0. Introduction
The China-Pakistan Karakoram Highway (KKH) serves as the vital land route connecting China and Pakistan, starting from Kashgar, Xinjiang, China in the north, traversing the convergence of the Hindu Kush, Karakorum, and Himalayan Mountains, and reaching Takot city in Pakistan's south [
1,
2,
3]. At 11:30 on January 4, 2010, a giant rocky landslide (N36°18'26.6″, E74°48'54.9″) occurred in Attabad village of Hunza River Valley along the KKH, with a total volume of about 25 million m
3 [
4,
5,
6]. The landslide body quickly formed a barrier dam of about 1100m in length, 600m in width and 200m in visible dam height, completely blocking the Hunza River Valley, formed a barrier lake about 23km long, burying 23km of the KKH and causing 25 deaths, the highway reconstruction project took 3 years to complete [
7,
8].
The real-time acquisition of hydrological characteristics of barrier lake has been a major difficulty in the process of barrier lake risk prevention and control and secondary disaster prevention and control [
9,
10,
11]. As the naturally formed barrier dam are not compacted and cemented, the risk factor of the dams increases dramatically which may cause secondary disasters at any time with the change of lake area and suspended sediment concentration (SSC) [
12,
13,
14,
15]. In addition, the change of sediment accumulation in the reservoir area of the lake will also affect the movement pattern of the breach flood and the peak flow rate of the breach, so it is important to obtain the change of the area and SSC of the barrier lake in time for the prediction and early warning of the lake breach and the safety prevention [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Since the formation of Attabad landslide-dammed lake, scholars have carried out more in-depth studies on the formation conditions and triggering mechanism of Attabad landslide, the process of landslide deformation movement, and the risk of lake failure [
1,
4,
22,
23,
24]. In response to the Attabad landslide and the barrier lake buried and damaged KKH and railroad, Chinese scholars have proposed the water damage characteristics, formation causes, prevention and control principles and main engineering measures of the highway along the river in Karakorum, as well as the design strategy of the new railroad disaster mitigation selection line [
25,
26]. From the existing literature, the current research on Attabad landslide-dammed lake is mainly focused on the formation mechanism of the landslide and the risk of lake failure, and there is a lack of research on the monitoring of long time series hydrological characteristics and long-term evolution trend of Attabad landslide-dammed lake. At the same time, due to the constraints of observation methods and instruments, the complexity of suspended sediment movement on the surface of the barrier lake and other conditions, no large-scale hydrological sediment observation has been conducted in the remote Hunza Valley of northern Pakistan, and long-term monitoring of the area and SSC of the lake is lacking.
With the development of remote sensing of lakes, remote sensing technology has been widely used in highland lake change and sea, estuarine and near-shore, lake suspended sediment monitoring studies, and many mature suspended sediment quantitative remote sensing inversion models have been established [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. In the study of lake changes, multispectral optical remote sensing images such as Landsat MSS/TM/ETM+/OLI, Gaofen series satellites (GF-1/2), and Sentinel data (Sentine-2) can realize the monitoring of lake area changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the 1970s, among which, Landsat series data are most widely used because they can provide more The Landsat series is the most widely used because it provides more high-quality free data [
34]. In terms of suspended sediment monitoring in lakes, many scholars analyzed the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of suspended sediment in the surface layer of marine waters using TM, ETM, MODIS and GF-1 images [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41] conducted a study on the identification of floods with high SSC based on remote sensing data. The above studies mainly focus on the water bodies with low SSC such as lakes and sea areas for quantitative inversion, and do not focus on the water bodies of barrier lake with high SSC in mountainous areas, so this paper draws on the mature quantitative inversion model of lake SSC to study the changes of SSC of Lake.
In this paper, based on the 10-phase QuickBird, Pleiades, and WorldView2 high-resolution satellite images of Attabad landslide-dammed lake for the past 15 years, (1) the normalized water body index is used as a research method to extract the extent of the lake from 2010 to 2020, and analyze the evolutionary trend of the lake in terms of its area change, landscape pattern index, and geometric features; (2) Based on the above extracted lake extent, a mature remote sensing quantitative inversion model of lake suspended sediment is used to extract the relative SSC of the lake, and analyze the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the suspended sediment and the dynamic changes of SSC of the lake from 2010 to 2020, with a view to providing data reference for the forecast and early warning of the lake failure and safety prevention.
