Submitted:
30 September 2023
Posted:
01 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
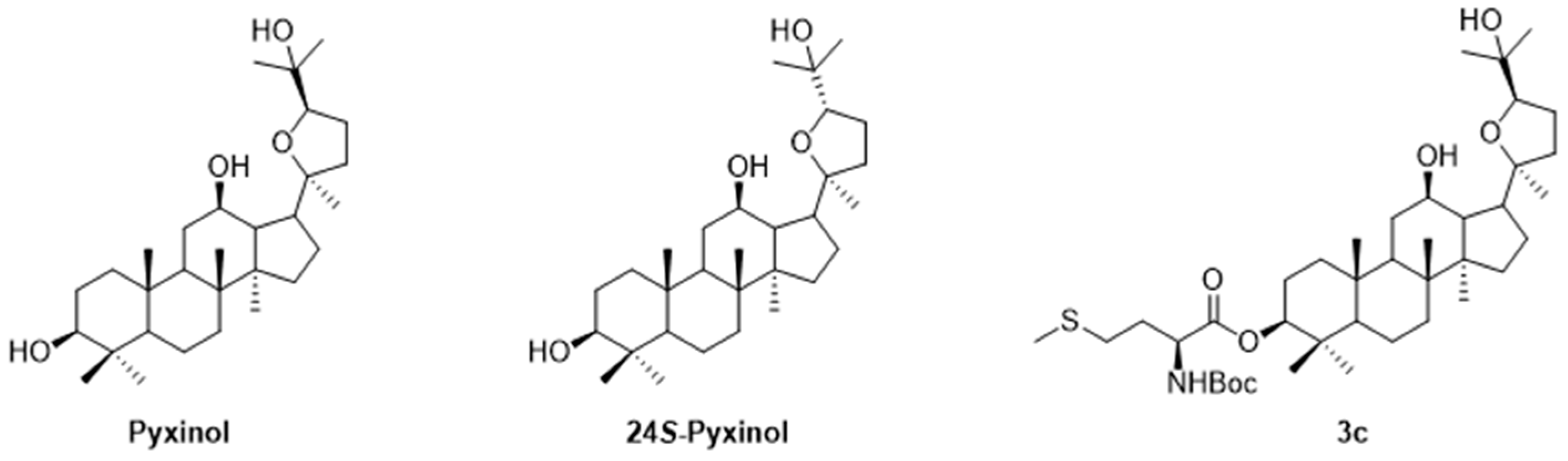
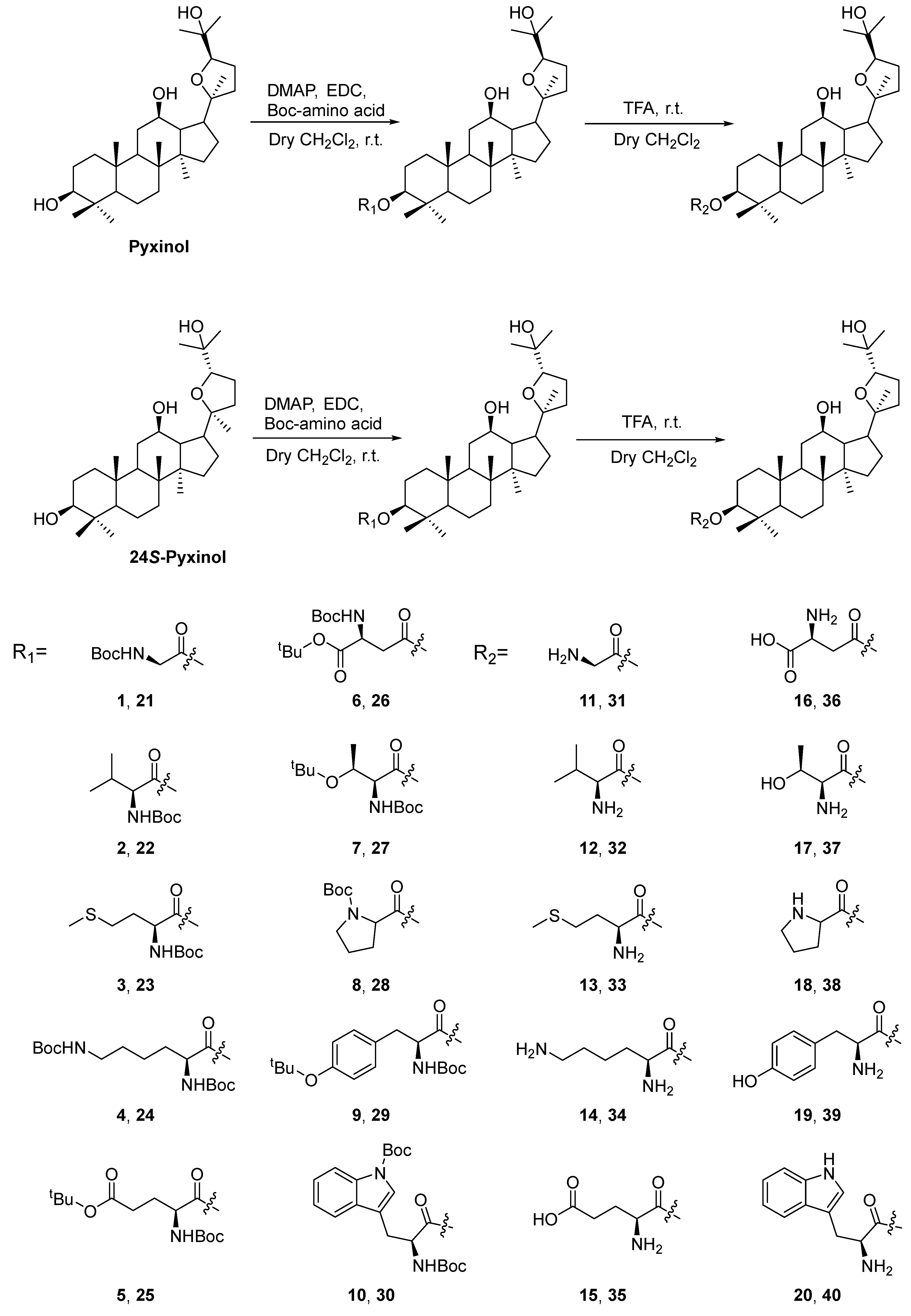
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Evaluation of Derivatives in reversing tumor multidrug resistance activity
2.2.1. Cytotoxicity determination
2.2.2. Evaluation of MDR reversal ability
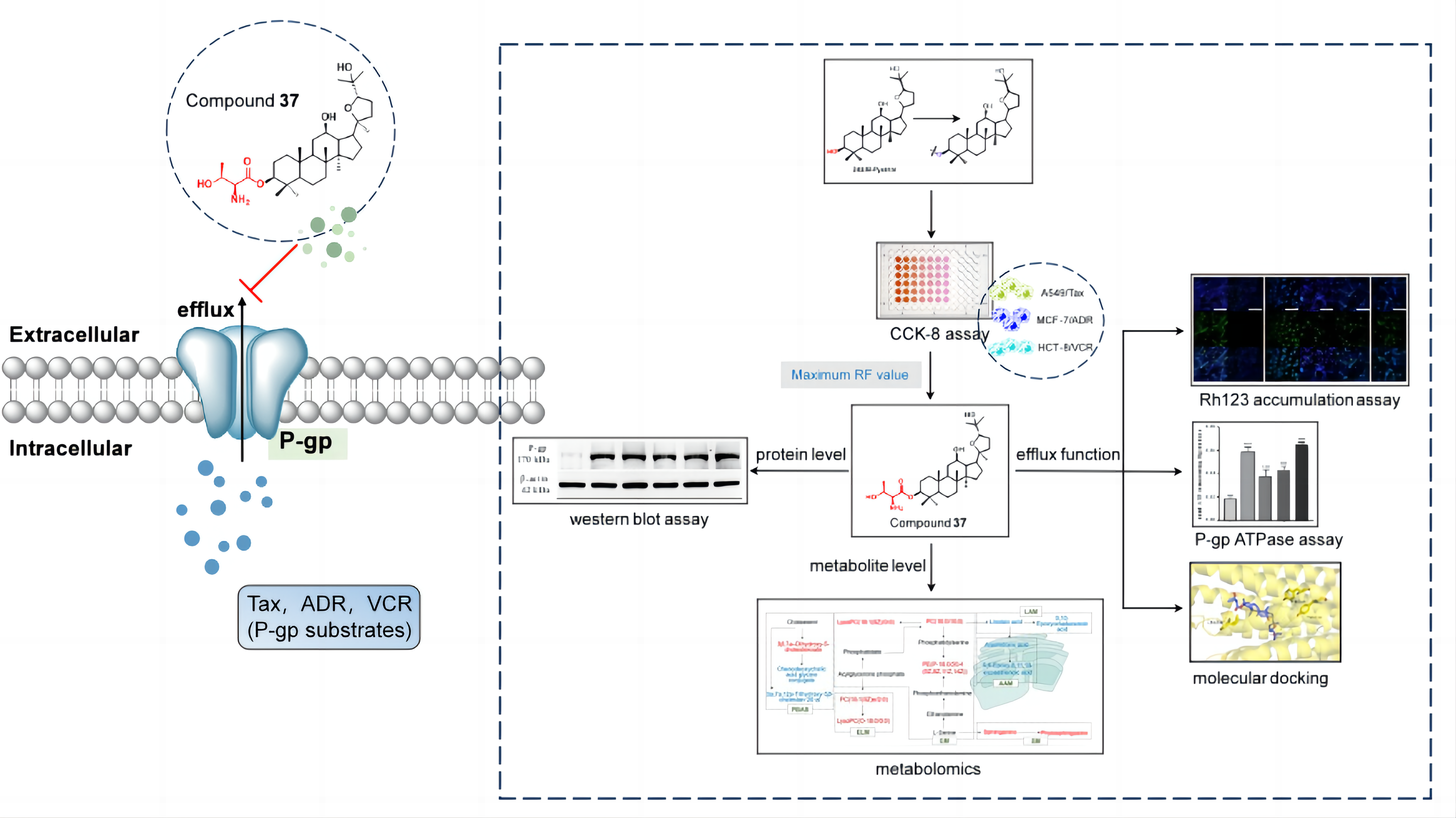
2.3. Effect of compound 37 on P-gp
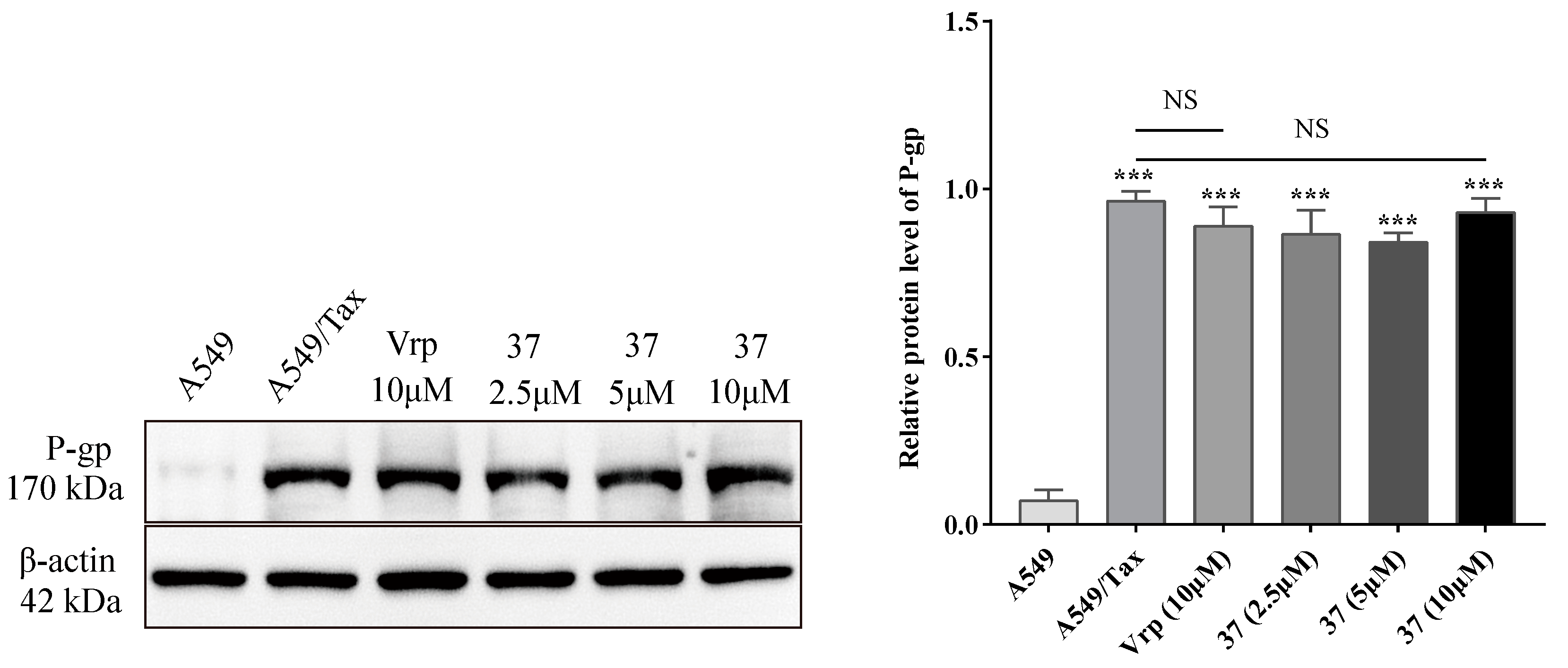
2.3.1. Effect on the expression level of P-gp
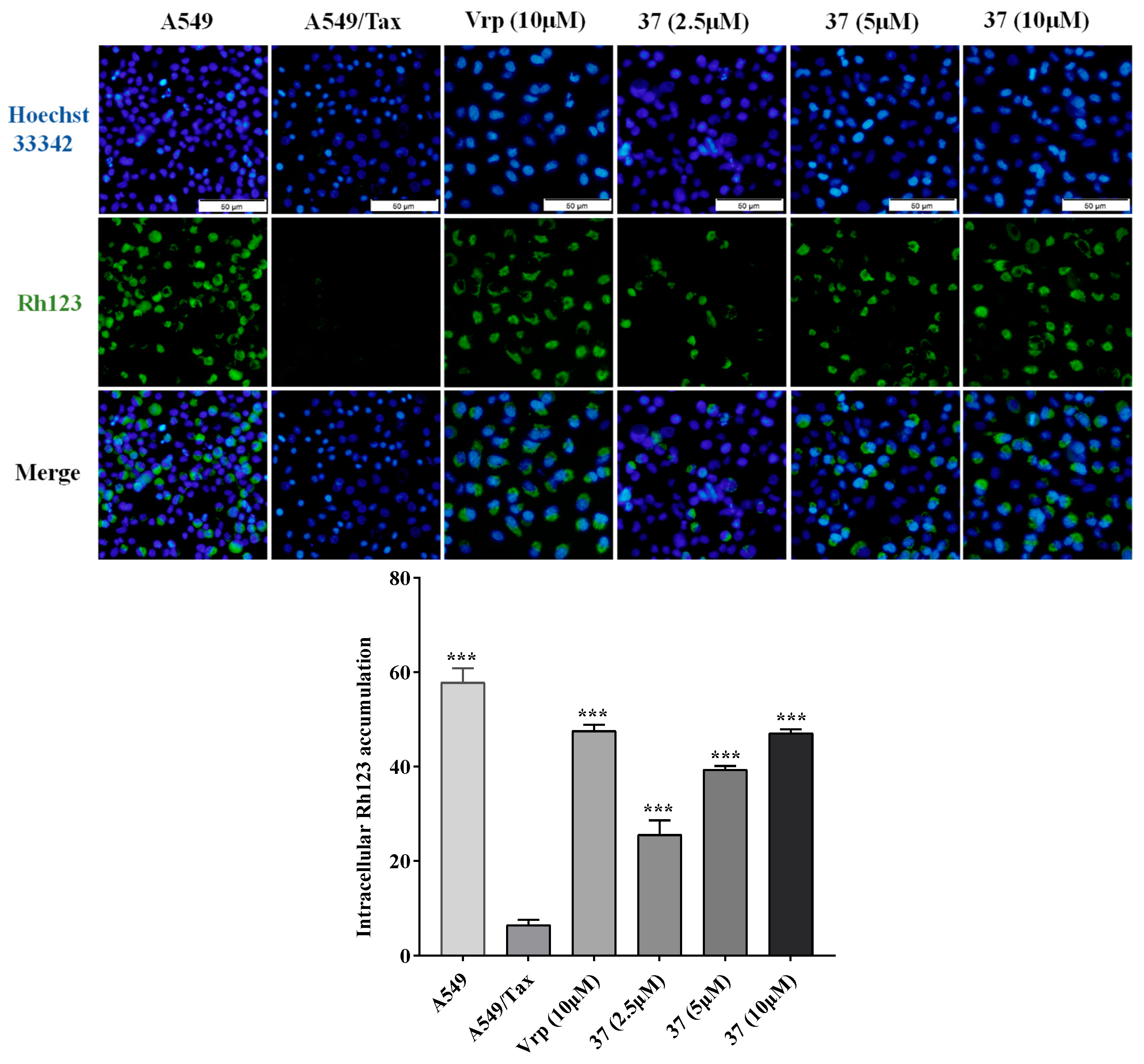
2.3.2. Effect on the efflux function of P-gp
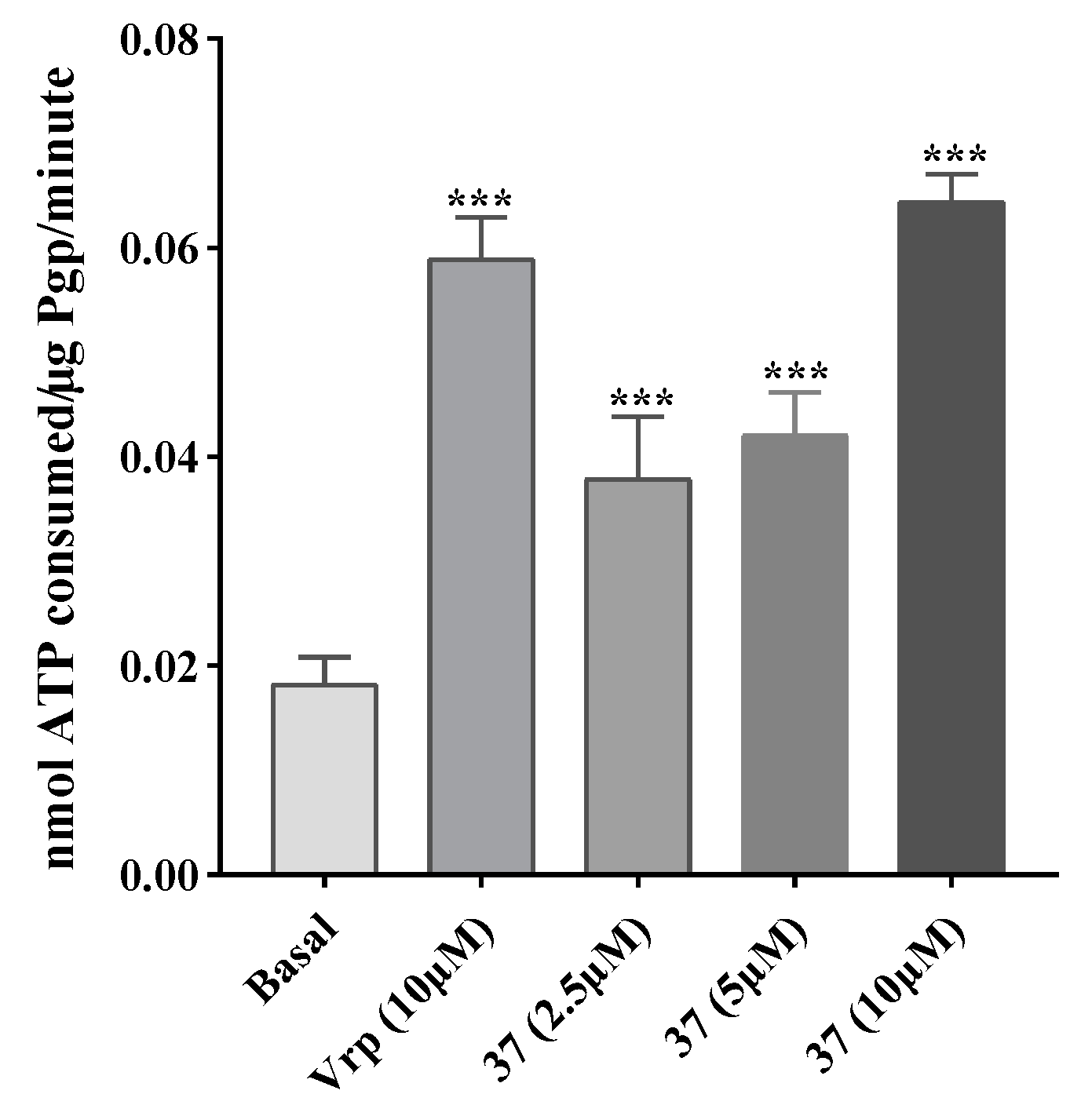
2.3.3. Effect on P-gp ATPase activity
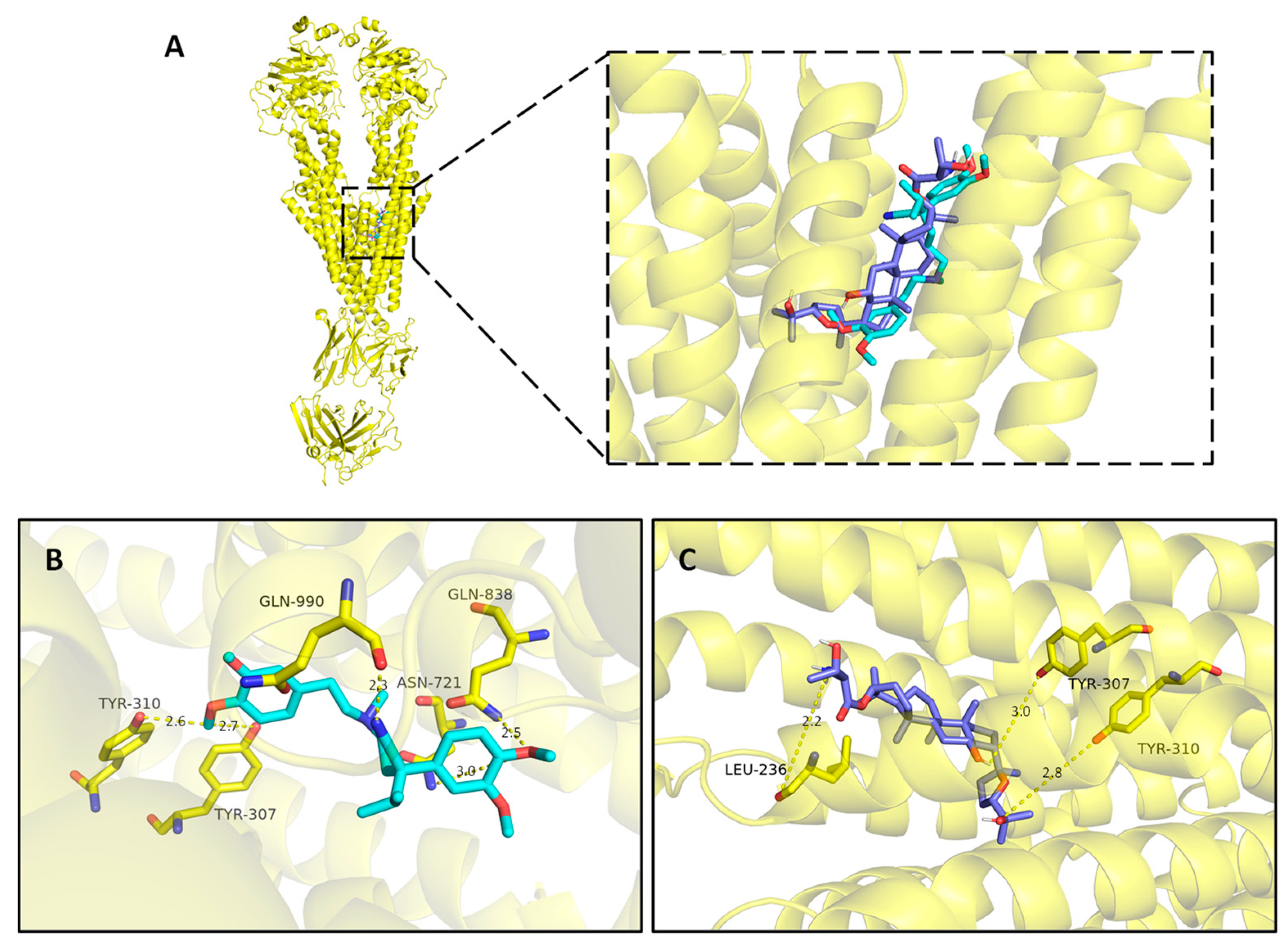
2.3.4. Molecular docking
2.4. Cellular metabolomics
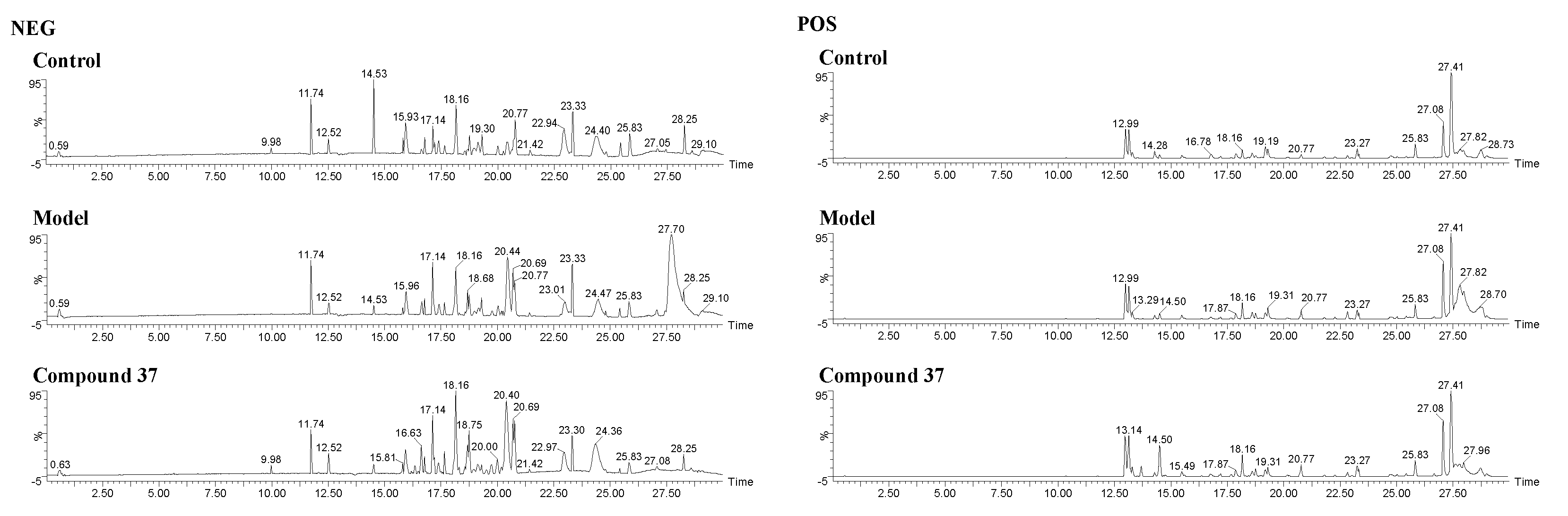
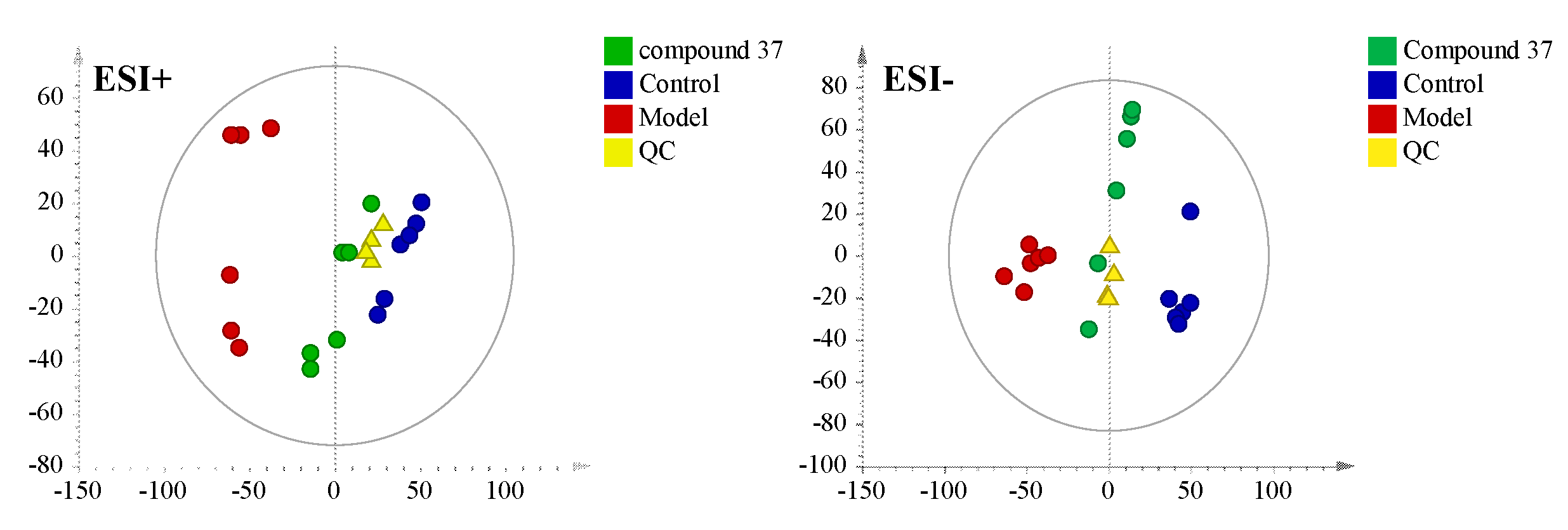
2.4.1. Validation of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS method
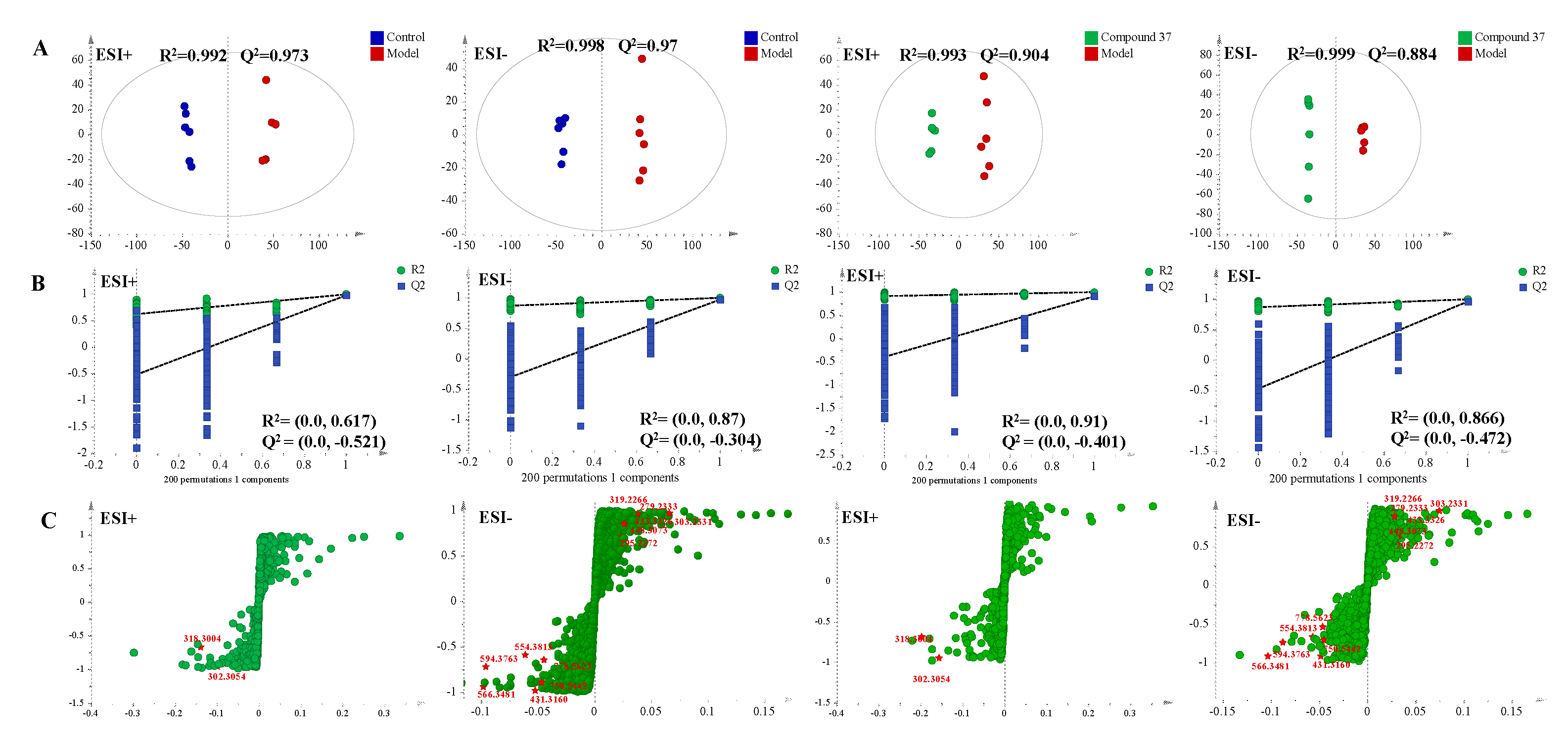
2.4.2. Metabolomics profile analysis of compound 37 intervention in A549/Tax cells
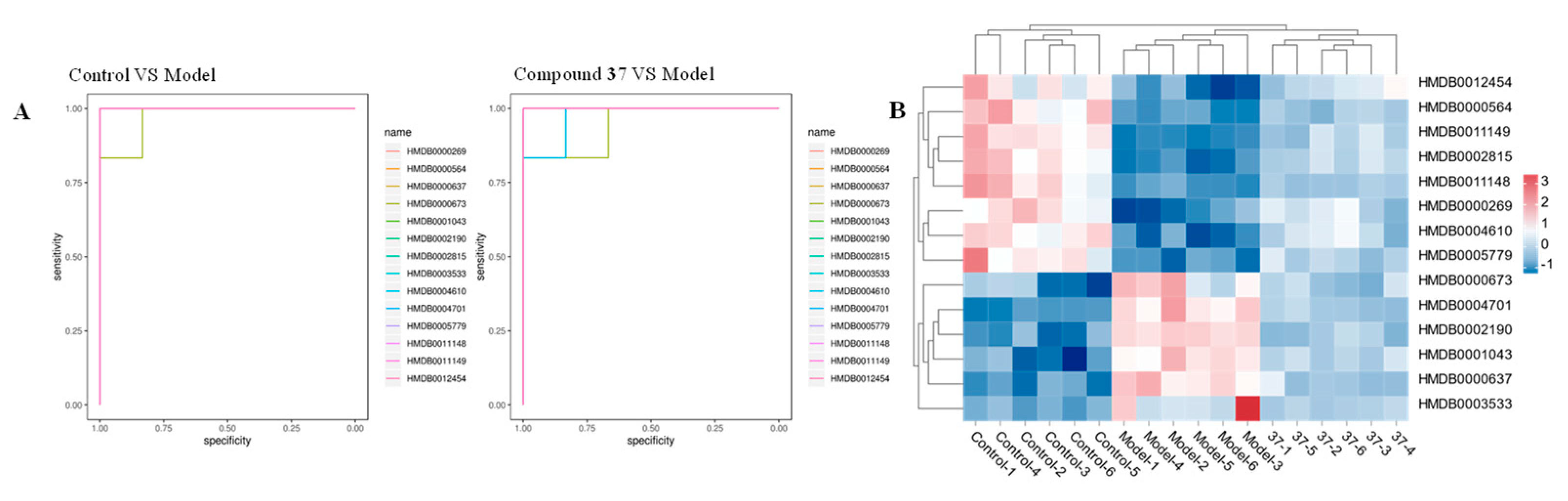
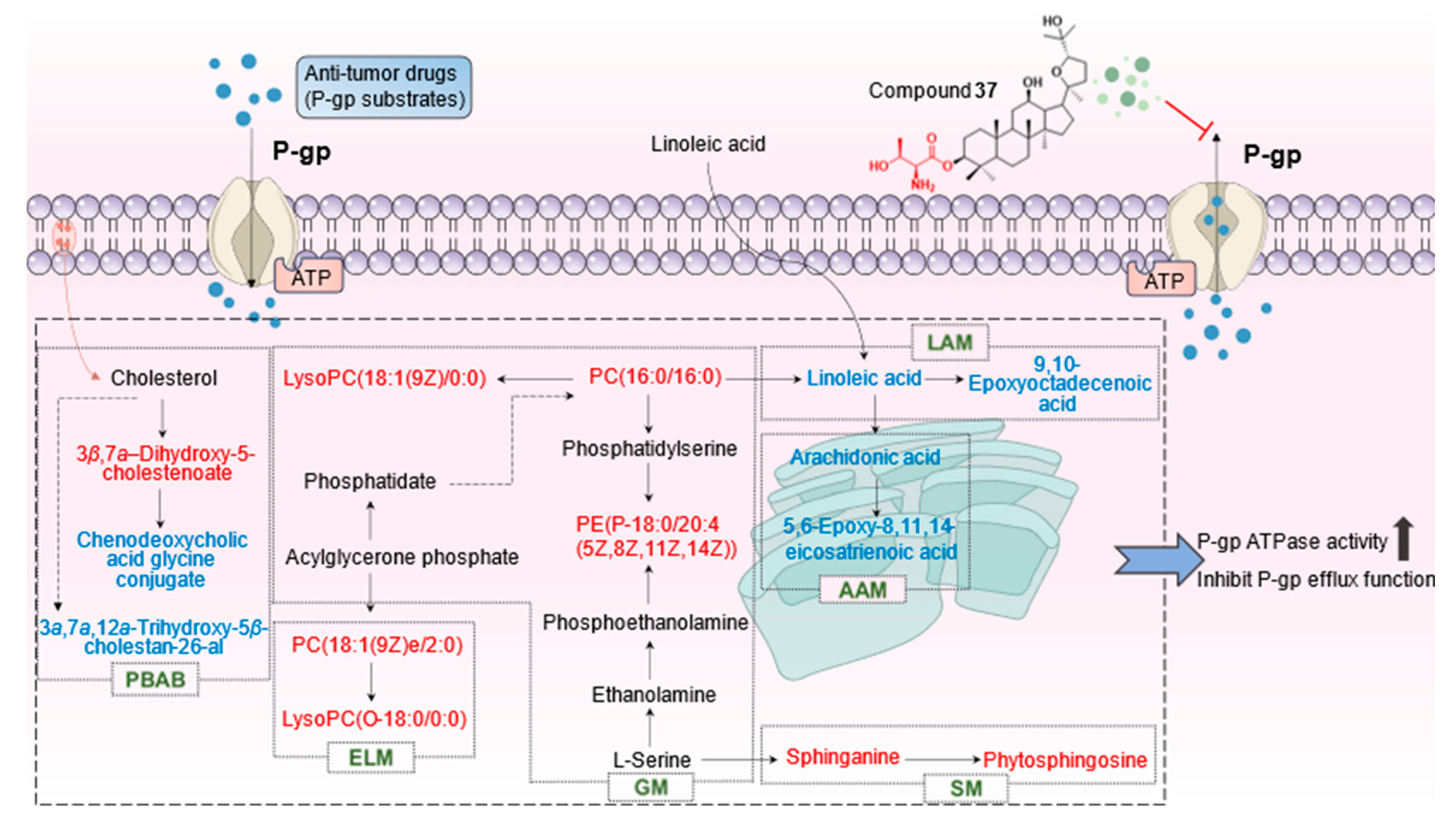
2.4.3. Identification of the differential metabolites and metabolic pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. General
4.1.2. Synthesis of Pyxinol and 24S-Pyxinol derivatives
4.1.2.1. Synthesis of known derivatives
4.1.2.2. Synthesis of new derivatives
4.2. Cell culture
4.3. Cytotoxicity and MDR reversal assay
4.4. Western blot assay
4.5. Intracellular Rh123 accumulation assay
4.6. ATPase activity assay
4.7. Molecular docking
4.8. Cellular metabolomics
4.8.1. Preparation of cell samples
4.8.1.1. Cell culture
4.8.1.2. Cell quenching and metabolites extraction
4.8.2. UPLC-Q/TOF-MS conditions
4.8.3. Validation of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS
4.8.4. Metabolomic data analysis
4.9. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kibria, G.; Hatakeyama, H.; Harashima, H. Cancer multidrug resistance: Mechanisms involved and strategies for circumvention using a drug delivery system. Archive pharmacal research 2014, 37, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.M.; Halt, W.N. Pharmacology of drugs that alter multidrug resistance in cancer. Pharmacological reviews 1990, 42, 155–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Jaitak, V. Natural products as multidrug resistance modulators in cancer. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2019, 176, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 3233–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal-Yandim, M.; Adan-Gokbulut, A.; Baran, Y. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance and its reversal in cancer. Critical reviews in biotechnology 2016, 36, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogman, K.; Peyer, A.K.; TöRöK, M.; Küsters, E.; Drewe, J. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and P-glycoprotein modulation. British journal of pharmacology 2001, 132, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, H. Importance of P-glycoprotein for drug-drug interactions. Handbook of experimental pharmacology 2011, 201, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. The modulation of ABC transportermediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resistant Update 2015, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Bharate, S.B. Natural alkaloids as P-gp inhibitors for multidrug resistance reversal in cancer. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2017, 138, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Ajazuddin; Bhattacharya, S. Role of natural P-gp inhibitor in the effective delivery for chemotherapeutic agents. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology 2023, 149, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.; Fortuna, A.