math Comput Simul. 2009; 79: 2021-2035. [CrossRef]
- Gerlee P, Anderson AR. A hybrid cellular automaton model of clonal evolution in cancer: the emergence of the glycolytic phenotype. J Theor Biol. 2008; 250: 705-722. [CrossRef]
- Smallbone K, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ, Maini PK, Gavaghan DJ. Metabolic changes during carcinogenesis: potential impact on invasiveness. J Theor Biol. 2007; 244: 703-713. [CrossRef]
- Anderson AR, Hassanein M, Branch KM, Lu J, Lobdell NA, Maier J, et al. Microenvironmental independence associated with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 8797-8806. [CrossRef]
- Anderson AR, Weaver AM, Cummings PT, Quaranta V. Tumor morphology and phenotypic evolution driven by selective pressure from the microenvironment. Cell. 2006; 127: 905-915. [CrossRef]
- Basanta D, Strand DW, Lukner RB, Franco OE, Cliffel DE, Ayala GE, et al. The role of transforming growth factor-β–mediated tumor-stroma interactions in prostate cancer progression: An integrative approach. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 7111-7120. [CrossRef]
- de Pillis LG, Mallet DG, Radunskaya AE. Spatial tumor-immune modeling. Comput Math Methods Med. 2006;7: 159-176. [CrossRef]
- Enderling H, Alexander NR, Clark ES, Branch KM, Estrada L, Crooke C, et al. Dependence of invadopodia function on collagen fiber spacing and cross-linking: computational modeling and experimental evidence. Biophys J. 2008; 95: 2203-2218. [CrossRef]
- Bankhead A, Magnuson NS, Heckendorn RB. Cellular automaton simulation examining progenitor hierarchy structure effects on mammary ductal carcinoma in situ. J Theor Biol. 2007; 246: 491-498. [CrossRef]
- Gevertz J, Torquato S. Growing heterogeneous tumors in silico. Phys Rev E. 2009;80: 51-91. [CrossRef]
- Anderson AR, Basanta D, Gerlee P, Rejniak KA. Evolution, regulation, and disruption of homeostasis, and its role in carcinogenesis. Multiscale Cancer Modeling. Boca Raton: Taylor and Francis; 2011. pp. 1–30.
- Silva AS, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ, Yunes JA. A quantitative theoretical model for the development of malignancy in ductal carcinoma in situ. J Theor Biol. 2010; 262: 601-613. [CrossRef]
- Putnins M, Campagne O, Mager D, Androulakis I. From data to QSP models: a pipeline for using Boolean networks for hypothesis inference and dynamic model building. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2022; p. 1–15.
- Steinway SN, Biggs MB, Loughran Jr TP, Papin JA, Albert R. Inference of network dynamics and metabolic interactions in the gut microbiome. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015; 11: e1004338. [CrossRef]
- Schlatter R, Schmich K, Avalos Vizcarra I, Scheurich P, Sauter T, Borner C, et al. ON/OFF and beyond-a Boolean model of apoptosis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009; 5: e1000595. [CrossRef]
- Mai Z, Liu H. Boolean network-based analysis of the apoptosis network: irreversible apoptosis and stable surviving. J Theor Biol. 2009; 259: 760-769. [CrossRef]
- Steinway SN, Zañudo JG, Ding W, Rountree CB, Feith DJ, Loughran Jr TP, et al. Network modeling of TGFβ signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reveals joint sonic hedgehog and Wnt pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2014; 74: 5963-5977. [CrossRef]
- Fumia HF, Martins ML. Boolean network model for cancer pathways: predicting carcinogenesis and targeted therapy outcomes. PLoS One. 2013; 8: e69008. [CrossRef]
- Wuensche A, Lesser M. Global dynamics of cellular automata: An atlas of basin of attraction fields of one-dimensional cellular automata. vol 1. Colorado: Westview Press; 1992.
- Wuensche, A. Attractor basins of discrete networks. Cogn Sci Res Paper 461, University of Sussex, D.Phil thesis.
- Wuensche, A. Exploring discrete dynamics. 1st ed. United Kingdom: Luniver Press; 2011.
