1. Introduction
Hydroelectric power accounts for 83 percent of Zambia's installed generation capacity, followed by coal at 9 percent, heavy fuel oil at 5 percent, and solar photovoltaic (PV) at 3 percent [
1,
2]. Zambia recently experienced extended hours of load shedding due to reduced hydroelectricity generation attributed to poor rainfall patterns [
3]. In light of this situation, there was a push toward diversification in the power generation mix. The quest to diversify the power generation mix has led to the inception of grid-scale wind power feasibility studies at ten sites nationwide. DNV GL has evaluated the wind resources at eight locations, including the long-term wind regime, and the estimated energy production. These assessments were based on a generic 4 MW wind turbine with a rotor of 140 m and a hub height of 130 m [
4,
5]. The second assessment was by RINA company on behalf of Kafue Gorge Regional Training Centre (KGRTC) [
6,
7]. The third wind resource assessment was conducted by the Technology Development and Advisory Unit (TDAU), University of Zambia, working with the Rural Electrification Authority (REA) in Lunga District, Luapula Province [
8,
9].
However, the findings from the above studies only provide a starting point for wind power development. In order to operate sustainably, the wind power industry depends on other/support industries. Suppliers tend to position themselves in specific market segments to preserve their competitive advantages and meet local requirements [
10]. This research intends to bridge the gap that the feasibility studies have not addressed: the capability of Zambian industries to manufacture grid-scale wind turbine blades and towers. A turbine blade typically costs 10-15 % of the system cost [
11], whereas the tower costs 20-25 % of the whole wind turbine system cost [
12]. Therefore, the combined cost of the blades and tower can be as high as 40 % of the system cost; hence, this research focused on the blades and tower. A wind farm's system cost might also be reduced if these two components can be locally manufactured because transportation and other costs associated with the importation of wind turbine blades and towers will be eliminated. Companies investing in manufacturing wind turbine blades and towers are likely to benefit from incentives and tax exemptions offered by promoting renewable energy in the country.
Potential manufacturers of wind turbine blades and towers considered for Zambia in this study include (as depicted in
Figure 1): (1) fiber-reinforced polymer/plastic (GFRP), (2) mechanical engineering, and (3) pre-cast concrete manufacturers. It should be acknowledged that if these modern technologies are available and applied, this will be a breakthrough for Zambia to start manufacturing WT blades and towers; therefore, only components such as nacelle, generators, and gearboxes will be imported. Zambia still needs to develop manufacturing plants for such components, but in the interim, this will reduce the cost of WT technology when WT blades and towers are manufactured locally. The investment in manufacturing WT and towers will spar investment in companies that can produce nacelle, generators, and gearboxes. Renewable energy technologies such as wind energy remain the priority for Zambia's wind sector.
According to Kaoma et al. [
13], the successful deployment of bioenergy technologies, as with other renewable energy technologies, including wind technologies in Zambia, relies on a conducive enabling environment.
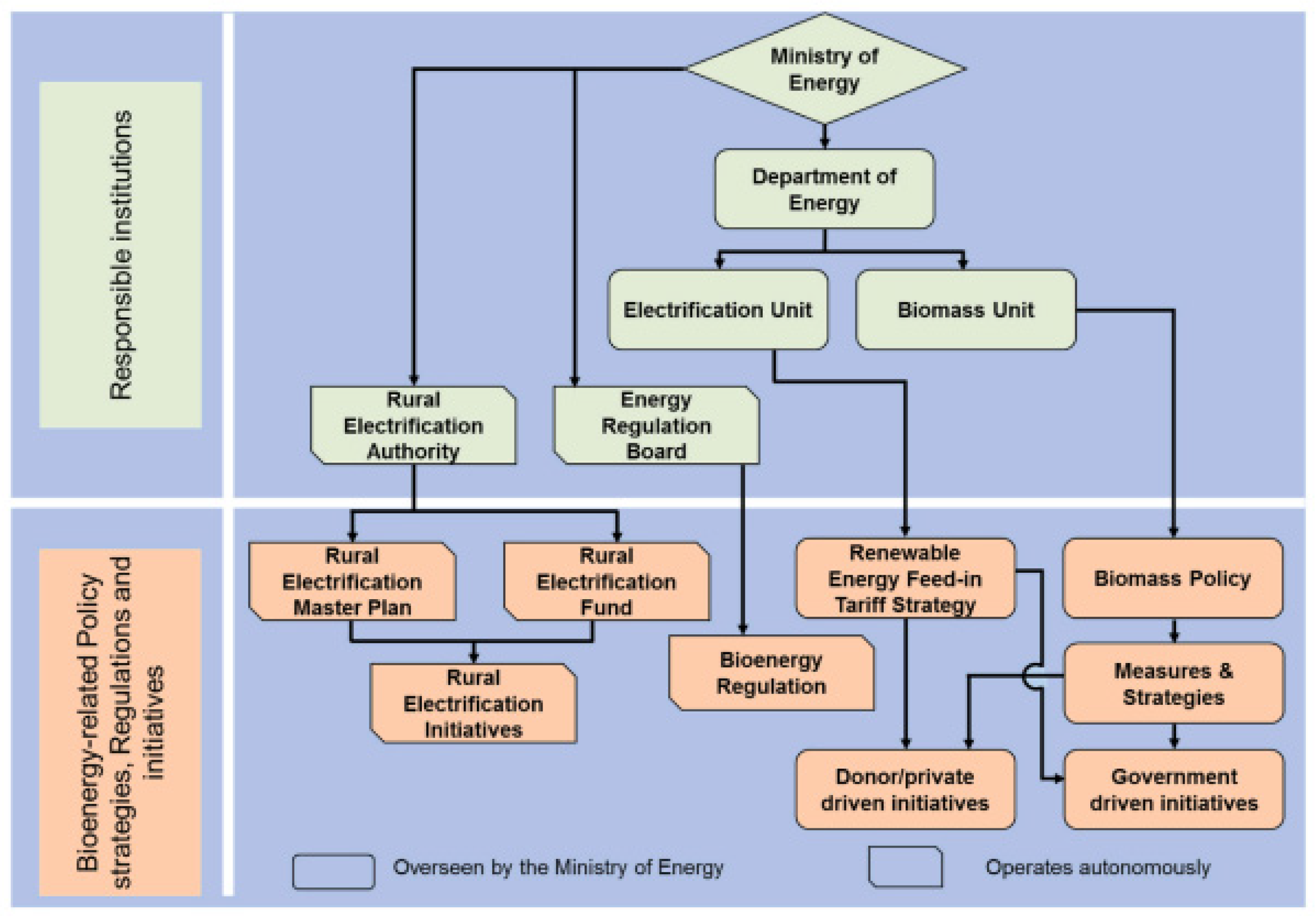
Figure 2 illustrates the institutional framework tasked with implementing policies related to bioenergy in Zambia, which is also applicable to other renewable energy technologies. The Ministry of Energy (MOE) [
14] in Zambia directly or indirectly oversees all aspects of promoting sustainable energy in the country. On the one hand, the Department of Energy, which is under the direct control of the ministry, comprises, among other units, formulating policies, strategies, and initiatives related to promoting sustainable energy. On the other hand, the Rural Electrification Authority (REA) and the Energy Regulation Board (ERB) were established through the Rural Electrification Act of 2003 and the Energy Regulation Act of 1995 Chapter 436, respectively, are government agencies that were established under the ministry but operate autonomously. The former is tasked to spearhead the rural electrification agenda for the country with an overall mandate of increasing the availability of electricity in rural areas from the current 4%–51% by the year 2030. At the same time, the latter is mandated to regulate the entire energy sector of the country [
13].
