1. Introduction
According to the 2023 World Cancer Statistics[
1], although the overall mortality rate of lung cancer (LC) has shown a decline in 2023 compared to previous years, it remains the second most prevalent cancer globally in terms of both overall cancer-related deaths and new cases. Approximately 230,000 individuals are newly diagnosed with LC each year globally, and among them about 120,000 suffer to malignancy. Clinically, LC can be roughly classified into non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is the majority which accounts for approximately 85% of LC cases [
2], and can further be categorized into adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma subtypes [
3]. Early detection and treatment of NSCLC typically lead to better prognoses and higher five-year survival rates [
3].
Current facility for early LC screening is primarily involved with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT), enabling rapid and large-scale diagnosis on individuals having high risk factors [
4]. However, these screenings generate a large amount of images that require interpretation by radiologists. This not only results in a substantial burden on human resources but also introduces variations in experience and subjective awareness among different radiologists, lacking unified diagnostic criteria [
5]. Within LDCT images, pulmonary nodules (PNs) represent areas suspected of being lesions and can be preliminarily categorized into three types: solid nodules (SN), part-solid nodules (PSN), and ground glass nodules (GGN) [
6]. Typically, radiologists rely on visible characteristics such as PNs size, edge shape, and nodule pattern for diagnosis [
7], such as Lung-RADS™ [
8]. However, this approach often yields a high rate of false positives [
9], ultimately needing a pathological biopsy for a final confirmation. This process often causes patients to have unnecessary and invasive risks [
10].
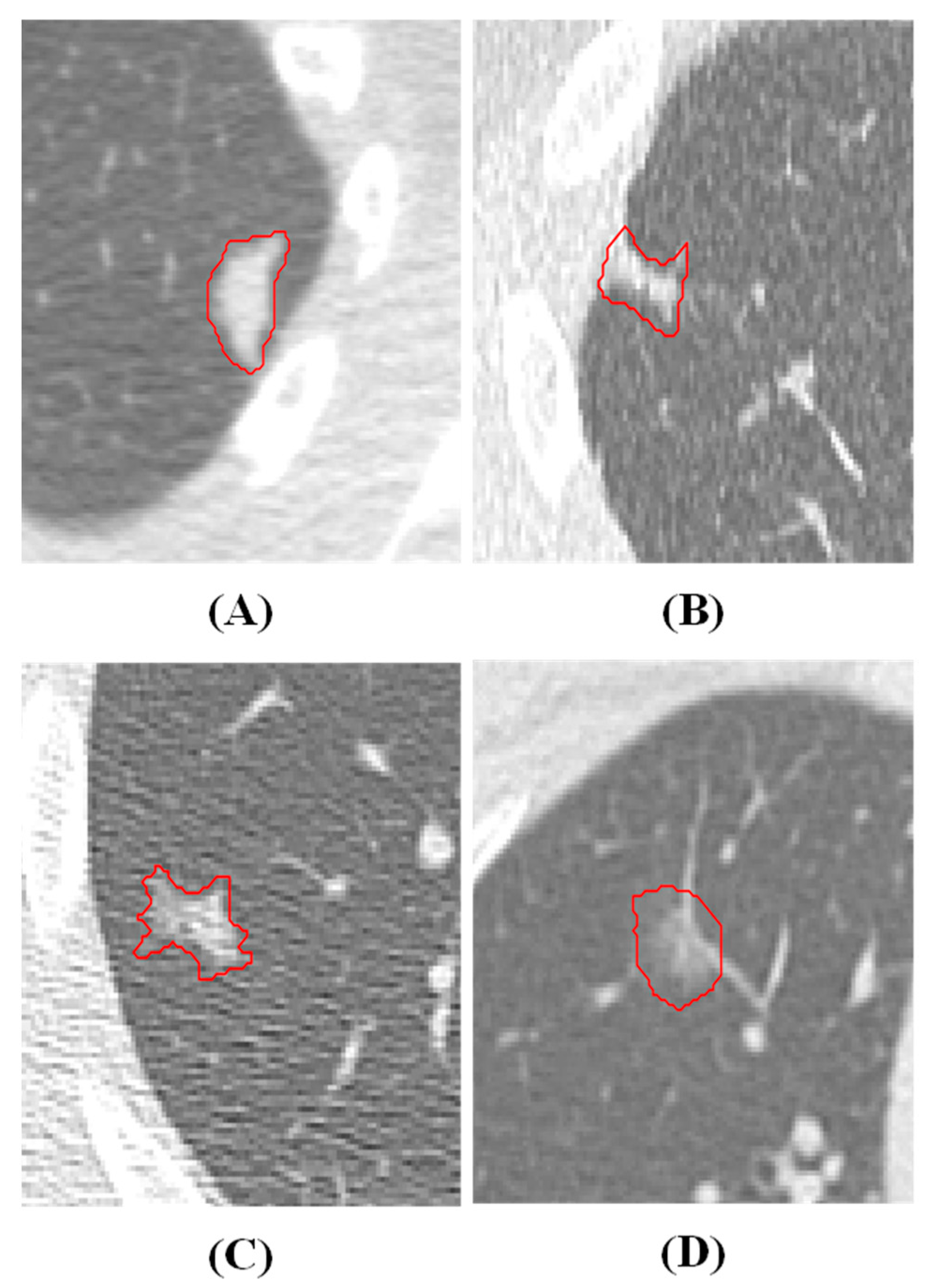
Figure 1 illustrates PNs, where benign and malignant nodules appear strikingly similar to our eyes, rendering precise diagnoses challenging.
