1. Introduction
Severe convective weather can cause significant damage to people on land and vessels at sea. On land, people can use radar for monitoring severe convective weather. Weather radar obtains information about the reflectivity of raindrops through active remote sensing[
1]. Radar composite reflectivity (REF) greater than 35dBz is typically considered as severe convective weather[
2]. Besides, weather radar also plays a crucial role in weather now-casting[
3]–[
5] and data assimilation for numerical weather prediction models[
6], [
7]. However, due to limitations in geographical coverage and construction costs, radar network has limited coverage and may struggle to cover sparsely populated areas and offshore regions.
In contrast, geostationary meteorological satellites have a wide detection range and are not constrained by geographical features such as land and sea. Nowadays, the development of geostationary meteorological satellites has enabled satellites to obtain products with spatial and temporal resolutions similar to radar. The Himawari-8/9 satellites have a temporal resolution of 10 minutes and a spatial resolution of 500 meters. Even in the infrared band, a spatial resolution of 2 km can be achieved[
8]. This enables the satellite to be widely applied in daily weather monitoring. An important application of satellite data is quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE). The Satellite quantitative precipitation estimation has extensively researched and widely applied in meteorological services[
9]–[
11]. However, due to the difficulty in obtaining direct precipitation observation data over the sea, a significant amount of validation work is based on land-based data[
10], [
11]. Similar to satellite QPE, some researchers have already attempted to use satellites for the retrieval of radar reflectivity[
12], [
13]. Since radar reflectivity–rainfall rates (Z–R) relationship can change with time, precipitation type, and other factors[
14], using precipitation to estimate radar REF may introduce additional errors. But the main solutions are quite similar to satellite QPE. Besides this approach allows for the full utilization of coastal radar data in the vicinity of offshore regions, enriched maritime samples enormously. Due to the differences in spatiotemporal distribution characteristics between satellite and radar data, some research work is limited to very small geographical areas[
12]. Other has also not taken into account regional variations in the relationship between satellite and radar[
13]. In fact, in the evaluation process of quantitative precipitation estimation, significant diurnal variations and regional differences in precipitation errors have been observed[
11]. So we plans to investigate the impact of latitude and diurnal cycles on the satellite retrieval of radar reflectivity. After that, we will try to establish a deep learning-based radar reflectivity inversion model that covers both land and sea. We are aware that precipitation serves as the most direct means of monitoring severe convective weather. However, due to the scarcity of precipitation observation data over the sea and the sparse distance between buoy points, this study primarily relies on the detection results from radar.
The article is organized with the following structure: the second section introduces the data used, the study area, and the deep learning models employed in the article. In the third section, we first conduct a spatiotemporal distribution analysis of radar composite reflectivity and satellite cloud-top brightness temperature. Subsequently, we establish 4 comparative models and conduct a comparative analysis and discussion of the results obtained from these 4 models. Through the comparison of different models, several conclusions have drawn, including that incorporating spatiotemporal features is beneficial for improving the accuracy of the model's output.
2. Materials and Methods
Datasets used in this paper contains land base radar network REF and the geostationary meteorological satellite Himawari-9 L1 product. Both datasets range from June 1st to August 31st, 2023.
2.1. Radar Composite Reflectivity
The REF data represents the maximum radar reflectivity at all levels. Weather radar is mainly divided into 3 types: S-band, C-band, and X-band. Different bands refer to the frequency wave used by the radar. Different bands of weather radars have different capabilities in observation and detection. Among them, the S-band radars have a lower frequency, with a limiting detection range of 460 km, and experience the least attenuation caused by raindrops; they are usually deployed in regions with abundant rainfall, such as coastal areas. The C-band radar has a medium echo power distribution and typically offers a detection range of 300 km; it is usually deployed in inland areas with less rainfall. The X-band radars have higher detection resolution but a shorter detection range. Due to severe echo attenuation, they are often used to complement other radars and fill in coverage gaps. The S-band and C-band radars are the mainstay of weather monitoring.