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C. The essential oil from the fruits of Peucedanum oreoselinum (L.) Moench (Apiaceae) as a natural source of P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Journal of herbal medicine 2021, 29, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sotto, A.; Irannejad, H.; Eufemi, M.; Mancinelli, R.; Abete, L.; Mammola, C.L.; Altieri, F.; Mazzanti, G.; Di Giacomo, S. Potentiation of Low-Dose Doxorubicin Cytotoxicity by Affecting P-Glycoprotein through Caryophyllane Sesquiterpenes in HepG2 Cells: An in Vitro and in Silico Study. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Dong, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Li, R. Lathyrane diterpenes from Euphorbia lathyris and the potential mechanism to reverse the multi-drug resistance in HepG2/ADR cells. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 121, 109663. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.D.; Ramalhete, C.; Spengler, G.; Mulhovo, S.; Molnar, J.; Ferreira, M.U. Triterpenes from Momordica balsamina (African pumpkin): ABCB1 inhibition and synergistic interaction with doxorubicin in resistant cancer cells. Phytochemistry 2022, 203, 113354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zha, B.S.; Niu, F.; Lu, M.; Hao, G.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, G. Cellular pharmacokinetic mechanisms of adriamycin resistance and its modulation by 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 in MCF-7/Adr cells. British journal of pharmacology 2012, 165, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; Yu, T.F. In vitro study on the reversal of multidrug resistance (MDR) in HL60/VCR cell line with Ginsenoside-Rb1. Journal-of-radioimmunology 2005, 18, 362–365. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Gong, Q.; Chen, T.; Lv, J.; Feng, Z.; Liu, P.; Deng, Z. Treatment with 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 reverses multidrug resistance in A549/DDP xenograft tumors. Oncology letters 2018, 15, 4376–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Zhou, F.; Niu, F.; Lu, M.; Wu, X.L.; Sun, J.G.; Wang, G.J. Stereoselective regulations of P-glycoprotein by ginsenoside Rh2 epimers and the potential mechanisms from the view of pharmacokinetics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhong, D. Identification of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol metabolites in human liver microsomes and human hepatocytes. Drug metabolism and disposition 2011, 39, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Meng, Q.; Liu, W. Stereoselective property of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol ocotillol type epimers affects its absorption and also the inhibition of P-glycoprotein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, M.; Liu, S.; Zou, Z.; Ren, R.; Zhang, C.; Xie, H.; Sun, J.; Qi, Y.; Qu, Q.; Song, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, H. Pyxinol bearing amino acid residues: Easily achievable and promising modulators of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2021, 216, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Yang, G.; Guo, M.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Yang, Q.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Qi, J.G.; Tian, J.; Wang, H. Design, synthesis, and discovery of ocotillol-type amide derivatives as orally available modulators of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2019, 161, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Cao, Y.C.; Xu, J.Y.; Ma, C.; Meng, Q.G.; Bi, Y. Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of 3-Substituted Ocotillol-Type Derivatives. Molecules 2018, 23, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Bi, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Xie, X.; Meng, Q.; Lewis, P.J.; Xu, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel ocotillol-type triterpenoid derivatives as antibacterial agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2013, 68, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Studies on Synthesis,Anti-tumor Activity and Pharmacokineticsof Amino Acid Ester Derivatives of Ginsengenins. Doctor’s Thesis, Jilin University,, Jilin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.R. The Mechanism Study of Chinese Medicine on Reversing Multidrug Resistance and Metastasis to Breast Cancer. Doctor’s Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.Z.; Zhou, F.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, G.J. Research advance on P-glycoprotein inhibitors and the structure-activity relationship. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2010, 15, 814–820. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, E.H.; Lee, M.B.; Seo, D.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Gupta, K. Sphingosine induces apoptosis and down-regulation of MYCN in PAX3-FOXO1-positive alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells irrespective of TP53 mutation. Anticancer research 2018, 38, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M. P-glycoprotein ATPase activity requires lipids to activate a switch at the first transmission interface. Biochemical & biophysical research communications 2016, 472, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.Y. The tumor-promoting effect and mechanism of glycerophospholipid-related gene LPCAT1 in endometrial cancer. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Fu, S.Z.; Tan, L.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Zhou, B.S.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, C.X.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and Anti-Hepatocarcinoma Effect of Amino Acid Derivatives of Pyxinol and Ocotillol. Molecules 2021, 26, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, C.; Ding, F.; Zou, H.; Liu, C. Ganoderic Acid A Enhances Tumor Suppression Function of Oxaliplatin via Inducing the Cytotoxicity of T Cells. Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry 2023, 23, 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Guan, D.; Lei, L.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, G.; Yan, C.; Zhai, R.; Tian, J.; Bi, Y.; Fu, F.; Wang, H. H6, a novel hederagenin derivative, reverses multidrug resistance in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology & Applied Pharmacology 2018, 341, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.F.; Si, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C.Z.; Lin, H.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, J.P.; Li, P.Y.; Li, Z. Comprehensive phytochemical profiling of American ginseng in Jilin province of China based on ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of mass spectrometry: JMS 2021, 56, e4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, Y.Z.; Pan, H.; Hsu, A.C.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, J.P.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, F. Protective Effect of Ocotillol, the Derivate of Ocotillol-Type Saponins in Panax Genus, against Acetic Acid-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats Based on Untargeted Metabolomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compounds | Cell survival (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | A549/Tax | |||||
| 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | |
| Pyxinol | 97.63±4.89 | 89.47±5.54 | 82.17±6.05 | 105.42±5.67 | 97.05±5.73 | 91.22±3.06 |
| 24S-Pyxinol | 92.70±5.27 | 87.05±5.66 | 78.50±8.70 | 98.84±2.33 | 94.62±3.50 | 89.37±3.76 |
| 1 | 99.02±1.83 | 97.40±3.11 | 91.21±3.21 | 96.72±1.99 | 92.83±2.37 | 86.21±3.18 |