1. Overview of the study area
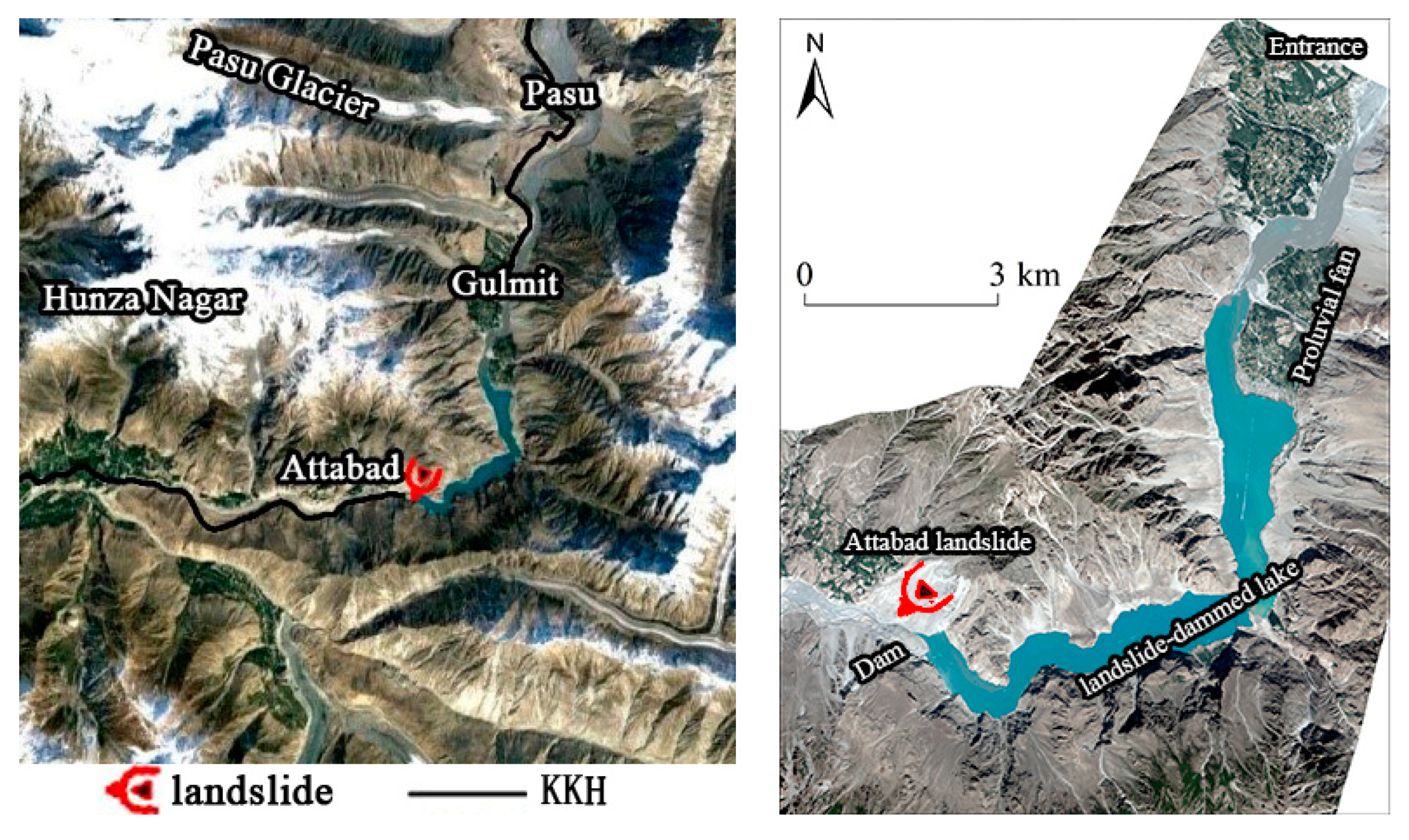
The Attabad landslide-dammed lake is located in the Kashmir region of northern Pakistan, about 570km from Kashgar, China, where the Hindu Kush, Karakorum and Himalayas meet, with strong neotectonic movements and frequent earthquakes [
3]. The overall shape of the lake is "L", the water level elevation is about 2379m, the water depth is 81.3m, the reservoir capacity is about 192 million m
3, and the overflow mouth is about 118m above the bottom of the old riverbed. Both sides of the lake are typical high mountain deep canyon landforms, with exposed high and steep slope mountains, the slope of which is mostly between 50°-60°. The middle and upper parts of the mountains are covered by permanent snow (thickness of 50-300 mm) and glaciers all year round, which are easy to produce abundant snow and ice melt water in summer [
42]. Attabad landslide-dammed lake is located in the arid and semi-arid alpine snow glacier zone, which belongs to the inland plateau mountain climate zone, with scarce annual rainfall, dry and cold climate, large temperature difference between day and night, strong freezing and thawing effect, fragile ecological environment and poor anti-disturbance ability. The water recharge of the lake mainly comes from the mainstream of Hongza River and three tributaries of Batura glacier meltwater, Pasu glacier meltwater and Ghulkin glacier meltwater, among which the inflow of Hongza River and Batura glacier meltwater tributaries is larger [
43]. The newly reconstructed KKH passes through the mountain tunnel on the right bank of the lake [
25,
44].
Figure 1.
Location of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake.
Figure 1.
Location of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
Previous studies on Suspended Sediment Concentration (SSC) in lakes and seas have primarily utilized Hyperspectral data with MODIS/TM/ETM medium resolution [
29,
45,
46]. However, considering the complex mountainous terrain and the small size of the lake in the study, a different approach was adopted. Seven periods of high-resolution panchromatic and multispectral historical archived data (
Table 1) were collected to ensure comprehensive coverage and accuracy. Subsequently, the panchromatic and multispectral images were fused, radiometrically calibrated, and atmospherically corrected using ENVI 5.3 [
47]. The main processing steps involved were as follows:
- (a)
Orthorectification: High-precision control information was used to orthorectify the panchromatic and multispectral data into the CGCS2000 coordinate system.
- (b)
Downscaling: The orthorectified results were downgraded to obtain 8-bit panchromatic and multispectral orthorectified images.
- (c)
Image Fusion: The orthorectified panchromatic and multispectral images were fused, resulting in a combined image with both high resolution and rich color information.
- (d)
Data Screening and Mosaic: After image fusion, data screening and image mosaic were performed to ensure seamless stitching and smooth transitions between each image's edges.
- (e)
Geometric Alignment: Due to the significant terrain deformation in the study area, remote sensing images from the seven phases exhibited differences in the same features at various times and with different sensors. To better visualize the trend of lake area change, geometric alignment was carried out, using the 2010 remote sensing images as a benchmark for absolute radiation correction and FLASH atmospheric correction on the other six phases of images.
2.1. Methods
The main methods for lake water body extraction are thematic classification method [
48,
49], linear mixed model, single-band threshold method and spectral water body index method [
30,
50,
51]. Previous studies, through experimental evaluation of these methods, generally concluded that the traditional normalized difference water body index (NDWI) method is more effective in extracting water body information and can distinguish water body and non-water body information in remote sensing images to the maximum extent, but it is vulnerable to mountain shadows, snow and ice, and mist [
31,
34,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58]. Although the Attabad landslide-dammed lake in this study is a special kind of lake, the water body information is also slightly different from that of lakes, and the topography of the study area is strongly deformed and there are more mountain shadows, so the water body information cannot be extracted directly using the traditional NDWI [
46,
59]. Therefore, this paper adopts the comprehensive water body index model (CWI) constructed by Wang et al. (2021) [
60] based on GF-2 images, which has the advantage of effectively expanding the difference of reflectance between NIR band and blue-green band to suppress the influence of mountain shadows. Finally, the visual interpretation check is then combined with the original images to exclude snow, shadows and other non-water bodies to further revise the boundary extent of the lake accurately. The formula of the comprehensive water body index model is follow:
where B
1 is the blue band, B
2 is the green band and B4 is the near infrared band.
