1. Background
Immune responses to vaccines depend on the quality of the used vaccine and the immune response by the host. In immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) the immune response by the host is altered due to intrinsic changes of the innate and adaptive immune system as well as the concomitant presence of immune modulatory drugs [
1]. Initial studies on the use of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with IMIDs were reassuring as to the efficacy of the vaccines, indicating the overall humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were good despite the use of different immune-modulatory drugs such as cytokine inhibitors [
2,
3,
4]. However, patients with systemic autoinflammatory diseases (sAID) were not included or highly underrepresented in these studies, which substantially limits our current knowledge on the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in this disease groups. Of note, sAID patients receive different drugs than other patient groups from the IMID disease spectrum. Thus, IL-1 inhibitors and colchicine are widely used to treat sAID but not typically used outside the sAID field [
5]. Furthermore, under certain circumstances, such as comorbidities and glucocorticoid use, sAID patients are at risk to develop severe COVID-19 [
6]. This observation indicates that a better knowledge on the response of sAID patients to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is of utmost importance.
We therefore addressed anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in a larger group of sAID patients treated with IL-1 inhibitors to find out whether sAID patients are able to mount sufficient humoral immunity against the coronavirus. We thereby analyzed primary antibody responses and booster responses and compared them to data obtained from healthy controls (HC). In addition, we analyzed whether additional use of colchicine influenced the vaccination response.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
After approval by the Research Ethics Committee of the Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU), 100 consecutive sAID patients were recruited. The healthy control group was age and gender matched from the large COVID-19 study at the Deutsche Zentrum fuer Immuntherapie, (DZI), Universitätsklinikum Erlangen, established in February 2020. Patient demographic data (age, sex, body mass index, comorbidities, medication) and information on SARS-CoV-2 vaccination (date, type of vaccine) and infection (date, general symptoms, severity of symptoms) were obtained in telephone interviews and supplemented by retrospective analysis of physician letters in the UKER electronic archive and document management system Soarian® until end of July 2022.
2.2. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing
Quantitative detection of specific antibodies of the IgG class against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was performed with the CE-marked version of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit from EUROIMMUN (Lübeck, Germany). The reagent vials were evaluated photometrically at an optic density (OD) of 450 nm with reference wavelength at 630 nm. The ratio was determined then by dividing the absorbances of the control or patient sample and the calibrator, a ratio ≥ 0,8 was considered positive.
The determination of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies was performed with the CE-In Vitro Diagnostics (CE-IVD)-certified cPass surrogate virus neutralization assay from the manufacturer GenScript (Piscataway, NJ USA). Per test run, neutralizing antibodies from 92 participant sera can be determined on a microtiter plate with two negative and two positive controls. Photometric analysis was performed at 450 nm and a calculation formula was used to determine the inhibition percentage. A cut-off value of 30% was considered a positive test result and indicated the presence of neutralizing antibodies.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Characteristics of the study groups were described using descriptive analyses- including mean, standard deviation (SD) and counts/percentages. We used the Wilcoxon rank sum test to compare controls with the sAID group. Since on average a longer time had elapsed after second vaccination to sample collection, we used linear regression to adjust for this time difference. Separate models were fitted for the antibody and the neutralizing antibody values as independent variables and OD ratio values from the antibody assay as the dependent variables. The visual image of an initial scatter plot in the analysis indicated that the use of a native scale did not adequately present the data, which is why the neutralizing antibodies were analyzed in the logit transformation and the SARS-CoV-2 antibody ratio in the log transformation. The freely available programming language “R v.4.01” (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), was used for all statistical analyses. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients and Controls
100 sAID patients were analyzed, of whom 58 were female and 42 were male (
Table 1). At the time of data collection in June 2022, the age (mean [min; max] +/- SD) of sAID patients was 43 [18; 80] +/- 16 years. The proportionally largest represented disease was familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) with more than one third (37%) of patients, followed by adult-onset Still’s disease (AoSD; 25%), gout (15%), cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS; 7%), sAID of unclear etiology (7%), Behcet’s disease (4%) and tumor necrosis receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS; 4%) and Yao syndrome (1%). At the time of vaccination, 48 patients were treated with IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RA) and 48 patients with an IL-1 inhibiting antibody. In addition to the IL-1 inhibitors, colchicine was used in 50% of sAID patients. Glucocorticoids and methotrexate were infrequently used treatments. By the end of July 2022, one patient had received only one shot of the COVID-19 vaccine while 13 patients (13%) had received two, the vast majority (73%) three and 9% had received four vaccinations. Only 4 patients (4%) have received no SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. In sAID patients, mRNA-based vaccines were by far the most frequently used whereas only a minority of patients received a vector-based vaccine. The HC group (N=100) had a similar age and sex distribution as the sAID patients and consisted of 57 females and 43 males with a mean age of 43 [18; 89] +/- 16 years.