| 2 | 95.71±4.21 | 94.64±2.90 | 89.25±2.02 | 93.47±3.14 | 90.02±2.66 | 87.13±2.54 |
| 3 | 98.04±2.29 | 90.84±7.09 | 84.05±3.11 | 96.34±4.17 | 83.36±2.68 | 78.66±3.27 |
| 4 | 98.39±1.06 | 95.20±1.42 | 84.17±7.46 | 93.27±2.75 | 89.41±4.50 | 76.64±4.00 |
| 5 | 98.12±4.50 | 94.59±2.60 | 89.19±2.01 | 94.84±1.67 | 89.44±2.19 | 84.81±4.63 |
| 6 | 103.08±1.79 | 92.58±4.28 | 86.13±3.19 | 95.77±2.27 | 85.00±3.15 | 83.50±2.75 |
| 7 | 97.34±2.34 | 93.98±0.54 | 85.43±3.28 | 94.98±2.10 | 86.94±2.35 | 82.40±1.95 |
| 8 | 98.84±3.53 | 92.13±1.24 | 79.90±0.67 | 98.19±2.84 | 88.77±2.11 | 83.77±3.32 |
| 9 | 96.63±2.21 | 88.36±2.40 | 71.72±2.35 | 93.09±3.08 | 88.78±2.61 | 84.80±3.36 |
| 10 | 99.18±4.02 | 93.55±5.17 | 78.96±6.94 | 90.79±3.07 | 86.10±3.54 | 79.51±3.74 |
| 11 | 98.26±1.14 | 93.46±1.50 | 88.01±1.53 | 90.90±3.22 | 83.62±1.88 | 79.99±2.40 |
| 12 | 95.12±1.49 | 89.81±2.51 | 83.51±0.74 | 91.85±3.07 | 88.56±3.21 | 83.47±2.24 |
| 13 | 95.16±1.04 | 88.69±7.60 | 78.35±4.88 | 92.37±2.84 | 87.71±2.03 | 80.07±1.75 |
| 14 | 93.68±5.64 | 86.85±4.10 | 79.49±3.58 | 96.55±1.90 | 88.68±2.25 | 85.13±2.03 |
| 15 | 97.11±2.16 | 86.90±2.17 | 82.25±1.63 | 92.67±3.20 | 86.51±2.85 | 77.28±2.18 |
| 16 | 94.05±4.09 | 86.13±7.23 | 78.35±4.88 | 98.90±3.00 | 97.10±2.23 | 85.29±1.84 |
| 17 | 96.43±2.37 | 85.23±3.41 | 81.82±1.40 | 91.83±2.66 | 82.58±1.54 | 79.01±2.96 |
| 18 | 97.61±3.47 | 86.61±3.01 | 80.07±2.85 | 89.99±5.51 | 90.86±3.57 | 89.43±2.41 |
| 19 | 100.41±4.20 | 95.45±2.70 | 87.31±6.78 | 102.54±4.60 | 101.40±2.86 | 97.27±3.28 |
| 20 | 99.54±0.88 | 93.31±0.68 | 86.66±3.89 | 93.81±2.52 | 91.52±3.02 | 90.99±3.28 |
| 21 | 97.97±1.63 | 90.03±1.25 | 81.79±1.82 | 94.34±2.32 | 89.55±2.86 | 87.74±2.64 |
| 22 | 97.17±1.97 | 87.95±2.32 | 82.13±1.82 | 96.13±3.07 | 92.92±3.55 | 87.65±2.21 |
| 23 | 98.84±0.58 | 90.34±2.52 | 83.32±3.21 | 96.82±2.90 | 94.06±4.96 | 86.48±3.61 |
| 24 | 96.30±1.28 | 94.41±0.97 | 88.01±1.33 | 95.39±4.82 | 91.60±2.93 | 86.55±2.11 |
| 25 | 95.90±0.62 | 93.18±1.17 | 88.02±0.76 | 98.35±3.45 | 92.36±2.72 | 82.68±3.97 |
| 26 | 95.37±2.27 | 87.87±4.03 | 80.53±1.96 | 98.69±1.56 | 94.58±2.33 | 87.27±3.61 |
| 27 | 92.65±5.37 | 84.46±2.26 | 79.33±2.10 | 95.66±2.91 | 90.85±2.70 | 88.32±3.95 |
| 28 | 96.22±5.22 | 85.74±4.19 | 75.90±2.53 | 98.47±0.81 | 90.54±2.47 | 84.98±2.61 |
| 29 | 96.95±1.92 | 93.22±0.77 | 87.79±3.30 | 98.07±2.23 | 90.56±3.56 | 86.09±3.21 |
| 30 | 97.11±0.82 | 94.28±1.93 | 90.17±0.79 | 91.53±3.27 | 87.41±2.70 | 79.79±2.68 |
| 31 | 96.41±1.81 | 89.01±1.89 | 82.82±1.82 | 97.12±2.81 | 93.42±1.09 | 89.71±3.58 |
| 32 | 96.53±1.82 | 92.49±1.10 | 88.62±2.34 | 97.84±3.54 | 90.05±5.72 | 83.62±5.38 |
| 33 | 98.15±0.59 | 95.65±0.78 | 87.24±0.60 | 99.19±3.35 | 93.88±4.51 | 87.81±8.25 |
| 34 | 96.81±1.87 | 86.87±5.00 | 77.26±3.53 | 96.98±3.60 | 92.45±3.26 | 86.91±4.33 |
| 35 | 98.33±0.97 | 91.76±1.65 | 81.65±3.17 | 97.09±2.80 | 89.30±2.44 | 86.56±2.87 |
| 36 | 94.96±0.42 | 93.13±0.45 | 83.51±2.49 | 96.69±3.18 | 88.96±3.75 | 81.74±3.58 |
| 37 | 102.88±6.35 | 95.97±5.76 | 82.54±3.00 | 97.81±1.99 | 92.90±3.78 | 78.65±3.33 |
| 38 | 98.12±1.20 | 90.51±2.10 | 80.91±0.84 | 96.01±2.84 | 88.56±3.26 | 78.40±3.95 |
| 39 | 106.69±3.24 | 97.15±3.15 | 79.76±2.72 | 98.63±2.79 | 89.67±2.61 | 87.97±2.27 |
| 40 | 96.92±1.37 | 87.97±0.71 | 79.74±0.34 | 94.46±2.84 | 92.67±2.00 | 87.85±4.80 |
| Vrp | 93.84±6.01 | 86.32±6.78 | 68.15±3.76 | 98.14±2.88 | 97.42±4.82 | 91.46±2.89 |
| Compounds | Cell survival (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | MCF-7/ADR | |||||
| 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | |
| Pyxinol | 100.62±3.02 | 97.43±2.67 | 94.42±3.19 | 99.18±3.10 | 93.12±1.53 | 88.49±2.76 |
| 24S-Pyxinol | 101.30±4.35 | 94.55±5.79 | 94.80±4.43 | 101.33±2.08 | 97.26±3.03 | 88.70±6.75 |