This study evaluates the ability to manufacture wind turbine blades and towers in Zambia. Manufacturing WT blades, steel tabular and lattice towers, and pre-cast concrete towers depend on modern production processes/operations. Further, the study analyses several gaps that could hinder the participation of local companies in wind power development directly or indirectly. By providing the enabling environment for companies to manufacture WT blades and towers, the wind sector will contribute to the supply of sustainable modern energy. Thus, this study aims to bridge this information gap by assessing the capability of Zambian industries to manufacture grid-scale wind turbine blades and towers, along with an assessment of the existing enabling environment that promotes the introduction of wind energy technology in Zambia. In addition, recommendations for improving the existing enabling environment for manufacturing WT blades and towers in Zambia are provided.
2. Research methodology
The methodology employed in the study used a mixed-method approach, which utilized the two basic approaches in a complementary manner to garner the benefits of both approaches simultaneously. Researchers use this method to collect and analyze quantitative and qualitative data within the same study. This approach explored the research situation using qualitative data and then measured and analyzed it quantitatively. In the study's first phase, qualitative data was collected from the Zambia Association of Manufacturers (ZAM). The data was organized into three distinct strata, namely, categories of manufacturers with the ability to manufacture wind turbine blades and towers. They included grass fiber reinforced polymer/plastic (GFRP), mechanical engineering, and pre-cast concrete manufacturers.
Figure 1 shows the production strata for wind turbine blades and towers considered for Zambia.
The qualitative data was used to define the study population and develop a quantitative data collection tool. A qualitative parameter defined the population in each stratum; hence, it was difficult to establish the standard deviation, and this further hints at a possibility of significant variability among individual members of the stratum. Therefore, the study was conducted on the whole population; the sample size was the population. Due to the small population size, it was possible to conduct the study on the whole population. The data collection tools/questionnaires were developed and tested. The questionnaires were distributed to all the individual companies involved in the study. The quantitative data was collected using questionnaires and then collated and fed into MS Excel. The MS Excel generated various statistics, which were used to inform the discussion, conclusion, and recommendations.
The decision method employed considered infrastructure and equipment for surface finishing, welding, cutting, straightening, punching, moulding, and numerical control (NC) or computer numerical control (CNC). Another critical parameter was adequate sheltered space to accommodate mould measuring up to 75 m long and 4.5 m wide. These companies should occupy an area greater than 0.7 ha, and this is also good enough for manufacturing both lattice and steel tubular towers.
Figure 2 summarises the information on the target product, the production strata employed, the process/operation, and the product targeted for production.
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Review of grid-scale wind power potential
Table 1 below summarizes the annual average wind speeds for the ten sites covered by the wind resource assessment projects undertaken in Zambia.
From the annual average wind speeds shown in the table above, it can be deduced that at least four out of ten sites have Class III wind speeds, while five have Class IV and one is below Class IV. If potential wind speeds at the Kasomalunga and KGRTC sites were extrapolated to 130 m height, it would be possible to have five sites with Class III wind speeds and five with Class IV wind speeds.
Table 2 shows the wind classes for further understanding according to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The study by TDAU indicated that annual average wind speeds of 6.8 m/s at 117m are available in Kasomalunga; this is adequate to sustainably operate a Class IV WT but not a Class III unless at a higher height. The annual average wind speeds obtained by RINA in Namalundu indicate average wind speeds of 5.2 m/s at 95 m above ground level; this is inadequate to operate a Class IV WT sustainably.
The above results have shown that a Class IV WT with a hub height above 117 m can be operated sustainably at nine of the ten sites under investigation. Further, at least four of the ten sites can operate a Class III WT with a hub height of 130 m. The three wind resource assessment projects being undertaken in Zambia have demonstrated that there is wind resource potential in certain parts of Zambia for grid-scale wind power generation [
6]. Despite almost all sites being capable of sustaining a Class IV WT, it is more economical to focus only on those that sustain a Class III WT. According to LM Wind Power, there is a clear trend in the market toward more Wind Class III turbines in low-wind sites [
15]; this has resulted in a bias among WT manufacturers to manufacture Class III WTs; this, in turn, lowers the initial cost of WTs due to economies of scale and competition among manufacturers. In 2010, Wiley predicted that larger machines beyond 5 MW should become economically viable with further advances in material and design technology, but a sudden change is unlikely over the next 5-year period [
16]. This prediction was precise; today, the most common turbine sizes for onshore applications are within the 2-4 MW rating. Considering what has been highlighted by the literature, to assess the capability of industries to manufacture WT blades and towers, this study adopted a Class III WT with a hub height of 130 m and a maximum rated capacity of 4 MW for the Zambian wind regime.
