1. Introduction
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a highly prevalent and potentially serious condition affecting up to 30% of the population, and it is also the most common cause of chronic liver disease (CLD) worldwide [
1]. NAFLD is characterized by the pathologic accumulation of fat in the liver with a proton density fat fraction detected with MRI (MRI-PDFF) in excess of 5.6%, or accumulation of lipid droplets in more than 5% of hepatocytes detected with liver biopsy [
2]. It can range from simple, benign fatty liver disease (FLD) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. NAFLD is also a diagnosis of exclusion that can be applied only to patients without known chronic liver disease, or a recent history of alcohol abuse. Meanwhile, in addition to demonstrating hepatic steatosis, the diagnosis of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is based on positive criteria such as the presence of obesity, metabolic dysregulation, and type 2 diabetes. The exclusion of other disease etiologies is not a prerequisite of the MAFLD diagnosis [
3].
Accurate diagnosis and monitoring of fatty liver disease are crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. While liver biopsy has traditionally been the gold standard for diagnosis, it is invasive, carries risks, and samples only a small portion of the liver [
4]. Non-invasive techniques are increasing in popularity for the detection of hepatic steatosis. Although very precise and recommended as a reference method for fat quantification, MRI-PDFF is expensive, and its availability is also limited [
5]. Quantitative ultrasound (QUS) has emerged as a promising non-invasive technique for the diagnosis of fatty liver disease [
6,
7]. Artificial intelligence (AI) aided diagnosis of hepatic steatosis by automated measurement of hepatorenal brightness index (HRI), which has also become available [
8].
Among the QUS parameters, the ultrasound attenuation coefficient (AC) and backscatter-distribution coefficient (BSC-D) have been extensively validated for the detection of hepatic steatosis in NAFLD [
9,
10,
11]. The AC attenuation coefficient measures the rate at which ultrasound waves weaken as they propagate through liver tissue [
12]. The BSC-D quantifies the amount of ultrasound energy that is scattered back toward the transducer after interacting with tissues [
13]. Both methods have been able to detect grade 1 and grade 2 steatosis with good to excellent accuracy, mitigating the need for a liver biopsy or other more expensive imaging methods [
10,
14]. On the other hand, a significant drawback is that due to technical variations, QUS parameters developed by different vendors may have different diagnostic thresholds making direct comparison between measurements at multiple sites difficult [
15,
16]. Also, both AC and BSC-D suffer from the exponential loss of signal in higher grades of steatosis, resulting in the saturation of the dynamic range and a non-linear relationship between QUS parameters and liver fat fraction [
8,
17,
18]. In a couple of recently published studies, multivariable regression models were tested for the prediction of MRI-PDFF from QUS parameters [
17,
18]. The conversion of QUS parameters to fat fraction also improves comparability in a clinical setting.
In the present study, we aimed for systematic evaluation of the relationship between AC, BSC-D, liver stiffness (LS), and steatosis measured with MRI-PDFF. We have developed a new prediction model using non-linear least squares analysis to calculate ultrasound-estimated fat fraction (USFF) based on a combination of AC and BSC-D parameters. According to our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate that USFF can be used for diagnosing NAFLD-related and MAFLD-related hepatic steatosis with similar accuracy.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Patient selection
This single-center retrospective study has been approved by the Institutional and Regional Science and Research Ethics Committee of our university. The patients have given written informed consent for QUS and MRI scans. All procedures and data processing were performed in compliance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, revised in Edinburgh in 2000. We retrospectively collected data on patients with suspected fatty liver disease who had QUS, shear wave elastography (SWE), and quantitative MRI scans between July 2020 and May 2023 from our institution's picture archiving and communication system (PACS). The patients` demographics, the results of laboratory tests, and medical history were collected from electronic medical reports (
Table 1).
The inclusion criteria in the NAFLD group were 18 years or older, signed informed consent, valid QUS, SWE, and MRI-PDFF measurements, and clinical findings consistent with NAFLD according to the European Association of Studying the Liver (EASL) guidelines [
2]. The MAFLD group contained patients with clinical findings consistent with MAFLD according to the international expert consensus, excluding the NAFLD group [
3]. Patients in the NAFLD group did not report significant
– over 20 g (2 drinks) for females or 30 g (3 drinks) for males
– daily alcohol consumption in the previous two years, and did not have a known history of chronic liver disease. Meanwhile, patients in the MAFLD group had at least one of the three conditions: obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic dysregulation, and known chronic liver disease. Three patients in the MAFLD group reported significant ongoing or recent alcohol consumption. Patients with acute liver failure, acute-on-chronic liver failure, and extrahepatic biliary obstruction were excluded from the study. We also excluded four patients with hemochromatosis whose high hepatic iron content impaired the MRI-PDFF measurement.
The liver status was assessed with QUS or SWE in 284 patients during the study period. After excluding 91 subjects with incomplete or invalid ultrasound scans and 52 patients who did not have a valid quantitative MRI scan, the final study cohort included 90 patients with clinically suspected NAFLD and 51 patients with suspected MAFLD.
2.2. Ultrasound
Patients fasted at least four hours before the ultrasound scan. All ultrasound examinations were performed with a Samsung RS85 Prestige (Samsung Medison Co. Ltd., Hongcheon, Republic of Korea) scanner and the CA 1-7S curvilinear probe. Patients were scanned in a supine position with an elevated right arm. The probe was placed into a right intercostal space perpendicular to the liver capsule and measurements were acquired during breath-holds in shallow inspiration. All scans were performed by one of three experts with at least five years of experience in liver ultrasounds. The examiners were blinded from the patients` medical history and the MRI-PDFF results.
The QUS protocol included tissue attenuation imaging (TAITM) and tissue scatter distribution imaging (TSITM) for measuring the AC and BSC-D, respectively. During QUS, regions of interest (ROIs) were positioned by the examiner in the right lobe of the liver at a depth of approximately 2 cm below the liver capsule, avoiding large vessels. TAI values with R2 <0.6 were considered non-reliable and were discarded. TAI and TSI were calculated as the average of five valid measurements. TAI was reported in dB/cm/MHz and TSI in arbitrary units.
A 2D SWE was performed simultaneously with QUS, as it has been described previously [
19]. For LS measurement, the Shear-Wave Imaging
TM application was selected. A fan-shaped measurement window was positioned by the examiner in the right liver lobe at least 2 cm below the liver capsule, avoiding large vessels. The software automatically generated two color-coded maps displaying the distribution of LS and the reliable measure index (RMI) within the window. The LS was measured within circular ROIs manually positioned in areas with the highest RMI. Measurements with an RMI < 0.4 were considered non-reliable and discarded. The LS was calculated as the average of at least five valid measurements with an interquartile range /median (IQR/med.) ratio of < 30%. The LS was reported in kPa units. Patients were also classified into fibrosis grades using cutoff values for F2 at ≥ 5 kPa, for F3 at ≥ 9 kPa, and for F4 at ≥ 13 kPa based on the “rule of four” recommendation [
20].
