1. Introduction
Bacillus cereus are opportunistic Gram-positive spore-forming bacteria [
1]. One of the key factors of bacterial pathogenicity is hemolytic toxin II (hemolysin II, HlyII), which belongs to the group of β-pore-forming toxins [
2]. This toxin is secreted by bacteria in the form of water-soluble monomers and oligomerizes in the presence of the plasma membrane of the target cell to form transmembrane pores leading to the disruption of osmotic pressure inside the cell and ultimately to its destruction, providing bacteria with access to nutrients [
3,
4]. HlyII of
B. cereus is capable of lysing erythrocytes [
3] and other eukaryotic cells [
5,
6,
7,
8]. It differs from other β-pore-forming toxins by the presence of a C-terminal extension of 94 amino acid residues, the C-terminal domain of HlyII (HlyIICTD) [
9]. Elimination of the C-terminal domain reduces the hemolytic activity towards rabbit erythrocytes eightfold [
3]. HlyIICTD has been shown to have an independent ability to bind oriented target-cell membranes [
10]. In the presence of cell and artificial membranes, it is capable of oligomerizing and forming ion channels. At a prolonged exposure to HlyIICTD, it lyses monocytes, macrophages, and T cells [
11].
The structure of HlyIICTD determined by NMR is a fold, a pseudo-barrel consisting of two α-helices surrounded by five β-sheets [
12]. Studying the role of HlyII individual domains can bring us closer to understanding the water-soluble state of the toxin, the stages of its secretion from bacterial cells into the external environment, as well as the pore formation stages. It has been previously assumed that the wild-type HlyIICTD domain exists in two states due to
cis/trans-isomerization of proline at position 405 of the full-length HlyII toxin [