Using machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) onto pulmonary nodule detection and diagnosis in chest CT images have been studied since decades. Especially, radiomics [
11] is a feature extraction technique usually combined with classifiers to establish models, which are able to provide physicians with an alternative opinion beyond visible characteristics. Previous study indicates that such models significantly enhance reading speed and diagnostic precision for physicians [
12]. Numerous studies focus on PN detection and classification can achieve promising results [13-23]. For example, Kumar et al. [
16] propose an approach utilizing autoencoders to extract features from raw images and employ a decision tree for binary classification, which achieves an accuracy of 0.7501. Shen et al. [
22] introduce a method using multi-scale convolutional neural networks (MCNN) to distinguish PN’s malignancy, capturing different-sized patches of each PN and simultaneously using convolutional neural networks (CNN) for discrimination, which achieves an accuracy of 0.8612 on the LIDC-IDRI dataset [
5]. Mehta et al. [
19] in 2021 present a model that utilizes 3D CNNs in combination with volumetric radiomics and imaging biomarkers to diagnose PNs malignancy. By incorporating 3D PNs images, radiomics, and LIDC-IDRI biomarkers, they achieve an ROC/AUC of 0.8659. In 2021, Lu et al.[
18] introduce a method that integrated the Marine Predators Algorithm with CNN for the diagnosis of PNs. This approach achieves an impressive performance with an accuracy of 0.934 and a sensitivity of 0.984. Halder et al. [
24] attain the best PNs diagnostic model performance using the LIDC-IDRI dataset in 2021. They employ morphology and two CNN networks, achieving an accuracy of 0.9610 and an AUC of 0.9936.
However, above mentioned studies face some common challenges. First, most patients in LIDC-IDRI dataset lack pathological biopsy results on nodule malignancy diagnosis, which are considered to be gold standard. LIDC-IDRI provides suspicion scores of nodule malignancy, ranging from 1 to 5 made by radiologists. Most previous studies classify nodules with scores of 1 and 2 as benign and those with scores of 4 and 5 as malignant, however, the actual malignancy of PNs remains uncertain. Second, previous studies typically use raw LDCT images as inputs to their models. They ignore a fact that images undergoing LDCT imaging may have different modality settings such as pixel spacing (PS) and slice thickness (SK). This ignorance results in a question whether the uniformity on voxel-size would affect model diagnostic performance or not. For instance, Kim et al. [
25] in 2019 review factors that could impact the quantification of CT image features, highlighting the significant influence of PS and SK on feature quantification. Most features demonstrate different impacts before and after normalization on PS and SK. Lu et al. [
26] in 2017 improve model diagnostic performance by reconstructing positron emission tomography (PET) images into uniform voxel-size. Through investigating the impacts of different voxel-sizes on PET image quantification or diagnosis, their study offers valuable insights. Above mentioned studies focus on traditional machine learning method, therefore they can examine feature impact accordingly. Recent studies often use neural networks (NN) and deep learning such as [
27], which is out of this study scope. This study is motivated by above mentioned problems so that we do not consider using NN and DL. Furthermore, DL models demand large dataset for training, which is not suitable to our small dataset in this study.
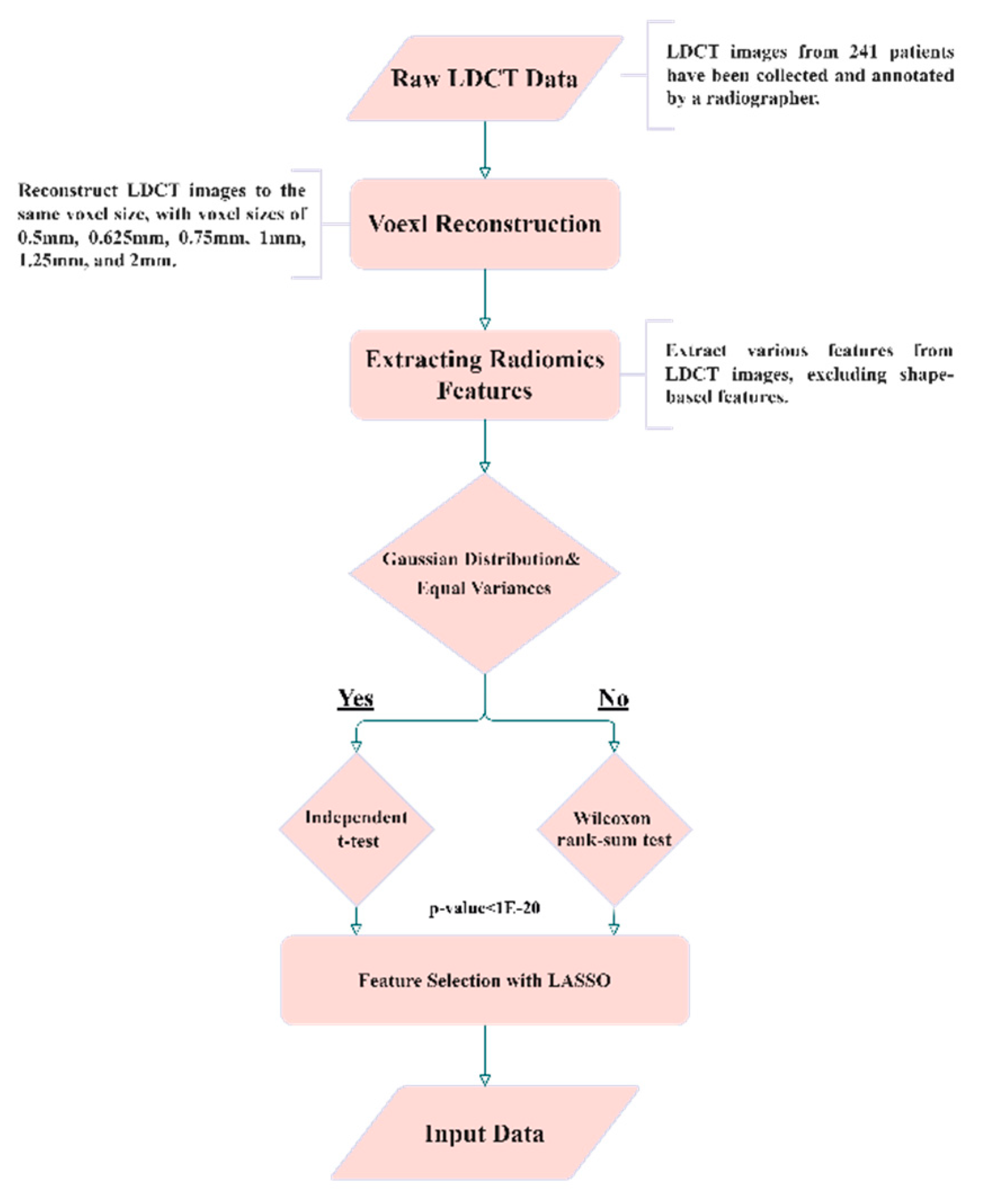
2. Materials and Methods
Figure 2.
