Key messages
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide and remains incurable even with appropriate treatment.
Advances in nano-ophthalmology appear to have the potential to revolutionize the current challenges of glaucoma treatment.
Nanotechnology-based glaucoma drainage devices promise to allow a more effective control over post-operative scarring and optimal IOP reduction through all phases of the post-operative period.
Despite the decreased post-operative complications and apparently enhanced biocompatibility of nano-based drainage devices, toxicity concerns and efficacy in humans must be addressed.
Introduction
Nanotechnology involves the creation and use of materials, systems, and devices at the size scale of intracellular structures and molecules, in the range of nanometers (<100 nm). 1 Nanomedicine consists in the use of these engineered nanodevices and nanostructures to intervene in human biological systems at the molecular level with the aim of achieving benefit and overcome current medical limitations. 2
Nanomaterials exhibit several attractive physical and chemical properties, that differ from those at the macroscopic scale, and that has been motivating the research of nanotechnology applications to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of several diseases. 3 The key feature is the size of nanoparticles that gives them an increased surface area-to-volume ratio, with more sites for chemical reactions than a macroscale material and allows penetration through small capillaries, absorption by surrounding cells, and therefore an efficient drug accumulation at target sites. 1,4
Over the last decade, nano-ophthalmology has been one of the subjects of interest of nanotechnology research, with solutions being presented to overcome current therapeutic challenges in glaucoma and other eye diseases. Concerning glaucoma treatment, both medical and surgical approaches can benefit from nanomedicine advances. 5
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide and the most frequent cause of irreversible blindness. 6,7 Tham et al. estimated that 76 million people globally had glaucoma in 2020, a number that has been projected to increase almost 1.5 times until 2040, reaching 111.8 million of affected people.
Glaucoma is a chronic, progressive optic neuropathy characterized by degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) in the inner retina, loss of their axons in the optic nerve and corresponding visual field loss. 8 A complex combination of risk factors contribute to glaucoma development and progression, such as IOP, increasing age, genetic mutations, ethnicity, structural ocular variations, and vascular abnormalities. 9 IOP is the only modifiable risk factor and its reduction the only proven method to decline glaucoma evolution. Thus, most of the therapies used to decrease disease progression rely on IOP lowering strategies. 8,9
Medical therapy with topical eye drops is usually the first-line treatment for glaucoma. 10 The IOP lowering agents act either by suppressing AH synthesis in the ciliary body - beta-blockers, alpha-agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - or by enhancing AH outflow through the trabecular meshwork (TM), Schlemm´s canal and uveoscleral pathways - cholinergic drugs and prostaglandin analogues. 11
Despite being the most common approach to glaucoma, topical therapy faces several limitations that compromise its effectiveness. First, it requires a rigid patient compliance, which is difficult to achieve due to frequent administration cycles, ocular discomfort when dropping the eye drops and local adverse effects 12, particularly frequent with the prostaglandin analogues. 8 Second, the intraocular bioavailability is very low. Only less than 5% of topically administered medications are biologically available because of limited ocular penetration - due to precorneal tear film rapid turnover and limited corneal epithelium permeability -, and rapid clearance from the AH. 13,14 Finally, the systemic absorption of these topical medications can lead to systemic side effects that can contraindicate the administration in some patients. 8
