Submitted:
10 October 2023
Posted:
12 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
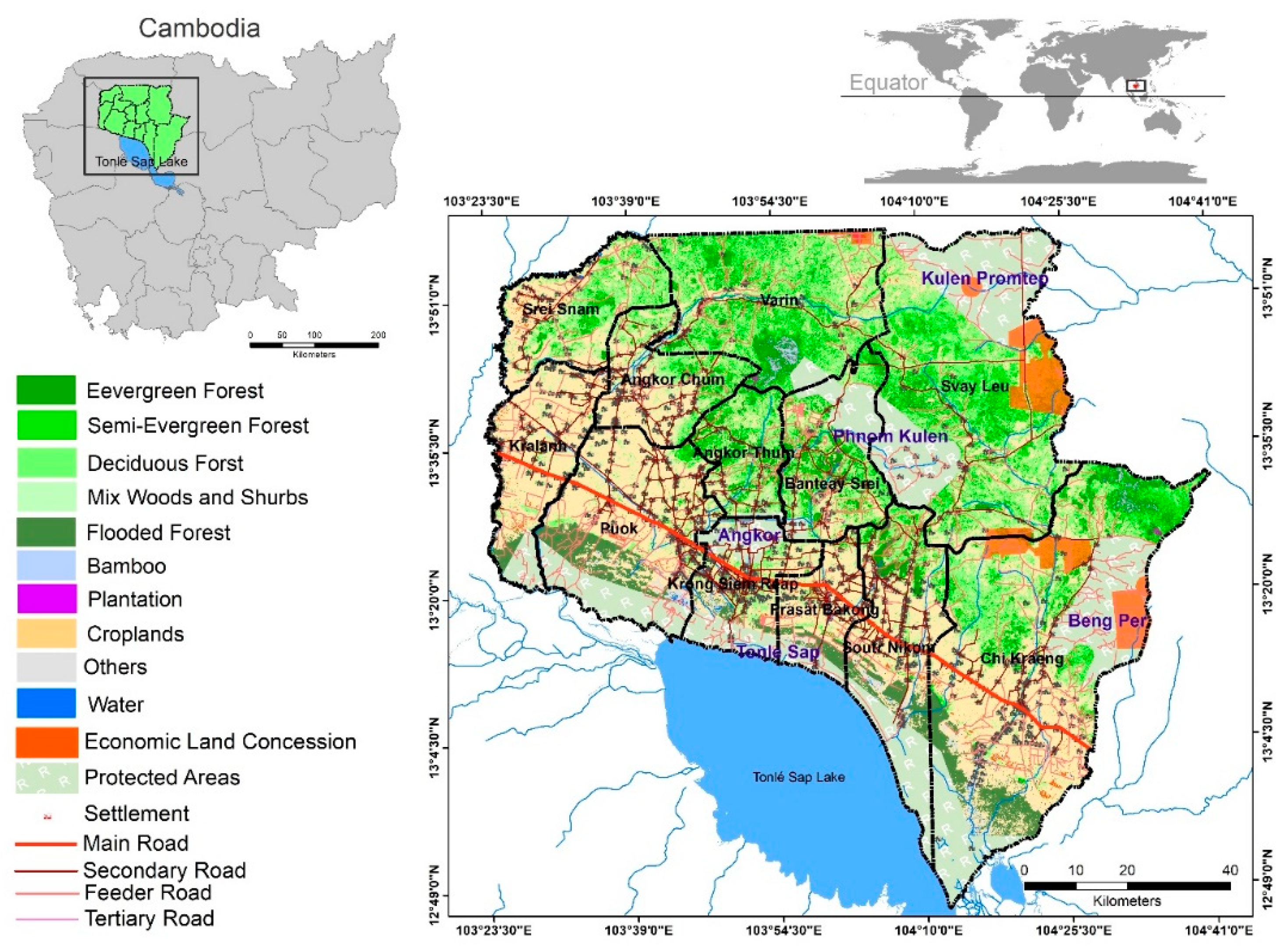
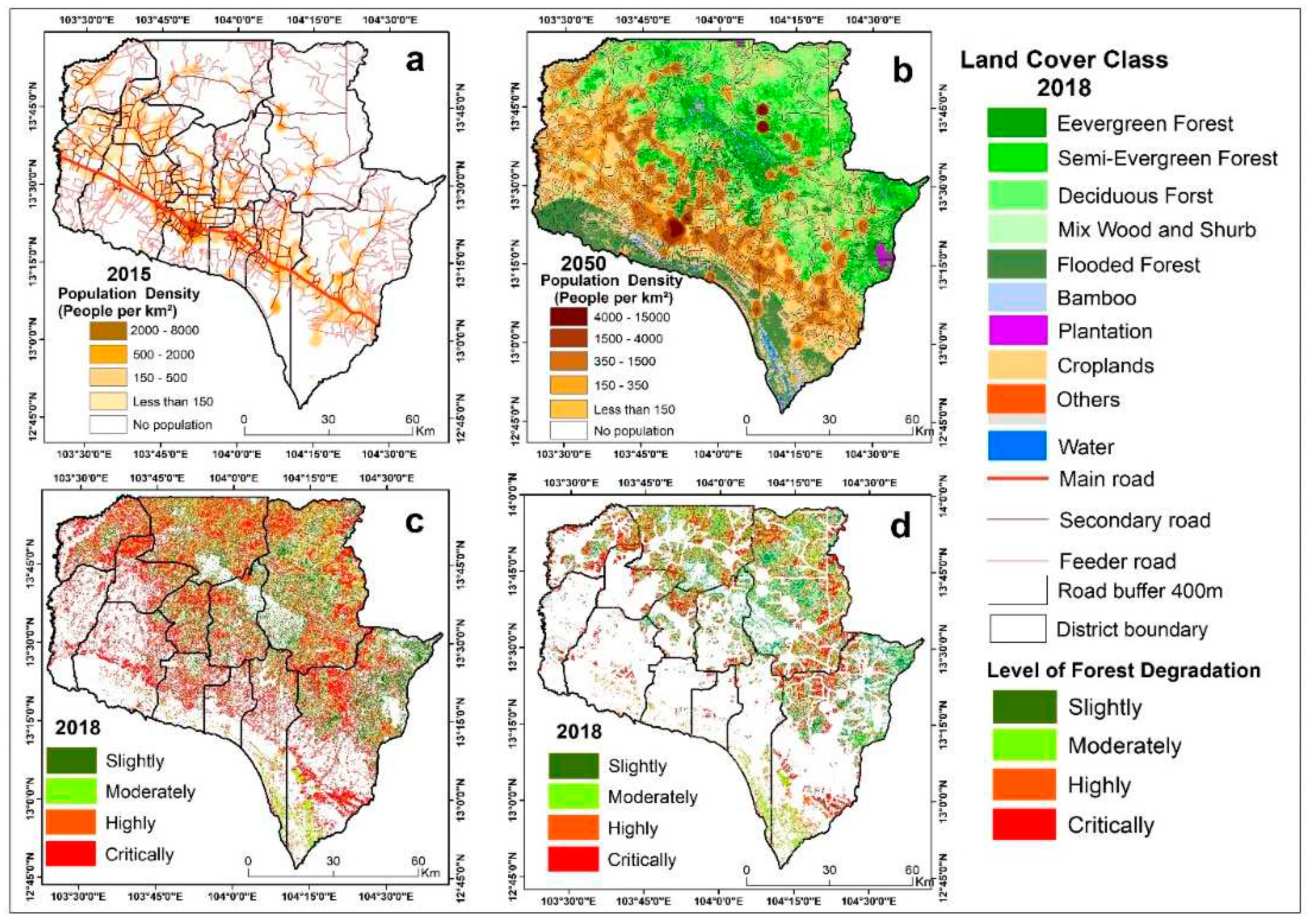
2.1. Study area
2.2. Forest cover data
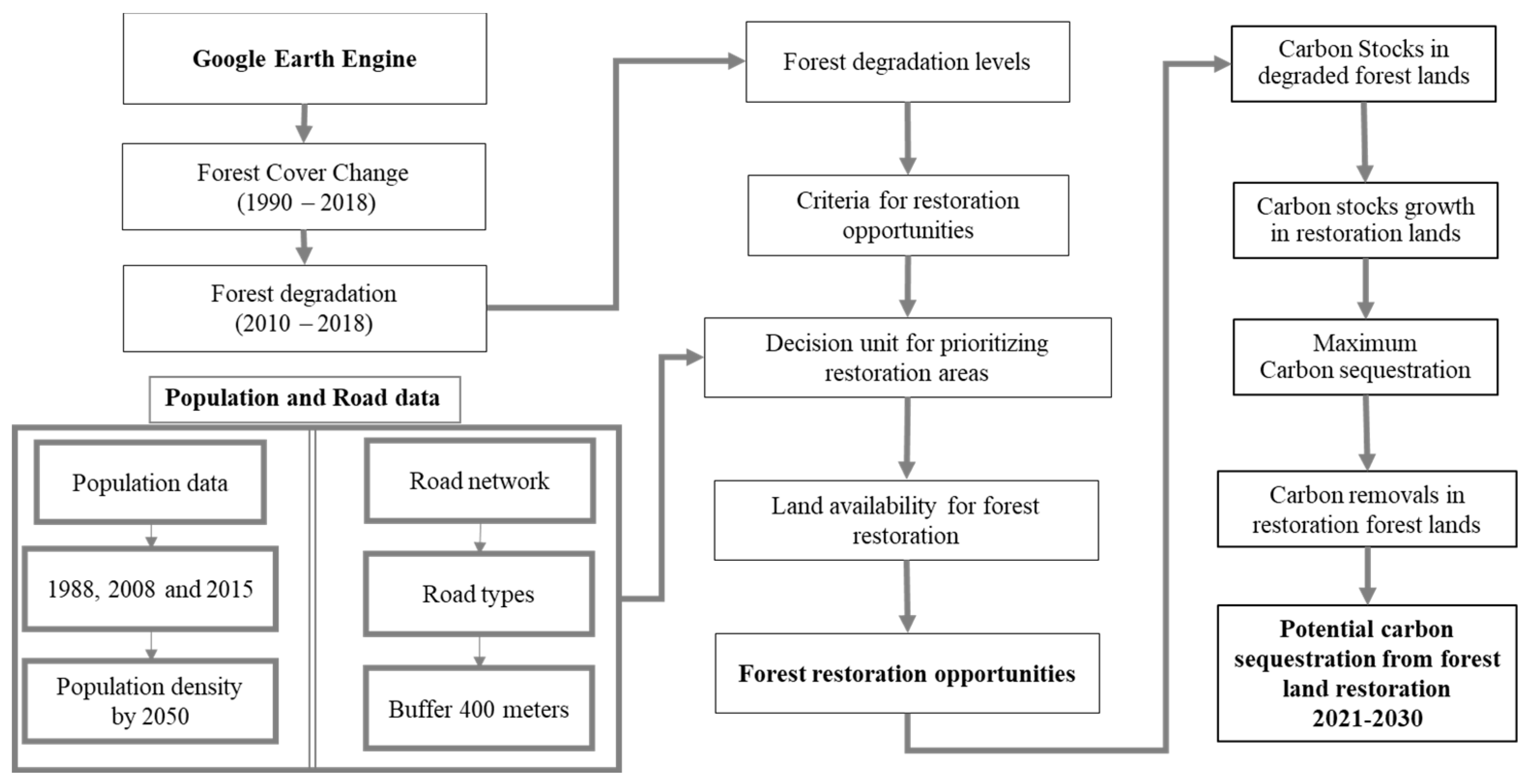
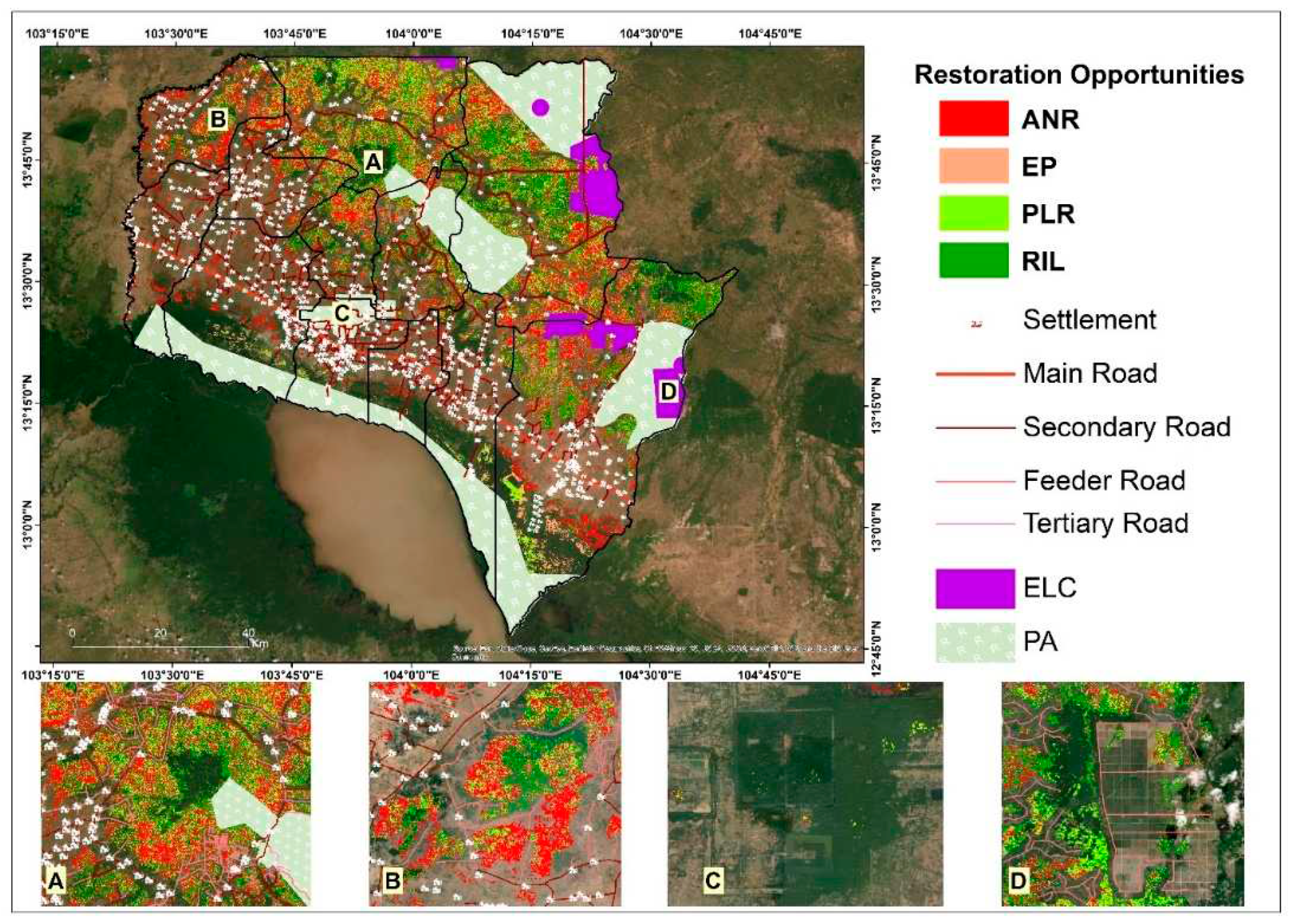
2.3. Methodological framework for determining potential degraded forests for restoration (PDFR)
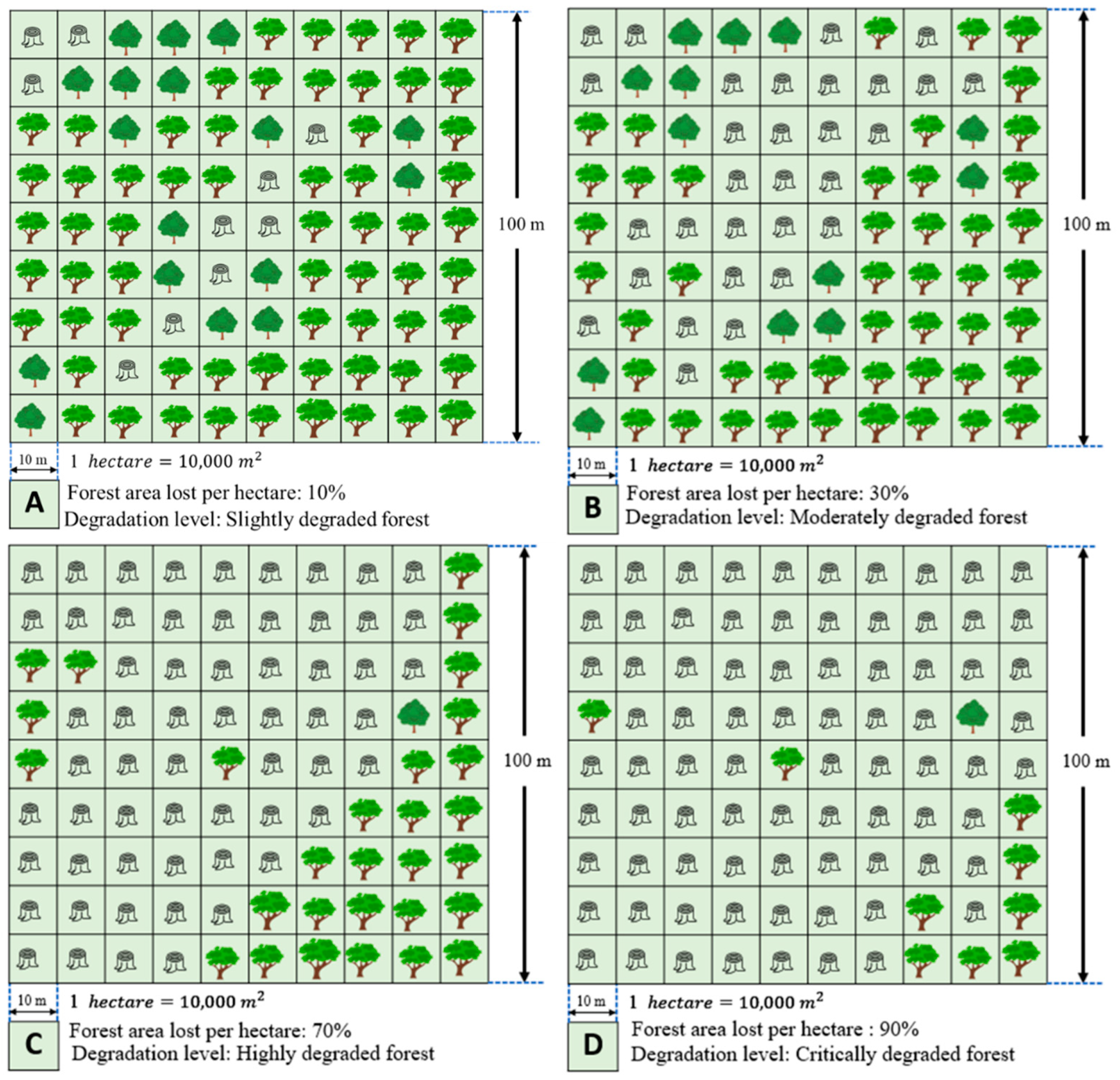
2.4. Levels of degraded forests
2.5. Criteria for selecting areas for restoration
2.5.1. Population distribution
2.5.2. Datasets of road networks
2.6. Degraded forests for potential restoration
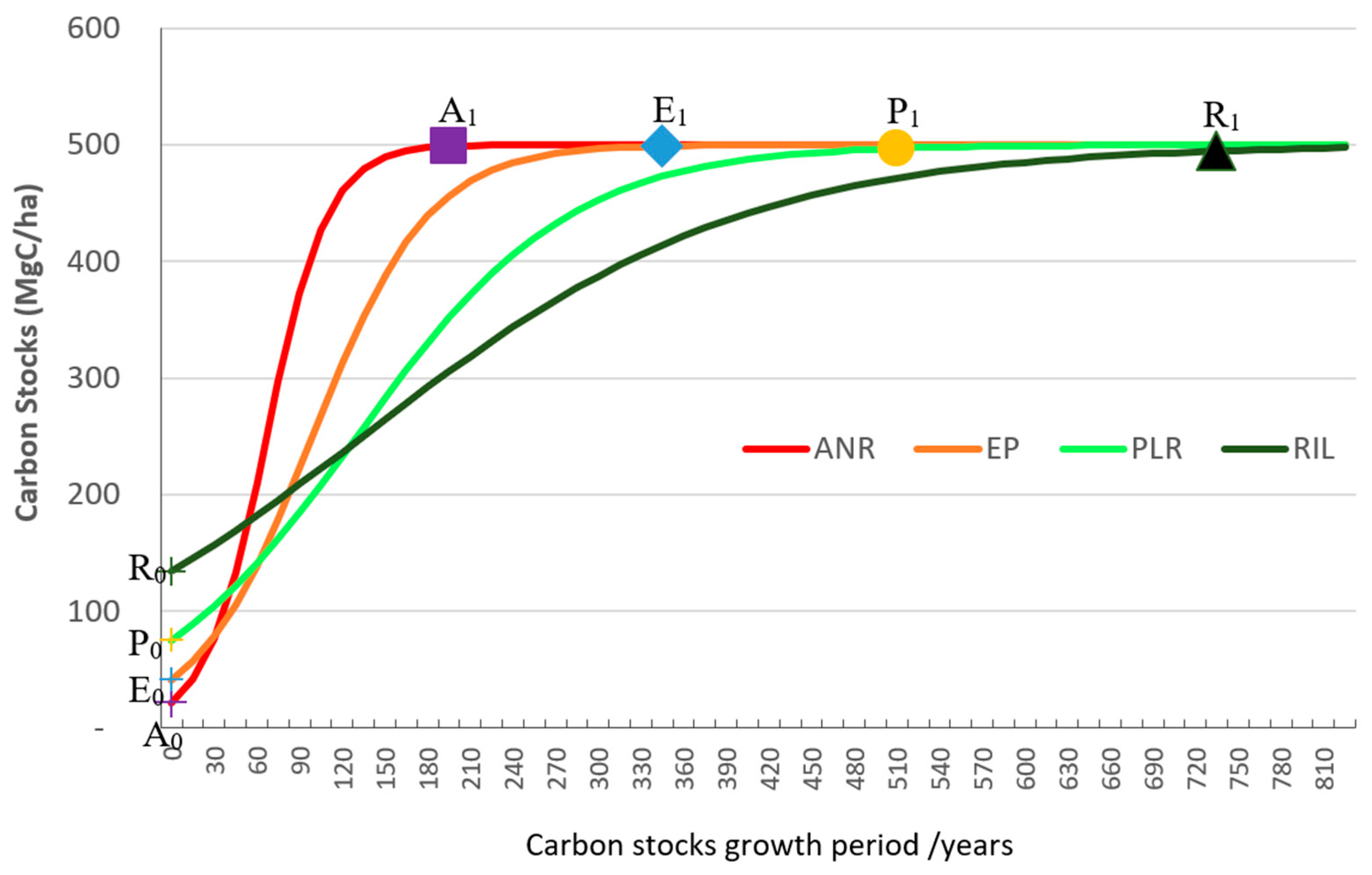
2.7. Carbon stocks and carbon revenues in restored forests
2.7.1. Carbon stocks per hectare in restored forests
2.7.2. Total carbon stocks in all restored forests
2.7.3. Carbon-based revenues
3. Results
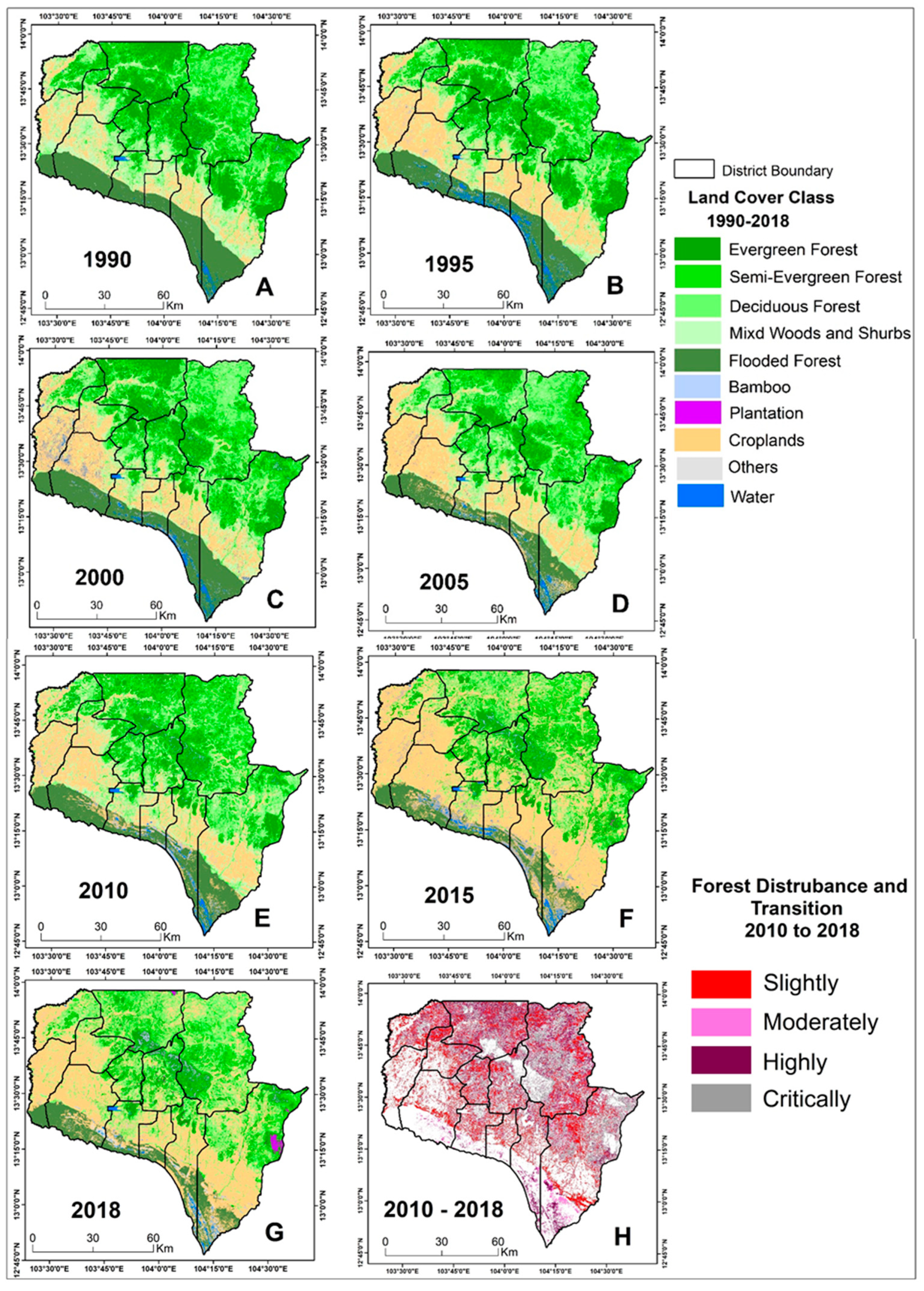
3.1. Forest cover change
3.2. Areal extent of degraded forests
3.3. Strategies for restoring degraded forests
3.4. Potential carbon stocks and sequestration in restored degraded forests