13], which can lead to a doubling of resonance signals. The NMR study of HlyIICTD structure has demonstrated the uniqueness of this domain. No molecules of a similar spatial structure have been found to date [
12,
13]. Presumably, HlyIICTD forms a separate domain and is close to the core part of the full-length molecule [
12]. Due to a problem that arises in this case, the NMR analysis is performed on the mutant form, where the proline residue is replaced by methionine. This mutant form exists only in the
trans state and provides modeling of this domain in the context of the full-length HlyII protein [
12,
14].
Previously, in [
15] we have described the HlyIIC-20 monoclonal antibody capable of strain-specific suppression of hemolysis caused by
B. cereus HlyII. It has been shown that the ability of the antibody to suppress hemolysis depends on the presence of Leu or Pro at position 324 in the full-length toxin molecule. This work, using the site-directed mutagenesis, which leads to the replacement of amino acid residues located on the surface of the spatial structure of HlyIICTD (6d5z), determined the amino acid residues included in the HlyIIC-20 epitope.
2. Results
2.1. Monoclonal Antibodies HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 Recognize Non-Overlapping Regions on the Surface of the Spatial Structure of HlyIICTD
Proline amino acid residues in a protein can significantly change its conformational state. Proline-dependent conformational rearrangements of the 3D protein structure can lead to changes in the accessibility of epitopes. In this regard, it can be assumed that the proline residue is not necessarily included in the composition of the epitope. The use of site-directed mutagenesis enables determining in detail the location of epitopes on the surface of the HlyII C-terminal domain.