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems can revolutionize glaucoma medical treatment by overcoming these current limitations. Various nanomaterials can be used in these new delivery systems, but the more widely used are nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, nanodiamonds, nanocrystals, liposomes, dendrimers, cyclodextrins, and other devices such as contact lenses. 15 These nano-delivery systems promise to provide more efficiency in crossing ocular barriers, a better drug solubility, a more targeted delivery with controlled and sustained drug release and consequently better bioavailability, while causing minimal tissue irritation. 16
In addition to the delivery of IOP lowering agents, these nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems can also be useful for delivering adjuvant anti-fibrotic drugs following glaucoma surgery, and for administration of neuroprotective and neuroregenerative agents: a new perspective of non-IOP-dependent glaucoma medical treatment that is focused on protection or promotion of RGCs regeneration. 17
When medical treatment isn’t enough to achieve adequate IOP reduction with acceptable adverse effects, laser trabeculoplasty, trabeculectomy, Glaucoma Drainage Devices (GDDs) implantation surgery, or minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries (MIGS) are indicated. 5,8
Trabeculectomy is still the most performed glaucoma surgical treatment 17,while GDDs implantation have been indicated in cases of high-risk glaucomatous eyes for failure of standard trabeculectomy and eyes that have undergone prior incisional surgery. 18
Ahmed®, Molteno®, Krupin® and Baerveldt® are the principal types of GDDs currently available commercially. 19 Although they differ in terms of their shape, surface area, composition and valved or non-valved profile, these GDDs present similar success rates in IOP control and vision preservation, and no relevant differences in the incidence of post-operative complications. 20,21
Despite GDDs implantation being associated with less immediate post-operative complications and a better control of IOP-lowering action than the standard techniques, there are still a significant number of complications that compromise surgical outcomes. 3 The most frequent are immediate hypotony, excessive capsule fibrosis and subsequent clinical failure, erosion of the tube or plate edge, strabismus, and infection. 22
Overall, fibrosis is the major cause of poor surgical outcome, decreasing the global success rate of GDDs implantation to about 40-50% at five years post-surgery. 23
Some strategies such as intraoperative and post-operative antimetabolite serial injections of mitomycin C (MMC) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) have been proved to reduce the likelihood of developing a post-operative hypertensive phase due to excessive post-surgical fibrosis. 23 However, serial injections represent an increased risk of infection and discomfort for patients, with an inherent risk of complications (e.g., endophthalmitis and conjunctival erosion over the tube) and more surgical interventions. 24
There is an obvious need of developing devices with more physiologic and inert biomaterials, devices that incorporate antifibrotic agents and innovative systems able to be adapted to the encapsulation process. 17 Nanomaterials can be manipulated to have a better biodegradability, biocompatibility, electrical conductivity, magnetic proprieties, and ultimately to induce a more effective response than conventional ones. 25,26
Research in nanotechnology applications to glaucoma surgery and GDDs has brought promising results. 3 The goal of this systematic review is to summarize the state of the art regarding nanodevices made to be used in glaucoma drainage surgery and exploit the solutions presented to overcome the current limitations of glaucoma surgical treatment.
Methods
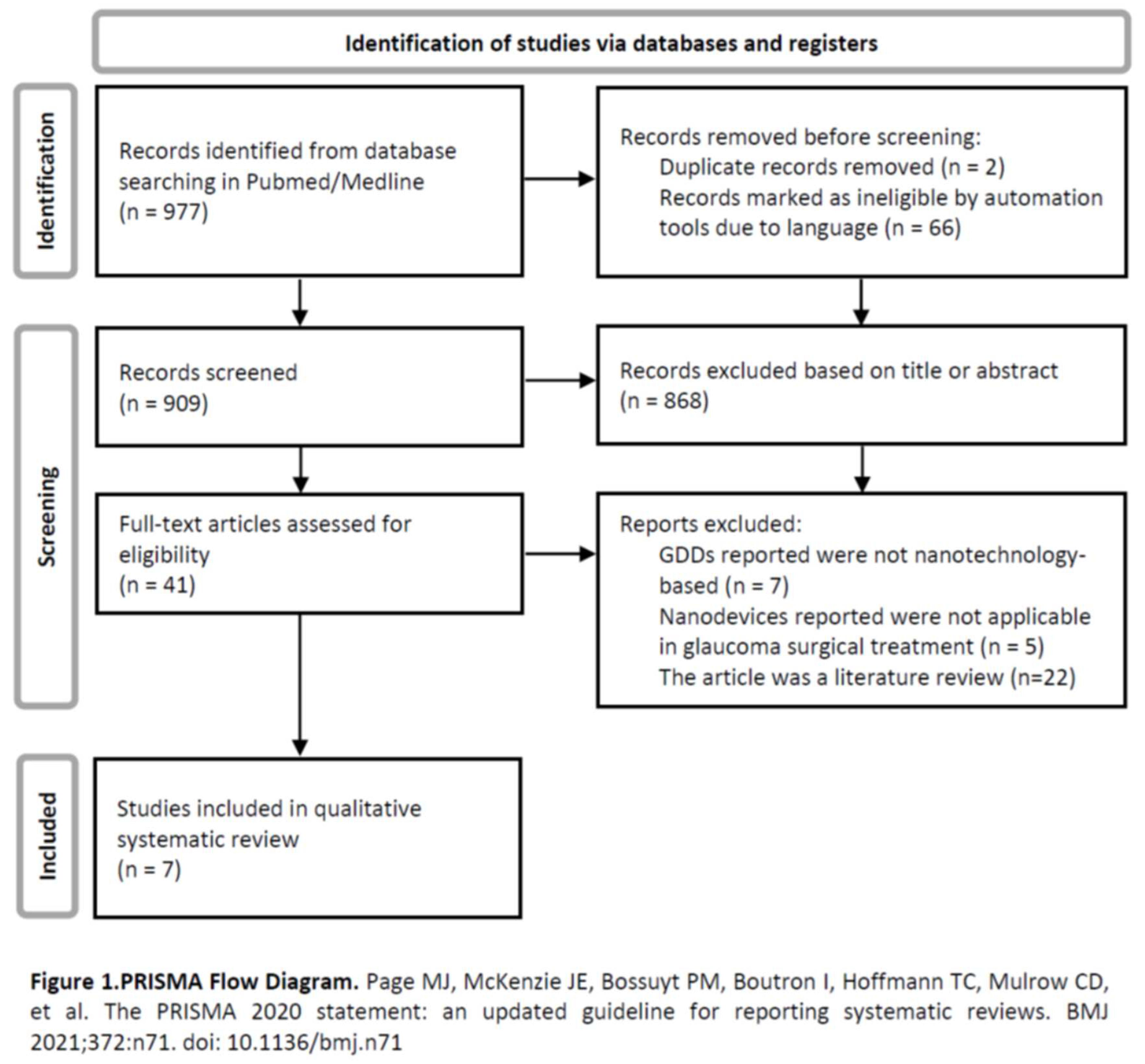