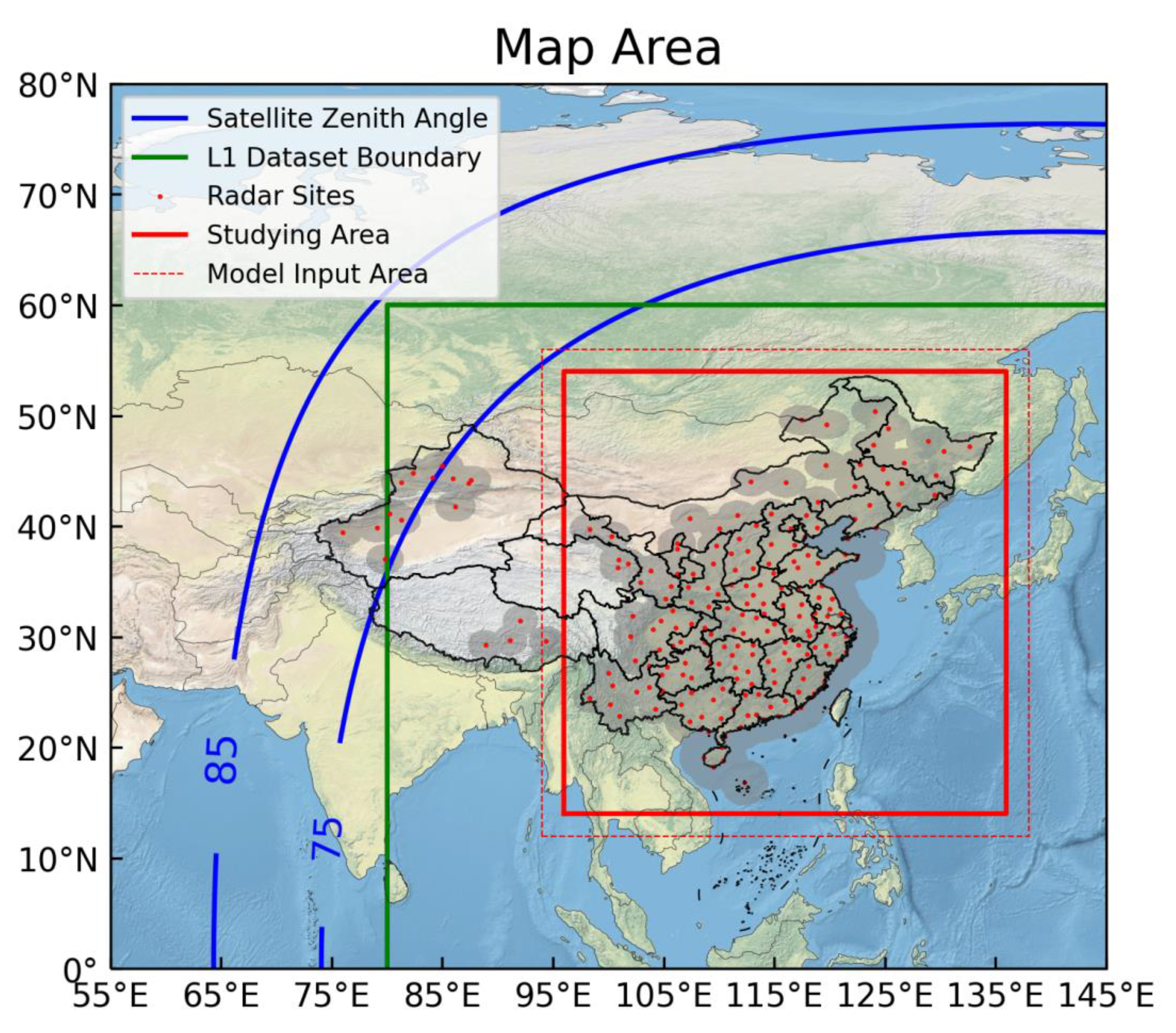
Although S-band weather radar has a farthest detection capability of 460km, due to the curvature of the Earth and the conical scanning of radar, the long distance reflectivity only scan very high above ground cloud, makes the product somewhat distorted. 230km cycle product are considered more accuracy. A radar cover mask was calculated based on radar site and radar type. The S-band radar covers 230km radius cycle, and the C-band radar covers 150km radius cycle. Data over this area were dropped. Radar cover map was calculated using radar location information and radar type. Results were show in the gray shading in
Figure 1. The red dot indicates the position of the radars.
2.2. Himawari-9 data
The Himawari-9 satellite is a new generation geostationary meteorological satellite equipped with the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI). The AHI features 16 bands ranging from the visible to the infrared spectrum, with spatial resolutions ranging from 500m to 2km. These 16 bands include 3 visible bands, 3 near-infrared bands, and 10 infrared bands[
8]. Having more channels enables the acquisition of more detailed meteorological information. Specifically, for water vapor detection, the AHI includes 3 bands to detect moisture at different altitude levels. Additionally, 3 infrared window channels are also incorporated. The sub-satellite point of the Himawari-9 is located near 140.7°E above the equator. Geostationary meteorological satellites offer advantages such as a large scanning range and a fixed scanning interval. The contours of the 85° and 75° satellite zenith angles are shown in
Figure 1, covering the entire area of China. The satellite scans approximately every 10 minutes, close to the radar's scanning interval of 6 minutes. Level-1 product data with an equal latitude-longitude resolution of 5km were obtained from ftp.ptree.jaxa.jp. The product covers the region from 60°N to 60°S, 80°E to 160°W, as indicated by the green line in
Figure 1. The types of data included in the product are albedos for visible and near-infrared bands, brightness temperature (TBB) for infrared bands, and geographic information such as solar zenith angle and solar azimuth angle. In order to invert radar reflectivity both during the day and night, we were focusing on the infrared bands, particularly infrared window channels and water vapor channels.
2.3. Study Area
All the map information is presented together in
Figure 1. Due to the observation scanning angle, areas with large the satellite zenith angle may experience image distortion. The distribution of radar sites across China is not uniform, with significantly fewer radars in the west compared to the east. To address this, we selected the red rectangle as the study area after combining all the detection areas. The specific latitude and longitude ranges are from 96°E to 136°E and 14°N to 54°N. Spatial resolution for all datasets was standardized to 0.05 degrees, approximately 5km. To mitigate potential boundary issues caused by the convolution process, the input array was extended by 2 degrees in each direction. The input range of the model is outlined by a red dashed box.