The interaction of mutant forms with HlyIIC-20 was studied using as a control the antibody HlyIIC-40, a representative of a panel of monoclonal antibodies, the production of which is described in [
10]. Antibodies HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 interacted both with HlyIICTD and full-length toxin in EIA and immunoblotting. They were chosen because their K
aff values characterizing their interaction with HlyIICTD proved to be close [
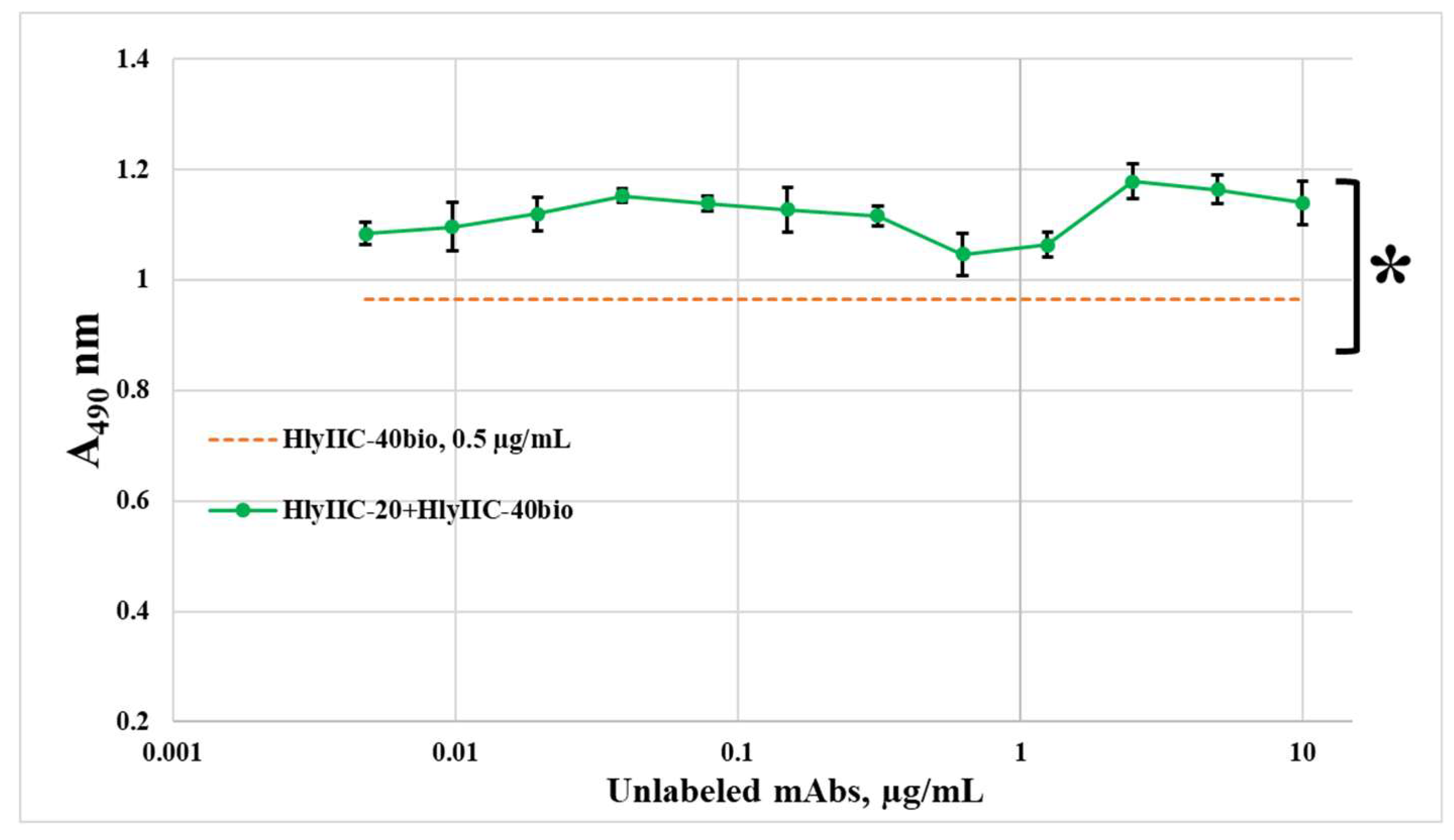
15]. At the same time, they did not compete with each other for binding to immobilized HlyIICTD during competitive EIA (see
Figure 1). Therefore, these antibodies recognize non-overlapping regions on the surface of the HlyIICTD 3D structure.
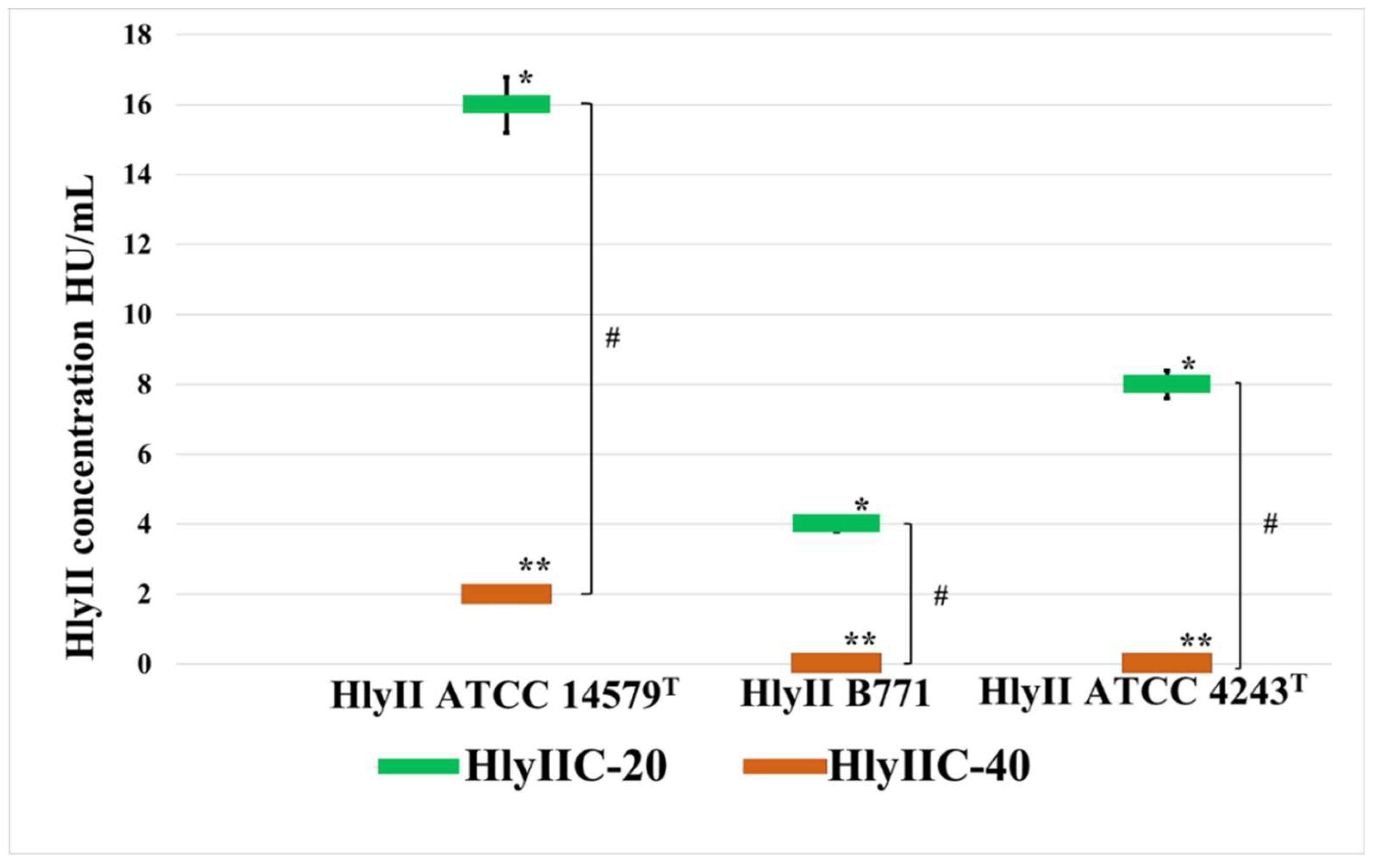
As shown in
Figure 2, HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 had different effects on the efficiency of hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes caused by hemolysins of strains ATCC 14579
T, B771, ATCC 4342
T. Unlike HlyIIC-20, the monoclonal antibody HlyIIC-40 suppressed the hemolysis of HlyII of ATCC 14579
T only partially and did not suppress the hemolysis caused by hemolysins of B. cereus strains B771, ATCC 4342
T. These results also confirm that HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 interact with different epitopes on the surface of the HlyIICTD 3D structure.
2.2. Efficiency of HlyIIC-20 Binding to Full-Length Hemolysins of B. cereus Strains ATCC 14579T, B771, ATCC 4342T
The work [
15] has demonstrated the influence of HlyIIC-20 on the hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes caused by HlyII of B. cereus strains ATCC 14579