A literature search in the PubMed/Medline database was performed using the following keywords: “glaucoma surgery” or “glaucoma drainage device”, and either “nanotechnology” or “nanoparticles” or “nanomedicine” or “valve”. There were included articles published until March 1, 2023, including publications not yet in print but available online. Were only included articles written in Portuguese, Spanish or English. No other restrictions were applied. Identification of relevant articles was first done through the title and abstract’s information. A second selection was done by full-text articles assessment. Seven articles were included in this systematic review. A PRISMA diagram that systematizes this search is presented - Figure 1.
Nanotechnology-Based Glaucoma Drainage Devices: Results
Nanotechnology-based GDDs have been developed with the aim of improving the outcomes of glaucoma surgery. Current available GDDs rely on flow resistance provided by the subconjunctival plate encapsulation to prevent early post-operative hypotony. Even the valved devices, despite not being usually associated with early post-operative hypotony, require subconjunctival implantation to achieve a closing pressure. The encapsulation process takes time, is often delayed and unpredictable due to variable degree of fibrosis of the bleb, contributing to most post-operative complications: early hypotony or later ocular hypertension. 27
Regarding that, Paschalis et al. designed a ferromagnetic valve using pressure-sensitive ferrofluid nanoparticles, for reliable and predictable IOP regulation without the need of subconjunctival encapsulation. Ferrofluid consisted of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles suspended in an inert, non-magnetic fluorocarbon carrier oil, and exhibited super-paramagnetic properties, such as drag force along field gradients. Two NdFeB rare-earth micromagnets were used to create a static magnetic field, with the primary micro magnet holding the ferrofluid in place and the secondary acting as a pressure regulator. When the AH pressure exerted on the ferrofluid exceeded the magnetic force between the secondary magnet and the ferrofluid, the valve opened. In in vitro experiments, the valves were calibrated to an opening and closing pressure of 10 and 7 mmHg, respectively. Flow/pressure response measurements showed reliable and reproducible results over a study period of three months, with pressure calibration maintenance only with minor variations of less than 0.5 mmHg. Implantation of the ferrofluid valve in 3 rabbit eyes showed predictable IOP regulation for at least 2 weeks, with the valve implanted eye having a mean IOP value (11.8 ± 2 mmHg) significantly lower than the contralateral control eye (14 ± 3 mmHg). No adverse events were noted, indicating that the valve was well tolerated and biocompatible. This device also offered the possibility of external placement of the outlet tip, while providing a good closing pressure, which could provide accessibility for observation and replacement of the device. The main limitation of this valve is the incompatibility with static magnetic fields, like those produced in magnetic resonant imaging systems. 27
Non valved GDDs have a higher risk of early post-operative hypotony that may lead to an anterior chamber (AC) flattening, choroidal effusions, hemorrhage, or other complications. Regarding that, Maleki et al. created a nano device with a mechanism that would limit the outflow at the early stages after surgery and vanish after bleb formation. The device consisted in a microfabricated biodegradable truncated-cone-shaped plug filter, designed to be placed into the silicone tube of a Baerveldt® glaucoma implant. Were tested two biodegradable polymers, polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) and poly-lactic-acid (PLA), that theoretically would degrade within a few weeks when the bleb formation has progressed, having no risks related with permanent valves that may become blocked or influence the AH flow rate in the long term. The fabricated plug filters were 500 μm long, with a 500 μm base diameter, an apex diameter of 300 μm and a central hole of 44 μm effective diameter. In vitro testing was conducted using phosphate buffered saline (PBS) in a 37 ◦C silicone oil bath to simulate the AH and body temperature. None of the tested polymers showed appropriate