- Jeras I, Dobnikar A. Algorithms for computing preimages of cellular automata configurations. Physica D. 2007; 233: 95-111. [CrossRef]
- Soto JMG. Computation of explicit preimages in one-dimensional cellular automata applying the De Bruijn diagram. J Cell Autom. 2008; 3: 219-230.
- West J, Newton PK. Cellular interactions constrain tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116: 1918-1923. [CrossRef]
- Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nature medicine. 2013; 19: 1423-1437. [CrossRef]
- Maley CC, Aktipis A, Graham TA, Sottoriva A, Boddy AM, Janiszewska M, et al. Classifying the evolutionary and ecological features of neoplasms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17 : 605-619. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022; 12: 31-46. [CrossRef]
- Cichorek M, Wachulska M, Stasiewicz A, Tymińska A. Skin melanocytes: biology and development. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013; 30: 30-41. [CrossRef]
- Berestovsky N, Nakhleh L. An evaluation of methods for inferring boolean networks from time-series data. PLoS One. 2013; 8: e66031. [CrossRef]
- Hopfensitz M, Mussel C, Wawra C, Maucher M, Kuhl M, Neumann H, et al. Multiscale binarization of gene expression data for reconstructing Boolean networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2011; 9: 487-498. [CrossRef]
- Müssel C, Hopfensitz M, Kestler HA. BoolNet—an R package for generation, reconstruction and analysis of Boolean networks. Bioinform. 2010;26(10):1378–1380. [CrossRef]
- Lähdesmäki H, Shmulevich I, Yli-Harja O. On learning gene regulatory networks under the Boolean network model. Mach Learn. 2003; 52: 147–167. [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, RA. The biology of cancer. WW Norton and Company. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzekry S, Lamont C, Beheshti A, Tracz A, Ebos JM, Hlatky L, et al. Classical mathematical models for description and prediction of experimental tumor growth. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10: e1003800. [CrossRef]
- Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961;25: 585-621. [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, L. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1965; 37: 614-636. [CrossRef]
- Blackburn EH, Gall JG. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978; 120: 33-53. [CrossRef]
- Poleszczuk J, Hahnfeldt P, Enderling H. Biphasic modulation of cancer stem cell-driven solid tumour dynamics in response to reactivated replicative senescence. Cell Prolif. 2014; 47: 267-76. [CrossRef]
- Poleszczuk J, Enderling H. A high-performance cellular automaton model of tumor growth with dynamically growing domains. Appl. Math. 2014; 5: 144-152. [CrossRef]
- Poleszczuk J, Hahnfeldt P, Enderling H. Evolution and phenotypic selection of cancer stem cells. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015; 11: e1004025. [CrossRef]
- Poleszczuk J, Enderling H. Cancer stem cell plasticity as tumor growth promoter and catalyst of population collapse. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016. [CrossRef]
- Morton CI, Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P, Enderling H. Non-stem cancer cell kinetics modulate solid tumor progression. Theor Biol Med Model. 2011; 8:1-13. [CrossRef]
- Shyntar A, Patel A, Rhodes M, Enderling H, Hillen T. The Tumor Invasion Paradox in Cancer Stem Cell-Driven Solid Tumors. Bull Math Biol. 2022; 84 :139. [CrossRef]
- Topman G, Sharabani-Yosef O, Gefen A. A method for quick, low-cost automated confluency measurements. Microsc Microanal. 2011; 17: 915-922. [CrossRef]
- Martin S, Zhang Z, Martino A, Faulon JL. Boolean dynamics of genetic regulatory networks inferred from microarray time series data. Bioinform. 2007; 23: 866-874. [CrossRef]