T, B771 and ATCC 4342
T, as well as by the mutant forms L324P (ATCC 14579
T) and P324L (B771).
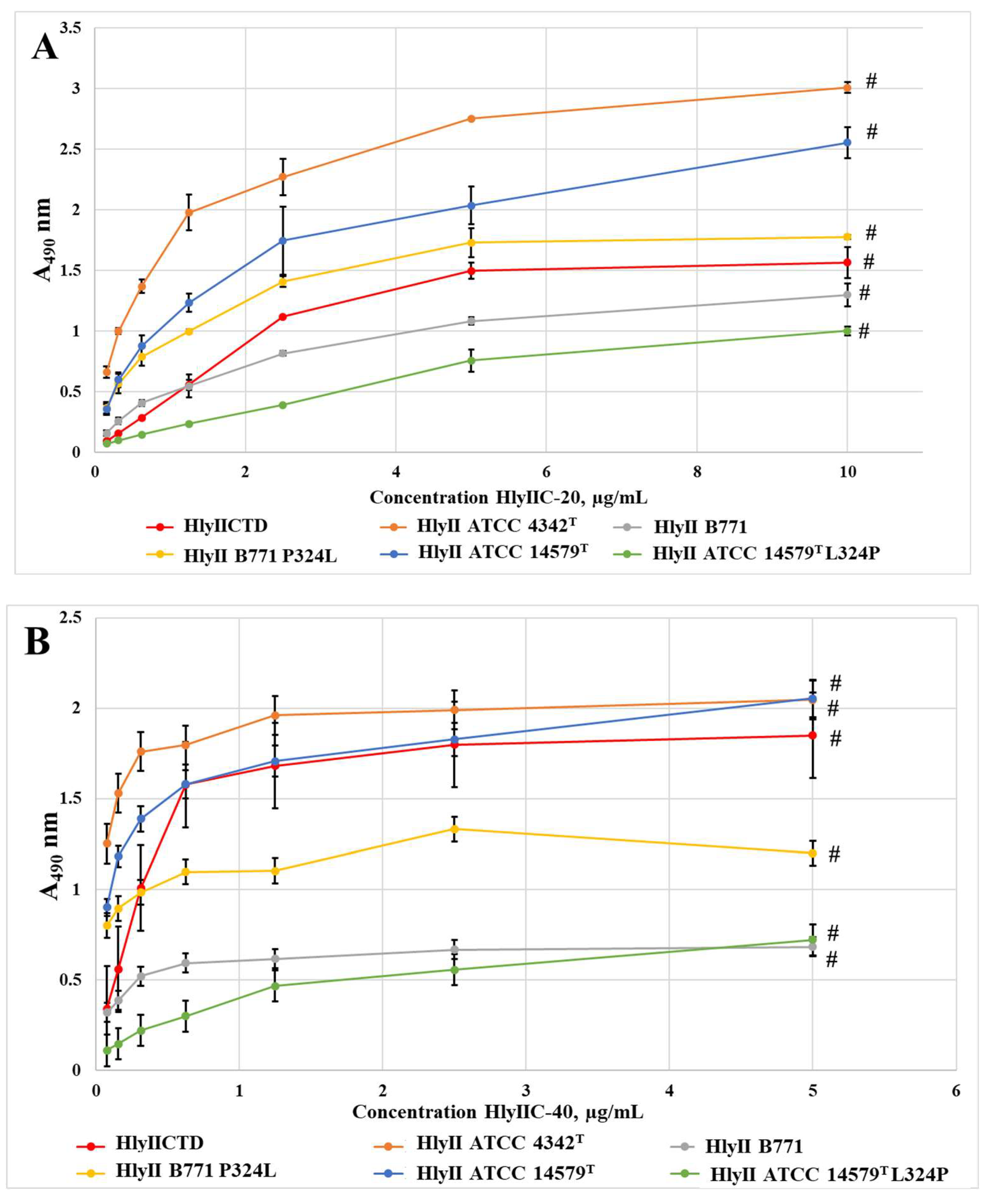
Figure 3 shows the interaction of HlyIIC-20 with the same forms of toxins in EIA. The substitution L324P in the hemolysin of strain ATCC 14579
T led to a marked decrease in the efficiency of antibody binding, which correlated with the data on the suppression of erythrocyte hemolysis. Hemolysis caused by HlyII of B. cereus strain ATCC 14579
T was suppressed by antibodies HlyIIC-20 the most effectively. In contrast, the substitution P324L in the hemolysin of B. cereus strain B771 led to an improvement in the interaction with antibodies, which is also consistent with the data on hemolysis suppression. These data suggest that a mutation at position 324 alters the affinity of the interaction of HlyIIC-20 with HlyII.
In this case, however, HlyIIC-20 interacted most effectively with the toxin of B. cereus strain ATCC 4342T, but the hemolysis suppression by the antibody was for this strain lower than for strain ATCC 14579T. Strain ATCC 4342T features the presence of Leu at position 324.
The control antibody HlyIIC-40 showed the same trends in interaction with full-length toxins and their mutant forms. The principal difference was in the interaction with the full-sized HlyII of ATCC 4342T. The availability of the epitope for HlyIIC-40 did not practically differ both for free HlyIICTD and in the full-length toxin. Possibly, the accessibility of the epitope is also affected by differences in the amino acid sequences of the C-terminal domains of the hemolysins in these strains.
2.3. Determination of HlyIIC-20 Epitope
To clarify the epitope location for HlyIIC-20 on the surface of HlyIICTD according to the 3D structure determined by NMR [