2.4. Deep Learning Model
Since our goal is to test the influence of latitude and the diurnal cycle, we haven't conducted an extensive model testing. We chose Unet++ as the research model, an upgraded version of Unet that incorporates numerous skip connections[
15]. Unet is a commonly used image segmentation model and performs quite well in medical images[
16]. We believe its upgraded version is already sufficient for this task. A three encoder-decoder layer Unet++ model with an 880×880 grid input was established.
Due to the non-uniformity of radar reflectivity, we established a loss function with weights, where the weight factors are the reciprocals of the probability density of REF. However, since the probability density of strong echoes approaches zero, causing its reciprocal to tend toward infinity, we added a small value of 0.001 to the denominator (Equation 1). When the probability density of echoes is relatively large, this value can be neglected, while when the probability density of echoes approaches zero, 0.001 limits the maximum value of the reciprocal to 1000.
The selection of model input factors is crucial to the modeling process. We chose the inputs of the model based on the physical meanings of different satellite channels (
Table 1). The physical meanings of different variables are obtained from the Zhuge and Mecikalki’ paper[
17], [
18]. The infrared window band (channel 13, IR10.4μm) is most indicative of cumulus cloud development. Generally, the lower the cloud-top temperature, the more vigorous the cumulus cloud development. However, the presence of stratocumulus clouds complicates this relationship. The cloud-top brightness temperature of stratocumulus clouds is generally low, but they rarely lead to precipitation. Therefore,
and
are introduced as input variables. These 2 values are commonly used for stratocumulus cloud identification[
19].
3. Results
3.1. Features of Different Variables
Precipitation exhibits a strong daily cycle and varies by latitude. Before constructing deep learning models, it is essential to analyze the data distribution. Temporal distribution and spatial distribution were applied to both REF and TBB data.
3.1.1. Radar Composite Reflectivity
The distribution of REF at different times is calculated, and the results are shown in
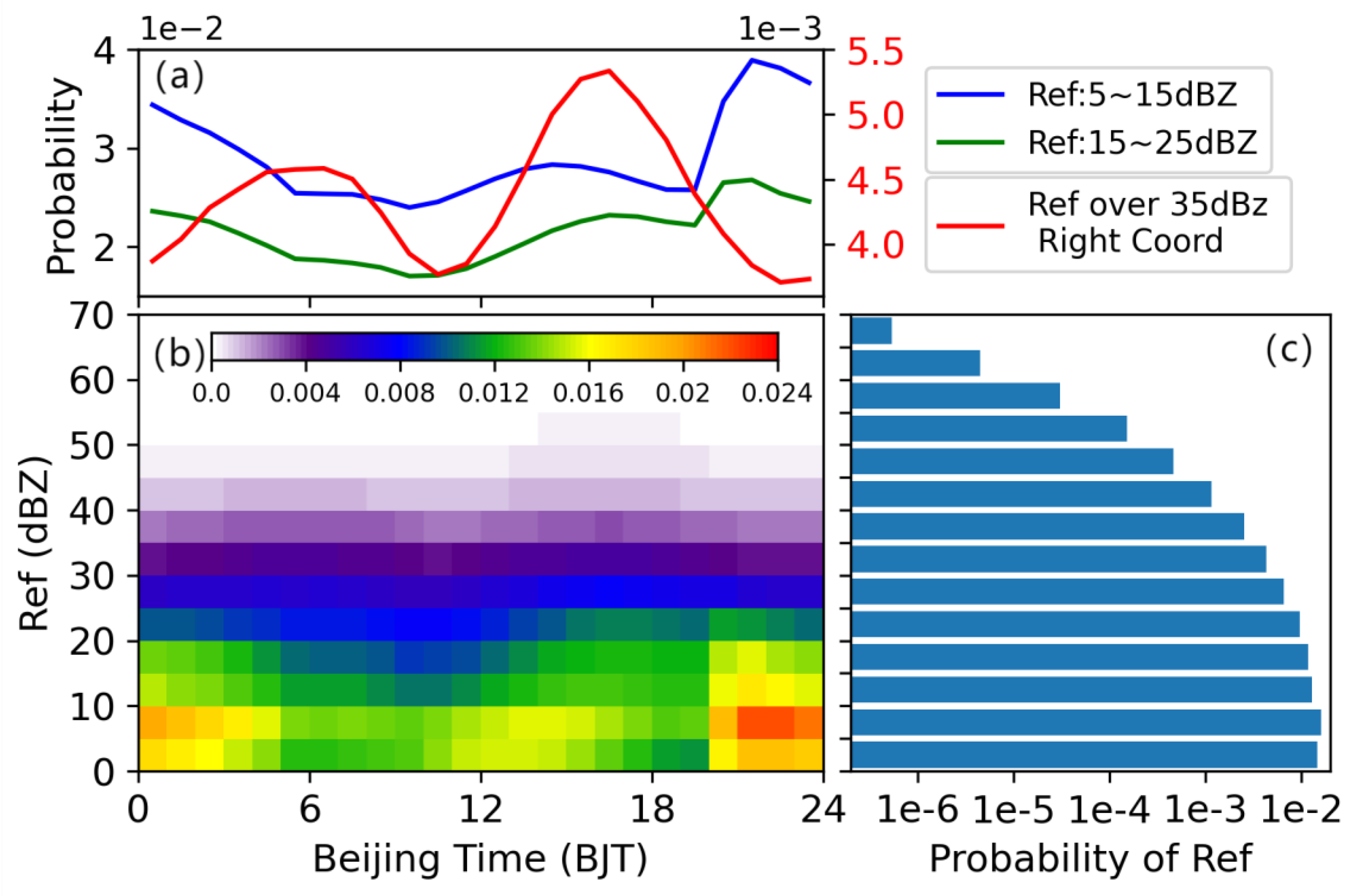
Figure 2. It is evident that the REF distribution exhibits a pronounced diurnal cycle, and the cycle for different reflectivity levels varies. The distribution of REF's probability is extremely uneven, experiencing an exponential decline from weak to strong reflectivity (
Figure 3c). The proportion of REF over 35dBz is very small, only about 0.04%. An interesting phenomenon can be observed in the difference in the diurnal cycle between strong and weak reflectivity in
Figure 2a and 2b. Strong reflectivity has a bimodal distribution with peaks at 8:00 and 16:00, respectively. Afternoon precipitation is stronger than the morning precipitation. Weak reflectivity, on the other hand, has a large proportion during nighttime, mainly caused by long and moderate rainfall.
