Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
29 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statistical Analysis
2.2. LLM Selection
2.3. ChatGPT API Usage
- openai.Completion.create() is used for single-turn conversations and supports completion models such as gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct and text-davinci-003, and
- openai.ChatCompletion.create() is used for single- or multi-turn conversations and supports chat completion models such as gpt-4 and gpt-3.5-turbo [54].
- user, for application- or API-user-submitted prompts;
- system, for constraints or special instructions that inform an entire conversation, which may be used by software developers to affect the experience of the application user; and
- assistant, for responses to user queries, i.e. ChatGPT responses [55].
2.4. LLM Structured Prompt for Narrative Generation
2.4.1. Experiments with Preliminary Designs
2.4.2. Final LLM Narrative Prompt Structure
- Narrative Event Type: What is the event for which a narrative is being created? This can anything deemed relevant for an agent such as a birth, marriage, change in education, etc.
- Subject of Narrative: the agent, person, etc. that is the focus of the narrative.
- Subject’s Relationship to Narrator: What is the relationship between the narrator and the subject? Is the narrator referring to itself, a family member, a friend, a co-worker, a romantic connection, etc.
- Subject’s Characteristics: A set of characteristics pertaining to the subject that are relevant to the narrative event.
- Narrator’s Characteristics: A set of characteristics that are relevant for the creation of the narrative with respect to the narrator, such as age or gender.
- Narrative Tense: Past, present, or future.
- Target Audience: Who are the intended readers of the narrative and/or what is the intended medium of the narrative, such as Twitter, email, text message, diary, etc.?
- Voice: Should the narrative use active or passive voice?
- Narrative Immediacy: Should the narrative be conveyed using immediacy? Immediacy provides a more intimate, generally first person, connection between the narrative and the reader.
- Maximum Temporal Proximity: In the narration, how much time has passed since the event occurred?
- Target Sentiment Value: The intended level of emotion to convey in the narrative from -1 to +1 with -1 being strongly negative, 0 being neutral, and +1 being strongly positive.
- Subject’s History: The set of historical events that support or expand upon the current narrative event, if any, such as prior birth events when narrating a new birth.
- Number of Narratives: The number of narratives to generate using the above criteria.
- Maximum Length: The maximum length and unit of measure of the narrative being generated, i.e., characters, words, tokens, etc.
- Special Tokens: Should the narrative include special tokens such as hashtag and @’s?
- Hyperlinks: A set of hyperlinks to include in the narrative, if any.
- Instructions: Set of instructions for getting the large language model to understand how to use this list of criteria as well as any additional instructions needed to hone focus onto only the desired narrative materials.
- Target sentiment value, -1: "Just got off the phone with Joyce, my unemployed mom. She’s been looking for work for over two years now. It’s disheartening to see her struggle. #Unemployment #JobSearch"
- Target sentiment value, 1: "It’s been 104 weeks since my mom, Joyce, faced unemployment. She’s a fighter and won’t give up. Let’s cheer her on! #Unemployment #Resilience"
- With narrative immediacy: "The world welcomes Baby Max, the precious son of Paul and Ally. May he grow up surrounded by love, joy, and all the wonders life has to offer. Congratulations on this incredible blessing, and may your family be filled with happiness. #BabyBoy #NewestMember"
- Without narrative immediacy: "Sending my heartfelt congratulations to Paul and Ally on the birth of their precious baby boy, Max! May this new journey be filled with endless love, joy, and beautiful memories. #NewParents #BabyMax"
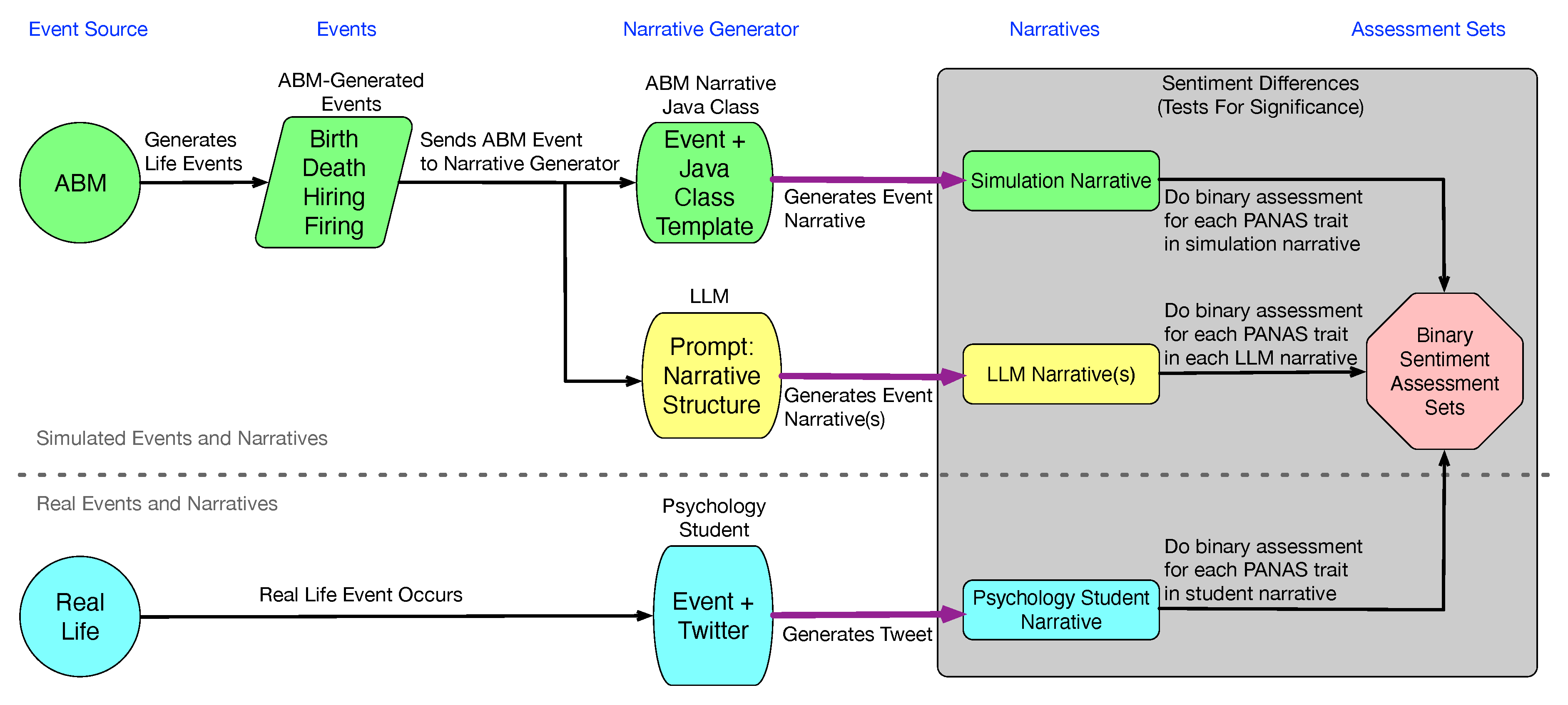
2.5. Data Sets
-
Narratives generated using structured Java classes based on simulated agents’ event information. One narrative generated per event.