2.3. Magnetic resonance imaging
We used quantitative MRI as the reference standard of fat fraction quantification. The MRI was performed within one month of QUS. All patients were scanned with a 1.5 T Philips Ingenia
TM MRI scanner (Philips Healthcare, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) and a Q-Body coil. A 2D multi-echo gradient echo sequence was acquired at the level of the porta hepatis, with 12 evenly spaced echos with echo time (TE) starting from 1.2 msec and increasing by 1.2 msec, repetition time (TR) of 120 msec, flip angle (FA) of 20 degrees, pixel bandwidth (Bw) of 2712 Hz, a field-of-view of typically 400 × 350 mm, a reconstruction matrix of 128 × 116 pixels, slice thickness and an interslice gap of 10 mm. Three circular ROIs were selected in the right lobe of the liver on the magnitude images with the MRQuantif (
https://imagemed.univ-rennes1.fr/en/mrquantif (accessed on 16 September 2022) software [
21]. The software calculated the R2* and the MRI-PDFF of the liver by fitting an exponential signal decay model corrected for signal variations caused by the six main fat peaks described by Hamilton et al. [
22]. Patients were classified into four severity grades using thresholds at 5%, 10%, and 20% MRI-PDFF, which have been previously used in multiple studies to diagnose mild, moderate, and severe steatosis [
14,
17,
23].
2.4. Statistical analysis
The distribution parameters were calculated for clinical and imaging variables in the dataset. Continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical variables as number and percentage. We used the Kruskal-Wallis test to compare MRI-PDFF values and QUS parameters between different grades of liver fibrosis and to compare LS values between MRI-PDFF-defined steatosis grades.
We constructed univariable and multivariable linear regression models to identify ultrasound and clinical biomarkers significantly associated with the severity of fatty liver disease in the NAFLD and MAFLD groups. In the multivariable models, AC, BSC-D, LS, and BMI were included as independent variables, while MRI-PDFF was the dependent variable. In the univariable models, AC, BSC-D, LS, and BMI were separately tested against MRI-PDFF.
We created three non-linear regression models to predict MRI-PDFF based on AC, BSC-D, or the combination of both in the NAFLD dataset. The models were optimized with a least squares analysis using the formula for each of the QUS parameters: MRI-PDFF = β1*exp( β2 * QUS) + β3. The fitted models were validated in a k-fold (k=3) cross-validation repeated five times on the NAFLD dataset and were also tested on the MAFLD dataset. We compared the models' performance by calculating the coefficients of determination (R2) adjusted for the number of independent variables and root mean square errors (RMSE) during cross-validation. We used the least-squares model that combined AC and BSC-D to calculate the ultrasound estimated fat fraction (USFF).
Pearson`s correlation coefficient (⍴) together with the 95% confidence intervals (CI), was calculated between USFF and MRI-PDFF in the NAFLD and MAFLD datasets. We also determined the intercept (c), regression slope (β), and significance of a simple linear model that used USFF to predict MRI-PDFF.
We compared the predicted USFF between the steatosis grades with the Kruskall-Wallis test. We performed a post-hoc analysis with Dunn`s test and adjusted p-values with Holm`s method to prevent false discoveries from multiple comparisons. We constructed box plots to visually examine the distribution of USFF across the four steatosis grades.
The diagnostic performance of the USFF in differentiating between <5% vs. ≥5%, as well as between <10% vs. ≥10% MRI-PDFF, was evaluated with receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analyses. We calculated the area under the curve (AUC) together with the CI and determined the “best” diagnostic threshold with the highest J value (J = true positive rate - false negative rate). We also calculated the sensitivity (SN), specificity (SP), negative predictive value (NPV), positive predictive value (PPV), and total accuracy (TA) for the classifications. We performed a power analysis for each binary classification problem to ensure that the sample size is large enough to keep the type 2 error <10%.
We applied a p<0.05 cutoff for all statistical tests to declare significance. The data analysis was performed in the R version 4.2.3 (
www.r-project.org, accessed on 20th April /2023) statistical computing environment.
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and characteristics of patient groups
We examined 141 patients with QUS and SWE to determine the severity of fatty liver and fibrosis in suspected diffuse liver disease. The etiology of the liver disease based on the clinical background was NAFLD in 90 cases, and MAFLD in 51 cases. All participants had an MRI scan within one month of the US examination for measuring MRI-PDFF. All participants were of European descent.
The patients were classified into steatosis grades using cutoff values at 5%, 10%, and 20% MRI-PDFF. In the NAFLD group, 19 (21.1%) patients had <5%, 22 (24.4%) 5 – 10%, 34 (37.8%) 10 – 20%, and 15 (16.7%) ≥20% MRI-PDFF (
Table 2). The distribution of patients in the MAFLD group among the same steatosis grades was 28 (54.9%), 8 (15.7%), 10 (19.6%) and 5 (9.8%), respectively. The SWE indicated significant liver fibrosis with LS ≥ 9 kPa in 14 (15.6%) NAFLD and 21 (41.2%) MAFLD patients.
The MRI-PDFF and the QUS parameters were not significantly different between the fibrosis grades in either etiology. Similarly, patients in MRI-PDFF-defined steatosis grades did not have significantly different LS.
3.2. Regression models
The regression analysis identified AC as a strong independent predictor of MRI-PDFF in both NAFLD and MAFLD groups (
Table 3). BSC-D was not an independent predictor in the multivariable analysis but showed a significant association with MRI-PDFF in the univariable analysis. AC and BSC-D were better predictors of MRI-PDFF in both NAFLD and MALD than BMI, which was only weakly associated with MRI-PDFF in the univariable analysis. Meanwhile, LS did not show a significant association with liver fat.