12], and taking into account the results of phage display, we chose amino acid residues that could be part of the epitope [
15]. Mutant forms of HlyIICTD were designed and the binding of HlyIIC-20 to mutant proteins was studied by EIA. Not only single but also multiple substitutions were created (two, three or four amino acid residues were simultaneously substituted), because a single substitution may slightly affect the interaction with the antibody.
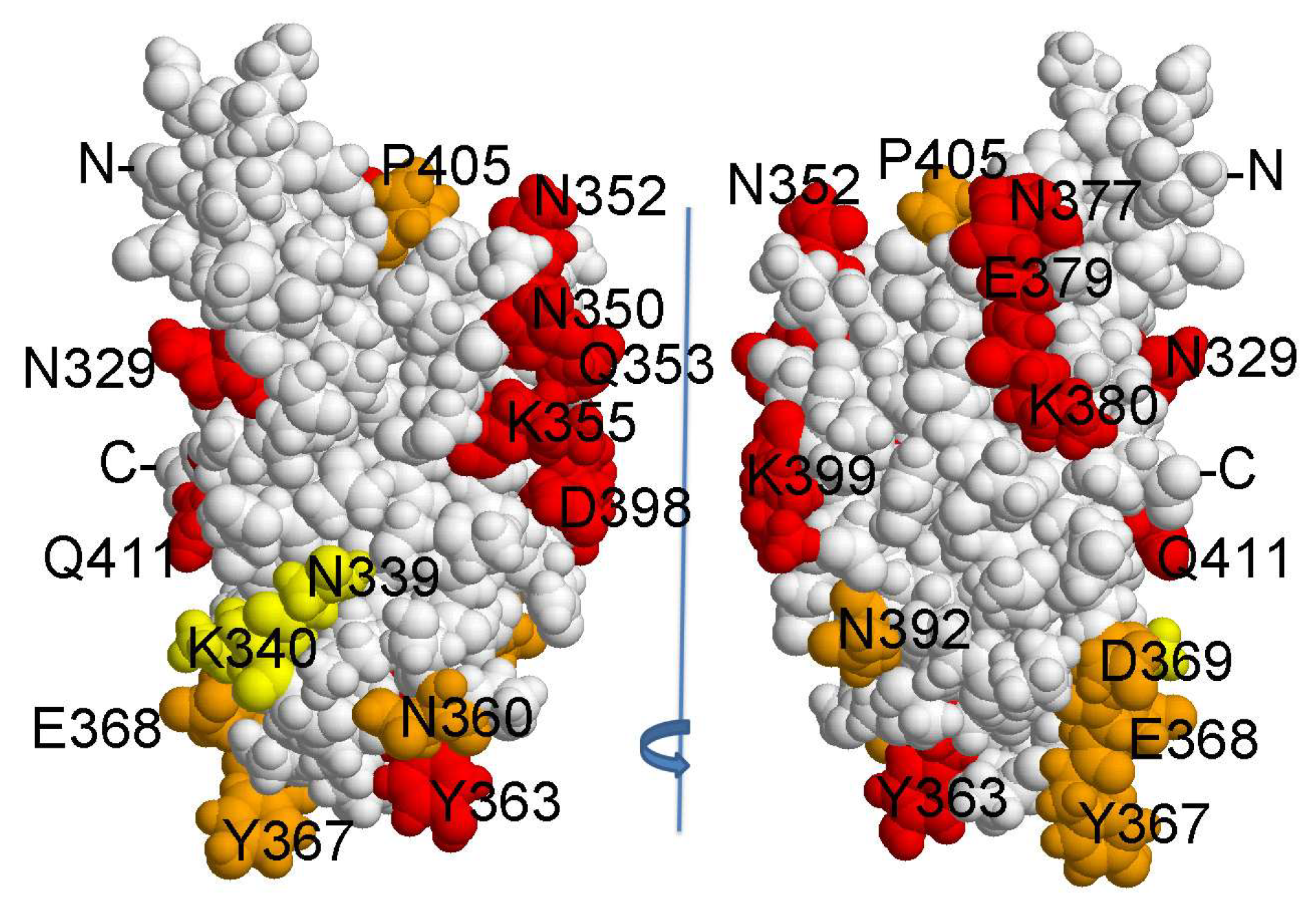
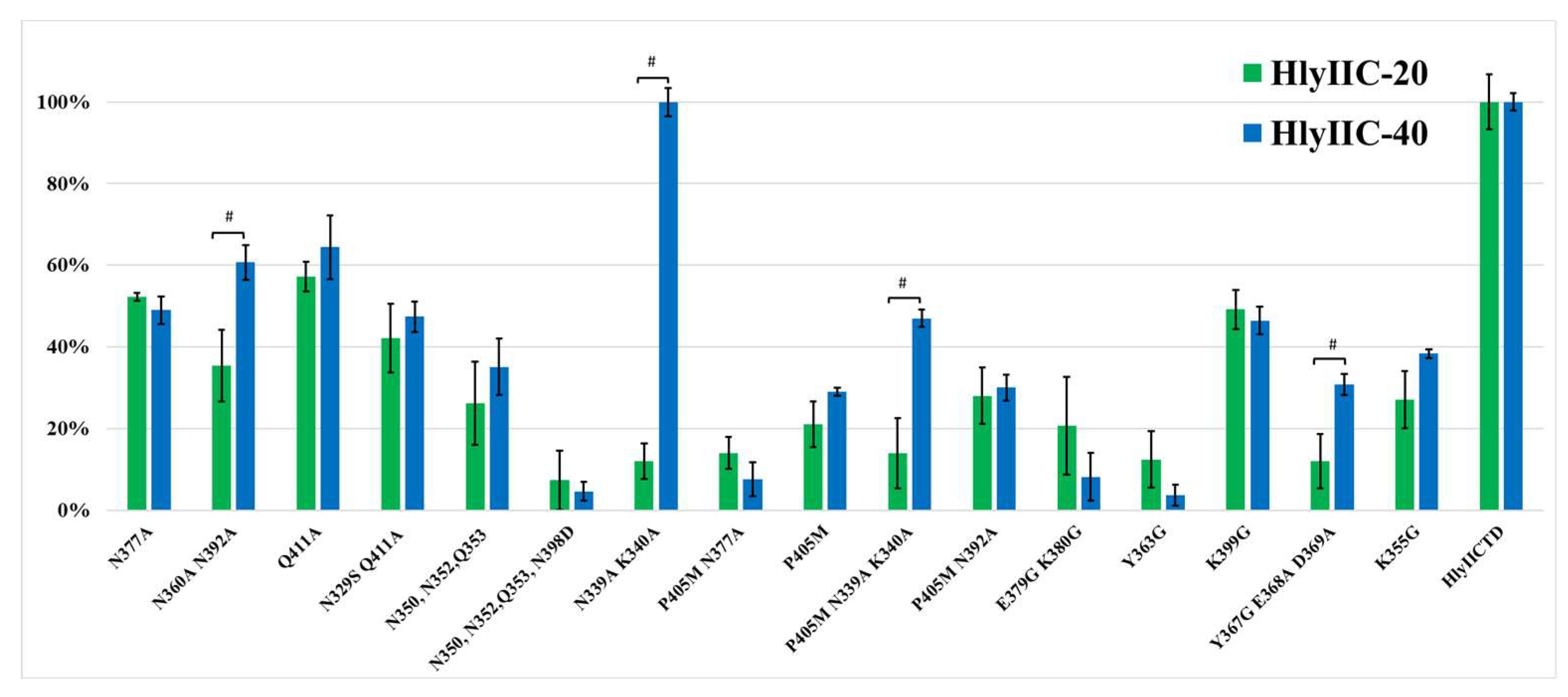
Figure 4 shows the 3D structure of HlyIICTD and the position of the substituted amino acids on its surface. It was logical to assume that the substitution of amino acid residues included in the epitope recognized by HlyIIC-20 would affect its interaction with the mutant form, and, in turn, the substitution of amino acid residues not included in the epitope should not affect this interaction. However, all engineered substitutions of amino acid residues on the surface of HlyIICTD reduced the level of this interaction with varying degrees of efficiency. Each of the mutations localized in the investigated area of the surface led to a decrease in the binding of the mutant form to the HlyIIC-20 antibody (
Figure 5). Such an effect of mutations on the binding of mutant forms to an antibody is possible under the assumption that amino acid substitutions affect the 3D structure of HlyIICTD, i.e., change the conformation of this protein. When HlyIICTD passes to another isoform, the mutual arrangement of amino acids on its surface changes, and the epitope is partially or completely “disrupted”, which leads to a decrease in the binding of the HlyIIC-20 to HlyIICTD.