characteristics to be used as the structural material alone. PLGA plug filters regulated the pressure for up to 2 days until it started to rise, due to plug filter deformation and collapse of the holes. PLA filters controlled the pressure for up to 15 days, however, this polymer has a long degradation time which increases the risk associated with clogging with inflammatory and red blood cells. A solution presented was the creation of 50/50 PLGA plug filters coated with SU-8 or UV-curing adhesive. These plug filters were able to regulate the pressure up to 45 days, a period long enough for bleb formation. However, the PLGA degradation scheme is bulk and not continuous over time, which results in a sharp drop in IOP after plug-filter degradation initiates. Further research is needed to adjust the plug composition. 28
Parikh et al. develop a new nano-structured glaucoma shunt via electrospinning that also promises to achieve optimal IOP reduction through all phases of the post-operative period. The group created two GDDs with 6 mm in length. The first, named PET shunt (PS), was a small-lumen cylindrical shunt composed of non-degradable polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers, with a static 50 µm inner lumen. The main goal of its creation was to determine the viability of an electrospun GDD. The second embodiment, the Pressure Control Shunt (PCS), was also composed by a non-degradable PET outer core, with a 75 µm inner lumen and a degradable inner core composed of polyglycolide (PGA) nanofibers that absorb over three weeks, thereby increasing the inner lumen diameter to 100 µm in order to modulate AH outflow over wound healing time. PS and PCS were evaluated in vitro by pumping a PBS fluid flow through the shunts. PS showed to be durable and leak-proof. The lumen remained patent, maintained its size and the inner surface of the shunt showed no degradation after one week of in vitro testing. PCS testing went for 28 days with inner diameter and pressure differential measurements at day 7, 14 and 28. No leakage was observed and the resistance to flow decreased linearly throughout the study, leading to minimal flow resistance at day 28, when the inner PGA core was fully degraded. For in vivo experiments the nano-structured shunts were implanted in normotensive rabbit eyes. Both PS and PCS prevented hypotony/flattening of the AC throughout the post-operative period and maintained patency during the study. PS demonstrated a 30% IOP reduction and PCS showed a 44% IOP reduction 27 days after implantation, with a sustained decline due to the inner core degradation. The used materials proved to be biocompatible, non-immunogenic, and to directly integrate ocular tissue through their nanoarchitecture, a feature that minimizes fibrosis. These results demonstrate potential for clinical utility. 29
Following a somewhat similar idea but a different research pathway, Olson et al. developed a GDD regulator implant that allows non invasive and customized post-operative control of AH drainage. A 23-gauge silicone tube from a regular GDD was adapted with a polyvinyldifluoride (PVDF) nanopore membrane. The device must be implanted beneath the scleral flap of traditional trabeculectomy and acts as an AH flow regulator. It allows a basal low rate of fluid flow across its surface and can be ruptured with a Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet) laser beam to increase the AH flow. Thus, it is expected to prevent hypotony in the early post-operative period and to allow flow regulation when IOP begins to rise. Both in vitro and ex vivo testing (in an enucleated porcine eye) were done using a fluid under the physiologic pressure of 20 mmHg. Experiments showed that increasing the number of membrane laser perforations allows an adjustable and predictable amount of flow through GDD, existing a stable relationship between flow rate and the number of laser spots applied to the membrane. 30