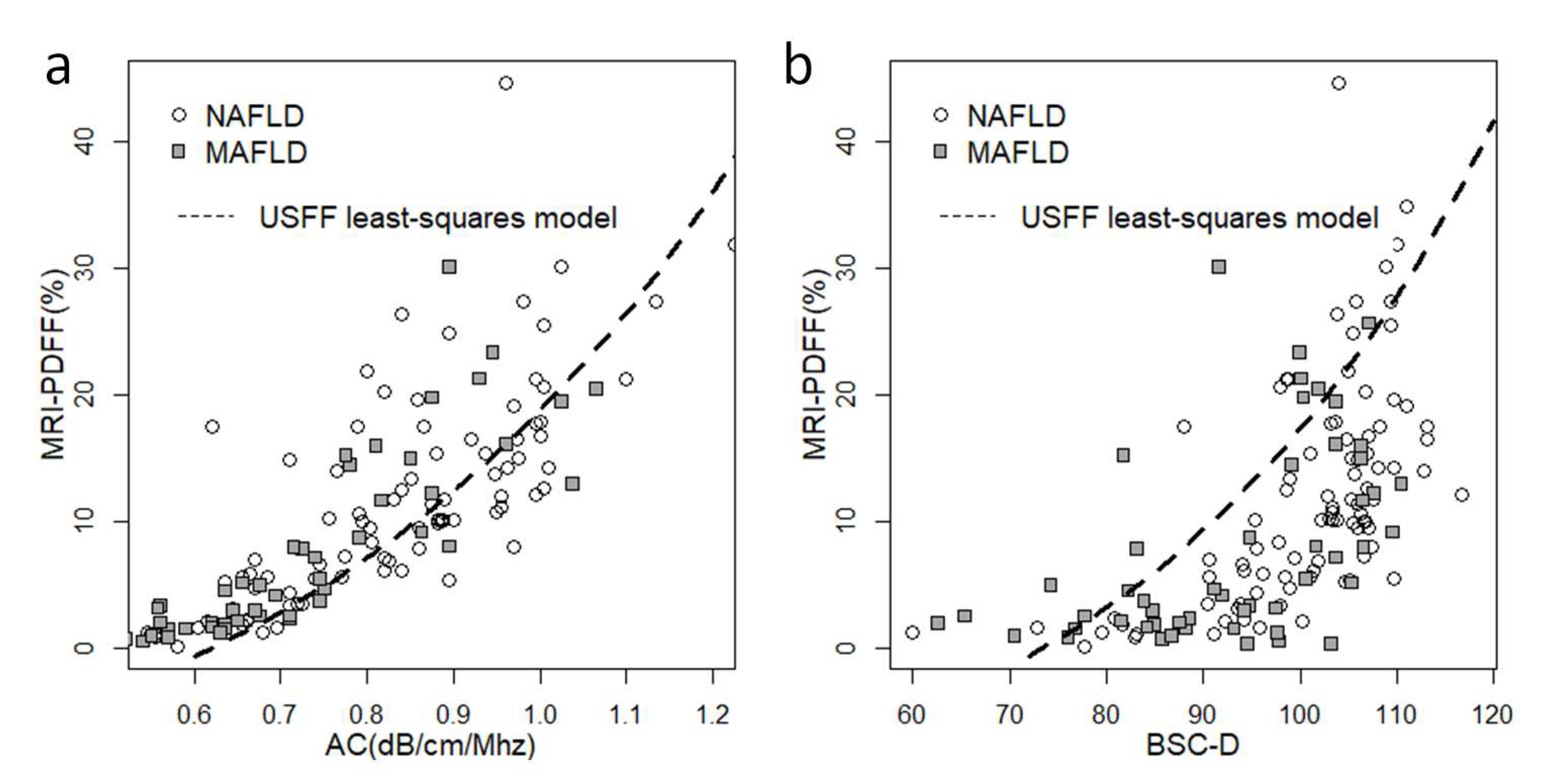
We constructed scatter plots to visualize the correlation between QUS biomarkers and MRI-PDFF (
Figure 1). The relationship between AC, BSC-D, and MRI-PDFF was non-linear, with measurements gradually plateauing at above 20% fat fraction. This effect was more pronounced in the case of BSC-D than AC. The distribution of the QUS parameters with respect to fat fraction was similar in the NAFLD and MAFLD groups.
3.3. Non-linear least-squares models
We developed three models using a non-linear least-squares analysis for the prediction of MRI-PDFF based on QUS. The model parameters were fitted on either AC or BSC-D or both in the NAFLD group, and the accuracy of the three models was validated in a three-fold cross-validation repeated five times. The AC model was the best fit for the validation set (mean ± SD, adj. R
2 = 0.498 ± 0.046) with a mean RMSE of 6.415% ± 0.561% in the cross-validation (
Table 4). The combined AC and BSC-D model yielded only a slightly lower coefficient of determination (adj. R
2 = 0.446 ± 0.152) and RMSE (RMSE = 7.347% ± 3.105%). The BSC-D model performed the worst with a mean adj. R
2 of 0.318 ± 0.075 and RMSE of 7.687% ± 0.696%
We also evaluated the same three models in the MAFLD dataset (
Table 4). The AC model (adj. R
2 = 0.733) was the best fit, followed by the combined (adj. R
2 =0.673) and the BSC-D (adj. R
2 = 0.253) models. The RMSE of the AC combined, and BSC-D models were 3.911%, 4.574%, and 6.608%, respectively.
3.4. Correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF
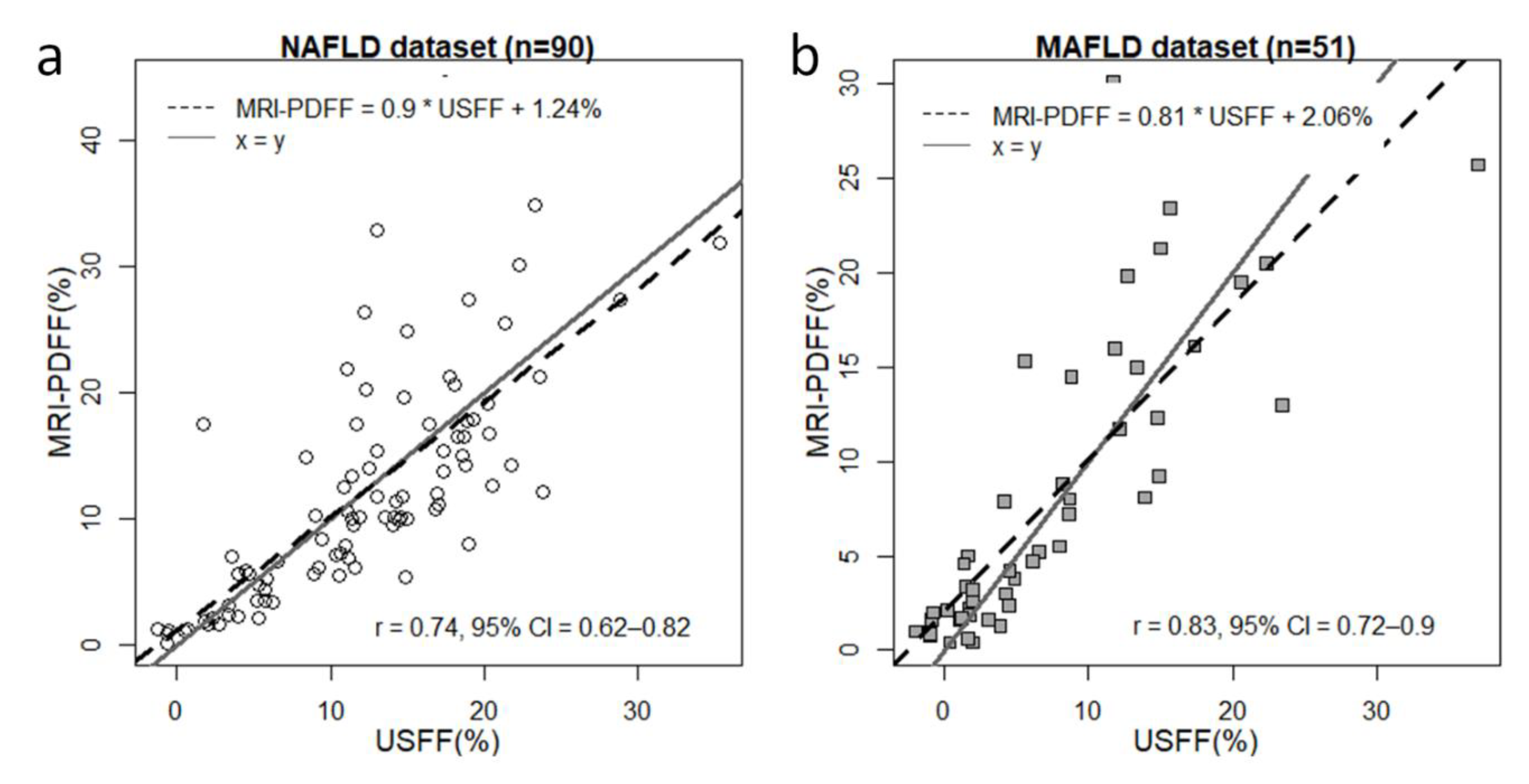
We chose the combined model to predict USFF in both the NAFLD and MAFLD datasets. The mean and SD of the USFF (12.06% ± 7.23%) were similar to the metrics calculated for MRI-PDFF. The correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF for all cases in the NAFLD group was strong (⍴ = 0.735, CI = 0.622–0.817, p<0.001) (
Figure 2). However, the correlation was strongest (⍴ = 0.886, CI = 0.81–0.933, p<0.001) in the range of 0 – 12.2% MRI-PDFF. The slope of the regression line between USFF and MRI-PDFF was β=0.9 with a significance of p<0.001, and the intercept was at c=1.238%.