The current methods used for the inversion of SSC in lakes are mainly single-band [
29], band-ratio, multi-band combinations [
35] and other methods. Han et al. (2022) [
61] pointed out that the correlation of single-band and band-ratio inversion is low, and the correlation of multi-band is good, and the correlation of near-infrared band in single-band is low, the correlation of green band and red band is good, and the correlation of green band/red band in band-ratio is good, and the correlation of B1/ (B2+B3) in multi-band is high. In addition, Cai (2020) [
62] pointed out that the green band B2 has certain penetration ability to the water body and can be used to reflect underwater characteristics, such as water turbidity. The red band B3 is more sensitive to the sediment in the water body, leading to B2+B3 can reflect the high and low sand content of the water body, and the correlation between B2/B3 and SSC is high. Therefore, this paper draws on the multi-band combination model proposed by Cai (2020) [
62] to extract the relative SSC of Attabad landslide-dammed lake and analyze the characteristics of sediment distribution changes in the lake during 2010-2002. The formula of SSC index model is follow:
where B
2 is the green band and B
3 is the red band.
The research process in this paper unfolds as follows: Firstly, 7-phase high-resolution satellite images (QuickBird, Pleiades, and WorldView2) of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake over the past decade are utilized. The lake's extent from 2010 to 2020 is extracted using the comprehensive water body index method, and the area change, landscape pattern index, and geometric characteristics of the lake are calculated to infer its evolutionary trend.
Secondly, building upon the extracted lake extent, a remote sensing quantitative inversion model for suspended sediment is employed. This model is based on existing lakes with similarities to our study area, allowing the relative Suspended Sediment Concentration (SSC) of the lake to be extracted. The spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the suspended sediment within the lake are then analyzed, and the dynamic changes of SSC from 2010 to 2020 are examined.
Finally, a comprehensive analysis of the hydrological characteristics' dynamic change process in the lake from 2010 to 2020 is conducted. This analysis provides valuable data reference for predicting and warning against potential lake failure and informs safety prevention measures.
3. Results
3.1. Change of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake area
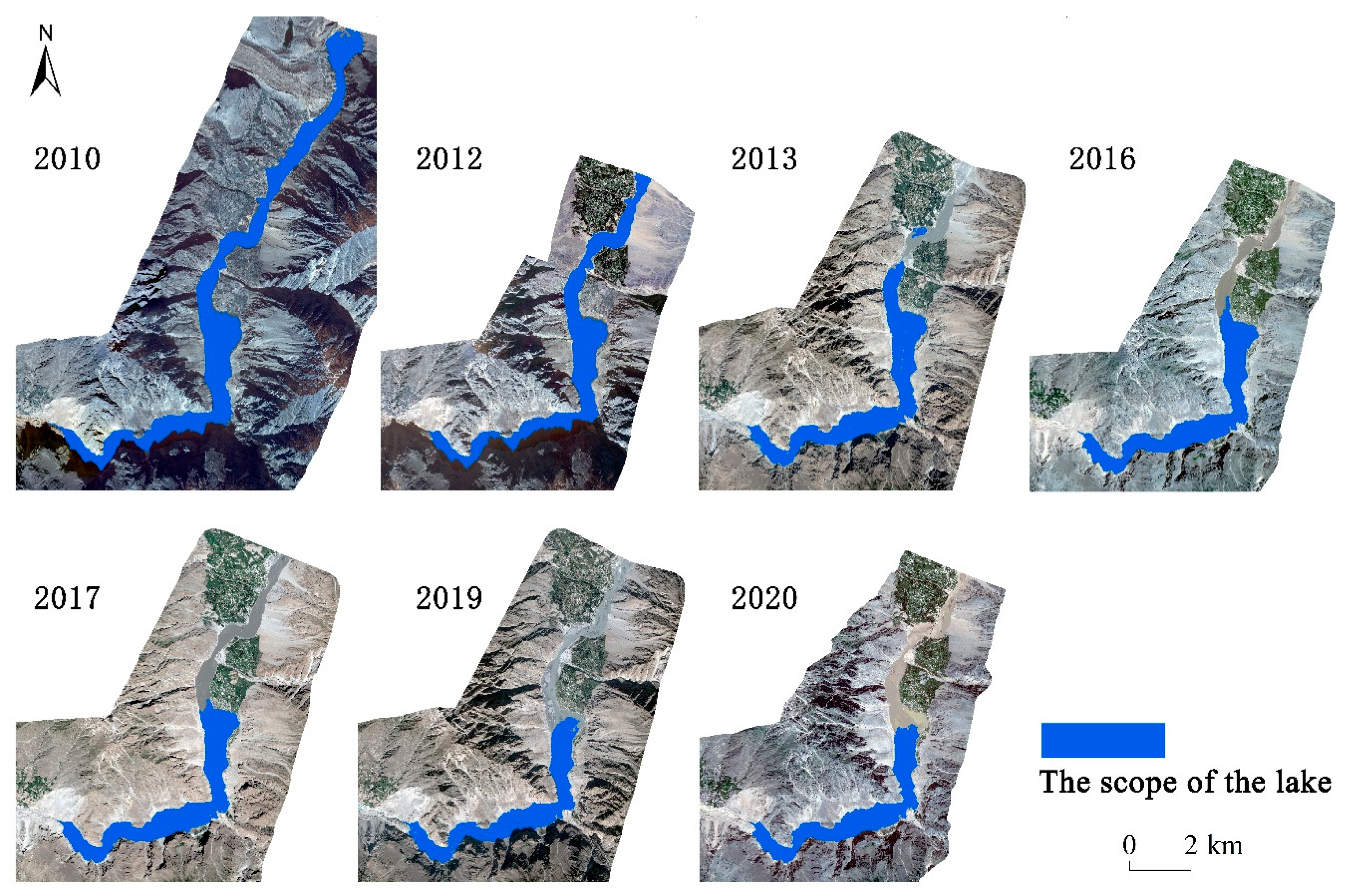
The watershed map of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake for the period spanning 2010 to 2020 was generated using the comprehensive water body index method (
Figure 2). The figure reveals that the Attabad lake has an overall north-south direction, following the course of the narrow river valley. Notably, the northern estuary of the lake exhibits more pronounced changes due to the steep terrain and high slope of the lake shore. In contrast, the east-west shoreline experiences relatively minor changes, and the lake gradually recedes downstream towards the dam. Analysis of the lake area extraction data indicates a consistent trend of gradual reduction in lake area over the 10-year period from 2010 to 2020. Specifically, the lake area contracts by 561 km2 during this time, with an average area of 581 km2. The lake reaches its largest extent in 2010 and gradually diminishes thereafter. As the lake recedes, sediment accumulates at the upstream northern estuary, leading to a gradual increase in the sediment area.
