Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Data Retrieval
2.2. Target Prediction
2.4. RNA22
2.6. RNAhybrid
2.7. RNAfold and RNAcofold
2.8. Mapping of Network-based miRNA-Target Interactions
2.9. Identification of miRNA Binding Site Distribution
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Genome Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Cotton miRNAs-mRNA Interaction Pairs in CLCuKoV-Lu Genome
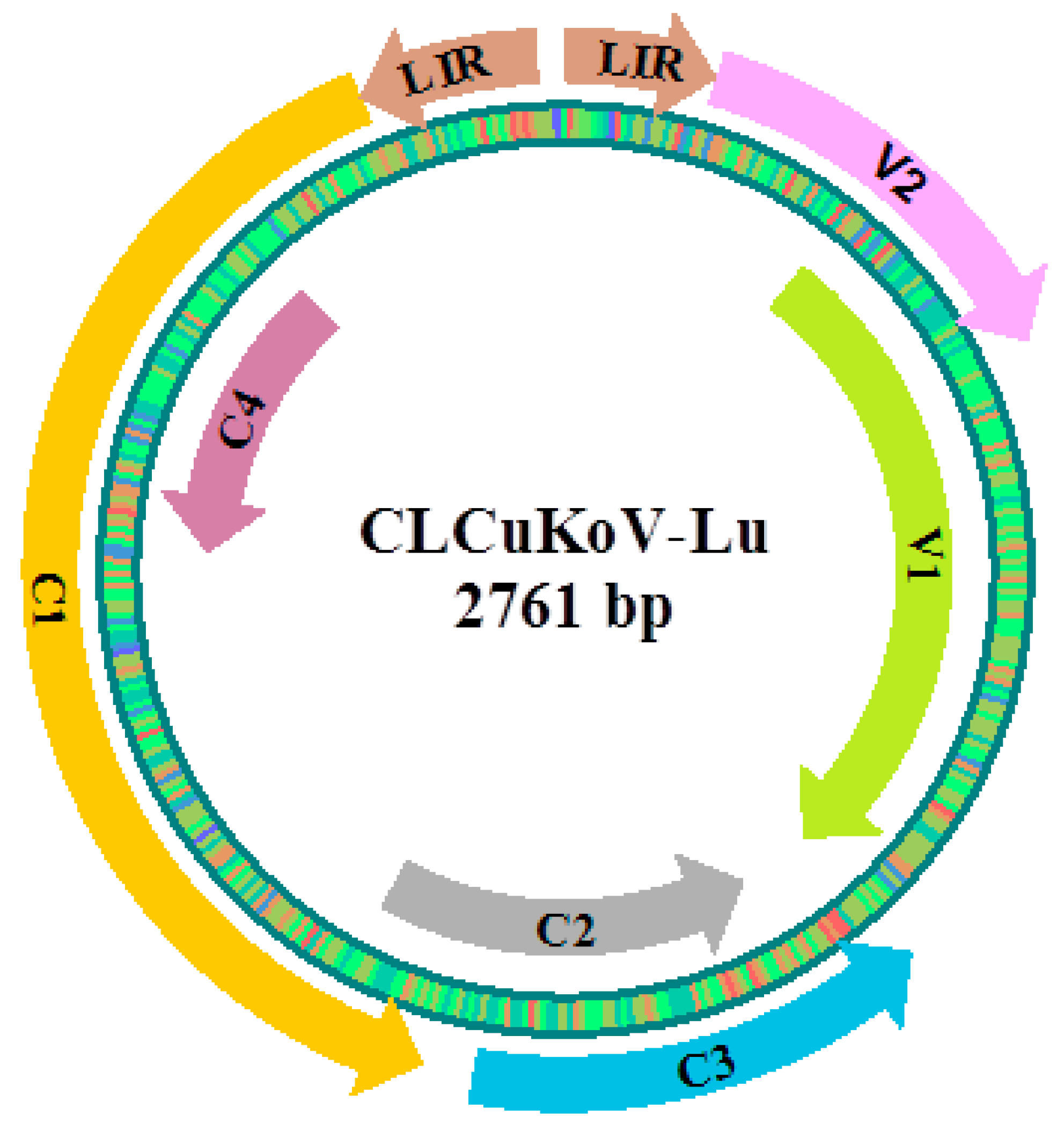
3.2. V1 encoding coat protein (CP)
3.3. V2 encoding pre-coat protein
3.4. C1 encoding replication-associated protein (Rep)
3.5. C2 encoding transcription activator protein (TrAP)
3.6. C3 encoding replication enhancer protein (REn)
3.7. C4 encoding transcription regulator protein
3.8. Large Intergenic Region
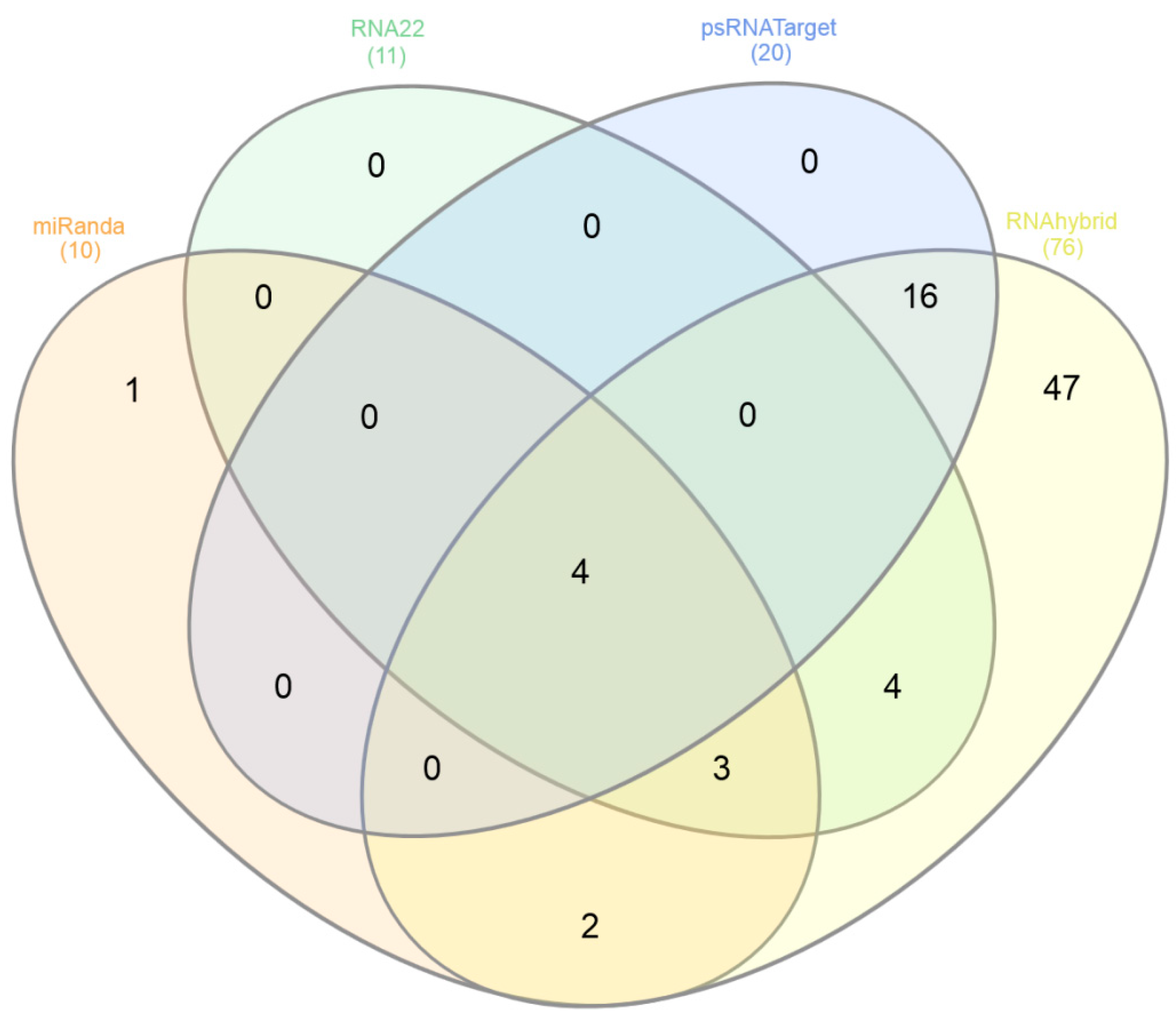
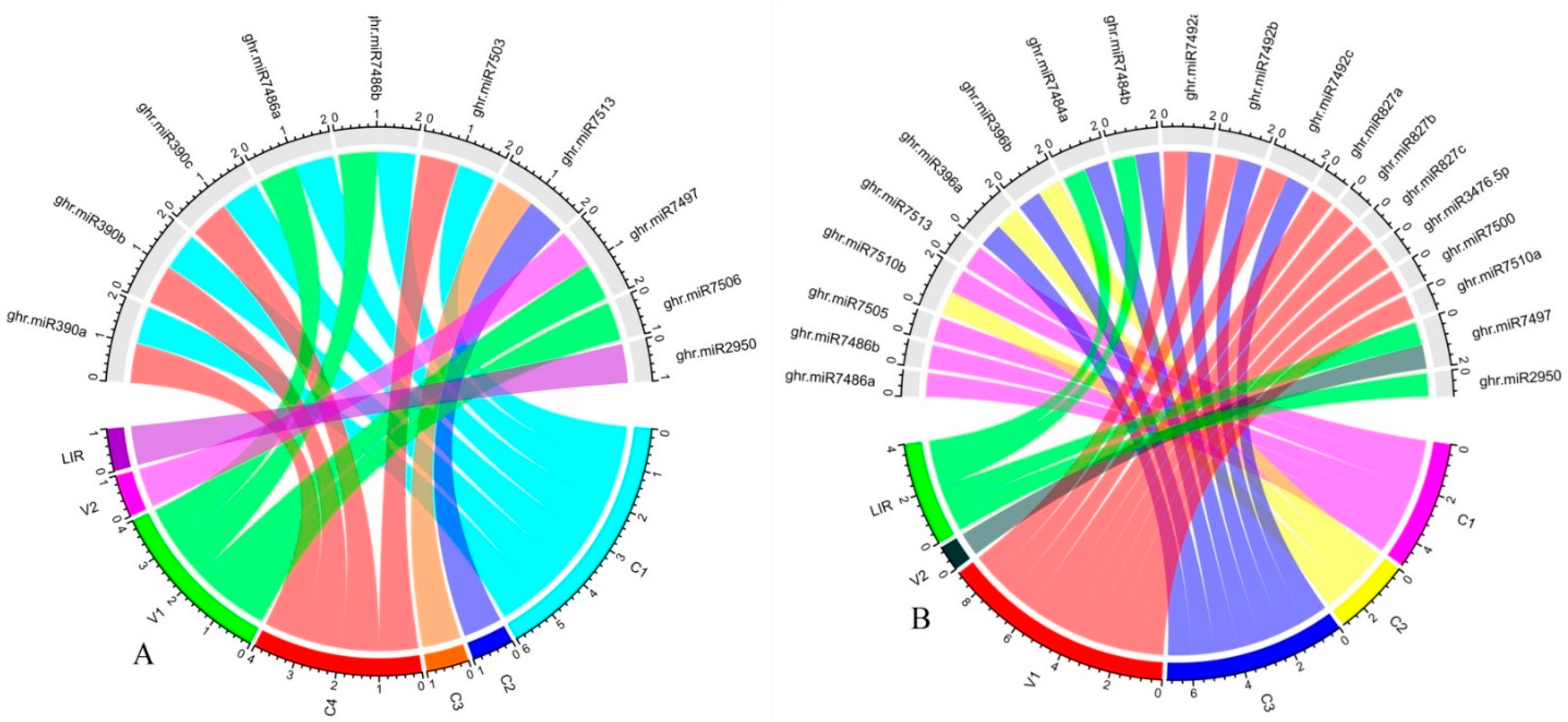
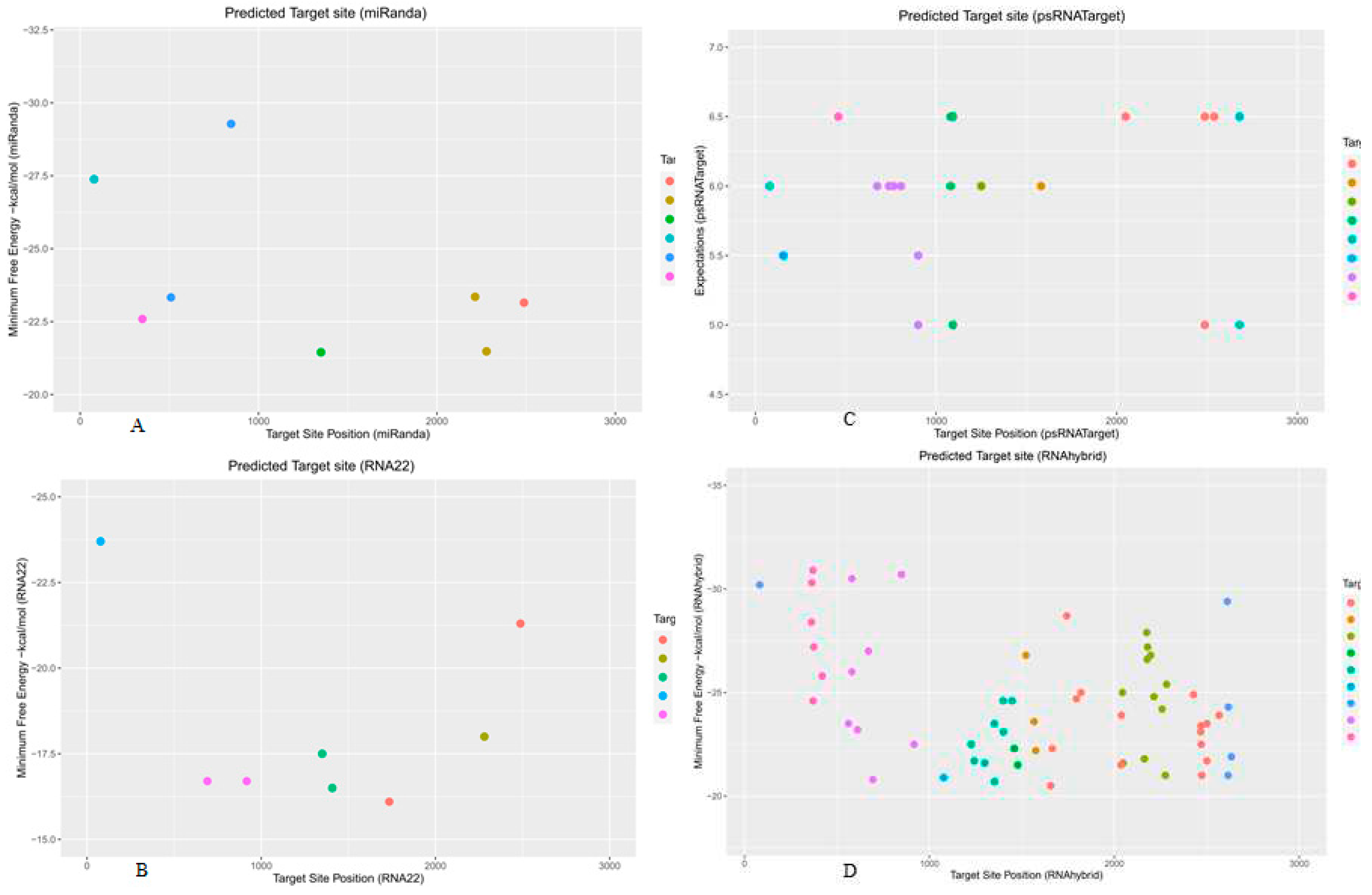
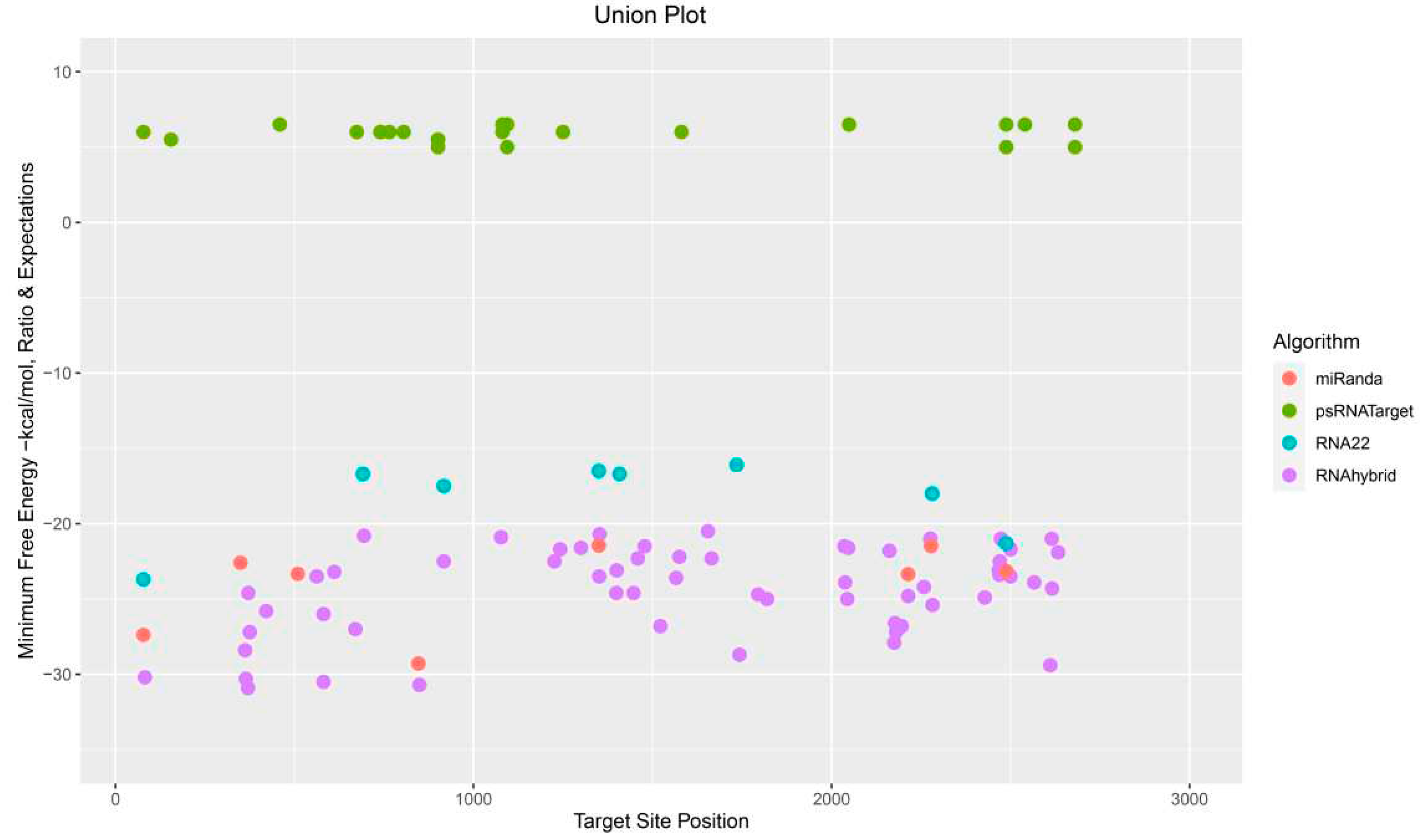
3.9. Predicting Common Cotton miRNAs
3.10. Predicting Consensual Cotton miRNAs
| Cotton miRNA |
Target Site miRanda |
Target Site RNA22 | Target Site psRNATarget |
Target Site RNAhybrid |
MFE * miRanda |
MFE ** RNA22 |
Expectation psRNATarget |
MFE * RNAhybrid |