Pan et al. developed an artificial nano-drainage implant known as ANDI, fabricated through microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanofabrication technologies. ANDI is composed of a nanoporous membrane connected to an integrated polymeric shaft that is inserted through the sclera into the AC, mimicking the drainage function of the TM and allowing a bypass route for the AH outflow to the subconjunctival space. The nanoporous membrane is made of silicon nitride covered with a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) layer and has a set of tapered pores, with a top opening of 400 nm and a bottom opening of 200 nm in diameter, to minimize the flow resistance and enable the nano-filtration membrane to provide the designed flow resistance to the AH. In vitro characterization of ANDI showed that though the membrane was able to give the designed flow resistance to saline solutions, when plasma perfusions with the same protein level as the AH are used, occurs clogging of proteins inside the nanopores that significantly increase the resistance. Further efforts will be necessary to apply surface chemistry modifications to the nanoporous membrane, to reduce AH proteins clogging and to reach the ideal AH outflow. 31
Excessive scar tissue develops in as many as 30% of eyes with implanted GDDs. Intraoperative and post-operative bleb injections with antifibrotic agents such as MMC or 5-FU seem to decrease GDD surgical failure by decreasing subconjunctival fibrosis and the hypertensive phase. However, as referred earlier, repeated bleb injections can be very discomfortable to the patient and represent a higher risk of infection. This invasive post-operative approach could be overcome by pre-coating the GDD with antifibrotic agents prior to implantation. This was what motivated Sahiner et al. to create a slow-release antifibrotic drug-coated GDD, using poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) disks loaded with mitomycin C (MMC) which were then attached to the lower half of a commercial Ahmed® glaucoma valve plate. The device was made using redox-polymerization techniques and was tested using in vitro and in vivo experiments. Semicircular pHEMA disks containing different concentrations of MMC were attached to the lower half of an Ahmed® glaucoma valve plate. Water was pumped through the modified Ahmed® GGD at a rate comparable to that of AH outflow. The device released MMC in vitro over 1 to 2 weeks. For in vivo testing, modified and unmodified Ahmed® glaucoma valves were implanted in a rabbit model, and drug release and fibrosis were assessed after 3 months. The slow release antifibrotic drug coated GDD released MMC during the 3 months of the study and histologic analysis demonstrated a significant reduction in inflammatory reaction and fibrosis in the resulting blebs, without differences among the different concentrations of MMC. Post-operative IOP was not evaluated because of the low accuracy of IOP measurements in the rabbit model due to their thin cornea. The authors consider that if these results can be reproduced in human beings, the device could reduce the failure rate of GDDs. 32
Ponnusamy et al. proposed another model of antifibrotic drug coated GDD. An Ahmed® glaucoma valve was coated with a double-layer porous film of biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA). 5-FU was loaded into the bottom layer and MMC into the top layer, with the aim of providing an initial release of MMC to limit immune cell infiltration in the critical period immediately after surgery, followed by a slow release of 5-FU created to inhibit fibroblast proliferation. The purpose was that the continuous drug release of antifibrotic agents to the subconjunctival space would prevent fibrosis over the most active period of post-operative wound healing – the first 28 days. In vitro experiments showed a very fast release of MMC with most of the active drug being delivered within 1 day, followed by the release of 5-FU initiating within 3 to 5 days and continuing for up to 28 days. Drug cytotoxicity was accessed using a COS-1 cell culture model that demonstrated PLGA biocompatibility and non-toxicity besides inhibition of cell proliferation from day 1 which persisted until the PLGA film was almost totally degraded. 33
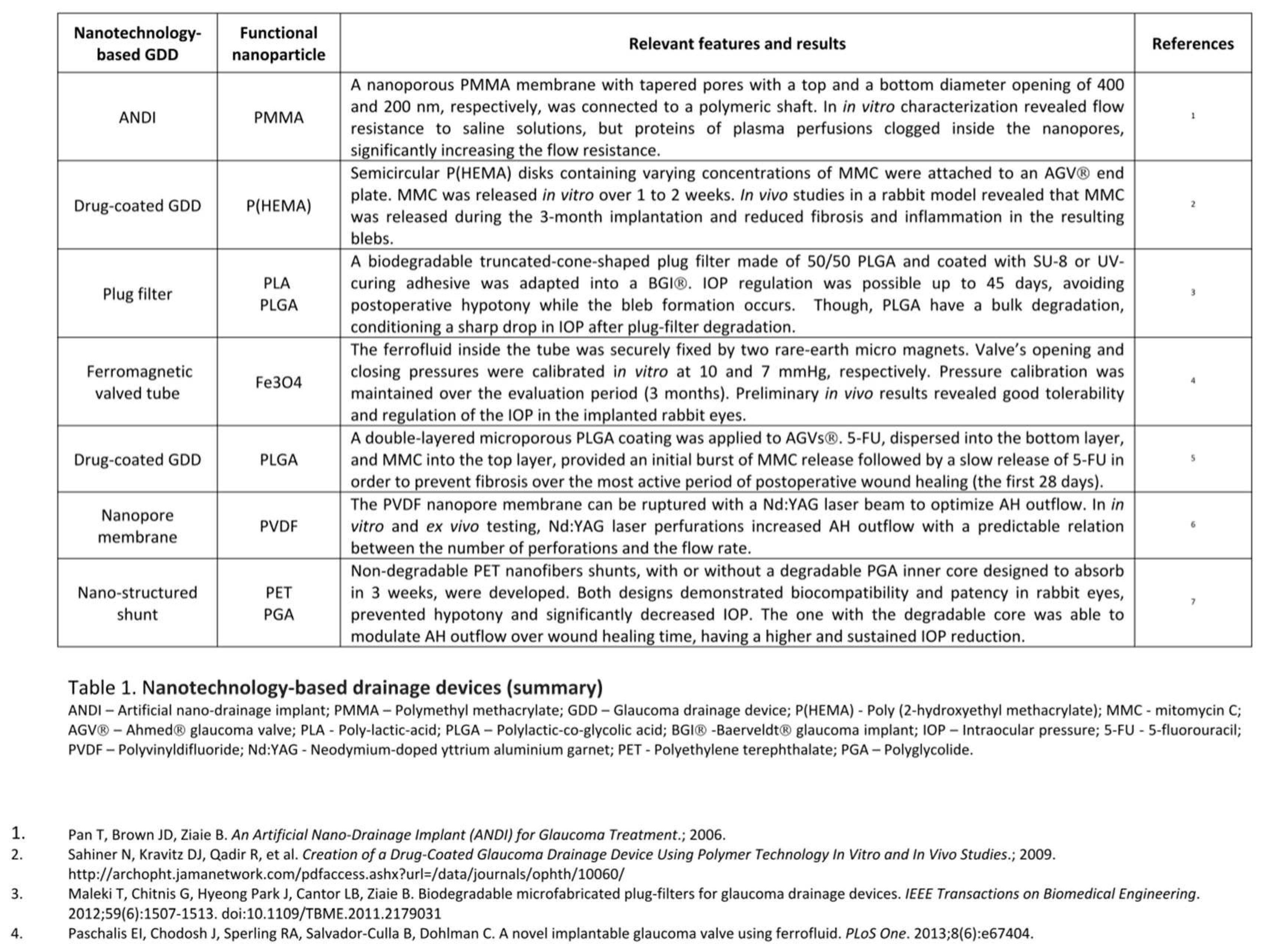
A summary of these devices is presented in Table 1.
