Submitted:
29 September 2023
Posted:
30 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
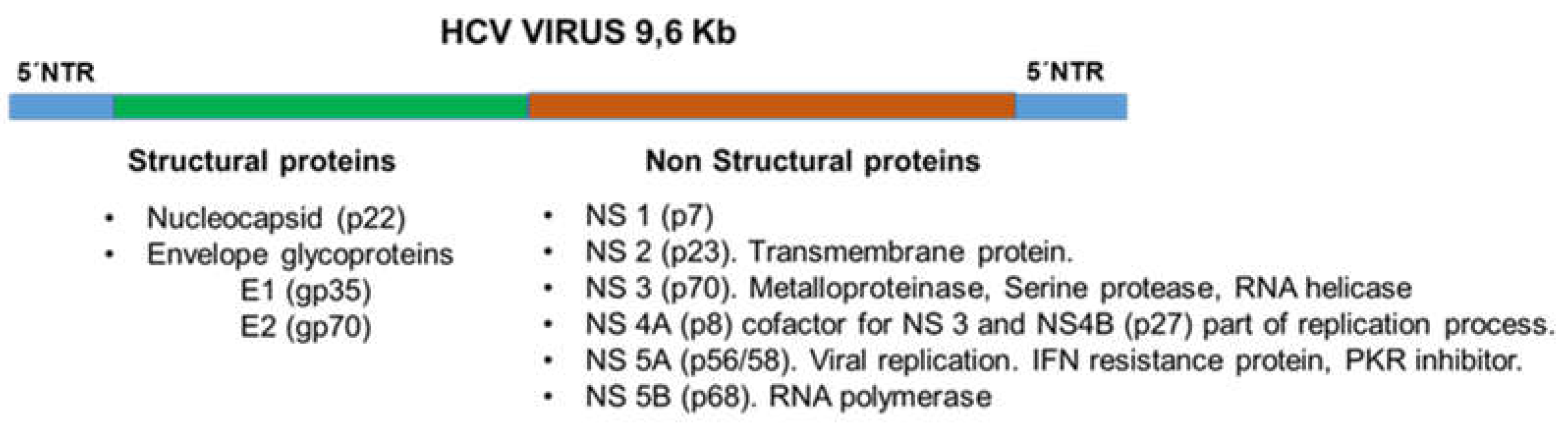
1. Introduction
2. Interferon α and Ribavirin
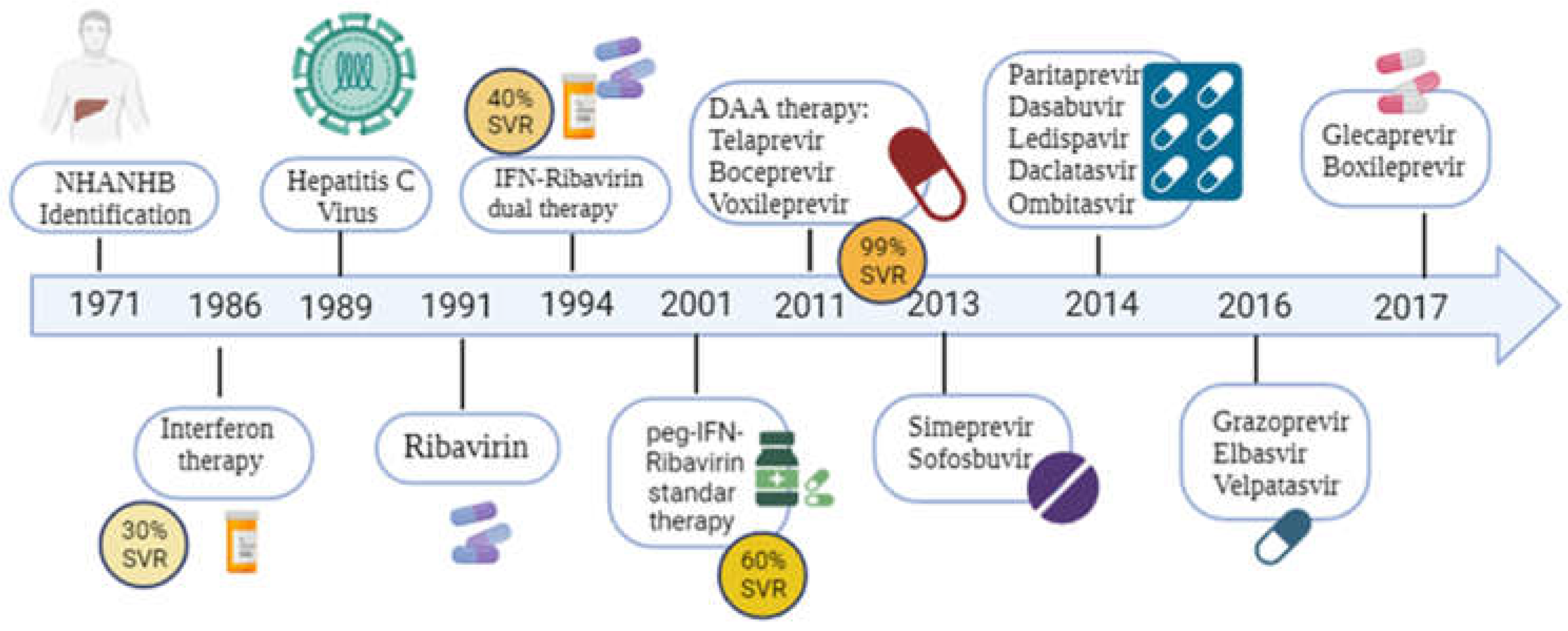
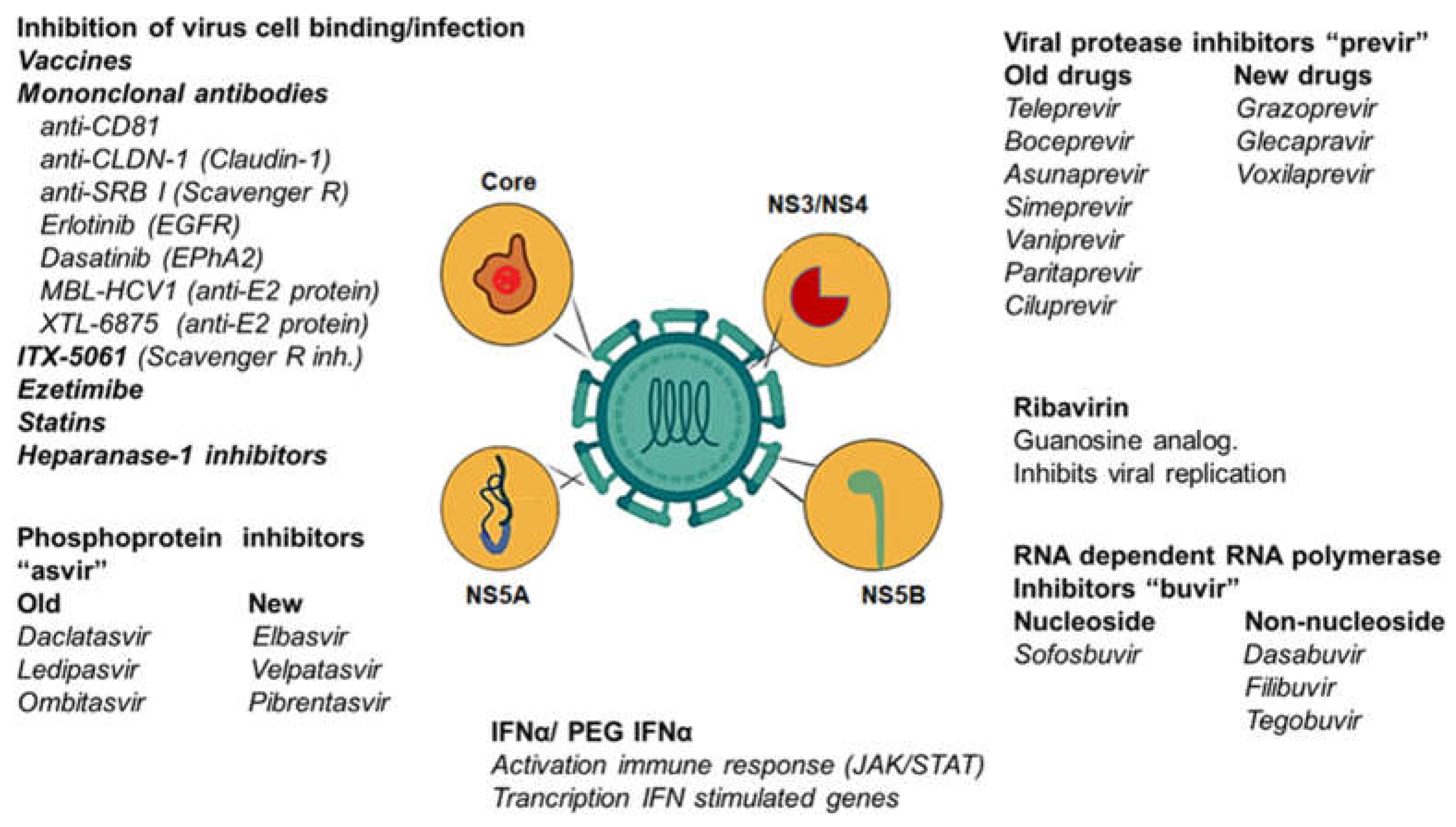
3. Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAA)
3.1. NS3/4-Protease Inhibitors
3.1.1. Telaprevir and Boceprevir
3.1.2. Asunaprevir
3.1.3. Simeprevir
3.1.4. Paritaprevir
3.1.5. Grazoprevir
3.1.6. Glecaprevir and Voxileprevir
3.2. NS5B Polymerase Inhibitors
3.2.1. Nucleotide: Sofosbuvir
3.2.2. Non-nucleotide: Dasabuvir
3.3. NS5A Polymerase Inhibitors
3.3.1. Ledipasvir (LDV)
3.3.2. Daclatasvir (DCV).
3.3.3. Ombitasvir
3.3.4. Elbasvir
3.3.5. Velpatasvir and Pibrentasvir
4. Treatment in Coinfection (HCV/HIV, HBV/HCV, HBV/HCV/HIV).
5. Treatment of Pregnant Women, Vertical Transmission. Pediatric Care.
6. Host Genetics, Infection and Response to HCV Treatments
7. Resistance Associated Substitutions
8. Other strategies
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghany, M.G.; Lok, A.S.F.; Dienstag, J.L.; Feinstone, S.M.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Jake Liang, T.; Seeff, L.B.; Cohen, D.E.; Bezerra, J.A.; Chung, R.T. The 2020 Nobel Prize for Medicine or Physiology for the Discovery of Hepatitis C Virus: A Triumph of Curiosity and Persistence. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Kao, J.-H. Acute hepatitis C virus infection: clinical update and remaining challenges. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, J. ; Cosset FL Virology and cell biology of the hepatitis C virus life cycle An update. J Hepatol. 2014;61(1):S3-13.
- Lee, M.-H.; Yang, H.-I.; Yuan, Y.; L'Italien, G.; Chen, C.-J. Epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis C virus infection. . 2014, 20, 9270–9280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alazard-Dany, N.; Denolly, S.; Boson, B.; Cosset, F.-L. Overview of HCV Life Cycle with a Special Focus on Current and Possible Future Antiviral Targets. Viruses 2019, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, H.; Tyagi, I.; Koirala, J. Hepatitis C. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL) 2023 Mar 26.: StatPearls Publishing. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430897/.
