Submitted:
28 September 2023
Posted:
03 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Calculations
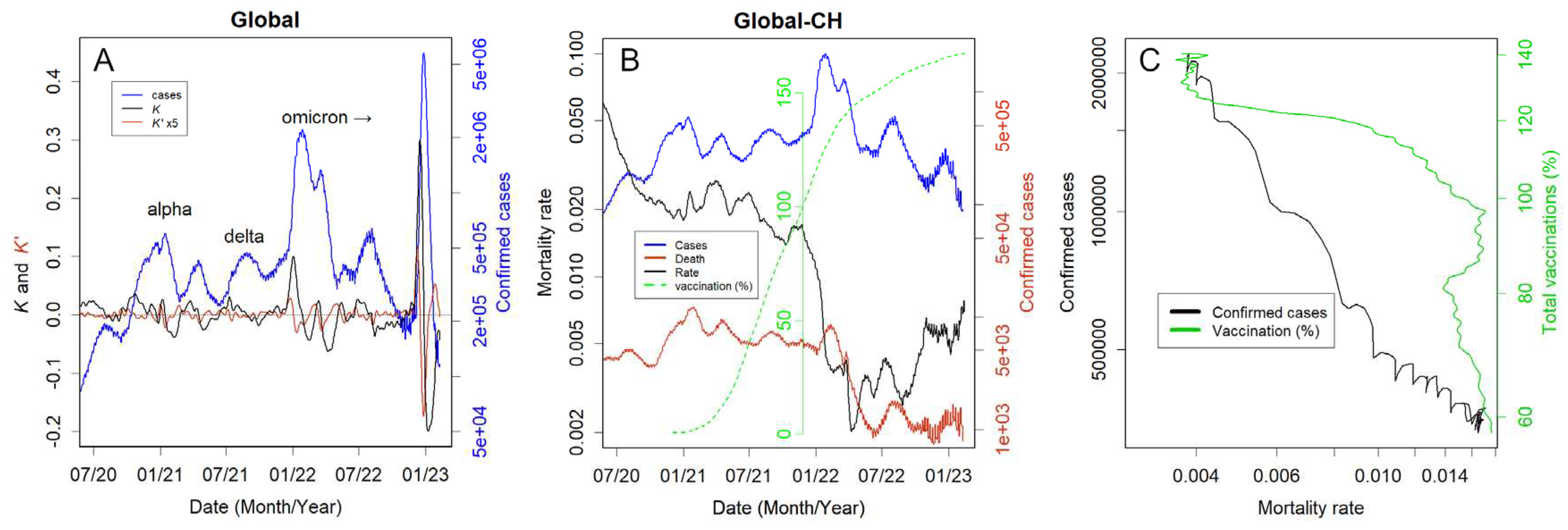
3. Results
3.1. Reliability of observations
3.2. Global data as an example.
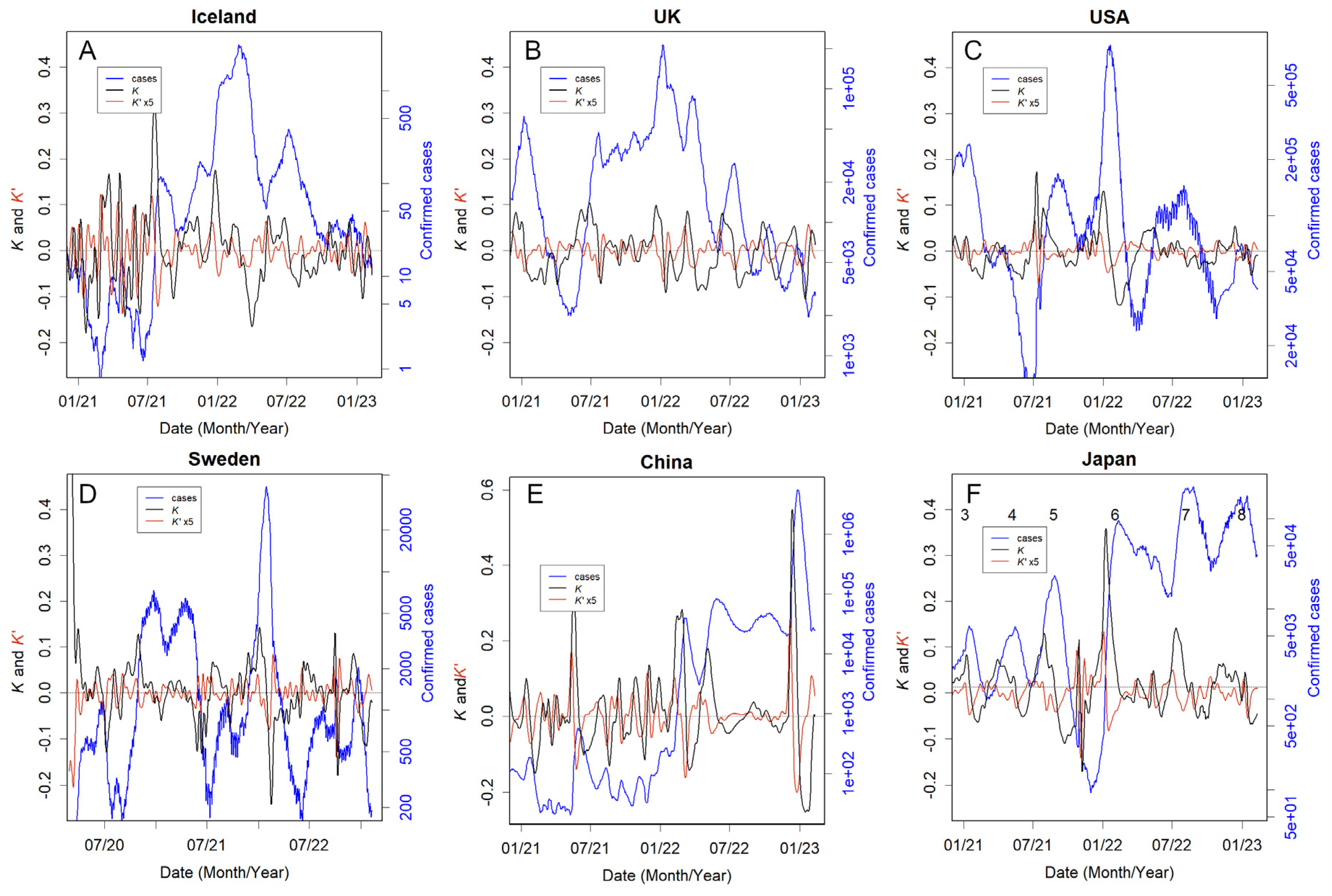
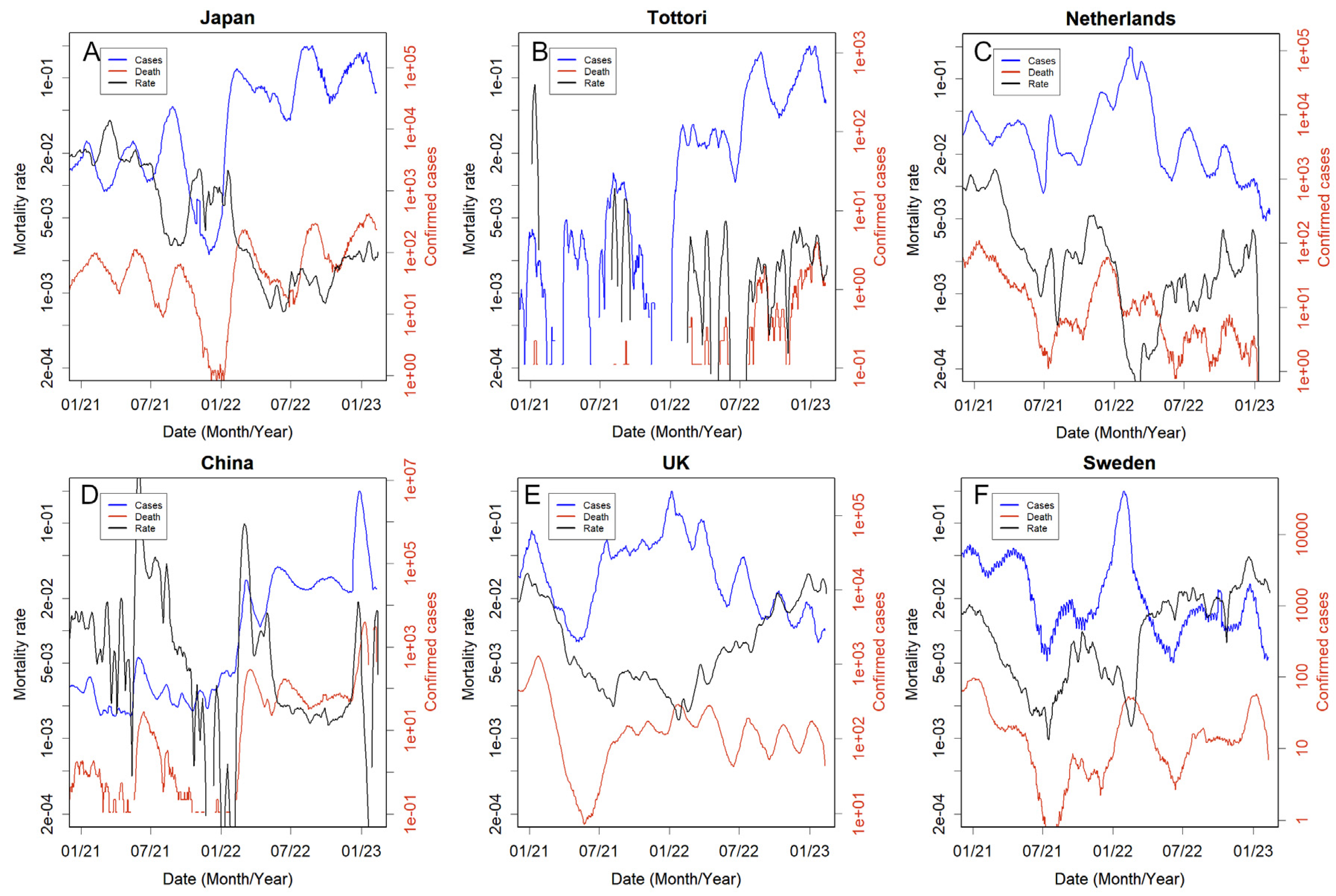
3.3. Country responses
3.4. Countries that could not take the necessary measures or made no attempt to do so
3.5. People defended themselves without recourse to the country
3.6. Countries that relied too heavily on lockdowns
3.7. What difference do the policies make?
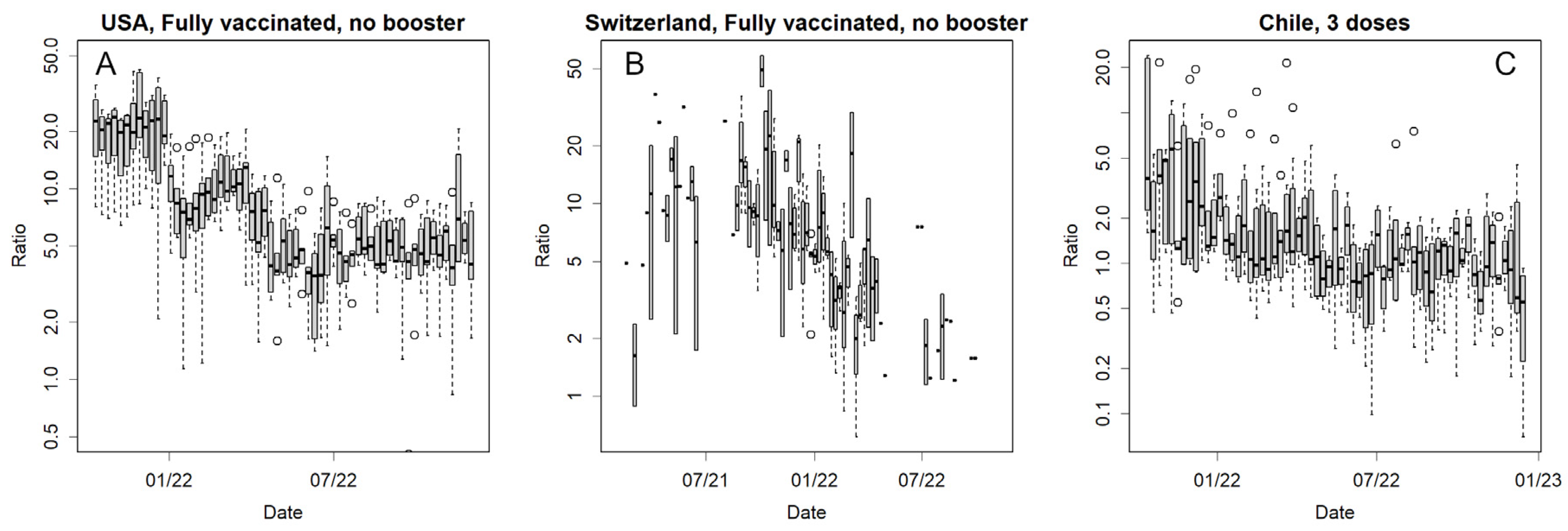
3.8. Vaccine Effectiveness
3.9. Convergence of the epidemics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard 2023. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/data.
- Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM, Topol EJ. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian A, Nirantharakumar K, Hughes S, Myles P, Williams T, Gokhale KM, et al. Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults. Nature Medicine. 2022;28(8):1706-14. [CrossRef]
- Bach, K. New data shows long Covid is keeping as many as 4 million people out of work 2023. Available from: https://www.brookings.edu/research/new-data-shows-long-covid-is-keeping-as-many-as-4-million-people-out-of-work/.
- Belluck, P. Long Covid Is Keeping Significant Numbers of People Out of Work, Study Finds 2023. Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/01/24/health/long-covid-work.html.
- COVID-19 Excess Mortality Collaborators. Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020-21. Lancet. 2022;399(10334):1513-36. Epub 20220310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)02796-3. PubMed PMID: 35279232; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC8912932.
- Hale, E. How Taiwan used simple tech to help contain Covid-19 2022. Available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-60461732.
- Kolbert, E. How Iceland beat the coronavirus 2021. Available from: https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2020/06/08/how-iceland-beat-the-coronavirus.
- Mackenzie, J. How Iceland clamped down to conquer coronavirus 2021. Available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-56412790.
- Aljazeera. WHO says China’s zero-COVID strategy unsustainable 2022. Available from: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/5/10/who-says-chinas-zero-covid-strategy-unsustainable.
- Konishi T. Effect of control measures on the pattern of COVID-19 Epidemics in Japan. . PeerJ. 2021;9:e12215. [CrossRef]
- Cowling B. The impact of ending ‘zero COVID’ in China. Nature. 2023 05 January 2023. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41591-023-00001-1.
- Deutsche Welle. Coronavirus: New Zealand abandons 'zero-COVID' strategy 2021. Available from: https://www.dw.com/en/coronavirus-digest-new-zealand-drops-zero-covid-strategy/a-59396717.
- BBC. Why has Australia switched tack on Covid zero? 2021. Available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-australia-58406526.
- Frans, E. Did sweden’s controversial covid strategy pay off? In many ways it did – but it let the elderly down: The Conversation; 2022. Available from: https://theconversation.com/did-swedens-controversial-covid-strategy-pay-off-in-many-ways-it-did-but-it-let-the-elderly-down-188338.