3.4.1. Initial carbon stocks in degraded forest lands
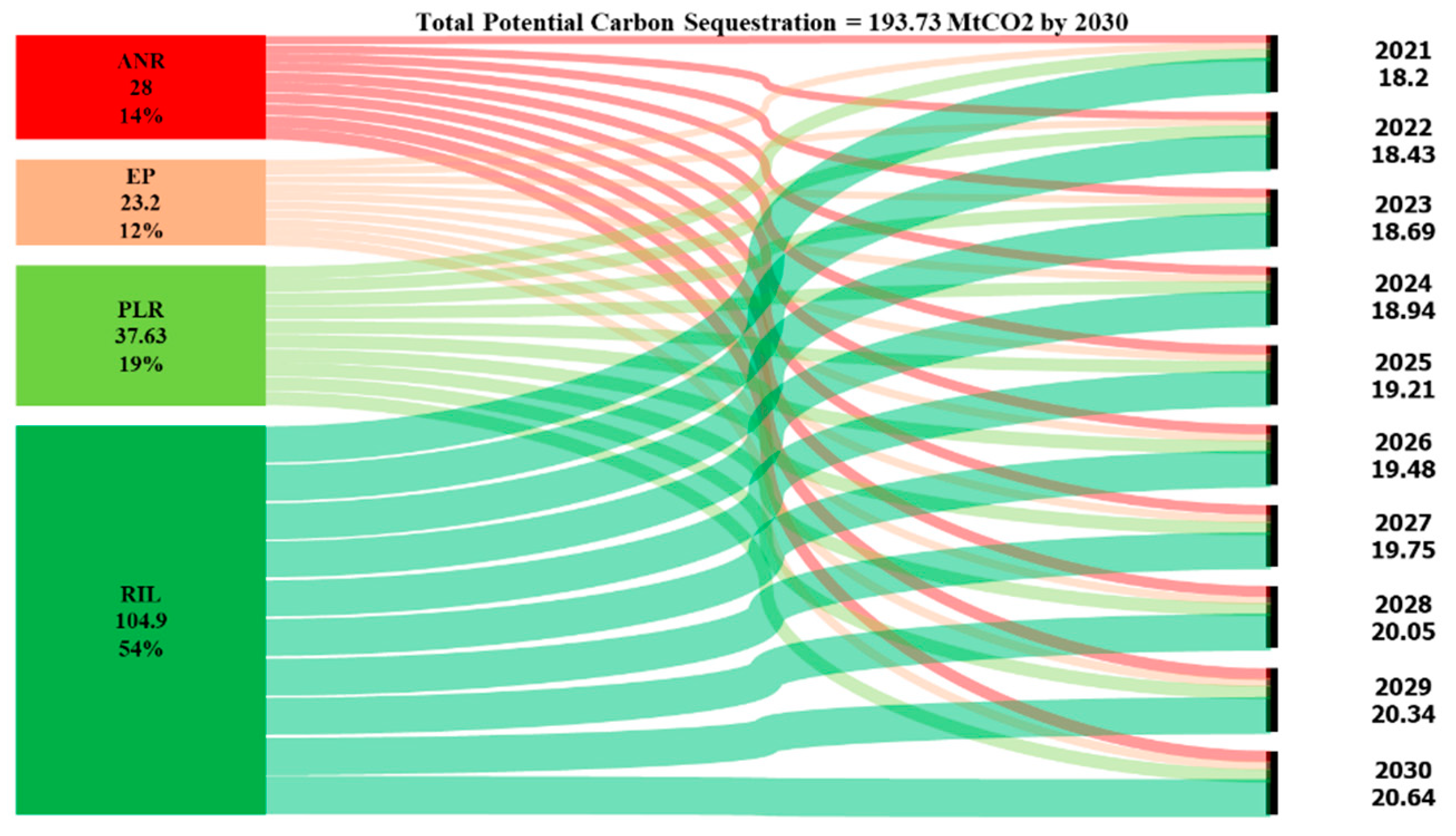
3.4.2. Potential carbon sequestration or removal through forest restoration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griscom, B.W., Ellis, P.W., Burivalova, Z., Halperin, J., Marthinus, D., Runting, R.K., Ruslandi, Shoch, D., Putz, F.E., 2019. Reduced-impact logging in Borneo to minimize carbon emissions and impacts on sensitive habitats while maintaining timber yields. For. Ecol. Manage. 438, 176–185. [CrossRef]
- Malhi, Y., Franklin, J., Seddon, N., Solan, M., Turner, M.G., Field, C.B., Knowlton, N., 2020. Climate change and ecosystems: Threats, opportunities and solutions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Karger, D.N., Kessler, M., Lehnert, M., Jetz, W., 2021. Limited protection and ongoing loss of tropical cloud forest biodiversity and ecosystems worldwide. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Turney, C., Ausseil, A.G., Broadhurst, L., 2020. Urgent need for an integrated policy framework for biodiversity loss and climate change. Nat. Ecol. Evol. [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC (2021) COP26: Pivotal Progress Made on Sustainable Forest Management and Conservation [WWW Document]. UNFCCC. URL https://unfccc.int/news/cop26-pivotal-progress-made-on-sustainable-forest-management-and-conservation, (accessed 16.9.2023).
- Gasser, T., Ciais, P., Lewis, S.L. 2022. How the Glasgow Declaration on Forests can help keep alive the 1.5 °C target. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA119(23): e2200519119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200519119.
- Vira, B., Wildburger, C., Mansourian, S., 2015. Forests, trees and landscapes for food security and nutrition: A global assessment report. IUFRO World Series Volume 33. International Union of Forest Research Organizations (IUFRO).
- Sasaki, N., Asner, G.P., Pan, Y., Knorr, W., Durst, P.B., Ma, H.O., Abe, I., Lowe, A.J., Koh, L.P., Putz, F.E., 2016. Sustainable Management of Tropical Forests Can Reduce Carbon Emissions and Stabilize Timber Production. Front. Environ. Sci. 4, 50. [CrossRef]
- Schwieder, M., Leitão, P.J., Pinto, J.R.R., Teixeira, A.M.C., Pedroni, F., Sanchez, M., Bustamante, M.M., Hostert, P., 2018. Landsat phenological metrics and their relation to aboveground carbon in the Brazilian Savanna. Carbon Balance Manag. 13, 7. [CrossRef]
- NYDF, 2020. Balancing forests and development: Addressing infrastructure and extractive industries, promoting sustainable livelihoods. Clim. Focus 110.
- Waltham, N.J., Elliott, M., Lee, S.Y., Lovelock, C., Duarte, C.M., Buelow, C., Simenstad, C., Nagelkerken, I., Claassens, L., Wen, C.K.-C., Barletta, M., Connolly, R.M., Gillies, C., Mitsch, W.J., Ogburn, M.B., Purandare, J., Possingham, H., Sheaves, M., 2020. UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration 2021–2030—What Chance for Success in Restoring Coastal Ecosystems? Front. Mar. Sci. 7, 71. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N., Asner, G.P., Knorr, W., Durst, P.B., Priyadi, H.R., Putz, F.E., 2011. Approaches to classifying and restoring degraded tropical forests for the anticipated REDD+ climate change mitigation mechanism. IForest 4, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- NYDF, 2019. Protecting and Restoring Forests: A Story of Large Commitments yet Limited Progress. New York Declaration on Forests Five-Year Assessment, Climate Focus (coordinator and editor).
- Weiskopf, S.R., Rubenstein, M.A., Crozier, L.G., Gaichas, S., Griffis, R., Halofsky, J.E., Hyde, K.J.W., Morelli, T.L., Morisette, J.T., Muñoz, R.C., Pershing, A.J., Peterson, D.L., Poudel, R., Staudinger, M.D., Sutton-Grier, A.E., Thompson, L., Vose, J., Weltzin, J.F., Whyte, K.P., 2020. Climate change effects on biodiversity, ecosystems, ecosystem services, and natural resource management in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.H.S., Amazonas, N.T., Chazdon, R.L., van Melis, J., Rodrigues, R.R., Silva, C.C., Sorrini, T.B., Holl, K.D., 2020. Exotic eucalypts: From demonized trees to allies of tropical forest restoration? J. Appl. Ecol. 57, 55–66. [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, K., Ray, S., Arakwiye, B., Morales, A.G., Singh, R., Maneerattana, O., Wicaksono, S., Chrysolite, H., Minnick, A., Johnston, L., 2018. Mapping Social Landscapes: A guide to identifying the newtorks, priorities, and values of restoration actors. World Resour. Inst. 96.
