Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF)
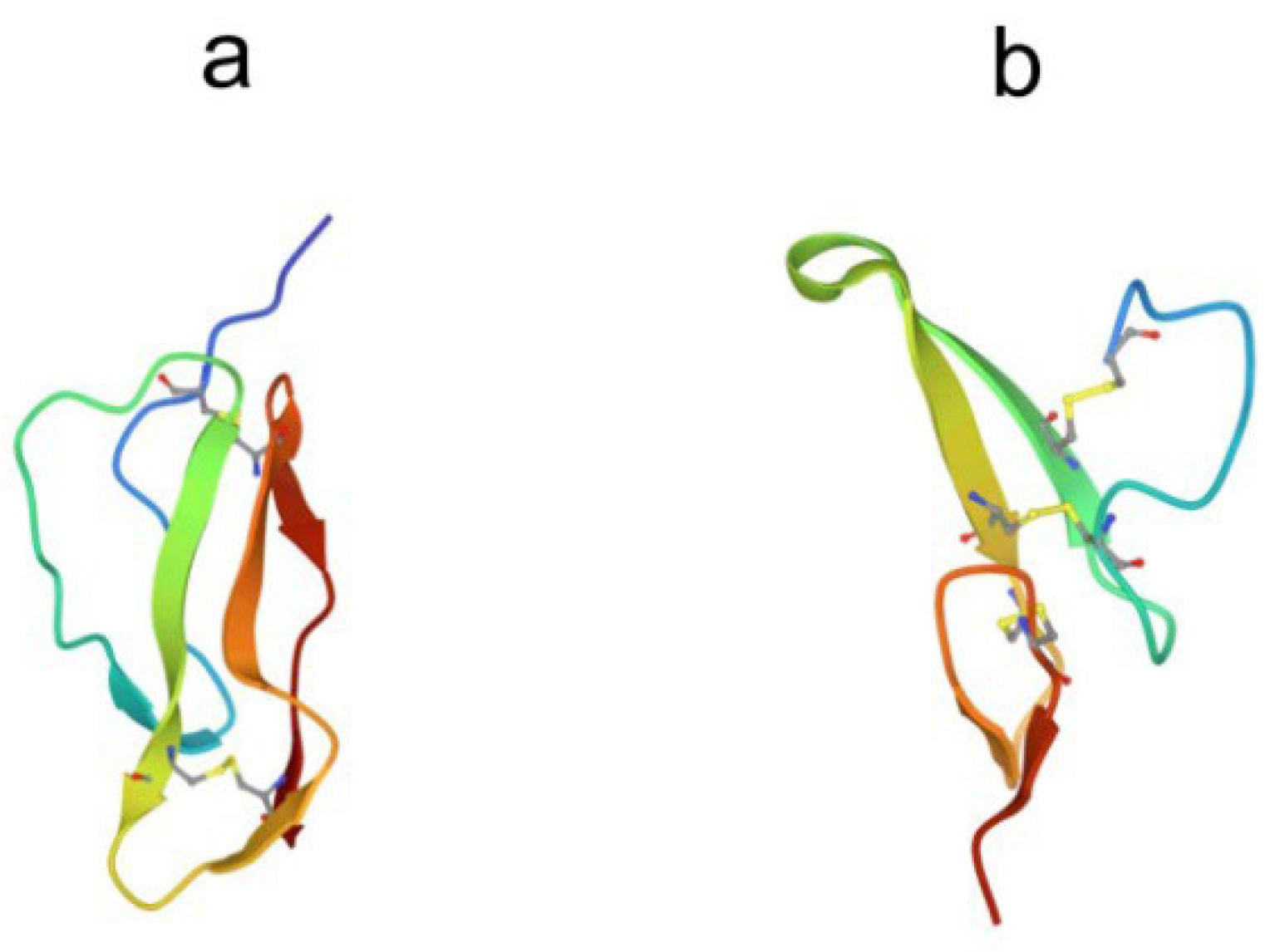
3. β-Hairpin peptides
3.1. Arenicins
3.2. Tachyplesins and polyphemusins
4. Big defensins
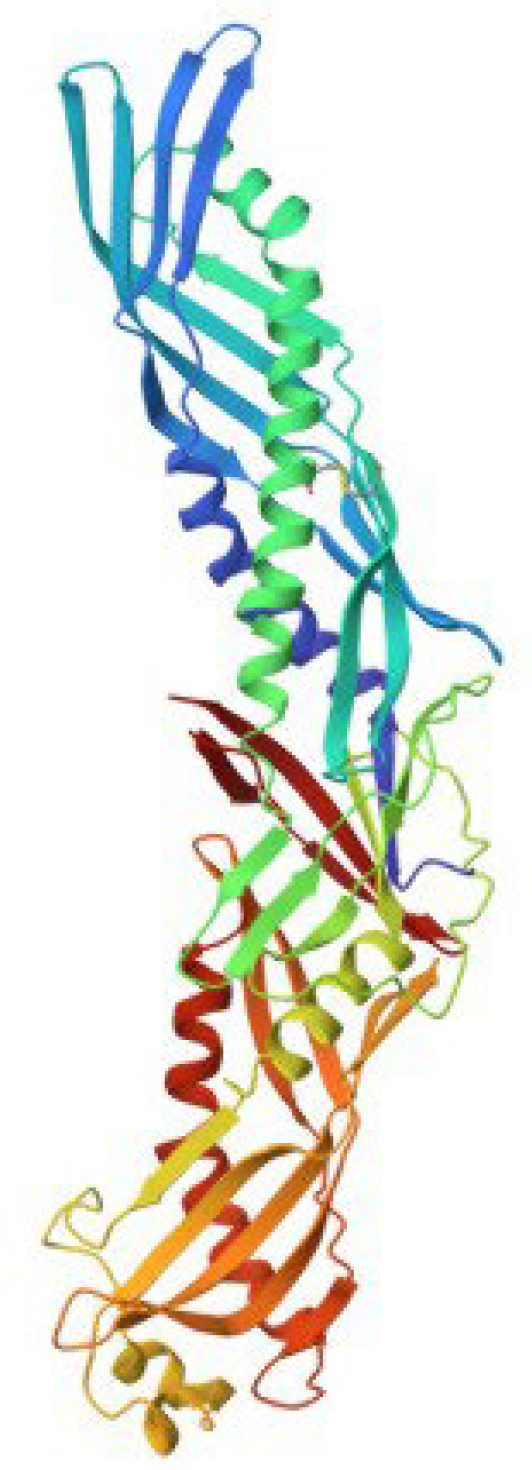
5. Factor C
6. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing proteins
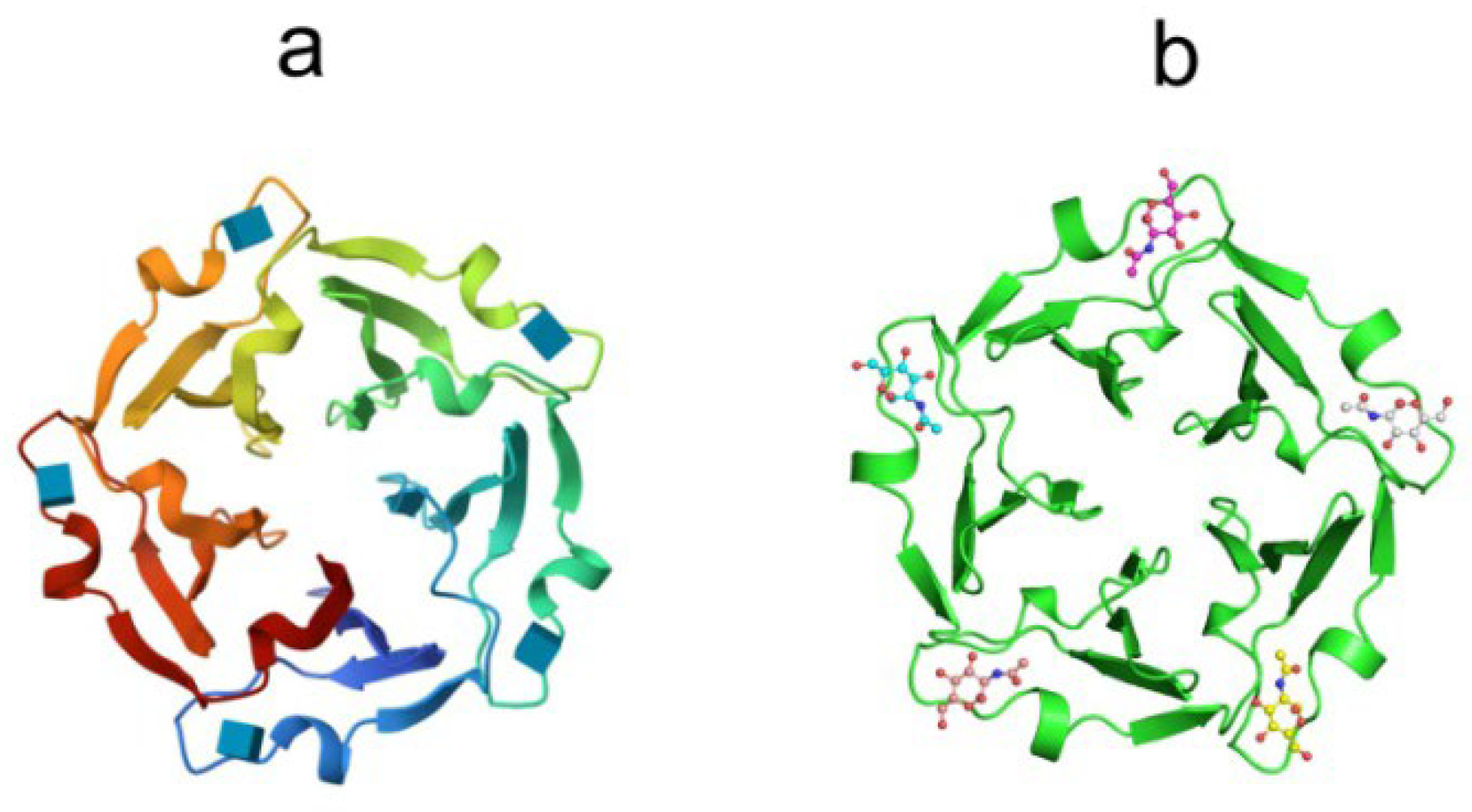
7. Lipopolysaccharide-binding lectins
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| ILBPs | invertebrate lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins. |
References
- Alexander, C.; Rietschel, E.T. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J. Endotoxin Res. 2001, 7, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, M.; Rossignol, D.P.; Wheeler, J.L.; Kao, R.J.; Perdomo, C.A.; Noveck, R.; Vargas, R.; D'Angelo, T.; Gotzkowsky, S.; McMahon, F.G. Blocking of responses to endotoxin by E5564 in healthy volunteers with experimental endotoxemia. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solov’eva, T.; Davydova, V.; Krasikova, I.; Yermak, I. Marine compounds with therapeutic potential in Gram-negative sepsis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerala, R.; Porro, M. Endotoxin neutralizing peptides. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, S.; Lee, B.L. Recent advances in the innate immunity of invertebrate animals. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 38, 128–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, T.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Limulus anti-LPS factor: An anticoagulant which inhibits the endotoxin-mediated activation of Limulus coagulation system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 105, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Ohtsubo, S.; Nakamura, T.; Tanaka, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Ohashi, K.; Niwa, M. Isolation and biological activities of limulus anticoagulant (anti-LPS factor) which interacts with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J. Biochem. 1985, 97, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muta, T.; Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Nakamura, T.; Iwanaga, S. Primary structure of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from american horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. J. Biochem. 1987, 101, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.I.; Su, D.; Child, A.H.; Wainwright, N.R.; Levin, J. Limulus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor prevents mortality late in the course of endotoxemia. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.S.; Glennon, M.L.; Wainwright, N.; Amato, S.F.; Black, K.M.; Kirsch, S.J.; Riveau, G.R.; Whyte, R.I.; Zapol, W.M.; Novitsky, T.J. Binding and neutralization of endotoxin by limulus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, C.; O'Hara, P.; Harlan, J. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from horseshoe crab, Tachypleus tridentatus, inhibits lipopolysaccharide activation of cultured human endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, G.; Baldwin, G.; Thompson, C.; Wainwright, N.; Novitsky, T.J.; Gillis, Z.; Parsonnet, J.; Fleisher, G.R.; Siber, G.R. Limulus antilipopolysaccharide factor protects rabbits from meningococcal endotoxin shock. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 165, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladino, C.T.; Garcia, C.M.; Thompson, B.K.; Hammer, J.; Parsonnet, T.J.; Novitsky, G.R.; Siber, G.R.; Fleisher, G. Efficacy of a recombinant endotoxin neutralizing protein in rabbits with Escherichia coli sepsis. Circ. Shock 1994, 42, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Supungul, P.; Klinbunga, S.; Pichyangkura, R.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Tassanakajon, A. Antimicrobial peptides discovered in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon using the EST approach. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 61, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, B.; Xiang, J. Molecular cloning and expression profile of putative antilipopolysaccharide factor in chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis). Mar. Biotechnol. (N Y) 2005, 7, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Vega, E.; O’Leary, N.A.; Shockey, J.E.; Robalino, J.; Payne, C.; Browdy, C.L.; Warr, G.W.; Gross, P.S. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor in Litopenaeus vannamei (LvALF): A broad spectrum antimicrobial peptide essential for shrimp immunity against bacterial and fungal infection. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, K.M.; Towle, D.W.; Jayasundara, N.; Smith, C.M.; Shields, J.D.; Small, H.J.; Greenwood, S.J. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factors in the american lobster Homarus americanus: Molecular characterization and transcriptional response to Vibrio fluvialis challenge. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genomics Proteomics 2008, 3, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Gai, Y.; Qiu, L.; Song, L. The second anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (EsALF-2) with antimicrobial activity from Eriocheir sinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imjongjirak, C.; Amparyup, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Sittipraneed, S. Antilipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) of mud crab Scylla paramamosain: Molecular cloning, genomic organization and the antimicrobial activity of its synthetic LPS binding domain. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsal, V.V.; Antony, S.P.; Sathyan, N.; Philip, R. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of two antimicrobial peptides: Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor and crustin from the brown mud crab, Scylla serrata. Results Immunol. 2011, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsal, V.V.; Antony, S.P.; Sanjeevan, V.N.; Kumar, P.A.; Singh, I.B.; Philip, R. A new isoform of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor identified from the blue swimmer crab, Portunus pelagicus: Molecular characteristics and phylogeny. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Amparyup, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Supungul, P. Cationic antimicrobial peptides in Penaeid shrimp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboonwiwat, K.; Marcos, M.; Tassanakajon, A.; Klinbunga, S.; Aumelas, A.; Romestand, B.; Gueguen, Y.; Boze, H.; Moulin, G.; Bachère, E. Recombinant expression and anti-microbial activity of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) from the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedery, R.D.; Reddy, K.V. Identification, cloning, characterization and recombinant expression of an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from the hemocytes of indian mud crab, Scylla serrata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Lv, X.; Xiang, J. Recombinant expression and functional analysis of an isoform of anti-lipopolysaccharide factors (FcALF5) from Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factors from the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, are encoded by two genomic loci. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponprateep, S.; Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Tassanakajon, A. Gene silencing reveals a crucial role for anti-lipopolysaccharide factors from Penaeus monodon in the protection against microbial infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Sun, Z.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Transcriptome analysis on Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis during WSSV acute infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.X.; Song, C.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, Q. Multiple isoforms of immune-related genes from hemocytes and eyestalk cDNA libraries of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, F. The anti-lipopolysaccharide factors in crustaceans. Subcell Biochem. 2020, 94, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Functional diversity of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoforms in shrimp and their characters related to antiviral activity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, G.M.; Schmitt, P.; Barreto, C.; Farias, N.D.; Toledo-Silva, G.; Guzmán, F.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Rosa, R.D. Massive gene expansion and sequence diversification is associated with diverse tissue distribution, regulation and antimicrobial properties of anti-lipopolysaccharide factors in shrimp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Jiao, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Molecular and antimicrobial characterization of a group G anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) from Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.G.; Wang, Y.; Hui, K.; Fang, W.H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.X.; Ma, H.; Li, X.C. A novel anti-lipopolysaccharide factor SpALF6 in mud crab Scylla paramamosain exhibiting different antimicrobial activity from its single amino acid mutant. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 72, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoess, A.; Watson, S.; Siber, G.R.; Liddington, R. Crystal structure of an endotoxin-neutralizing protein from the horseshoe crab, Limulus antiLPS factor, at 1.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3351–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharntada, S.; Ponprateep, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Liu, H.; Söderhäll, I.; Söderhäll, K.; Tassanakajon, A. Role of antilipopolysaccharide factor from the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, in protection from white spot syndrome virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Y.; Chao, T.T.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, W.C.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, C.M. Shrimp (Penaeus monodon) antilipopolysaccharide factor reduces the lethality of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Li, S.H.