| ghr-miR390 (a, b, c) | 2278 | 2281 | −21.48 | −18.00 | ||||
| ghr–miR2950 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 82 | −27.38 | −23.70 | 6.5 | −30.20 |
| ghr–miR7484 (a, b) | 1081 | 1077 | 6.5 | −20.90 | ||||
| ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | 2488/846 | 2488 | 2488 | 849 | −23.15/−29.28 | −21.48 | 5.0 | −30.70 |
| ghr-miR7503 | 2214 | 2214 | −23.35 | −27.00 | ||||
| ghr-miR7512 | 917 | 917 | −16.70 | −23.50 | ||||
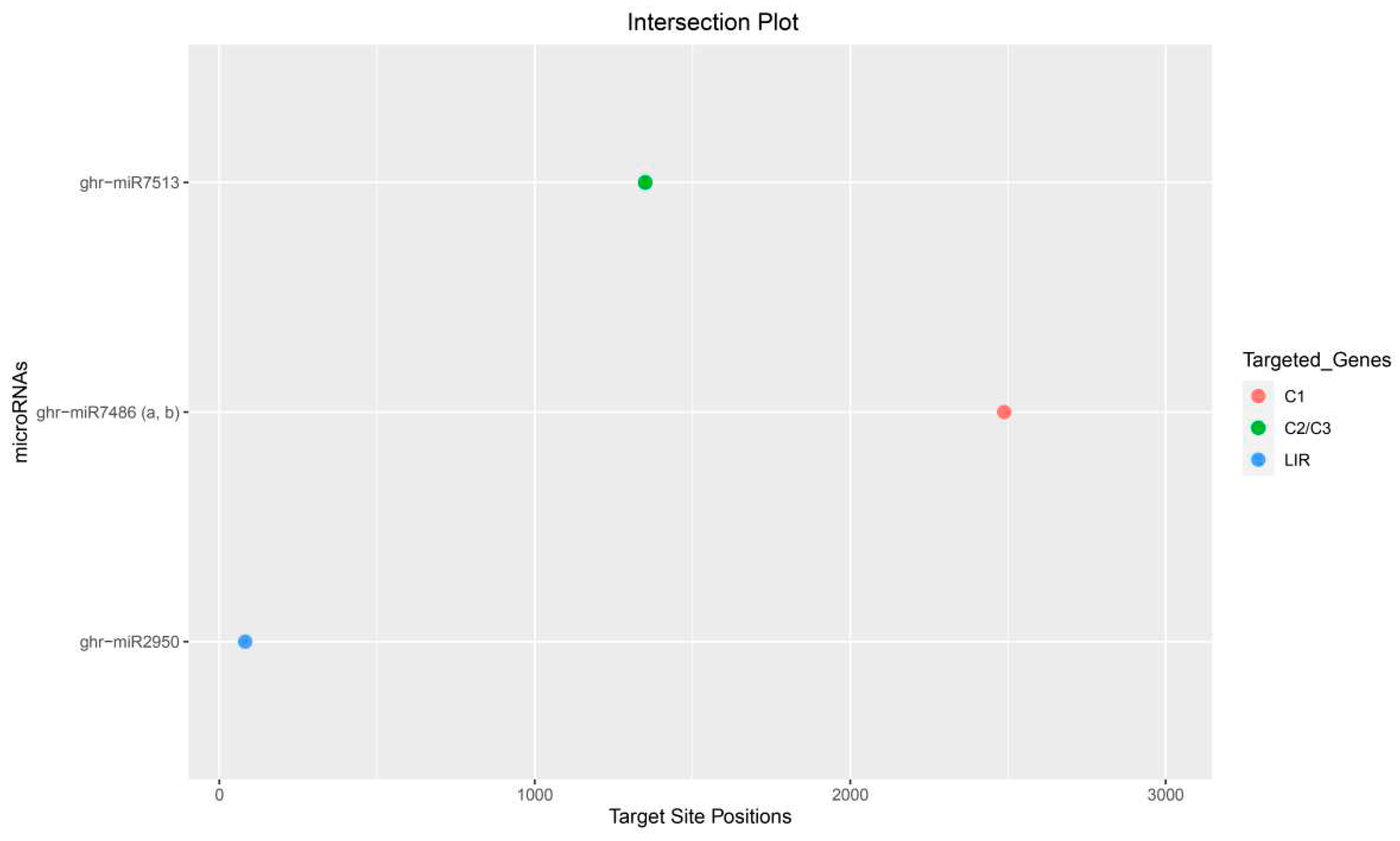
| ghr-miR7513 | 1350 | 1350 | 1351 | −21.45 | −17.50 | −26.80 |
| miRNA ID | Accession ID | Mature Sequence (5′–3′) |
Target Genes ORF(s) |
Target Binding Locus Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ghr-miR390a | MIMAT0005815 | AAGCUCAGGAGGGAUAGCGCC | C1/C4 | 2278–2298 |
| ghr-miR390b | MIMAT0005816 | AAGCUCAGGAGGGAUAGCGCC | C1/C4 | 2278–2298 |
| ghr-miR390c | MIMAT0005817 | AAGCUCAGGAGGGAUAGCGCC | C1/C4 | 2278–2298 |
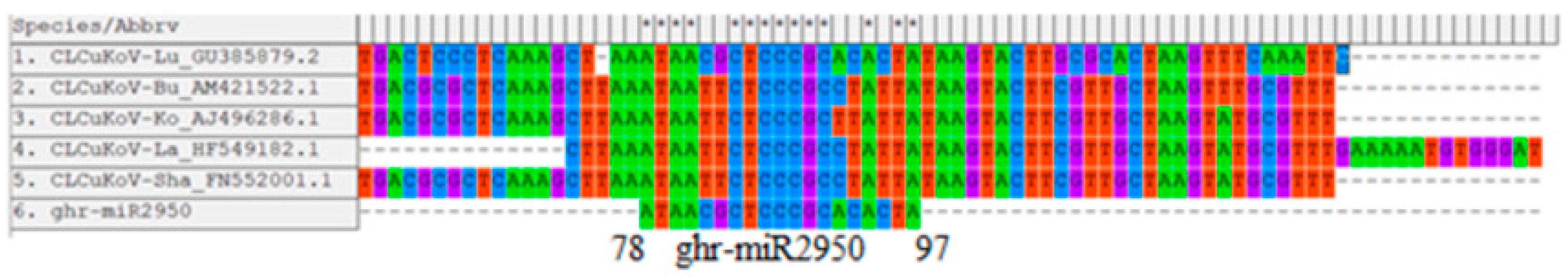
| ghr-miR2950 | MIMAT0014348 | UGGUGUGCAGGGGGUGGAAUA | LIR | 78–97 |
| ghr-miR7484a | MIMAT0029124 | UUUGUAUAUUAGAUCAAAGAGCAA | C3 | 1081–1105 |
| ghr-miR7484b | MIMAT0029125 | UUUGUAUAUUAGAUCAAAGAGCAA | C3 | 1081–1105 |