Discussion
Despite being the second leading cause of blindness worldwide 6, glaucoma remains an incurable disease even with appropriate treatment.
The current glaucoma treatment is mainly focused on delaying the disease progression because once damaged the optic nerve system cannot be recovered. IOP reduction is the most effective strategy to decline glaucoma evolution.
Medical therapy is the most consensual initial approach to the disease although, it relies on a delivery system that has various drawbacks.
More invasive treatments are the choice when medical therapy fails. Trabeculectomy still is the most common surgical treatment performed 17 and typically GDD are reserved for eyes with previous glaucoma surgeries or with high risk for failure of standard glaucoma filtration surgery. 18 However, the Tube versus Trabeculectomy (TVT) study demonstrated that GDD are being increasingly used at an earlier stage. 34
GDDs consist in a silicone tube connected to an end plate. The tube provides an alternative route to the AH, by channeling it from the AC to the collection plate positioned beneath the conjunctiva in the equatorial sclera. A potential space between the end plate and an overlying fibrous capsule that develops post-operatively works as a temporary reservoir for AH that then passively diffuses through this capsule wall into periocular spaces, capillaries, and lymphatics. 18
There are several complications contributing to short- and long-term failure of these devices, most of them related with the endplate encapsulation process. After GDD implantation, an inflammatory response occurs over the device endplate. This tissue response will culminate with the bleb formation that is needed to provide primary resistance to AH. Early post-operative hypotony due to lack of resistance to AH drainage is a relevant complication, especially in the non-valved devices. 18,35 Following this hypotensive phase, gradual congestion and edema of the capsule leads to a transient increase in flow resistance and to a hypertensive phase. 18 Eventually, continuous inflammation and fibrovascular proliferation of the bleb may lead to excessive bleb fibrosis, reduction of AH absorption and long-term surgical failure. 35
The reasons behind the intensity of this reaction are not fully known. The type of biomaterial, design and size of the endplate, patient’s immune response and even the presence of AH in the subconjunctival space can all contribute to inflammation and fibrovascular proliferation. 17,19
Nanotechnology based GDDs have been proposed to overcome these limitations. This systematic review summarizes the state of the art regarding nanodevices made to be used in glaucoma drainage surgery.
These nanotechnology based GDDs can be divided, somehow, according to the general mechanism on which they are based.
Considering the inconveniences of the current approach to avoid excessive scar tissue development following GDD implantation, Ponnusamy et al. and Sahiner et al. developed antifibrotic drug-coated devices. Both devices had the same principle: the slow and continuous release of the antimetabolites impregnated in the GDD would reduce inflammatory reaction and modulate bleb fibrosis, preventing the hypertensive postsurgical phase. Pre-coated devices promise to offer a more secure and comfortable alternative to 5-FU and MMC serial injections strategy used nowadays.
On the other hand, the remaining devices focused IOP control and modulation during wound healing time. The device proposed by Pan et al. is probably the simplest, aiming to limit early AH outflow by using a nanoporous membrane. The device success was compromised by protein clogging in the membrane with consequent IOP elevation. Maleki et al. and Parikh et al. made use of biodegradable nano polymers to occlude the shunt inner lumen of the proposed GDDs, offering an initial extra resistance to AH outflow to avoid the postsurgical hypotensive phase. As time goes by and encapsulation process occurs, polymers degradation allows an increased AH outflow, maintaining IOP at desirable values. At last, Paschalis et al. and Olson et al. proposed systems that provide early resistance to AH outflow and allow IOP control during all the phases of encapsulation, either by using a ferromagnetic valve or by rupturing the nanopore membrane with an Nd:YAG laser to increase AH outflow.