Table 2.
Table of watershed area of Attabad landslide-dammed lake.
Table 2.
Table of watershed area of Attabad landslide-dammed lake.
| Year |
2010 |
2012 |
2013 |
2016 |
2017 |
2019 |
2020 |
| Area/104 m2
|
984 |
619 |
585 |
510 |
517 |
427 |
423 |
3.1.1. Rate of change of lake area
The rate of change of lake area K is the rate of change of lake area in the study area with time, which can visually reflect the real degree of change of lake area. The formula is as follows:
where K is the rate of change of lake area in the study period, Sa and Sb are the lake areas in the initial and final periods, respectively, and T is the study duration. A positive K value indicates that the lake area increases, while the opposite indicates that the lake area decreases, and the larger the absolute value of K, the more drastic the lake area changes [
55].
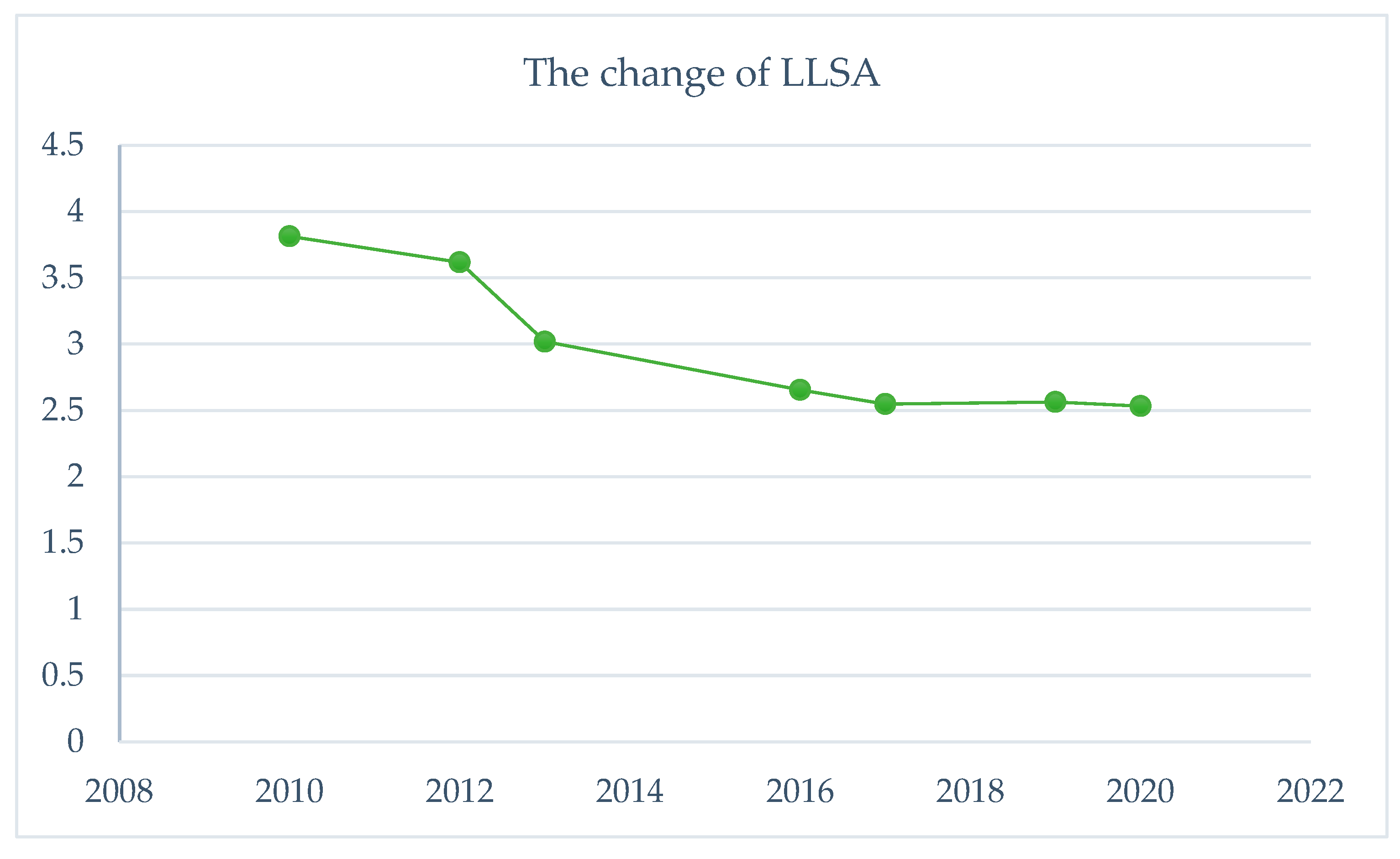
3.1.2. Lake landscape shape index
The Landscape Shape Index (LLSI) serves as a valuable tool to analyze the susceptibility of natural landscapes to external disturbances, including human influences. Additionally, it provides insights into landscape complexity and vulnerability.