This assumption was confirmed by a similar effect of amino acid substitutions on the interaction of HlyIIC-40 with HlyIICTD.
Figure 5 shows the results of HlyIIC-40 binding to HlyIICTD in comparison with those for HlyIIC-20. Most amino acid substitutions designed affected the affinity of HlyIIC-40 for the mutant forms in the same way as HlyIIC-20. Herewith, some amino acid substitutions had a more significant effect on the level of antibody binding to HlyIICTD. For example, addition of mutation N398D to a mutant containing the substitutions N350A, N352A, or Q353A resulted in a significant reduction of the interaction.
HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 do not compete for binding sites with HlyIICTD. The identical effects of the same amino acid substitutions on the binding of completely different mAbs can only be explained by structural rearrangements of HlyIICTD, which in turn affect the “structure” or accessibility of epitopes on the surface of the protein globule. At the same time, the double substitution for N339A, K340A did not affect the binding of HlyIIC-40 at all, but noticeably inhibited the binding to HlyIIC-20. A similar result was obtained for these mutations with the P405M substitution. These data suggest that the N339A, K340A substitution does not lead to the transition of HlyIICTD to another isoform, but affects the epitope for HlyIIC-20. Thus, the results of the comparative analysis indicate that the HlyIIC-20 epitope includes amino acid residues N339A, K340A.
Some amino acid substitutions show more effective suppression of HlyIIC-20 recognition than HlyIIC-40. These amino acid substitutions marked in
Figure 4 as double N360A, N392A and triple Y367G, E368A, D369A affect the recognition efficiency of HlyIIC-20 to a greater extent than the recognition efficiency of HlyIIC-40. Possibly, some of these amino acid residues and, even less likely, all of these amino acids are part of the HlyIIC-20 epitope.
The results obtained using site-directed mutagenesis confirm that the HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 epitopes are located in non-overlapping regions of the HlyIICTD protein globule.
3. Discussion
The presence of a proline residue in the polypeptide chain causes its bending; therefore, the presence or absence of this amino acid residue significantly changes the spatial structure of the protein, which in turn affects the accessibility or change of conformational epitopes. Substitutions of proline residues at positions 324 and 405 resulted in significant changes in the affinity of antibodies HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40 for the C-terminal domain (
Figure 3,
Figure 5). Herewith, almost every amino acid substitution, not only Pro, in the protein sequence led to a change in the accessibility of epitopes recognized by HlyIIC-20 and HlyIIC-40, despite the fact that the introduced mutations were localized both in close and remote areas from each other on the surface of the protein globule. These results indicate the high lability of the HlyIICTD 3D structure.
It has been shown that pre-treatment of HlyII with HlyIIC-20 prevents hemolysis by inhibiting the oligomerization stage [
15]. The data obtained enable an assumption of in which manner HlyIIC-20, unlike other antibodies, prevents hemolysis caused by HlyII of ATCC 14579
T. We hypothesize that HlyIIC-20 stabilizes the structure of HlyIICTD, decreasing its lability and, thereby, preventing its transition into different isoforms. The lability of HlyIICTD, in turn, affects the assembly of the pore-forming oligomer HlyII, as the result of which hemolysis is prevented [
15].