| 1 | 98.79±1.37 | 93.77±3.60 | 84.73±1.41 | 97.46±1.04 | 93.02±2.86 | 84.63±2.90 |
| 2 | 97.24±2.78 | 86.89±3.80 | 76.34±3.78 | 98.64±2.11 | 90.08±2.92 | 85.34±2.22 |
| 3 | 99.25±4.05 | 92.66±3.20 | 85.82±3.30 | 96.83±1.80 | 93.18±2.30 | 87.58±2.80 |
| 4 | 96.85±3.03 | 89.45±2.95 | 82.92±2.23 | 97.91±1.05 | 95.57±2.81 | 89.56±3.37 |
| 5 | 96.88±2.85 | 88.90±3.00 | 84.47±3.81 | 98.87±1.58 | 93.42±1.88 | 90.93±1.94 |
| 6 | 95.68±3.93 | 87.85±2.88 | 81.53±2.35 | 98.55±1.68 | 91.89±1.72 | 88.02±2.15 |
| 7 | 92.29±3.38 | 88.64±4.82 | 82.38±2.57 | 93.85±3.32 | 88.84±2.31 | 79.88±3.07 |
| 8 | 91.25±3.06 | 87.03±2.88 | 84.59±2.73 | 94.67±4.54 | 94.54±2.93 | 84.61±1.24 |
| 9 | 96.90±3.11 | 95.01±3.14 | 86.13±3.38 | 96.89±3.17 | 90.86±2.24 | 85.58±1.67 |
| 10 | 92.30±2.06 | 87.41±1.83 | 82.23±2.78 | 98.70±0.84 | 95.48±3.51 | 86.42±2.73 |
| 11 | 95.97±2.10 | 90.93±2.07 | 79.89±5.63 | 94.38±1.86 | 88.10±3.02 | 79.99±2.33 |
| 12 | 96.82±1.64 | 92.01±2.60 | 85.34±2.67 | 95.09±2.03 | 90.53±2.99 | 84.11±2.15 |
| 13 | 95.93±2.75 | 93.51±2.22 | 88.63±2.12 | 96.19±3.55 | 88.52±2.43 | 83.73±1.53 |
| 14 | 95.95±3.47 | 88.65±2.49 | 84.16±3.55 | 95.24±4.43 | 86.66±2.77 | 78.36±2.25 |
| 15 | 95.21±2.57 | 87.14±2.49 | 83.07±1.81 | 97.98±3.40 | 90.65±2.41 | 78.76±2.52 |
| 16 | 91.87±3.08 | 87.97±3.82 | 83.74±3.26 | 99.54±2.47 | 95.34±3.50 | 87.66±2.65 |
| 17 | 94.00±4.03 | 90.64±2.41 | 80.64±2.62 | 96.27±3.37 | 85.33±3.62 | 82.93±5.05 |
| 18 | 91.80±3.86 | 87.20±2.91 | 78.21±4.40 | 98.49±2.85 | 88.98±3.06 | 82.77±2.62 |
| 19 | 89.65±5.91 | 89.58±6.23 | 84.02±2.03 | 96.28±6.25 | 91.52±6.30 | 84.41±4.20 |
| 20 | 98.55±0.94 | 94.50±2.08 | 89.17±1.06 | 97.44±2.44 | 89.52±2.82 | 81.54±2.57 |
| 21 | 97.47±3.48 | 86.18±3.70 | 81.21±5.81 | 97.68±3.49 | 91.92±2.12 | 84.56±1.71 |
| 22 | 96.23±2.75 | 87.75±4.73 | 82.39±3.44 | 101.21±2.63 | 96.10±3.46 | 89.93±1.42 |
| 23 | 93.47±2.90 | 85.35±2.16 | 82.33±4.02 | 95.51±3.44 | 88.04±2.96 | 81.95±2.55 |
| 24 | 95.67±1.97 | 89.47±1.32 | 82.23±3.20 | 95.44±2.06 | 88.39±2.63 | 82.87±2.45 |
| 25 | 96.40±2.46 | 87.49±4.95 | 84.60±2.31 | 96.40±1.97 | 91.52±1.96 | 85.27±1.98 |
| 26 | 98.93±1.65 | 92.48±1.41 | 88.56±3.25 | 91.45±2.44 | 85.34±2.49 | 80.55±3.13 |
| 27 | 90.40±4.72 | 82.43±4.59 | 78.08±3.82 | 93.68±4.41 | 87.21±2.30 | 85.11±2.81 |
| 28 | 94.52±5.13 | 91.93±4.83 | 82.71±2.52 | 94.13±4.59 | 87.58±1.01 | 86.38±3.45 |
| 29 | 90.27±4.34 | 85.40±3.58 | 79.87±1.67 | 95.27±3.81 | 88.04±1.60 | 79.57±2.72 |
| 30 | 90.37±3.80 | 85.99±3.88 | 81.79±2.67 | 97.99±1.93 | 89.27±3.75 | 80.21±4.03 |
| 31 | 96.59±2.46 | 91.92±3.00 | 82.49±2.64 | 98.70±1.16 | 94.84±2.89 | 87.76±1.24 |
| 32 | 93.84±5.82 | 88.27±4.22 | 84.16±5.41 | 95.54±2.45 | 87.80±2.39 | 82.86±3.33 |
| 33 | 95.81±2.44 | 89.11±1.76 | 85.86±0.77 | 100.87±3.16 | 90.28±2.85 | 83.38±3.14 |
| 34 | 96.82±2.29 | 94.39±2.27 | 87.39±2.54 | 98.05±1.12 | 92.44±2.75 | 83.24±4.17 |
| 35 | 90.45±9.36 | 85.40±4.88 | 81.12±5.47 | 92.87±3.84 | 88.71±4.08 | 79.15±1.90 |
| 36 | 96.17±2.21 | 86.13±3.13 | 79.43±2.28 | 97.55±2.01 | 87.74±3.93 | 85.54±2.91 |
| 37 | 93.54±2.04 | 92.86±6.15 | 79.21±2.67 | 98.65±1.99 | 94.40±5.10 | 87.30±2.48 |
| 38 | 96.95±2.06 | 88.94±2.80 | 78.65±3.60 | 96.70±2.22 | 91.47±1.81 | 84.56±2.62 |
| 39 | 99.47±4.38 | 97.41±3.10 | 93.90±5.84 | 96.82±3.22 | 97.30±4.29 | 92.09±6.24 |
| 40 | 97.82±1.38 | 93.87±2.33 | 81.10±3.09 | 94.17±2.05 | 85.66±2.37 | 76.43±3.27 |
| Vrp | 99.02±2.65 | 96.24±3.01 | 90.21±3.53 | 98.98±6.77 | 88.81±2.65 | 84.32±3.96 |
| Compounds | Cell survival (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT-8 | HCT-8/VCR | |||||
| 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | 5 μM | 10 μM | 20 μM | |
| Pyxinol | 96.09±3.96 | 91.74±4.38 | 89.50±2.62 | 98.69±0.47 | 94.04±1.34 | 88.30±2.48 |
| 24S-Pyxinol | 96.09±3.55 | 90.82±2.65 | 89.01±3.18 | 100.72±2.44 | 95.24±1.33 | 87.09±4.36 |