In the context of this study focusing on lake landscapes, the calculation formula for LLSI is as follows:
where LLSI is the lake landscape shape index, L is the length of the lake, and A is the area of the lake. The smaller the landscape index is, the more vulnerable the lake is to external disturbance [
55].
3.1.3. Offset of the lake center of mass
The offset of the lake center of mass can, to some extent, reflect the evolution of the lake and the pattern of its spatial properties, calculated as follows:
where δ is the offset of the lake center of mass,
and
are the transverse and longitudinal coordinates of the mass center of the lake after ∆t time, respectively, and
and
are the transverse and longitudinal coordinates of the original mass center of the lake [
55].
During the period from 2010 to 2020, the lake area exhibited an overall decreasing trend, with a slight increase observed in 2017 (
Figure 3). The most significant reduction in lake area occurred between 2010 and 2013, while changes in the lake area after 2016 were comparatively smaller, indicating a trend towards stability (
Figure 3). The Landscape Shape Index (LLSI) showed a gradual decrease from 2010 to 2020, suggesting a diminishing degree of external disturbance to the lake and a reduced risk of lake collapse (
Figure 4).
Moreover, the center of mass of the lake underwent an overall offset reduction, indicating a gradual movement towards the downstream of the lake (dam). This shift in the center of mass, combined with the decreasing lake area, further supports the trend of the lake gradually stabilizing (
Figure 5).
3.2. Changes in SSC of Attabad landslide-dammed lake
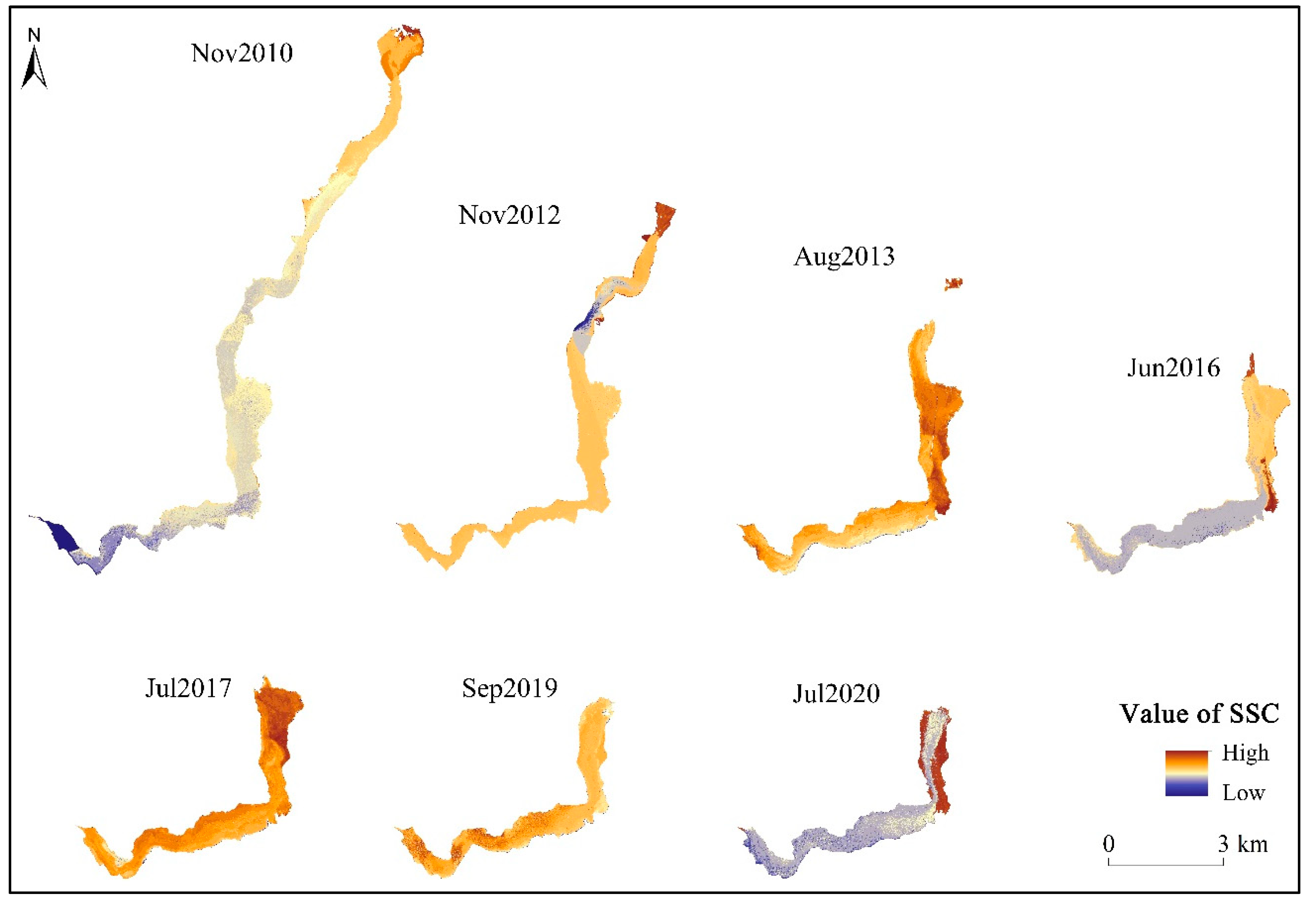
The SSC map of Attabad landslide-dammed lake for the periods from 2010 to 2020 was produced using the SI method (
Figure 6). The spatial distribution of SSC exhibited a consistent strip-like pattern, aligned with the north-south direction, in accordance with the lake's bank. SSC gradually decreased from the lake's entrance towards the downstream dam, and from the lake bank towards the lake center. In November 2010, higher SSC levels were observed at the lake's entrance and shore, gradually decreasing downstream, with lower SSC levels at the dam. By November 2012, higher SSC was observed at the entrance, with lower SSC in the middle and upper parts of the lake, gradually increasing towards the lake shore. In August 2013, SSC was primarily concentrated in the middle of the lake, with relatively lower SSC in the lower-middle downstream area, while higher SSC was found near the dam. By June 2016, higher SSC was observed in the middle and upper-middle parts of the lake, with lower SSC in the downstream region, increasing towards the lake shore. In July 2017, higher SSC was observed at the entrance and in the lower-middle part of the lake, gradually decreasing downstream. In September 2019, higher SSC was mainly located near the lower-middle part of the downstream dam. By July 2020, higher SSC was present in the middle and upper parts of the lake, near the lake shore, and lower SSC was observed near the dam.