3.2. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralizing Antibodies Responses in sAID
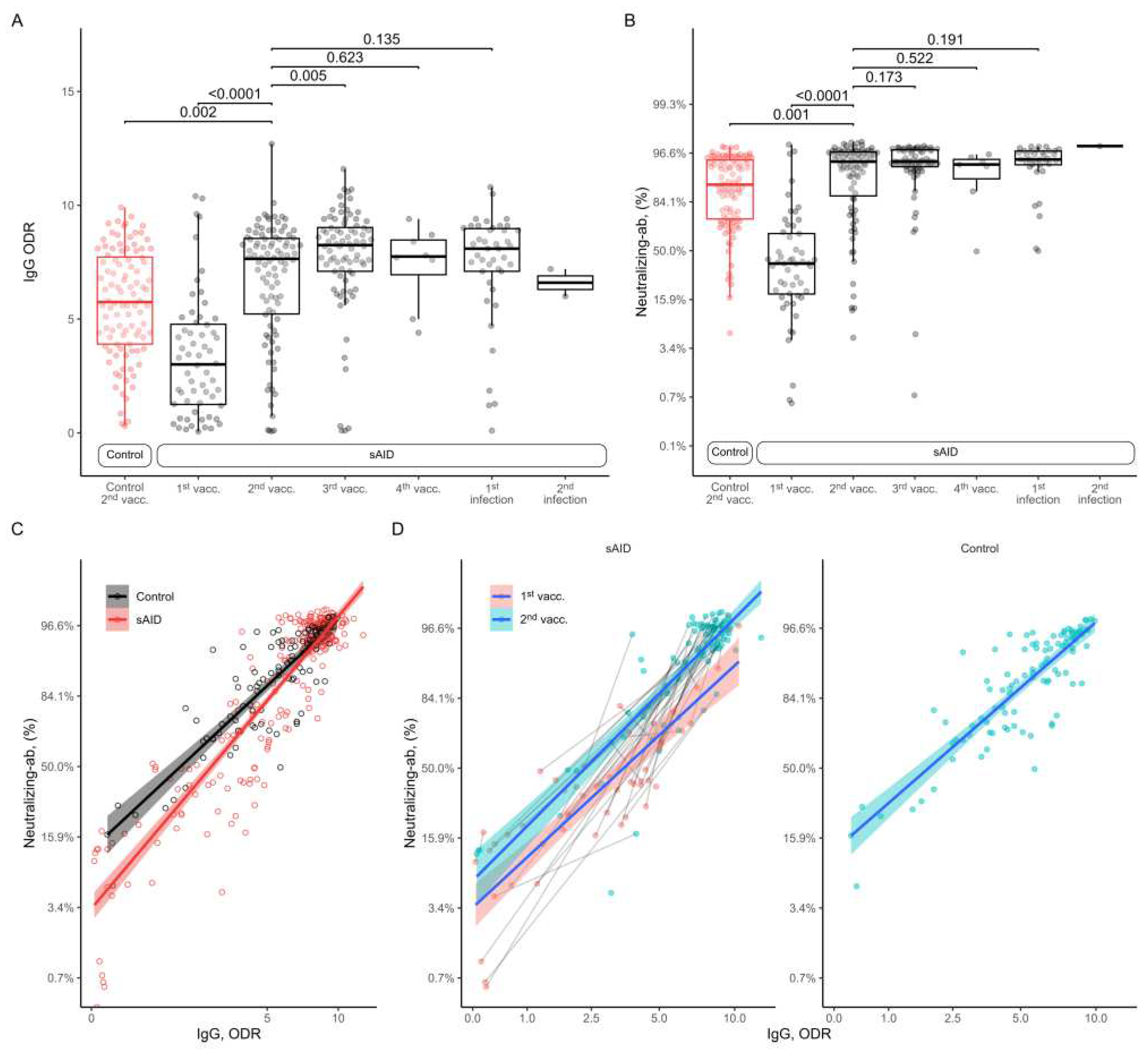
All analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in sAID patients showed an increase from the 1st to the 2nd vaccination with similar antibody levels after the 2nd vaccination in sAID patients compared to HC (
Figure 1A). Further vaccinations did not increase anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody responses. Also, anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody levels after additional SARS-CoV-2 infection were comparable to the ones found after vaccination. That HC (5.7 [2.4]) had even lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels than sAID patients (7 [2.7]; p=0.0017) after two vaccinations was based on the the timing of sample collection after second vaccination, which was 9.1 [7.5] weeks in the sAID group as compared to 21.9 [6.5] weeks in the control group. When we adjusted for the time to sample collection after the second vaccination no difference in antibody levels between HC and the sAID group was found (0.17; 95%CI -0.80 to 1.13, p= 0.73). The results for neutralizing antibodies were very similar with increase in neutralizing capacity from first to second vaccination, a peak after 2nd vaccination and no major differences between vaccination and vaccination and additional SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as between vaccinated HC and sAID patients (
Figure 1B).
3.3. Relation between Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels and Neutralizing Capacity
We have also analyzed the association between anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels and the neutralizing capacity.