- Konishi, T. COVID-19 Epidemics Monitored Through the Logarithmic Growth Rate and SIR Model. J Clin Immunol Microbiol. 2022;3(3):1-45. [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. Progressing adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 to humans. Chem-Bio Informatics Journal. 2022;22:1-12. [CrossRef]
- Konishi T. Continuous mutation of SARS-CoV-2 during migration via three routes at the beginning of the pandemic. . PeerJ 2022;10:e12681. [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. SARS-CoV-2 mutations among minks show reduced lethality and infectivity to humans. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0247626. [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 are on the increase against the acquired immunity. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0271305. [CrossRef]
- MWLW, Japan. New corona vaccination results 2023. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/vaccine_sesshujisseki.html.
- Our World in Data. How do death rates from COVID-19 differ between people who are vaccinated and those who are not? 2021. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-deaths-by-vaccination.
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2020.
- Qasmieh SA, Robertson MM, Teasdale CA, Kulkarni SG, Jones HE, McNairy M, et al. The prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long COVID in US adults during the BA.4/BA.5 surge, June–July 2022. Preventive Medicine. 2023:107461. [CrossRef]
- Park S, Marcus GM, Olgin JE, Carton T, Hamad R, Pletcher MJ, et al. Unreported SARS-CoV-2 Home Testing and Test Positivity. JAMA Network Open. 2023;6(1):e2252684-e. [CrossRef]
- Stowe J, Andrews N, Kirsebom F, Ramsay M, Bernal JL. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron and Delta hospitalisation, a test negative case-control study. Nature Communications. 2022;13(1):5736. [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann C, Mayer CK, Claassen M, Maponga T, Burgers WA, Keeton R, et al. Breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 omicron despite mRNA vaccine booster dose. The Lancet. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Staff, T. Israeli trial, world’s first, finds 4th dose ‘not good enough’ against Omicron: The Times of Israel; 2022. Available from: https://www.timesofisrael.com/israeli-trial-worlds-first-finds-4th-dose-not-good-enough-against-omicron/.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Transmission-Based Precautions 2023. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/basics/transmission-based-precautions.html.
- Chu VT, Schwartz NG, Donnelly MAP, Chuey MR, Soto R, Yousaf AR, et al. Comparison of Home Antigen Testing With RT-PCR and Viral Culture During the Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Internal Medicine. 2022;182(7):701-9. [CrossRef]
- Wakita M, Idei M, Saito K, Horiuchi Y, Yamatani K, Ishikawa S, et al. Comparison of the clinical performance and usefulness of five SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0246536.
- Yamamoto M, Okazaki K, Kitai Y, Shinohara K, Yukawa S, Noguchi T, et al. Comparison of six antibody assays and two combination assays for COVID-19. Virology Journal. 2022;19(1):24. [CrossRef]
- Medicine JHU. Taiwan 2023. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/region/taiwan.
- Parker CF, Stern EK. The Trump Administration and the COVID-19 crisis: Exploring the warning-response problems and missed opportunities of a public health emergency. Public Adm. 2022. Epub 20220329. doi: 10.1111/padm.12843. PubMed PMID: 35601345; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC9115435.
- Head, M. Boris Johnson’s pandemic legacy – where he went wrong managing COVID (and some things he got right) 2022. Available from: https://theconversation.com/boris-johnsons-pandemic-legacy-where-he-went-wrong-managing-covid-and-some-things-he-got-right-189666.
- Hamada K, Miki I. Hotel patients in COVID-19 complain of a harsh and anxious life under house arrest: "If my condition suddenly changes here, I'm afraid I won't survive." 2020. Available from: https://www.businessinsider.jp/post-211965.
- Takata, N. East Japan pref. to pay over $50K to family of COVID-19 patient found dead after systemic flaw 2021. Available from: https://mainichi.jp/english/articles/20210907/p2a/00m/0na/005000c.