Experimental flowchart of this study.
Figure 2.
Experimental flowchart of this study.
Dataset in House and Annotation
LDCT image data are collected from Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital (KVGH), including 160 malignant and 81 benign PNs from a total of 241 patients. The data collection process has been approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of KVGH with the IRB number VGHKS18-CT5-09. The malignancy status of each PN is defined by pathological biopsy and the boundary of PN is annotated by an experienced radiological technician. LifeX (Version 6.2.0, C. Nioche, Inserm, France) is open-source software that was first published in the year 2018 [
28]. Its application involves reading DICOM images and synchronizing the display and annotation of medical images in coronal, sagittal, and axial slices. It also concurrently supports users in the extraction of radiomics features within regions of interest (ROIs). We use LifeX as annotation tool, and we can output nearly raw raster data (NRRD) format for image feature extraction. However, due to technical problems of LifeX, 3 benign and 13 malignant patients in which ROI annotations result in errors. Therefore, these 16 patient data are excluded for following process. The final images (for following training and test usage) have either a size of 512×512 or 768×768 depending on the raw data. Notably, the radiomics features are extracted only in ROIs in the reconstructed images, not directly from LDCT raw images.
Isotropic Voxel Normalization and Image Reconstruction
To explore the reproducibility and model performance of PN malignancy diagnosis using ML method, we normalize PS and ST of all LDCT images using bicubic interpolation. This reconstruction aims to achieve consistent spatial resolution across all LDCT images, making them isotropic in three axes. Furthermore, to evaluate the influence of different voxel sizes and spatial resolutions on the model and features, we reconstruct all images to various voxel-sizes, including 0.5, 0.625, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, and 2 (mm) of side length.
Radiomics and Feature Selection
We employ radiomics to extract 2112 features from the PN regions of the reconstructed images. Radiomics encompass various quantitative image feature extraction methods, including first-order statistics, shape-based, and texture-based methods [
11]. Not all extracted features contribute significantly to PNs malignancy diagnosis, therefore, feature selection is necessary and crucial. Given that PN malignancy is often related to its size [
10], we intentionally exclude features with size information. Before feature dimension reduction, in total 14 features related to shape and size are manually excluded (see
Table A1 in
Appendix A). Moreover, 123 features with identical feature values having no discriminability are also manually excluded. The remaining 1975 features undergo further feature dimension reduction in the following paragraph.
In order to reduce the number of input features for our model, we utilize different methods. First, we utilize the independent t-test [
29] and the Wilcoxon rank-sum [
30] test to examine significant features for differentiating benign and malignant nodule. To apply the independent t-test, some prerequisites are needed including a normal distribution on a certain feature and modulating equal variance to that distribution. Meeting these prerequisites is crucial for using the independent t-test. Therefore, we first examine normality tests [
31] and Levene tests [
32] to assess the equality of variances and the type of distribution for both benign and malignant pulmonary nodule groups. If data meet the criteria of a normal distribution and equal variance, we then proceed using independent t-tests for analysis, otherwise, we employ the Wilcoxon rank-sum test for getting p-values. Features with p-values between two classes less than 10
-20 are considered to be significantly different, which means they are good and distinguishable features. Second, we employ well-known LASSO [
33] algorithm. LASSO algorithm effectively reduces coefficients to zero for those features having less contribution to classification, thus achieves feature selection. Third, we apply t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) [
34] for dimension reduction of selected feature combinations to visualize the distribution of patients in two-dimensional space. t-SNE, belonging to manifold learning, achieves dimension reduction and meanwhile preserves local structure of data distribution. This t-SNE can be found for data visualization and dimension reduction in recent publications.
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Hyperparameter Optimization
SVM is a classic classifier [
35] known from its strong performance in various classification tasks, particularly in dealing with small datasets. It exhibits better generalization ability compared to DL models in dealing with small dataset [
36]. In our study, we compare four combinations on feature selection: 1) all features without exclusion, 2) features with p-value less than 10
-20, 3) features selected by LASSO, and 4) features selected by the t-SNE algorithm. Prior inputting all features into the SVM model, we perform Min-Max Normalization on all features to ensure that different features have comparable numeric ranges. This is a basic feature normalization process. In SVM, the choice of kernel function, which determines the decision boundary, is crucial. We employ the Gaussian Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel function for our SVM model because most feature distributions are normal distribution after feature selection. In ML models, hyperparameter optimization is highly correlated to final model performance. We use Gaussian Bayesian optimization [
37] to tune hyperparameters of SVM model to achieve a better performance.