The spatial distribution of sediment is influenced by the topography of the lake and the location of the sediment recharge source. The topography of the lake is a long and narrow river valley from north to south, and the river channel changes to the southwest under the influence of the fault in the lower and middle position. The SSC of upstream and downstream at the turning point of the river channel change direction is obviously different in the upper-middle and lower-middle position of the lake in 2010, the upper-middle position in 2012, the middle of the 2013, the middle of the 2016, the middle-lower position in 2017, the middle-lower position in 2019, the middle and middle-lower position in 2020, and the SSC of the downstream is obviously lower than that of the upstream, indicating that the turning point of the river channel has the effect of sand interception; In addition, the SSC in the inner bay is lower than that in the outer bay when the river channel changes direction and bends, and the sediment is mostly deposited in the outer bay. The main sources of sediment recharge of the lake are glacial debris flow and loose avalanche accumulation on the bank slope. The debris flow is mainly the glacial debris flow generated by the Pasu glacier movement at the entrance of the lake and the Shishkat debris flow (flood fan) in the middle and upper part of the lake [
43]. So there are more sediment deposits at the entrance of the lake and the middle and upper part of the lake, and the lake is also wider and has higher SSC. The SSC is relatively low in the narrow part of the lake. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the slope of the lake shore is large and the sediment in the narrow area is not easy to be deposited. In addition, the shore slopes of the lake are mostly unstable slopes with many small landslides, landslides and debris flows, so the loose landslide accumulation keeps entering the lake, resulting in a higher SSC on the shore of the lake than in the middle of the lake.
Between 2012 and 2019, higher SSC values migrated from the upper and central sections of the lake to the lower part, suggesting continuous sediment movement from the upper to the lower regions. From 2012 to 2016, higher SSC was observed at the lake's entrance and near the floodplain fan, while from 2017 to 2019, higher SSC was evident near the floodplain fan and in the middle-lower areas of the lake. This indicated a trend of sediment gradually shifting from the upper to the dam-end of the lake.
The SSC of the lake is generally higher in summer than in winter. November 2010 and November 2012 exhibited lower SSC than other years (mainly summer) due to fewer sediment recharge sources during the freezing period when glaciers and seasonal permafrost are less active. Conversely, during the melting period from June to September, an influx of snow and ice meltwater, as well as groundwater, carried sediment into the lake, resulting in increased SSC at the entrance and near the floodplain fan. Additionally, the ongoing influence of groundwater led to continuous avalanche slide accumulation slipping into the lake from both sides of the bank slope.
Temporally, the average SSC of the lake gradually decreases overall from 2010-2020, and the SSC of the lake gradually increases from 2010-2013, gradually decreases from 2013-2016, gradually increases from 2016-2017, and gradually decreases from 2017-2020, with the lowest SSC of the lake in 2020. In the recent 2017-2020, the SSC in the lower-middle part of the lake is higher, while the SSC is lower near the dam, resulting in less influence of sediment on the dam.
In summary, the spatial distribution of suspended sediment in Attabad landslide-dammed lake follows a north-south and then northeast-southwest trending strip, corresponding to the direction of the lake bank. The SSC gradually decreases from the lake's entrance to the downstream dam and from the lake shore to the center. This distribution is primarily influenced by the lake's topography and sediment recharge sources. From 2012 to 2019, higher SSC values shifted from the upper-middle to the lower part of the lake, indicating continuous sediment movement. Overall, SSC is higher in summer compared to winter, and the average SSC of the lake decreased from 2010 to 2020. During the recent period of 2017 to 2020, higher SSC was observed in the lower-middle parts of the lake, while lower SSC was evident near the dam.
4. Conclusion and discussion
From 2010 to 2020, the area of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake showed a gradual decreasing trend, with the center of mass moving toward the dam and the lake tending to a stable state. The waters of the lake with more obvious changes were mainly located at the northern estuary of the lake, while the east and west shorelines did not change much, and the lake gradually retreated toward the downstream dam. During the lake's recession, sedimentation appeared at the upstream northern estuary, and the sediment area gradually increased.
The suspended sediment in the lake followed a strip-like pattern, trending from north to south and then northeast to southwest, aligning with the lake bank's direction. The suspended sediment concentration (SSC) decreased gradually from the lake's entrance to the downstream dam and from the lake bank to its center. Temporally, the average SSC of the lake showed a gradual decrease from 2010 to 2020, with higher SSC values generally observed in summer compared to winter. Notably, during the recent period of 2017 to 2020, higher SSC was noted in the lower-middle parts of the lake, while lower SSC was observed near the dam, indicating reduced sediment impact on the dam.
However, it is essential to acknowledge some limitations in this study due to the lack of objective data. The analysis of the lake's SSC mainly relied on remote sensing technology, lacking actual measured SSC values, resulting in derived SSC being relative rather than quantitatively analyzed. Additionally, the boundary between the water body and slope in the lake extent during 2010 and 2013 was not clearly defined due to mountain shadows.
Despite these limitations, the findings provide valuable insights into the changes in the Attabad landslide-dammed lake's area and suspended sediment concentration over the past decade. The observed trends and spatial patterns offer critical information for understanding the lake's dynamics and potential implications for safety concerns related to sedimentation and lake failure.
