Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatpistica (IBGE). Produção da Pecuária Municipal. 2022. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/periodicos/84/ppm_2015_v43_br.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- McManus, C.; Barcellos, J.O.J; Formenton, B.K.; Hermuche, P.M. Dynamics of cattle production in Brazil. Plos One 2016, 11, e0147138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas Junior, A.M.; Barros, P.H.B. Cattle’s expansion to the legal Amazon: spatial externalities, credit market access and intensification of production. Nova Eco. 2021, 31, 303–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowey, R. Cattle Lameness and Hoofcare. 3ª ed. Sheffield: 5M Publishing; 2015. 177p.
- Ebling, R.C.; Krummenguer, A.; Machado, G.; Zeni, D.; Carazzo, L.P.; Leal, M.L.R. Prevalence and distribution of feet lesions in dairy cows raised in the Freestal. Semina 2019, 40, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, T.F.; Nicolino, R.R.; Andrade, L.S.; Facury Filho, E.J.; Carvalho, A.U. Prevalence of lameness and hoof lesions in all year-round grazing cattle in Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.B.; Possidonio, B.I.O.; Oliveira, H.G.S.; Barbosa Neto, J.D.; Salvarani, F.M. Paradigit Pododermatitis in Cattle: Literature review. Res. Societ. Develop. 2022 11, 15. e201111537027. [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.S.; Silva, N.S.; Albernaz, T.T.; Bomjardim, H.A.; Belo Reis, A.S.; Oliveira, C.M.C.; Duarte, M.D.; Barbosa, J.D. Epidemiological and clinical study of foot diseases in beef cattle extensive management in southeastern Pará, Brazil. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 3–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.S.; Albernaz, T.T.; Oliveira, C.M.C.; Duarte, M.D.; Barbosa, J.D. Foot disorders in cows from basin milk of Rondon do Pará. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2009, 29, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.; Leite, R.C.; Carvalho, A.U.; Facury Filho, E.J.; Souza, R.C.; Ferreira, M.G. Results and costs of treatment for bovine laminitis sequelae: study of 112 lameness cases in lactating cows in free-stall system. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2004, 56, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.S.; Silva, N.S.; Albernaz, T.T.; Bomjardim, H.A.; Andrade, S.J.T.; Oliveira, C.M.C.; Barbosa, J.D. Afecções podais em bovinos associado à sodomia. Vet. Zootec. 2011, 18, 294–297. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.; Silva, D.C.; Azevedo Junior, W.C. Redução do desmatamento na Amazônia: o papel dos mecanismos institucionais. Rev. Adm. Neg. Amazônia 2018, 10, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, S.; Almeida, O.; Ávila, S.; Oliveira, W. Pecuária e desmatamento: uma análise das principais causas diretas do desmatamento na Amazônia. Nova Econ. 2009, 19, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daros, R.R.; Eriksson, H.K.; Weary, D.M.; Keyserlignk, M.A.G. Lamenes during the dry period: Epidemiology and associated factors. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11414–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Filho, D.F.; Lira, B.R.P.; Crispim, D.L.; Pessoa, F.C.L.; Fernandes, L.L. Análise pluviométrica no estado do Pará: comparação entre dados obtidos de estações pluviométricas e do satélite GPCC. Rev. Bras. Climatolog. 2020, 16, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celso, A. Rodrigues, Maria C.R. Luvizotto, Ana Liz G. Alves, Piero H.M. Teodoro and Elisa A. Gregório. Digital dermatitis of the accessory digits of dairy cows. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2010, 30, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitgaard, K.; Nielsen, M. W.; Ingerslev, H. C.; Boye, M.; Jensen, T. K. Discovery of bovine digital dermatitis-associated Treponema spp. in the dairy herd environment by a targeted deep-sequencing approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4427–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M. J. R.P.; Huertas, S.M.; Gallo, C.; Costa, O.A.D. Strategies to promote farm animal welfare in Latin America and their effects on carcass and meat quality traits. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushen, J.; Passillé, A.M.B.; Munksgaard, L. Fear of people by cows and effects on milk yield, behavior, and heart rate at milking. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, R.J.; Melville, G.J.; Greenwood, P.L. Individual differences in the reaction of beef cattle to situations involving social isolation, close proximity of humans, restraint and novelty. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2006, 99, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrow, H. M. The effects of inbreeding on productive and adaptive traits and temperament of tropical beef cattle. Livest. Product. Scien. 1998, 55, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrell, S.P.; Reinhardt, C.D.; Larson, C.K.; Vahl, C.I.; Thomson, D.U. Incidence of lameness and association of cause and severity of lameness on the outcome for cattle on six commercial beef feedlots. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 250, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, X.; Le Neindre, P.; Chupin, J. M. (1992) Establishment of cattle-human relationships. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci., 1992, 32, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.S.; Alvarez, J.; Bicout, D.J.; Calistri, P.; Canali, E.; Drewe, J.A.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Gonzales Rojas, J.L.; Gortázar Schmidt, C.; Michel, V.; Miranda Chueca, M.Á.; Padalino, B.; Pasquali, P.; Roberts, H.C.; Spoolder, H.; Stahl, K.; Velarde, A.; Viltrop, A. Winckler, C.; Earley, B.; Edwards, S.; Faucitano, L.; Marti, S. de La Lama. G.C.M.; Costa, L.N.; Thomsen, P.T.; Ashe, S.; Mur, L.; Van der Stede, Y.; Herskin, M. Welfare of cattle during transport. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, P.M.; Sant´Anna, A.C.; Valente, T.S.; Costa, M.J.R.P. Impact of the temperament of Nellore cows on the quality of handling and pregnancy rates in fixed-time artificial insemination. Livest. Sci. 2015, 177, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.R.; Carvalho, A.U.; Facury Filho, E.J.; Ferreira, P.M.; Ferreira, V.C.P. Prevalence and classification of foot problems in lactating dairy cows in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 1999, 51, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, K.E.; Faerevik, G. Grouping and social preference in calves, heifers and cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2003, 80, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackshaw, J.K.; Blackshaw, A.W.; McGlone, J.J. Buller steer syndrome review. Appl. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1997, 54, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros ATM, Ravaglia E, Aquino WS, Passos WM, Leite LTB. Avaliação de Extratos Vegetais na Prevenção e tratamento de Miíases Umbilicais em Bezerros no Pantanal. Brasília: EMBRAPA; 2010b. pp. 1–4.