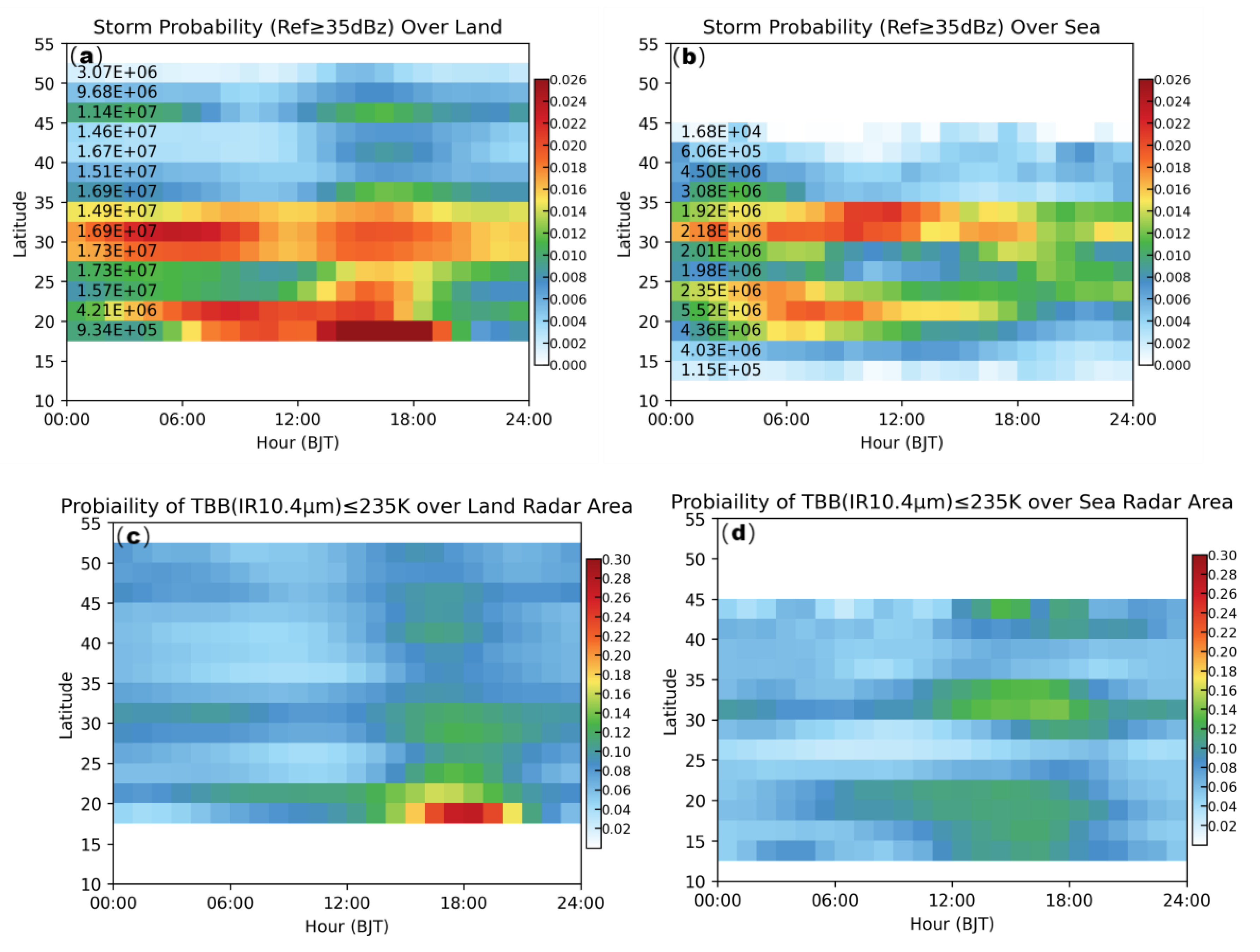
Besides the diurnal cycle feature, the reflectivity also varies with latitude. We calculated the probability of REF over 35dBz at different latitudes and different times. Probabilities over land and sea were calculated separately, and the results are shown in
Figure 3a and 3b. Three rain belts can be observed with the increasing latitude over land. The southern one was the strongest, located at 17.5°N to 22.5°N. The peak of strong probability was in the afternoon, suggesting that heavy precipitation in southern China usually occurs in the afternoon. The middle rain belt, located at 27.5°N to 35°N, has totally different distribution characteristics. It has two peaks, in the early morning and afternoon, and the early morning peak is stronger, probably related to the stationary front located in this area. The northern belt was much weaker than the other two. The probability over the sea was much different; limited by the radar’s coverage, most of the samples were from near-shore areas. The number of samples is printed on the left side of the image. Storm probability over the sea also has different belts located in southern and middle China. The peak of storm probability shifted to noon.