To overcome the limitations of this study and enhance future research, it is recommended to incorporate actual measured SSC data to quantitatively assess sediment concentrations. Moreover, exploring advanced technologies and methodologies, such as in-situ measurements and high-resolution imaging, could lead to more accurate and comprehensive results. Furthermore, further investigation into the impact of sediment redistribution on the lake's ecological environment and surrounding communities would add significant value to the understanding of the overall dynamics of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake.
In conclusion, this study sheds light on the changing dynamics of the Attabad landslide-dammed lake and its suspended sediment concentrations over a decade. While the findings offer valuable insights, continuous research and data refinement are essential for a comprehensive understanding of the lake's behavior and its potential implications for safety and environmental management.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection and analysis were performed by Hongkui Yang, Youhui Qi, Yanhe Wang, Wenqian Ye and Guangchao Cao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yousan Li and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Geological survey project of China Geological Survey [DD20191016, ZD20220409, ZD20220125, DD20211570].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Geological survey project of China Geological Survey. The authors are grateful to insightful comments suggested by the editor and the anonymous reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Butt, M.J.; Umar, M.; Qamar, R. Landslide dam and subsequent dam-break flood estimation using HEC-RAS model in Northern Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2012, 65, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.-M.; Yue, D.-X.; Ma, J.-H.; Guo, F.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Rehman, M.U.; Khalid, Z.; Chen, G.; et al. Landslide mapping and analysis along the China-Pakistan Karakoram Highway based on SBAS-InSAR detection in 2017. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 2540–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Huai, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T. Surge-type glaciers in Karakoram Mountain and possible catastrophes alongside a portion of the Karakoram Highway. Nat. Hazards 2017, 90, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, P.; You, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Khan, A.; Ye, C.; Zhang, S. Dam-break risk analysis of the Attabad landslide dam in Pakistan and emergency countermeasures. Landslides 2016, 14, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhong, Y.G.; Reng, Y. Analyses and prevention and treatment measures of water-distroyed highway along rivers in Karakorum range area in Pakistan. Highway (in Chinese). 2013, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Shafique, M.; Khan, M.A.; Bacha, M.A.; Shah, S.U.; Calligaris, C. Landslide susceptibility assessment using Frequency Ratio, a case study of northern Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 22, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Rogers, J.D.; Abu Bakar, M.Z. Hunza river watershed landslide and related features inventory mapping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, A.S.; Shafique, M.; van der Werff, H. Landslide inventory and susceptibility modelling using geospatial tools, in Hunza-Nagar valley, northern Pakistan. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brideau, M.-A.; Shugar, D.H.; Bevington, A.R.; Willis, M.J.; Wong, C. Evolution of the 2014 Vulcan Creek landslide-dammed lake, Yukon, Canada, using field and remote survey techniques. Landslides 2019, 16, 1823–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Cheng, Z.L.; Cui, P.; Chen, N.S. Dammed lake and risk management; Science press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vergara, I.; Garreaud, R.; Moreiras, S.; Araneo, D.; Beigt, D. Exploring the association between landslides and fluvial suspended sediment in a semi-arid basin in central Chile. Geomorphology 2022, 402, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Shi, Z.; Peng, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M. Longevity analysis of landslide dams. Landslides 2020, 17, 1797–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gupta, V.; Jamir, I.; Chattoraj, S.L. Evaluation of potential landslide damming: case study of Urni landslide, Kinnaur, Satluj valley, India. Geosci Front 2018, 10, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, T.K.; Wu, H.; Chen, G.Q.; Zheng, D.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, D.Y. Research progress on stability evaluation method and disaster chain effect of landslide dam. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 2018, 37, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yan, K. A destructive mudstone landslide hit a high-speed railway on 15 September 2022 in Xining city, Qinghai province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yang, S.; Ye, S. Integrated Application of Remote Sensing, GIS and Hydrological Modeling to Estimate the Potential Impact Area of Earthquake-Induced Dammed Lakes. Water 2017, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-W.; Cui, P.; Fang, H. Dynamic process analysis for the formation of Yangjiagou landslide-dammed lake triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, C.Z.; Zhou, Y.L.; Pang, J.L.; Zha, X.C.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Zheng, Z.X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, G.M.; Liu, T. Formation and development of the prehistorical landslide dammed-lake in the Jishixia gorge along the upper Yellow River. Sci Sin Terrae 2017, 47, 1357–1370. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.M.; Xiao, T.; He, J.; Chen, C. Erosion-based analysis of breaching of Baige landslide dams on the Jinsha River, China, in 2018. Landslides 2019, 16, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentin, A.-L.; Hauthaler, T.; Liebl, M.; Robl, J.; Hergarten, S.; Prasicek, G.; Salcher, B.; Hölbling, D.; Pfalzner-Gibbon, C.; Mandl, L.; et al. Influence of rheology on landslide-dammed lake impoundment and sediment trapping: Back-analysis of the Hintersee landslide dam. Geomorphology 2022, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, W.; Borthwick, A. Hydro-sediment-morphodynamic processes of the baige landslide-induced barrier Lake, Jinsha River, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhao, W.Y.; Luo, Z.G. The effects of Attabad landslide secondary geohazard on the Karakoram Highway. Journal of Catastrophology 2019, 34, 81–85 (in Chinese). (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.T.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.W. Analyses on formation conditions and triggering mechanism of Attabad landslide. China Safety Science Journal 2020, 30, 148–155 (in Chinese). (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gardezi, H.; Bilal, M.; Cheng, Q.; Xing, A.; Zhuang, Y.; Masood, T. A comparative analysis of attabad landslide on january 4, 2010, using two numerical models. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Yao, L.K.; Huang, Y.D.; Ali, S. Railway Alignment design in high risk area of landslide and collapse damming with the chain of quake lake disasters. Railway Station Design (in Chinese). 2019, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Wei, Y.X.; Liu, J.F.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, G.Z. Mountain disasters and countermeasures of traffic engineering along China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. High Speed Railway Technology 2018, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Dang, T.M. Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Downstream of the Ba River Basin using Remote Sensing Images. Inzynieria Miner. Pol. Miner. Eng. Soc. 2021, 1, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, P.M.; Wang, C.-K.; Huang, A.-T. The Spatial-Temporal Distribution of GOCI-Derived Suspended Sediment in Taiwan Coastal Water Induced by Typhoon Soudelor. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Mantravadi, V.S. Study on Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Sediment in Yellow River Estuary Based on Remote Sensing. J. Indian Soc. Remote. Sens. 2019, 47, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Peng, J.; Jiang, L.; Feng, J. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Lakes Based on Satellite Remote Sensing and Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 87849–87856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ni, Y.; Pang, Z.; Li, X.; Ju, H.; He, G.; Lv, J.; Yang, K.; Fu, J.; Qin, X. An Effective Water Body Extraction Method with New Water Index for Sentinel-2 Imagery. Water 2021, 13, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.D. Multi-Spectral Water Index (MuWI): A Native 10-m Multi-Spectral Water Index for Accurate Water Mapping on Sentinel-2. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Lyu, S. Investigating mixing patterns of suspended sediment in a river confluence using high-resolution hyperspectral imagery. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, M.M.; Zhou, T.; Chen, W.F. Progress in remote sensing monitoring of lake area. Remote Sensing Bulletin 2022, 26, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Xu, S.-D.; Lin, Q. Quantitative application study on remote sensing of suspended sediment. China Ocean Eng. 2012, 26, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.M. Multi-temporal analyses of remote sensing on distribution of suspended sediment in Xiamen Estuary. Port & Water Engineering 2008, 422, 51–57 (in Chinese). (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.M.; Huang, Y.G. An analysis of distribution of suspended sediment in Estuary by using remote sensing technology. Port & Waterway Engineering (in Chinese). 2008, 421, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, R.; Ding, J. Application of MODIS data in monitoring suspended sediment of Taihu Lake, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kong, J.L.; Sun, X.M.; Du, D.; Chen, P. Retrieval of sea surface suspended sediment concentration of Bohai gulf offshore area based on semi-analysis model. Geography and Geo-Information Science 2014, 30, 33–36 (in Chinese). (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Han, Y.C.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.J. Observation of suspended sediment in sea area around Dajin Island based on multi-source remote sensing data. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science) 2020, 54, 985–995 (in Chinese). (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.K. Identifying flood with high bedload content using MODIS data. Journal of Catastrophology 2005, 20, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Liu, D.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Hassan, J. Glacier surging controls glacier lake formation and outburst floods: The example of the Khurdopin Glacier, Karakoram. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2022, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Hagemann, S. Estimating the characteristics of runoff inflow into Lake Gojal in ungauged, highly glacierized upper Hunza River Basin, Pakistan. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 24, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Hassan, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Jin, W. Increasing glacial lake outburst flood hazard in response to surge glaciers in the Karakoram. Earth-Science Rev. 2020, 212, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Yang, H. Multiscale water body extraction in urban environments from satellite images. Remote Sens 2014, 7, 4301–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaras, E.; Falchi, U.; Parente, C.; Vallario, A. Accuracy evaluation for coastline extraction from Pléiades imagery based on NDWI and IHS pan-sharpening application. Appl. Geomatics 2022, 15, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Latif, A. Extraction of Urban Water Bodies from High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Imagery Using Deep Learning. Water 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Zhou, R.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q. Classification for High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using a Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.C.; Zhou, T.G.; Li, C.F. () Urban water extraction based on multi-source remote sensing images. International Conference on Ecological Protection of Lakes-Wetlands-Watershed and Application of 3S Technology (EPLWW3S 2011) 2011, 3: 312-315.
- Xiong, L.; Deng, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. Water 2018, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Luo, J.; Sheng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ming, D. An Adaptive Water Extraction Method from Remote Sensing Image Based on NDWI. J. Indian Soc. Remote. Sens. 2011, 40, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, K.; Liang, Z.L. Change monitoring of key lakes in Jiangsu province in 2009-2019 based on remote sensing. Journal of Geomatics 2021. [CrossRef]
- Özelkan, E. Water Body Detection Analysis Using NDWI Indices Derived from Landsat-8 OLI. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawak, S.; Luis, A. A Rapid Extraction of Water Body Features from Antarctic Coastal Oasis Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.S.; Gulgen, F.; Sanli, F.B.; Ates, A.M. The Performance Analysis of Different Water Indices and Algorithms Using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 Images in Determining Water Surface: Demirkopru Dam Case Study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 7883–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Water extraction technique in mountainous areas from satellite images. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Phoumilay, *!!! REPLACE !!!*. Construction and validation of GF-2 image water body index in complex environment. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources (in Chinese). 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Du, C.; Liu, F.Q.; Li, R. Analysis of suspended sediment concentration in Songhua River based on remote sensing technology. Journal of Engineering of Heilongjiang University (in Chinese). 2022, 13, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.L. Retrieve of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Suspended Sediment in Bohai Bay Based on GF-1 Remote Sensing Satellite. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics (in Chinese). 2020, 15, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Dhakal, S.; Cui, P.; Rijal, C.P.; Su, L.-J.; Zou, Q.; Mavrouli, O.; Wu, C.-H. Landslide characteristics and its impact on tourism for two roadside towns along the Kathmandu Kyirong Highway. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1840–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuksina, L. Variations of Water Runoff and Suspended Sediment Yield in the Kamchatsky Krai, Russia. Water 2018, 10, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsoom, A.; Aslam, B.; Khalil, U.; Kazmi, Z.A.; Azam, S.; Mehmood, T.; Nawaz, A. Landslide susceptibility mapping along the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) route using multi-criteria decision-making method. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Mei, C.Q.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, X.H. Information extraction of suspended sediment's relative density and distribution change in Lake Chaohu based on Landsat TM/ETM+ data. Journal of Lake Sciences 2007, 19, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).