3.2. WT Blade Manufacturing Capability
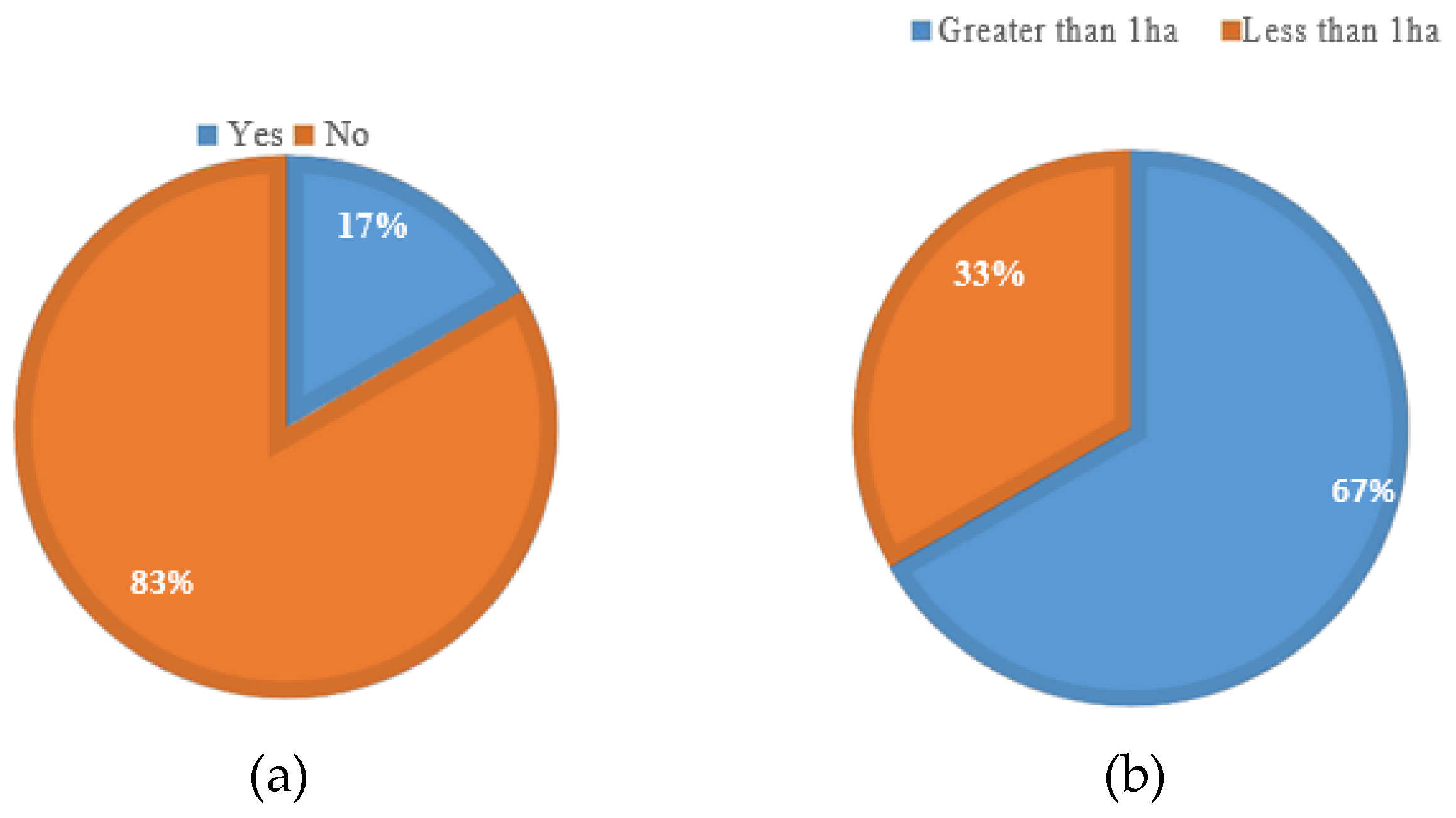
Figure 3(a) below shows the percentage of companies that can manufacture GFRP products in Zambia, and
Figure 3(b) shows the area occupied by the said companies.
Figure 3(a) indicates that 17 % of the companies who responded to the questionnaire can manufacture GFRP products, while 83 % cannot. This process is very similar to the one used in mechanical engineering WT blade manufacturing except for the scale and quality requirements. In order to achieve superior quality, blade manufacturers employ a process called polymer infusion, where the polymer is spread consistently throughout the glass fibers with the help of an artificially created vacuum in the mold. This process is not currently practiced in the Zambian GFRP production processes. The processes currently being practiced are rudimentary due to the nature of the products being manufactured.
In Figure 3(b), the chart shows that 33 % of companies have adequate sheltered space to accommodate a mould measuring up to 75 m long and 4.5 m wide.
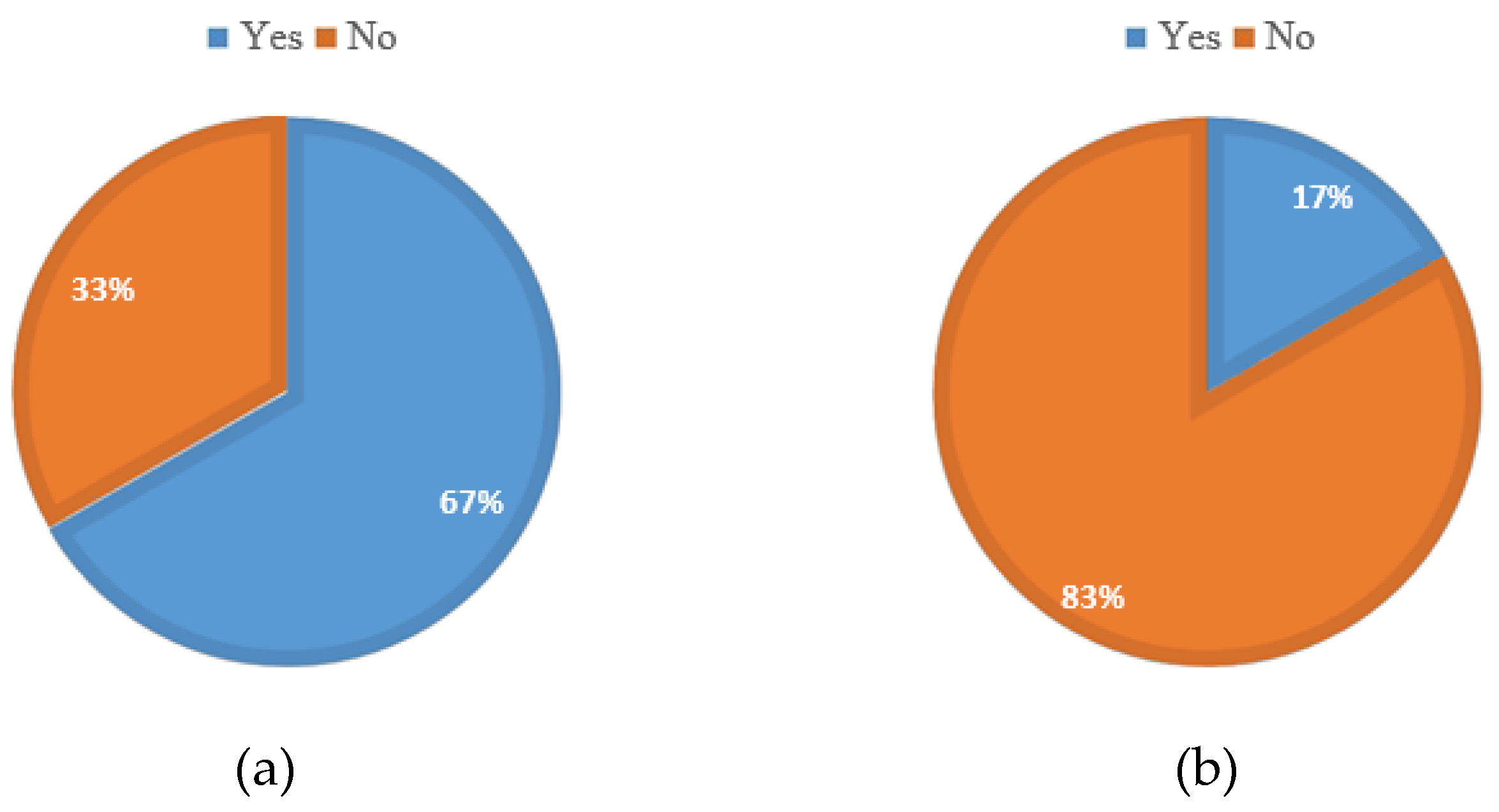
The results from the survey (
Figure 4a) indicate that 67 % of the companies who responded to the survey occupy an area greater than one hectare. A one-hectare area is adequate to house all the necessary infrastructure for manufacturing grid-scale WT blades. However, only 33 % of the companies have adequate sheltered space to accommodate a mould measuring 75 m long and 4.5 m wide. Further, it should be noted that most of these infrastructures are old and were not meant for WT blade manufacturing; hence, they need more supplementary equipment, such as overhead cranes. In order to use these infrastructures for blade manufacturing, there is a need to overhaul them, and some might require complete replacement.