| 1 | 93.48±4.95 | 88.37±6.15 | 82.39±5.90 | 96.96±1.13 | 89.52±3.13 | 84.88±1.85 |
| 2 | 93.25±4.05 | 86.72±6.11 | 79.84±8.48 | 96.43±2.03 | 90.82±0.97 | 86.72±2.25 |
| 3 | 94.43±3.19 | 92.47±0.71 | 86.72±1.54 | 97.13±1.21 | 92.25±3.18 | 88.19±2.15 |
| 4 | 96.66±1.14 | 89.80±1.95 | 89.36±1.74 | 97.88±1.11 | 92.54±1.52 | 88.60±1.57 |
| 5 | 94.50±2.88 | 87.19±3.57 | 83.87±1.84 | 97.35±1.67 | 91.11±1.57 | 87.51±2.59 |
| 6 | 94.38±1.58 | 90.97±2.88 | 86.17±4.26 | 93.09±2.91 | 88.03±1.49 | 79.97±1.06 |
| 7 | 95.59±5.08 | 94.03±2.39 | 87.51±0.87 | 93.82±2.75 | 92.51±2.66 | 89.31±3.20 |
| 8 | 95.79±1.29 | 86.70±2.38 | 76.03±4.69 | 97.00±2.85 | 93.40±1.64 | 89.41±2.47 |
| 9 | 94.55±3.56 | 91.03±3.30 | 87.70±6.26 | 98.41±0.91 | 97.50±1.71 | 87.96±1.54 |
| 10 | 94.37±3.01 | 89.12±2.77 | 84.10±4.46 | 94.90±3.31 | 88.86±3.69 | 80.11±3.47 |
| 11 | 91.85±3.05 | 86.83±2.63 | 76.27±2.46 | 95.46±2.91 | 86.73±1.87 | 84.14±1.80 |
| 12 | 91.15±4.98 | 90.49±3.35 | 82.87±2.48 | 96.03±2.51 | 87.66±2.48 | 84.44±3.02 |
| 13 | 97.19±2.40 | 91.65±6.80 | 87.96±2.93 | 94.17±1.72 | 91.77±2.27 | 87.52±1.79 |
| 14 | 99.77±2.08 | 90.76±4.02 | 80.81±3.07 | 94.69±2.63 | 89.63±5.34 | 86.24±3.17 |
| 15 | 94.10±1.68 | 85.79±2.54 | 82.04±1.87 | 95.06±2.11 | 91.58±1.26 | 88.19±2.40 |
| 16 | 92.92±2.32 | 85.17±2.77 | 81.77±2.97 | 98.78±1.05 | 93.02±1.81 | 87.43±2.97 |
| 17 | 93.13±2.57 | 85.82±1.57 | 77.99±3.83 | 99.71±3.13 | 93.78±2.00 | 89.40±2.58 |
| 18 | 96.54±2.09 | 87.83±3.04 | 83.94±4.39 | 96.83±2.92 | 91.16±3.63 | 81.58±3.99 |
| 19 | 93.14±4.54 | 91.17±2.41 | 86.50±2.25 | 94.32±2.89 | 91.49±3.61 | 86.98±2.12 |
| 20 | 92.99±2.93 | 86.91±2.30 | 82.81±2.16 | 96.81±3.36 | 91.87±2.68 | 88.31±2.75 |
| 21 | 91.01±2.39 | 86.22±3.44 | 83.90±2.04 | 97.96±2.74 | 91.60±2.52 | 90.33±3.73 |
| 22 | 95.15±2.43 | 94.17±1.95 | 86.74±2.86 | 98.55±1.60 | 94.36±2.73 | 87.07±1.98 |
| 23 | 94.10±2.30 | 87.38±2.21 | 79.90±2.13 | 98.45±1.01 | 91.58±2.74 | 87.45±2.28 |
| 24 | 97.23±1.88 | 89.22±1.62 | 76.79±5.23 | 93.39±2.13 | 89.15±3.05 | 82.61±2.60 |
| 25 | 96.23±2.29 | 92.97±1.51 | 86.52±1.95 | 96.43±2.74 | 94.91±1.93 | 92.03±1.06 |
| 26 | 95.57±2.31 | 92.98±2.68 | 87.26±1.44 | 96.01±2.96 | 94.47±6.82 | 86.00±4.44 |
| 27 | 96.54±1.39 | 86.82±1.91 | 84.29±3.00 | 96.58±3.55 | 95.82±4.88 | 88.67±8.42 |
| 28 | 95.82±2.04 | 87.58±2.94 | 80.78±1.61 | 97.15±2.13 | 91.74±3.07 | 87.33±2.27 |
| 29 | 91.46±2.70 | 89.74±3.06 | 82.96±2.04 | 98.60±2.92 | 90.70±1.56 | 87.37±2.72 |
| 30 | 96.26±3.35 | 89.38±3.70 | 79.28±2.76 | 98.19±1.57 | 91.09±2.49 | 82.42±3.06 |
| 31 | 96.34±1.91 | 88.07±2.57 | 76.67±5.49 | 98.47±1.36 | 90.59±1.51 | 85.70±2.39 |
| 32 | 98.00±0.91 | 95.08±2.99 | 85.34±0.78 | 95.35±2.81 | 89.50±2.52 | 85.28±1.86 |
| 33 | 94.68±2.05 | 91.22±1.10 | 82.31±0.98 | 92.16±4.16 | 87.47±2.48 | 79.36±3.40 |
| 34 | 95.40±2.27 | 86.49±5.22 | 80.59±3.57 | 93.59±3.40 | 86.36±1.46 | 79.71±1.75 |
| 35 | 93.27±9.55 | 80.68±4.00 | 75.99±3.40 | 94.00±2.02 | 91.57±1.74 | 86.40±3.45 |
| 36 | 94.36±1.10 | 87.97±3.35 | 80.54±1.78 | 94.20±2.41 | 89.95±3.57 | 83.21±1.55 |
| 37 | 93.17±3.54 | 82.56±6.98 | 74.26±6.62 | 99.19±1.90 | 91.18±3.77 | 86.10±2.41 |
| 38 | 96.82±2.59 | 84.77±2.93 | 79.39±3.20 | 93.42±3.92 | 86.09±1.65 | 80.44±2.18 |
| 39 | 95.28±2.74 | 88.69±2.84 | 80.74±2.29 | 98.86±2.46 | 94.96±1.01 | 88.19±2.13 |
| 40 | 96.19±1.88 | 93.71±0.96 | 84.74±2.50 | 93.76±3.21 | 85.60±2.49 | 80.90±2.60 |
| Vrp | 96.53±1.18 | 91.96±3.22 | 87.22±5.07 | 99.96±1.96 | 96.72±2.62 | 84.65±3.50 |
| Cell lines | Tax | ADR | VCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | RI | IC50 (μM) | RI | IC50 (μM) | RI | |
| A549 | 2.64±0.46 | 130.81 | 7.38±0.23 | 33.61 | 3.37±0.53 | 19.27 |
| A549/Tax | 345.33±12.33 | 248.07±8.00 | 64.95±1.14 | |||
| MCF-7 | 8.07±3.12 | 16.71 | 2.91±0.29 | 75.12 | 5.86±0.11 | 5.99 |