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Xiang, J.H. Modification of a synthetic LPS-binding domain of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp reveals strong structure-activity relationship in their antimicrobial characteristics. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Boze, H.; Chemardin, P.; Padilla, A.; Moulin, G.; Tassanakajon, A.; Pugniere, M.; Roquet, F.; Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E.; Aumelas, A. NMR structure of rALF-Pm3, an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp: Model of the possible lipid A-binding site. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrä, J.; Howe, J.; Garidel, P.; Rössle, M.; Richter, W.; Leiva-León, J.; Moriyon, I.; Bartels, R.; Gutsmann, T.; Brandenburg, K.; Brandenburg, K. Mechanism of interaction of optimized Limulus-derived cyclic peptides with endotoxins: Thermodynamic, biophysical and microbiological analysis. Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsmann, T.; Razquin-Olazarán, I.; Kowalski, I.; Kaconis, Y.; Howe, J.; Bartels, R.; Hornef, M.; Schürholz, T.; Rössle, M.; Sanchez-Gómez, S.; Moriyon, I.; Martinez de Tejada, G.; Brandenburg, K. New antiseptic peptides to protect against endotoxin mediated shock. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3817–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Nadezhdin, K.D.; Balandin, S.V.; Zhmak, M.N.; Kudelina, I.A.; Finkina, E.I.; Kokryakov, V.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Recombinant expression, synthesis, purification, and solution structure of arenicin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, A.; Huang, J.; Neve, S.; Zuegg, J.; Edwards, I.; Cain, A.; Boinett, C.; Barquist, L.; Lundberg, C.; Steen, J.; Butler, M.; Mobli, M.; Porter, K.; Blaskovich, M.; Lociuro, S.; Strandh, M.; Cooper, M. An amphipathic peptide with antibiotic activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Balandin, S.V.; Trunov, K.I.; Paramonov, A.S.; Sukhanov, S.V.; Barsukov, L.I.; Arseniev, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Molecular mechanism of action of β-hairpin antimicrobial peptide arenicin: Oligomeric structure in dodecylphosphocholine micelles and pore formation in planar lipid bilayers. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6255–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Shenkarev, Z. O.; Balandin, S.V.; Nadezhdin, K.D.; Paramonov, A.S.; Kokryakov, V.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Molecular insight into mechanism of antimicrobial action of the β-hairpin peptide arenicin: Specific oligomerization in detergent micelles. Biopolymers: Original Research on Biomolecules 2008, 89, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, T. V.; Aleshina, G. M.; Balandin, S. V.; Krasnosdembskaya, A. D.; Markelov, M. L.; Frolova, E. I.; Kokryakov, V. N. Purification and primary structure of two isoforms of arenicin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from marine polychaeta Arenicola marina. FEBS Lett. 2004, 577, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrä, J.; Jakovkin, I.; Grötzinger, J.; Hecht, O.; Krasnosdembskaya, A. D.; Goldmann, T.; Gutsmann, T.; Leippe, M. Structure and mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide arenicin. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.K.; Sandvang, D.; Neve, S.; Kruse, T.; Kristensen, H.H. Transcriptional profiling indicates a dual mode-of-action of arenicin-3, poster F1-2072. 50th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC.