In the MAFLD dataset, the mean and SD of USFF (7.08% ± 7.86%) were nearly identical to those calculated for MRI-PDFF. The USFF was in very strong correlation (⍴ = 0.828, CI = 0.716–0.899, p<0.001) with MRI-PDFF, peaking (⍴ = 0.902, CI = 0.813–0.95, p<0.001) between 0.7% and 14.5%. The regression slope was β=0.81 ( p<0.001) with a regression intercept of c = 2.06%.
3.5. Comparison of USFF between steatosis grades
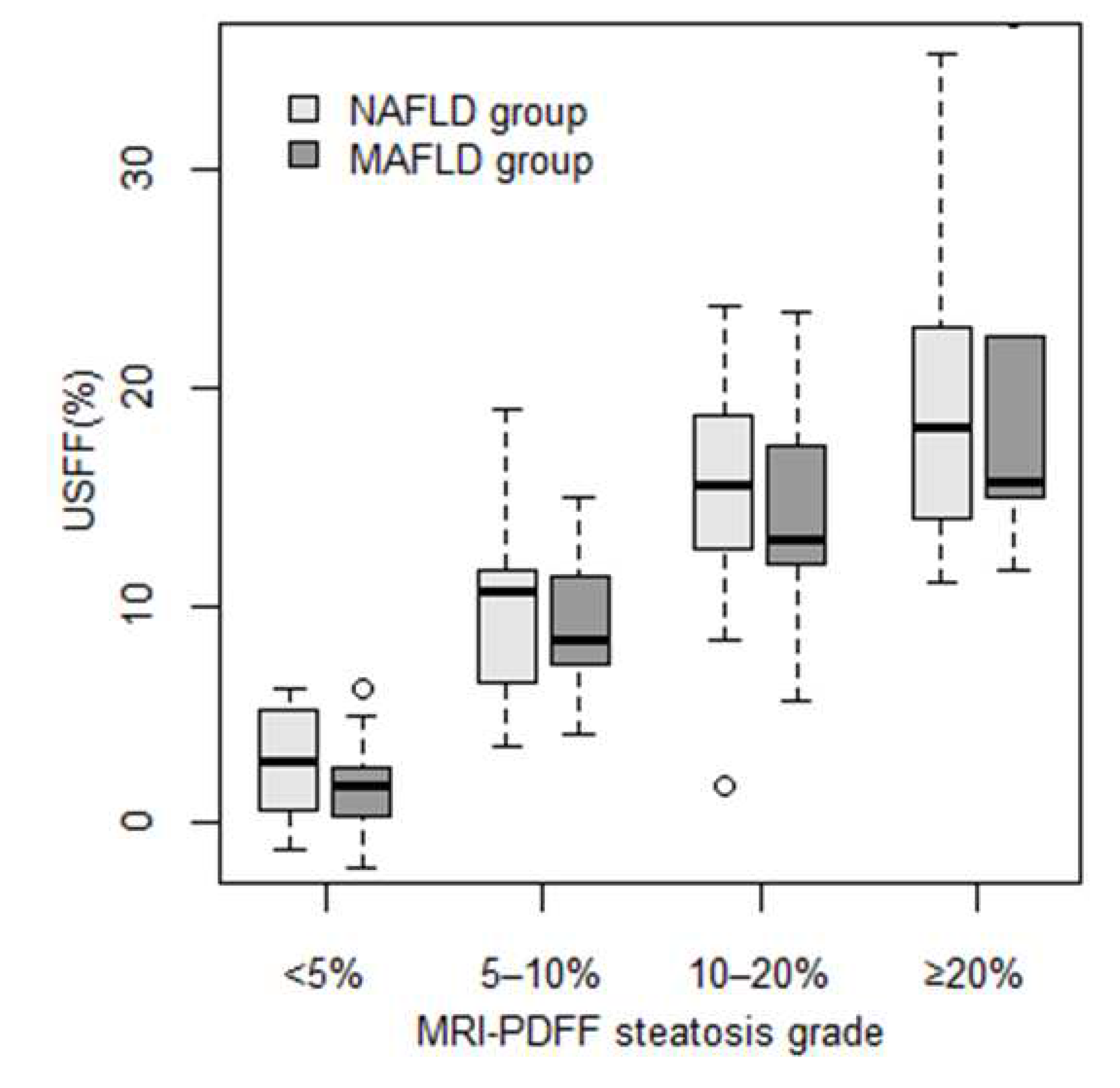
We divided patients into four grades: none (<5%), mild (5–10%), moderate (10–20%), and severe (≥ 20%) based on the severity of steatosis measured by MRI-PDFF. We calculated the mean and SD of the USFF predicted by the combined least-squares model for each grade. In the NAFLD group, the USFF was significantly different between <5% ( 2.70% ± 2.48%, p<0.0048) and 5–10% (10.1% ± 4.03%), as well as between 5–10% and 10–20% (15.3% ± 4.45%, p<0.006) MRI-PDFF steatosis (
Figure 3). In the MAFLD group, the USFF was significantly different between none (1.65% ± 2.04%, p<0.001) and mild (9.12% ± 3.6%) steatosis; meanwhile, the difference was non-significant between mild and moderate (14.1% ± 5.3%) and between moderate and severe (20.3% ± 10.1%) steatosis.