3.3. Steel tower manufacturing
The study considered three types of towers: steel tubular, steel lattice, and concrete. Information on available infrastructure was obscure as most respondents felt uncomfortable availing technical details of their infrastructures; this made it challenging to determine the size of the infrastructure and supplementary equipment.
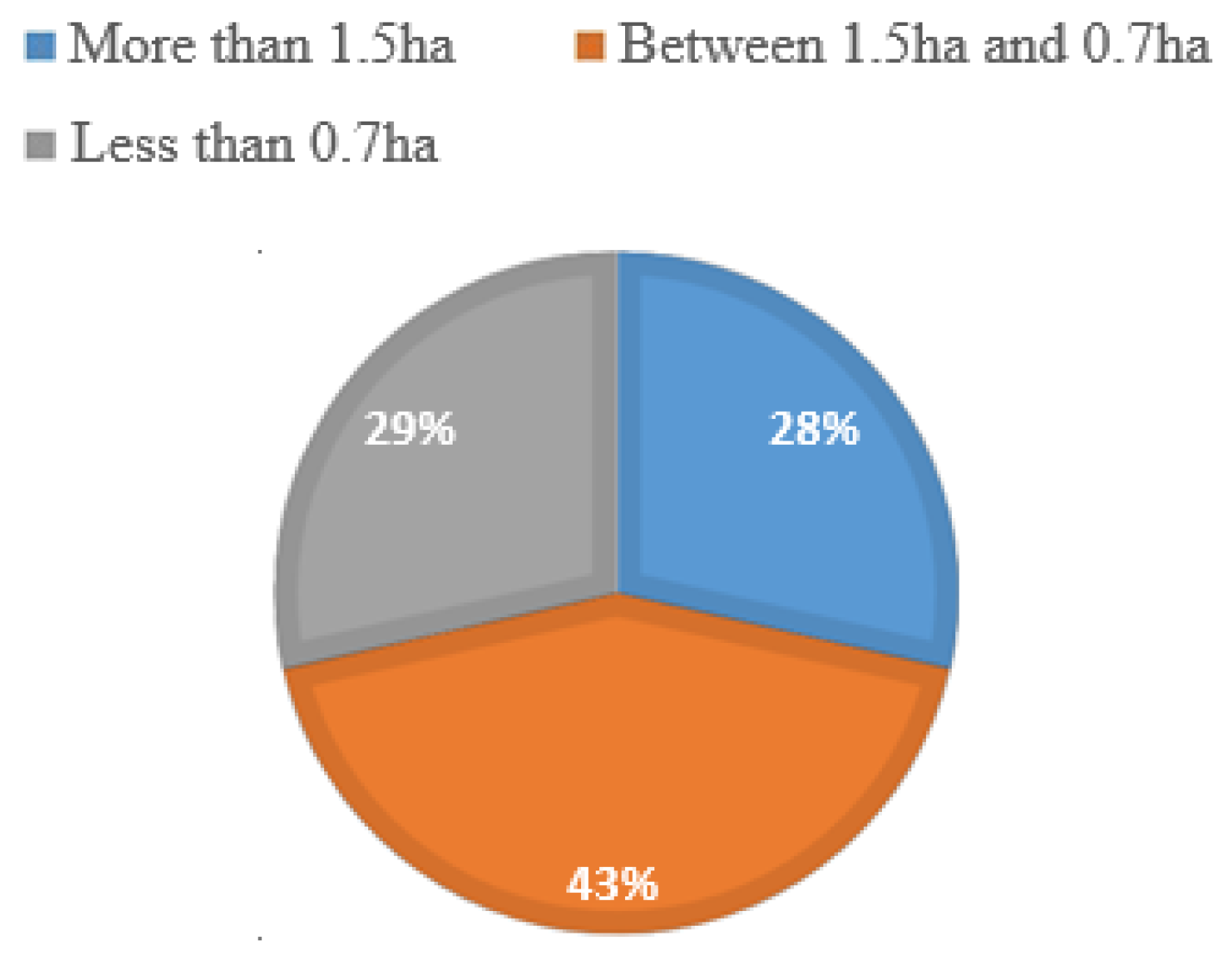
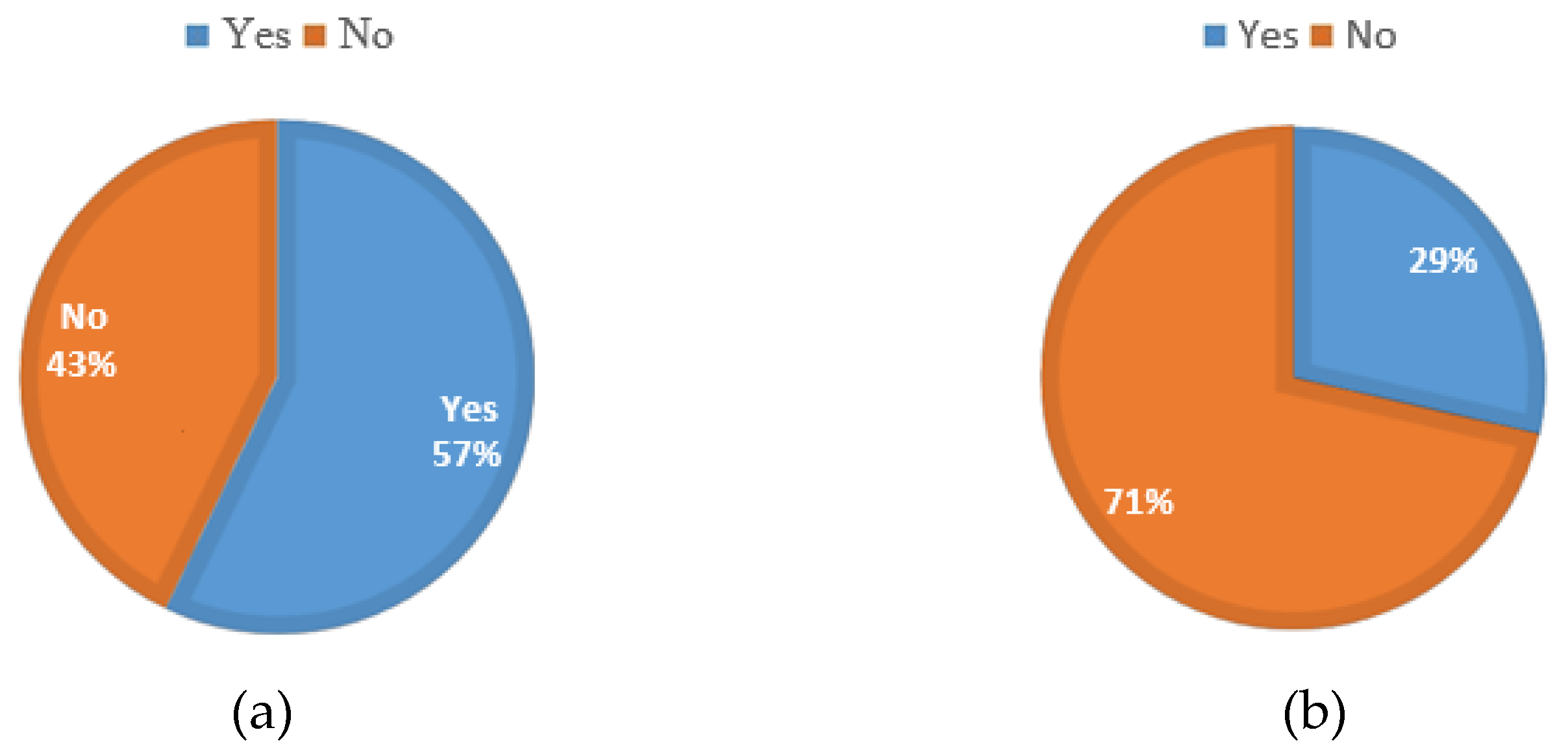
Figure 5 shows the total area occupied by companies that participated in the study. The results above indicate that 28 % of the respondents occupy an area greater than 1.5 ha, 43 % occupy an area greater than 0.7 ha but less than l.5 ha, and 29 % occupy less than 0.7 ha. These results imply that 29 % of the respondents need more land requirements to manufacture either steel tubular towers or lattice towers.
Furthermore, 71 % satisfy land requirements to manufacture steel tubular towers, and 28 % have adequate land requirements to manufacture steel lattice towers. However, it should be noted that these structures may not have been built for heavy applications such as those involved in WT tower manufacturing and, therefore, cannot be used for WT tower manufacturing on an as-is basis.