- Grisi, L.; Leite, R.C.; Martins, J.R.; Barros, A.T.; Andreotti. R.; Cançado, P.H.; León, A.A.; Pereira, J.B.; Villela, H.S. Reassessment of the potential economic impact of cattle parasites in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.F.; Fioravanti, M.C.S.; Trindade, B.R.; Silva, O.C.; Eurides, D.; Cunha, P.H.J.; Silva, L.M.; Moura, M.I. Foot diseases in dairy cows: association with clinical mastitis, metrites and predisposed factors. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2004, 24, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, R.G.; Benesi, F.J.; Birgel Junior, E.H.; Libera, A.M.M.P.D.; Gregory, L.; Sucupira, M.C.A.; Ortolani, E.L.; Gomes, V.; Pogliani, F.C. Retrospective study of locomotor disorders in ruminants attended in the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, University of São Paulo from 2000 to 2012. Braz. J. Vet. Res. An. Sci. 2013, 50, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
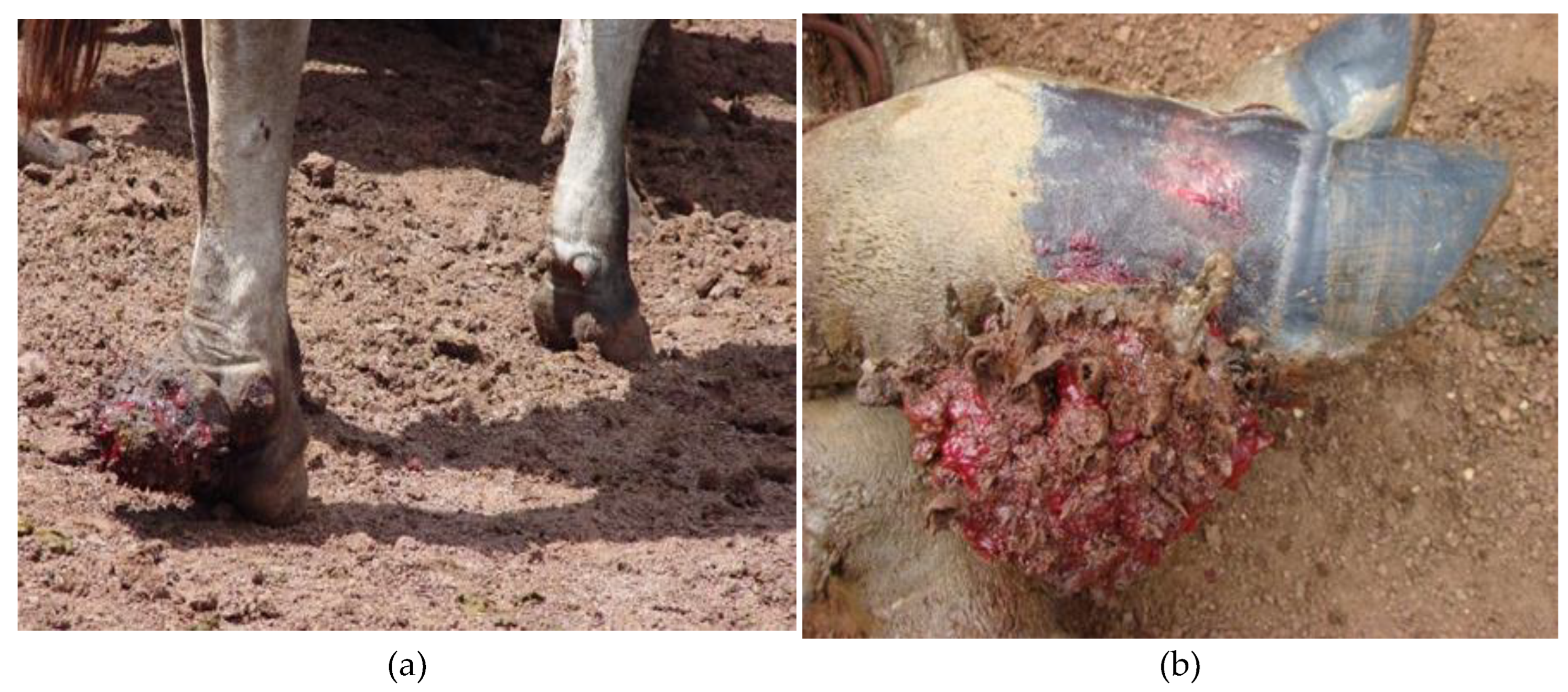





| Farms | Inspected animals |
Animals with BDD | Limbs | Animals with BDD in more than one limb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL* | PL** | ||||
| A | 90 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 2 |
| B | 75 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| C | 30 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| D | 80 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| E | 120 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 6 |
| F | 115 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 4 |
| G | 120 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
| H | 76 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Total | 706 | 49 (6.94%) | 4 (7.57%) | 45 (92.42%) | 15 (30.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





