Submitted:
10 October 2023
Posted:
12 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
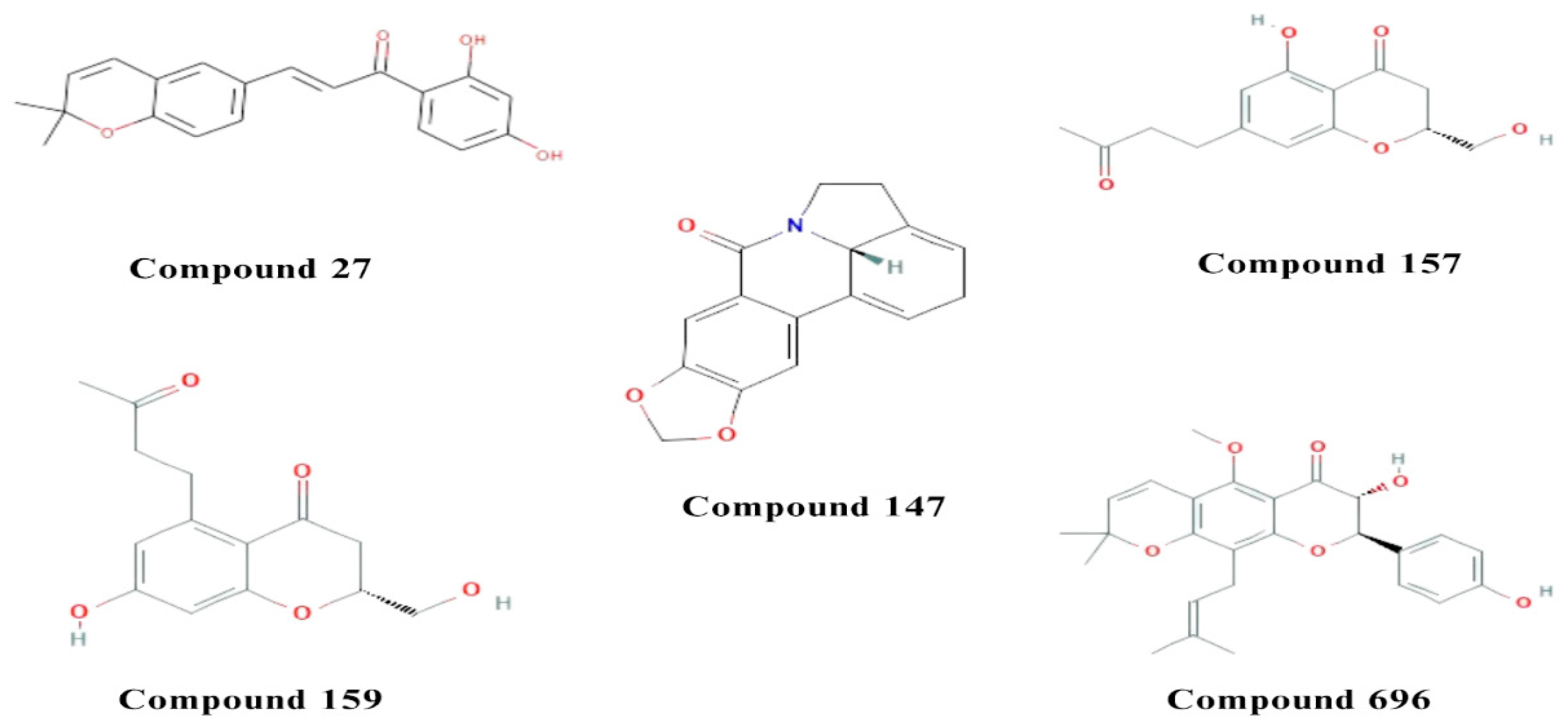
2. Results
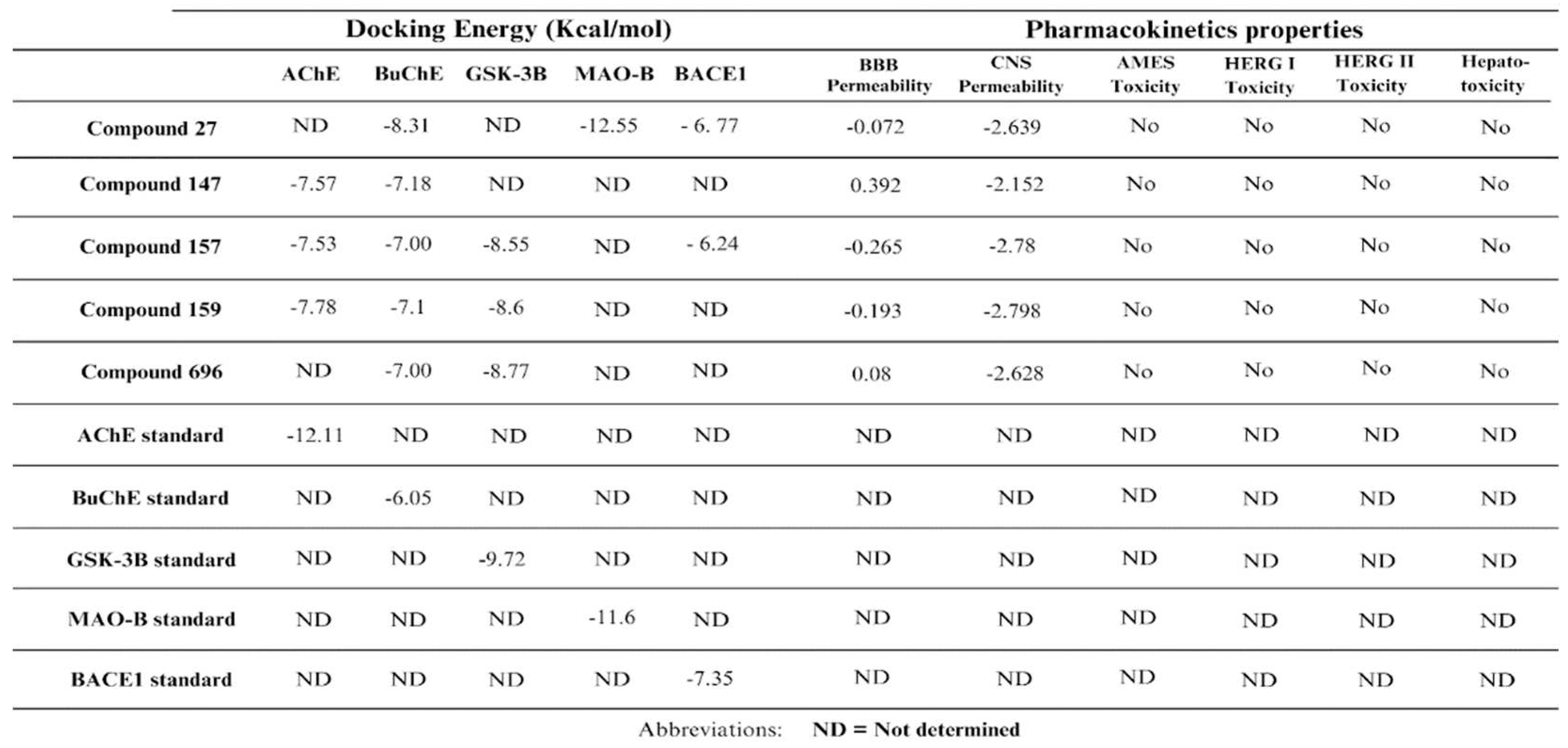
2.1. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity prediction
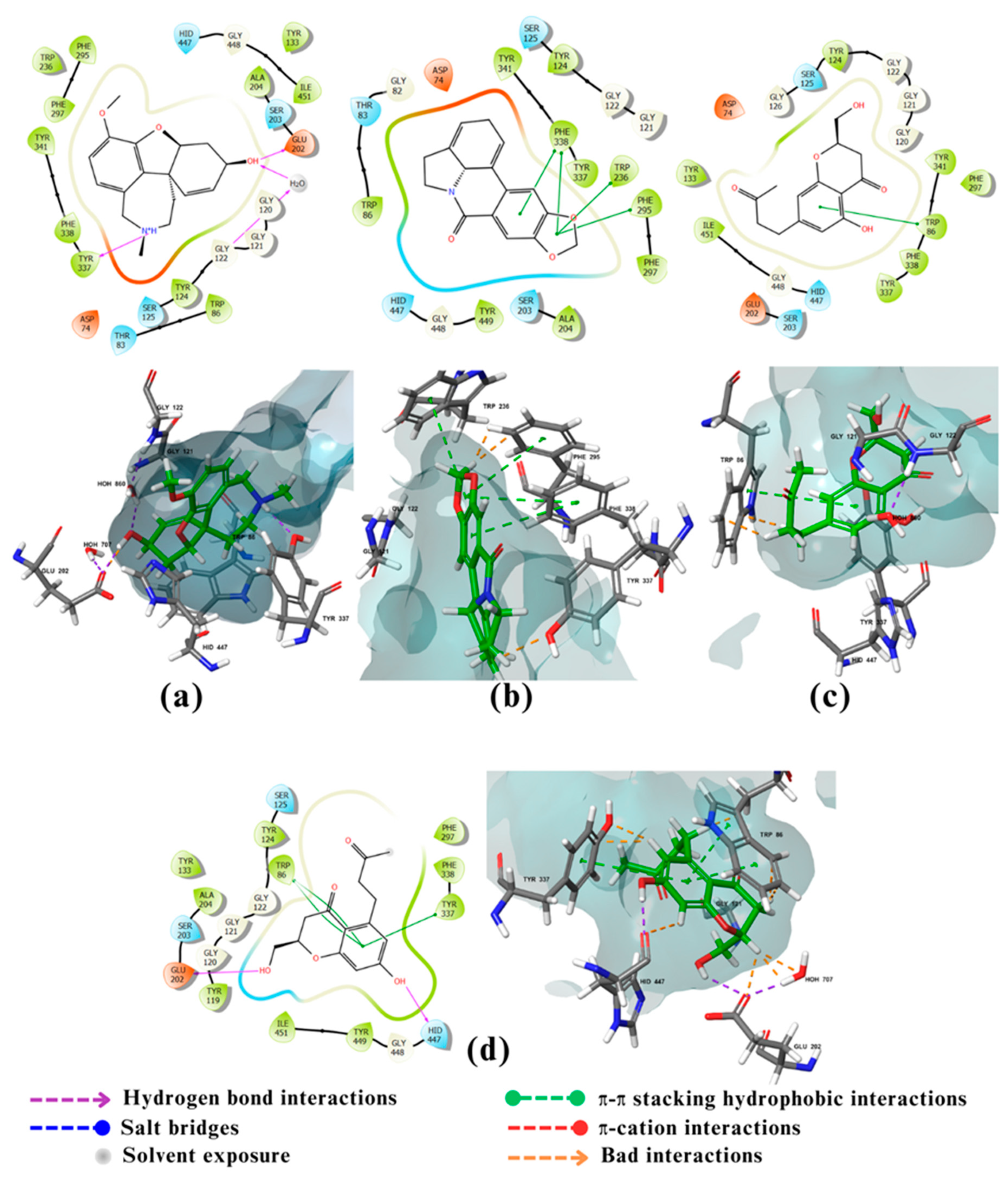
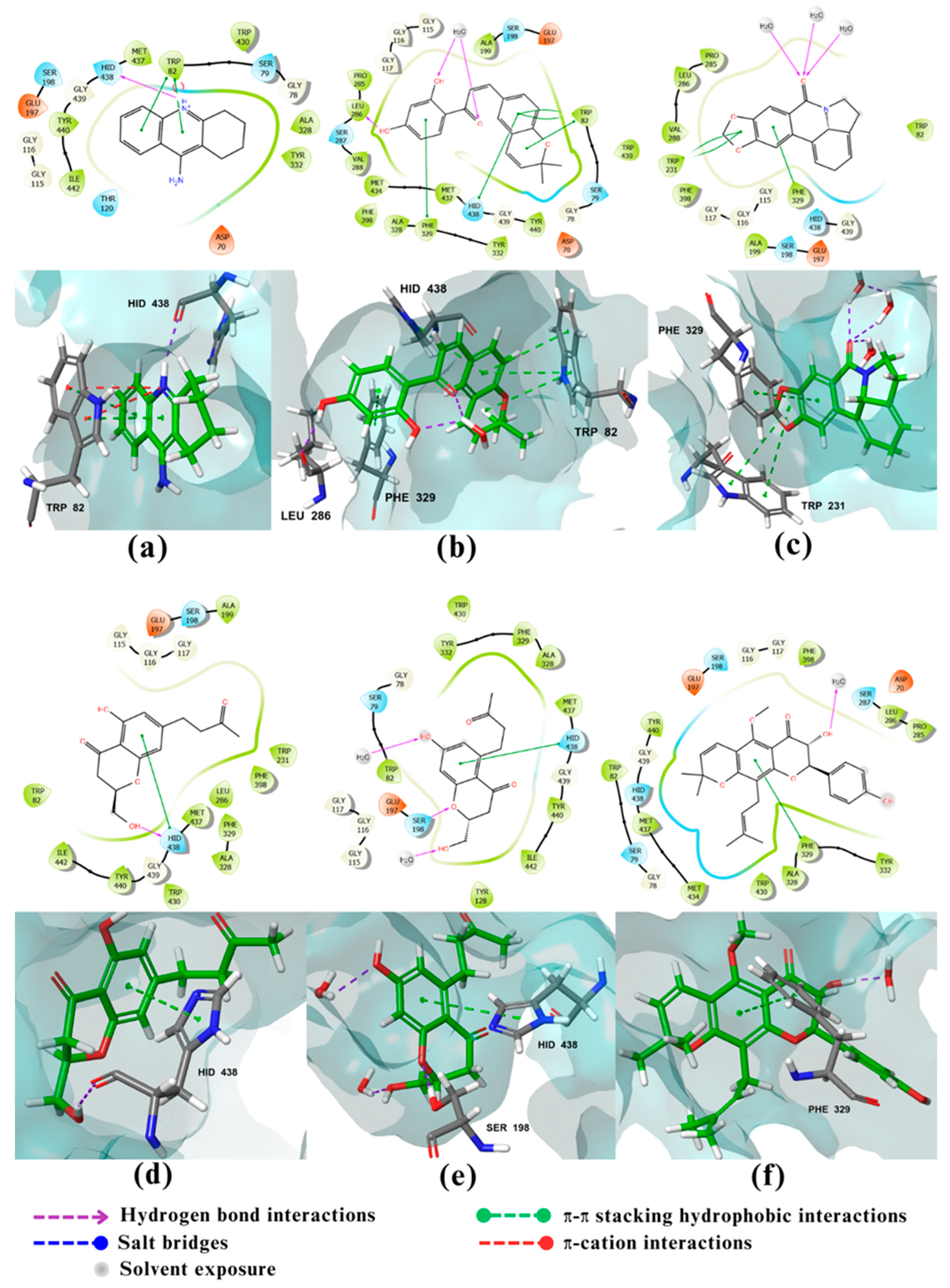
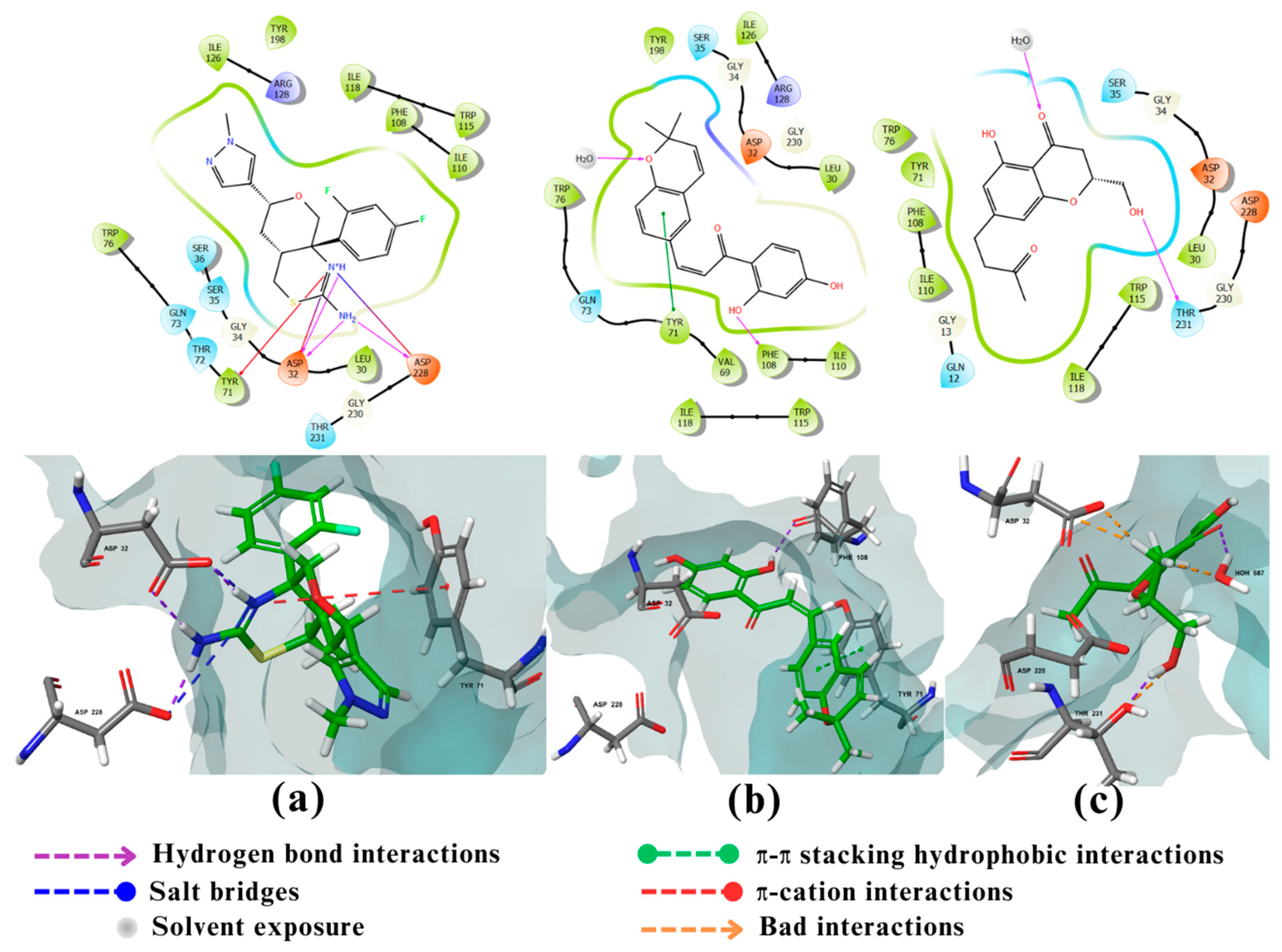
2.2. Molecular docking
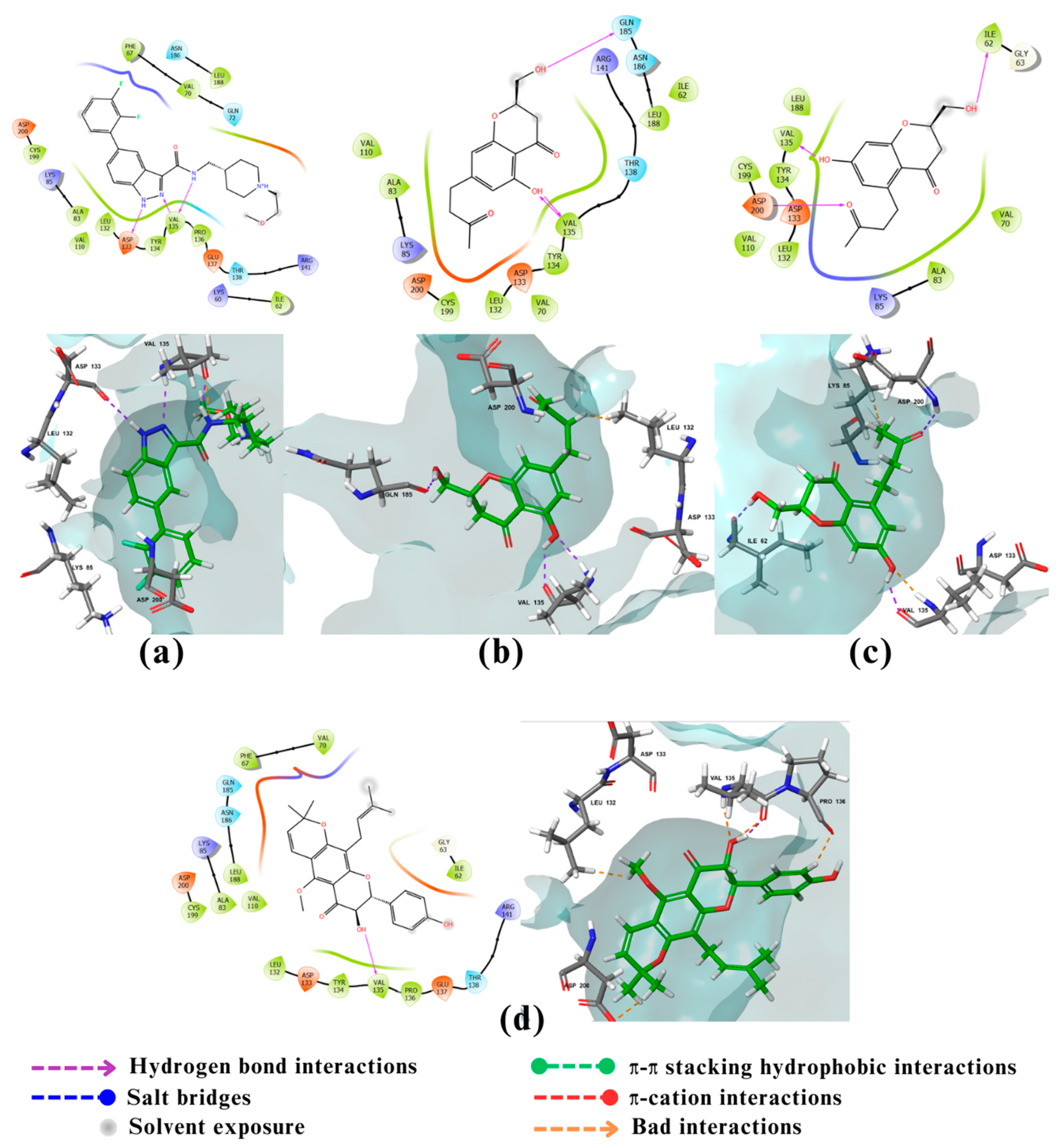
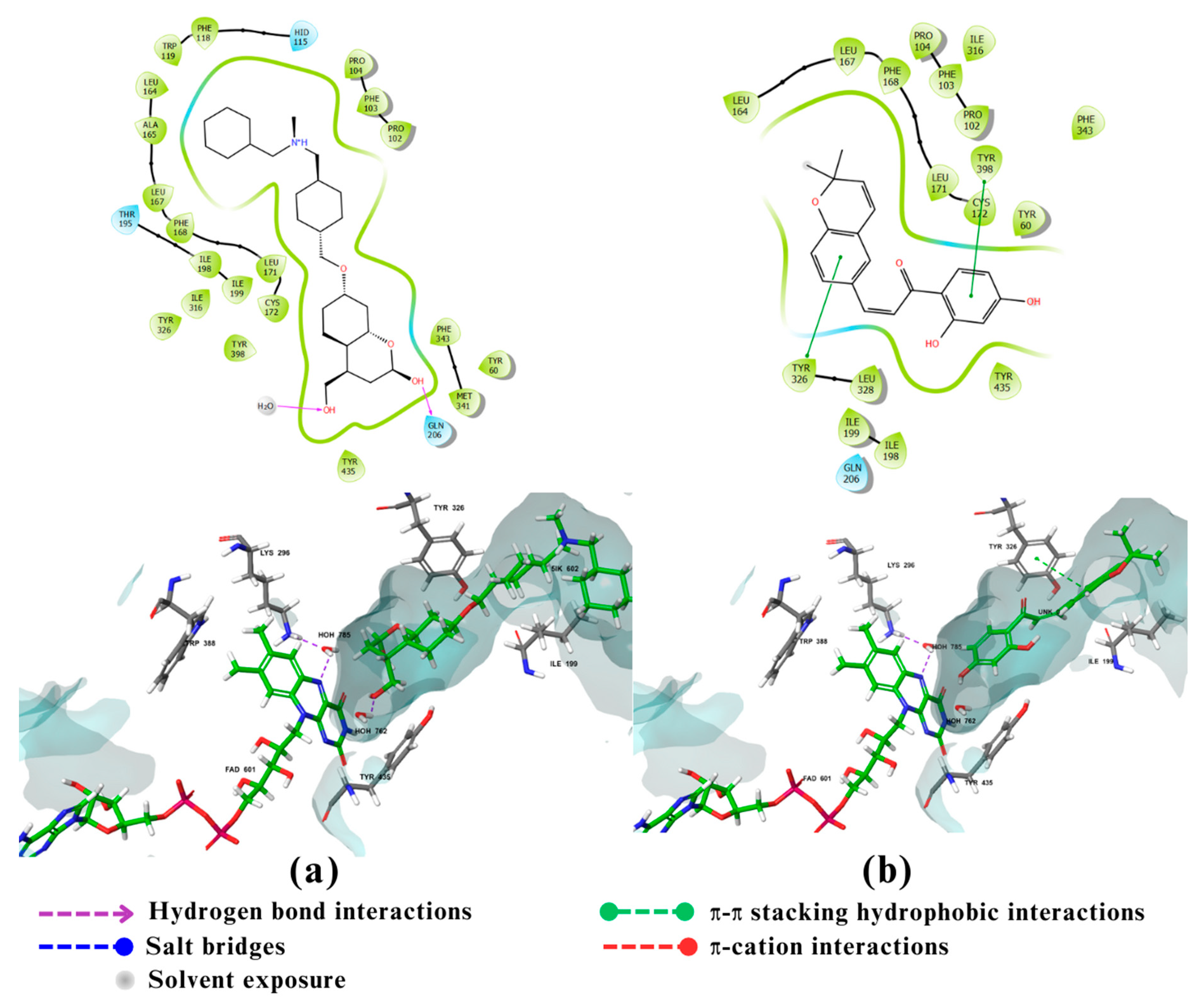
2.3. Visualization and analysis
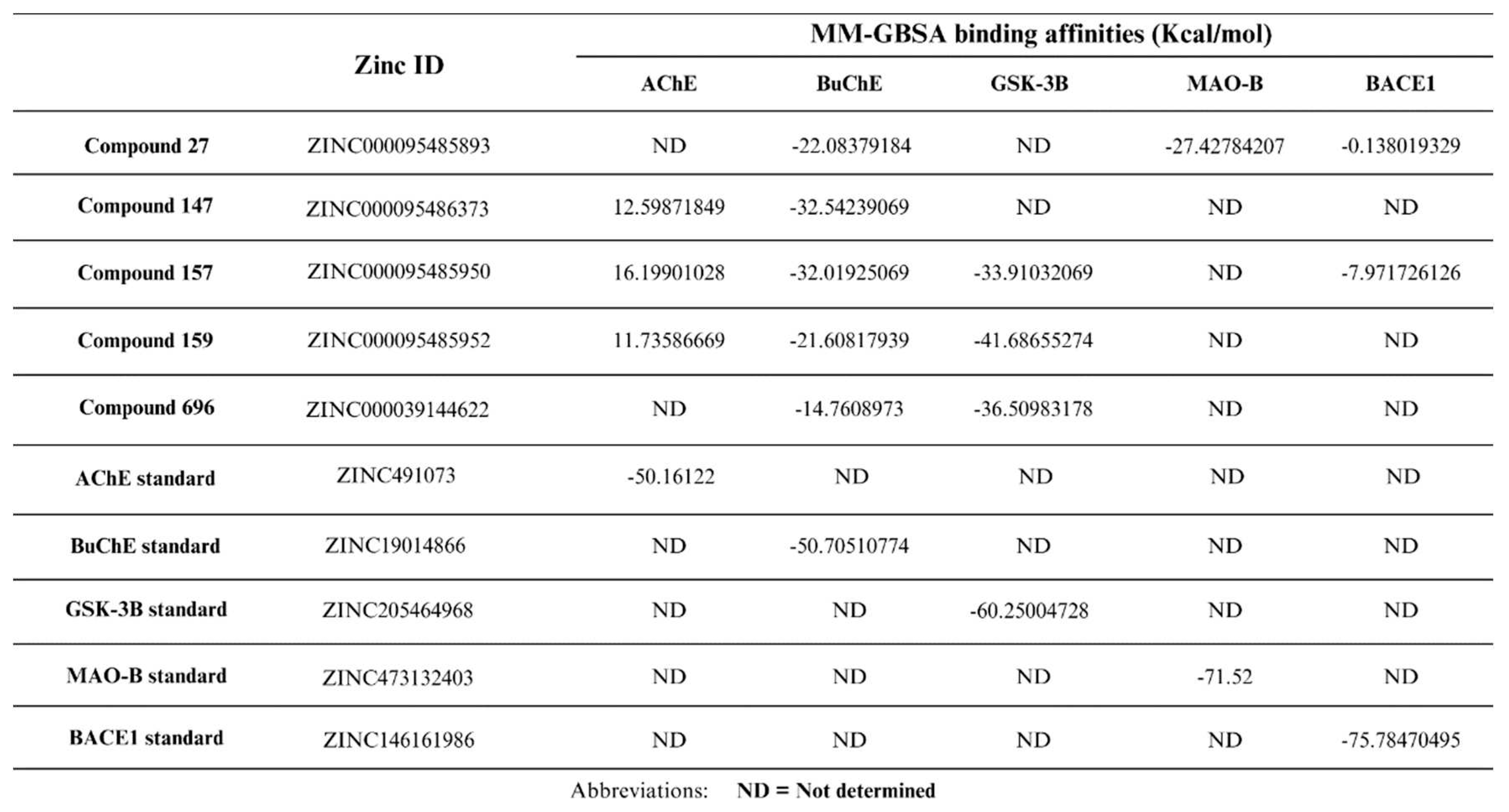
2.4. Free Binding Energy Calculations (MM-GBSA):
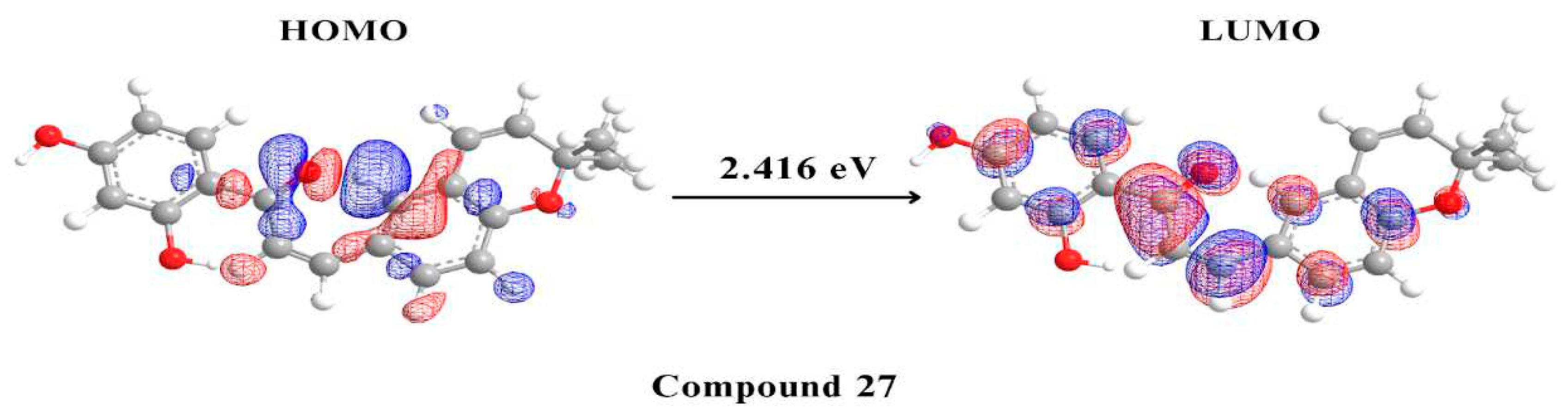
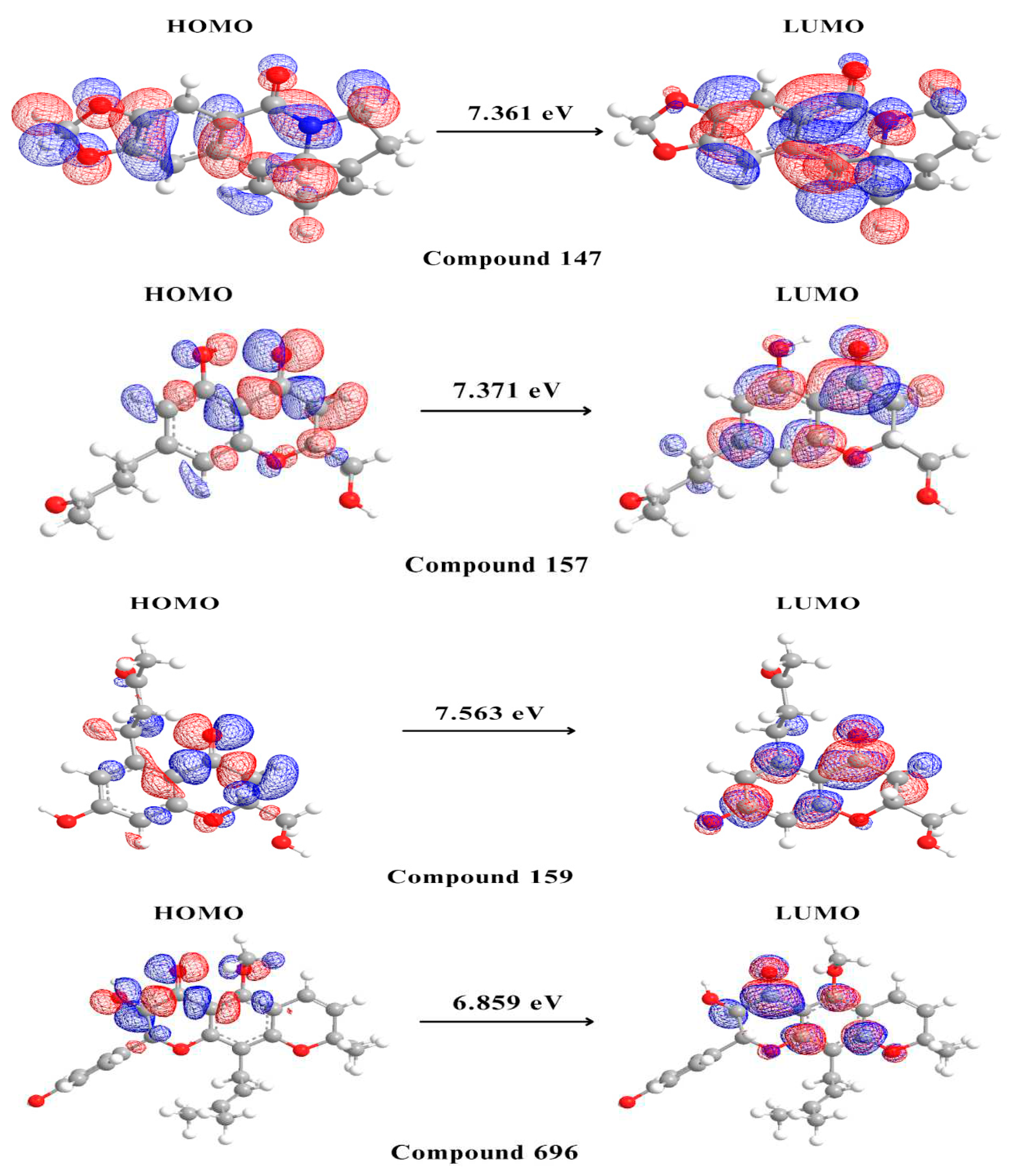
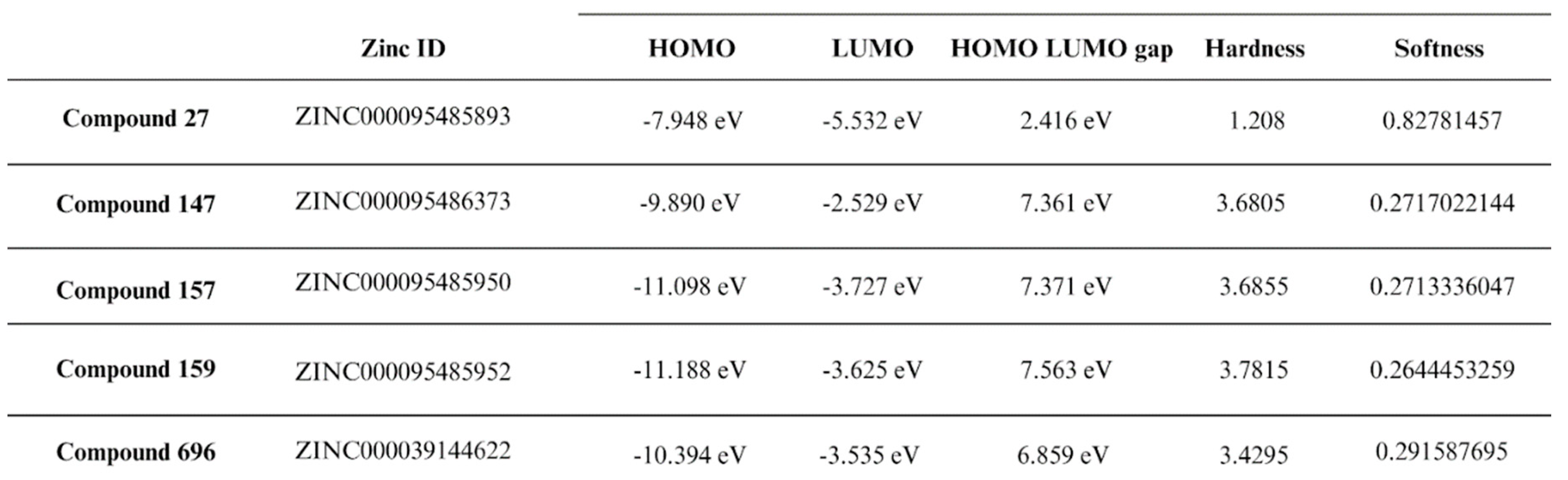
2.5. Density Functional Theory
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data sources
4.2. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity prediction:
4.3. In silico molecular docking
4.3.1. Protein and ligand preparation:
4.3.2. Molecular docking:
4.4. Free Binding Energy Calculations (MM-GBSA) And Density Functional Theory (DFT):
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Sidhu, J.; Goyal, A.; Tsao, J.W. Alzheimer Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- What Are the Signs of Alzheimer’s Disease? Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-are-signs-alzheimers-disease (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Dementia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Alzheimer’s: Facts, Figures & Stats. Available online: https://www.brightfocus.org/alzheimers/article/alzheimers-disease-facts-figures (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-X.; Dai, C.-L.