- Hofmeister, M.G.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Barker, L.K.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Barranco, M.A.; Hall, E.W.; Edlin, B.R.; Mermin, J.; Ward, J.W.; Ryerson, A.B. Estimating Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the United States, 2013-2016. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, C.; Silvestri, C.; Voller, F. Update on Hepatitis C Epidemiology: Unaware and Untreated Infected Population Could Be the Key to Elimination. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fénéant, L.; Levy, S.; Cocquerel, L. CD81 and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection. Viruses 2014, 6, 535–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhaus, S.; Deest, M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Stanke, F.; Heckl, D.; Costa, R.; Schambach, A.; Manns, M.P.; Berg, T.; Vondran, F.W.; et al. Scavenger receptor class B member 1 ( SCARB1 ) variants modulate hepatitis C virus replication cycle and viral load. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, L.; Turner, J.R.; Coyne, C.B.; Wang, T. Tight Junction Proteins Claudin-1 and Occludin Control Hepatitis C Virus Entry and Are Downregulated during Infection To Prevent Superinfection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupberger, J.; Zeisel, M.B.; Xiao, F.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Zona, L.; Davis, C.; Mee, C.J.; Turek, M.; Gorke, S.; et al. EGFR and EphA2 are host factors for hepatitis C virus entry and possible targets for antiviral therapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, B.; Banerjee, A.; Meyer, K.; Ray, R. Hepatitis C virus E1 envelope glycoprotein interacts with apolipoproteins in facilitating entry into hepatocytes. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, M.; Dubuisson, J. Interplay between hepatitis C virus and lipid metabolism during virus entry and assembly. Biochimie 2017, 141, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K. NPC1L1 identified as a novel HCV entry factor. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 124–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Martinez, P.; Séron, K.; Luo, G.; Allain, F.; Dubuisson, J.; Belouzard, S. Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus Interaction with Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3846–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, R.; Deibis, L.; De Sanctis, J.B.; Bianco, N.E.; Toro, F. Interaction of immune complexes isolated from hepatitis C virus-infected individuals with human cell lines. Med Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 194, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumori, A.; Shimada, M.; Obata, T. Leukocytes are the major target of hepatitis C virus infection: Possible mechanism of multiorgan involvement including the heart. Glob. Hear. 2010, 5, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, F.; Conesa, A.; Garcia, A.; Deibis, L.; Bianco, N.E. ; De Sanctis, JB HCV RNA sequences in eosinophils of chronic HCV-infected patients. J Med. 1999; 30(3-4):279-288.
- Corado, J.; Toro, F.; Rivera, H.; Bianco, N.E.; Deibis, L. ; De Sanctis, JB Impairment of natural killer (NK) cytotoxic activity in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997;109(3):451-457.
- Dustin, L.; Bartolini, B.; Capobianchi, M.; Pistello, M. Hepatitis C virus: life cycle in cells, infection and host response, and analysis of molecular markers influencing the outcome of infection and response to therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak M, Caraballo Cortes K, Demkow U, Radkowski M. Spontaneous Elimination of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1039:45-54.
- Chigbu, D.I.; Loonawat, R.; Sehgal, M.; Patel, D.; Jain, P. Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host–Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence. Cells 2019, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axley, P.; Ahmed, Z.; Ravi, S.; Singal, A.K. Hepatitis C Virus and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, J.J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanism of action of interferon and ribavirin in treatment of hepatitis C. Nature 2005, 436, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Kim, S.S.; Yeung, E.; Kamegaya, Y.; Blackard, J.T.; Kim, K.A.; Holtzman, M.J.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein Blocks Interferon Signaling by Interaction with the STAT1 SH2 Domain. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9226–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.J. ; He, SF; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Bian, ZQ; Qi, ZT Inhibition of STAT Pathway Impairs Anti-Hepatitis C Virus Effect of Interferon Alpha. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016; 40(1-2):77-90.
- Yamauchi, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Chihara, K.; Honjoh, C.; Kato, Y.; Yoshiki, H.; Hotta, H.; Sada, K. STAT1 is essential for the inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by interferon-λ but not by interferon-α. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, S.J.; Khabar, K.S.A.; Rezeiq, M.; Gretch, D.R. Elevated Levels of Interleukin-8 in Serum Are Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Resistance to Interferon Therapy. J. Virol. 2007, 75, 6209–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.R.; Shi, S.T.; Romano, P.R.; Barber, G.N.; Lai, M.M.C. Inhibition of the Interferon- Inducible Protein Kinase PKR by HCV E2 Protein. Science 1999, 285, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, T.; Michiels, T. Inhibition of PKR by Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 757238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xin, X.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Shen, C. Myxovirus resistance protein A inhibits hepatitis C virus replication through JAK-STAT pathway activation. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbaglia, M.N.; Harris, J.M.; Smirnov, A.; Burlone, M.E.; Rigamonti, C.; Pirisi, M.; Minisini, R.; Magri, A. 17β-Oestradiol Protects from Hepatitis C Virus Infection through Induction of Type I Interferon. Viruses 2022, 14, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, E.; Ramamurthy, N.; Ansari, M.A.; E Harrer, C.; Barnes, E.; Klenerman, P.; Hcv, S. Defining the key intrahepatic gene networks in HCV infection driven by sex. Gut 2023, 72, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, J.D.; Salinas, E.; Grakoui, A. Immune system control of hepatitis C virus infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 46, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, L.B. Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in Chronic HCV Infection. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corado, J.A.; Toro, F.I.; Baroja, M.L.; Bianco, N.E.; Machado, I.V.; Shapiro; Gershtein; Elias; Zuckerman; Salman; et al. CD3- and CD28-Activating Pathways in HCV Infection. Viral Immunol. 1994, 7, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auma, A.W.N.; Shive, C.L. ; Kostadinova, L:; Anthony, D.D. Variable Normalisation of Naïve CD4+ Lymphopenia and Markers of Monocyte and T Cell Activation over the Course of Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Viruses. 2021;14(1):50.
- Ferrufino, R.Q.; Rodrigues, C.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Gleison, D.; Yapura, S.; de Matos, M.L.M.; Witkin, S.S.; Mendes-Correa, M.C. Factors Associated with Spontaneous Clearance of Recently Acquired Hepatitis C Virus among HIV-Positive Men in Brazil. Viruses 2023, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.-C.; Sung, P.S.; Park, S.-H. Immune responses and immunopathology in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marascio, N.; Torti, C.; Liberto, M.C.; Focá, A. Update on different aspects of HCV variability: focus on NS5B polymerase. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14 (Suppl 5), S1.
- Echeverría, N.; Moratorio, G.; Cristina, J.; Moreno, P. Hepatitis C virus genetic variability and evolution. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(6):831-845.