| ghr-miR7486a | MIMAT0029127 | AAGGAAGCGCUUUGUCCACGUGGA | C1/V1 | 2488–2510/846-871 |
| ghr-miR7486b | MIMAT0029128 | AAGGAAGCGCUUUGUCCACGUGGA | C1/V1 | 2488–2510/871 |
| ghr-miR7503 | MIMAT0029150 | AGAUCGAUGGCUGAACAAGUUAGA | C4/C1 | 2214–2237 |
| ghr-miR7512 | MIMAT0029161 | UGCUACUUGUAGUUAUGCAUG | V1 | 917–938 |
| ghr-miR7513 | MIMAT0029162 | AAUCAGCCAGGAAUCGUUUGA | C2/C3 | 1350–1372 |
| Cassava miRNA |
miRNA-Target Pair | Locus Position |
MFE (Kcal/mol) |
Score | Complementarity (%) |
Mode of Inhibition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ghr-miR2950 | Query: 3' auaagGUGGGGGACGUGUGGu 5' | : | : | | | | | | | | | : Ref: 5' aataaCGCTCCC-GCACACTa 3' |
78-97 | −27.38 | 142 | 93.33 | Cleavage | |
| ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | Query: 3' aggUGCACCUGUUUCGCGAAGGAa 5' | : | | | : | | | | : | | | | | | | Ref: 5' tgaATTTGGG-AAAGTGCTTCCTc 3' |
2488-2510 | −23.15 | 171 | 90.00 | Cleavage | |
| ghr-miR7513 | Query: 3' agUUUGCUAA--GGACCGACUAa 5' : : | | | : | | | | | | | | | | | Ref: 5' atGGACGGTTGACGTGGCTGATg 3' |
1350-1372 | −21.45 | 162 | 85.00 | Cleavage | |
3.10.1. Visualization of miRNA Target
3.10.2. Secondary Structure Analysis
| miRNA ID | Accession ID |
Length Precursor |
MFE*/Kcal/mol | AMFE** | MFEI*** | (G+C)% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ghr-MIR2950 | MI0013555 | 108 nt | −48.10 | −44.53 | −1.002 | 44.44 |
| ghr-MIR7486a | MI0024169 | 105 nt | −81.90 | −78.00 | −1.436 | 54.29 |
| ghr-MIR7486b | MI0024170 | 101 nt | −69.50 | −68.81 | −1.336 | 51.49 |
| ghr-MIR7513 | MI0024204 | 103 nt | −36.70 | −35.63 | −0.965 | 36.89 |
3.10.3. Free Energy (ΔG) Computation
3.10.4. Conserved Genomic Binding Sites Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Geng, S.; Pang, B.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Rui, C.; Cui, J.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, W. Revealing Genetic Differences in Fiber Elongation between the Offspring of Sea Island Cotton and Upland Cotton Backcross Populations Based on Transcriptome and Weighted Gene Coexpression Networks. Genes 2022, 13, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.; Liu, Z.; Guo, C.; Sun, X. Molecular Regulation of Cotton Fiber Development: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, T. World natural fibre production and employment. In Handbook of natural fibres; Elsevier: 2020; pp. 15-36.