Overall, the devices showed promising results, addressing solutions to the challenges of GDDs implantation surgery.
Nanotechnology-based GDDs have a great potential to be incorporated in glaucoma therapeutic options soon, providing new systems of drug deliver with better bioavailability (e.g., antifibrotic drug-coated GDD), an improved safety profile and an enhanced surgical efficacy with better IOP control and less adverse outcomes. In fact, recently in March 2020, the first nano-based glaucoma therapeutic was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 36 It consists in a biodegradable sustained release intracameral implant containing the prostaglandin analogue bimatoprost, known commercially as Durysta™. 37 Despite this major milestone for glaucoma therapeutics, all the devices discussed in this work are still in the research or development stage having a long way to go until their approval for clinical use. 3
One of the main obstacles to the incorporation of nanotechnology in the medical practice is the lack of studies regarding toxicity, biocompatibility and safety of the nanomaterials used. Many studies have extensively examined the toxicity of nanoparticles on main organs, but the eye have been neglect. 38 Despite that, several nano-based devices have been developed in ophthalmology, making use of various types of nanomaterials and nanoparticles. Each nanoparticle has unique physiochemical properties including chemical composition, surface area, and charge that can affect its toxicity on the eye, so each one must be investigated in vitro and in vivo. 39 Among the most widely used nanomaterials, PLGA, the biodegradable polymer used in the devices proposed by Maleki et al. and Ponnusamy et al., is considered the least toxic and is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 40 Nanomaterials used in the remaining devices presented in this review, and that underwent in vivo testing, have shown good results regarding safety and biocompatibility, however it is imperative to address more studies to test their local and systemic toxicity.
The scarcity of in vivo testing of these devices brings us to other limitation of nanotechnology. Although these nanodevices reveal promising results, available data have been collected mostly from in vitro studies and in vivo studies done in small scale. Moreover, most animal studies use the rabbit eye as model, whose characteristics are not precisely as the human eye, meaning that the results may not translate to human beings. 41 Olson, Paschalis and Sahiner and their teams, reinforce the importance of doing more in vivo studies to corroborate their initial results and to evaluate the device’s biocompatibility and efficacy.
The future of nanotechnology based GDD seems promising and probably will be revolutionary to the disease approach, but more efforts in research need to be done until this innovation becomes available in the daily clinical practice and ready to be used in human eyes.
Conclusion
Advances in nano-ophthalmology have the potential to revolutionize the current therapeutic approach to glaucoma. Particularly nanotechnology-based glaucoma drainage devices, the subject of this systematic review, promise to overcome the challenges of glaucoma surgical treatment by allowing a more effective control over post-operative scarring, a noninvasive and customized post-operative control of AH drainage while achieving optimal IOP reduction through all phases of the post-operative period.
Despite the decreased post-operative complications and apparently enhanced biocompatibility of nano-based drainage devices, safety concerns need to be addressed. Toxicity issues and unintended biological effects of nanomaterials use have yet to be exploit. Further in vivo tests and human studies are needed to evaluate cytotoxicity and corroborate the biocompatibility and efficacy showed in the initial testing results of these devices.
Statement and Declarations Competing Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. No funding was received for conducting this systematic review.
References
- Zarbin MA, Montemagno C, Leary JF, Ritch R. Nanotechnology in ophthalmology. Can J Ophthalmol. 2010, 45, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, RA. What is nanomedicine? Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine. 2005, 1, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardigos J, Ferreira Q, Crisóstomo S, et al. Nanotechnology-Ocular Devices for Glaucoma Treatment: A Literature Review. Current Eye Research. 2019, 44, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim NJ, Harris A, Gerber A, et al. Nanotechnology and glaucoma: A review of the potential implications of glaucoma nanomedicine. British Journal of Ophthalmology. 2014, 98, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana FR, Kesse S, Boakye-Yiadom KO, Veroniaina H, Wang H, Sun M. Promising Approach in the Treatment of Glaucoma Using Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine-Based Systems. Molecules. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya’ D, et al. Global Data on Visual Impairment in the Year 2002, 82, 2004.
- Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb RN, Aung T, Medeiros FA. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association. 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita-Thomas DW, Goldberg JL. Nanotechnology and glaucoma: Little particles for a big disease. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. 2013, 24, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz GF, Hollander DA, Williams JM. Evaluation of eye drop administration technique in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2013, 29, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhara D, Aref AA. Glaucoma management: Relative value and place in therapy of available drug treatments. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 2014, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleath B, Robin AL, Covert D, Byrd JE, Tudor G, Svarstad B. Patient-reported behavior and problems in using glaucoma medications. Ophthalmology. 2006, 113, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janagam DR, Wu L, Lowe TL. Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the anterior segment of the eye. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2017, 122, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudana R, Ananthula HK, Parenky A, Mitra AK. Ocular drug delivery. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinel S, Montemagno C. Nanotechnology applications for glaucoma. Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology. 2016, 5, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal G, Garg T, Rath G, Goyal AK. Current Nanotechnological Strategies for Treating Glaucoma. Vol 31.; 2014. www.begellhouse.com.