- Gower, E.; Estes, C.; Blach, S.; Razavi-Shearer, K.; Razavi, H. Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S45–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzziello, A.; Marigliano, S.; Loquercio, G.; Cozzolino, A.; Cacciapuoti, C. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: An up-date of the distribution and circulation of hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7824–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobran, S.T.; Ancuta, P.; Shoukry, N.H. A Tale of Two Viruses: Immunological Insights Into HCV/HIV Coinfection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Araf, Y.; Ahmad, R.; Kattel, P.; Sah, G.S.; Rahaman, T.I.; Sadiea, R.Z.; Sultana, S.; Islam, S.; Zheng, C.; et al. Insights Into the Coinfections of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis B Virus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis C Virus, and Hepatitis B Virus-Hepatitis C Virus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 780887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, D.; Deutsch, M. The spectrum of HBV/HCV coinfection: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, viral interactions and management. Ann gastroenterol. 2015; 28(2), 221–228.
- Wieland, S.; Makowska, Z.; Campana, B.; Calabrese, D.; Dill, M.T.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V.; Heim, M.H. Simultaneous detection of hepatitis C virus and interferon stimulated gene expression in infected human liver. Hepatology 2013, 59, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkongolo, S.; Mahamed, D.; Kuipery, A.; Vasquez, J.D.S.; Kim, S.C.; Mehrotra, A.; Patel, A.; Hu, C.; McGilvray, I.; Feld, J.J.; et al. Longitudinal liver sampling in patients with chronic hepatitis B starting antiviral therapy reveals hepatotoxic CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e158903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, C.; Beach, N.M.; Gallego, I.; Soria, M.E.; Quer, J.; Esteban, J.I.; Rice, C.; Domingo, E.; Sheldon, J. Response of Hepatitis C Virus to Long-Term Passage in the Presence of Alpha Interferon: Multiple Mutations and a Common Phenotype. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7593–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, J. M.; Alejo, A.; Martín, V.; Sevilla, N. Viral pathogen-induced mechanisms to antagonise mammalian interferon (IFN) signalling pathway. CMLS 2021, 78(4), 1423–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertowska, P.; Smolak, K.; Mertowski, S.; Grywalska, E. Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Mullen, K.D.; Jones, D.B.; Rustgi, V.; Di Bisceglie, A.; Peters, M.; Waggoner, J.G.; Park, Y.; Jones, E.A. Treatment of Chronic Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis with Recombinant Human Alpha Interferon. New Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeckel, E.; Cornberg, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Santantonio, T.; Mayer, J.; Zankel, M.; Pastore, G.; Dietrich, M.; Trautwein, C.; Manns, M.P. Treatment of Acute Hepatitis C with Interferon Alfa-2b. New Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghemo, A. , Rumi, M. G., & Colombo, M. (2010). Pegylated interferons alpha2a and alpha2b in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 7(9), 485–494.
- McHutchison, J.G.; Gordon, S.C.; Schiff, E.R.; Shiffman, M.L.; Lee, W.M.; Rustgi, V.K.; Goodman, Z.D.; Ling, M.-H.; Cort, S.; Albrecht, J.K. Interferon Alfa-2b Alone or in Combination with Ribavirin as Initial Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis C. New Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Marcellin, P.; Lee, S.S.; Niederau, C.; Minuk, G.S.; Ideo, G.; Bain, V.; Heathcote, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Trepo, C.; et al. Randomised trial of interferon α2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon α2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. Lancet 1998, 352, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Ghany, M.G.; Liang, T.J. The Application and Mechanism of Action of Ribavirin in Therapy of Hepatitis C. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2012, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, M.W.; Shiffman, M.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Smith, C.; Marinos, G.; Gonçales, F.L.J.; Häussinger, D.; Diago, M.; Carosi, G.; Dhumeaux, D.; et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. New Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziyannis, S. J. , Sette, H., Jr, Morgan, T. R., Balan, V., Diago, M., Marcellin, P., Ramadori, G., Bodenheimer, H., Jr, Bernstein, D., Rizzetto, M., Zeuzem, S., Pockros, P. J., Lin, A., Ackrill, A. M., & PEGASYS International Study Group. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomised study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med 2004; 140(5), 346–355.
- Ascione, A.; De Luca, M.; Tartaglione, M.T.; Lampasi, F.; Di Costanzo, G.G.; Lanza, A.G.; Picciotto, F.P.; Marino–Marsilia, G.; Fontanella, L.; Leandro, G. Peginterferon Alfa-2a Plus Ribavirin Is More Effective Than Peginterferon Alfa-2b Plus Ribavirin for Treating Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, M.G.; Aghemo, A.; Prati, G.M.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Donato, M.F. , Soffredini, R., et al. Randomised Study of Peginterferon-α2a Plus Ribavirin vs Peginterferon-α2b Plus Ribavirin in Chronic Hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(1):108-15.