3.6. Diagnosis of different grades of steatosis with USFF
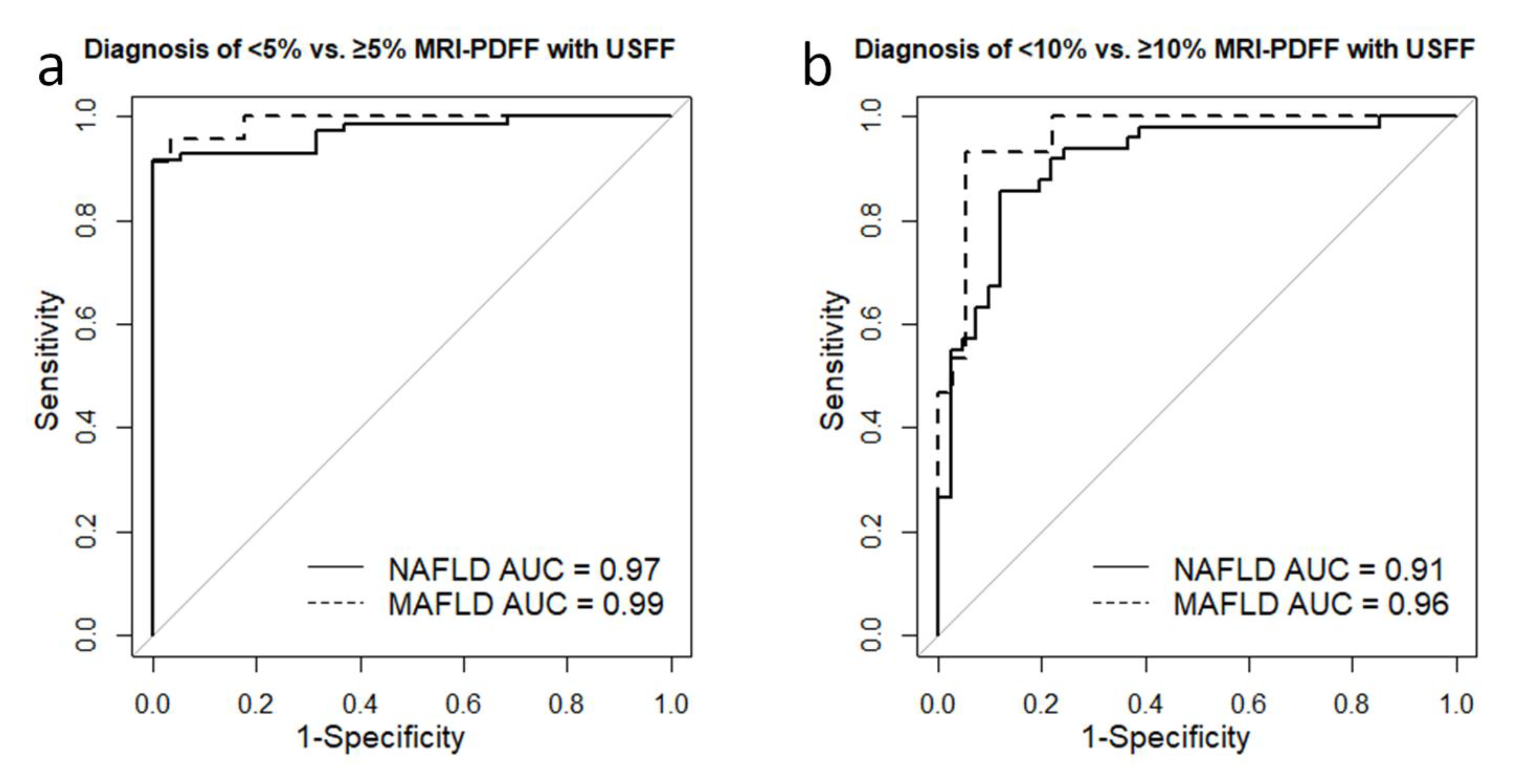
The ROC analysis showed that USFF could separate ≥5% from <5% MRI-PDFF with excellent accuracy (AUC = 0.971, CI =0.942–1) in the NAFLD group. The best cutoff was at 6.36%, achieving a sensitivity of 0.92, specificity of 1, NPV of 0.76, PPV of 1, and TA of 0.93 (
Table 5). The USFF was similarly successful in differentiating between mild (≥5% MRI-PDFF) vs. no steatosis (AUC = 0.99, CI = 0.973–1) in MAFLD (
Figure 4). The sensitivity, specificity, NPV, PPV, and TA of the classification were all 0.96 using a diagnostic threshold of 5.22% (
Figure 4).
For detecting ≥10% MRI-PDF in NAFLD, the AUC for USFF was 0.91 (CI = 0.848–0.972), and sorting with an 11.64% threshold yielded sensitivity, specificity, NPV, PPV, and TA of 0.86, 0.88, 0.89, 0.84 and 0.87, respectively. Meanwhile, in the MAFLD group, the AUC for diagnosing ≥10% MRI-PDFF was 0.961 (CI = 0.913 –1). The optimal USFF cutoff was at 8.74, which could predict moderate-severe steatosis with sensitivity, specificity, NPV, PPV, and TA of 0.93, 0.94, 0.88, 0.97 and 0.94, respectively.
4. Discussion
We fitted a model using non-linear least squares analysis to predict USFF based on AC and BSC-D parameters as input, and MRI-PDFF as the reference standard on 90 NAFLD cases. We found that the correlation between predicted USFF and MRI-PDFF was strong (⍴=0.735), and that the USFF model was able to diagnose ≥5% (AUC = 0.97) and ≥10% MRI-PDFF (AUC = 0.91) steatosis with excellent accuracy in NAFLD. We have also validated our USFF model in multiple ways. We performed a three-fold cross-validation repeated five times on the NAFLD dataset, which showed that the AC and combined AC and BSC-D models were the best fit on the NAFLD dataset producing nearly identical mean coefficients of determination (adj. R2 = 0.498 vs. 0.446). We also tested our models on a dataset collected from MAFLD patients with various etiologies of CLD. Our results show that the USFF model developed for NAFLD patients can also be applied to predict steatosis in MAFLD with good accuracy. The coefficient of determination for the USFF model trained on the NAFLD dataset did not decrease on the MAFLD dataset (adj. R2 =0.673). The predicted USFF very strongly correlated with MRI-PDFF (⍴=0.828) and could detect patients with ≥5% (AUC=0.99) and ≥10% (AUC = 0.96) MRI-PDFF with nearly perfect accuracy. Thus, our results suggest that a USFF model can be implemented for diagnosing low- and moderate-grade hepatic steatosis with similar accuracy to MRI-PDFF in both NAFLD and MAFLD.
A handful of studies have already reported prediction models for estimating hepatic fat fraction based on a selection of QUS parameters [
14,
17]. Another approach to developing an ultrasonic fat fraction estimator is to use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on either radiofrequency or image data [
24,
25]. The correlation between predicted fat fraction and MRI-PDFF (⍴ = 0.76–0.87) and the classification accuracy for low-grade (≥5% MRI-PDF) steatosis (AUC = 0.89–0.98) reported for these models were similar to the results of our model. Notably, thresholds for diagnosing ≥5% (6.36% vs. 6.34%) and ≥10% (11.64% vs. 11.7%) MRI-PDFF with the USFF model in NAFLD were almost identical to cutoff values reported for the UDFF model [
17]. The novelty of our approach was that we applied a non-linear least-squares analysis on AC measured with the TAI and BSC-D measured with the TSI applications. This is important since BSC-D measured with a different technique had a higher coefficient of determination in a least-squares analysis compared to TSI (R
2 = 0.76 vs. R
2 = 0.32) [
17]. In addition, all prior studies were performed in a single-center setting and analyzed only QUS data from NAFLD patients without an external validation set, which may raise concerns about overfitting the models. We tested the USFF model on data collected from MAFLD patients and did not see a drop in the model`s performance, suggesting that our model does not over-fit on the NAFLD dataset.
Previous studies have already demonstrated the saturation of QUS parameters in high-grade steatosis [
17,
24,
25]. The correlation between MRI-PDFF and the predicted fat fraction was linear below 18% MRI-PDFF; outside this range, the correlation decreased, and the prediction models underestimated the severity of steatosis [
24,
25]. We found that the correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF was the highest (⍴ = 0.89) in the range of <12.2% MRI-PDFF in the NAFLD group. The higher correlation and better prediction accuracy observed in the MAFLD group in part, can also be explained by saturation effects as the percentages of patients with ≥10% (16.7% vs. 37.8%) and ≥20% (9.8% vs. 19.6%) MRI-PDFF were lower compared to the NAFLD group.