3.1.2. Brightness temperature
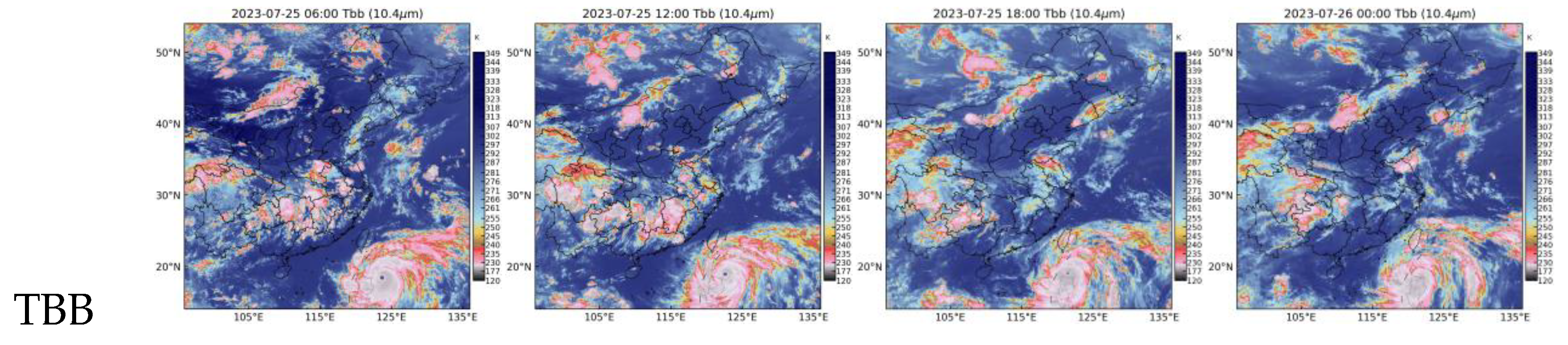
The Brightness temperature of different IR 10.4μm represents the cloud top temperature. Or in another simple concept the cloud top’s height. The colder the TBB, the more vigorous the cloud development. TBB colder than 235K can be recognized as mature convection. We calculated the probability of TBB colder than 235K by time and latitude. In order to keep consistent with radar REF statistical results, radar cover mask was applied to TBB datasets. Land and sea statistical results were show in
Figure 3c and 3d. Some interesting results can be found by compare this result to the REF ones.
Some similar patterns can be summarized. Firstly, the three belts were obvious in the TBB results, coinciding with the REF results; Secondly, two peaks can be found in the middle and northern belts; Thirdly, in the sea area, peaks turned to one, just like the REF with time duration. However, some different patterns have drawn our attention. Firstly, the two peaks over middle China have opposite strength compared to the REF. In the TBB results, the afternoon one was stronger than the early morning one. Secondly, the northern belts were almost equal to the middle belt, which was totally different from the REF ones.
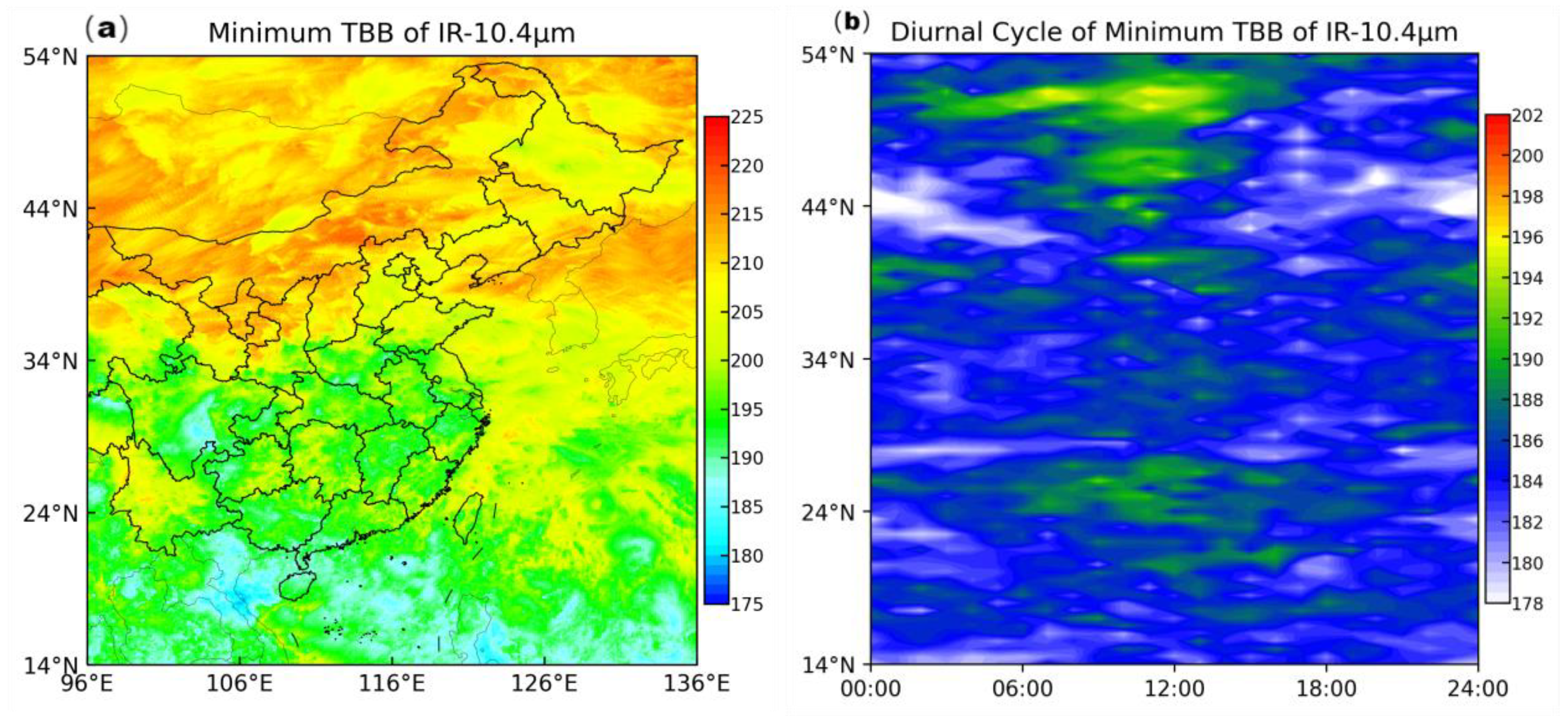
We conducted a statistical analysis of the minimum cloud-top brightness temperatures at different latitude and examined the diurnal variation of the minimum cloud-top brightness temperature.
Figure 4 illustrates the statistical results of IR-10.4μm. It is evident that the TBB shows a trend of being lower in the south and higher in the north. The same trend is observed in the diurnal variation cycle graph. Simultaneously, it can be observed that in the northern regions, the difference between high and low temperatures is more significant, with extreme high TBB around noon and low TBB at night. Therefore, in the subsequent modeling and testing processes, we will introduce these differential features in different ways and establish distinct models.