- TNC, 2002. Choosing a Restoration Guide for Your Project [WWW Document]. URL https://www.nature.org/en-us/about-us/where-we-work/united-states/minnesota/stories-in-minnesota/choosing-a-restoration-guide-for-your-project/ (accessed 4.11.19).
- Lamb, David and Gilmour, D., 2003. Rehabilitation and Restoration of Degraded Forests.
- FAO, 2015. Global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands: building resilience and benefiting livelihoods., Forestry Paper No. 175. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- IUCN, 2014. A guide to the Restoration Opportunities Assessment Methodology (ROAM) Assessing forest landscape restoration opportunities at the national or sub-national level. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN.
- IUCN, 2020. Guidance for using the IUCN Global Standard for Nature-based Solutions: first editions, Guidance for using the IUCN Global Standard for Nature-based Solutions: first editions. IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature. [CrossRef]
- IPBS, 2018. The Assessment Report on Land degradation and restoration, The IPBES Assessment repor on land degradation and restoration.
- Löf, M., Madsen, P., Metslaid, M., Witzell, J., Jacobs, D.F., 2019. Restoring forests: regeneration and ecosystem function for the future. New For. [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N., Hancher, M., Dixon, M., Ilyushchenko, S., Thau, D., Moore, R., 2017. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 202, 18–27. [CrossRef]
- FAO, 2020. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020. FAO, Rome, Italy.
- NISc, 2019. General Population Census of the Kingdom of Cambodia 2019, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Tourism, 2018. Cambodia Tourism Statistics - Tourist Information Center | Tourism Cambodia [WWW Document]. URL https://www.tourismcambodia.com/tourist-information/tourist-statistic.htm (accessed 4.8.21).
- UNESCO, 2021. Peru - UNESCO World Heritage Centre [WWW Document]. Unesco. URL https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/668/ (accessed 4.8.2021).
- GDANCP, 2017. Zoning Guidelines for the Protected Areas in Cambodia. Phnom Penh.
- Icem, 2003. Cambodia National Report on Protected Areas and Development. Rev. Prot. Areas Dev. Low. Mekong River Reg. 148.
- Venkatappa, M., Sasaki, N., Anantsuksomsri, S., Smith, B., 2020b. Applications of the Google Earth Engine and Phenology-Based Threshold Classification Method for Mapping Forest Cover and Carbon Stock Changes in Siem Reap Province, Cambodia. Remote Sens. 12, 3110. [CrossRef]
- Mackay Logan, G., 2012. World Heritage Area Tourism Management Plan.
- Gaughan, A.E., Binford, M.W., Southworth, J., 2009. Tourism, forest conversion, and land transformations in the Angkor basin, Cambodia. Appl. Geogr. 29, 212–223. [CrossRef]
- Venkatappa, M., Anantsuksomsri, S., Castillo, J.A., Smith, B., Sasaki, N., 2020a. Mapping the Natural Distribution of Bamboo and Related Carbon Stocks in the Tropics Using Google Earth Engine, Phenological Behavior, Landsat 8, and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 12, 3109. [CrossRef]
- Chander, G., Markham, B.L., Helder, D.L., 2009. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 113, 893–903.
- GEE, 2020. Google Earth Engine [WWW Document]. URL https://earthengine.google.com/ (accessed 2.16.20).
- Venkatappa, M., Sasaki, N., Shrestha, R.P., Tripathi, N.K., Ma, H.O., 2019. Determination of vegetation thresholds for assessing land use and land use changes in Cambodia using the Google Earth Engine cloud-computing platform. Remote Sens. 11, 1514. [CrossRef]
- MoE, 2018. Cambodia Forest Cover [WWW Document]. URL https://redd.unfccc.int/uploads/54_3_cambodia_forest_cover_resource__2016_english.pdf (accessed 6.10.20).
- MoE, 2009. Cambodia Evnvironment Outlook [WWW Document]. URL https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/8689/Cambodia_environment_outlook.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (accessed 11.19.18).
- Sangermano, F., Toledano, J., Eastman, R., 2012. Land cover change in the Bolivian Amazon and its implications for REDD+ and endemic biodiversity. Landsc. Ecol. 27, 571–584. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.J., Cayuela, L., Echeverria, C., Salas, J., Rey Benayas, J.M., 2010. Monitoring land cover change of the dryland forest landscape of Central Chile (1975-2008). Appl. Geogr. 30, 436–447. [CrossRef]
- Václavík, T., Rogan, J., 2009. Identifying trends in land use/land cover changes in the context of post-socialist transformation in Central Europe: A case study of the greater Olomouc region, Czech Republic. GIScience Remote Sens. 46, 54–76. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.T., Kanemoto, K., 2021. Mapping the deforestation footprint of nations reveals growing threat to tropical forests. Nat. Ecol. Evol. In Press. [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, H.M., Prescott, G.W., Carrasco, L.R., Rao, M., Symes, W.S., 2021. Drivers of deforestation and degradation for 28 tropical conservation landscapes. Ambio 50, 215–228. [CrossRef]
- Rija, A.A., Critchlow, R., Thomas, C.D., Beale, C.M., 2020. Global extent and drivers of mammal population declines in protected areas under illegal hunting pressure. PLoS One 15. [CrossRef]
- Tritsch, I., Tourneau, F. Le, 2017. Population densities and deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon : New insights on the current human settlement patterns To cite this version : HAL Id : hal-01425695 Keywords 76, 163–172. [CrossRef]
- ODC, 2018. Open Development Cambodia [WWW Document]. URL https://opendevelopmentcambodia.net/map-explorer (accessed 8.17.20).
- MOP, 2016. Ministry of Planning, Cambodia [WWW Document]. URL http://www.mop.gov.kh/en-us/Home/Home (accessed 6.17.19).
- Haddock, S., Leahy, E., Engelman, R., 2008. Population Growth. Int. Encycl. Public Heal. 181–190. [CrossRef]
- Erbaugh, J.T., Pradhan, N., Adams, J., Oldekop, J.A., Agrawal, A., Brockington, D., Pritchard, R., Chhatre, A., 2020. Global forest restoration and the importance of prioritizing local communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 4, 1472–1476. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N., 2021. Timber production and carbon emission reductions through improved forest management and substitution of fossil fuels with wood biomass. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 173, 105737. [CrossRef]
- FAO, 2001. Carbon budgets of tropical forest ecosystems in Southeast Asia: implications for climate change, in: Carbon Budgets of Tropical Forest Ecosystems in Southeast Asia: Implications for Climate Change.
- World Bank, 2021. State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2021, State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2021. The World Bank, Washington, DC. [CrossRef]
- World Bank, 2023. State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2023. The World Bank, Washington, DC.