3. Results
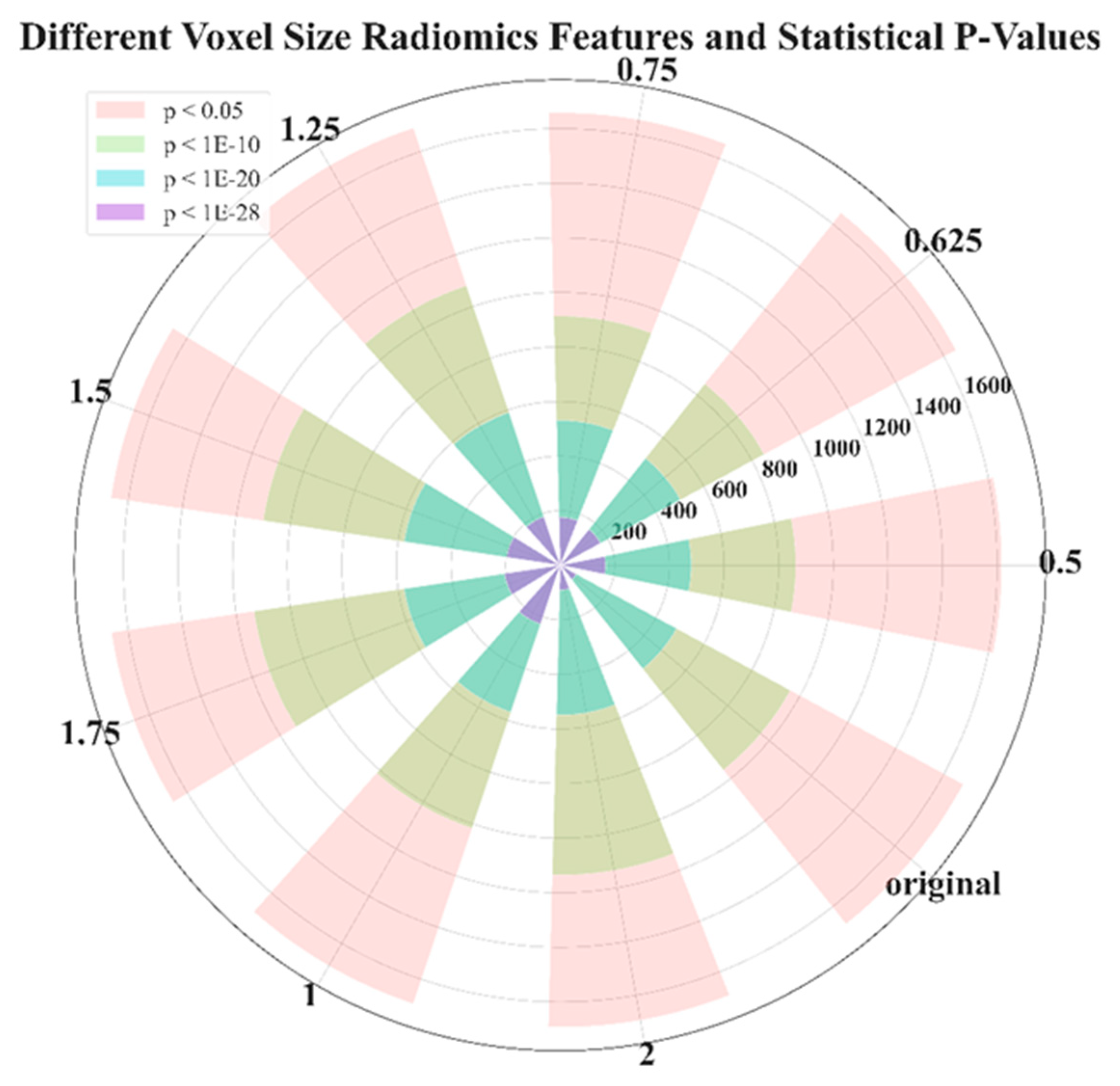
In
Figure 3, we demonstrate the distribution of p-values for features extracted at different voxel sizes reconstructed from the raw image data (LDCT). The value started from 0.5, 0.625 to 2 is the side-length of the isotropic voxel in mm. The word ‘original’ means there is no reconstruction, it is raw LDCT data. The value started from 200, 400 to 1600 is the number of features. We categorize p-value into four groups: less than 0.05, 1E-10, 1E-20, and 1E-28. It is interesting to find from
Figure 3, the majority of features has p-values locating in the range: [0.05, 1E-10]. However, p-value in this range is not able to distinguish or to classify. Therefore, the most part features are useless. We also find that features extracted from the original LDCT images without uniform voxel sizes has the least useful features. Here the useful feature we mean the purple part (p-value < 1E-28). This indicates that voxel normalization indeed affects feature extraction. Through this voxel normalization process using