3.2. Model output
We conducted a total of 4 comparative experiments. Data for the entire summer were divided into a training set and test set. Samples before the 20th of each month were used as the training set and the remaining data as the test set. Models setting was listed in
Table 2.
The basic model was using the variables listed in
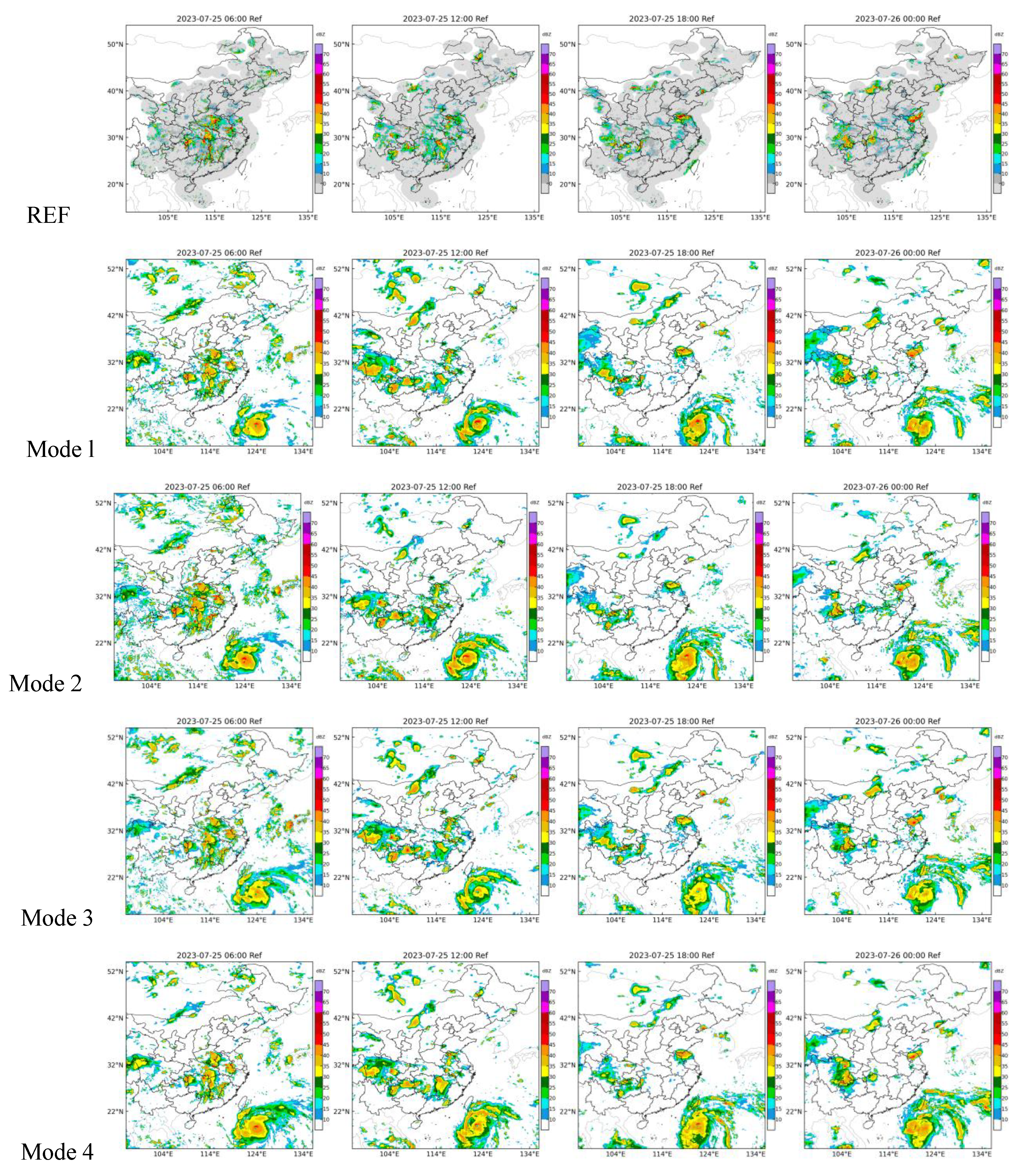
Table 1 as inputs. In model 2, we introduced the solar zenith angle. Since different latitudes have variations in solar zenith angle at different times, introducing the solar zenith angle (SZA) can to some extent reflect spatiotemporal features. In model 3, we introduced the latitude and local time information. In Models 2 and 3, the added data is relatively static and does not directly showcase the features of cloud-top temperature. They were utilizing the deep learning model to discover patterns from the static geographical information. Finally, in Model 4, we added the minimum temperature distribution maps of all the channels used at different times. In here refers to the minimum TBB maps of channels 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15. Model outputs for super typhoon Doksuri were show in
Figure 5.
4. Discussion
By comparing the images of TBB and REF, it can be observed that their relationship is quite complex. The area covered by cold clouds is usually much larger than the coverage of strong REF. Especially in the northern regions, many cloud structures do not have corresponding echoes on the radar image. This is mainly due to the limited penetration capability