3.3.1. Steel tubular tower manufacturing
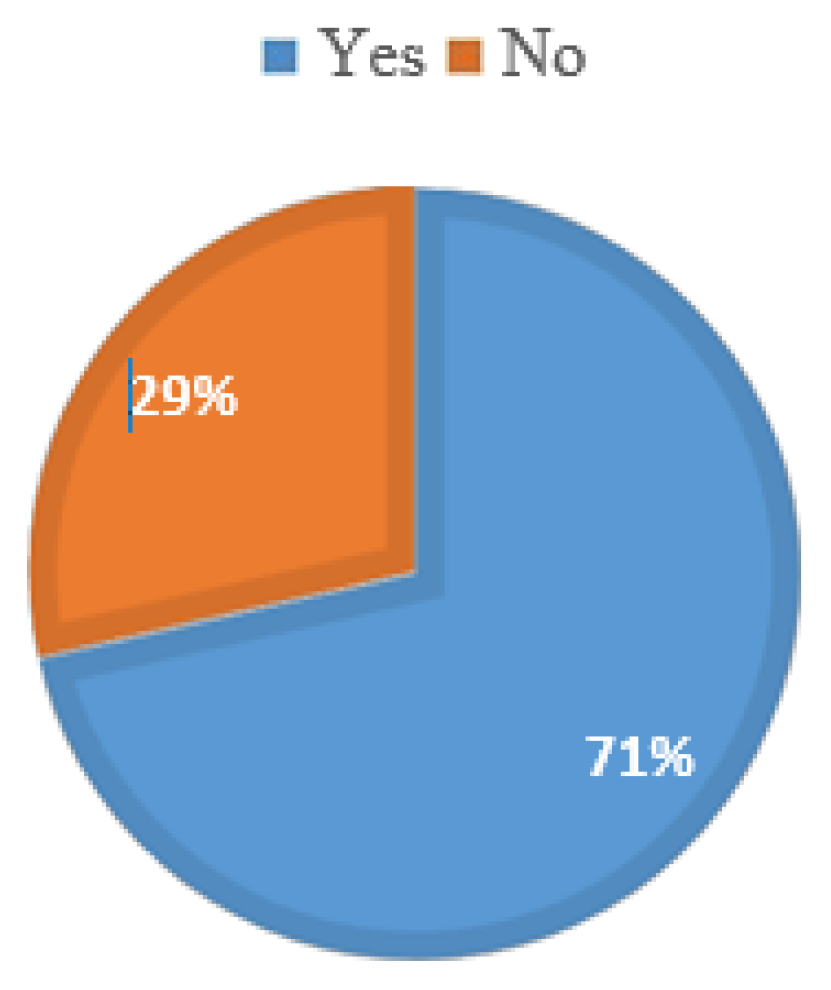
Figure 6(a) below indicates that 57 % of the respondents can cut steel plates with up to 25 mm thicknesses.
Figure 6(b) shows that 29 % of the respondents can weld steel plates up to 25 mm thick, while 71 % need equipment. Further,
Figure 7 indicates that 71 % of the respondents can conduct surface finish operations on steel surfaces. These operations include but are not limited to surface cleaning and application of an apoxy/polyurethane paint. The results indicate that 57 % of the respondents can cut 25 mm thick steel plates, 29 % can weld together 25 mm thick steel plates, and 71 % can conduct surface finishing operations on steel surfaces. Respondents cannot conduct rolling or bending operations on 25 mm thick steel plates. It has been deduced that no company can manufacture steel tubular towers on an as-is basis because none can roll or bend 25mm thick steel plates.