- Beasley, J. The origin of American tetraploid Gossypium species. The American Naturalist 1940, 74, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COTTON, C.S.I. IV. CHROMOSOME CONJUGATION IN INTERSPECIFIC HYBRIDS. Jour. Genetics 1937, 34, 5–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nature biotechnology 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.W. Cotton leaf curl disease, a multicomponent begomovirus complex. Molecular Plant Pathology 2003, 4, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.-u.-. .; Khan, A.Q.; Rahmat, Z.; Iqbal, M.A.; Zafar, Y. Genetics and genomics of cotton leaf curl disease, its viral causal agents and whitefly vector: a way forward to sustain cotton fiber security. Frontiers in Plant Science 2017, 8, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Zaidi, S.S.-e.-A.; Shakir, S.; Farooq, M.; Amin, I.; Scheffler, J.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Mansoor, S. Multiple begomoviruses found associated with cotton leaf curl disease in Pakistan in early 1990 are back in cultivated cotton. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.K.; Bhattacharyya, U.K.; Palchoudhury, S.; Balram, N.; Kumar, A.; Arora, R.; Sain, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Khetarpal, R.K.; Sanyal, A. Dominance of recombinant cotton leaf curl Multan-Rajasthan virus associated with cotton leaf curl disease outbreak in northwest India. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0231886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrao, L.; Amin, I.; Shahid, M.S.; Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S. Cotton leaf curl disease in resistant cotton is associated with a single begomovirus that lacks an intact transcriptional activator protein. Virus research 2010, 152, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Shahid, A.A.; Mohamed, B.B.; Dahab, A.A.; Bajwa, K.S.; Rao, A.Q.; Khan, M.A.U.; Ilyas, M.; Haider, M.S.; Husnain, T. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of a variant of highly infectious cotton leaf curl Burewala virus associated with CLCuD from Pakistan. Australian Journal of Crop Science 2013, 7, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Shuja, M.N.; Tahir, M.; Briddon, R.W. Occurrence of a recombinant molecule carrying sequences derived from an alphasatellite and the helper virus in cotton affected with cotton leaf curl disease. Tropical Plant Pathology 2017, 42, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, R.; He, Z. Identification of the cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci transmitting Cotton leaf curl Multan virus. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica 2016, 43, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, D. Genomic variation and diversification in begomovirus genome in implication to host and vector adaptation. Plants 2021, 10, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Saeed, Q.; He, Z.; Lu, L. Transmission efficiency of Cotton leaf curl Multan virus by three cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci complex in cotton cultivars. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Montero, J.R.; Hameed, U.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Rasool, G.; Haider, M.S.; Herrmann, H.-W.; Brown, J.K. Demographic expansion of the predominant Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)(Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) mitotypes associated with the Cotton leaf curl virus epidemic in Pakistan. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 2019, 112, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Zerbini, F.M.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E.; Ramos-Sobrinho, R.; Silva, J.C.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Briddon, R.W.; Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Idris, A. Revision of Begomovirus taxonomy based on pairwise sequence comparisons. 2015.
- Kumar, J.; Kumar, A.; Roy, J.; Tuli, R.; Khan, J. Identification and molecular characterization of begomovirus and associated satellite DNA molecules infecting Cyamopsis tetragonoloba. Virus Genes 2010, 41, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Shahid, A.A.; Rao, A.Q.; Bajwa, K.S.; Husnain, T. Functional characterization of a bidirectional plant promoter from cotton leaf curl Burewala virus using an Agrobacterium-mediated transient assay. Viruses 2014, 6, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Shahid, A.A.; Rao, A.Q.; Brown, J.K.; Husnain, T. Development and Evaluation of the Cotton Leaf Curl Kokhran Virus-Burewala Bidirectional Promoter for Enhanced Cry1Ac Endotoxin Expression in Bt Transgenic Cotton. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornancini, V.A.; Irazoqui, J.M.; Flores, C.R.; Vaghi Medina, C.G.; Amadio, A.F.; López Lambertini, P.M. Reconstruction and characterization of full-length begomovirus and alphasatellite genomes infecting pepper through metagenomics. Viruses 2020, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchoudhury, S.; Khare, V.; Balram, N.; Bhattacharyya, U.; Das, S.; Shukla, P.; Chakraborty, P.; Biswas, K. A multiplex polymerase chain reaction for the simultaneous detection of the virus and satellite components associated with cotton leaf curl begomovirus disease complex. Journal of Virological Methods 2022, 300, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, S.; Raghavendra, K.; Monga, D.; Nagrale, D.; Prabhulinga, T.; Hiremani, N.; Meshram, M.; Kranthi, S.; Gokte-Narkhedkar, N.; Waghmare, V. Development of Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A new tool for rapid diagnosis of cotton leaf curl viral disease. Journal of Virological Methods 2022, 114541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Albuquerque, L.C.; Rocha, W.B.; Nagata, T. A simple method for cloning the complete begomovirus genome using the bacteriophage φ29 DNA polymerase. Journal of virological methods 2004, 116, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Ali, I.; Abbas, Q.; Mansoor, S.; Briddon, R.W.; Amin, I. Real-time quantitative PCR assay for the quantification of virus and satellites causing leaf curl disease in cotton in Pakistan. Journal of virological methods 2017, 248, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haible, D.; Kober, S.; Jeske, H. Rolling circle amplification revolutionizes diagnosis and genomics of geminiviruses. Journal of virological methods 2006, 135, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Amin, I.; Zaidi, S.S.-e.-A.; Rahman, S.U.; Farooq, M.; Fauquet, C.M.; Mansoor, S. Circular DNA enrichment sequencing reveals the viral/satellites genetic diversity associated with the third epidemic of cotton leaf curl disease. Biology Methods and Protocols 2021, 6, bpab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.-L.; Cui, X.-Y.; Chen, Q.-F.; Wang, X.-W.; Liu, S.-S. Cotton leaf curl disease: which whitefly is the vector? Phytopathology 2018, 108, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H. Small RNAs Participate in Plant–Virus Interaction and Their Application in Plant Viral Defense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, Q.; Ai, X.