- (a)
- Java narrative-generating classes
- (b)
- ABM simulation event data and generated narratives
-
Narratives generated using ChatGPT based on simulated agents’ event information. Ten narratives generated per simulation event.
- (a)
- Structured ChatGPT API prompts
- (b)
- Sets of ChatGPT response narratives
-
Real tweets obtained from Twitter [57].
- (a)
- Tweet set with PII removed (dropped IDs and screen names)
- (b)
- IRB documentation
-
Also included,
- (a)
- Source codes (R): sentiment analysis and statistical significance scripts
- (b)
- Source codes (Python): ChatGPT prompt generation, prompt submission, and analysis preparation scripts
- (c)
- ABM simulation output data on Agents’ Life Events in CSV format
- (d)
- PANAS sentiment keyword lexicon
2.6. Sentiment Scoring of Narratives and Tweets
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Lessons Learned
- Using the ChatGPT API for generating multiple, independent narratives. We discovered the ChatGPT API is not well-suited to generating multiple instances of a requested narrative in one response. There is a strong tendency to narrate a continuous, temporally-advancing story instead of a set of independent narratives describing a single event. Using the n parameter in the Python API ChatCompletion function call appears to remedy this behavior, as ChatGPT generates a set of n independent responses, that is, they are not connected. ChatGPT appears to not retain knowledge of narratives 1 through i when generating narrative , when the n parameter is used.
- Balancing creativity with correctness. The level of stochasticity that ChatGPT employs for choosing the next token during text completion is moderated by the temperature parameter. A zero temperature outputs identical responses for repeated identical inputs; increasing the temperature increases the set of next available tokens in the completion, effectively increasing the response space and allowing for greater variation among the responses. However, this increased creative capacity can come at the cost of correctness, if the temperature is too high and ChatGPT selects inappropriate tokens. However, even with a temperature of zero used for the API, ChatGPT still sometimes produced categorically incorrect responses, e.g. narratives about car fires and house fires, when the prompt was to generate narratives about being fired from a job. A temperature of zero was used in this work, to attempt to limit incorrect narratives, and specifically to address ChatGPT’s tendency toward "storytelling", instead of generating multiple independent narratives in one response. This ultimately was not very effective, as noted in the previous lesson learned. Conversely, when using the n parameter to generate multiple, different narratives, the temperature value must not be zero, else each response will be identical.
- ChatGPT API time-out errors. The API fails frequently due to request time-out errors, so the experimental setup should account for this and be able to resume efficiently after an error. For this work, a Python script reads prompt files from a directory, and moves them to another directory after a successful response is received: if the script is restarted due to a time-out error, no prompts are lost or repeated.
4.2. Limitations
- Problem type. For this work, ChatGPT was not required to solve complex problems or rely heavily on factual information from training data. All the required factual information, including narrator and subject characteristics, was provided in the prompt. ChatGPT appears to be well-suited to this type of creative task, the output of which is technically correct as long as the instructions and constraints in the input prompt are observed. Narratives can easily be validated manually. This differs from other types of tasks, e.g. asking ChatGPT to solve a mathematical problem or to diagnose a medical condition [13], which requires knowledge of and "understanding" of much more complex background information, which is not included in the prompt. These problem types are much less subjective and not as easily validated. Further, ChatGPT currently cannot accurately provide sources, for validating the response information. In this case, the human reader has to determine if the response is legitimate or if ChatGPT has "hallucinated" some trustworthy-sounding but incorrect response, without the benefit of reliable references [12].
- Use case. For this work, narratives were not actually tweeted or broadcast in any way, but were used solely for analysis. Incorrect narratives were identified manually and incurred no negative consequences. For use cases in which responses are not or cannot be validated by a human before utilization, there is a risk of dissemination of erroneous information. Numerous correct prior responses do not guarantee an incorrect response cannot happen in the future: in other words, there is no way to bound or know the response space [12]. As noted in the second lesson learned, even with minimal stochasticity, ChatGPT generated completely incorrect narratives about car fires and house fires, which could not have been predicted by the hundreds of other responses for that event type that did not do this.
- ChatGPT API response speed. As noted in the third lesson learned, the Python API regularly failed due to time-out errors, so this currently might not be an appropriate tool for situations with strict time constraints.
- Token volume in real time / quicker than real time. The ability to generalize our approach for real-time applications of ChatGPT for narrative generation is limited based on the token limit of the API. The current ChatGPT API version has a rate limit of 3,500 requests per minute and 90,000 tokens per minute [67].
- Domain expertise. The creation of LLMs are based on broad ranges volumes of reference literature. It is important to determine that generated results are in line with the domain expertise of the targetted problem or system [68]. This article does not attempt to refine the learning base of the LLM for the narration of key events, as the broad range of potential response types for individuals was desireable as the starting point for this effort. However, future avenues of research include assessing the validity of narrative within their respective domains, such as for births and death events, and tailored within a larger context, such as refugee camps, natural distaster response, etc.
- Underspecification hinders narrative generation. Greater levels of specificity in the prompting of desired narratives from ChatGPT has been beneficial in reducing the number of iterations for generating and assessing the correctness of the narratives. Similar to ML pipeline problems with underspecification, where underspecification in training leads to problems in reliability and validity [69], underspecification of narrative requests from ChatGPT led to many more erroneous responses and the expansion of the structure provided in this article.
- Tweet comparison sets. Tweets were not categorized per event type like the generated narratives. The tweet set is utilized assuming that it represents a general sample of the population. As such, the generalizibility of the sentiment findings should not be extended to other sample populations without proper supporting justifications about the reasonableness of the extension.