- Alavian, S.M.; Behnava, B.; Tabatabaei, S.V. The Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Peginterferon Alpha-2a vs. 2b for the Treatment of Chronic HCV Infection: A Meta-Analysis. 2010, 10, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Kanda, T.; Miyamura, T.; Wu, S.; Nakamoto, S.; Yokosuka, O. Alanine Aminotransferase Elevation during Peginterferon Alpha-2a or Alpha-2b plus Ribavirin Treatment. Int. J. Med Sci. 2013, 10, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, M.P.; McHutchison, J.G.; Gordon, S.C.; Rustgi, V.K.; Shiffman, M.; Reindollar, R.; Goodman, Z.D.; Koury, K.; Ling, M.-H.; Albrecht, J.K. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 2001, 358, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-H.; Chang, M.-L.; Huang, T.-J.; Yeh, C.-T.; Chiu, W.-N.; Chiang, M.-S.; Chen, M.-Y. Comparison of Compliance and Efficacy of Pegylated Interferon α-2a and α-2b in Adults with Chronic Hepatitis C. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.H.; Dieterich, D.T.; Pockros, P.J.; Schiff, E.R.; Shiffman, M.L.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Wright, T.; Younossi, Z.; Goon, B.L.; Tang, K.; et al. Epoetin alfa maintains ribavirin dose in HCV-infected patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Thiel, D.H.; Faruki, H.; Friedlander, L.; Fagiuoli, S.; Caraceni, P.; Molloy, P.J.; Kania, R.J.; I Wright, H. Combination treatment of advanced HCV associated liver disease with interferon and G-CSF. . 1995, 42, 907–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.H.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Giannini, E.G.; Chen, P.; Han, K.; Mohsin, A.; Rodriguez–Torres, M.; Rugina, S.; Bakulin, I.; Lawitz, E.; et al. Eltrombopag Increases Platelet Numbers in Thrombocytopenic Patients With HCV Infection and Cirrhosis, Allowing for Effective Antiviral Therapy. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 442–452.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Leary, J.G.; Davis, G.L. Review: Hepatitis C virus replication and potential targets for direct-acting agents. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Basimi, P.; Agi, E.; Bolhassani, A. Pharmaceutical Approaches for Treatment of Hepatitis C virus. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4304–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bernal, L.; Soti, V. Hepatitis C Virus: Insights Into Its History, Treatment, Challenges, and Future Directions. Cureus 2023, 15, e43924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, C.; Tomei, L.; De Francesco, R. Both NS3 and NS4A are required for proteolytic processing of hepatitis C virus nonstructural proteins. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata K, Neufeldt CJ, Bartenschlager R. Hepatitis C Virus Replication. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. a: 2020;10(3), 2020.
- Kiang, T.K.L.; Wilby, K.J.; Ensom, M.H.H. Telaprevir: Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Drug–Drug Interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.H.; Gordon, L.A.; Fung, H.B. Boceprevir: A Protease Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hepatitis C. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S. C. , Reddy, K. R., Jacobson, I. M., Poordad, F., Bronowicki, J. P., Bacon, B., Buti, M., Hu, K. Q., Pedicone, L. D., Burroughs, M., Brass, C. A., Albrecht, J. K., & Lawitz, E. J. (2014). Boceprevir plus peginterferon α-2b/ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C genotype 1: impact of baseline viral load on sustained virologic response. Journal of clinical gastroenterology, 48(5), 435–443.
- Akamatsu, N.; Sugawara, Y.; Kokudo, N. Asunaprevir (BMS-650032) for the treatment of hepatitis C virus. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2015, 13, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, M. , Ueno, T., Shiozaki, T., Li, H., & Garimella, T. (2019). Safety Exposure-Response Analysis for Daclatasvir, Asunaprevir, and Beclabuvir Combinations in HCV-Infected Subjects. Journal of clinical pharmacology, 59(4), 557–565.
- Cao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Xia, W.; Wu, H.; Wei, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, X. Resistance-associated mutations to HCV protease inhibitors naturally pre-existed in HIV/HCV coinfected, treatment-naïve patients. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2016, 40, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs-Kean, L.M.; Hand, E.O. Simeprevir and Sofosbuvir for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulkowski, M.S.; Vargas, H.E.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Kuo, A.; Reddy, K.R.; Lim, J.K.; Morelli, G.; Darling, J.M.; Feld, J.J.; Brown, R.S.; et al. Effectiveness of Simeprevir Plus Sofosbuvir, With or Without Ribavirin, in Real-World Patients With HCV Genotype 1 Infection. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibanov, O.M.; Gale, S.E.; Santevecchi, B. Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir and Dasabuvir Tablets for Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir Plus Dasabuvir: A Review in Chronic HCV Genotype 1 Infection. Drugs 2015, 75, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salama, Z.T.; Deeks, E.D. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir: A Review in Chronic HCV Genotypes 1 and 4. Drugs 2017, 77, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Abushouk, A.I.; Menshawy, A.; Attia, A.; Mohamed, A.; Negida, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Meta-Analysis of Grazoprevir plus Elbasvir for Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb Y., N. (2017). Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir: First Global Approval. Drugs, 77(16), 1797–1804.
- Chahine, E.B.; Kelley, D.; Childs-Kean, L.M. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir: A Pan-Genotypic Direct-Acting Antiviral Combination for Hepatitis C. Ann. Pharmacother. 2018, 52, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puoti, M. , Panzeri, C., Rossotti, R., & Baiguera, C. (2014). Efficacy of sofosbuvir-based therapies in HIV/HCV infected patients and persons who inject drugs. Digestive and liver disease : official journal of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver, 46 Suppl 5, S206–S211.
- Smith, M. A. , Chan, J., & Mohammad, R. A. (2015). Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir: interferon-/ribavirin-free regimen for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. The Annals of pharmacotherapy, 49(3), 343–350.
- Devan, P.; Tiong, K.L.A.; Neo, J.E.; Mohan, B.P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Tam, Y.C.S.; Coppola, N.; Preda, C.M.; Wong, Y.J. Treatment Outcomes of Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir in Direct-Acting Antiviral-Experienced Hepatitis C Virus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, I.; Buonomo, A.R.; Borgia, G. Dasabuvir: A Non-Nucleoside Inhibitor of NS5B for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2014, 9, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamal, N.; Andreone, P. Working together to tackle HCV infection: ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir combination. Drugs Today 2015, 51, 303–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.R.; Zha, J.; Khatri, A.; Dutta, S.; Menon, R.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Dasabuvir. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, S.; Gamal, N.; Andreone, P. NS5A inhibitors for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 24, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlière, M.; Adhoute, X.; Ansaldi, C.; Oules, V.; Benali, S.; Portal, I.; Castellani, P.; Halfon, P. Sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir in combination for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belperio, P.S.; Shahoumian, T.A.; Loomis, T.P.; Mole, L.A.; Backus, L.I. Real-world effectiveness of daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir and velpatasvir/sofosbuvir in hepatitis C genotype 2 and 3. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, N.; Kamel, A.M.; Cordie, A.; Esmat, G. Daclatasvir as a hepatitis C infection treatment option: an up-to-date evaluation. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2023, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.G.; Aghemo, A.; Chen, P.-J.; Dan, Y.Y.; Gane, E.; Gani, R.; Gish, R.G.; Guan, R.; Jia, J.D.; Lim, K.; et al. Management of hepatitis C virus infection in the Asia-Pacific region: an update. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, Y.; Eley, T.; Fura, A.; Li, W.; Bertz, R.J.; Garimella, T. Daclatasvir: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 911–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badri, P.S.; Shuster, D.L.; Dutta, S.; Menon, R.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ombitasvir. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-J.; Huang, C.-F.; Yu, M.-L. Elbasvir and grazoprevir for the treatment of hepatitis C. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2021, 19, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahser, F.C.; Bystol, K.; Curry, S.; McMonagle, P.; Xia, E.; Ingravallo, P.; Chase, R.; Liu, R.; Black, T.; Hazuda, D.; et al. The Combination of Grazoprevir, a Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor, and Elbasvir, an HCV NS5A Inhibitor, Demonstrates a High Genetic Barrier to Resistance in HCV Genotype 1a Replicons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2954–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.-D.; Fu, X.; He, Y.-Q.; Li, C.-Y.; Guo, M.; Qiao, M. Safety and efficacy of sofosbuvir-velpatasvir: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e31183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghany MG, Morgan TR; AASLD-IDSA Hepatitis C Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C Guidance 2019 Update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases-Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Hepatology. 2020 Feb;71(2):686-721.