image reconstruction, the extracted image features exhibit significant statistical differences between benign and malignant nodules. This result convinces our hypothesis. Notably, features extracted from reconstructed data normalized to 2mm in side-length perform poorly compared to other side-length. We provide
Table 1 for exact quantity of features plotted in
Figure 3.
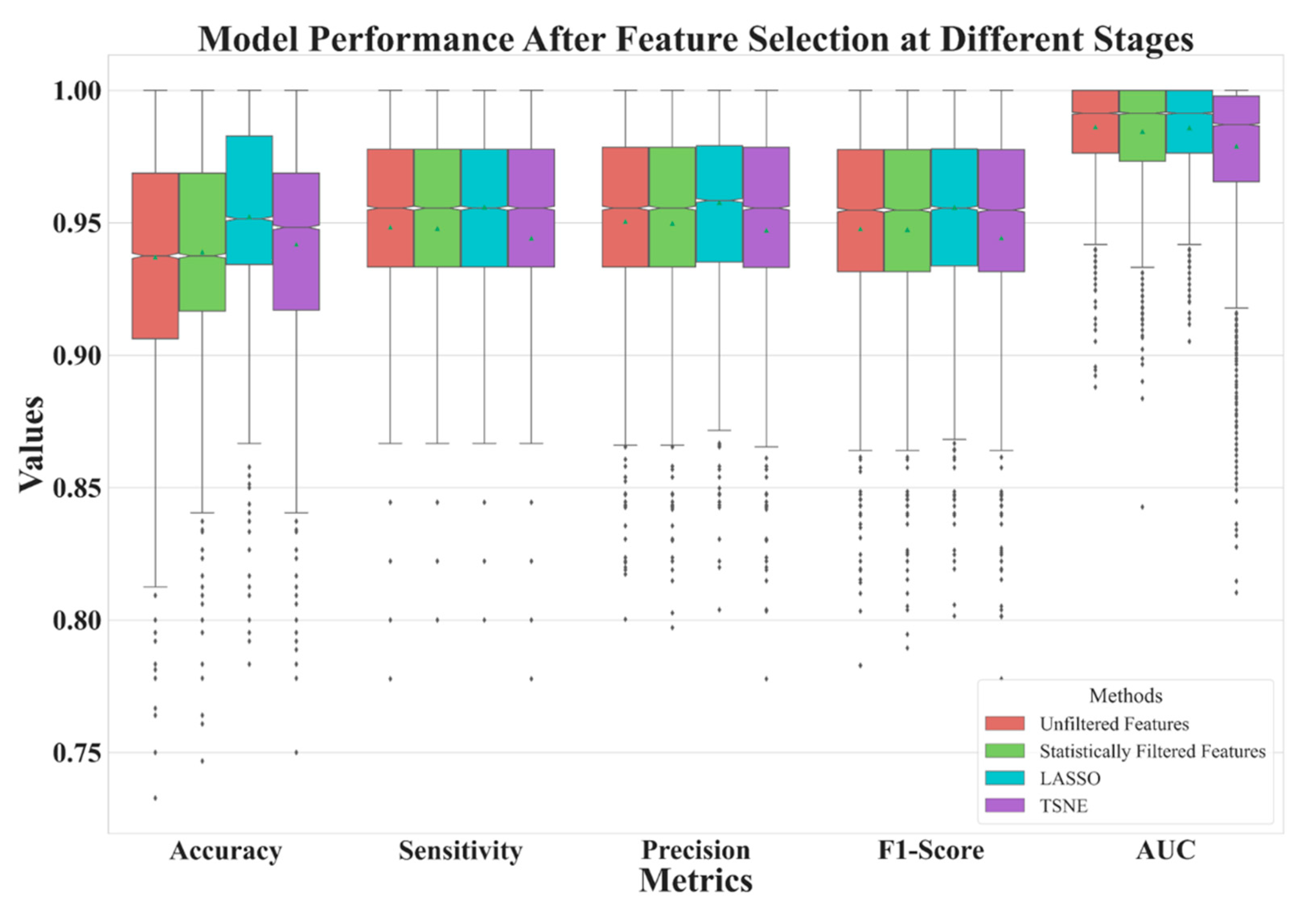
In
Table 2, we illustrate the number of features before (the baseline) and after feature selection. In
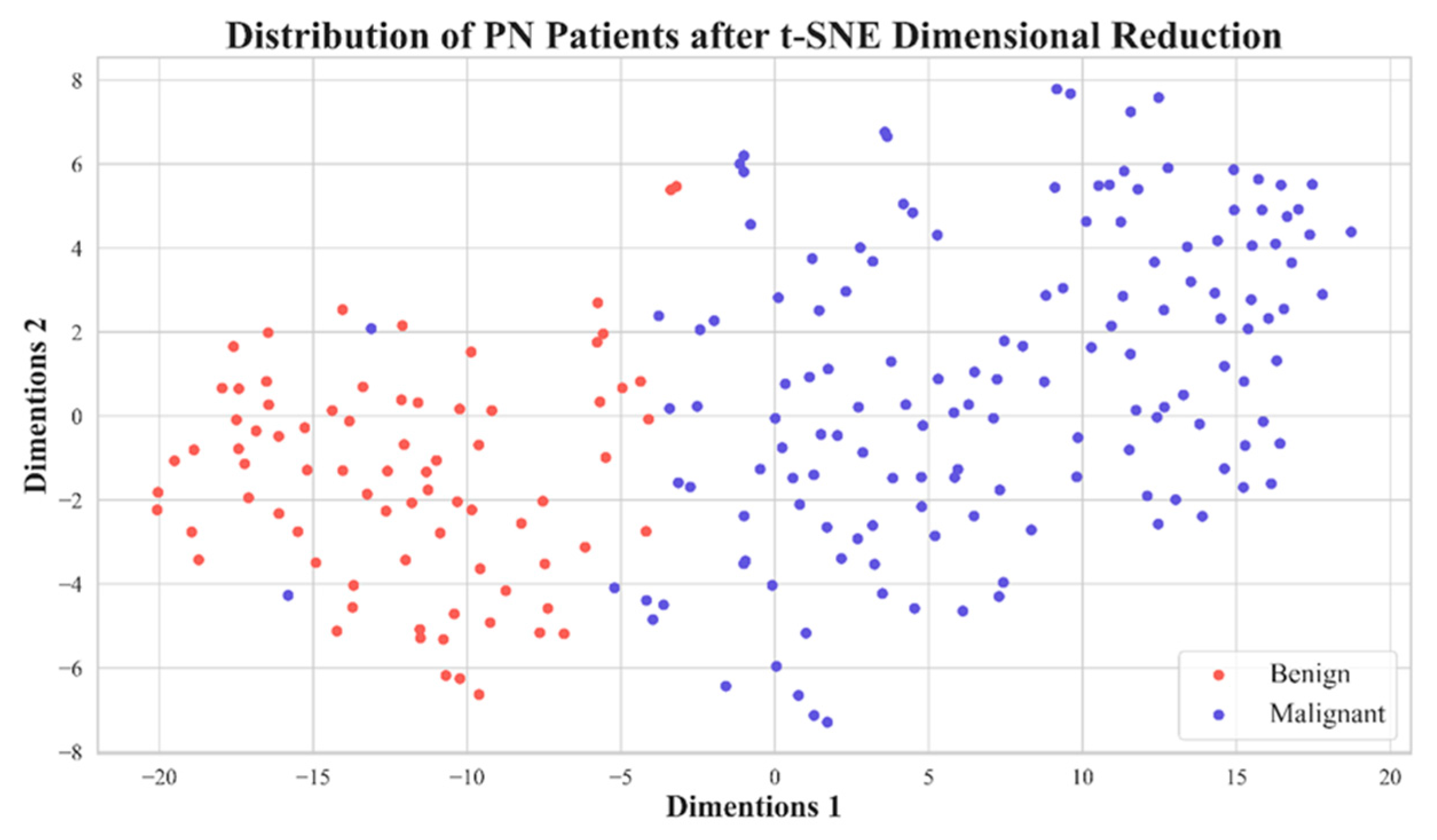
Figure 4, we demonstrate the model performance for comparison using 5 metrics illustrated in Equations 1–5. From the result, it shows the best feature selection method is LASSO using only 11 features. Astonished, the second best performance is achieved by reducing the dimensionality of 11 LASSO-selected features to 2 ‘features’ (actually here means 2 directions in the feature space) using t-SNE, resulting in an outstanding performance. The feature distribution on these 2 directions are shown in
Figure 7.