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yan, F. Transgenic Rice Plants Expressing Artificial miRNA Targeting the Rice Stripe Virus MP Gene Are Highly Resistant to the Virus. Biology 2022, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Estrada, B.; Sánchez, M.A.; Valencia-Jiménez, A. Foliar Infiltration of Virus-Derived Small Hairpin RNAs Triggers the RNAi Mechanism against the Cucumber Mosaic Virus. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.-Q. RNA Interference: Promising Approach to Combat Plant Viruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zheng, B.; Yu, Y.; Won, S.Y.; Mo, B.; Chen, X. The role of Mediator in small and long noncoding RNA production in Arabidopsis thaliana. The EMBO journal 2011, 30, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y. Transcription and processing of primary microRNAs are coupled by Elongator complex in Arabidopsis. Nature Plants 2015, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavella, P.A.; Koenig, D.; Weigel, D. Plant secondary siRNA production determined by microRNA-duplex structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhong, L.; Weng, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.-J. Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2020, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.-H.; Slotkin, R.K. The initiation of RNA interference (RNAi) in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2021, 61, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Weinstein, E.G.; Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes & development 2002, 16, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; You, C.; Chen, X. The evolution of microRNAs in plants. Current opinion in plant biology 2017, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, J.C.; Ambros, V. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 2003, 301, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B. MicroRNA expression profiles during cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L) fiber early development. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, S.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Identification and profiling of upland cotton microRNAs at fiber initiation stage under exogenous IAA application. BMC genomics 2019, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y.; Ismayil, A. Plant Defense and Viral Counter-Defense during Plant–Geminivirus Interactions. Viruses 2023, 15, 510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hull, J.J.; Liang, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Mansoor, S.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S. Genome-wide analysis of cotton miRNAs during whitefly infestation offers new insights into plant-herbivore interaction. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 5357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Hua, C.-L.; Ding, S.-W.; Guo, H.-S. Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen. Nature plants 2016, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Hu, M.; Dong, J.; Shen, F. MicroRNA414c affects salt tolerance of cotton by regulating reactive oxygen species metabolism under salinity stress. RNA biology 2019, 16, 362–375. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, X.; Mo, J.; Long, L.; Xiang, L.; Xie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y. Identification of novel microRNAs in the Verticillium wilt-resistant upland cotton variety KV-1 by high-throughput sequencing. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Sui, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tian, D.; Zhao, Y. Identification of microRNAs involved in drought stress responses in early-maturing cotton by high-throughput sequencing. Genes & genomics 2018, 40, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Li, F. An asymmetric bulge enhances artificial microRNA-mediated virus resistance. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2020, 18, 608. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.-W.; Lin, S.-S.; Reyes, J.L.; Chen, K.-C.; Wu, H.-W.; Yeh, S.-D.; Chua, N.-H. Expression of artificial microRNAs in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers virus resistance. Nature biotechnology 2006, 24, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Bourexis, D.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Comeau, D.C.; Funk, K.; Kim, S.; Klimke, W. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, A.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome biology 2003, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human microRNA targets. PLoS biology 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, K.C.; Huynh, T.; Tay, Y.; Ang, Y.-S.; Tam, W.-L.; Thomson, A.M.; Lim, B.; Rigoutsos, I. A pattern-based method for the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell 2006, 126, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loher, P.; Rigoutsos, I. Interactive exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3322–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic acids research 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic acids research 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic acids research 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms for molecular biology 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhart, S.H.; Tafer, H.; Mückstein, U.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. Partition function and base pairing probabilities of RNA heterodimers. Algorithms for Molecular Biology 2006, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome research 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MEGA, X. molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms; S Kumar, G Stecher, M Li, C Knyaz, K Tamura. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC bioinformatics 2004, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błażewicz, J.; Formanowicz, P.; Kasprzak, M.; Michalak, K.; Wierzejewski, P. Clustal W algorithm for multiple sequence alignment revisited. Foundations of Computing and Decision Sciences 2001, 26, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Gandrud, C. Reproducible research with R and RStudio; Chapman and Hall/CRC: 2018.