4.3. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABM | Agent Based Model |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| GPT | Generative Pretrained Transformer |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| PANAS | Positive and Negative Affect Schedule |
Appendix A. PANAS Lexicon
Appendix A.1
| PANAS_trait | PANAS_group | PANAS_polarity | lexicon | lexicon_subgroup | lexicon_subgroup_description | comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| interested | interested | alert | attentive | positive | NRC | anticipation | 839 words associated with anticipation through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include positive words |
| alert | interested | alert | attentive | positive | General Inquirer | Perceiv | 167 words associated with perception and perceiving | only include positive words |
| attentive | interested | alert | attentive | positive | NRC | anticipation | 839 words associated with anticipation through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include positive words |
| excited | excited | enthusiastic | inspired | positive | General Inquirer | Arousal | 67 words indicating excitation; aside from pleasures or pains; but including arousal of affiliation and hostility | only include positive words |
| enthusiastic | excited | enthusiastic | inspired | positive | General Inquirer | Arousal | 67 words indicating excitation; aside from pleasures or pains; but including arousal of affiliation and hostility | only include positive words |
| inspired | excited | enthusiastic | inspired | positive | NRC | joy | 689 words associated with joy through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include positive words |
| proud | proud | determined | positive | NRC | trust | 1231 words associated with trust through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include positive words |
| determined | proud | determined | positive | General Inquirer | Pleasur | 168 words indicating the enjoyment of a feeling. Including words indicating confidence; interest and commitment | only include positive words |
| active | strong | active | positive | General Inquirer | Active | 1902 words implying strength | only include positive words |
| strong | strong | active | positive | General Inquirer | Strong | 2045 words implying an active orientation | only include positive words |
| distressed | distressed | upset | negative | General Inquirer | Pain | 254 words indicating suffering; lack of confidence; or commitment | only include negative words |
| upset | distressed | upset | negative | NRC | sadness | 1191 words associated with sadness through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
| guilty | guilty | ashamed | negative | General Inquirer | Vice | 685 words indicating an assessment of moral disapproval or misfortune | only include negative words |
| ashamed | guilty | ashamed | negative | NRC | disgust | 1058 words associated with disgust through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
| hostile | hostile | irritable | negative | General Inquirer | Arousal | 67 words indicating excitation; aside from pleasures or pains; but including arousal of affiliation and hostility | only include negative words |
| irritable | hostile | irritable | negative | NRC | anger | 1247 words associated with anger through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
| nervous | nervous | jiittery | negative | LWIC | anxiety | 196 words associated with anxiety in the LWIC 2015 dictionary | only include negative words |
| jittery | nervous | jiittery | negative | NRC | anticipation | 839 words associated with anticipation through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
| afraid | afraid | scared | negative | NRC | fear | 1476 words associated with fear through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
| scared | afraid | scared | negative | NRC | surprise | 534 words associated with surprise through MTurk crowdsourcing | only include negative words |
Appendix B. Tests for Statistically Significant Differences per PANAS Category
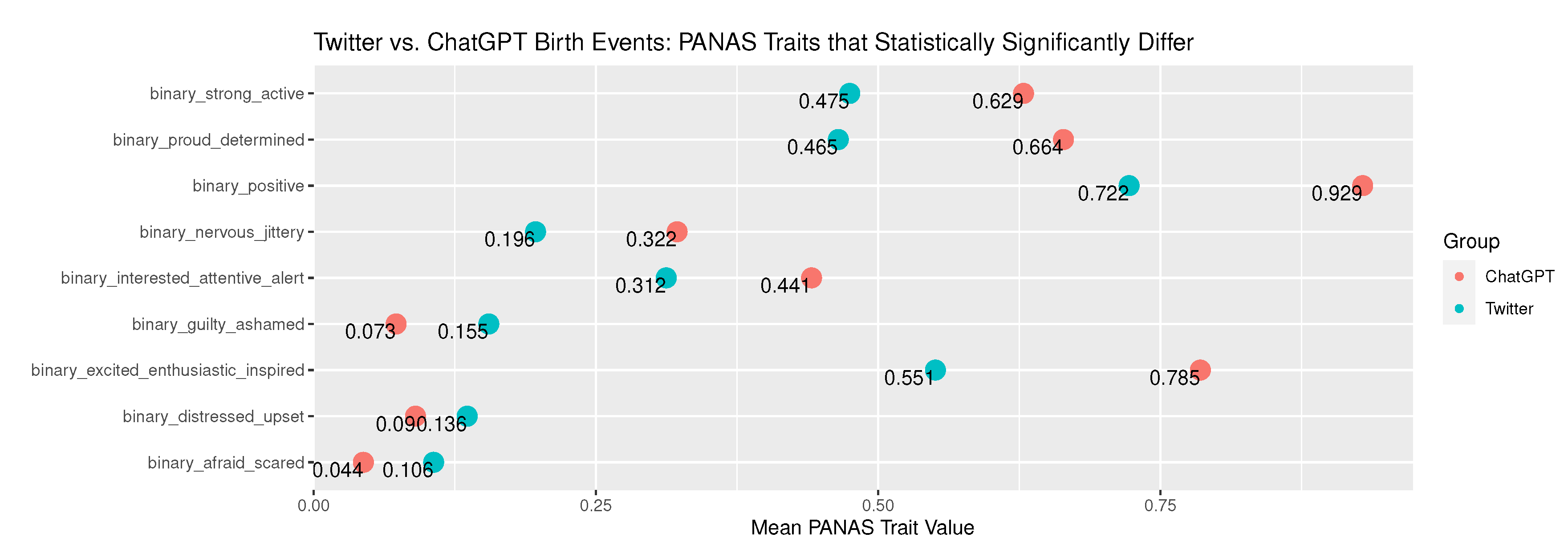
Appendix B.1. Birth Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus ChatGPT
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 1.08e-36 | 160.099506102967 | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0.929184549356223 | 0.0658712999543617 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 4.71e-01 | 0.519321805771216 | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0.405579399141631 | 0.24134370260415 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 2.47e-11 | 44.5577138071836 | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0.440987124463519 | 0.246782268362507 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 1.27e-33 | 146.050770865262 | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0.785407725321888 | 0.168723464086335 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 2.78e-23 | 98.806762544465 | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0.664163090128755 | 0.223290061450376 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 1.87e-14 | 58.6678829706207 | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0.628755364806867 | 0.233672777898148 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 5.61e-04 | 11.9000737571625 | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0.0901287553648069 | 0.0820936461324986 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.21e-09 | 36.9539156769644 | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0.0729613733905579 | 0.0677106623087455 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 7.38e-01 | 0.112077435897854 | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0.336909871244635 | 0.223641568667223 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 2.78e-13 | 53.3603859555868 | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0.321888412017167 | 0.218510715783942 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 4.23e-08 | 30.0427370366321 | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0.0439914163090129 | 0.0421013447167889 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
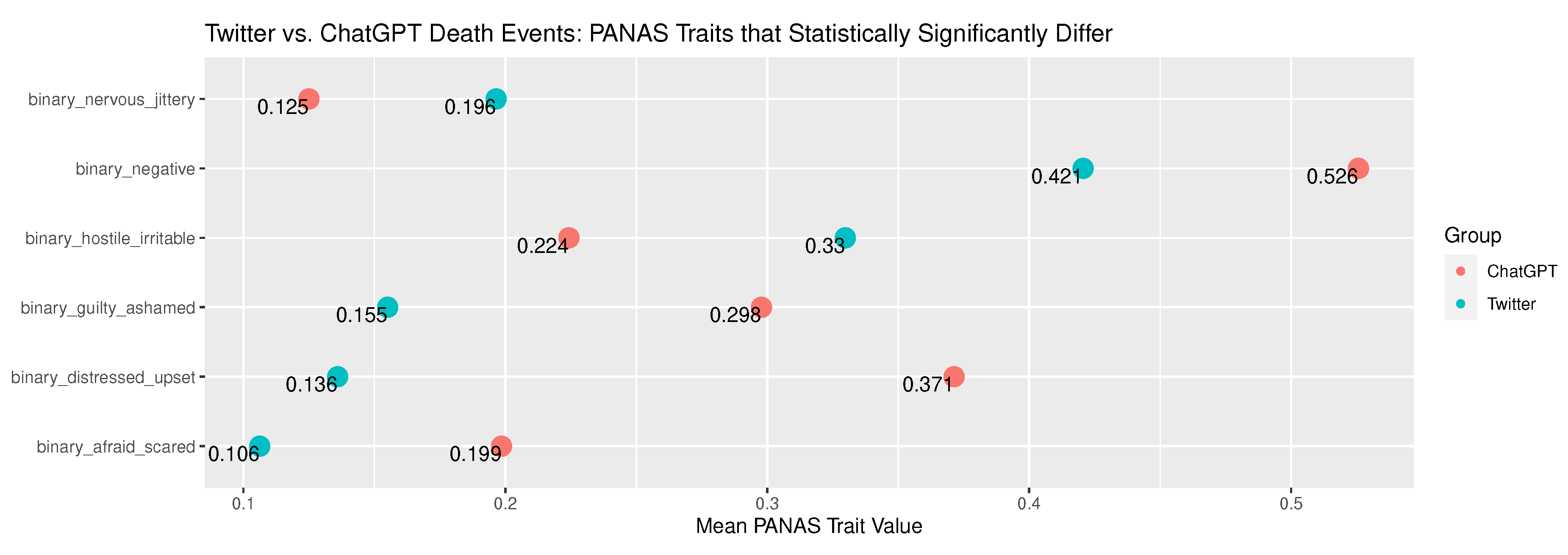
Appendix B.2. Death Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus ChatGPT