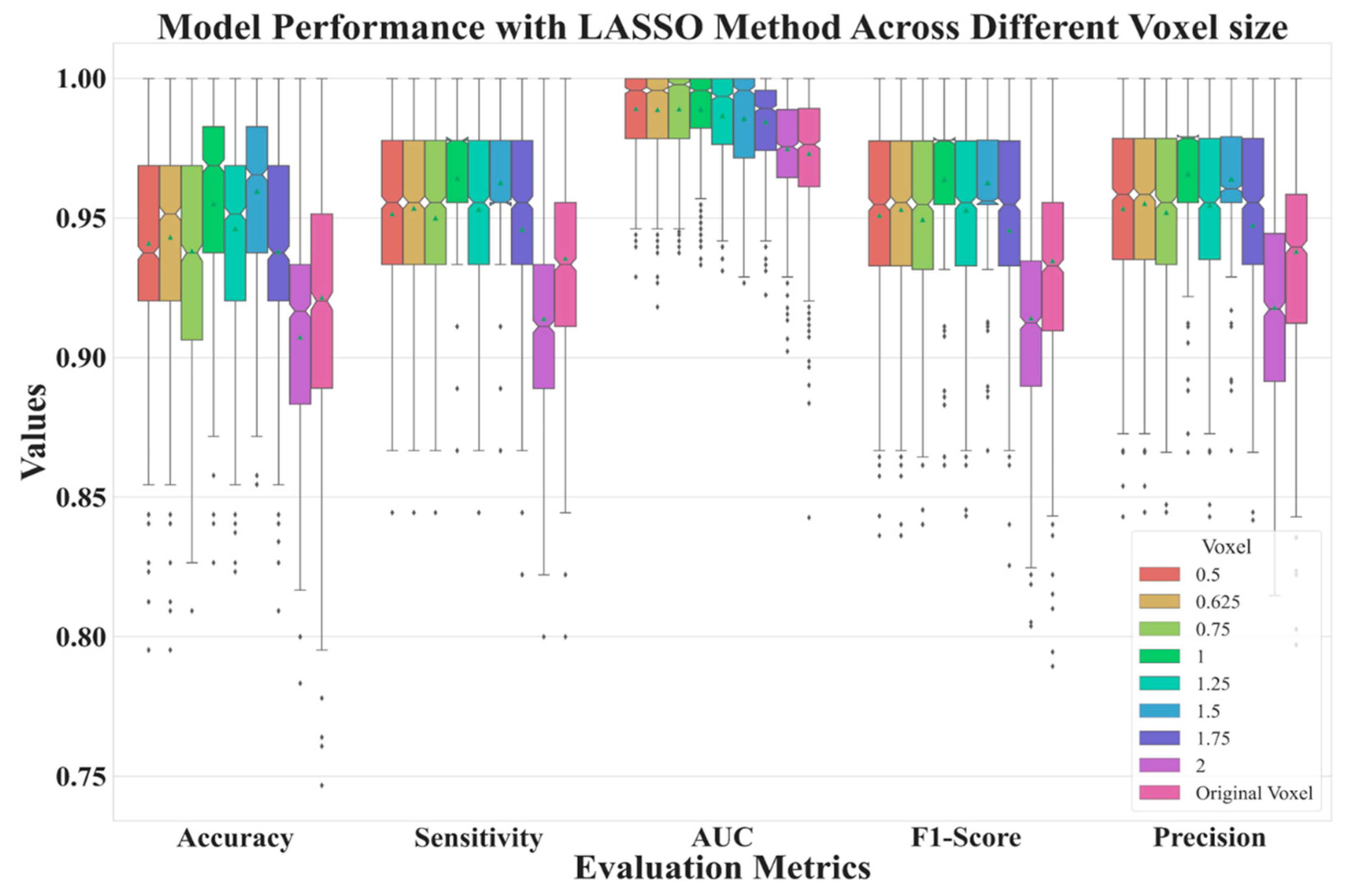
Figure 5 depicts the performance of features extracted from different voxel sizes reconstruction. We here use LASSO to select features. From the figure, it is obvious to observe that the model has better performances with voxel normalization having side-lengths less than 2 mm. The best model is achieved with features extracted from LDCT images with a side-length of 1.5 mm.
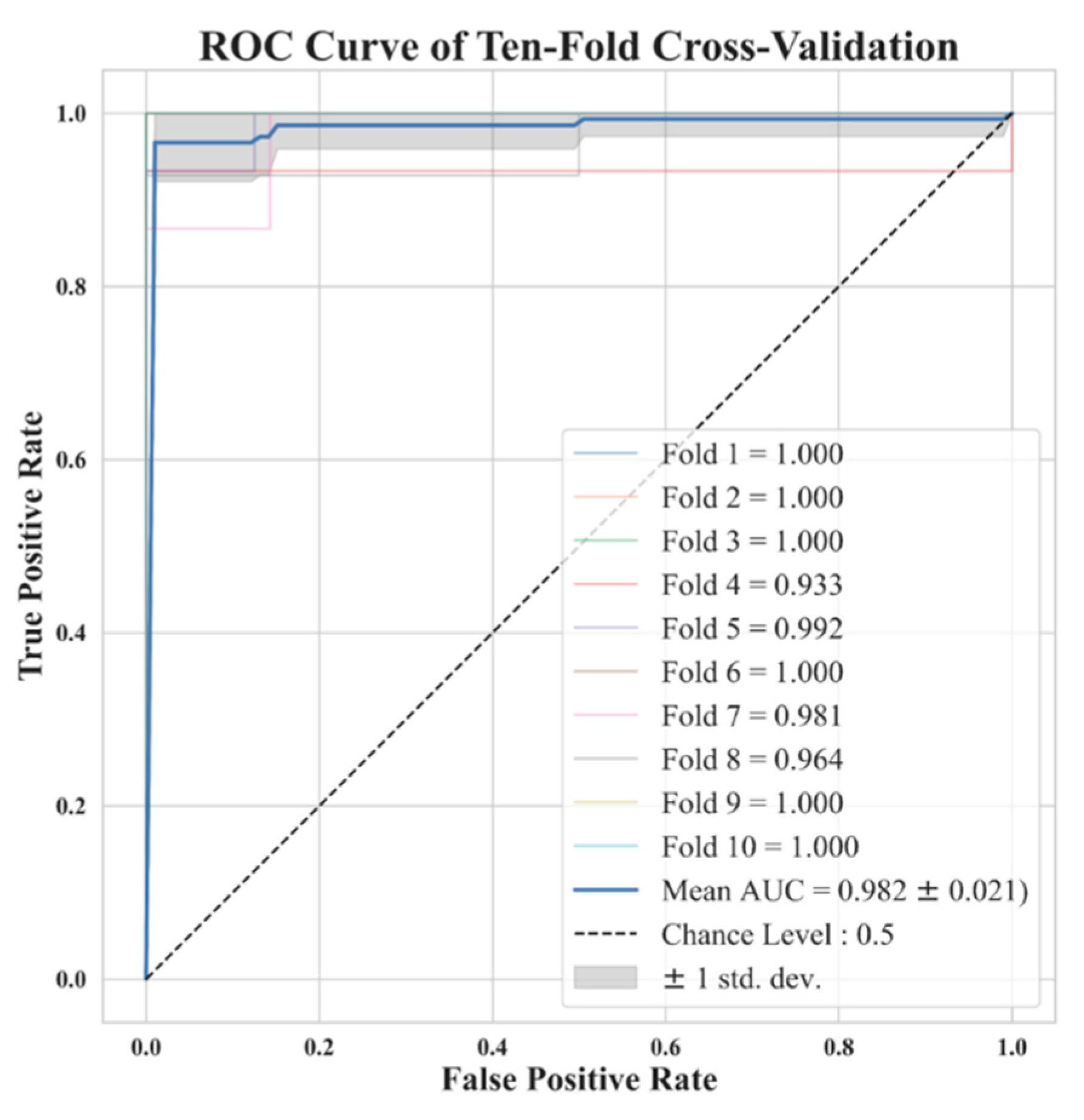
In
Figure 6, we show ROCs using ten-fold cross-validation with radiomic features selected by LASSO from image reconstruction with a side-length of 1.5 mm. The model average AUC reaches 0.982, indicating a stable diagnostic performance. This is clinically acceptable for PNs diagnosis. In
Figure 7 we demonstrate the distribution on 2D feature space, with two dimension directions. After dimensionality reduction, only 2 features are selected by t-SNE. From this distribution, it is obvious to see that these 11 features are able to effectively classify benign and malignant nodules.
Figure 6.
Ten-fold cross-validation ROC curve for the model trained with 11 features selected by LASSO with a voxel having a side-length of 1.5 mm.
Figure 6.
Ten-fold cross-validation ROC curve for the model trained with 11 features selected by LASSO with a voxel having a side-length of 1.5 mm.
Figure 7.
Distribution plot of 11 features extracted from PNs with voxel having a side-length of 1.5 mm after dimension reduction using t-SNE.
Figure 7.
Distribution plot of 11 features extracted from PNs with voxel having a side-length of 1.5 mm after dimension reduction using t-SNE.
Finally,
Table 3 we compare different results. These results are the averaged values of various metrics in different voxel-size of reconstruction over 4000 times of repetitions. We also compare to state-of-the-art models. Our best result outperforms the most previous methods and is comparable to the best previous study [
24]. Besides, deep learning approaches need more time in training than the traditional method.
4. Discussions
Due to the diversity of patients in clinics and orders from physicians, radiographers use various parameter settings to acquire LDCT images. If these parameter settings are not consistent, it is difficult to compare because of vacancy on baseline. Particularly we mean texture features; different pixel-size on images can cause different results, such as features extracted from Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), Gray Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM), Gray Level Size Zone Matrix (GLSZM), and other texture features. Many previous studies have indicated, texture features are crucial for distinguishing the benign and malignant nature of PNs.
Table 4 presents the 11 radiomic features selected by the LASSO in this study. Notably, 7 from the 11 selected features are all texture-related, demonstrating the important role in discriminating benign and malignant PNs. Therefore, voxel normalization is essential and has a profound impact on the reproducibility.