This process is the principal operation in manufacturing steel tubular towers, while other operations are either preparatory or finishing. Although 57 % of the respondents can cut 25 mm thick plates, the equipment available is rudimentary and will negatively affect the quality and productivity while raising the cost of production. CNC cutting technologies are best suited for these cutting operations as they can make high-precision cuts with increased productivity at a lowered cost of production; this is in agreement with Sainz [
17]. The author highlighted that increased automation technology in wind turbine manufacturing is a laborious alternative and requires substantial financial investment. However, it achieves simplicity and economy and increases the final quality of each turbine. According to Elia et al. [
18], wind energy technologies have seen a rapid decline in costs in the last two decades. There is an interplay between industry and policies, and how market-based measures and direct policy intervention through R&D investments have contributed to the decline in onshore wind turbine costs.
The survey revealed that 71 % of respondents who can conduct surface finish listed sandblasting and spray painting for cleaning and painting operations. The mentioned operations are manually operated; this may have an advantage in quality control over automated operations, as human intervention can be introduced earlier in the process, saving time.
3.3.2. Steel lattice tower manufacturing
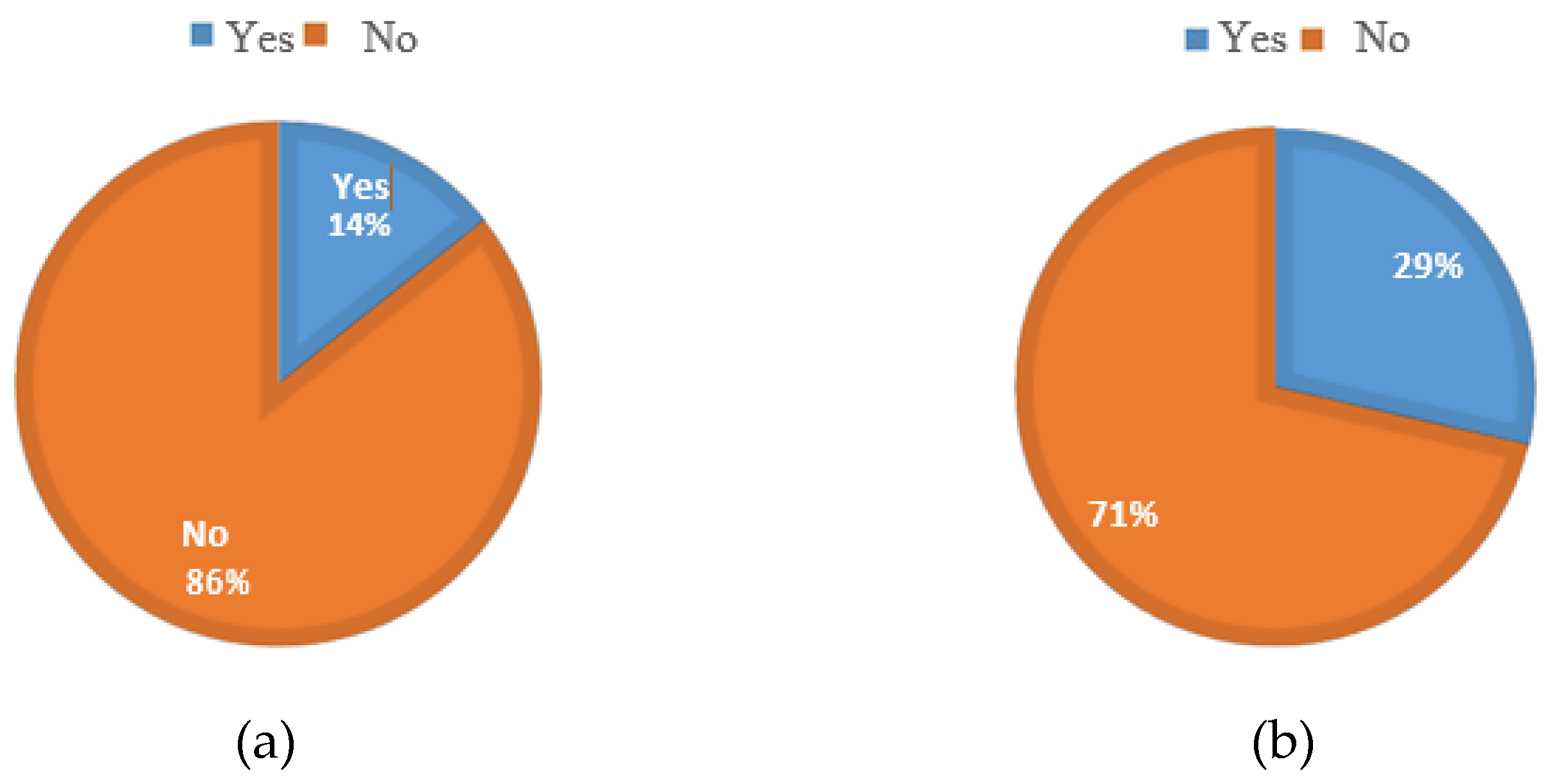
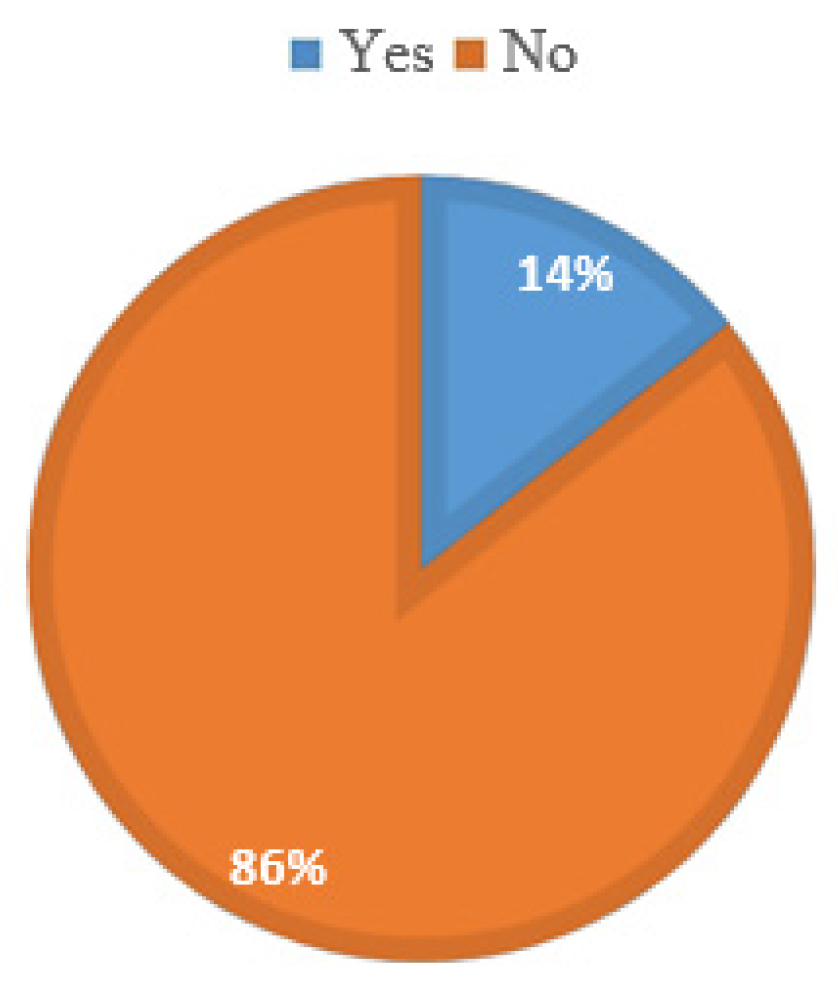
Figure 8(a) below indicates that 14 % of the respondents have the equipment to straighten angle bars measuring 150 mm by 150 mm before further processing, while 86 % cannot conduct this operation. The equipment which was mentioned for angle bar straightening is a press machine. It should be noted that this machine is not ideal for angle straightening at a mass production scale, such as would be involved in grid-scale WT lattice tower manufacture.