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 9.02e-01 | 0.0152569643464454 | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0.727941176470588 | 0.198773605383113 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 1.35e-03 | 10.2704541122394 | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0.525735294117647 | 0.250257759930541 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 5.11e-01 | 0.432584567290359 | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0.290441176470588 | 0.20684556110267 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 2.25e-01 | 1.47113496472166 | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0.591911764705882 | 0.242443564141524 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 4.24e-01 | 0.638297879874122 | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0.492647058823529 | 0.250868243976557 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.48e-01 | 0.360204684907635 | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0.496323529411765 | 0.250908942912959 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 3.93e-22 | 93.5649780798951 | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0.371323529411765 | 0.234303776861298 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.00e-08 | 32.8349109954337 | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0.297794117647059 | 0.209884415020621 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 6.08e-04 | 11.7523704114126 | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0.224264705882353 | 0.174612003472976 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 6.13e-03 | 7.51289996116507 | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0.125 | 0.109778597785978 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.61e-05 | 18.6029049368609 | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0.198529411764706 | 0.159702626438029 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
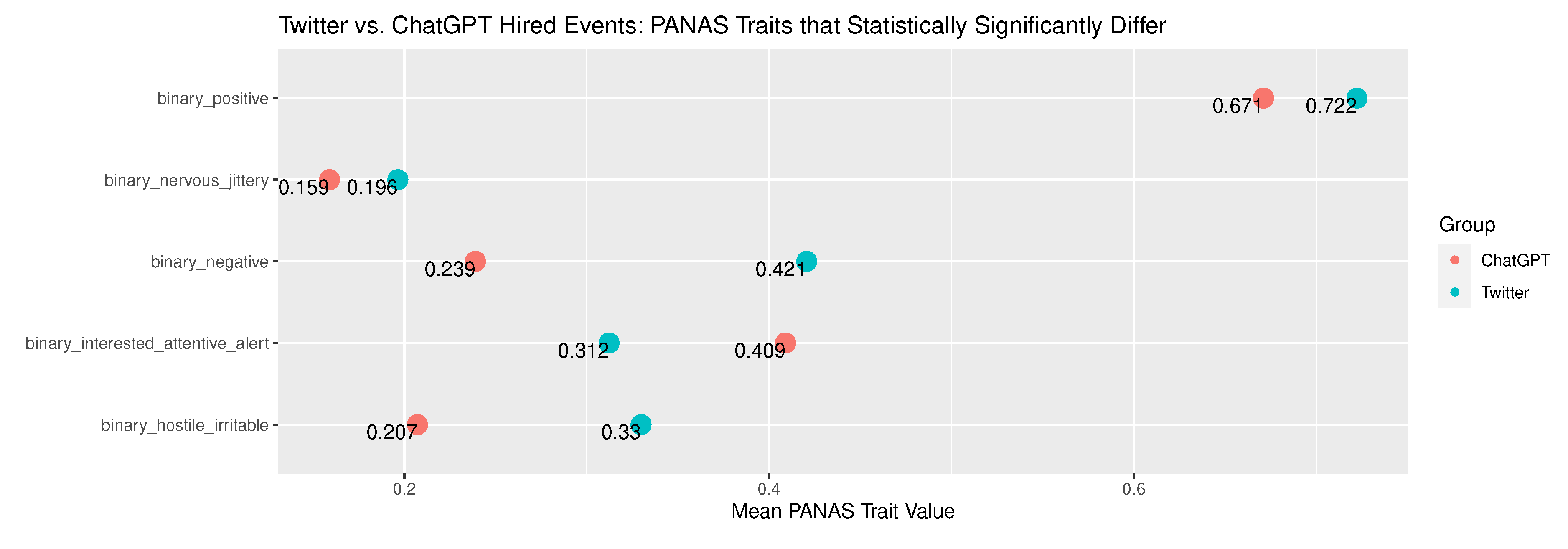
Appendix B.3. Hired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus ChatGPT
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 6.14e-03 | 7.50806773042741 | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0.671052631578947 | 0.220983303483737 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 1.09e-20 | 86.9872222350499 | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0.239035087719298 | 0.182096982302078 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 5.58e-07 | 25.0512925345889 | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0.408991228070175 | 0.241982735378512 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 7.63e-02 | 3.14223253585284 | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0.514254385964912 | 0.25007101315308 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 5.36e-02 | 3.72415611415799 | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0.504385964912281 | 0.250255165905983 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.05e-01 | 0.445143713062267 | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0.460526315789474 | 0.24871454156797 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 8.58e-01 | 0.0321455897504964 | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0.139254385964912 | 0.119994174514222 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 6.86e-02 | 3.31684350864536 | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0.128289473684211 | 0.111954041250217 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 2.90e-11 | 44.2449976096182 | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0.207236842105263 | 0.164470073372234 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 1.90e-02 | 5.50274102380948 | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0.158991228070175 | 0.133859793556339 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 4.65e-01 | 0.533497011846064 | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0.116228070175439 | 0.10283186011131 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
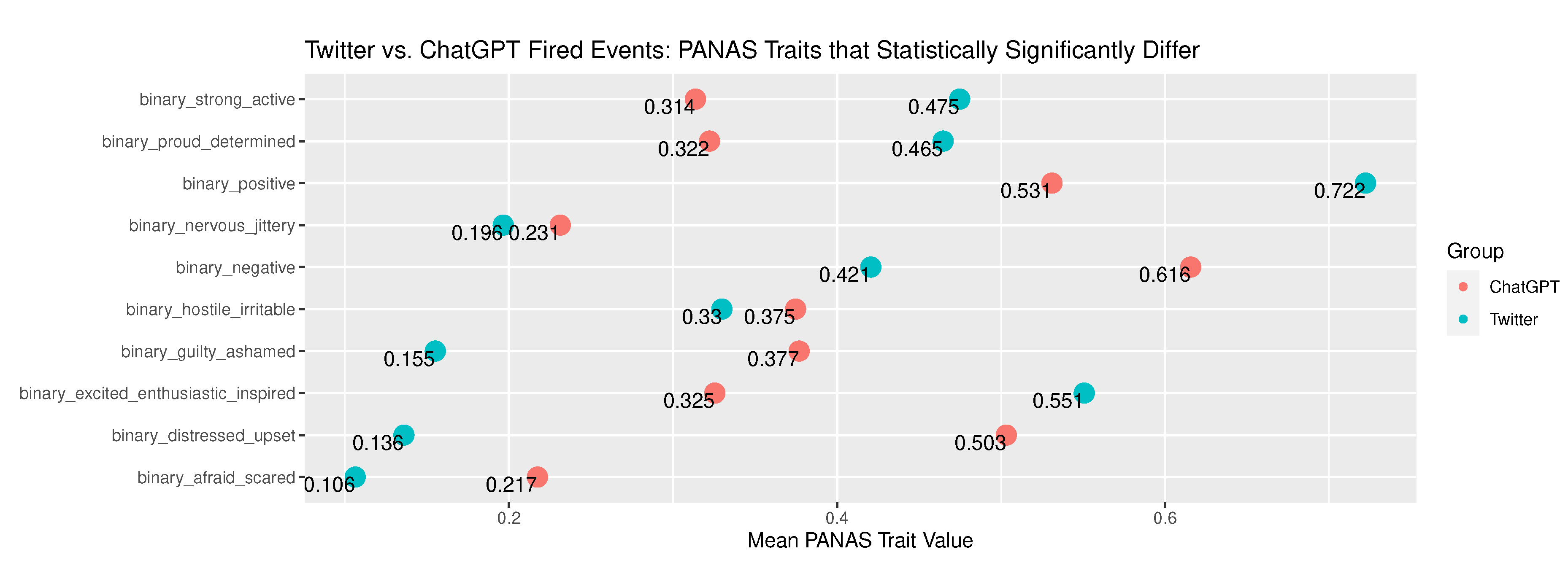
Appendix B.4. Fired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus ChatGPT
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 1.07e-23 | 100.698711966595 | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0.531049250535332 | 0.249302863595365 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 2.73e-22 | 94.2886931329851 | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0.615631691648822 | 0.236882933871305 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 6.62e-01 | 0.191199239916657 | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0.321199143468951 | 0.218263941006768 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 2.95e-29 | 126.080313021453 | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0.325481798715203 | 0.219778706527951 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 7.22e-13 | 51.4844982068129 | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0.322269807280514 | 0.218646075035976 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.06e-16 | 65.7725100599171 | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0.313704496788009 | 0.21552474002263 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 2.58e-97 | 438.269725064649 | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0.50321199143469 | 0.250257624893565 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.71e-39 | 172.912873408962 | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0.376873661670236 | 0.235091608887542 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 2.03e-02 | 5.3848042948889 | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0.374732334047109 | 0.234559145855854 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 3.65e-02 | 4.37235716734963 | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0.231263383297645 | 0.177971178143311 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 3.45e-15 | 61.9914948424431 | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0.217344753747323 | 0.170288333321858 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and ChatGPT for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.5. Fired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 2.01e-01 | NA | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 4.62e-02 | NA | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 1.07e-01 | NA | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 1.91e-02 | NA | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 4.76e-03 | NA | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.53e-03 | NA | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 6.03e-01 | NA | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 6.04e-01 | NA | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 1.03e-01 | NA | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 3.57e-01 | NA | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.00e+00 | NA | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.6. Fired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 2.70e-19 | NA | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 1.21e-08 | NA | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 4.98e-06 | NA | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 2.24e-12 | NA | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 8.55e-10 | NA | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.71e-10 | NA | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 1.78e-02 | NA | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 6.35e-03 | NA | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 2.29e-06 | NA | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 1.38e-03 | NA | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 4.31e-02 | NA | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.7. Hired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 4.57e-16 | NA | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 4.31e-07 | NA | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 4.06e-05 | NA | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 2.42e-10 | NA | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 3.91e-08 | NA | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 3.35e-08 | NA | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 2.55e-02 | NA | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.53e-02 | NA | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 1.93e-05 | NA | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 3.27e-03 | NA | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.09e-01 | NA | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.8. Fired Narrative Comparison - Twitter versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 1.47e-53 | NA | 0.722251725969198 | 0.20071076125499 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 1.44e-23 | NA | 0.420605416887945 | 0.243825988217188 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 2.55e-16 | NA | 0.312267657992565 | 0.214870678586808 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 4.01e-34 | NA | 0.550716941051514 | 0.247559262555569 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 7.72e-27 | NA | 0.464684014869888 | 0.248884955892055 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 1.46e-27 | NA | 0.474774296335635 | 0.249496163164688 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 1.56e-06 | NA | 0.13595326606479 | 0.117532393138902 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.22e-07 | NA | 0.155071694105151 | 0.131094083592612 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 2.53e-17 | NA | 0.329792883696229 | 0.221146981522126 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 1.04e-09 | NA | 0.196494954859267 | 0.15796857954414 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 4.40e-05 | NA | 0.106213489113117 | 0.0949826260241108 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between Twitter and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.9. Fired Narrative Comparison - ChatGPT versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 1.00e+00 | NA | 0.929184549356223 | 0.0658712999543617 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 4.59e-02 | NA | 0.405579399141631 | 0.24134370260415 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 2.05e-02 | NA | 0.440987124463519 | 0.246782268362507 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 3.56e-01 | NA | 0.785407725321888 | 0.168723464086335 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 1.03e-01 | NA | 0.664163090128755 | 0.223290061450376 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.13e-02 | NA | 0.628755364806867 | 0.233672777898148 | 1 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 1.00e+00 | NA | 0.0901287553648069 | 0.0820936461324986 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.00e+00 | NA | 0.0729613733905579 | 0.0677106623087455 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 1.02e-01 | NA | 0.336909871244635 | 0.223641568667223 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 1.04e-01 | NA | 0.321888412017167 | 0.218510715783942 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.00e+00 | NA | 0.0439914163090129 | 0.0421013447167889 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Birth in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Fail to reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.10. Fired Narrative Comparison - ChatGPT versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 8.22e-18 | NA | 0.727941176470588 | 0.198773605383113 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 1.11e-10 | NA | 0.525735294117647 | 0.250257759930541 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 3.37e-05 | NA | 0.290441176470588 | 0.20684556110267 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 9.37e-13 | NA | 0.591911764705882 | 0.242443564141524 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 7.06e-10 | NA | 0.492647058823529 | 0.250868243976557 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 6.03e-10 | NA | 0.496323529411765 | 0.250908942912959 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 7.81e-07 | NA | 0.371323529411765 | 0.234303776861298 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 1.82e-05 | NA | 0.297794117647059 | 0.209884415020621 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 4.45e-04 | NA | 0.224264705882353 | 0.174612003472976 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 2.05e-02 | NA | 0.125 | 0.109778597785978 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.40e-03 | NA | 0.198529411764706 | 0.159702626438029 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Death in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.11. Hired Narrative Comparison - ChatGPT versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 7.21e-14 | NA | 0.671052631578947 | 0.220983303483737 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 9.34e-04 | NA | 0.239035087719298 | 0.182096982302078 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 1.03e-06 | NA | 0.408991228070175 | 0.241982735378512 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 4.93e-09 | NA | 0.514254385964912 | 0.25007101315308 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 5.84e-09 | NA | 0.504385964912281 | 0.250255165905983 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 4.89e-08 | NA | 0.460526315789474 | 0.24871454156797 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 2.43e-02 | NA | 0.139254385964912 | 0.119994174514222 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 3.92e-02 | NA | 0.128289473684211 | 0.111954041250217 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 2.96e-03 | NA | 0.207236842105263 | 0.164470073372234 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 1.46e-02 | NA | 0.158991228070175 | 0.133859793556339 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 6.35e-02 | NA | 0.116228070175439 | 0.10283186011131 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Hired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