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Multi-Targets: An Unconventional Drug Development Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 837649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-X.; Dai, C.-L.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Multi-Targets: An Unconventional Drug Development Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 837649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa-Pacha, N.M.; Abdin, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Alniss, H.; Al-Tel, T.H. BACE1 Inhibitors: Current Status and Future Directions in Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 339–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, D.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S.; Bumbu, A.G. Role of Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Insight into the Therapeutic Potential of Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Andrisano, V.; Milelli, A. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β: A New Gold Rush in Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Multitarget Drug Discovery? J. Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayas, C.L.; Ávila, J. GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jasiecki, J.; Targońska, M.; Wasąg, B. The Role of Butyrylcholinesterase and Iron in the Regulation of Cholinergic Network and Cognitive Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highly Potent and Selective Aryl-1,2,3-Triazolyl Benzylpiperidine Inhibitors toward Butyrylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 931–943. [CrossRef]
- Sayas, C.L.; Ávila, J. GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.L.; Tiew, J.K.; Fong, Y.H.; Leong, H.W.; Chan, Y.M.; Chan, Z.L.; Kong, E.W.J. Current Pharmacotherapy and Multi-Target Approaches for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 1179573520907397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Ferrucci, L.; Kapogiannis, D. Effects of Monoclonal Antibodies against Amyloid-β on Clinical and Biomarker Outcomes and Adverse Event Risks: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Phase III RCTs in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.L.; Tiew, J.K.; Fong, Y.H.; Leong, H.W.; Chan, Y.M.; Chan, Z.L.; Kong, E.W.J. Current Pharmacotherapy and Multi-Target Approaches for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Popovic-Nikolic, M.R.; Nikolic, K.; Uliassi, E.; Bolognesi, M.L. A Perspective on Multi-Target Drug Discovery and Design for Complex Diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Wang, K.; Dong, J.; Tang, L. Alzheimer’s Disease: Updated Multi-Targets Therapeutics Are in Clinical and in Progress. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabec, R.; Blunden, G.; Cahlíková, L. Natural Alkaloids as Multi-Target Compounds towards Factors Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Popovic-Nikolic, M.R.; Nikolic, K.; Uliassi, E.; Bolognesi, M.L. A Perspective on Multi-Target Drug Discovery and Design for Complex Diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettevi, E.J.; Maina, M.; Simpong, D.L.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Ocloo, A. A Review of African Medicinal Plants and Functional Foods for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Phenotypes, Treatment of HSV-1 Infection And/or Improvement of Gut Microbiota. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tettevi, E.J.; Maina, M.; Simpong, D.L.