- Pearlman, B.; Perrys, M.; Hinds, A. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir for Previous Treatment Failures With Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reau, N. , Cheng, W. H., Shao, Q., Marx, S. E., Brooks, H., & Martinez, A. (2023). Real-World Effectiveness of 8-Week Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir in Treatment-Naïve, Compensated Cirrhotic HCV Patients. Infectious diseases and therapy, 12(7), 1849–1860.
- Solomon, S.S.; Wagner-Cardoso, S.; Smeaton, L.; A Sowah, L.; Wimbish, C.; Robbins, G.; Brates, I.; Scello, C.; Son, A.; Avihingsanon, A.; et al. A minimal monitoring approach for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection (ACTG A5360 [MINMON]): a phase 4, open-label, single-arm trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Aronsohn, A.; Price, J.; Re, V.L.; Heald, J.; Demisashi, G.; Durzy, E.; Davis-Owino, A.; Tynes, S. ; Aasld-Idsa Hcv Guidance the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases–Infectious Diseases Society of America HCV Guidance Panel Hepatitis C Guidance 2023 Update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases– Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavilia, M.G.; Wu, G.Y. HBV-HCV Coinfection: Viral Interactions, Management, and Viral Reactivation. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisaturo, M.; Macera, M.; Alessio, L.; Calò, F.; Coppola, N. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Reactivation Following Pharmacological Eradication of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). Viruses 2019, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, Q.; Sumrin, A.; Iqbal, M.; Younas, S.; Hussain, N.; Mahnoor, M.; Wajid, A. Hepatitis C virus/Hepatitis B virus coinfection: Current prospectives. Antivir. Ther. 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairoli, V.; Valle-Millares, D.; Terrón-Orellano, M.C.; Luque, D.; Ryan, P.; Dominguez, L.; Martín-Carbonero, L.; Santos, I.D.L.; De Matteo, E.; Ameigeiras, B.; et al. MicroRNA signature from extracellular vesicles of HCV/HIV co-infected individuals differs from HCV mono-infected. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, R.; Karampoor, S.; Korotkova, N.L. The emerging role of miRNA-122 in infectious diseases: Mechanisms and potential biomarkers. Pathol. - Res. Pr. 2023, 249, 154725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benova L, Mohamoud YA, Calvert C, Abu-Raddad LJ. Vertical Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59(6):765-73.
- US Preventive Services Task Force, Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, Barry MJ, Cabana M, et al. Screening for Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Adolescents and Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 10 de marzo de 2020;323(10):970.
- Schillie, S.; Wester, C.; Osborne, M.; Wesolowski, L.; Ryerson, A.B. CDC Recommendations for Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults — United States, 2020. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2020, 69, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C Guidance 2018 Update: AASLD-IDSA Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, T.; Lange, M.; Sperling, R.; Dieterich, D. Treatment of Women With Hepatitis C Diagnosed in Pregnancy: a Co-Located Treatment Approach. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1454–1456.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdAllah M, Alboraie M, Abdel-Razek W, et al. Pregnancy outcome of anti-HCV direct-acting antivirals: real-life data from an Egyptian cohort. Liver Int 2021; 41:1494–7.
- Hughes, B.L.; Page, C.M.; Kuller, J.A. Hepatitis C in pregnancy: screening, treatment, and management. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, B2–B12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Chappell, C.; Scarsi, K.K.; Kirby, B.J.; Suri, V.; Gaggar, A.; Bogen, D.L.; Macio, I.S.; A Meyn, L.; E Bunge, K.; E Krans, E.; et al. Ledipasvir plus sofosbuvir in pregnant women with hepatitis C virus infection: a phase 1 pharmacokinetic study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e200–e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitnun, A. The management of infants, children, and youth at risk for hepatitis C virus infection. Paediatr. Child Heal. 2021, 26, 440–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.B.; Rosenthal, P.; Murray, K.F.; Honegger, J.R.; Hardikar, W.; Hague, R.; Mittal, N.; Massetto, B.; Brainard, D.M.; Hsueh, C.; et al. Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir for 12 Weeks in Children 3 to <6 Years Old With Chronic Hepatitis C. Hepatology 2020, 71, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, V.; Seetharaman, K.; Anushree, N. Treatment of hepatitis C in children and adolescents: how far have we reached? World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Peralta, R.P.; Wirth, S.; Squires, R.H.; Mutschler, F.; Lang, T.; Pawlowska, M.; Sluzewski, W.; Majda-Stanislawska, E.; Fischler, B.; Balistreri, W.F.; et al. Elbasvir/grazoprevir in children aged 3–18 years with chronic HCV genotype 1 or 4 infection: a pharmacokinetic modeling study. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0031–e0031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Heck, J.; Wu, C.-K.; Huang, X.; Chew, K.W.; Tong, M.; Federman, N.; Ritz, B.; A Arah, O.; Li, C.-Y.; Yu, F.; et al. Cohort study of familial viral hepatitis and risks of paediatric cancers. Leuk. Res. 2021, 51, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, H.H.; Fazeli, P.; Ali-Hassanzadeh, M.; Bemani, P.; Kabelitz, D.; Kalantar, K. Correlation between IL-28 polymorphism and spontaneous clearance in HCV patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Fellay, J.; Thompson, A.J.; Simon, J.S.; Shianna, K.V.; Urban, T.J.; Heinzen, E.L.; Qiu, P.; Bertelsen, A.H.; Muir, A.J.; et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009, 461, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; Watanabe, T.; Tanaka, Y. Role of IL28B for chronic hepatitis C treatment toward personalised medicine. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 ;29:241-9.
