Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
24 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
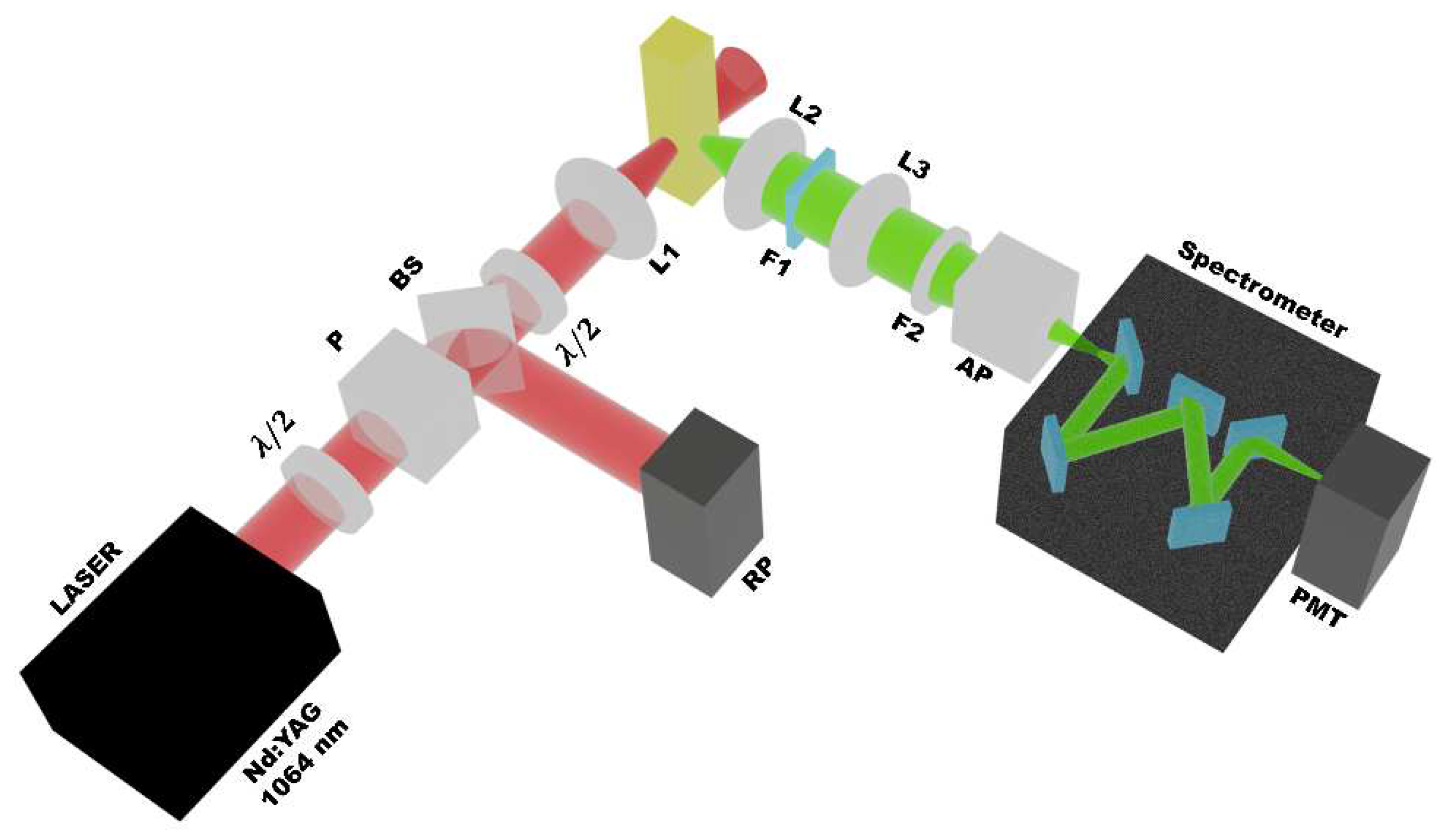
2. Experimental Details
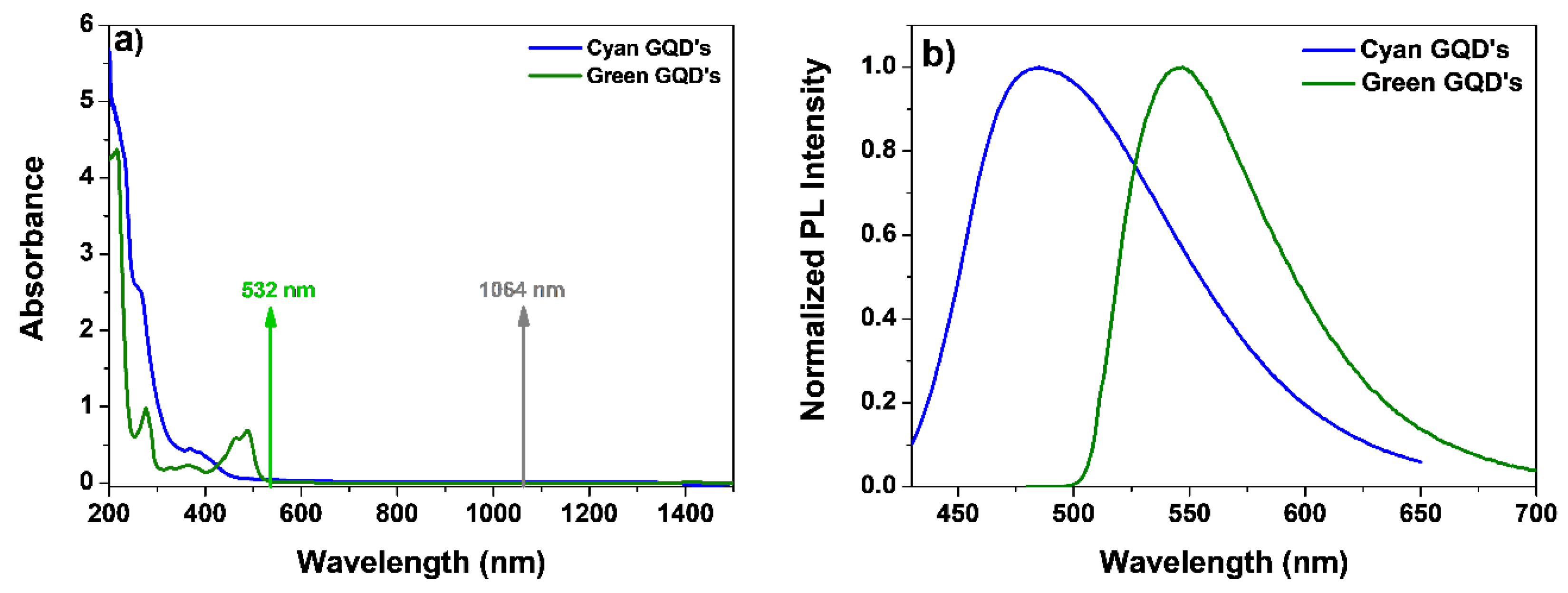
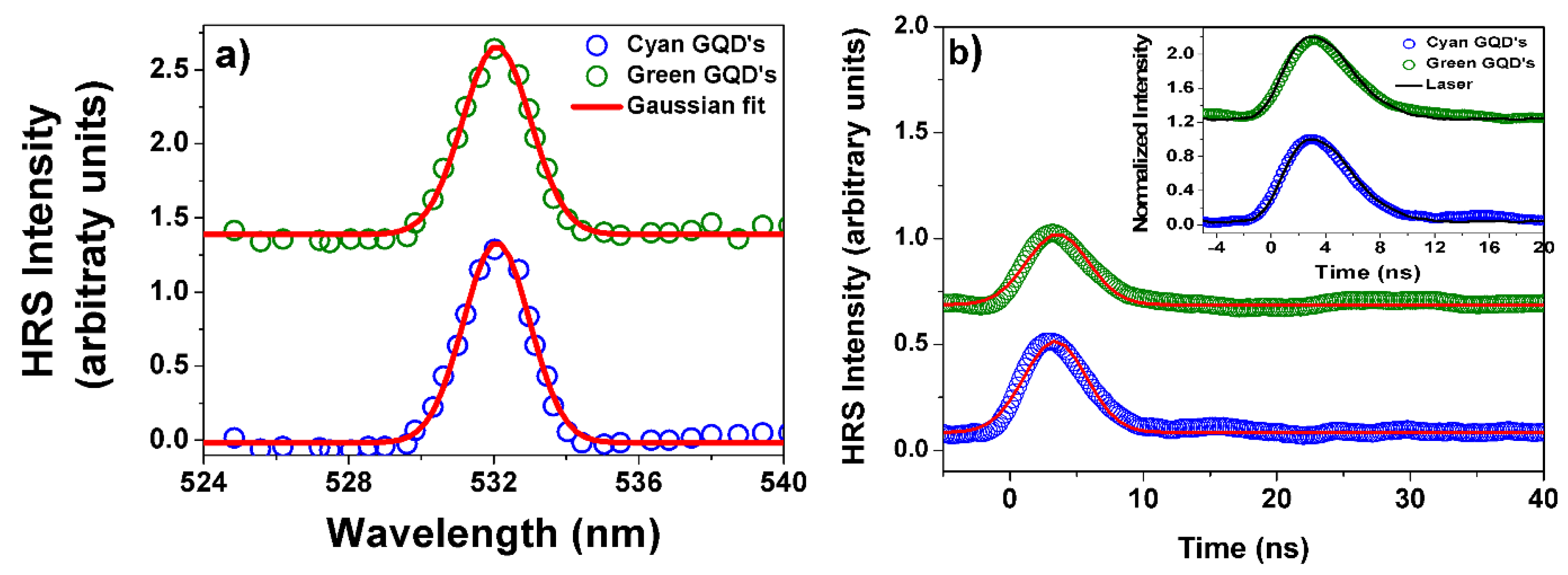
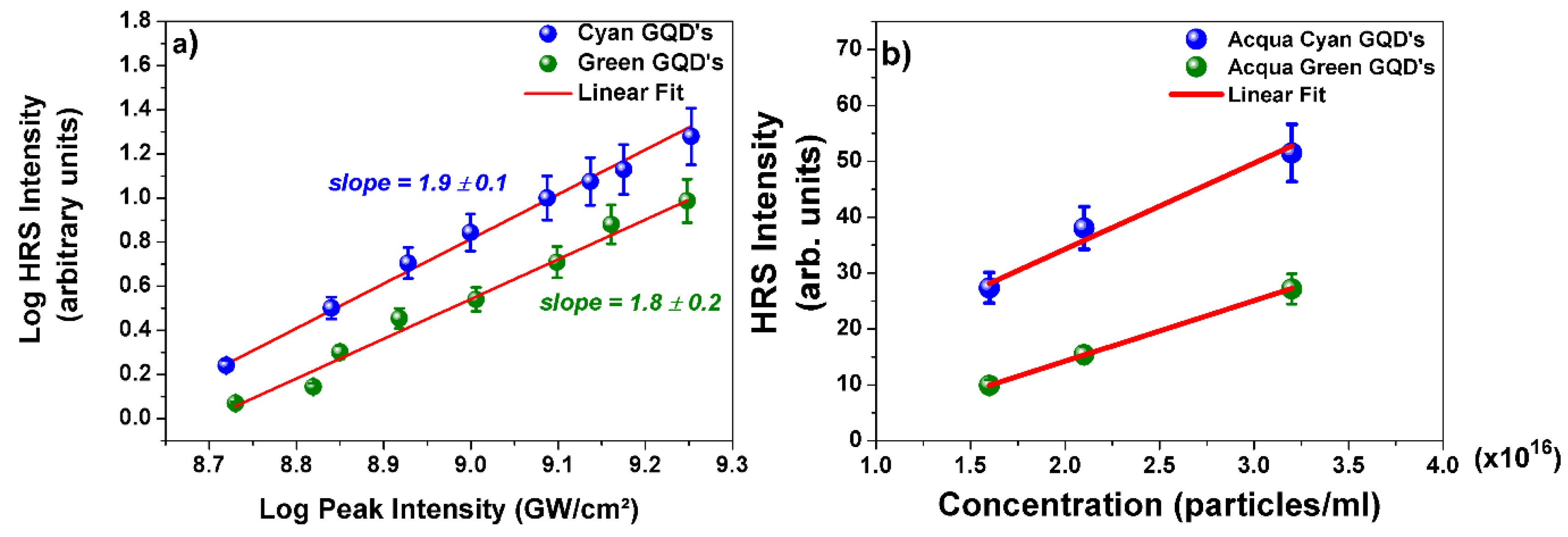
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Charactersation of the GQDs
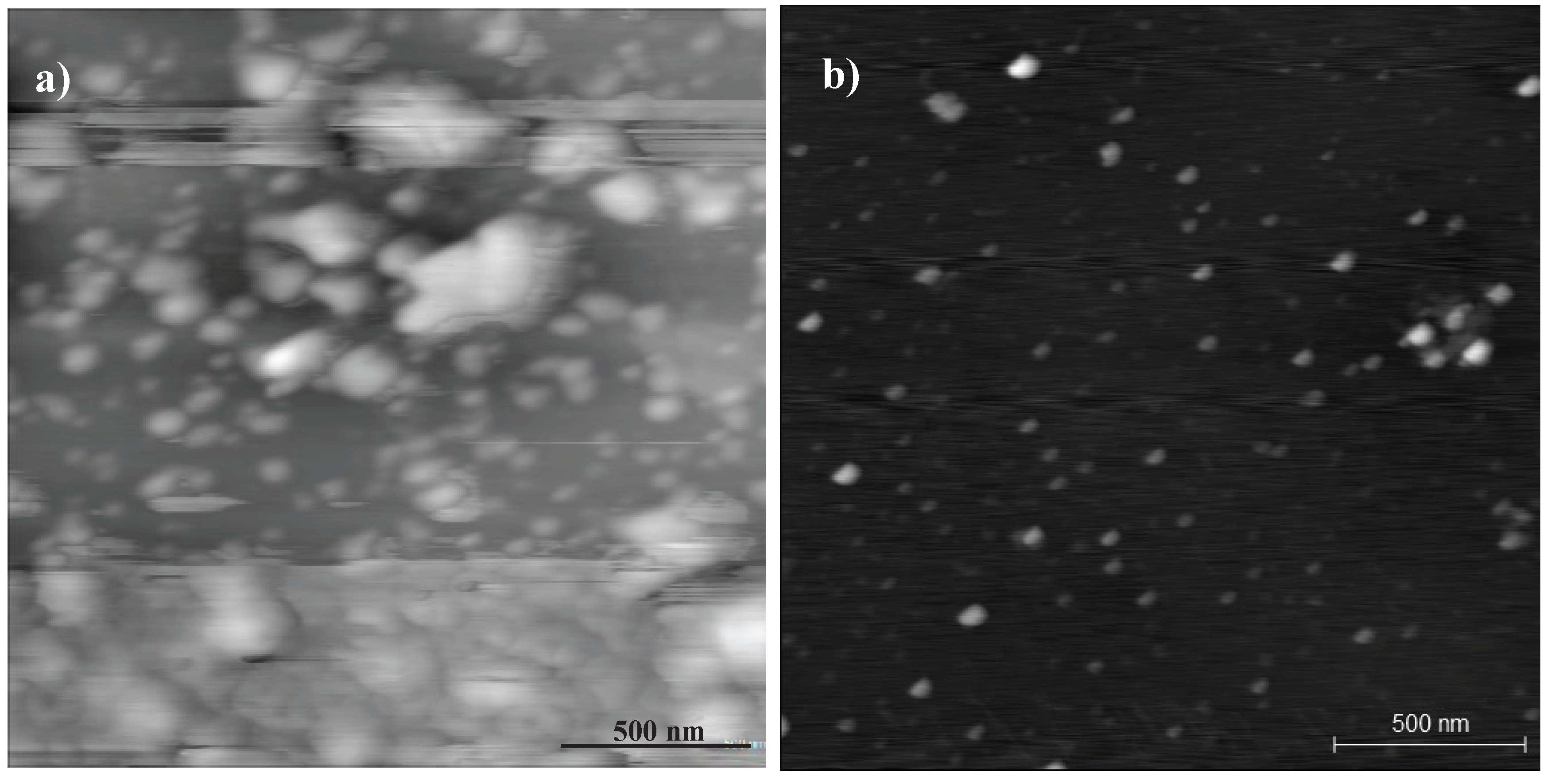
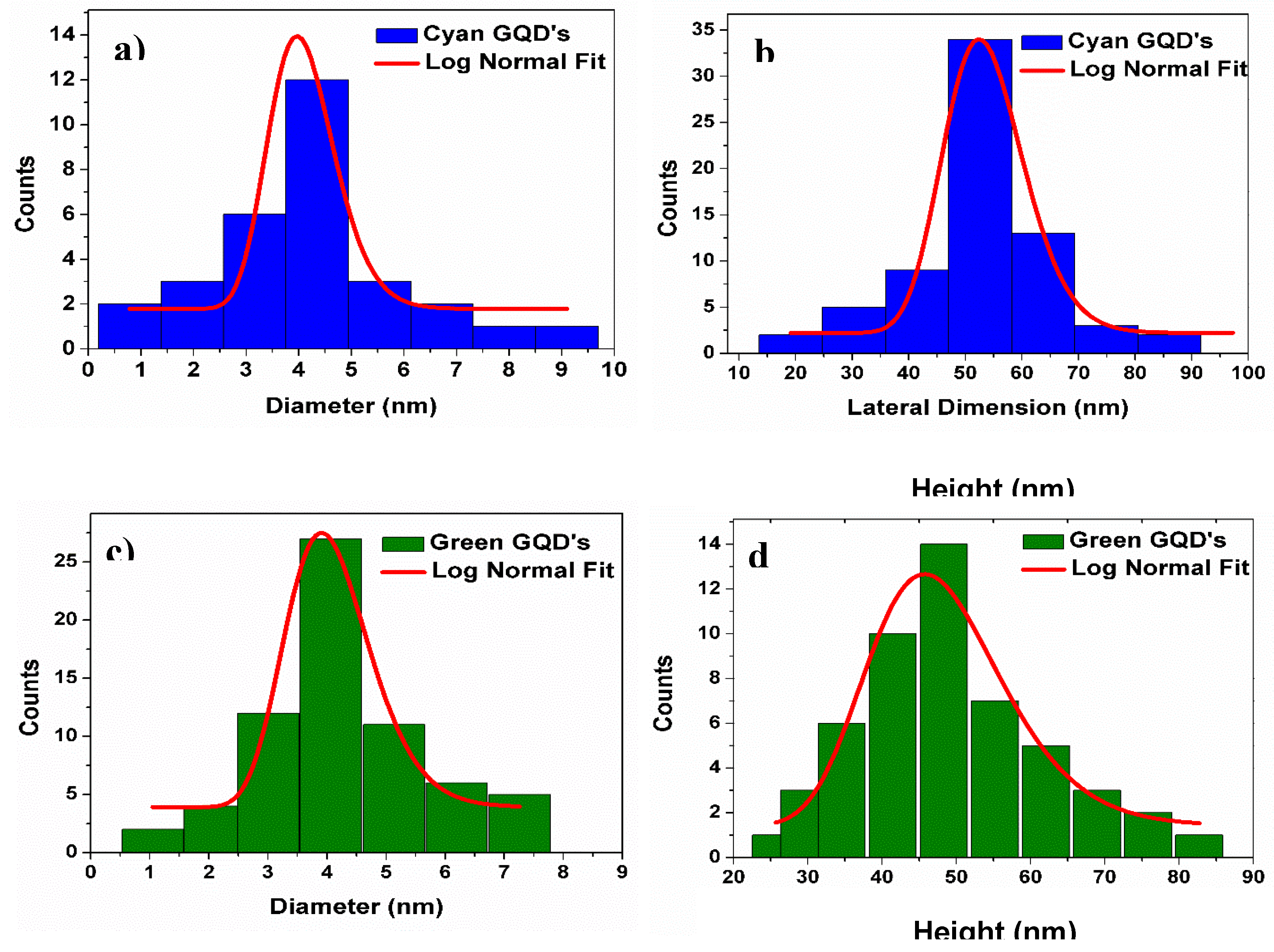
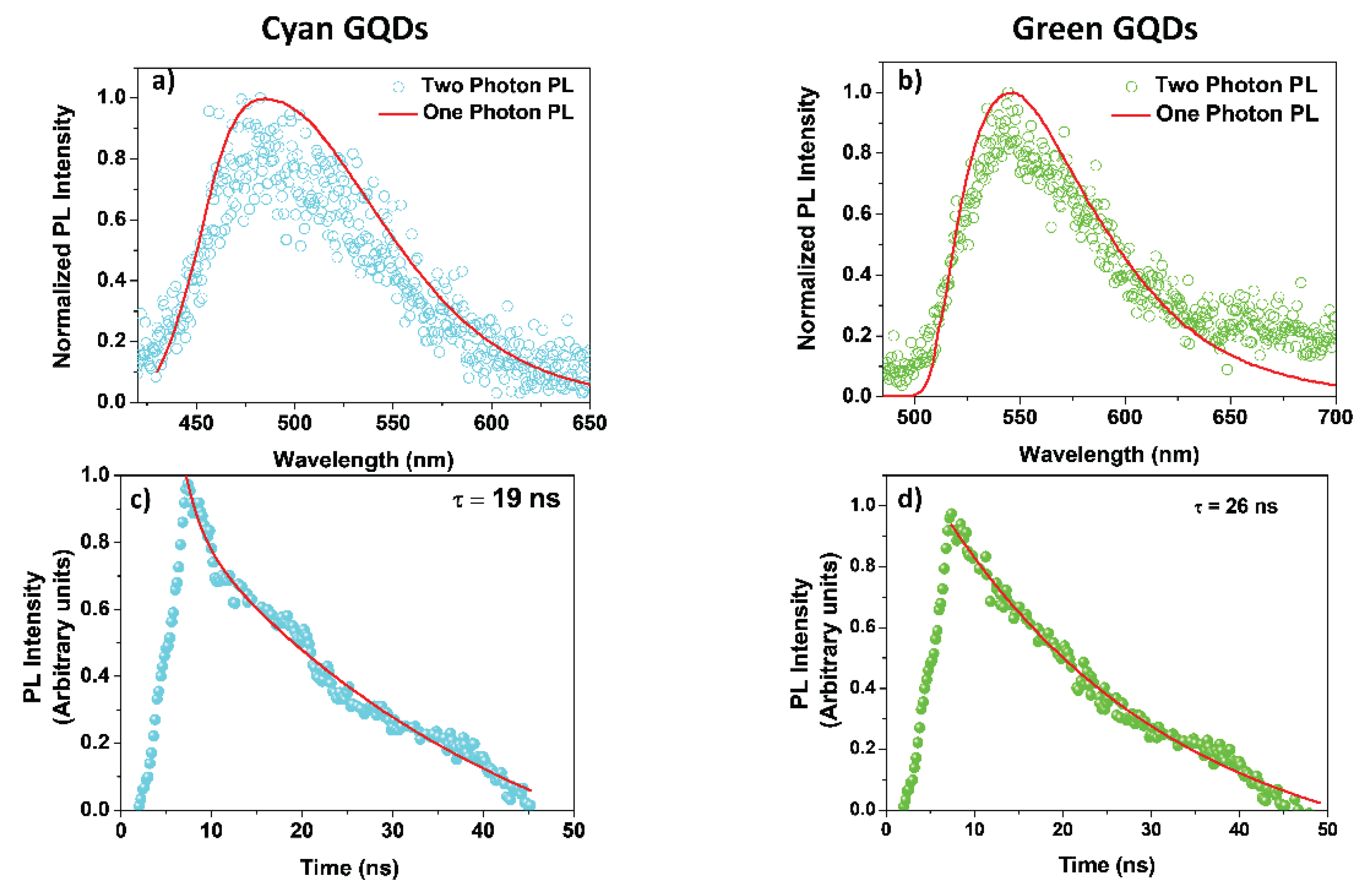
References
- Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Teng, K. S.; Luk, C. M.; Zeng, S.; Hao, J.; Lau, S. P. Deep Ultraviolet Photoluminescence of Water-Soluble Self-Passivated Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Somers, L. A.; Johnson, A. C. High Yield Preparation of Macroscopic Graphene Oxide Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 898–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, M.; Bradley, S. J.; Nann, T. Graphene Quantum Dots. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, G.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Dai, Z. Synthesis and Applications of Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review. Nanotech. Reviews 2018, 7, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettstein, C. M.; Bonafé, F. P.; Oviedo, M.B.; Sánchez, C.G. Optical Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes: Shape Matters. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 224305. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y. Size and Edge Dependence of Two-Photon Absorption in Rectangular Graphene Quantum Dots. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7132–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M. L.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Valcárcel, M. Semiconductor and Carbon-Based Fluorescent Nanodots: the Need for Consistency. Chem. Commun. 2006, 52, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Giant Two-Photon Absorption in Circular Graphene Quantum Dots in Infrared Region. Sci. Reports 2016, 6, 33260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C. Song, X., Liu, Y., Fu, Y., Ye, L., Wang, N.,... & Liu, J. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkal, A., Kadian, S., Pradhan, R., Manik, G., & Packirisamy, G. Recent advances in graphene quantum dot-based optical and electrochemical (bio) analytical sensors. Materials Advances 2021, 2(17), 5513-5541.
- Iannazzo, D.; Ziccarelli, I.; Pistone, A. Graphene Quantum Dots: Multifunctional Nanoplatforms for Anticancer Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6471–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Kumawat, M. K.; Srivastava, R. Multifunctional Graphene Quantum Dots for Combined Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy Coupled with Cancer Cell Tracking Applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5251–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, H. Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Possible Energy Applications: A Review. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots for Optoelectronic and Energy Devices: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, W.; Lin, W.; Lin, B.; Jin, Y.; Deng., X. New opportunities: second harmonic generation of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for stem cells imaging and ultraprecise tracking in wound healing. Adv. Funct. Materials. 2019, 29, 1902235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. P; Bi, Z. T.; Xu, R. F; Han, K.; Li, M. X.; Shen, X. P.; Wu, Y. X. Theoretical Study on Electronic Polarizability and Second Hyperpolarizability of Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots: Effects of Size, Substituent, and Frequency. Carbon 2017, 122, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ciret, C.; Cassagne, C.; Boudebs, G. Measurement of the Third Order Optical Nonlinearities of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water at 355 nm, 532 nm and 1064 nm. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J. L.; Vermeulen, N.; Sipe, J. E. Numerical Study of the Optical Nonlinearity of Doped and Gapped Graphene: From Weak to Strong Field Excitation. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 235307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J. R. Strong Two-Photon-Induced Fluorescence from Photostable, Biocompatible Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Cellular and Deep-Tissue Imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudebs, G.; Cherukulappurath, S. Nonlinear refraction measurements in presence of nonlinear absorption using phase object in a 4f system. Opt. Commun. 