In this research, normalizing the voxel size from LDCT images to 1mm-1.5mm yields good model performance. Typically, CT has a spatial resolution ranging from 0.5 mm to 0.625 mm in x-y axis, our collected data fall in the range from 0.6 mm to 0.8 mm. The resolution on z-axis depends on the temporal resolution. Our dataset in house, most images on z-axis resolution fall in the range from 1 mm to 5 mm. We do not have data in z-axis less than 1 mm. The image reconstruction has to consider the spatial and temporal resolution of the raw data, otherwise, it can lead to partial volume effect and subsequently impacts the model performance. Further, reconstructing images with a voxel larger than 1.5 mm on side-length will significantly decrease spatial resolution, making it impossible to capture fine texture of PNs. Therefore, we recommend that future studies consider voxel reconstruction within the range of 1 mm-1.5 mm, based on a prerequisite that data has higher spatial and temporal resolution than 1 mm in x-y-z axis, i.e., ≤ 1 mm.
One advantage of our study compared to previous researches is that all our patients have pathological diagnoses to confirm the PN's nature, i.e., benign or malignant. This advantage is not present in the large open dataset such as LIDC-IDRI. Research limitations regarding this study are discussed below. This study mainly analyze Asian ethnic groups, and most malignant lesions are adenocarcinoma spectrum. Therefore, the predictive ability for other pathological types of lung cancer may be lower. Particularly, this study mainly distinguishes lung adenocarcinoma spectrum lesions from other benign lesions. Therefore, there is no further study and analysis on the clinical management of these nodules.
5. Conclusion
This study uses a ML method combined with radiomic features extracted from reconstructed images with voxel normalization from LDCT. We mainly explore the impact of voxel normalization to prediction performance between benign and malignant pulmonary nodules. Our study offers a recommendation: before using radiomics, the voxel normalization is important and crucial to texture-related studies. The reconstruction has to consider the limitation on raw data temporal resolution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.-C.C.; methodology, D.-C.C., C.-H.P.; software, C.-H.P.; validation, C.-H.P.; formal analysis, D.-C.C. and C.-H.P.; investigation, D.-C.C. and C.-H.P.; resources, F.-Z.W.; data curation, C.-C.H.; writing—original draft preparation, D.-C.C. and C.-H.P.; writing—review and editing, D.-C.C. and F.-Z.W; visualization, C.-H.P.; supervision, D.-C.C.; project administration, D.-C.C.; funding acquisition, C.-C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, grant number KSVGH112-110.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of KVGH with the IRB number VGHKS18-CT5-09 (protocol code:18-CT5-09, April 3, 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Table A1.