The stabilizing effect of HlyIIC-20 on HlyIICTD is confirmed by the data in
Figure 1, which shows that the interaction of immobilized HlyIICTD with HlyIIC-20 leads to a statistically significant and reliable increase in the degree of binding (up to 18%) of HlyIIC-40 with HlyIICTD. Apparently, upon binding of HlyIIC-20 to HlyIICTD, the 3D structure of HlyIICTD is stabilized, which can lead to an increase in the efficiency of binding of HlyIIC-40 to HlyIICTD. The interaction of a full-size toxin with the membranes of a target cell proceeds through the stage of the oligomerization of monomers followed by the formation of a prepore and then of a mature pore capable of passing ions and other low-molecular substances, which leads to cell death. Each of these stages is accompanied by conformational rearrangements [
11]. Thus, the lability of the 3D structure of HlyIICTD corresponds to the general concept of pore formation in the presence of the target cell membrane.
Identification of epitopes is important in the development of highly specific and harmless vaccines, therapeutic and diagnostic antibodies, since namely epitopes allow the immune system to recognize and respond to specific pathogens [
16]. Therefore, it is especially important to determine the epitope of an antibody capable of neutralizing one of the significant pathogenic factors of
B. cereus in order to design a mimetic, based on which the protection against the action of HlyII of various
B. cereus strains can be created.
HlyII of
B. cereus is a member of the family of β-barrel pore-forming toxins, the closest of which by amino acid composition is the well-studied α-hemolysin of
Staphylococcus aureus [
17,
18]. In this regard, the
S. aureus α-hemolysin model is used to analyze the putative 3D structure of the full-length HlyII of
B. cereus. The structure of toxins of this group is characterized by the presence of a large number of β-sheets and is formed predominantly by amino acid residues from different parts of the polypeptide chain linked together. That is to say, epitopes on the surface of a molecule are most likely conformational, representing a 3D structure formed as a result of protein folding.
The conformational epitope of HlyIIC-20 includes amino acid residues N339A, K340A located one after the other. Substitution of extra-epitope amino acid residues has been shown to alter the accessibility of conformational epitopes of the C-terminal domain of B. cereus HlyII. In our opinion, one of the most interesting results of this work is that it shows the lability of the spatial structure of HlyIICTD. This result explains the difficulties that arise when searching for antibodies that inhibit the functioning of mobile proteins, in particular toxins, the structure of which changes greatly during their functioning.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids and Enzymes
Restriction endonucleases KpnI and NdeI (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA USA), T4-DNA ligase (NEB, USA), protein markers and DNA electrophoresis markers (Thermo Scientific, Lithuania), TaqSE-DNA polymerase (SibEnzyme, Russia), dNTP mix (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA USA) were used. The PCR product was cloned using the pET29b (+)vector at NdeI and KpnI.
4.2. Molecular Cloning and Site-Directed Mutagenesis
The pET29-containing
hlyIIctd sequence was used as a template for the subsequent mutagenesis experiments [
10]. The
hlyIIctd mutants were generated using the overlap extension PCR [
19]. The
hlyIIctd fragments were amplified using the overlap primers shown in
Table 1. For all mutants, the overlapping region of the primers contained the mutation of interest. All plasmids had been previously verified by sequencing before transformation into the expression strain BL21(DE3).
4.3. Expression and Purification of HlyIICTD His6 and Its Mutant Forms
Expression and purification of HlyIICTD His6 and its mutant forms was carried out as described in [
10].
4.4. Enzyme Immunosorbent Assay
HlyIICTD, its mutant forms, HlyII and its mutant forms were adsorbed on the surface of wells of EIA immune plates (Sovtech, М-011, Russia) from a 1 µg/mL-1 (50 µL) overnight at 4°C. The free binding sites of plastic were blocked with PBST (PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20) for 30 min. Then, the antibody solution in PBST was introduced into plate wells. Incubation with antigen was carried out for 1 h at 37°C. Then, the plates were washed with PBST no less than 6 times, and the conjugate of antibodies against mouse immunoglobulins was added (Thermo Scientific 31432, USA, Goat anti-Mouse IgG [H+L] HRP conjugate) in PBST, diluted as indicated by the manufacturer and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. A 4-mM solution of ortho-phenylenediamine peroxidase substrate in a citrate–phosphate buffer (26 mM citric acid, 50 mM Na2HPO4, pH 5.0) containing 0.003% (v/v) Н2O2 was used for detection. After the development of the color, the reaction was stopped by adding an equal volume of 10% (v/v) sulfuric acid, and optical absorption was measured at 490 nm using an iMark microplate reader (Bio-Rad, USA).
In the case of the inhibition of the interaction of biotinylated HlyIIC-40 with immobilized HlyIICTD by unlabeled HlyIIC-20, solutions of biotin-labeled and -unlabeled antibodies were simultaneously introduced into the wells of EIA immune plates in PBST. The wells were pretreated sequentially with HlyIICTD and PBST. The reaction was carried out as described in the previous paragraph. Biotinylated antibodies bound to HlyIICTD were detected using horseradish peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (Thermo Scientific, 21126, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.5. Conjugation of Antibodies with Biotin
A solution of antibodies (1 µg/mL-1) in 0.1 M bicarbonate buffer (pH 9.0) was supplemented with biotin N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (Sigma-Aldrich, H1759, USA) in dimethylsulfoxide (Sigma-Aldrich, 471267, USA) (1 µg/mL-1) at a molar ratio of 1:20. After incubation for 4 h at room temperature, the solution was dialyzed against PBS.