We also examined if liver fibrosis had a confounding effect on QUS or MRI-PDFF. We did not see that LS had a significant influence on either MRI-PDFF or other QUS parameters. The LS was not significantly different between MRI-defined steatosis grades; also, MRI-PDFF, AC, and BSC-D did not differ between the fibrosis grades. Furthermore, LS was not a significant predictor of MRI-PDFF in a linear regression. The AC has been extensively investigated as an imaging biomarker of hepatic steatosis in a multitude of publications [
12,
26]. A recent prospective study has reported that in a cohort of 124 patients, a QUS-derived fat fraction was more accurate for diagnosing NAFLD-related hepatic steatosis than the controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) [
23]. Another study, which used a 2D CNN to predict fat fraction in 173 NAFLD patients, also found that the accuracy of the CNN model was superior to AC for the detection of steatosis [
25]. Interestingly, among the least-squares models built from our QUS data, the simple AC model had a slightly better mean coefficient of determination (adj. R
2 = 0.498 vs. 0.446) and lower RMSE (6.42 % vs. 7.35%) in the cross-validation than the combined model. The goodness-of-fit was also better with the AC model in the MAFLD group (adj. R
2 = 0.73 vs. 0.67). These results may imply that a solely AC-based model does not significantly underperform the combined model while being less susceptible to overfitting due to the higher number of trainable parameters; thus, it could be more generalized. Meanwhile, the addition of a second variable such as BSC-D, to the model may improve the robustness of the prediction by compensating for the noise in the measurements. These questions should be further addressed in large-scale multi-center studies.
Our study had several limitations: first, data collection was retrospective, and relatively small patient cohorts with clinically suspected NAFLD (90 cases) and MAFLD (51 cases) were examined in a single center. Therefore, our results cannot be generalized to large patient populations. Second, there was a selection bias towards steatosis, as high-risk patients were preselected during clinical screening. Therefore, the percentage of negative cases in the NAFLD (21.2%) and MAFLD (54.9%) groups does not represent the general population. Third, AC and BSC-D were measured with the TAI and TSI applications, which might have slightly different technical specifications compared to similar QUS parameters available from different vendors.
5. Conclusions
With the recent advancements in image analysis, new algorithmic and artificial intelligence-based methods have become available for the objective assessment of both diffuse and focal liver diseases [
27,
28]. The prevalence of FLD is steadily increasing worldwide, which necessitates the introduction of new quantitative imaging techniques that can be used for objective and early diagnosis of hepatic steatosis [
1]. In the present study, we have developed a new, easily interpretable biomarker, USFF, for the quantification of steatosis based on QUS parameters. We have demonstrated that USFF is capable of diagnosing NAFLD with an accuracy similar to MRI-PDFF. Moreover, the USFF also showed a high degree of agreement with MRI-PDFF in MAFLD patients. Thus, USFF may be an ideal screening tool for FLD, but requires further validation in large-scale, multi-center studies.
Author Contributions
P.N.K.—conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing original draft, supervision; Z.Z.—conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing original draft; project administration; A.D.R.—investigation, data curation, project administration; B.K.B.—data curation, project administration; B.C.— investigation, data curation; R.S.—software, validation, data curation; I.K.—resources, supervision; G.G.—investigation, resources, supervision; V.B.—validation, writing— review & editing; K.W. —investigation, resources, supervision; P.M.-H.—resources, writing— review & editing, supervision; A.F.—conceptualization, investigation, resources, writing— review & editing; K.H.—conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, writing— review & editing; supervision; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Z.Z. was partly founded by the Ph.D. scholarship from the New National Excellence Program ( ÚNKP–23–3–SE–) of the Ministry of Culture and Innovation of Hungary.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This retrospective study was approved by Semmelweis University’s Regional and Institutional Science and Research Ethics Committee (Protocol number: SE RKEB 140/2020, 16 July 2020, and SE RKEB 6/2023, 9 February 2023), and conducted in accordance with ethical standards specified in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
All patients gave informed written consent to participate in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Ms. Lilla Petovsky for preparing the MRI scans.
Conflicts of Interest
P.N.K. has been a consultant and invited speaker for Samsung Medison Ltd. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Hepatol 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A New Definition for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. J Hepatol 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbantoglu, I.L.K.; Brunt, E.M. Role of Liver Biopsy in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 9026–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y. Diagnostic Value of MRI-PDFF for Hepatic Steatosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Eur Radiol 2019, 29, 3564–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Berzigotti, A.; Barr, R.G.; Choi, B.I.; Cui, X.W.; Dong, Y.; Gilja, O.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Moriyasu, F.; et al. Quantification of Liver Fat Content with Ultrasound: A WFUMB Position Paper. Ultrasound Med Biol 2021, 47, 2803–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.-Y.; Bao, W.-Y.-G.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liao, M.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.-Y.; Lu, Q. Non-Invasive Evaluation of Liver Steatosis with Imaging Modalities: New Techniques and Applications. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2023, 29, 2534–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsombor, Z.; Rónaszéki, A.D.; Csongrády, B.; Stollmayer, R.; Budai, B.K.; Folhoffer, A.; Kalina, I.; Győri, G.; Bérczi, V.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; et al. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence-Calculated Hepatorenal Index for Diagnosing Mild and Moderate Hepatic Steatosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.K.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Park, S.J. Quantitative Ultrasound Radiofrequency Data Analysis for the Assessment of Hepatic Steatosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Reference Standard. Korean J Radiol 2021, 22, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónaszéki, A.D.; Budai, B.K.; Csongrády, B.; Stollmayer, R.; Hagymási, K.; Werling, K.; Fodor, T.; Folhoffer, A.; Kalina, I.; Győri, G.; et al. Tissue Attenuation Imaging and Tissue Scatter Imaging for Quantitative Ultrasound Evaluation of Hepatic Steatosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e29708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şendur, H.N.; Özdemir Kalkan, D.; Cerit, M.N.; Kalkan, G.; Şendur, A.B.; Özhan Oktar, S. Hepatic Fat Quantification With Novel Ultrasound Based Techniques: A Diagnostic Performance Study Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Proton Density Fat Fraction as Reference Standard. Can Assoc Radiol J 2023, 74, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Kumar, V.; Ozturk, A.; Nam, K.; de Korte, C.L.; Barr, R.G. US Attenuation for Liver Fat Quantification: An AIUM-RSNA QIBA Pulse-Echo Quantitative Ultrasound Initiative. Radiology 2022, 302, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, K.A.; Han, A.; Rubin, J.M.; Gao, J.; Lavarello, R.; Cloutier, G.; Bamber, J.; Tuthill, T. US Backscatter for Liver Fat Quantification: An AIUM-RSNA QIBA Pulse-Echo Quantitative Ultrasound Initiative. Radiology 2022, 305, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.K.; Joo, I.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, J.K.; Park, J.; Park, H.S.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, J.M. Quantitative Ultrasound Radiofrequency Data Analysis for the Assessment of Hepatic Steatosis Using the Controlled Attenuation Parameter as a Reference Standard. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, C.K.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Insana, M.F. Effects of Frequency and Bandwidth on Diagnostic Information Transfer in Ultrasonic B-Mode Imaging. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 2012, 59, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Raimondi, A.; Maiocchi, L.; De Silvestri, A.; Poma, G.; Kumar, V.; Barr, R.G. Liver Fat Quantification With Ultrasound: Depth Dependence of Attenuation Coefficient. J Ultrasound Med 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labyed, Y.; Milkowski, A. Novel Method for Ultrasound-Derived Fat Fraction Using an Integrated Phantom. J Ultrasound Med 2020, 39, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Zhang, Y.N.; Boehringer, A.S.; Montes, V.; Andre, M.P.; Erdman, J.W.; Loomba, R.; Valasek, M.A.; Sirlin, C.B.; O’Brien, W.D. Assessment of Hepatic Steatosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Using Quantitative US. Radiology 2020, 295, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi, P.N.; Unger, Z.; Fejér, B.; Kucsa, A.; Tóth, A.; Folhoffer, A.; Szalay, F.; Bérczi, V. Interobserver Agreement and Diagnostic Accuracy of Shearwave Elastography for the Staging of Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Liver Fibrosis. J Clin Ultrasound 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G.; Wilson, S.R.; Rubens, D.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ferraioli, G. Update to the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Liver Elastography Consensus Statement. Radiology 2020, 296, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcel, T.; Chau, H.T.; Turlin, B.; Chaigneau, J.; Bannier, E.; Otal, P.; Frampas, E.; Leguen, A.; Boulic, A.; Saint-Jalmes, H.; et al. Evaluation of Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF) Obtained from a Vendor-Neutral MRI Sequence and MRQuantif Software. Eur Radiol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.; Yokoo, T.; Bydder, M.; Cruite, I.; Schroeder, M.E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Middleton, M.S. In Vivo Characterization of the Liver Fat 1H MR Spectrum. NMR Biomed 2011, 24, 10–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Han, A.; Madamba, E.; Bettencourt, R.; Loomba, R.R.; Boehringer, A.S.; Andre, M.P.; Erdman, J.W.; O’Brien, W.D.; Fowler, K.J.; et al. Direct Comparison of Quantitative US versus Controlled Attenuation Parameter for Liver Fat Assessment Using MRI Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Reference Standard in Patients Suspected of Having NAFLD. Radiology 2022, 304, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, A.; Byra, M.; Heba, E.; Andre, M.P.; Erdman, J.W.; Loomba, R.; Sirlin, C.B.; O’Brien, W.D. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Quantification of Liver Fat with Radiofrequency Ultrasound Data Using One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks. Radiology 2020, 295, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.K.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, G. Two-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network Using Quantitative US for Noninvasive Assessment of Hepatic Steatosis in NAFLD. Radiology 2023, 307, e221510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Alquiraish, M.H.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Cepin, S.; Fortney, L.E.; Ajmera, V.; Bettencourt, R.; Collier, S.; Hooker, J.; et al. Optimal Threshold of Controlled Attenuation Parameter with MRI-PDFF as the Gold Standard for the Detection of Hepatic Steatosis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stollmayer, R.; Budai, B.K.; Tóth, A.; Kalina, I.; Hartmann, E.; Szoldán, P.; Bérczi, V.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Kaposi, P.N. Diagnosis of Focal Liver Lesions with Deep Learning-Based Multi-Channel Analysis of Hepatocyte-Specific Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2021, 27, 5978–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budai, B.K.; Tóth, A.; Borsos, P.; Frank, V.G.; Shariati, S.; Fejér, B.; Folhoffer, A.; Szalay, F.; Bérczi, V.; Kaposi, P.N. Three-Dimensional CT Texture Analysis of Anatomic Liver Segments Can Differentiate between Low-Grade and High-Grade Fibrosis. BMC Med Imaging 2020, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Scatter plots show the correlation between quantitative ultrasound (QUS) biomarkers and MRI-PDFF. (a) We observed a non-linear distribution of the attenuation coefficient (AC) and (b) the backscatter-distribution coefficient (BSC-D) in relation to MRI-PDFF, in both the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, empty circle) and the metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, gray square) groups. We fitted a non-linear least-squares model (dashed line) onto the NAFLD dataset using a combination of AC and BSC-D values to compensate for the saturation effect at higher fat fractions.
Figure 1.
Scatter plots show the correlation between quantitative ultrasound (QUS) biomarkers and MRI-PDFF. (a) We observed a non-linear distribution of the attenuation coefficient (AC) and (b) the backscatter-distribution coefficient (BSC-D) in relation to MRI-PDFF, in both the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, empty circle) and the metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, gray square) groups. We fitted a non-linear least-squares model (dashed line) onto the NAFLD dataset using a combination of AC and BSC-D values to compensate for the saturation effect at higher fat fractions.
Figure 2.
Correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF. The ultrasound-estimated fat fraction (USFF) was predicted with a combined least-squares model fitted on the attenuation coefficient (AC) and backscatter-distribution coefficient (BSC-D). (a) The correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF was strong (Pearson`s r = 0.73, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 6.22–0.817) in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) group. (b) We found a very strong correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF (r = 0.828, CI = 0.716–0.899) by applying the same model to the metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) group. The slope and the offset of the correlation line (dashed line) were 0.9 and 1.24% in the NAFLD and 0.81 and 2.06% in the MAFLD dataset. The x=y identity line (continuous gray line) is shown as a reference.
Figure 2.
Correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF. The ultrasound-estimated fat fraction (USFF) was predicted with a combined least-squares model fitted on the attenuation coefficient (AC) and backscatter-distribution coefficient (BSC-D). (a) The correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF was strong (Pearson`s r = 0.73, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 6.22–0.817) in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) group. (b) We found a very strong correlation between USFF and MRI-PDFF (r = 0.828, CI = 0.716–0.899) by applying the same model to the metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) group. The slope and the offset of the correlation line (dashed line) were 0.9 and 1.24% in the NAFLD and 0.81 and 2.06% in the MAFLD dataset. The x=y identity line (continuous gray line) is shown as a reference.
Figure 3.
Distribution of USFF across steatosis grades. Patients were classified into four steatosis severity grades based on MRI-PDFF using cutoff values at 5%, 10%, and 20% fat fractions. The box plots represent the median (thick line), the range between 25% and 75% percentiles (box), and the minimum and maximum values (whiskers) of USFF predicted by the combined least-squares model for patients in each grade. Two sets of box plots were calculated, one for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, light-gray), and another for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, dark-gray). .
Figure 3.
Distribution of USFF across steatosis grades. Patients were classified into four steatosis severity grades based on MRI-PDFF using cutoff values at 5%, 10%, and 20% fat fractions. The box plots represent the median (thick line), the range between 25% and 75% percentiles (box), and the minimum and maximum values (whiskers) of USFF predicted by the combined least-squares model for patients in each grade. Two sets of box plots were calculated, one for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, light-gray), and another for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, dark-gray). .
Figure 4.