Appendix B.12. Fired Narrative Comparison - ChatGPT versus Simulation
| PANAS_Group | P Value | Chi Square |
Sample 1 Mean |
Sample 1 Variance |
Sample 2 Mean |
Sample 2 Variance |
Null Hypothesis Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary_positive | 3.27e-31 | NA | 0.531049250535332 | 0.249302863595365 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_positive. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_negative | 6.52e-39 | NA | 0.615631691648822 | 0.236882933871305 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_negative. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_interested_attentive_alert | 2.55e-16 | NA | 0.321199143468951 | 0.218263941006768 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_interested_attentive_alert. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired | 1.24e-16 | NA | 0.325481798715203 | 0.219778706527951 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_excited_enthusiastic_inspired. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_proud_determined | 2.56e-16 | NA | 0.322269807280514 | 0.218646075035976 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_proud_determined. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_strong_active | 5.74e-16 | NA | 0.313704496788009 | 0.21552474002263 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_strong_active. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_distressed_upset | 1.15e-28 | NA | 0.50321199143469 | 0.250257624893565 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_distressed_upset. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_guilty_ashamed | 7.93e-20 | NA | 0.376873661670236 | 0.235091608887542 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_guilty_ashamed. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_hostile_irritable | 9.29e-20 | NA | 0.374732334047109 | 0.234559145855854 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_hostile_irritable. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_nervous_jittery | 2.37e-11 | NA | 0.231263383297645 | 0.177971178143311 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_nervous_jittery. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
| binary_afraid_scared | 1.38e-10 | NA | 0.217344753747323 | 0.170288333321858 | 0 | 0 | There is no difference in association between ChatGPT and Simulation for event type Fired in relation to PANAS group: binary_afraid_scared. | Reject the null hypothesis. |
References
- Goodman, A.; Morgan, R.; Kuehlke, R.; Kastor, S.; Fleming, K.; Boyd, J.; others. “We’ve been researched to death”: Exploring the research experiences of urban Indigenous Peoples in Vancouver, Canada. The International Indigenous Policy Journal 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, N. ‘Over-researched’and ‘Under-researched’refugee groups: Exploring the phenomena, causes and consequences. Journal of Human Rights Practice 2020, 12, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, A.M.; Raile, E.D.; Izurieta, C.; McEvoy, J.; King, H.W.; Poole, G.C.; Ready, R.C.; Bergmann, N.T.; Shanahan, E.A. Persuasion with Precision: Using Natural Language Processing to Improve Instrument Fidelity for Risk Communication Experimental Treatments. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, E.A.; Jones, M.D.; McBeth, M.K. How to conduct a Narrative Policy Framework study. The Social Science Journal 2018, 55, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, S.Y.; Lynch, C.J.; Rechowicz, K.J.; Zacharewicz, G. How to Create Empathy and Understanding: Narrative Analytics in Agent-Based Modeling. 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1286–1297. [CrossRef]
- Shults, F.L.; Wildman, W.J.; Diallo, S.; Puga-Gonzalez, I.; Voas, D. The artificial society analytics platform. Advances in Social Simulation: Looking in the Mirror; Springer, 2020; pp. 411–426. [Google Scholar]
- Alawida, M.; Mejri, S.; Mehmood, A.; Chikhaoui, B.; Isaac Abiodun, O. A Comprehensive Study of ChatGPT: Advancements, Limitations, and Ethical Considerations in Natural Language Processing and Cybersecurity. Information 2023, 14, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazary, F.; Deldjoo, Y.; Di Noia, T. ChatGPT-HealthPrompt. Harnessing the Power of XAI in Prompt-Based Healthcare Decision Support using ChatGPT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09731, arXiv:2308.09731 2023. [CrossRef]
- Stokel-Walker, C.; Van Noorden, R. The Promise and Peril of Generative AI. Nature 2023, 614, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M. ChatGPT Utility in Healthcare Education, Research, and Practice: Systematic Review on the Promising Perspectives and Valid Concerns. Healthcare 2023, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dis, E.A.; Bollen, J.; Zuidema, W.; van Rooij, R.; Bockting, C.L. ChatGPT: five priorities for research. Nature 2023, 614, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.; Harvey, H.; Melvin, T.; Vollebregt, E.; Wicks, P. Large Language Model AI Chatbots Require Approval as Medical Devices. Nature Medicine, 2023; 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Bubeck, S.; Petro, J. Benefits, Limits, and Risks of GPT-4 as an AI Chatbot for Medicine. New England Journal of Medicine 2023, 388, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large language models in medicine. Nature Medicine, 2023; 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabacak, M.; Margetis, K. Embracing Large Language Models for Medical Applications: Opportunities and Challenges. Cureus 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.H.; Entwistle, D.; Pfeffer, M.A. Creation and Adoption of Large Language Models in Medicine. JAMA 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.; Danis, D.; Caufield, J.H.; Casiraghi, E.; Valentini, G.; Mungall, C.J.; Robinson, P.N. On the limitations of large language models in clinical diagnosis. medRxiv, 2023; 2023–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K.; Urs, V.L.; Agrawal, A.A.