2005, 250, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukulappurath, S.; Boudebs, G.; Monteil, A. 4f coherent imager system and its application to nonlinear optical measurements. JOSA B 2004, 21, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamijala, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Pati, S.K. Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12079–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. J.; Li, X. P.; Ma, F.; Liu, Z. B.; Li, Z. R.; Huang, X. R.; Sun, C. C. Exceptionally Large Second-Order Nonlinear Optical Response in Donor–Graphene Nanoribbon–Acceptor Systems. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2414–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Liu, Z.B.; Li, Z.R.; Huang, X.R.; Su, C.C. Shape Effect of Graphene Quantum Dots on Enhancing Second-Order Nonlinear Optical Response and Spin Multiplicity in NH2-GQD-NO2 System. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16282–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clays, K.; Persoons, A. Hyper-Rayleigh Scattering in Solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 2980–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clays, K.; Olbrechts, G.; Munters, T.; Persoons, A.; Kim, O.-K.; Choi, L.-S. Enhancement of the Molecular Hyperpolarizability by a Supramolecular Amylose–Dye Inclusion Complex, Studied by Hyper-Rayleigh Scattering with Fluorescence Suppression. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 293, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M. B.; Shelton, D. P. What is Measured by Hyper Rayleigh Scattering from a Liquid? J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 134504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J. T.; Rusimova, K. R.; Hooper, D. C.; Jeong, H. H.; Ohnoutek, L.; Pradaux-Caggiano, F.; Valev, V. K. First Observation of Optical Activity in Hyper-Rayleigh Scattering. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 011024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, R.; Nogueira, M.A.M.; Souza, H.D.S.; Lira, B.F.; de Athaide-Filho, P.F.; de Araújo, C.B. First Hyperpolarizability of 1,3-Thiazolium-5-Thiolates Mesoionic Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harfouch, Y.; Benichou, E.; Bertorelle, F.; Russier-Antoine, I.; Jonin, C.; Lascoux, N.; Brevet, P.F. Hyper-Rayleigh Scattering from Gold Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 118, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russier-Antoine, I.; Lee, H. J.; Wark, A. W.; Butet, J.; Benichou, E.; Jonin, C.; Brevet, P. F. Second Harmonic Scattering from Silver Nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 17447–17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khebbache, N.; Maurice, A.; Djabi, S.; Russier-Antoine, I.; Jonin, C.; Skipetrov, S. E.; Brevet, P. F. Second-Harmonic Scattering from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Random Medium. ACS Photon. 2017, 4, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulaud, C; Mugnier, Y.; Djanta, G.; Dubled, M.; Marty, J. C.; Galez, C.; Wolf, J. P.; Bonacina, L.; Dantec, R. L. Characterization of the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Nanocrystals by Hyper Rayleigh Scattering. J. Nanobiotech. 2013, 11 (Suppl.1), S8.