Diagnostic performance of USFF in separating steatosis grades. (a) The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis showed that USFF could separate <5% from ≥5% MRI-PDFF steatosis with excellent area under the ROC curve (AUC) accuracy in both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, AUC = 0.97, continuous line) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, AUC = 0.99, dashed line). (b) The USFF proved to be just slightly less successful in differentiating between <10% vs. ≥10% MRI-PDFF with an AUC of 0.91 in NAFLD (continuous line) and an AUC of 0.96 in MAFLD (dashed line).
Figure 4.
Diagnostic performance of USFF in separating steatosis grades. (a) The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis showed that USFF could separate <5% from ≥5% MRI-PDFF steatosis with excellent area under the ROC curve (AUC) accuracy in both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, AUC = 0.97, continuous line) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD, AUC = 0.99, dashed line). (b) The USFF proved to be just slightly less successful in differentiating between <10% vs. ≥10% MRI-PDFF with an AUC of 0.91 in NAFLD (continuous line) and an AUC of 0.96 in MAFLD (dashed line).
Table 1.
Demographics and etiology of the patient groups.
Table 1.
Demographics and etiology of the patient groups.
| |
NAFLD (n = 90) |
MAFLD (n = 51) |
| Sex |
|
|
| female (%) |
44 (48.9%) |
26 (51.0%) |
| male (%) |
46 (51.1%) |
25 (49.0%) |
| Age (years) |
|
|
| mean (±SD) |
55.1 (13.3) |
54.3 (13.4) |
| range |
23–78 |
21–82 |
| BMI (kg/m2) |
|
|
| mean (±SD) |
29.3 (4.4) |
26.6 (3.9) |
| range |
18.6–45.3 |
19.7–35.3 |
| T2DM (%) |
24 (35.3%) |
1 (2.7%) |
| |
|
|
| Etiology of chronic liver disease (%) |
|
| AIH |
|
5 (9.8%) |
| alcoholic |
|
3 (5.9%) |
| chr. HBV |
|
3 (5.9%) |
| chr. HCV |
|
7 (13.7%) |
| hemochr. |
|
6 (11.8%) |
| hepatotoxic med. |
|
15 (29.4%) |
| PBC/PSC |
|
8 (15.7%) |
| Wilson`s disease |
|
4 (7.8%) |
| none |
91 (100%) |
|
Table 2.
Distributions of the imaging parameters.
Table 2.
Distributions of the imaging parameters.
| |
NAFLD (n = 90) |
MAFLD (n = 51) |
| AC (dB/cm/Mhz) |
|
|
| mean ± SD |
0.83 ± 0.15 |
0.73 ± 0.17 |
| range |
0.55 – 1.22 |
0.49 – 1.26 |
| BSC-D (arbitrary unit) |
|
|
| mean ± SD |
100.54 ± 9.6 |
92.68 ± 11.87 |
| range |
60 – 116.62 |
62.52 – 110.38 |
| LS (kPa) |
|
|
| mean ± SD |
7.24 ± 3.2 |
11.26 ± 8.9 |
| range |
3.2 – 21.8 |
3.9 – 39.7 |
| MRI-PDFF (%) |
|
|
| mean ± SD |
12.1 ± 8.86 |
7.8 ± 7.7 |
| range |
0.2 – 44.6 |
0.4 – 30.1 |
| USFF (%)1 |
|
|
| mean ± SD |
12.06 ± 7.23 |
7.08 ± 7.86 |
| range |
-1.25 – 35.3 |
-1.99 – 37.03 |
| Steatosis grade2 |
|
|
| <5% |
19 (21.1%) |
28 (54.9%) |
| 5–10% |
22 (24.4%) |
8 (15.7%) |
| 10–20% |
34 (37.8%) |
10 (19.6%) |
| ≥20% |
15 (16.7%) |
5 (9.8%) |
| Fibrosis grade3 |
|
|
| F0/F1 |
12 (13.3%) |
5 (9.8%) |
| F2 |
64 (71.1%) |
25 (49.1%) |
| F3 |
8 (8.9%) |
12 (23.5%) |
| F4 |
6 (6.7%) |
9 (17.6%) |
Table 3.
Results of the regression analysis.
Table 3.
Results of the regression analysis.
| |
Univariable analysis |
Multivariable analysis |
| |
adj. R2
|
F stat. |
ß |
p-value |
adj. R2
|
F stat. |
ß |
p-value |
| NAFLD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| AC |
0.504 |
91.47 |
43.04 |
<0.001 |
0.485 |
18.65 |
36.16 |
<0.001 |
| BSC-D |
0.31 |
14.01 |
0.52 |
<0.001 |
0.485 |
18.65 |
0.18 |
0.118 |
| LS |
0.0009 |
1.08 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.485 |
18.65 |
0.06 |
0.781 |
| BMI |
0.078 |
7.36 |
0.63 |
0.008 |
0.485 |
18.65 |
0.07 |
0.696 |
| MAFLD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| AC |
0.748 |
149.2 |
40.19 |
<0.001 |
0.775 |
34.49 |
44.82 |
<0.001 |
| BSC-D |
0.235 |
16.38 |
0.32 |
<0.001 |
0.775 |
34.49 |
0.07 |
0.298 |
| LS |
0.049 |
3.57 |
-0.22 |
0.065 |
0.775 |
34.49 |
0.05 |
0.521 |
| BMI |
0.23 |
12.65 |
1.07 |
0.001 |
0.775 |
34.49 |
-0.21 |
0.38 |
Table 4.
Performance of the non-linear least-squares fitted prediction models.
Table 4.
Performance of the non-linear least-squares fitted prediction models.
| |
NAFLD group1
|
MAFLD group2
|
| model |
adj. R2
|
RMSE |
Cor. coef. |
p-value |
adj. R2
|
RMSE |
Cor. coef. |
p-value |
| AC |
0.498 ± 0.046 |
6.415 ± 0.561 |
0.7160.6–0.8 |
<0.001 |
0.733 |
3.911 |
0.8590.76–0.92 |
<0.001 |
| BSC-D |
0.318 ± 0.075 |
7.687 ± 0.696 |
0.5810.43–0.7 |
<0.001 |
0.253 |
6.608 |
0.5180.28–0.69 |
<0.001 |
| AC + BSC-D |
0.446 ± 0.152 |
7.347 ± 3.105 |
0.7350.62–0.82 |
<0.001 |
0.673 |
4.574 |
0.8280.72–0.9 |
<0.001 |
Table 5.
Diagnostic performance of USFF in separating MRI-PDFF-defined steatosis grades.
Table 5.
Diagnostic performance of USFF in separating MRI-PDFF-defined steatosis grades.
| |
<5% vs. ≥5% MRI-PDFF |
10% vs. ≥10% MRI-PDFF |
| |
NAFLD group |
MAFLD group |
NAFLD group |
MAFLD group |
| Cutoff |
6.36% |
5.22% |
11.64% |
8.74% |
| AUC |
0.97 |
0.99 |
0.91 |
0.96 |
| SN |
0.92 |
0.96 |
0.86 |
0.93 |
| SP |
1 |
0.96 |
0.88 |
0.94 |
| PPV |
1 |
0.96 |
0.89 |
0.88 |
| NPV |
0.76 |
0.96 |
0.84 |
0.97 |
| TA |
0.93 |
0.96 |
0.87 |
0.94 |
| Power |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).