of the infrared band. However, the REF retrieved by the all the four models can distinguish these cloud structures. This confirms the effectiveness of the retrieving method. Through this method, REF maps over sea can be obtained. From the map, the intense convective area of typhoon Doksuri can be clearly seen. However, constrained by the limited penetration capability of the infrared band, many very vigorous cloud structures exhibit similar features in satellite cloud images. This leads to the inverted strong REF regions being larger than the actual ones.
To quantitatively evaluate the results of different models, we used Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Critical Success Index (CSI, Eqution 2). The RMSE is primarily used to assess the overall accuracy of the inversion, while the 35dBz CSI is mainly used to evaluate the accuracy of strong echoes.
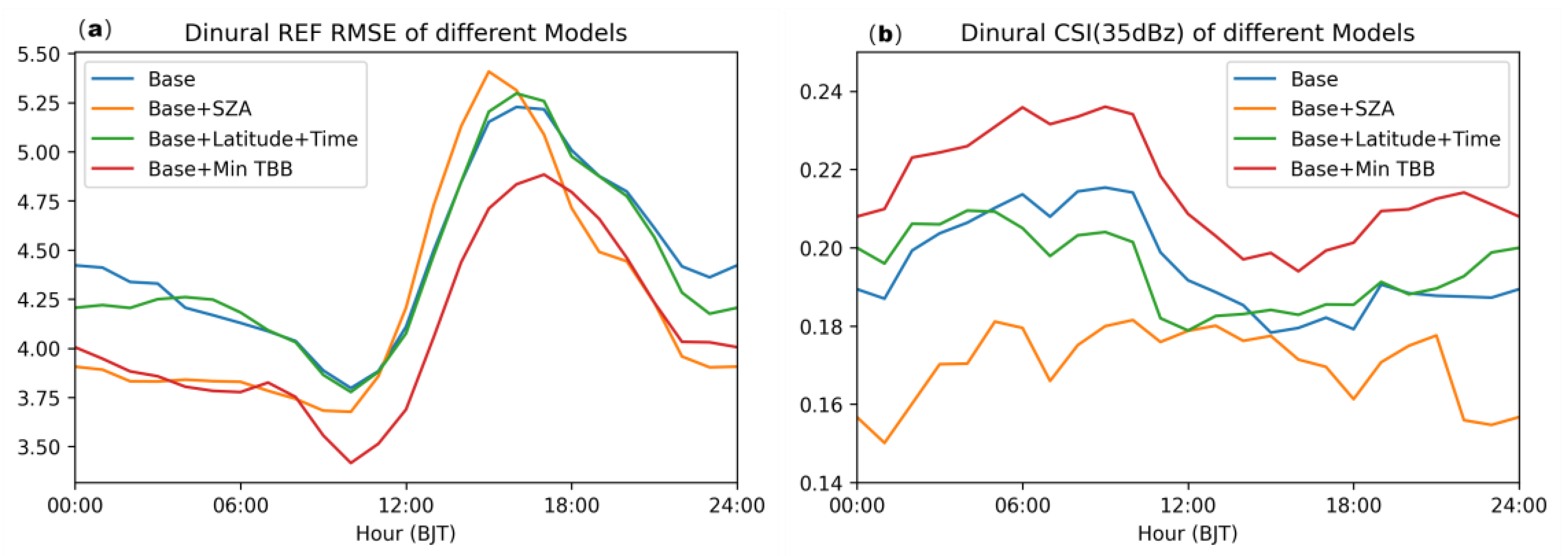
All test datasets were evaluated, and the RMSE and 35dBz CSI were calculated for each hour. Results were show in
Figure 6. In all models, the one incorporating the Minimum TBB performed the best. It consistently reduced the RMSE and improved the CSI across all hours of the day. While the other three models each had their own advantages at different time periods. This gives us great inspiration. 1) Simply feeding static geographic information to deep learning models and adding new feature parameters to the model may not necessarily improve its accuracy; 2) The minimum T can be considered as a background field and is an effective variable that can improve the model's performance; 3) Although there are variations in the relationship between TBB and REF at different locations and times, introducing the right variables can enhance the model, some new variables can be study and tested in the further.