| MCF-7/ADR | 134.87±10.93 | 218.60±37.01 | 35.10±2.19 | |||
| HCT-8 | 8.28±0.47 | 4.03 | 4.37±0.11 | 49.92 | 0.24±0.07 | 225.21 |
| HCT-8/VCR | 33.37±1.91 | 218.17±23.86 | 54.05±5.45 | |||
| Compounds | A549/Tax | MCF-7/ADR | HCT-8/VCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (Tax) | RF | IC50 (ADR) | RF | IC50 (VCR) | RF | |
| Pyxinol | 100.20±6.60 | 3.45 | 106.46±4.07 | 2.05 | 43.23±1.71 | 5.21 |
| 24S-Pyxinol | 111.83±5.13 | 3.09 | 105.89±20.51 | 2.06 | 26.90±0.70 | 8.37 |
| 1 | 33.97±0.32 | 10.17 | 69.70±11.46 | 3.14 | 30.38±2.15 | 7.41 |
| 2 | 46.64±1.79 | 7.40 | 69.84±1.48 | 3.13 | 25.50±1.48 | 8.83 |
| 3 | 31.61±0.94 | 10.92 | 63.41±2.17 | 3.45 | 20.29±1.48 | 11.10 |
| 4 | 53.34±2.90 | 6.47 | 94.47±4.96 | 2.31 | 46.64±1.99 | 4.83 |
| 5 | 37.55±0.38 | 9.20 | 68.81±2.38 | 3.18 | 35.38±9.87 | 6.37 |
| 6 | 69.74±11.19 | 4.95 | 183.50±12.32 | 1.19 | 62.06±10.47 | 3.63 |
| 7 | 67.94±6.71 | 5.08 | 71.58±2.50 | 3.05 | 50.03±4.01 | 4.50 |
| 8 | 54.81±2.73 | 6.30 | 47.14±2.22 | 4.64 | 33.19±5.15 | 6.79 |
| 9 | 75.37±3.01 | 4.58 | 114.93±3.91 | 1.90 | 111.35±27.33 | 2.02 |
| 10 | 75.63±1.52 | 4.57 | 80.74±1.41 | 2.71 | 52.72±3.46 | 4.27 |
| 11 | 44.60±1.71 | 7.74 | 77.87±1.77 | 2.81 | 32.25±1.20 | 6.98 |
| 12 | 49.60±3.61 | 6.96 | 202.60±7.95 | 1.08 | 48.26±2.12 | 4.67 |
| 13 | 38.41±3.12 | 8.99 | 100.53±2.83 | 2.17 | 39.81±2.52 | 5.66 |
| 14 | 51.52±1.50 | 6.70 | 47.38±3.79 | 4.61 | 24.29±2.88 | 9.27 |
| 15 | 59.55±6.15 | 5.80 | 162.50±1.73 | 1.35 | 39.86±4.46 | 5.65 |
| 16 | 32.21±3.54 | 10.72 | 46.35±0.87 | 4.72 | 27.15±0.39 | 8.30 |
| 17 | 31.44±1.89 | 10.98 | 51.78±4.94 | 4.22 | 20.56±0.82 | 10.95 |
| 18 | 32.25±6.13 | 10.71 | 44.74±3.36 | 4.89 | 25.00±0.98 | 9.01 |
| 19 | 62.97±18.64 | 5.48 | 62.49±3.01 | 3.50 | 40.61±3.85 | 5.55 |
| 20 | 52.00±6.80 | 6.64 | 72.11±7.09 | 3.03 | 27.90±1.26 | 8.07 |
| 21 | 41.56±5.94 | 8.31 | 79.71±7.14 | 2.74 | 32.21±3.51 | 7.00 |
| 22 | 118.73±1.59 | 2.91 | 52.36±5.93 | 4.17 | 22.77±1.65 | 9.89 |
| 23 | 66.56±4.50 | 5.19 | 49.60±3.23 | 4.41 | 47.23±4.14 | 4.77 |
| 24 | 92.98±4.75 | 3.71 | 272.23±36.41 | 0.80 | 42.74±1.45 | 5.27 |
| 25 | 69.83±5.41 | 4.95 | 42.13±1.31 | 5.19 | 19.42±1.08 | 11.60 |
| 26 | 76.34±3.70 | 4.52 | 74.74±9.80 | 2.92 | 44.36±4.39 | 5.08 |
| 27 | 107.03±7.71 | 3.23 | 103.20±6.91 | 2.12 | 24.06±0.99 | 9.36 |
| 28 | 94.69±12.11 | 3.65 | 114.57±2.48 | 1.91 | 26.33±2.87 | 8.55 |
| 29 | 73.83±9.12 | 4.68 | 59.72±3.77 | 3.66 | 59.52±13.63 | 3.78 |
| 30 | 125.47±2.80 | 2.75 | 80.79±3.10 | 2.71 | 37.56±1.45 | 6.00 |
| 31 | 78.26±7.40 | 4.41 | 124.27±4.52 | 1.76 | 32.43±1.21 | 6.94 |
| 32 | 120.17±13.70 | 2.87 | 149.47±13.16 | 1.46 | 111.56±18.75 | 2.02 |
| 33 | 86.07±1.47 | 4.01 | 106.11±16.45 | 2.06 | 75.26±8.69 | 2.99 |
| 34 | 64.60±5.68 | 5.35 | 43.98±4.08 | 4.97 | 25.87±0.33 | 8.71 |
| 35 | 87.28±3.44 | 3.96 | 154.90±9.99 | 1.41 | 50.18±0.14 | 4.49 |
| 36 | 60.33±4.29 | 5.72 | 48.09±1.89 | 4.55 | 25.64±2.86 | 8.78 |
| 37 | 22.55±1.79 | 15.31 | 35.33±0.95 | 6.19 | 16.14±0.45 | 13.95 |
| 38 | 54.80±15.83 | 6.30 | 58.95±10.72 | 3.71 | 21.99±1.95 | 10.24 |
| 39 | 71.14±2.15 | 4.85 | 66.51±1.37 | 3.29 | 37.04±2.79 | 6.08 |
| 40 | 87.31±7.19 | 3.96 | 100.64±2.72 | 2.17 | 25.99±4.77 | 8.67 |
| Vrp | 17.98±0.47 | 19.21 | 34.27±1.45 | 6.38 | 26.79±0.67 | 8.41 |
| Experiments | ESI+ mode | ESI- mode | ||
| Peak intensity | Retention time | Peak intensity | Retention time | |
| System stability | 1.35~2.89 | 0.29~2.51 | 1.23~2.86 | 0.22~2.69 |
| Precision | 0.57~2.35 | 0.16~2.47 | 1.16~2.74 | 0.28~2.16 |
| Reproducibility | 1.78~2.52 | 0.17~2.88 | 1.17~2.63 | 0.18~2.58 |
| Sample stabililty | 0.45~2.65 | 0.21~2.54 | 0.71~2.62 | 0.53~2.24 |
| NO. | RT(min) | VIP | Formula | Biomarkers | Measured乐mass(Da) | Mass error (ppm) | Adducts | HMDB ID | Pathway | Change trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/C | D/M | ||||||||||