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Ocloo, A. A Review of African Medicinal Plants and Functional Foods for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Phenotypes, Treatment of HSV-1 Infection And/or Improvement of Gut Microbiota. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tettevi, E.J.; Maina, M.; Simpong, D.L.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Ocloo, A. A Review of African Medicinal Plants and Functional Foods for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Phenotypes, Treatment of HSV-1 Infection And/or Improvement of Gut Microbiota. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tettevi, E.J.; Maina, M.; Simpong, D.L.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Ocloo, A. A Review of African Medicinal Plants and Functional Foods for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Phenotypes, Treatment of HSV-1 Infection And/or Improvement of Gut Microbiota. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tettevi, E.J.; Maina, M.; Simpong, D.L.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Ocloo, A. A Review of African Medicinal Plants and Functional Foods for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Phenotypes, Treatment of HSV-1 Infection And/or Improvement of Gut Microbiota. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ntie-Kang, F.; Zofou, D.; Babiaka, S.B.; Meudom, R.; Scharfe, M.; Lifongo, L.L.; Mbah, J.A.; Mbaze, L.M.; Sippl, W.; Efange, S.M.N. AfroDb: A Select Highly Potent and Diverse Natural Product Library from African Medicinal Plants. PLoS One 2013, 8, e78085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichota, A.; Gwozdzinski, K. Anticancer Activity of Natural Compounds from Plant and Marine Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Website Available online: ADMET. [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Docking and Scoring. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com/science-articles/docking-and-scoring (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