- Davis, K.F., Yu, K., Rulli, M.C., Pichdara, L., D’Odorico, P., 2015. Accelerated deforestation driven by large-scale land acquisitions in Cambodia. Nat. Geosci. 8, 772–775. [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R., Brancalion, P., 2019. Restoring forests as a means to many ends: an urgent need to replenish tree canopy cover calls for holistic approaches. Science (80-. ). 364, 24–25.
- Andrade, R.B., Balch, J.K., Parsons, A.L., Armenteras, D., Roman-Cuesta, R.M., Bulkan, J., 2017. Scenarios in tropical forest degradation: Carbon stock trajectories for REDD+. Carbon Balance Manag. [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P., Knapp, D.E., Broadbent, E.N., Oliveira, P.J.C., Keller, M., Silva, J.N., 2005. Ecology: Selective logging in the Brazilian Amazon. Science (80-.). 310, 480–482. [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F., Geist, H.J., Lepers, E., 2003. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 28, 205–241. [CrossRef]
- Appanah, S., 2016. Forest landscape restoration for Asia-Pacific forests. the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and RECOFTC – The Center for People and Forest Bangkok, 2016.
- Di Sacco, A., Hardwick, K.A., Blakesley, D., Brancalion, P.H.S., Breman, E., Cecilio Rebola, L., Chomba, S., Dixon, K., Elliott, S., Ruyonga, G., Shaw, K., Smith, P., Smith, R.J., Antonelli, A., S Brancalion, P.H., Breman, E., Cecilio Rebola, L., Chomba, S., Dixon, K., Elliott, S., Ruyonga, G., Shaw, K., Smith, P., Smith, R.J., Antonelli, A., Kate Hardwick, C.A., 2021. Ten golden rules for reforestation to optimize carbon sequestration, biodiversity recovery and livelihood benefits. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1328–1348. [CrossRef]
- Koh, L.P., Zeng, Y., Sarira, T.V., Siman, K., 2021. Carbon prospecting in tropical forests for climate change mitigation. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Soto-Navarro, C., Ravilious, C., Arnell, A., De Lamo, X., Harfoot, M., Hill, S.L.L., Wearn, O.R., Santoro, M., Bouvet, A., Mermoz, S., Le Toan, T., Xia, J., Liu, S., Yuan, W., Spawn, S.A., Gibbs, H.K., Ferrier, S., Harwood, T., Alkemade, R., Schipper, A.M., Schmidt-Traub, G., Strassburg, B., Miles, L., Burgess, N.D., Kapos, V., 2020. Mapping co-benefits for carbon storage and biodiversity to inform conservation policy and action. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 375, 20190128. [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W., Busch, J., Cook-Patton, S.C., Ellis, P.W., Funk, J., Leavitt, S.M., Lomax, G., Turner, W.R., Chapman, M., Engelmann, J., Gurwick, N.P., Landis, E., Lawrence, D., Malhi, Y., Murray, L.S., Navarrete, D., Roe, S., Scull, S., Smith, P., Streck, C., Walker, W.S., Worthington, T., 2020. National mitigation potential from natural climate solutions in the tropics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 375, 20190126. [CrossRef]
- Budiharta, S., Meijaard, E., Erskine, P.D., Rondinini, C., Pacifici, M., Wilson, K.A., 2014. Restoring degraded tropical forests for carbon and biodiversity. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 114020. [CrossRef]
- Meyfroidt, P., Lambin, E.F., 2011. Global Forest Transition: Prospects for an End to Deforestation. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 36, 343–371. [CrossRef]
- Shono, K., Cadaweng, E.A., Durst, P.B., 2007. Application of assisted natural regeneration to restore degraded tropical forestlands. Restor. Ecol. [CrossRef]
- Köhl, M., Neupane, P.R., Mundhenk, P., 2020. REDD+ measurement, reporting and verification – A cost trap? Implications for financing REDD+MRV costs by result-based payments. Ecol. Econ. 168, 106513. [CrossRef]
- Le, H.D., Smith, C., Herbohn, J., 2014. What drives the success of reforestation projects in tropical developing countries? The case of the Philippines. Glob. Environ. Chang. 24, 334–348. [CrossRef]
- Pye-Smith C, 2010. A Rural Revival in Tanzania:How agroforestry is helping farmers to restore the woodlands in Shinyanga Region. World Agroforestry Centre, Nairobi.
- FAO, 2013. Climate-Smart Agriculture Sourcebook. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Sourcebook on Climate-Smart Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
| Original PDFR dataset category | FA degradation priority |
Assessment score | Constraint | Restoration Strategy* | AGC (MgC ha-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Critically degraded forest | High (4) | 4 x 1.5 = 5.5 | - Suitable land use should be degraded forest land. - Forest restoration land should not be within a rubber plantation. - Forest restoration land should not be within 400 m of all road types. - Forest restoration land should not be within the 2050 predicted population density radius. |
Assisted natural regeneration | 27 |
| Highly degraded forest | High (3) | 3 x 1.5 = 4.5 | Enrichment planting | 32 | |
| Moderately degraded forest | Medium (2) | 2 x 1.5 = 3.5 | Preventing logging reentry | 60 | |
| Slightly degraded forest | Slightly (1) | 1 x 1.5 = 2.5 | Reduced impact logging | 148 | |
| Not degraded | Eliminated (0) | 0 x 0 = 0 | Restoration is not needed |