| 1# | 12.91 | 1.54 | C26H43NO5 | Chenodeoxycholic acid glycine conjugate | 448.3073 | 2.23 | M-H | 0000637 | PBAB | ↑ | ↓ |
| 2* | 13.15 | 8.44 | C18H39NO3 | Phytosphingosine | 318.3004 | -1.26 | M+H | 0004610 | SM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 3* | 15.49 | 2.67 | C18H39NO2 | Sphinganine | 302.3054 | -1.65 | M+H | 0000269 | SM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 4# | 17.68 | 1.10 | C20H32O3 | 5,6-Epoxy-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid | 319.2266 | -2.19 | M-H | 0002190 | AAM | ↑ | ↓ |
| 5# | 18.75 | 15.34 | C26H52NO7P | LysoPC(18:1(9Z)/0:0) | 566.3481 | 4.06 | M-H+FA | 0002815 | GM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 6# | 19.86 | 1.49 | C18H32O3 | 9,10-Epoxyoctadecenoic acid | 295.2272 | -0.34 | M-H | 0004701 | LAM | ↑ | ↓ |
| 7# | 21.14 | 2.06 | C28H56NO7P | PC(18:1(9Z)e/2:0) | 594.3763 | -1.35 | M-H+FA | 0011148 | ELM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 8# | 21.4 | 1.66 | C26H56NO6P | LysoPC(O-18:0/0:0) | 554.3813 | -1.62 | M-H+FA | 0011149 | ELM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 9* | 22.98 | 9.16 | C20H32O2 | Arachidonic acid | 303.2331 | 2.31 | M-H | 0001043 | AAM | ↑ | ↓ |
| 10# | 23.13 | 3.02 | C27H46O4 | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-al | 433.3326 | 1.85 | M-H | 0003533 | PBAB | ↑ | ↓ |
| 11* | 23.28 | 4.12 | C18H32O2 | Linoleic acid | 279.2333 | 3.22 | M-H | 0000673 | LAM | ↑ | ↓ |
| 12# | 25.8 | 1.79 | C40H80NO8P | PC(16:0/16:0) | 778.5623 | 3.21 | M-H+FA | 0000564 | LAM,GM | ↓ | ↑ |
| 13# | 26.49 | 1.32 | C27H44O4 | 3β,7a -Dihydroxy-5-cholestenoate | 431.316 | -0.23 | M-H | 0012454 | PBAB | ↓ | ↑ |
| 14# | 26.84 | 1.38 | C43H78NO7P | PE(P-18:0/20:4 (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | 750.5442 | 0.53 | M-H | 0005779 | GM | ↓ | ↑ |
| HMDB | Model group vs Control group | Compound 37 group vs Model group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | p | AUC | p | |
| HMDB 0000637 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0004610 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.972 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0000269 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 0.972 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0002190 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0002815 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0004701 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0011148 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0011149 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0001043 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0003533 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 1.000 | 0.01 |
| HMDB 0000673 | 0.972 | 0.01 | 0.944 | 0.01 |
| HMDB 0000564 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0012454 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| HMDB 0005779 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 |
| NO. | Pathway Name | Match status | P | -log(P) | Holm p | FDR | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linoleic acid metabolism | 3/5 | 5.81E-06 | 5.2355 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 1.0000 |
| 2 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 3/36 | 0.0035 | 2.4540 | 0.2918 | 0.0984 | 0.2163 |
| 3 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 3/36 | 0.0035 | 2.4540 | 0.2918 | 0.0984 | 0.3337 |
| 4 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 3/46 | 0.0071 | 2.1498 | 0.5737 | 0.1487 | 0.0442 |
| 5 | Ether lipid metabolism | 2/20 | 0.0131 | 1.8820 | 1.0000 | 0.2020 | 0.2289 |
| 6 | Sphingolipid metabolism | 2/21 | 0.01443 | 1.8408 | 1.0000 | 0.2020 | 0.1582 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