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Paliwal, V.; Kar, S.K. Exploring the Role of Chat GPT in patient care (diagnosis and Treatment) and medical research: A Systematic Review. medRxiv, 2023; 2023–06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, V.W.; Lei, P.; Cho, W.C. The potential impact of ChatGPT in clinical and translational medicine. Clinical and Translational Medicine 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.J.; Wakene, A.D.; Lehmann, C.U.; Medford, R.J. Assessing Racial and Ethnic Bias in Text Generation for Healthcare-Related Tasks by ChatGPT. medRxiv 2023, 2023–08. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.L.; Ong, C.W.; Chen, C.L. Exploring the use of large language models (LLMs) in chemical engineering education: Building core course problem models with Chat-GPT. Education for Chemical Engineers 2023, 44, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, J. Engineering education in the era of ChatGPT: Promise and pitfalls of generative AI for education. 2023 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON); IEEE, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Lee, S.S.; Chakraborty, C. A Domain-Specific Next-Generation Large Language Model (LLM) or ChatGPT is Required for Biomedical Engineering and Research. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2023; 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, S.; Adhikari, S. ChatGPT, Bard, and Large Language Models for Biomedical Research: Opportunities and Pitfalls. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2023; 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Filippi, S. Measuring the Impact of ChatGPT on Fostering Concept Generation in Innovative Product Design. Electronics 2023, 12, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikayat Ray, A.; Cole, B.F.; Pinon Fischer, O.J.; Bhat, A.P.; White, R.T.; Mavris, D.N. Agile Methodology for the Standardization of Engineering Requirements Using Large Language Models. Systems 2023, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, A. A categorical archive of chatgpt failures. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.03494, arXiv:2302.03494 2023. [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Petropoulos, F.; Kang, Y. Large Language Models: Their Success and Impact. Forecasting 2023, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, A.H.; Aktas, K.; Rizhinashvili, D.; Kuklianov, D.; Alisinanoglu, F.; Ofodile, I.; Ozcinar, C.; Anbarjafari, G. Ethical AI in facial expression analysis: Racial bias. Signal, Image and Video Processing 2023, 17, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, P. Can we trust AI not to further embed racial bias and prejudice? BMJ 2020, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyed-Kalantari, L.; Zhang, H.; McDermott, M.B.; Chen, I.Y.; Ghassemi, M. Underdiagnosis bias of artificial intelligence algorithms applied to chest radiographs in under-served patient populations. Nature medicine 2021, 27, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.N.; Lee, M.S.; Kassamali, B.; Mita, C.; Nambudiri, V.E. Bias in, bias out: underreporting and underrepresentation of diverse skin types in machine learning research for skin cancer detection—a scoping review. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2022, 87, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; Hosny, K.M.; Damaševičius, R.; Eltoukhy, M.M. Machine learning and deep learning methods for skin lesion classification and diagnosis: a systematic review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, N. What ChatGPT Tells Us about Gender: A Cautionary Tale about Performativity and Gender Biases in AI. Social Sciences 2023, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, P.; Tavast, M.; Kunnari, A. Evaluating large language models in generating synthetic hci research data: a case study. Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2023, pp. 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Sankararaman, K.A.; Wang, S.; Fang, H. Bayesformer: Transformer with uncertainty estimation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.00826 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shelmanov, A.; Tsymbalov, E.; Puzyrev, D.; Fedyanin, K.; Panchenko, A.; Panov, M. How certain is your Transformer? In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume; 2021; pp. 1833–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Vallès-Peris, N.; Domènech, M. Caring in the in-between: a proposal to introduce responsible AI and robotics to healthcare. AI & SOCIETY 2023, 38, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, G.J. Fisher’s exact test. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) 1992, 155, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, K.M. When to use Fisher’s exact test. American Society for Quality, Six Sigma Forum Magazine. American Society for Quality Milwaukee: WI, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Quantitative identification of urban functions with fishers’ exact test and POI data applied in classifying urban districts: A case study within the sixth ring road in Beijing. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2019, 8, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pęksa, M.; Kamieniecki, A.; Gabrych, A.; Lew-Tusk, A.; Preis, K.; Świątkowska-Freund, M. Loss of E-cadherin staining continuity in the trophoblastic basal membrane correlates with increased resistance in uterine arteries and proteinuria in patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, C.; He, N.; He, J.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z. Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Animals 2022, 12, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Al Mahmuda, N.; Munesue, T.; Hayashi, K.; Yagi, K.; Yamagishi, M.; Higashida, H. Association study between the CD157/BST1 gene and autism spectrum disorders in a Japanese population. Brain Sciences 2015, 5, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñana-Signes, V.; Monfort-Pañego, M.; Bosh-Bivià, A.H.; Noll, M. Prevalence of low back pain among primary school students from the city of Valencia (Spain). In Healthcare; MDPI, 2021; Volume 9, p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, Ö. Google Bard Generated Literature Review: Metaverse. Available at SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; Rodriguez, A.; Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Lample, G. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:cs.CL/2302.13971]. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S. ; others. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288, arXiv:2307.09288 2023. [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser. ; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- openAI. ChatGPT, 23 version. 20 August.