5. Conclusions
In this article, we utilized the Himawari-9 satellite to establish a model for reconstructing radar REF over sea. Through the spatiotemporal analysis of REF and TBB, we identified three rain belts in the Chinese region. There is a clear diurnal cycle in the convective weather in the three rain belts. However, the diurnal cycle of convective activity shows differences in its manifestation on REF and TBB maps. We employed the Unet++ model to experiment with different input variables and conduct 4 models. Results show that Unet++ model can reconstruct radar REF well. Contrastive results show that after adding the minimum TBB of different channels as a background parameter, the model's forecast RMSE and 35dBZ CSI both significantly improved. This approach might be applicable to satellite-based quantitative precipitation estimation as well.
Funding
This research was funded by Jiangsu Funding Program for Excellent Postdoctoral Talente (grant no. 2023ZB012).
References
- R. A. Houze, M. I. Biggerstaff, S. A. Rutledge, and B. F. Smull, “Interpretation of Doppler Weather Radar Displays of Midlatitude Mesoscale Convective Systems,” Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 608–619, 1989.
- R. D. Roberts and S. Rutledge, “Nowcasting storm initiation and growth using GOES-8 and WSR-88D data,” Weather Forecast., vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 562–584, 2003. 2003. [CrossRef]
- S. Ravuri et al., “Skilful precipitation nowcasting using deep generative models of radar,” Nature, vol. 597, no. 7878, pp. 672–677, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, M. Long, J. Wang, Z. Gao, and P. S. Yu, “PredRNN: Recurrent Neural Networks for Predictive Learning using Spatiotemporal LSTMs,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, vol. 30.
- Y. Zhang et al., “Skilful nowcasting of extreme precipitation with NowcastNet,” Nature, vol. 619, no. 7970, pp. 526–532, 2023. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Bauer, A. Thorpe, and G. Brunet, “The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction,” Nature, vol. 525, no. 7567, pp. 47–55, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. Sheng, S. Gao, and M. Xue, “Short-range prediction of a heavy precipitation event by assimilating Chinese CINRAD-SA radar reflectivity data using complex cloud analysis,” Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., vol. 94, no. 1–4, pp. 167–183, 2006. [CrossRef]
- K. Bessho et al., “An introduction to Himawari-8/9 — Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites,” J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan, vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 151–183, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Kuligowski, Y. Li, Y. Hao, and Y. Zhang, “Improvements to the GOES-R rainfall rate algorithm,” J. Hydrometeorol., vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 1693–1704, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Sun, H. Yuan, X. Liu, and X. Jiang, “Evaluation of the latest satellite-gauge precipitation products and their hydrologic applications over the Huaihe River basin,” J. Hydrol., vol. 536, pp. 302–319, 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. Tang, M. P. Clark, S. M. Papalexiou, Z. Ma, and Y. Hong, “Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets,” Remote Sens. Environ., vol. 240, no. September 2019, p. 111697, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Duan et al., “Reconstruction of the radar reflectivity of convective storms based on deep learning and himawari-8 observations,” Remote Sens., vol. 13, no. 16, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Sun, B. Li, M. Min, and D. Qin, “Deep learning-based radar composite reflectivity factor estimations from fengyun-4a geostationary satellite observations,” Remote Sens., vol. 13, no. 11, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Wang, L. Liu, and Y. Ding, “Improvement of radar quantitative precipitation estimation based on real-time adjustments to Z-R relationships and inverse distance weighting correction schemes,” Adv. Atmos. Sci., vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 575–584, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhou, M. M. R. Siddiquee, N. Tajbakhsh, and J. Liang, “UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation,” 2018.
- O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, and T. Brox, “U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation BT - Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015,” 2015, pp. 234–241.
- X. Zhuge and X. Zou, “Summertime convective initiation nowcasting over southeastern China based on advanced himawari imager observations,” J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan, vol. 96, no. 4, pp. 337–353, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Mecikalski and K. M. Bedka, “Forecasting convective initiation by monitoring the evolution of moving cumulus in daytime GOES imagery,” Mon. Weather Rev., vol. 134, no. 1, pp. 49–78, 2006. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, H. Han, J. Im, E. Jang, and M. I. Lee, “Detection of deterministic and probabilistic convection initiation using Himawari-8 Advanced Himawari Imager data,” Atmos. Meas. Tech., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1859–1864, 2017. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).