- Campbell NR, Rao A, Hunter MV, Sznurkowska MK, Briker L, Zhang M, et al. Cooperation between melanoma cell states promotes metastasis through heterotypic cluster formation. Dev Cell. 2021; 56: 2808-2825. [CrossRef]
- Hatzikirou H, Basanta D, Simon M, Schaller K, Deutsch A. ‘Go or grow’: the key to the emergence of invasion in tumour progression? Math Med Biol. 2012; 29: 49-65. [CrossRef]
- Gallaher J, Anderson AR. Evolution of intratumoral phenotypic heterogeneity: the role of trait inheritance. Interface Focus. 2013; 3: 20130016. [CrossRef]
- Kimmel GJ, Dane M, Heiser LM, Altrock PM, Andor N. Integrating mathematical modeling with high-throughput imaging explains how polyploid populations behave in nutrient-sparse environments. Cancer Res. 2020; 80: 5109-5120. [CrossRef]
- Garay T, Juhász É, Molnár E, Eisenbauer M, Czirók A, Dekan B, et al. Cell migration or cytokinesis and proliferation?–revisiting the “go or grow” hypothesis in cancer cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2013; 319: 3094-3103. [CrossRef]
- Vittadello ST, McCue SW, Gunasingh G, Haass NK, Simpson MJ. Examining go-or-grow using fluorescent cell-cycle indicators and cell-cycle-inhibiting drugs. Biophys J. 2020; 118: 1243-1247. [CrossRef]
- Kon S, Ishibashi K, Katoh H, Kitamoto S, Shirai T, Tanaka S, et al. Cell competition with normal epithelial cells promotes apical extrusion of transformed cells through metabolic changes. Nat Cell Biol. 2017; 19: 530-541. [CrossRef]
- Hill W, Zaragkoulias A, Salvador-Barbero B, Parfitt GJ, Alatsatianos M, Padilha A, et al. EPHA2-dependent outcompetition of KRASG12D mutant cells by wild-type neighbors in the adult pancreas. Curr Biol. 2021; 31: 2550-2560. [CrossRef]
- Martins VC, Busch K, Juraeva D, Blum C, Ludwig C, Rasche V, et al. Cell competition is a tumour suppressor mechanism in the thymus. Nature. 2014; 509: 465-470. [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff L, Goschorska M, Kozyrska K, Duclos G, Kucinski I, Chessel A, et al. Mechanical cell competition kills cells via induction of lethal p53 levels. Nature Commun. 2016; 7: 11373.
- Alowaidi F, Hashimi SM, Alqurashi N, Alhulais R, Ivanovski S, Bellette B, et al. Assessing stemness and proliferation properties of the newly established colon cancer ‘stem’cell line, CSC480 and novel approaches to identify dormant cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2018; 39: 2881-2891. [CrossRef]
- Gao X, McDonald JT, Hlatky L, Enderling H. Acute and fractionated irradiation differentially modulate glioma stem cell division kinetics. Cancer Res. 2013; 73: 1481-1490. [CrossRef]
- Tang J, Fernandez-Garcia I, Vijayakumar S, Martinez-Ruis H, Illa-Bochaca I, Nguyen DH, et al. Irradiation of juvenile, but not adult, mammary gland increases stem cell self-renewal and estrogen receptor negative tumors. Stem Cells. 2014; 32: 649-661. [CrossRef]
- Grimes DR, Fletcher AG. Close encounters of the cell kind: The impact of contact inhibition on tumour growth and cancer models. Bull Math Biol. 2020; 82: 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Pavel M, Renna M, Park SJ, Menzies FM, Ricketts T, Füllgrabe J, et al. Contact inhibition controls cell survival and proliferation via YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis. Nature Commun. 2018; 9: 2961. [CrossRef]
- Enderling, H. , Wolkenhauer, O. Are all models wrong? Comput Sys Oncol. 2020; 1: e1008. [CrossRef]
- Wittmann DM, Krumsiek J, Saez-Rodriguez J, Lauffenburger DA, Klamt S, Theis FJ. Transforming Boolean models to continuous models: methodology and application to T-cell receptor signaling. BMC Syst Biol. 2009; 3: 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Krumsiek J, Pölsterl S, Wittmann DM, Theis FJ. Odefy-from discrete to continuous models. BMC Bioinform. 2010;11: 1-10. [CrossRef]
 |
| Parameters | Melanoma | Keratinocytes |
|---|---|---|
| K | 0.16 | 0.7 |
| rho | 1.63 | 1.20 |
| tau | 2.7 | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