- MWLW, Japan. A survey of the actual antibody retention rate of novel coronavirus using residual blood samples for testing at the time of blood donation. 2023. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10906000/001070846.pdf.
- CNBC. China says Covid outbreak has infected 80% of population 2023. Available from: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/01/21/china-says-covid-outbreak-has-infected-80percent-of-population.html.
- Yong, N. China Covid: More than 88 million people in Henan infected, official says: BBC; 2023. Available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-64208127.
- The Guardian. 90% of people in China province infected with Covid, says local health official: Guardian; 2023. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/jan/09/life-is-moving-forward-china-enters-new-phase-in-covid-fight-as-borders-open.
- NHK. Corona What will change with the all-knowing review? 2022. Available from: https://www.nhk.or.jp/shutoken/newsup/20220825b.html.
- Murata, T. High Death Toll in 8th Wave "Caused by More Infections than Reported" Volunteer Expert Analysis 2023. Available from: https://mainichi.jp/articles/20230222/k00/00m/040/380000c.
- MWLW, Japan. Preliminary Vital Statistics January 2023 2023 [cited 2023 26 Mar]. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/jinkou/geppo/s2023/dl/202301.pdf.
- Yomiuri Shinbun. Corona deaths somehow the most in Osaka, 3 factors compared to Tokyo...Prefectures continue to be at the mercy of mutant stocks. 2023. Available from: https://www.yomiuri.co.jp/national/20220904-OYT1T50064/.
- 1 News. Australia amassed nearly 20,000 more deaths last year than expected, and experts say Covid-19 is largely to blame. 2023. Available from: https://www.1news.co.nz/2023/03/06/experts-blame-covid-after-nearly-20000-extra-australian-deaths/.
- The Guardian. Covid temporarily reduced Australia’s average life expectancy and lifted death rates to historic highs 2023. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2023/jan/06/covid-reduced-australias-average-life-expectancy-and-lifted-death-rates-to-historic-highs.
- Pandemic. Excess severity in Australia and New Zealand 2023. Available from: https://pandem-ic.com/excess-severity-in-australia-and-new-zealand/.
- Clark-Dow, E. Deaths in New Zealand up by 10% in 2022, impacted by Covid-19 2023. Available from: https://www.stuff.co.nz/national/health/300811491/deaths-in-new-zealand-up-by-10-in-2022-impacted-by-covid19.
- MWLW, Japan. Number of positive cases and deaths from novel coronavirus infection by age group - also examining vaccination by age group - (July 2021) 2021. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000826597.pdf.
- Human Rights Watch. China: Free ‘White Paper’ Protesters 2023. Available from: https://www.hrw.org/news/2023/01/26/china-free-white-paper-protesters.
- Chaudhary N, Weissman D, Whitehead KA. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: principles, delivery and clinical translation. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2021;20(11):817-38. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Interim Statement on COVID-19 vaccines in the context of the circulation of the Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Variant from the WHO Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). 2022.
- Wisnivesky JP, Govindarajulu U, Bagiella E, Goswami R, Kale M, Campbell KN, et al. Association of Vaccination with the Persistence of Post-COVID Symptoms. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2022;37(7):1748-53. [CrossRef]
- Reardon, S. Long COVID risk falls only slightly after vaccination, huge study shows. Natue. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts HA, Clark DA, Kalina C, Sherman C, Brislin S, Heitzeg MM, et al. To vax or not to vax: Predictors of anti-vax attitudes and COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy prior to widespread vaccine availability. PLoS ONE 2022;17(2):e0264019. [CrossRef]
- Jonson AG, Linde L. & Ali AR, et al. COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality Among Unvaccinated and Vaccinated Persons Aged ≥12 Years by Receipt of Bivalent Booster Doses and Time Since Vaccination. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:145–52. [CrossRef]
- Hotez, PJ. Will anti-vaccine activism in the USA reverse global goals? Nature Reviews Immunology. 2022;22(9):525-6. [CrossRef]
- Nikkei Shinbun. Corona Vaccinations for the Elderly to Begin in May, Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare Japan 2023. Available from: https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXZQOUA221560S3A220C2000000/.