- Yang, N.; Liu, X.; Teng, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Mao, R.; Wang, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J. Antibacterial and detoxifying activity of NZ17074 analogues with multi-layers of selective antimicrobial actions against Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Yang, N.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J. Combined systems approaches reveal a multistage mode of action of a marine antimicrobial peptide against pathogenic Escherichia coli and its protective effect against bacterial peritonitis and endotoxemia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01056-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegenhaug, H.H.K.; Mygind, P.H.; Kruse, T.; Segura, D.R.; Sandvang, D.; Neve, S. Antimicrobial peptide variants and polynucleotides encoding same. US patent 20110306750 A1. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Yoneya, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Iwanaga, S.; Niwa, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y. Antimicrobial peptides, isolated from horseshoe crab hemocytes, tachyplesin II, and polyphemusins I and II. Chemical structures and biological activity. J. Biochem. 1989, 106, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Furunaka, H.; Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Muta, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Niwa, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus): Isolation and chemical structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 16709–16713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muta, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Nakajima, H.; Iwanaga, S. Tachyplesins isolated from hemocytes of southeast Asian horseshoe crabs (Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda and Tachypleus gigas): Identification of a new tachyplesin, tachyplesin III, and a processing intermediate of its precursor. J. Biochem. 1990, 108, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigenaga, T.; Mutat, T.; Toh, Y.; Tokunaga, F.; Iwanaga, S. Antimicrobial tachyplesin peptide precursor cDNA cloning and cellular localization in the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 21350–21354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K.; Yoneya, T.; Miyata, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Tokunaga, F.; Terada, Y.; Iwanaga, S. Antimicrobial peptide, tachyplesin I, isolated from hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). NMR determination of the beta-sheet structure. J. Biol. Chem 1990, 265, 15365–15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laederach, A.; Andreotti, A.H.; Fulton, D.B. Solution and micelle-bound structures of tachyplesin I and its active aromatic linear derivatives. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12359–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.-P.S.; Rozek, A.; Hancock, R.E.W. Structure-activity relationships for the β-hairpin cationic antimicrobial peptide polyphemusin I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1698, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernen, F.; Harvey, P.J.; Dias, S.A.; Veiga, A.S.; Huang, Y.-H.; Craik, D.J.; Lawrence, N.; Troeira Henriques, S. Characterization of tachyplesin peptides and their cyclized analogues to improve antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsuzaki, K. Specific interactions of the antimicrobial peptide cyclic β-sheet tachyplesin I with lipopolysaccharides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembranes 2002, 1562, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushibiki, T.; Kamiya, M.; Aizawa, T.; Kumaki, Y.; Kikukawa, T.; Mizuguchi, M.; Demura, M.; Kawabata, S.; Kawano, K. Interaction between tachyplesin I, an antimicrobial peptide derived from horseshoe crab, and lipopolysaccharide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Proteins and Proteomics 2014, 1844, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Scott, M.G.; Yan, H.; Mayer, L.D.; Hancock, R.E. Interaction of polyphemusin I and structural analogs with bacterial membranes, lipopolysaccharide, and lipid monolayers. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14504–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, I.A.; Elliott, A.G.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Zuegg, J.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Cooper, M.A. Contribution of amphipathicity and hydrophobicity to the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of β-hairpin peptides. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Hu, J.; Ke, F. Experimental induction of bacterial resistance to the antimicrobial peptide tachyplesin I and investigation of the resistance mechanisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6067–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Gonzalez, A.J.; Magalhaes, B.S.; Garcia-Villarino, M.; Lopez-Abarrategui, C.; Sousa, D.A.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates as a new frontier for microbial infection control. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.P.S.; Tan, A.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Hancock, R.E.W. Solution structure and interaction of the antimicrobial polyphemusins with lipid membranes. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15504–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kawabata, S.I.; Shigenaga, T.; Takayenoki, Y.; Cho, J.; Nakajima, H.; Hirata, M.; Iwanaga, S.A. Novel big defensin identified in horseshoe crab hemocytes: Isolation, amino acid sequence, and antibacterial activity. J. Biochem. 1995, 117, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouno, T.; Fujitani, N.; Mizuguchi, M.; Osaki, T.; Nishimura, S.; Kawabata, S.; Aizawa, T.; Demura, M.; Nitta, K.; Kawano, K. A novel beta-defensin structure: A potential strategy of big defensin for overcoming resistance by Gram-positive bacteria. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10611–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouno, T.; Mizuguchi, M.; Aizawa, T.; Shinoda, H.; Demura, M.; Kawabata, S.; Kawano, K.A. novel beta-defensin structure: Big defensin changes its N-terminal structure to associate with the target membrane. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7629–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhople, V.; Krukemeyer, A.; Ramamoorthy, A. The human beta-defensin-3, an antibacterial peptide with multiple biological functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembranes 2006, 1758, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrigault, M.; Tanguy, A.; Allam, B. Identification and expression of differentially expressed genes in the hard clam, Mercenaria mercenaria, in response to quahog parasite unknown (QPX). BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.D.; Santini, A.; Fievet, J.; Bulet, P.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Bachère, E. Big defensins, a diverse family of antimicrobial peptides that follows different patterns of expression in hemocytes of the oyster Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Zheng, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H. Cloning of a big defensin gene and its response to Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge in the noble scallop Chlamys nobilis (Bivalve: Pectinidae). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, L.; Gao, B.; Zhang, S. The first chordate big defensin: Identification, expression and bioactivity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loth, K.; Vergnes, A.; Barreto, C.; Voisin, S.N.; Meudal, H.; Da Silva, J.; Bressan, A.; Belmadi, N.; Bachère, E.; Aucagne, V.; Cazevielle, C.; Marchandin, H.; Rosa, R.D.; Bulet, P.; Touqui, L.; Delmas, A.F.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. The ancestral N-terminal domain of big defensins drives bacterially triggered assembly into antimicrobial nanonets. mBio 2019, 10, e01821-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Song, L.; Li, C.; Ni, D.; Wu, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, W. Molecular cloning, expression of a big defensin gene from bay scallop Argopecten irradians and the antimicrobial activity of its recombinant protein. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Chen, A.; Li, L.; Su, X.; Li, T. Molecular characterization of a novel big defensin from clam Venerupis philippinarum. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.L.; Ho, B. A new era in pyrogen testing. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiba, T.; Hashii, T.; Kawabata, S. I. A structural perspective on the interaction between lipopolysaccharide and factor C, a receptor involved in recognition of Gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3962–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariki, S.; Koori, K.; Osaki, T.; Motoyama, K.; Inamori, K.I.; Kawabata, S.I. A serine protease zymogen functions as a pattern-recognition receptor for lipopolysaccharides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehler, M.; Roeder, R.; Blessing, S.; Reich, J. Comparison of LAL and rFC assays-participation in a proficiency test program between 2014 and 2019. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ho, B.; Ding, J.L. Recombinant factor C competes against LBP to bind lipopolysaccharide and neutralizes the endotoxicity. J. Endotoxin Res. 2007, 13, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine-protease zymogen (factor C) found in Limulus hemocytes: Isolation and characterization. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 154, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, F.; Miyata, T.; Nakamura, T.; Morita, T.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T.; Iwanaga, S. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine-protease zymogen (factor C) of horseshoe crab hemocytes. Identification and alignment of proteolytic fragments produced during the activation show that it is a novel type of serine protease. Eur J Biochem. 1987, 167, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, F.; Nakajima, H.; Iwanaga, S. Further studies on lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine protease zymogen (factor C): Its isolation from Limulus polyphemus hemocytes and identification as an intracellular zymogen activated by α-chymotrypsin, not by trypsin. J. Biochem. 1991, 109, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.L.; Navas, M.A.; Ho, B. Two forms of factor C from the amoebocytes of Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda: Purification and characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1993, 1202, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
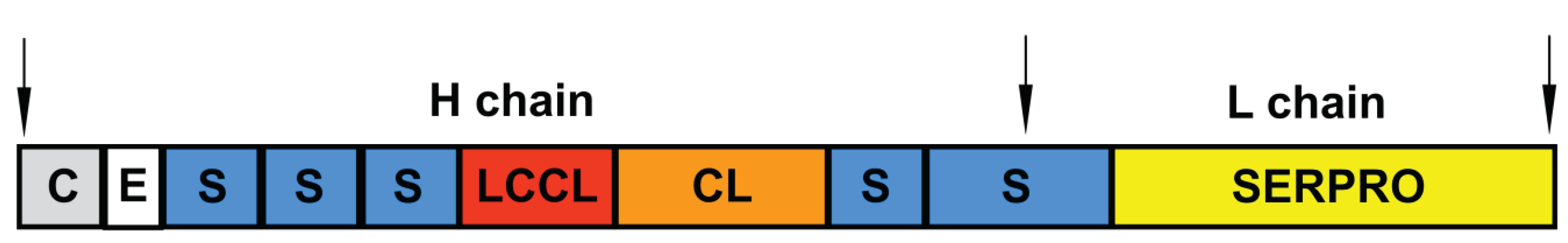
- Muta, T.; Miyata, T.; Misumi, Y.; Tokunaga, F.; Nakamura, T.; Toh, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Iwanaga, S. Limulus factor C. An endotoxin-sensitive serine protease zymogen with a mosaic structure of complement-like, epidermal growth factor-like, and lectin-like domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6554–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, M.; Banyai, L.; Patthy, L. The LCCL module. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5751–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.G.; Barlow, P.N.; Baron, M.; Day, A.J.; Sim, R.B.; Campbell, I.D. Three-dimensional structure of a complement control protein module in solution. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 219, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.R.; Hash, J.H.; Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 7669–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullner, M.; Selander, M.; Persson, E.; Stenflo, J.; Drakenberg, T.; Teleman, O. Three-dimensional structure of the apo form of the N-terminal EGF-like module of blood coagulation factor X as determined by NMR spectroscopy and simulated folding. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 5974–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.S.; Chai, J.J.; Li, M.; Huang, B.R.; He, C.H.; Bi, R.C. Crystal structure of human epidermal growth factor and its dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34913–34917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Shiba, P.; Kobayashi, T.; Inoue, K. Intracellular serine protease zymogen factor C, from horseshoe crab hemocytes: Its activation by synthetic lipid A analogues and acidic phospholipids. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 176, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Interaction between lipopolysaccharide and intracellular serine protease zymogen, factor C, from horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) hemocytes. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1988, 103, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.S.; Ho, B.; Ding, J.L. High-affinity LPS binding domain(s) in recombinant factor C of a horseshoe crab neutralizes LPS-induced lethality. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.S.; Ng, M.L.; Yau, Y.H.; Chong, P.K.; Ho, B.; Ding, J.L. Definition of endotoxin binding sites in horseshoe crab factor C recombinant sushi proteins and neutralization of endotoxin by sushi peptides. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristovsek, P.; Feher, K.; Szilagyi, L.; Kidric, J. Structure of a synthetic fragment of the LALF protein when bound to lipopolysaccharide. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, N.S.; Ho, B.; Ding, J.L. Modular arrangement and secretion of a multidomain serine protease. Evidence for involvement of proline-rich region and N-glycans in the secretion pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36363–36372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, P.S.; Mathison, J.C.; Ulevitch, R.J. A family of lipopolysaccharide binding proteins involved in responses to Gram-negative sepsis. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13479–13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O. Antimicrobial proteins and peptides: Anti-infective molecules of mammalian leukocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, N.M.; Elsbach, P.; Weiss, J. An opsonic function of the neutrophil bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein depends on both its N- and C-terminal domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997, 94, 10973–10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI) and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP): Structure, function and regulation in host defence against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theprungsirikul, J.; Skopelja-Gardner, S.; Rigby, W.F. Killing three birds with one BPI: Bactericidal, opsonic, and anti-inflammatory functions. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.; Franson, R.C.; Beckerdite, S.; Schmeidler, K.; Elsbach, P. Partial characterization and purification of a rabbit granulocyte factor that increases permeability of Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Invest. 1975, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.; Elsbach, P.; Olsson, I.; Odeberg, H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, L.J.; Carroll, S.F.; Eisenberg, D. Crystal structure of human BPI and two bound phospholipids at 2.4 angstrom resolution. Science 1997, 276, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiger, G.; Beamer, L.J.; Grothe, R.; Mallick, P.; Eisenberg, D. The 1.7 A crystal structure of BPI: A study of how two dissimilar amino acid sequences can adopt the same fold. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasity, B.C.; Troll, J.V.; Weiss, J.P.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. LBP/BPI proteins and their relatives: Conservation over evolution and roles in mutualism. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Gueguen, Y.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Romestand, B.; Fievet, J.; Pugnière, M.; Roquet, F.; Escoubas, J.-M.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Levy, O.; Saune, L.; Bulet, P.; Bachere, E. Evidence of a bactericidal permeability increasing protein in an invertebrate, the Crassostrea gigas Cg-BPI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17759–17764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.G.; Kelner, D.N.; Lim, E.; Burke, D.J.; Conlon, P.J. Functional domains of recombinant bactericidal/permeability increasing protein (rBPI23). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodici, C.; Weiss, J. Both N- and C-terminal regions of the bioactive N-terminal fragment of the neutrophil granule bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein are required for stability and function. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, L.J.; Carroll, S.F.; Eisenberg, D. The BPI/LBP family of proteins: A structural analysis of conserved regions. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, A.H.; Leigh, S.D.; Abrahamson, S.; Gazzano-Santoro, H.; Liu, P.S.; Williams, R.E.; Carroll, S.F.; Theofan, G. Expression and characterization of cysteine-modified variants of an amino-terminal fragment of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 1996, 8, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Beckerdite-Quagliata, S.; Elsbach, P. Resistance of Gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: Relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J. Clin. Invest. 1980, 65, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodici, C.; Chen, S.; Sidorczyk, Z.; Elsbach, P.; Weiss, J. Effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) chain length on interactions of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and its bioactive 23-kilodalton NH2-terminal fragment with isolated LPS and intact Proteus mirabilis and Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Li, X.; Fu, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z. The second bactericidal permeability increasing protein (BPI) and its revelation of the gene duplication in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Krasity, B.C.; Peyer, S.M.; Koehler, S.; Ruby, E.G.; Zhang, X.