Figure 8(b) shows that 29 % of the respondents can cut angle bars measuring 150 mm by 150 mm into required lengths. Further,
Figure 9 indicates that 14 % of the respondents can punch holes into angle bars according to specifications.
The study revealed that respondents capable of cutting the angle bars own a profile cutter, power saw, or guillotine. All three pieces of equipment mentioned are operated manually; therefore, the productivity is low and may lead to increased cost of production for large-scale applications such as WT lattice towers. It would be more practical to employ numerical Control (NC) or computer numerical control (CNC) equipment for such application as this will be less labor intensive but highly productive. Two types of machines have been mentioned for punching holes: press machines equipped with punching dies and drilling machines. The latter may not be practical for WT lattice tower manufacturing due to its low productivity, and the fact that it is not automated means it is labor intensive. The press machines equipped with punching dies are preferred over the drilling machines as they have higher productivity. No respondent had a galvanizing plant, which means that although some companies can cut and punch angle bars, the process is only complete if the sections are galvanized according to design specifications for corrosion protection.
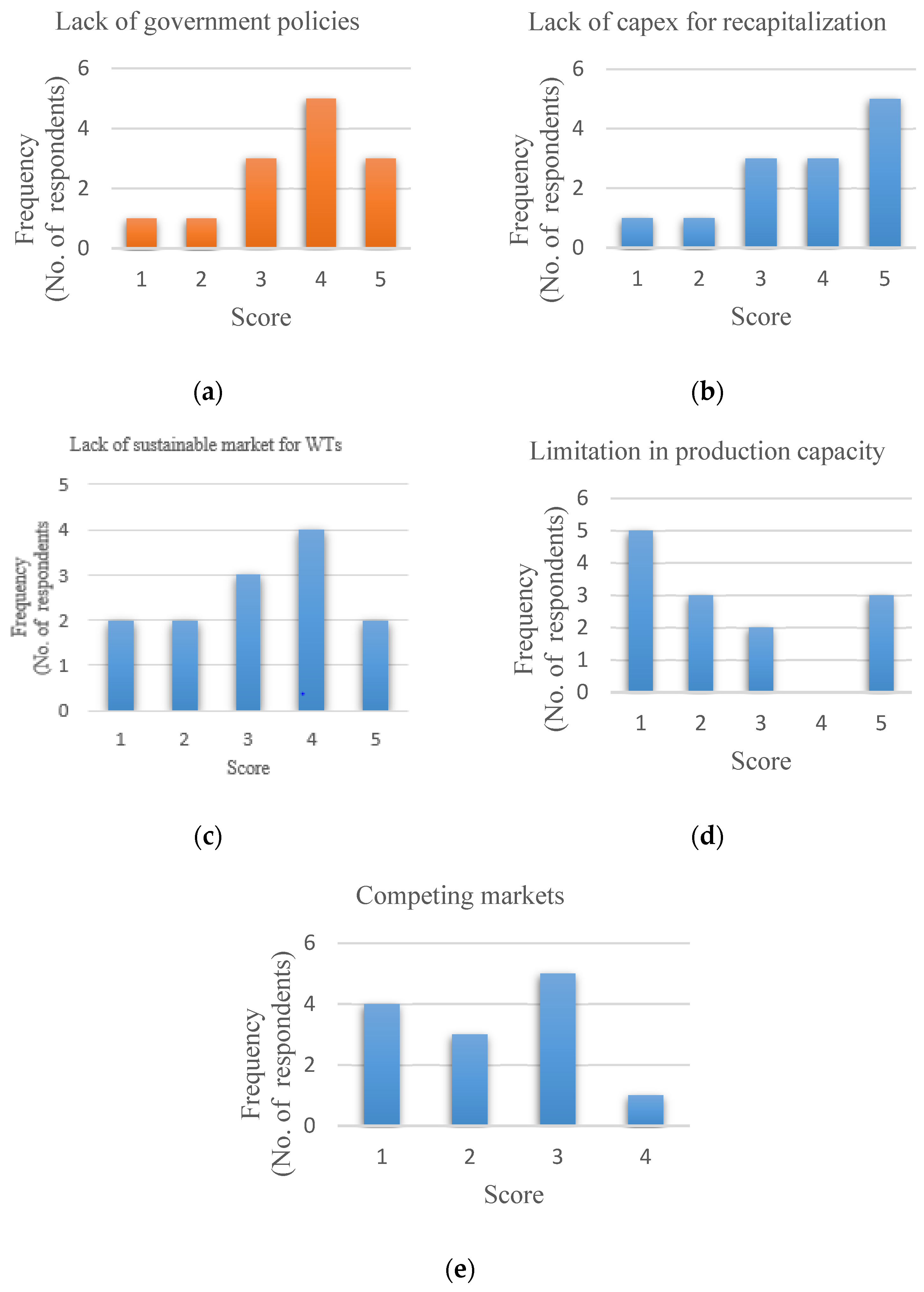
3.4. Priority gap analysis
Several gaps that could hinder local companies' participation in wind power development were investigated in this study. Numerous gaps can be investigated; however, this study focused on five: lack of clear government policies, lack of capital expenditure (capex) for recapitalization, lack of sustainable market for WTs, limitation in production capacity, and competing markets. These gaps cut across four main sectors: policy, financial, economic, and technical. The results from the survey are presented as histograms in
Figure 10 below.