- Hayes, C.N.; Imamura, M.; Aikata, H.; Chayama, K. Genetics of IL28B and HCV—response to infection and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, A.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Chinnaswamy, S. Confounding by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism rs117648444 (P70S) Affects the Association of Interferon Lambda Locus Variants with Response to Interferon-α-Ribavirin Therapy in Patients with Chronic Genotype 3 Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2017, 37, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Higami, K.; Masaki, N.; Sugiyama, M.; Mukaide, M.; Saito, H.; Aoki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Imamura, M.; Murata, K.; et al. The rs8099917 Polymorphism, When Determined by a Suitable Genotyping Method, Is a Better Predictor for Response to Pegylated Alpha Interferon/Ribavirin Therapy in Japanese Patients than Other Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with Interleukin-28B. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva E, Scagnolari C, Turriziani O, Antonelli G. Hepatitis C virus and interferon type III (interferon-λ3/interleukin-28B and interferon-λ4): genetic basis of susceptibility to infection and response to antiviral treatment. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(12):1237-45.
- Ibrahim MK, AbdElrahman M, Bader El Din NG, Tawfik S, Abd-Elsalam S, Omran D, Barakat AZ, Farouk S, Elbatae H, El Awady MK. The impact of genetic variations in sofosbuvir metabolising enzymes and innate immunity mediators on treatment outcome in HCV-infected patients. Microb Pathog. 2022 Jan;162:105311.
- Loucks CM, Lin JJ, Trueman JN, Drögemöller BI, Wright GEB, Chang WC, Li KH, Yoshida EM, Ford JA, Lee SS, Crotty P, Kim RB, Al-Judaibi B, Schwarz UI, Ramji A, Farivar JF, Tam E, Walston LL, Ross CJD, Carleton BC. Patient-specific genetic factors predict treatment failure in sofosbuvir-treated patients with chronic hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2022 Apr;42(4):796-808.
- Abdelnajid, D.M.; Elmowafy, A.Y.; Rostaing, L.; Elrakaiby, M.T. Prediction of response to sofosbuvir-based therapy using serum interleukin-12 and single nucleotide polymorphism of the interleukin 28B gene as predictive factors in HCV positive genotype-4 patients. Medicine 2023, 102, e34125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, V.; Moldovan, M.; Ahlenstiel, G.; Berg, T.; Weltman, M.; Abate, M.L.; Bassendine, M.; Spengler, U.; Dore, G.J.; Powell, E.; et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-α and ribavirin therapy. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nishida, N.; Sugiyama, M.; Kurosaki, M.; Matsuura, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Korenaga, M.; Hino, K.; Hige, S.; et al. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, M.H.; Bochud, P.-Y.; George, J. Host – hepatitis C viral interactions: The role of genetics. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, S22–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asthana, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Mohanty, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Das, P.; Chattopadhya, N.R.; Chatterjee, K.; Singh, S.P.; Rajasubramaniam, S.; et al. Role of Interleukin 28B Polymorphisms in Response to Interferon Based Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Clearance. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M. A. , Aranday-Cortes, E., Ip, C. L., da Silva Filipe, A., Lau, S. H., Bamford, C., Bonsall, D., Trebes, A., Piazza, P., Sreenu, V., Cowton, V. M., STOP-HCV Consortium, et al. (2019). Interferon lambda 4 impacts the genetic diversity of hepatitis C virus. eLife, 8, e42463.
- Ferreira, J.; Oliveira, M.; Bicho, M.; Serejo, F. Role of Inflammatory/Immune Response and Cytokine Polymorphisms in the Severity of Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC) before and after Direct Acting Antiviral (DAAs) Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Justice, A.C.; Marconi, V.C.; Aouizerat, B.E.; Xu, K. Co-occurrence of injection drug use and hepatitis C increases epigenetic age acceleration that contributes to all-cause mortality among people living with HIV. Epigenetics 2023, 18, 2212235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y. , Nepal, N., & Jin, S. Z. (2021). Toll-like receptors and hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatobiliary & pancreatic diseases international : HBPD INT, 20(6), 521–529.
- Jiménez-Sousa et al. (2015) Jiménez-Sousa MA. TLR3 polymorphisms are associated with virologic response to hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment in HIV/HCV coinfected patients. Journal of Clinical Virology. 6: 2015;66, 2015.
- Xu, Y.; Xue, W.; Gao, H.; Cui, J.; Zhao, L.; You, C. Association of toll-like receptors single nucleotide polymorphisms with HBV and HCV infection: research status. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, R.M.; Elsayed, S.S.; Abdel-Hakem, N.E.; El-Shenawy, S.Z. Genetic Polymorphism in Toll-Like Receptor 3 and Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients: Correlation with Liver Cirrhosis. Viral Immunol. 2022, 35, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öksüz, Z.; Gragnani, L.; Lorini, S.; Temel, G. .; Serin, M.S.; Zignego, A.L. Evaluation of Plasma miR-17-5p, miR-24-3p and miRNA-223-3p Profile of Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients after Treatment with Direct-Acting Antivirals. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V. , Jayakumar, S., Mohan, M., & Kulkarni, S. (2023). Aid or Antagonise: Nuclear Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate Host Responses and Outcomes of Viral Infections. Cells, 12(7), 987.
- Mushtaq S, Hashmi AH, Khan A, Asad Raza Kazmi SM and Manzoor S (2022) Emergence and Persistence of Resistance-Associated Substitutions in HCV GT3 Patients Failing Direct- Acting Antivirals. Front. Pharmacol. 13:8944heng60.