Figure 1C shows a descriptive plot showing the neutralizing antibody levels observed at each total antibody measurement. The regression lines fit separately for HC and sAID patients suggest that at the lower range of antibody levels, HC show higher levels of neutralizing capacity compared to sAID patients and neutralizing capacity becomes similar with higher antibody levels. We have analyzed this relationship using a mixed effects linear regression model with the logit transformed neutralizing antibody levels as the dependent variable, log-transformed antibody levels and study groups as fixed effects, patient identifier and sample collection timepoint (i.e., vaccination or infection) as crossed random effects. By adding an interaction term between study group and the log-transformed antibody levels we tested the equality of the slopes between sAID and HC for the relationship between the antibody levels and neutralizing capacity. This interaction term was non-zero, indicating that the relationship between the total antibody levels and neutralizing antibody levels depended on the study group (p for interaction=0.0051).
3.4. Association between Immunomodulatory Treatment and Vaccination Response
As we did not observe lower antibody levels in sAID patients compared to HC and since the vast majority of sAID patients but none of the HC received IL-1 inhibition, there seems to be no effect of IL-1 inhibitors on SARS-CoV-2 vaccination response. In accordance, the few sAID patients who did not use IL- inhibitors did not show different vaccination responses compared to those using IL- inhibitors (
Figure 2A,B). We next assessed whether additional therapies with colchicine, methotrexate or glucocorticoids affected vaccination reponses in sAID patients but no major differences in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies as well as the neutralizing antibodies was found. Only one patient receiving mycopheolate and tacrolimus treatment at different timepoints showed negative results in both ELISA tests at all time points.
Table 2.
Mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralizing antibodies.
Table 2.
Mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralizing antibodies.
| |
|
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG |
Neutralizing antibodies in % |
| event |
sex |
sAID |
HC |
sAID |
HC |
| 1st vacc. |
F |
3.3 ±2.9 (N=37)** |
- |
42.5 ±30.2 (N=32) |
- |
| |
M |
3.4 ±2.3 (N=23) |
- |
40.2 ±25.5 (N=20) |
- |
| |
All |
3.4 ±2.7 (N=60) |
- |
41.6 ±28.2 (N=52) |
- |
| 2nd vacc. |
F |
7.2 ±2.2 (N=56) |
6.2 ±2.2 (N=57) |
89.9 ±15.5 (N=54) |
86.5 ±17.6 (N=57) |
| |
M |
6.0 ±3.2 (N=38) |
5.1 ±2.5 (N=43) |
77.2 ±30.1 (N=33) |
77.3 ±21.3 (N=43) |
| |
All |
6.7 ±2.7 (N=94) |
5.7 ±2.4 (N=100) |
85.1 ±22.9 (N=87) |
82.5 ±19.7 (N=100) |
| 3rd vacc. |
F |
8.1 ±1.7 (N=45) |
- |
94.6 ±5.3 (N=43) |
- |
| |
M |
7.2 ±2.9 (N=35) |
- |
85.3 ±27.5 (N=33) |
- |
| |
All |
7.7 ±2.3 (N=80) |
- |
90.5 ±19.1 (N=76) |
- |
| 4th vacc. |
F |
7.3 ±2.2 (N=3) |
- |
92.4 ±5.7 (N=2) |
- |
| |
M |
7.4 ±1.7 (N=5) |
- |
86.1 ±20.6 (N=5) |
- |
| |
All |
7.4 ±1.8 (N=8) |
- |
87.9 ±17.2 (N=7) |
- |
| 1st infection |
F |
7.4 ±2.4 (N=29) |
- |
92.9 ±9.8 (N=23) |
- |
| |
M |
7.3 ±2.8 (N=13) |
- |
90.7 ±14.1 (N=12) |
- |
| |
All |
7.3 ±2.5 (N=42) |
- |
92.1 ±11.3 (N=35) |
- |
| 2nd infection |
F |
6.6 ±0.8 (N=2) |
- |
97.3 ±NA (N=1) |
- |
| |
M |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| |
All |
6.6 ±0.8 (N=2) |
- |
97.3 ±NA*** (N=1) |
- |
Figure 2.
Distribution of antibody levels by type of treatment. (A) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies and (B) SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for sAID patients and HC after COVID-19 vaccination and disease. HC, healthy controls; IgG, here: anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies; Neutralizing-ab, neutralizing antibodies; sAID systemic autoinflammatory disease; vacc., vaccination.
Figure 2.
Distribution of antibody levels by type of treatment. (A) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies and (B) SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for sAID patients and HC after COVID-19 vaccination and disease. HC, healthy controls; IgG, here: anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies; Neutralizing-ab, neutralizing antibodies; sAID systemic autoinflammatory disease; vacc., vaccination.
4. Discussion
This study shows that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines trigger adequate humoral responses in sAID patients. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies as well as neutralizing antibodies are already formed after primary vaccination and increased after second vaccination to a level that is comparable to HC. These results acquired in a rather large sAID population treated with IL-1 inhibitors confirm initial data obtained in a small group of sAID patients [
7].
One unexpected finding of this study was that antibody responses appeared to be even higher in sAID patients than in HC. These differences, however, disappeared after adjusting for the time-interval between vaccination and sample acquisition. On the other hand, we also found a slightly lower neutralizing antibody response in sAID patients for a given total antibody level at the lower range. While the reason for this observation is not fully clear, it is known that a functional toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 signaling pathway is essential for subsequent affinity maturation of low-affinity IgM antibodies to high-affinity specific IgG antibodies [
6]. During inflammatory episodes of sAID, upregulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome leads to increased IL-1 production, both end members of the TLR-4 pathway [
8]. Hence, the observed difference in the relation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralizing antibodies in sAID and HC in the lower range of the responses may be explained by interference with TLR-4 signaling. However, this concept is speculative at the moment and requires further research. In any case, overall SARS-CoV-2 vaccination responses were good in the sAID group.