- Forcherio, G.T.; Riporto, J.; Dunklin, J.R.; Mugnier, Y.; Dantec, R.L.; Bonacina, L.; Roper, D.K. Nonlinear Optical Susceptibility of Two-Dimensional WS2 Measured by Hyper Rayleigh Scattering. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 5018–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, E.; de Araújo, C. B.; Lipovskii, A. A. Second Harmonic Scattered Light from a Transparent Glass-Ceramic Containing Sodium Niobate Nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 031901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.V.; de Araújo, C.B.; Brito-Silva, A.M.; Ivanenko, V.I.; Lipovskii, A.A. Hyper-Rayleigh Scattering from BaTiO3 and PbTiO3 Nanocrystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 467, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, R.; Silva, J.F.; Rocha, U.; Jacinto, C.; de Araújo, C.B. Second-Order Nonlinearity of NaNbO3 Nanocystals with Orthorhombic Crystalline Structure. J. Lumin. 2019, 211, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.strem.com/uploads/resources/documents/graphene_quantum_dots_-_dotz_nano.pdf (Items # 06-0332 & 06-0340). 0332.
- Marder, S.R.; Beratan, D.N.; Cheng, L.T. Approaches for Optimizing the First Electronic Hyperpolarizability of Conjugated Organic Molecules. Science 1991, 252, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://www.strem.com/catalog/gl/12/carbon.
- Pauley, M.A.; Guan, H.W.; Wang, C.H.; Jen, A.K.Y. Determination of First Hyperpolarizability of Nonlinear Optical Chromophores by Second Harmonic Scattering Using an External Reference. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 104, 7821–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemla, D.S. Nonlinear Optical Properties of Organic Molecules and Crystals; Academic Press: New York, U. S., 1987.
- Fedus, K.; Boudebs, G.; de Araujo, C.B.; Cathelinaud, M.; Charpentier, F.; Nazabal, V. Photoinduced effects in thin films of Te20As30Se50 glass with nonlinear characterization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadap, Jerry I.; Shan, Jie; Heinz, Tony F. Theory of optical second-harmonic generation from a sphere of centrosymmetric material: small-particle limit. JOSA B, 2004, 7, 1328–1347.
- Bachelier, G.; Russier-Antoine, I.; Benichou, E.; Jonin, C.; Brevet, P.F. Multipolar second-harmonic generation in noble metal nanoparticles. JOSA B, 2008, 25, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappa, J.; Revillod, G.; Russier-Antoine, I.; Benichou, E.; Jonin, C.; Brevet, P.F. Electric dipole origin of the second harmonic generation of small metallic particles. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71, 165407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevet, P.F. Second harmonic generation in nanostructures. In Handbook of Nanoscale Optics and Electronics; Wiederrecht, G.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2010; pp. 351–381. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Lingling; Song, Bin; Liang, Huimin; Liu, Jia; Feng, Xiaoli; Deng, Bin; Sun, Ting; Shao, Longquan, Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: a general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicology. 2016, 13, 57.