4.6. Measurement of Hemolytic Activity of Hemolysin II in the Presence of mAbs
In a 96-well microplate, a series of 2-fold decreasing dilutions of hemolysin II (from 32 HU/ml) were incubated with an equal volume of monoclonal antibodies at a constant concentration of 0.5 μM for 15 minutes at 37°C. An equal volume of 1% rabbit erythrocyte suspension was added to the mixtures (HlyII + mAbs). The mixtures was incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. The hemolytic activity was measured as described in [
5].
Author Contributions
N.R., A.N., B.M. and A.S.S., designed the research and wrote the paper; N.R., A.N., A.K., O.V., A.Z., Z.A.-K., A.S.V. and M.S., performed the research; F.B., data curation.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 22-74-10026).
Conflicts of Interest
We declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Logan, N.A. Bacillus and relatives in foodborne illness. J Appl Microbiol. 2012, 3, 417–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramarao, N.; Sanchis, V. The pore-forming haemolysins of Bacillus cereus: a review. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 6, 1119–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, G.; Bayley, H.; Cheley, S. Properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II: a heptameric transmembrane pore. Protein Sci. 2002, 7, 1813–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, Z.I.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Fomkina, M.G.; Ternovsky, V.I.; Suzina, N.E.; Bakulina, A.Y.; Solonin, A.S.; Sineva, E.V. The properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II pores depend on environmental conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007, 2, 253–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, Z.I.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Yurkov, I.S.; Budarina, Z.I.; Sineva, E.V.; Solonin, A.S. Purification and cytotoxic properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II. Protein Expr Purif. 2006, 1, 186–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholodkov, O.A.; Budarina, Zh.; Kovalevskaya, J.I.; Siunov, A.V.; Solonin, A. A. Effect of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II on hepatocyte cells. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2015, 2, 258–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataev, A.A.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Z.I.; Solonin, A.S.; Ternovsky, V.I. Bacillus cereus can attack the cell membranes of the alga Chara corallina by means of HlyII. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 5, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplova, V.V.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Z.I.; Sineva, E.V.; Solonin, A.S. Quick assessment of cytotoxins effect on Daphnia magna using in vivo fluorescence microscopy. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2010, 6, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baida, G.; Budarina, Z.I.; Kuzmin, N.P.; Solonin, A.S. Complete nucleotide sequence and molecular characterization of hemolysin II gene from Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, N.V.; Karatovskaya, A.P.; Zamyatina, A.V.; Siunov, A.V.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Z.I.; Nagel, A.S.; Brovko, F.A.; Solonin, A.S. C-terminal domain of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II is able to interact with erythrocytes. Russ J Bioorg Chem. 2020, 46, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, N.; Siunov, A.; Zamyatina, A.; Melnik, B.; Nagel, A.; Karatovskaya, A.; Borisova, M.; Shepelyakovskaya, A.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Zh.; Kolesnikov, A.; Surin, A.; Brovko, F.; Solonin, A. The C-terminal domain of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II oligomerizes by itself in the presence of cell membranes to form ion channels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022, 200, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.R.; Kaus, K.; De, S.; Olson, R.; Alexandrescu, A.T. NMR structure of the Bacillus cereus hemolysin II C-terminal domain reveals a novel fold. Sci Rep. 2017, 1, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.R.; Maciejewski, M.W.; Olson, R.; Alexandrescu, A.T. NMR assignments for the cis and trans forms of the hemolysin II C-terminal domain. Biomol NMR Assign. 2014, 2, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.R.; Olson, R.; Alexandrescu, A.T. Protein yoga: conformational versatility of the hemolysin II C-terminal domain detailed by NMR structures for multiple states. Protein Sci. 2021, 5, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, N.; Nagel, A.; Zamyatina, A.; Karatovskaya, A.; Salyamov, V.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Zh.; Siunov, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Shepelyakovskaya, A.; Boziev, Kh.; Melnik, B.; Brovko, F.; Solonin, A. A monoclonal antibody against the C-terminal domain of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II inhibits HlyII cytolytic activity. Toxins 2020, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway's immunobiology / Kenneth Murphy, Casey Weaver; with contributions by Allan Mowat, Leslie Berg, David Chaplin; with acknowledgment to Charles A. Janeway Jr., Paul Travers, Mark Walport. Murphy, Kenneth (Kenneth M.), New York, NY Garland Science/Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, 9th edition, 2017.
- Gouaux, E. alpha-Hemolysin from Staphylococcus aureus: an archetype of beta-barrel, channel-forming toxins. J Struct Biol. 1998, 121, 110–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y., Mengist, H.M., Shi, C., Zhang, C., Wang, B., Li, T., Huang, Y., Xu, Y., Jin, T. Structural basis of the pore-forming toxin/membrane interaction. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13, 128.
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Site-specific mutagenesis by overlap extension. CSH Protoc. 2006, 1, pdb.prot3468. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).