Whether vaccination protects sAID patients from severe COVID-19 is beyond the scope of our study. However, it was interesting to observe that a large proportion of sAID patients (79% of all infected persons) only contracted the virus during the “fifth Corona wave” (from calendar week 51/2021 on), when a majority of patients had already received triple vaccination. The four unvaccinated patients only had low anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies after infection. Whether a certain immunomodulatory treatment used for the treatment of sAIDs dampens vaccination responses is another important question: Our results suggest that therapy with an IL-1 inhibitor, which the vast majority of our patients received, did not have a negative impact on vaccination response. Also, further treatment with colchicine did not affect the vaccination response. Only one patient treated with a combination of mycophenolate showed low antibody titers across all measurement time points, which could be ascribed to the mycophenolate treatment as previously observed [
9].
Our study has some limitations. Although the HC group had a similar age and sex distribution as the sAID group, we were only able to compare the sAIDs to HC at different average time intervals after second vaccination. We have addressed this issue with regression adjustments and observed that the apparently higher antibody levels in sAID patients were explained by this time difference in sample collection. Our findings on the non-uniform association between total and neutralizing antibody levels in controls vs. sAIDs could also have been affected for the same reason, therefore this finding needs to be interpreted accordingly. Finally, we did not have data on the persistence of the vaccination response in sAID patients.
5. Conclusions
Primary SARS-CoV-2 vaccination as well as booster vaccinations showed efficacy in sAID patients. In general, immunosuppressive therapy with IL-1 inhibitors could not be associated with a weakened immune response to the vaccination. Hence, we do not see the necessity to control anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses and neutralizing antibodies in sAID patients to ensure the vaccination success. The data provide the basis for recommendations and guidelines for the clinician in the consultation of sAID patients in vaccination planning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R. and L.G.; data collection, validation and curation: L.G., J.R., D.S., A.K., Writing- original draft preparation; L.G., K.T., G.S., J.R.; visualization; L.G., K.T.; writing-review and editing: K.T., G.S., J.R., visualization: L.G., K.T.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Based on ethics approval #157_20 B and the TARDA Database patient consent for publication.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data can be found in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The present work was performed in fulfillment of the requirements for obtaining the doctoral degree “Dr. med.” For Leonie Geck at the Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- A Atagunduz P, Keser G, Soy M. Interleukin-1 Inhibitors and Vaccination Including COVID-19 in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Nonsystematic Review. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:734279. [CrossRef]
- Geisen UM, Berner DK, Tran F, Sumbul M, Vullriede L, Ciripoi M, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and immunosuppressive therapy in a monocentric cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(10):1306-11. [CrossRef]
- Simon D, Tascilar K, Fagni F, Kronke G, Kleyer A, Meder C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination responses in untreated, conventionally treated and anticytokine-treated patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(10):1312-6. [CrossRef]
- Simon D, Tascilar K, Fagni F, Kleyer A, Krönke G, Meder C, et al. Intensity and longevity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination response in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022;4(9): e614-e25.
- Rodriguez Y, Novelli L, Rojas M, De Santis M, Acosta-Ampudia Y, Monsalve DM, et al. Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19. J Autoimmun. 2020; 114:102506. [CrossRef]
- Bourguiba R, Kyheng M, Koné-Paut I, Rouzaud D, Avouac J, Devaux M, et al. COVID-19 infection among patients with autoinflammatory diseases: a study on 117 French patients compared with 1545 from the French RMD COVID-19 cohort: COVIMAI—the French cohort study of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patient with systemic autoinflammatory diseases. RMD Open. 2022;8(1). [CrossRef]
- Valor-Méndez L, Tascilar K, Simon D, Distler J, Kleyer A, Schett G, et al. Correspondence on ‘Immunogenicity and safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and immunosuppressive therapy in a monocentric cohort’. Annals of rheumatic diseases. 2021;80(10): e161-e. [CrossRef]
- Garin A, Meyer-Hermann M, Contie M, Figge MT, Buatois V, Gunzer M, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by follicular dendritic cells is pivotal for germinal center onset and affinity maturation. Immunity. 2010;33(1):84-95. [CrossRef]
- Ruddy JA, Connolly CM, Boyarsky BJ, Werbel WA, Christopher-Stine L, Garonzik-Wang J, et al. High antibody response to two-dose SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccination in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Annals of rheumatic diseases. 2021;80(10):1351-2. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).