- Fan, Y.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-W.; Zhao, J.; Chi, Y.; Bouvaine, S.; Liu, S.-S.; Seal, S.E.; Wang, X.-W. Bemisia tabaci vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 interacts with begomoviruses and plays a role in virus acquisition. Cells 2021, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, M.; Popovski, S.; Kollenberg, M.; Gorovits, R.; Brown, J.K.; Cicero, J.M.; Czosnek, H.; Winter, S.; Ghanim, M. Implication of Bemisia tabaci heat shock protein 70 in begomovirus-whitefly interactions. Journal of virology 2012, 86, 13241–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima Priyadarshini, C.; Ambika, M.; Tippeswamy, R.; Savithri, H. Functional characterization of coat protein and V2 involved in cell to cell movement of Cotton leaf curl Kokhran virus-Dabawali. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, A.; Castillo, A.G.; Safaie, N.; Bejarano, E.R.; Luna, A.P.; Shams-Bakhsh, M. Functional analysis of V2 protein of Beet curly top Iran virus. Plants 2022, 11, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Jiang, K.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Wu, G.; Qing, L. Characterization of pathogenicity-associated V2 protein of tobacco curly shoot virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Ismayil, A.; Yuan, Y.; Lian, B.; Jia, Q.; Han, M.; Deng, H.; Hong, Y. Geminiviral V2 protein suppresses transcriptional gene silencing through interaction with AGO4. Journal of virology 2019, 93, e01675–01618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipp, K.; Rau, P.; Schäfer, B.; Gronenborn, B.; Jeske, H. The RXL motif of the African cassava mosaic virus Rep protein is necessary for rereplication of yeast DNA and viral infection in plants. Virology 2014, 462, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X. Cryo-EM structure of a begomovirus geminate particle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Herrera, S.I.; Romero-Osorio, A.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.; Pastor-Palacios, G.; Cardenas-Conejo, Y.; Ramírez-Prado, J.H.; Riego-Ruiz, L.; Minero-García, Y.; Ambriz-Granados, S.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R. A lineage of begomoviruses encode Rep and AC4 proteins of enigmatic ancestry: hints on the evolution of geminiviruses in the New World. Viruses 2019, 11, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, J.; Regedanz, E.; Lu, L.; Ruan, J.; Bisaro, D.M.; Sunter, G. Manipulation of the plant host by the geminivirus AC2/C2 protein, a central player in the infection cycle. Frontiers in plant science 2020, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Díaz, T.; Macho, A.P.; Beuzón, C.R.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Bejarano, E.R. The C2 protein from the geminivirus Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus decreases sensitivity to jasmonates and suppresses jasmonate-mediated defences. Plants 2016, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluthambi, K.; Sunitha, S. Targets and mechanisms of geminivirus silencing suppressor protein AC2. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12, 645419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settlage, S.B.; See, R.G.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L. Geminivirus C3 protein: replication enhancement and protein interactions. Journal of virology 2005, 79, 9885–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondong, V.N. Geminivirus protein structure and function. Molecular plant pathology 2013, 14, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Puche, L.; Orílio, A.F.; Zerbini, F.M.; Lozano-Durán, R. Small but mighty: Functional landscape of the versatile geminivirus-encoded C4 protein. PLoS Pathogens 2021, 17, e1009915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.-W.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; Lin, N.-S.; Hu, C.-C. Identification of Crucial Amino Acids in Begomovirus C4 Proteins Involved in the Modulation of the Severity of Leaf Curling Symptoms. Viruses 2022, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Abdin, M.Z.; Khan, J.A. Functional characterization of a strong bi-directional constitutive plant promoter isolated from cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodersen, P.; Sakvarelidze-Achard, L.; Bruun-Rasmussen, M.; Dunoyer, P.; Yamamoto, Y.Y.; Sieburth, L.; Voinnet, O. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 2008, 320, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, Z.; Akhtar, K.P.; Hameed, A.; Sarwar, N.; Imran-Ul-Haq; Khan, S. A. Biochemical alterations in leaves of resistant and susceptible cotton genotypes infected systemically by cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. Journal of Plant Interactions 2014, 9, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrao, L.; Akhter, S.; Tahir, M.N.; Amin, I.; Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S. Cotton leaf curl disease in Sindh province of Pakistan is associated with recombinant begomovirus components. Virus research 2010, 153, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Tariq, H.K.; Hu, X.-W.; Khan, J.; Zou, Z. Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches Identify Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) Genome Encoded MicroRNAs Targeting Rubber Tree Virus 1. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Ashraf, F.; Shen, L.; Iqbal, M.S.; Zhang, S. In silico identification of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) genome encoded microRNAs targeting sugarcane bacilliform virus. PloS one 2022, 17, e0261807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ashraf, F.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Shen, L.; Khan, J.; Zhang, S. Potential targets for evaluation of sugarcane yellow leaf virus resistance in sugarcane cultivars: in silico sugarcane miRNA and target network prediction. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2021, 35, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.N.; Rasheed, S.; Iqbal, M.S.; Jamal, A.; Khalid, S.; Shamim, Z. IN SILICO PREDICTION OF POTENTIAL miRNAs TO TARGET ZYMV IN CUCUMIS MELO. Pak. J. Bot 2022, 54, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, F.; Ashraf, M.A.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S. A novel computational approach to the silencing of Sugarcane Bacilliform Guadeloupe A Virus determines potential host-derived MicroRNAs in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). PeerJ 2020, 8, e8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, Y.Z.A.; Ziebell, H. Novel targets for engineering Physostegia chlorotic mottle and tomato brown rugose fruit virus-resistant tomatoes: in silico prediction of tomato microRNA targets. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, B.; Iqbal, M.S.; Batcho, A.A.; Nasir, I.A.; Rashid, B.; Husnain, T.; Henry, R.J. Target prediction of candidate miRNAs from Oryza sativa for silencing the RYMV genome. Computational biology and chemistry 2019, 83, 107127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Jabbar, B.; Sharif, M.N.; Ali, Q.; Husnain, T.; Nasir, I.A. In silico MCMV silencing concludes potential host-derived miRNAs in maize. Frontiers in plant science 2017, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ali, B.; Brown, J.K.; Shahid, I.; Yu, N. In Silico Identification of Cassava Genome-Encoded MicroRNAs with Predicted Potential for Targeting the ICMV-Kerala Begomoviral Pathogen of Cassava. Viruses 2023, 15, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillet, A.; Anouar, Y.; Lecroq, T.; Dubessy, C. Prediction methods for microRNA targets in bilaterian animals: Toward a better understanding by biologists. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2021, 19, 5811–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Bovolenta, L.A.; Nachtigall, P.G.; Herkenhoff, M.E.; Lemke, N.; Pinhal, D. Combining results from distinct microRNA target prediction tools enhances the performance of analyses. Frontiers in genetics 2017, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Yoon, S. Got target?: computational methods for microRNA target prediction and their extension. Experimental & molecular medicine 2010, 42, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Riffo-Campos, Á.L.; Riquelme, I.; Brebi-Mieville, P. Tools for sequence-based miRNA target prediction: what to choose? International journal of molecular sciences 2016, 17, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchthai, U.; Yee, C.S.L.; Wong, S.-M. Resistance to CymMV and ORSV in artificial microRNA transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana plants. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Tahir, M.N.; Amin, I.; Mansoor, S. Amplicon-based RNAi construct targeting beta-C1 gene gives enhanced resistance against cotton leaf curl disease. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Hameed, U.; Qayyum Rao, A.; Ahad, A.; Yasmeen, A.; Akram, F.; Bajwa, K.S.; Scheffler, J.; Nasir, I.A. Engineered disease resistance in cotton using RNA-interference to knock down Cotton leaf curl Kokhran virus-Burewala and Cotton leaf curl Multan betasatellite expression. Viruses 2017, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, A.; Kiani, S.; Butt, A.; Rao, A.Q.; Akram, F.; Ahmad, A.; Nasir, I.A.; Husnain, T.; Mansoor, S.; Amin, I. Amplicon-based RNA interference targeting V2 gene of cotton leaf curl Kokhran Virus-Burewala strain can provide resistance in transgenic cotton plants. Molecular biotechnology 2016, 58, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Amin, I.; Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S. Artificial microRNA-mediated resistance against the monopartite begomovirus Cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. Virology journal 2013, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Shen, F. Genome-wide profiling of miRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs in the Verticillium dahliae–inoculated cotton roots. PloS one 2012, 7, e35765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Shen, F. Identification of miRNAs and their targets in cotton inoculated with Verticillium dahliae by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2015, 16, 14749–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Deng, P.; Saha, S.; Jenkins, J.N.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Abdurakhmonov, I.Y.; Buriev, Z.T.; Pepper, A.; Ma, D.-P. Genome-wide identification and characterization of microRNAs differentially expressed in fibers in a cotton phytochrome A1 RNAi line. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0179381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Woodward, A.W.; Agarwal, V.; Guan, X.; Ha, M.; Ramachandran, V.; Chen, X.; Triplett, B.A.; Stelly, D.M.; Chen, Z.J. Genome-wide analysis reveals rapid and dynamic changes in miRNA and siRNA sequence and expression during ovule and fiber development in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Genome biology 2009, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedden, P.; Kamiya, Y. Gibberellin biosynthesis: enzymes, genes and their regulation. Annual review of plant biology 1997, 48, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Li, C.; Sun, R.; Zhang, B.; Nichols, R.L.; Hake, K.D.; Pan, X. Small RNA and degradome deep sequencing reveals important roles of microRNAs in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) response to root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita infection. Genomics 2021, 113, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Nichols, R.L.; Li, C.; Zhang, B. MicroRNA-target gene responses to root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) infection in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Genomics 2019, 111, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.J. The use of RNAi-based screens to identify host proteins involved in viral replication. Future microbiology 2010, 5, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, M.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Tsai, J.C.; Bassik, M.C.; Gilbert, L.A.; Villalta, J.E.; Kwon, S.C.; Chang, H.; Kim, V.N. Next-generation libraries for robust RNA interference-based genome-wide screens. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, E3384–E3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Chiramel, A.I.; Schmidt, M.L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Whitt, N.; Watt, A.; Dunham, E.C.; Shifflett, K.; Traeger, S.; Leske, A. A genome-wide siRNA screen identifies a druggable host pathway essential for the Ebola virus life cycle. Genome medicine 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

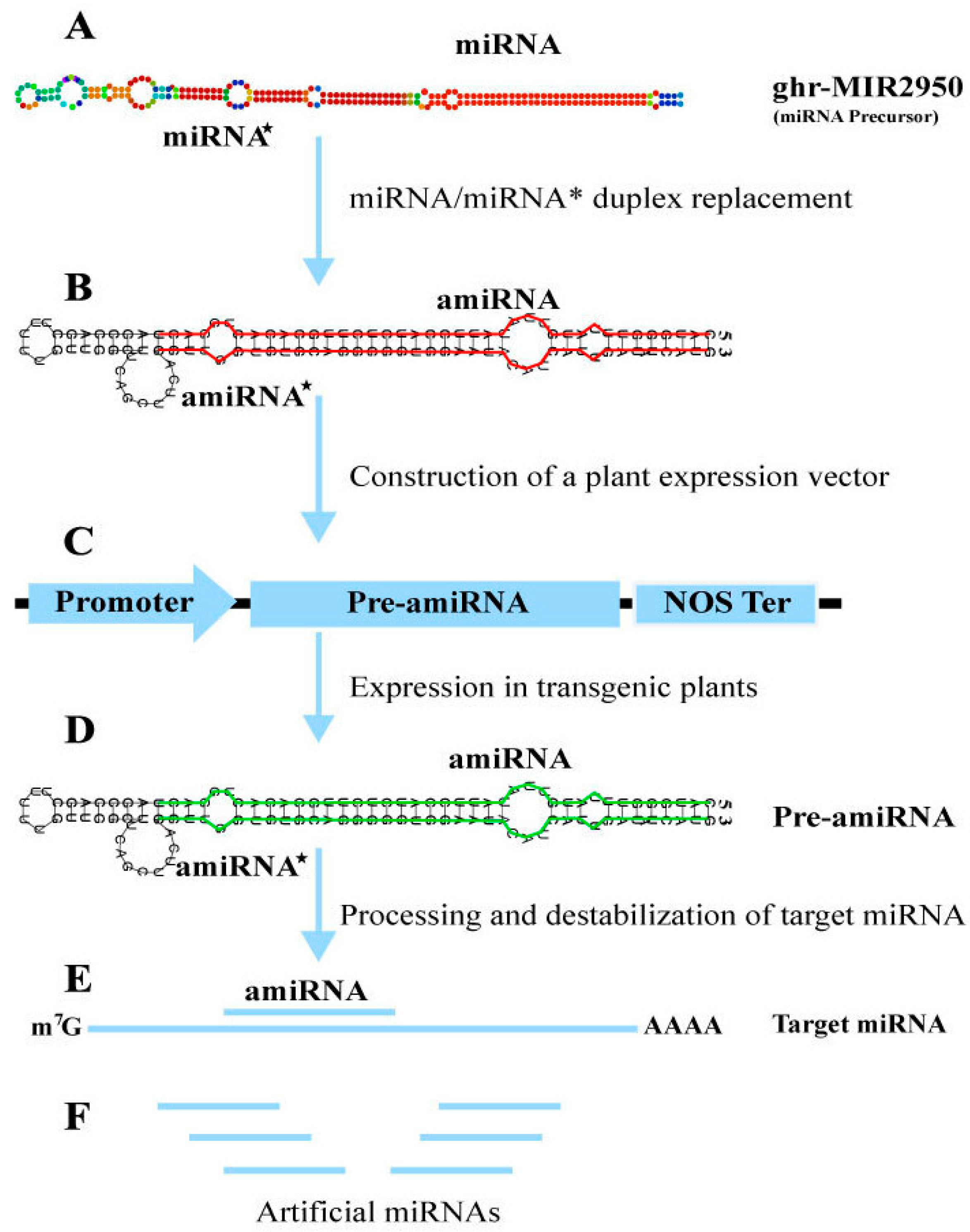
| Tools | Algorithms | Seed Pairing | Multiple Target Sites | Translation inhibition | Free Energy | Availability (web /code) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRanda | Local alignment | + | + | + | + | +/+ |
| RNA22 | FASTA | − | + | − | + | +/− |
| psRNATarget | Smith-Waterman | − | + | + | − | +/− |
| RNAhybrid | Intermolecular hybridization | + | + | + | + | +/− |
| Tapirhybrid | FASTA | + | + | − | + | +/+ |
| TargetSpy | FASTA | − | + | − | + | −/+ |
| Targetfinder | FASTA | + | − | − | + | −/+ |
| CLCuKoV-Lu gene |
miRanda | RNA22 | psRNATarget | RNAhybrid | |
| V1 | ghr-miR7486 (a, b), ghr-miR7506 | ghr-miR169a, ghr-miR7512 | ghr-miR827 (a, b, c), ghr-miR3476-5p | ghr-miR393, ghr-miR482 (a, b), | |
| ghr-miR7492 (a, b, c), ghr-miR7500 ghr-miR7510a |
ghr-miR7486 (a, b), ghr-miR7490, ghr-miR7504a, ghr-miR7510a, ghr-miR7512 |
||||
| V1/V2 | ghr-miR7497 | ghr-miR7497 | ghr-miR164, ghr-miR479, ghr-miR3476-5p, ghr-miR7497, ghr-miR7498, ghr-miR7507 | ||
| C1 | ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | ghr-miR398, ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | ghr-miR156 (a, b, c, d), ghr-miR162a, ghr-miR166b, ghr-miR169a, ghr-miR398, ghr-miR827 (a, b, c), ghr-miR2949-3p, ghr-miR3476-3p, ghr-miR7491, ghr-miR7492 (a, b, c), ghr-miR7500, ghr-miR7501, ghr-miR7505, ghr-miR7506 |
|
| C2 | ghr-miR394 (a, b), ghr-miR7504b | ||||
| C1/C2 | ghr-miR7510b | ghr-miR7485, ghr-miR7487, ghr-miR7514 | |||
| C3 | ghr-miR7484 (a, b), ghr-miR7492 (a, b, c) | ghr-miR7484 (a, b) | |||
| C2/C3 | ghr-miR7513 | ghr-miR7489, ghr-miR7513 | ghr-miR396 (a, b) | ghr-miR167 (a, b), ghr-miR396 (a, b), ghr-miR2949(a-5p, b, c),ghr-miR7489, ghr-miR7493, ghr-miR7494, ghr-miR7511, ghr-miR7513 | |
| C4/C1 | ghr-miR390 (a, b, c), ghr-miR7503 | ghr-miR390 (a, b, c) | ghr-miR160, ghr-miR172, ghr-miR390 (a, b, c), ghr-miR399d ghr-miR7488, ghr-miR7495 (a, b), ghr-miR7503, ghr-miR7508, ghr-miR7509, ghr-miR7510b |
||
| LIR | ghr-miR2950 | ghr-miR2950 | ghr-miR2950 | ghr-miR399 (a, b, c, e), ghr-miR2948-5p, ghr-miR2950, | |
| miRNA ID | miRNA-mRNA Sequence (5′–3′) |
ΔG Duplex (Kcal/mol) |
ΔG Binding(Kcal/mol) | |
| ghr-miR2950 | 5′ UGGUGUGCAGGGGGUGGAAUA 3′ 5′ AATAACGCTCCCGCACACTA 3′ |
−24.80 | −24.37 | |
| ghr-miR7486 (a, b) | 5′ AAGGAAGCGCUUUGUCCACGUGGA 3′ 5′ TGAATTTGGGAAAGTGCTTCCTC3′ |
−22.70 | −17.41 | |
| ghr-miR7513 | 5′AAUCAGCCAGGAAUCGUUUGA 3’ 5′ ATGGACGGTTGACGTGGCTGATG 3’ |
−20.90 | −17.74 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