- Wang, Shujun; Cole, Ivan S.; Li, Qin, The toxicity of graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89867–89878.
- Ghosh, Shampa; Sachdeva, Bhuvi; Sachdeva, Punya; Chaudhary, Vishal; Rani, Gokana Mohana; Sinha, Jitendra Kumar, Graphene quantum dots as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic tool for the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1381–1394.
- Fedus, K.; Boudebs, G.; Coulombier, Q.; Troles, J.; Zhang, X.H. Nonlinear characterization of GeS2–Sb2S3–CsI glass system. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
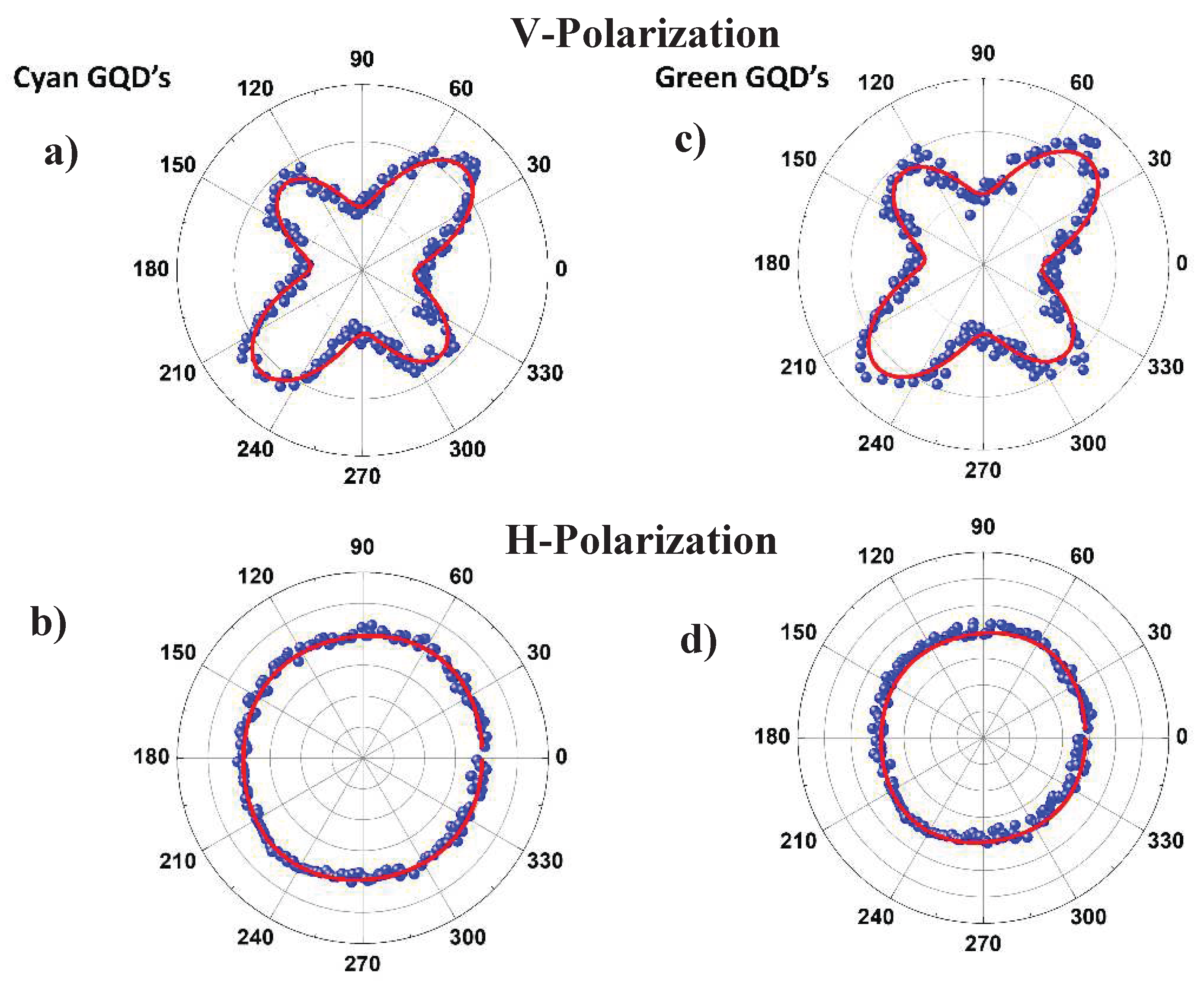
| Sample Parameters | Cyan GQD V polarization |
Green GQD V polarization |
|---|---|---|
| 0.87 | 0.79 | |
| 0.56 | 0.59 | |
| 0.14 | 0.19 | |
| 0.81 | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