Description of the 14 manually excluded features.
Table A1.
Description of the 14 manually excluded features.
| Feature Description |
Types |
| original_shape_Elongation |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Flatness |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_LeastAxisLength |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_MajorAxisLength |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Maximum2DDiameterColumn |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Maximum2DDiameterRow |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Maximum2DDiameterSlice |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Maximum3DDiameter |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_MeshVolume |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_MinorAxisLength |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_Sphericity |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_SurfaceArea |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_SurfaceVolumeRatio |
Shape-Based |
| original_shape_VoxelVolume |
Shape-Based |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. Ca Cancer J Clin 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.B.; Crosbie, P.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017.
- Jemal, A.; Fedewa, S.A. Lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography in the United States—2010 to 2015. JAMA oncology 2017, 3, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato III, S.G.; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Medical physics 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, C.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Improvement in imaging diagnosis technique and modalities for solitary pulmonary nodules: from ground-glass opacity nodules to part-solid and solid nodules. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 2016, 10, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensen, S.J.; Viggiano, R.W.; Midthun, D.E.; Müller, N.L.; Sherrick, A.; Yamashita, K.; Naidich, D.P.; Patz, E.F.; Hartman, T.E.; Muhm, J.R. Lung nodule enhancement at CT: multicenter study. Radiology 2000, 214, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelala, L.; Hossain, R.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Christensen, J.D.; Dyer, D.S.; White, C.S. Lung-RADS version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. American Journal of Roentgenology 2021, 216, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensen, S.J.; Silverstein, M.D.; Edell, E.S.; Trastek, V.F.; Aughenbaugh, G.L.; Ilstrup, D.M.; Schleck, C.D. Solitary pulmonary nodules: clinical prediction model versus physicians. Proceedings of Mayo Clinic Proceedings; pp. 319–329.
- Khan, T.; Usman, Y.; Abdo, T.; Chaudry, F.; Keddissi, J.I.; Youness, H.A. Diagnosis and management of peripheral lung nodule. Annals of Translational Medicine 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K. Current status and future potential of computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging. The British journal of radiology 2005, 78, s3–s19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, R.; Lu, Z.; Hong, Y. Diagnostic classification of lung nodules using 3D neural networks. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018); pp. 774–778.
- Huang, H.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Peng, C. Self-supervised transfer learning based on domain adaptation for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on thoracic CT. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2022, 26, 3860–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Liu, K.; Hou, B.; Zhang, N. 3D multi-view convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. PloS one 2017, 12, e0188290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Wong, A.; Clausi, D.A. Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th conference on computer and robot vision; 2015; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Kang, G. Multiview convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology 2017, 27, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Nanehkaran, Y.A.; Karimi Fard, M. A method for optimal detection of lung cancer based on deep learning optimized by marine predators algorithm. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Jain, A.; Mangalagiri, J.; Menon, S.; Nguyen, P.; Chapman, D.R. Lung nodule classification using biomarkers, volumetric radiomics, and 3D CNNs. Journal of Digital Imaging 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saihood, A.; Karshenas, H.; Nilchi, A.R.N. Deep fusion of gray level co-occurrence matrices for lung nodule classification. Plos one 2022, 17, e0274516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.; Yang, C.; Tian, J. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. Proceedings of Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 24th International Conference, IPMI 2015, Sabhal Mor Ostaig, Isle of Skye, UK, 2015, Proceedings 24, June 28-July 3; pp. 588–599.
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.; Yu, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, C.; Zang, Y.; Tian, J. Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognition 2017, 61, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, S.; Falcionelli, N.; Sernani, P.; Burattini, L.; Dragoni, A.F. Lung nodule diagnosis and cancer histology classification from computed tomography data by convolutional neural networks: A survey. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 146, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Dey, D. Adaptive morphology aided 2-pathway convolutional neural network for lung nodule classification. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 72, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Goo, J.M.; Ohno, Y.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Hoffman, E.A.; Gee, J.C.; Van Beek, E.J. Effect of reconstruction parameters on the quantitative analysis of chest computed tomography. Journal of thoracic imaging 2019, 34, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fontaine, K.; Germino, M.; Mulnix, T.; Casey, M.E.; Carson, R.E.; Liu, C. Investigation of sub-centimeter lung nodule quantification for low-dose PET. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences 2017, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonekaboni, S.; Joshi, S.; McCradden, M.D.; Goldenberg, A. What clinicians want: contextualizing explainable machine learning for clinical end use. In Proceedings of the Machine learning for healthcare conference; 2019; pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Nioche, C.; Orlhac, F.; Boughdad, S.; Reuzé, S.; Goya-Outi, J.; Robert, C.; Pellot-Barakat, C.; Soussan, M.; Frouin, F.; Buvat, I. LIFEx: a freeware for radiomic feature calculation in multimodality imaging to accelerate advances in the characterization of tumor heterogeneity. Cancer research 2018, 78, 4786–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, T.; D'Agostino, R. Robustness of the two independent samples t-test when applied to ordinal scaled data. Statistics in medicine 1987, 6, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B.; Glynn, R.J.; Ting Lee, M.L. Incorporation of clustering effects for the Wilcoxon rank sum test: a large-sample approach. Biometrics 2003, 59, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.R.; Imon, A. A brief review of tests for normality. American Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics 2016, 5, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, B.B. Levene's test for relative variation. Systematic Zoology 1985, 34, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonti, V.; Belitser, E. Feature selection using lasso. VU Amsterdam research paper in business analytics 2017, 30, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of machine learning research 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Suthaharan, S.; Suthaharan, S. Support vector machine. Machine learning models and algorithms for big data classification: thinking with examples for effective learning 2016, 207-235.
- Cervantes, J.; Garcia-Lamont, F.; Rodríguez-Mazahua, L.; Lopez, A. A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: Applications, challenges and trends. Neurocomputing 2020, 408, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.I. A tutorial on Bayesian optimization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02811. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).