- Webster, J.J.; Kit, C. Tokenization as the initial phase in NLP. COLING 1992 volume 4: The 14th international conference on computational linguistics; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; others. Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D. ChatGPT and Open-AI Models: A Preliminary Review. Future Internet 2023, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. API Reference-OpenAI API, 2023. Accessed: , 2023. 18 September.
- OpenAI. GPT-OpenAI API, 2023. Accessed: , 2023. 18 September.
- Reynolds, L.; McDonell, K. Prompt programming for large language models: Beyond the few-shot paradigm. Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2021, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Gore, Ross J and Lynch, Christopher J. [1902417-1] Understanding Twitter Users. Old Dominion University Institutional Review Board, 2022. IRB Exempt Status, Exemption Category #2.
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of personality and social psychology 1988, 54, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.L.; Ashokkumar, A.; Seraj, S.; Pennebaker, J.W. The development and psychometric properties of LIWC-22. Austin, TX: University of Texas at Austin, 2022, pp. 1–47.
- Mohammad, S.M.; Turney, P.D. Nrc emotion lexicon. National Research Council, Canada 2013, 2, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Taboada, M.; Brooke, J.; Tofiloski, M.; Voll, K.; Stede, M. Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Computational linguistics 2011, 37, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.R.; Henry, J.D. The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS): Construct validity, measurement properties and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. British journal of clinical psychology 2004, 43, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, Ross J and Lynch, Christopher J. Effective & Individualized Risk Communication. Old Dominion University, 2023. Number 300916-010, Funding Agency: Old Dominion University.
- Mitchell, L.; Frank, M.R.; Harris, K.D.; Dodds, P.S.; Danforth, C.M. The geography of happiness: Connecting twitter sentiment and expression, demographics, and objective characteristics of place. PloS one 2013, 8, e64417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, R.J.; Diallo, S.; Padilla, J. You are what you tweet: connecting the geographic variation in America’s obesity rate to twitter content. PloS one 2015, 10, e0133505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.J.; Kavak, H.; Lynch, C.J.; Gore, R.J.; Diallo, S.Y. Temporal and spatiotemporal investigation of tourist attraction visit sentiment on Twitter. PloS one 2018, 13, e0198857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenAI. How can I use the ChatGPT API? | OpenAI Help Center. https://help.openai.com/en/articles/7232945-how-can-i-use-the-chatgpt-api, 2023. Accessed: 2023-09-20.
- National Academies of Sciences, E. ; Medicine.; others. Fostering Responsible Computing Research: Foundations and Practices 2022. [CrossRef]
- D’Amour, A.; Heller, K.; Moldovan, D.; Adlam, B.; Alipanahi, B.; Beutel, A.; Chen, C.; Deaton, J.; Eisenstein, J.; Hoffman, M.D.; Hormozdiari, F.; Houlsby, N.; Hou, S.; Jerfel, G.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Lucic, M.; Ma, Y.; McLean, C.; Mincu, D.; Mitani, A.; Montanari, A.; Nado, Z.; Natarajan, V.; Nielson, C.; Osborne, T.F.; Raman, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Sayres, R.; Schrouff, J.; Seneviratne, M.; Sequeira, S.; Suresh, H.; Veitch, V.; Vladymyrov, M.; Wang, X.; Webster, K.; Yadlowsky, S.; Yun, T.; Zhai, X.; Sculley, D. Underspecification Presents Challenges for Credibility in Modern Machine Learning. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2022, 23, 10237–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, E. ; Medicine.; others. The Roles of Trust and Health Literacy in Achieving Health Equity: Clinical Settings: Proceedings of a Workshop-in Brief 2023. [CrossRef]



| LLM Benefits | LLM Challenges |
|---|---|
|
|
| ]4*Event Type | Num. Total Agent Messages |
Num. Filtered Agent Messages |
Num. Sampled Agent Messages |
Num. ABM Narratives |
Num. ChatGPT Narratives |
Num. Tweets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth | 4,728 | 4155 | 100 | 100 | 1,000 | 6,148* |
| Death | 389 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 340 | 6,148* |
| Hiring | 26,317 | 3924 | 100 | 100 | 1,000 | 6,148* |
| Firing | 25,026 | 2860 | 100 | 100 | 1,000 | 6,148* |
| Real-Life Tweets (total) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6,148 |
| Real-Life Tweets (filtered) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4,163 |
| ]5*Event Type | Num. PANAS Sentiment ABM Narratives |
Num. PANAS Sentiment ChatGPT Narratives |
Num. PANAS Sentiment Tweets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth | 7 | 932 | 1883* |
| Death | † | 272 | 1883* |
| Hiring | † | 912 | 1883* |
| Firing | † | 934 | 1883* |
| ]5*Grouping | ]5*Event | Number of Cases for Rejecting the Null Hypothesis |
Number of Cases for Failing to Reject the Null Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth | 9 | 2 | |
| Twitter-ChatGPT | Death | 6 | 5 |
| Hired | 5 | 6 | |
| Fired | 10 | 1 | |
| Birth | 0* | 7 | |
| Twitter-Simulation | Death | 0* | 0* |
| Hired | 0* | 0* | |
| Fired | 10 | 1 | |
| Birth | 0* | 9 | |
| ChatGPT-Simulation | Death | 0* | 0* |
| Hired | 0* | 1 | |
| Fired | 0* | 0* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