- Occhiutto ML, Maranhão RC, Costa VP, Konstas AG. Nanotechnology for Medical and Surgical Glaucoma Therapy-A Review. Adv Ther. 2020, 37, 155–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref AA, Gedde SJ, Budenz DL. Glaucoma Drainage Implant Surgery. Developments in Ophthalmology. 2017, 59, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong CH, Arosemena A, Zurakowski D, Ayyala RS. Glaucoma drainage devices: A systematic literature review and current controversies. Survey of Ophthalmology. 2005, 50, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed HM, Law SK, Nam SH, Li G, Caprioli J, Coleman A. Baerveldt-350 Implant versus Ahmed Valve for Refractory Glaucoma A Case-Controlled Comparison.; 2004.
- Yalvac IS, Eksioglu U, Satana B, Duman S. Long-term results of Ahmed glaucoma valve and Molteno implant in neovascular glaucoma. Eye. 2007, 21, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisian, SR. Tube shunt complications and their prevention. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. 2009, 20, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado JA, Hollander DA, Juster RP, Lee LC. Ahmed Valve Implantation with Adjunctive Mitomycin C and 5-Fluorouracil: Long-term Outcomes. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2008, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozgar B, Lin SC, Han Y, Kuo J. A role for antimetabolites in glaucoma tube surgery: Current evidence and future directions. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. 2016, 27, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner V, Dullaart A, Bock AK, Zweck A. The Emerging Nanomedicine Landscape. Vol 24.; 2006. http://scientific.thomson.com/products/sci/. /: http.
- United States National Nanotechnology Initiative. What’s so special about the nanoscale? National Nanotechnology Institute. https://www.nano.gov/about-nanotechnology/what-is-so-special-about-nano.
- Paschalis EI, Chodosh J, Sperling RA, Salvador-Culla B, Dohlman C. A novel implantable glaucoma valve using ferrofluid. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e67404. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki T, Chitnis G, Hyeong Park J, Cantor LB, Ziaie B. Biodegradable microfabricated plug-filters for glaucoma drainage devices. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 2012, 59, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh KS, Josyula A, Omiadze R, et al. Nano-structured glaucoma drainage implant safely and significantly reduces intraocular pressure in rabbits via post-operative outflow modulation. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson JL, Bhandari R, Groman-Lupa S, Velez-Montoya R. A nanopore membrane regulator device for laser modulated flow after glaucoma surgery. Biomed Microdevices. 2015, 17, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Pan T, Brown JD, Ziaie B. An Artificial Nano-Drainage Implant (ANDI) for Glaucoma Treatment.; 2006.
- Sahiner N, Kravitz DJ, Qadir R, et al. Creation of a Drug-Coated Glaucoma Drainage Device Using Polymer Technology In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.; 2009. http://archopht.jamanetwork.com/pdfaccess.ashx?url=/data/journals/ophth/10060/.
- Ponnusamy T, Yu H, John VT, Ayyala RS, Blake DA. A novel antiproliferative drug coating for glaucoma drainage devices. Journal of Glaucoma. 2014, 23, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosentreter A, Strzalkowski P, Bula AM, Alnawaiseh M. Glaucoma Drainage Devices: Tube versus Trabeculectomy Study. Klinische Monatsblatter fur Augenheilkunde. 2018, 235, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Gedde SJ. New developments in tube shunt surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belamkar A, Harris A, Zukerman R, et al. Sustained release glaucoma therapies: Novel modalities for overcoming key treatment barriers associated with topical medications. Annals of Medicine. 2022, 54, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. Bimatoprost Implant: First Approval. Drugs and Aging. 2020, 37, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu S, Gong L, Li Y, Xu H, Gu Z, Zhao Y. Safety Assessment of Nanomaterials to Eyes: An Important but Neglected Issue. Advanced Science. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvicens N, Marco MP. Multifunctional nanoparticles - properties and prospects for their use in human medicine. Trends in Biotechnology. 2008, 26, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prow, TW. Toxicity of nanomaterials to the eye. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology. 2010, 2, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo J, Gonzalez E, Egea MA, Garcia ML, Souto EB. Nanomedicines for ocular NSAIDs: safety on drug delivery. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine. 2009, 5, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).