- Sølund C, Pedersen MS, Fahnøe U, Filskov J, Jenssen H, Weis N, Schønning K, Bukh J. Pre-existing, treatment-specific resistance-associated substitutions in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 and 3 and viral RNA titers during treatment with direct-acting antivirals. APMIS. 2023 Aug;131(8):426-433.
- Devan, P.; Tiong, K.L.A.; Neo, J.E.; Mohan, B.P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Tam, Y.C.S.; Coppola, N.; Preda, C.M.; Wong, Y.J. Treatment Outcomes of Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir in Direct-Acting Antiviral-Experienced Hepatitis C Virus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S. Direct-acting Antiviral in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C: Bonuses and Challenges. Int. J. Med Sci. 2020, 17, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malandris, K. , Kalopitas, G., Theocharidou, E., & Germanidis, G. (2021). The Role of RASs /RVs in the Current Management of HCV. 2096. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.L. Global Elimination of Chronic Hepatitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia A, Fernandez S, Toro F, Sanctis J. An Overview of Hepatitis C Vaccines. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 21 de julio de 2014;8(2):85-91.
- Bailey JR, Barnes E, Cox AL. Approaches, Progress, and Challenges to Hepatitis C Vaccine Development. Gastroenterology. enero de 2019;156(2):418-30.
- Duncan, J.D.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; Tarr, A.W.; Ball, J.K. Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine: Challenges and Prospects. Vaccines 2020, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardani, K.; Sadat, S.M.; Kardani, M.; Bolhassani, A. The next generation of HCV vaccines: a focus on novel adjuvant development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, M.-L.; Wrensch, F.; Pierce, B.G.; Baumert, T.F.; Foung, S.K.H. Mapping Determinants of Virus Neutralization and Viral Escape for Rational Design of a Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbahrawy, A.; Atalla, H.; Alboraie, M.; Alwassief, A.; Madian, A.; El Fayoumie, M.; Tabll, A.A.; Aly, H.H. Recent Advances in Protective Vaccines against Hepatitis Viruses: A Narrative Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adugna, A. Therapeutic strategies and promising vaccine for hepatitis C virus infection. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023;11(8):e977.
- Fauvelle C, Colpitts CC, Keck Z yong, Pierce BG, Foung SKH, Baumert TF. Hepatitis C virus vaccine candidates inducing protective neutralising antibodies. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016;15(12):1535-44.
- Landi, A.; Law, J.; Hockman, D.; Logan, M.; Crawford, K.; Chen, C.; Kundu, J.; Ebensen, T.; Guzman, C.; Deschatelets, L.; et al. Superior immunogenicity of HCV envelope glycoproteins when adjuvanted with cyclic-di-AMP, a STING activator or archaeosomes. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6949–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kwon, T.; Polo, J.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Coates, S.; Crawford, K.; Dong, C.; Wininger, M.; Hall, J.; Selby, M.; et al. Induction of Broad CD4 + and CD8 + T-Cell Responses and Cross- Neutralizing Antibodies against Hepatitis C Virus by Vaccination with Th1-Adjuvanted Polypeptides Followed by Defective Alphaviral Particles Expressing Envelope Glycoproteins gpE1 and gpE2 and Nonstructural Proteins 3, 4, and 5. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7492–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Escobar, E.; Roingeard, P.; Beaumont, E. Current Hepatitis C Vaccine Candidates Based on the Induction of Neutralizing Antibodies. Viruses 2023, 15, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkrekshi, A.; Tamaskar, I. Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Cancer and Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Oncol. 2021, 26, e827–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, R.; Tsai, E. Hepatitis C Virus Treatment and Solid Organ Transplantation. . 2022, 18, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desombere I, Mesalam AA, Urbanowicz RA, Van Houtte F, Verhoye L, Keck ZY, Farhoudi A, Vercauteren K, Weening KE, Baumert TF, Patel AH, Foung SKH, Ball J, Leroux-Roels G, Meuleman P. A novel neutralising human monoclonal antibody broadly abrogates hepatitis C virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 2017 Dec;148:53-64.
- Bailly, C.; Thuru, X. Targeting of Tetraspanin CD81 with Monoclonal Antibodies and Small Molecules to Combat Cancers and Viral Diseases. Cancers 2023, 15, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriquí-Madroñal, B.; Lasswitz, L.; von Hahn, T.; Gerold, G. Genetic and pharmacological perturbation of hepatitis-C virus entry. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2023, 62, 101362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Cypel, M.; Kumar, D.; Dahari, H.; Ribeiro, R.V.P.; Marks, N.; Kamkar, N.; Bahinskaya, I.; Onofrio, F.Q.; A Zahoor, M.; et al. Short-course, direct-acting antivirals and ezetimibe to prevent HCV infection in recipients of organs from HCV-infected donors: a phase 3, single-centre, open-label study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallard, C.; Lebsir, N.; Khursheed, H.; Reungoat, E.; Plissonnier, M.-L.; Bré, J.; Michelet, M.; Chouik, Y.; Zoulim, F.; Pécheur, E.-I.; et al. Heparanase-1 is upregulated by hepatitis C virus and favors its replication. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhou, H.; Quan, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Potential roles of heparanase in cancer therapy: Current trends and future direction. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 896–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviano, A.; Habersetzer, F.; Lupberger, J.; Simo-Noumbissie, P.; Schuster, C.; Doffoël, M.; Schmidt-Mutter, C.; Baumert, T.F. Safety and Antiviral Activity of EGFR Inhibition by Erlotinib in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients: A Phase Ib Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Tawar, R.G.; Mailly, L.; Thumann, C.; Heydmann, L.; Durand, S.C.; Xiao, F.; Robinet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Zeisel, M.B.; et al. Humanisation of a claudin-1-specific monoclonal antibody for clinical prevention and cure of HCV infection without escape. Gut 2018, 67, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascut, D.; Hoang, M.; Nguyen, N.N.Q.; Pratama, M.Y.; Tiribelli, C. HCV Proteins Modulate the Host Cell miRNA Expression Contributing to Hepatitis C Pathogenesis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