| Forest Category | Total Forest Area (ha) | 1990-2018 | 2010-2018 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | Change (ha) | Annual Change (ha) | Rate of Change (%) | Change (ha) | Annual Change (ha) | Rate of Change (%) | |
| Evergreen | 188,332 | 186,923 | 178,249 | 157,350 | 142,451 | 127,240 | 91,254 | -97,078 | -3,467 | -0.018 | -51,197 | -2,844 | -0.020 |
| Semi-evergreen | 162,797 | 159,084 | 151,325 | 144,430 | 143,221 | 116,251 | 104,529 | -58,268 | -2,081 | -0.013 | -38,692 | -2,150 | -0.015 |
| Deciduous | 240,205 | 232,976 | 233,940 | 228,943 | 226,331 | 181,153 | 173,010 | -67,194 | -2,400 | -0.010 | -53,321 | -2,962 | -0.013 |
| Wood and Shrubland | 130,876 | 127,360 | 121,764 | 136,065 | 146,432 | 67,562 | 68,782 | -62,095 | -2,218 | -0.017 | -77,650 | -4,314 | -0.029 |
| Bamboo | 6,162 | 5,600 | 5,211 | 7,768 | 8,364 | 7,276 | 8,865 | 2,703 | 97 | 0.016 | 501 | 28 | 0.003 |
| Flooded Forest | 141,083 | 140,331 | 130,415 | 112,502 | 107,614 | 79,966 | 79,662 | -61,420 | -2,194 | -0.016 | -27,952 | -1,553 | -0.014 |
| Rubber | 0 | 0 | 0 | 388 | 2,677 | 6,219 | 20,658 | 20,270 | 1,559 | 4.019 | 17,981 | 999 | 0.373 |
| Total | 869,454 | 852,274 | 820,903 | 787,446 | 777,090 | 585,666 | 546,760 | -322,694 | -11,524 | -0.013 | -230,330 | -12,796 | -0.016 |
| Terms | Definition and intervention |
|---|---|
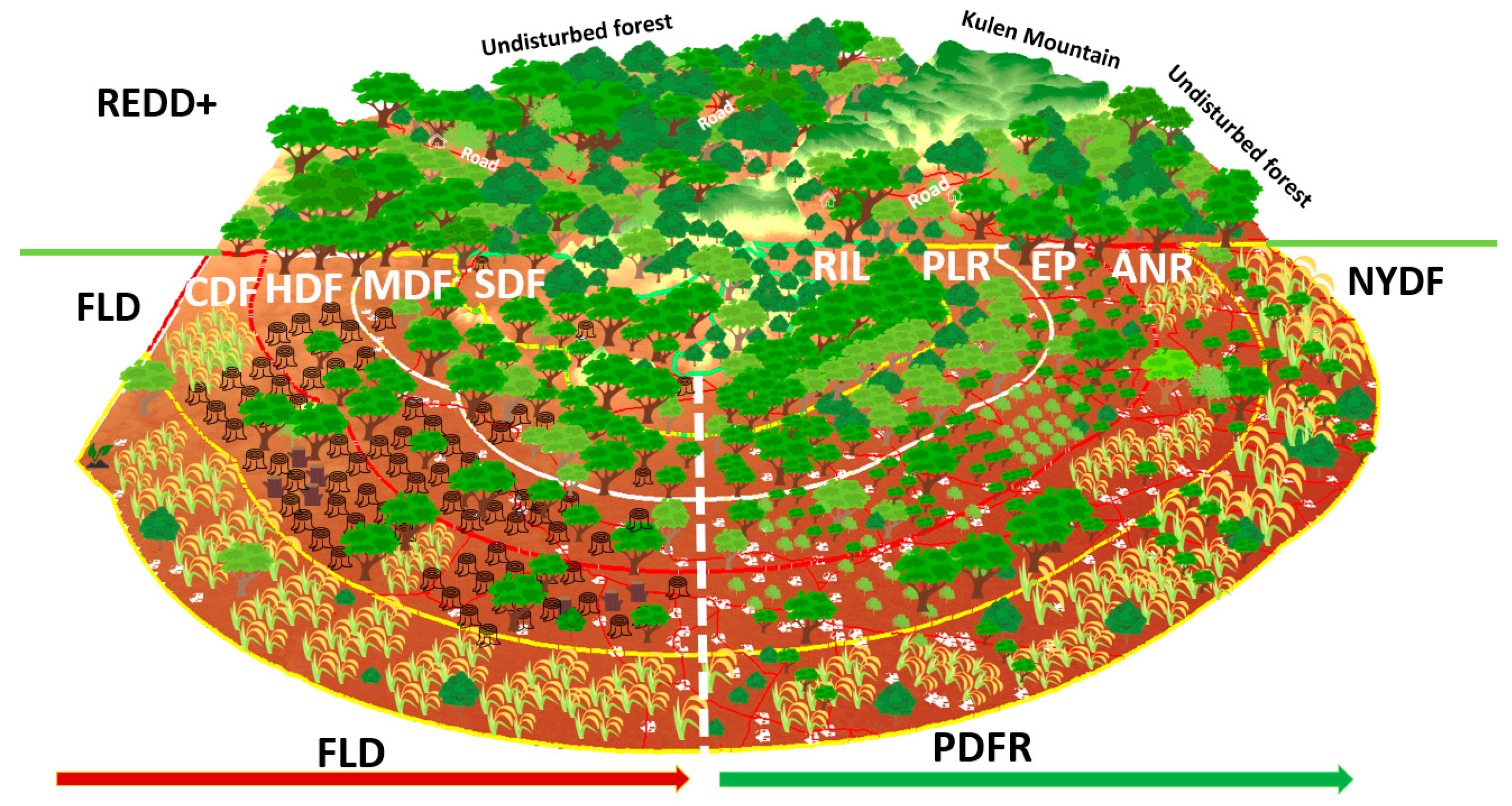
| FLD | Forest land degradation zone refers to the reduction of a forest area’s capacity to provide the full suite of forest ecosystem services, such as biodiversity, carbon, or hydrological services [13]. Tropical forests are degraded in a way that reduces tree cover and carbon stocks through the removal of trees or woody material (e.g., logging or infrastructure construction, shifting cultivation, and harvesting trees for charcoal production) or through the collection of non-timber forest products [57,58,59]. Categorizing forests based on FLD levels; SDF = Slightly degraded forest, MDF = Moderately degraded forest, HDF = Highly degraded forest, CDR = Critically degraded Forest (Figure 3) can aid in preparing guidelines for critical decisions [12] concerning the priorities and strategies for forest restoration (Figure 7). |
| NYDF | New York Declaration on Forest. Two of the declaration’s goals are to end natural forest loss and restore forests by 2030 [2,10,15]. Further goals include the promotion of sustainable and equitable development by supporting livelihoods that do not result in further deforestation [3,14]. The PDFR model suggests selecting from among four approaches (ANR, EP, PLR, and RIL). This should provide more assurance of the success of the NYDF goals with low financial costs, better biodiversity, and social environmental benefits (Figure 7). If proper restoration, protection, and forest management initiatives are not implemented, then the FLD may continue and pose serious environmental and socioeconomic problems that adversely affect people who depend on forest products and services. |
| PDFR | The potential degraded forests for restoration model refer to the process of assisting the restoration of forest land that has been degraded, damaged, or destroyed. The aim of the PDFR is to improve forest ecosystem services, such as biodiversity and carbon sequestration using defined strategies to meet NYDF goals 1 and 5 by 2030 (Figure 7). |
| REDD+ | REDD+ refers to the incentive mechanism defined under the UNFCCC to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation, effect the conservation and sustainable management of forests, and enhance forest carbon stocks [60,61,62,63]. Introducing the REDD+ result-based financial scheme can combat deforestation and forest degradation in the tropics where most forest disturbance takes place. If REDD+ activities are implemented where native forests are still intact or undisturbed, about 8,256,746 MgCO2 of carbon emissions could be reduced in the Siem Reap province by 2030 [31]. If interventions (REDD+ or forest land restoration under the NYDF) are not implemented, then deforestation and forest degradation emissions are likely to continue. This may initially occur along roads and surrounding settlements, and may extend into undisturbed and mountain forest lands (Figure 7). |
| Degraded Forests by Levels | Restoration Strategies | PDFR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Area (ha) | Costs (US$ Millions) | ||
| Critically degraded forest | Assisted natural regeneration | 96,693 | 193.39 |
| Highly degraded forest | Enrichment planting | 48,878 | 97.76 |
| Moderately degraded forest | Preventing logging reentry | 46,487 | 92.97 |
| Slightly degraded forest | Reduced impact logging | 75,567 | 151.13 |
| Total | 267,625 | 535.25 | |
| Forest Forest degradation level |
PDFR | |
| Forest Area (ha) | AGC (MgC yr-1) | |
| Critically degraded forest | 96,693 | 2,088,570 |
| Highly degraded forest | 48,878 | 2,003,989 |
| Moderately degraded forest | 46,487 | 3,495,838 |
| Slightly degraded forest | 75,567 | 10,125,939 |
| Total | 267,625 | 17,714,336 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