- Silva, L.B.; Ferreira, E.F.B.; Maryam; Espejo-Román, J.M.; Costa, G.V.; Cruz, J.V.; Kimani, N.M.; Costa, J.S.; Bittencourt, J.A.H.M.; Cruz, J.N.; et al. Galantamine Based Novel Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme Inhibitors: A Molecular Modeling Design Approach. Molecules 2023, 28. [CrossRef]
- Mouchlis, V.D.; Melagraki, G.; Zacharia, L.C.; Afantitis, A. Computer-Aided Drug Design of β-Secretase, γ-Secretase and Anti-Tau Inhibitors for the Discovery of Novel Alzheimer’s Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodney, M.A.; Beck, E.M.; Butler, C.R.; Barreiro, G.; Johnson, E.F.; Riddell, D.; Parris, K.; Nolan, C.E.; Fan, Y.; Atchison, K.; et al. Utilizing Structures of CYP2D6 and BACE1 Complexes to Reduce Risk of Drug-Drug Interactions with a Novel Series of Centrally Efficacious BACE1 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3223–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, F.J.R.; Alexander, R.; Cleiren, E.; De Groot, A.; Carpentier, M.; Dijkmans, J.; Fierens, K.; Masure, S.; Moechars, D.; Palomino-Schätzlein, M.; et al. Fragment Binding to β-Secretase 1 without Catalytic Aspartate Interactions Identified via Orthogonal Screening Approaches. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, R.; Cheng, X.; Chen, S.-P.; Zhou, L.-H. Exploring the Binding of BACE-1 Inhibitors Using Comparative Binding Energy Analysis (COMBINE). BMC Struct. Biol. 2012, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, Q.M.S.; Alharbi, A.H. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Studies of Cigarette Smoke Carcinogens Interacting with Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzymes of the Central Nervous System. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 61972–61992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, Q.M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Alharbi, A.H.; Ahmad, V.; Yadav, B.S. Identification of Natural Compounds of the Apple as Inhibitors against Cholinesterase for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation and ADMET Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Z.Y.; Mathew, S.; Yeong, K.Y. Butyrylcholinesterase: A Multifaceted Pharmacological Target and Tool. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.-Y. Crystal Structures of Human Cholinesterases in Complex with Huprine W and Tacrine: Elements of Specificity for Anti-Alzheimer’s Drugs Targeting Acetyl- and Butyryl-Cholinesterase. Biochem. J 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, T.; Schmidt, B.; Lo Monte, F. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of GSK-3: Structural Insights and Their Application to Alzheimer’s Disease Models. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; DeGrado, T.R. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3)-Targeted Therapy and Imaging. Theranostics 2016, 6, 571–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, S.; Babu, V.S.; Kannoji, A.; Hariharan, R.; Balaji, V.N. GSK3beta: Role in Therapeutic Landscape and Development of Modulators. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Liu, G.J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Mu, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y. [Total residue analysis of Amitraz in the rabbit tissue by gas chromatography]. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 1988, 19, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, K.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jin, J. Integrating Machine Learning-Based Virtual Screening with Multiple Protein Structures and Bio-Assay Evaluation for Discovery of Novel GSK3β Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 566058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippin, I.; Khazanov, N.; Ben Joseph, S.; Kudinov, T.; Berent, E.; Arciniegas Ruiz, S.M.; Marciano, D.; Levy, L.; Gruzman, A.; Senderowitz, H.; et al. Discovery and Design of Novel Small Molecule GSK-3 Inhibitors Targeting the Substrate Binding Site. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, B.; Tripathi, S.K.; Veronesi, M.; Russo, D.; Penna, I.; Giabbai, B.; Bandiera, T.; Storici, P.; Girotto, S.; Cavalli, A. Identification of Novel GSK-3β Hits Using Competitive Biophysical Assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, Q.; Jin, Q.; Ke, K.; Hu, M.; Chen, X. Designing of Dual Inhibitors for GSK-3 β and CDK5: Virtual Screening and in Vitro Biological Activities Study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18118–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finberg, J.P.M.; Rabey, J.M. Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B in Psychiatry and Neurology. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 209773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geha, R.M.; Chen, K.; Wouters, J.; Ooms, F.; Shih, J.C. Analysis of Conserved Active Site Residues in Monoamine Oxidase A and B and Their Three-Dimensional Molecular Modeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, F.; Gottinger, A.; Forsgren, N.; Catto, M.; Iacovino, L.G.; Pisani, L.; Binda, C. Dual Reversible Coumarin Inhibitors Mutually Bound to Monoamine Oxidase B and Acetylcholinesterase Crystal Structures. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Teicoplanin: A Mechanistic Insight by Docking, MM/GBSA and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1246, 131124. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Lateef, H.M.A.; Khalaf, M.M.; Shehata, M.R.; Abu-Dief, A.M. Fabrication, DFT Calculation, and Molecular Docking of Two Fe(III) Imine Chelates as Anti-COVID-19 and Pharmaceutical Drug Candidate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, K.M.; Maowa, J.; Alam, A.; Dey, S.; Hosen, A.; Hasan, I.; Fujii, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Kawsar, S.M.A. In Silico DFT Study, Molecular Docking, and ADMET Predictions of Cytidine Analogs with Antimicrobial and Anticancer Properties. In Silico Pharmacology 2021, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adejumo, T.T.; Tzouras, N.V.; Zorba, L.P.; Radanović, D.; Pevec, A.; Grubišić, S.; Mitić, D.; Anđelković, K.K.; Vougioukalakis, G.C.; Čobeljić, B.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, Catalytic Activity, and DFT Calculations of Zn(II) Hydrazone Complexes. Molecules 2020, 25, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chromone Derivatives Bearing Pyridinium Moiety as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands against Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 110, 104750. [CrossRef]
- [Schrödinger Release 2023-3: Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2023.].
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