- NHK. Why? New COVID-19 vaccines expired and discarded one after another 2023. Available from: https://www3.nhk.or.jp/news/html/20220428/k10013603311000.html.
- Nikkei Shinbun. Corona reserve fund of 12 trillion yen, 90% of the use of which cannot be tracked. Transparency is an issue. 2022. Available from: https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXZQOUA143WV0U2A410C2000000/.
- J-cast news. Corona budget of 16 trillion yen is a suspicious destination. Huge facilities are not used, and benefit fraud is frequent. 2022. Available from: https://www.j-cast.com/trend/2022/05/31438429.html?p=all.
- Zhou P, Shi Z-L. SARS-CoV-2 spillover events. Science. 2021;371(6525):120-2. [CrossRef]
- Hyogo Medical Practitioners Association. The State's New COVID-19 Response Filled with Scientific Neglect 2022. Available from: http://www.hhk.jp/hyogo-hokeni-shinbun/backnumber/2022/1015/100002.php.
- Fraiman J, Erviti J, Jones M, Greenland S, Whelan P, Kaplan RM, et al. Serious adverse events of special interest following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in randomized trials in adults. Vaccine. 2022;40(40):5798- 805. Epub 20220831. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.08.036. PubMed PMID: 36055877; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC9428332.
- Imai M, Watanabe T, Hatta M, Das SC, Ozawa M, Shinya K, et al. Experimental adaptation of an influenza H5 HA confers respiratory droplet transmission to a reassortant H5 HA/H1N1 virus in ferrets. Nature. 2012;486(7403):420-8. [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. Re-evaluation of the evolution of influenza H1 viruses using direct PCA. Scientific Reports. 2019;9(1):19287. [CrossRef]
- Irrgang P, Gerling J, Kocher K, Lapuente D, Steininger P, Habenicht K, et al. Class switch toward noninflammatory, spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after repeated SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Science Immunology. 2023;8(79):eade2798. [CrossRef]
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Acute and postacute sequelae associated with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. Nature Medicine. 2022;28(11):2398-405. [CrossRef]
- Normandin E, Rudy M, Barkas N, Schaffner SF, Levine Z, Padera RF, et al. High-depth sequencing characterization of viral dynamics across tissues in fatal COVID-19 reveals compartmentalized infection. Nature Communications. 2023;14(1):574. [CrossRef]
- Sumi T, Harada K. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in severe disease and long COVID-19. iScience. 2022;25(8):104723. [CrossRef]
- Shinbun, T. The Division over Masks? The government says it's a personal decision...but can it be removed in Japan, a society of peer pressure? 2023. Available from: https://www.tokyo-np.co.jp/article/228322.
- TBS. Behind Prime Minister Kishida's Decision to "No Masks by G7": TBS; 2023. Available from: https://newsdig.tbs.co.jp/articles/-/299633?display=1.
- MHLW, Japan. Wearing a mask is based on personal discretion 2023. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/001056979.pdf.
- Mainichi Shinbun. Death toll to be announced in 2 months at the earliest, MHLW due to transition of COVID-19 to category 5. 2023. Available from: https://mainichi.jp/articles/20230326/ddm/001/040/122000c.
- Ollila H, Partinen M, Koskela J, Borghi J, Savolainen R, Rotkirch A, et al. Face masks to prevent transmission of respiratory infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on face mask use. PLoS ONE 2022;17(12):e0271517. [CrossRef]
- Howard J, Huang A, Li Z, Tufekci Z, Zdimal V, Westhuizen H-Mvd, et al. An evidence review of face masks against COVID-19. PNAS. 2021;118 (Perspective):e2014564118.
- Li H, Yuan K, Sun Y-K, Zheng Y-B, Xu Y-Y, Su S-Z, et al. Efficacy and practice of facemask use in general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Translational Psychiatry. 2022;12(1):49. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