Government policies create an enabling environment that facilitates the establishment and growth of entrepreneurship in a particular sector. Therefore, there is a need for favorable government policies in the sector to avert many challenges in executing projects in that sector. The results in
Figure 10(a) below show that the lack of clear government policies was ranked as a high-priority gap because there are no wind power policies in Zambia. The wind power sector in Zambia is in its cradle, hence the absence of appropriate policies; however, this is the best time to formulate these policies so that there is clear guidance and motivation for companies that wish to venture into this sector.
The study investigated the lack of capex for recapitalization, which is very significant, especially since this study has already suggested that all the industries that need to venture into WT manufacturing need to recapitalize. The results in
Figure 10(b) indicate that the gap for lack of capex for recapitalization is a very high priority; this was expected as the results from the technical section of this study suggest that on an as-is basis, there are no Zambian companies that can manufacture WT blades or towers unless major overhauls are conducted on their infrastructure. It will be financially stressful for these companies to finance this scale of recapitalization on their own.
A sustainable market is very significant in any business; it ensures that the products being produced will be sold at a rate that will enable the company to recoup its investment. Therefore, the lack of a sustainable market for WTs will result in companies making losses and eventual closure. The results in
Figure 10(c) indicate that the gap for a sustainable market is a high priority; this is because the wind energy sector is very new, with no grid-scale wind farms installed at the moment; therefore, the demand for WTs only exists in potential form, and it is not certain. It is a matter of logic that creating a sustainable market for WTs is highly prioritized to safeguard the investment of companies that will venture into the sector.
Figure 10(d) shows the Limitation in production capacity highlighted in the previous sections. This study investigated companies that are already in existence and are conducting business. Therefore, introducing a new product on their production line will naturally introduce a competing market to the existing one. In
Figure 10(e), the study ranked the gap for competing markets as moderate, and this is with the view that most of these companies will have to establish a new infrastructure for WT manufacturing; this will not affect their current production as the existing infrastructure will continue to supply the demands from the existing market.
4. Conclusions and recommendations
4.1. Conclusions
The three wind potential studies in Zambia show wind resource potential for wind power generation in most parts of the country. These studies have shown that a Class IV WT with a hub height exceeding 116.5 m can be operated sustainably at 90 % of the ten sites that have been analyzed. Further, at least 40 % of the ten sites can operate a Class III WT with a hub height of 130 m. The study considered the capability of manufacturing companies based on wind potential results for Class III and Class IV, which exist in some sites. The findings of this study have revealed that on an as-is basis, there are no companies in Zambia that can manufacture WT blades or towers unless heavy overhauls are conducted to upgrade the infrastructure and equipment or set up new plants altogether. Further, several gaps have been identified and given a priority ranking, indicating what gaps should be considered more thoughtfully.
4.2. Recommendations
Grid-scale wind power generation is possible in certain parts of Zambia; however, this industry is still in its cradle and requires much nurturing if its true potential is to be realized. This study makes the following recommendations to develop the wind power industry:
The Government of Zambia should formulate policies that will create a suitable environment for companies wishing to venture into local WT blade and tower manufacturing;
Financial institutions, in conjunction with the Government of Zambia, should formulate financing mechanisms and fiscal incentives to attract local WT blade and tower manufacturers;
A study on the current electricity grid network should be conducted, and possible upgrades should be suggested in order to facilitate power take-off from the wind farms;
A holistic study of the capacity of the Zambian haulage industry to haul WT components, such as tower sections, blades, nacelle, generators, and gearboxes, should be undertaken.
Author Contributions
Sydney Mutale: draft and writing, reviewing and editing. Amos Banda: draft and writing, reviewing and editing. Jan Yasir: review and editing. Yong Wang: Supervision, review and editing.
Data Availability Statement
To be made available when requested.
Acknowledgments
This work was also supported by the School of New Energy, North China Electric Power University (Chinese Scholarship Council - 2020) and the University of Zambia (Staff Development Programme,Technology Development and Advisory Unit (TDAU) and School of Engineering).
Conflicts of Interest
None.
References
- Ministry of Energy, Department of Energy, Lusaka, Zambia, https://www.moe.gov.zm/?page_id=2198 (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Sibote, K.O. Measures to Diversify the Power Sector in Zambia. Lusaka: Department of Energy.
- Mutale, S., Wang, Y., Yasir, J., Aboubacar, T. Economic feasibility of onshore wind energy potential for electricity generation in Zambia. September 2023.
- Department of Energy. Renewable Energy Wind Mapping for Zambia, 24-month Site Resource Report. 2019, https://www.moe.gov.zm/?page_id=2397 .
- DNV-GL. Wind Resource Mapping in Zambia - 12 Month Site Resource Report. Washington DC : World Bank, 2018.
- Banda, A., Simukoko, L., Mwenda, H.M. A Review of wind resource potential ror grid-scale power generation in Zambia. UNESCO 6th Africa Engineering Week, 4th Africa Engineering Conference, Avani Victoria Falls Resort, Livingstone, Zambia, 18th – 20th September 2019; 59, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336022304.
- RINA. KGRTC Wind Farm - Feasibility Report. Chikankata : KGRTC, 2018.
- Mutale, S., Wang, Y., Yasir, J., Banda, A. Evaluation and assessment of wind energy potential in Lunga District, Luapula Province, Zambia, 2023.
- TDAU. Wind Resource Assessment in Lunga - Technical Feasibility. Lusaka, Rural Electrification Authority, 2018.
- The DTI, SA. The Wind Energy Industry Localisation Roadmap in Support of Large-Scale Roll-Out in South Africa 2012.
- Research Directions in Wind Turbine Blades: Materials and Fatigue. Sandia National Laboratories. Stanford: GCEP - Stanford, unkwon.
- Lim, S., Kong, C., Park, H. A Study on Optimal Design of Filament Winding Composite Tower for 2 MW Class Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Systems. International Journal of Composite Materials 2013, 3, pp. 15-23. [CrossRef]
- Kaoma, M., Gheewala, S.H. Evaluation of the enabling environment for the sustainable development of rural-based bioenergy systems in Zambia. Energy Policy 2021b, 154. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Energy, Department of Energy, Lusaka, Zambia, 2023, https://www.moe.gov.zm/?page_id=1606.
- LM Wind Power. What is a Wind Class, https://www.lmwindpower.com/en/stories-and-press/stories/learn-about-wind/what-is-a-wind-class (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Willey, L.D. Chapter 6 - Design and Development of MeggaWat Wind Turbines. [ed.] Wei Tong. Wind Power Generation and Wind Turbine Design. Boston: WIT Press, 2010, pp. 187-256.
- Sainz, J.A. New Wind Turbine Manufacturing Techniques., Procedia Engineering, 2015, 135, Elsevier, pp. 880-886. [CrossRef]
- Elia, A., Taylor, M., Gallachoir, B.O., Rogan, F. Wind turbine cost reduction: A detailed bottom-up analysis of innovation drivers. Energy Policy 2020, 147, 111912. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).