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. Bactericidal permeability-increasing proteins shape host-microbe interactions. mBio 2017, 8, e00040-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altincicek, B.; Vilcinskas, A. Analysis of the immune-related transcriptome of a lophotrochozoan model, the marine annelid, Platynereis dumerilii. Front. Zool. 2007, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Aravena, M.; Pérez-Troncoso, C.; Urtubia, R.; Branco, P.; Silva, J. R.; Mercado, L.; Lorgeril, J.; Bethke, J.; Paschke, K. Immune response of the Antarctic Sea urchin Sterechinus neumayeri: Cellular, molecular and physiological approach. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2015, 63, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Yan, T.; Fang, J.; Zhu, W. Identification and expression analysis on bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI)/lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) of ark shell, Scapharca broughtonii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Holst, O.; Hardt, W. The bactericidal activity of the C-type lectin RegIIIβ against Gram-negative bacteria involves binding to lipid A. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34844–34855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.H.; Chuang, S.C.; Chang, S.Y.; Liang, P.H. Ligand specificities and structural requirements of two Tachypleus plasma lectins for bacterial trapping. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Kawabata, S.I.; Hirata, M.; Iwanaga, S. A novel type of Limulus lectin-L6 – Purification, primary structure, and antibacterial activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14493–14499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, N.; Kawabata, S.; Saito, T.; Hirata, M.; Takagi, T.; Iwanaga, S. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a 27-kDa lectin (L10) from horseshoe crab hemocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31008–31015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, S.-L.; Iwanaga, S. Role of lectins in the innate immunity of horseshoe crab. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamori, K.; Saito, T.; Iwaki, D.; Nagira, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Arisaka, F.; Kawabata, S. A newly identified horseshoe crab lectin with specificity for blood group A antigen recognizes specific O-antigens of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hatada, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Kawabata, S.I. A newly identified horseshoe crab lectin with binding specificity to O-antigen of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30703–30708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Yen, C.H.; Yeh, M.S.; Huang, C.J.; Liu, T.Y. Biochemical properties and cDNa cloning of two new lectins from the plasma of Tachypleus tridentatus: Tachypleus plasma lectin 1 and 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9631–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.K.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Low, E.L.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, S.L.; Mao, L.C.; Chang, M.D.T. A recombinant horseshoe crab plasma lectin recognizes specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns of bacteria through rhamnose. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, S.C.; Chao, C.F.; Liu, T.Y. Isolation and characterization of proteins that bind to galactose, lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli, and protein A of Staphylococcus aureus from the hemolymph of Tachypleus tridentatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisel, H.G.; Kawabata, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Huber, R.; Bode, W. Tachylectin-2: Crystal structure of a specific GlcNAc/GalNAc-binding lectin involved in the innate immunity host defense of the Japanese horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, S.; Tsuda, R. Molecular basis of non-self recognition by the horseshoe crab lectins. J. Endotoxin Res. 2002, 8, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, H.C.; Ushijima, H.; Krasko, A.; Gamulin, V.; Thakur, N.L.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Muller, I.M.; Muller, W.E. Emergence and disappearance of an immune molecule, an antimicrobial lectin, in basal metazoa: A tachylectin-related protein in the sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32810–32817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Wang, R.; Soderhall, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Wang, R.; Soderhall, K.A. Lipopolysaccharide- and b-1,3-glucan-binding protein from hemocytes of the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus: Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaosomboon, A.; Phupet, B.; Rattanaporn, O.; Runsaeng, P.; Utarabhand, P. Lipopolysaccharide- and β-1,3-glucan-binding protein from Fenneropenaeus merguiensis functions as a pattern recognition receptor with a broad specificity for diverse pathogens in the defense against microorganisms. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 67, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.T.; Li, X.J.; Wang, S.C.; Li, D.; Li, W.-W.; Wang, Q. Lipopolysaccharide and beta-1, 3-glucan binding protein (LGBP) stimulates prophenoloxidase activating system in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Qui, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; Song, L.; Wang, C. A scallop C-type lectin from Argopecten irradians (AiCTL5) with activities of lipopolysaccharide binding and Gram-negative bacteria agglutination. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amparyup, P.; Sutthangkul, J.; Charoensapsri, W.; Tassanakajon, A. Pattern recognition protein binds to lipopolysaccharide and β-1,3-glucan and activates shrimp prophenoloxidase system. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Song, L. CfLGBP, a pattern recognition receptor in Chlamys farreri involved in the immune response against various bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakholdina, S.I.; Naberezhnykh, G.A.; Gorbach, V.I.; Isaeva, M.P.; Solov’eva, T.F. Invertebrates of the Sea of Okhotsk as new sources of lipopolysaccharide binding proteins. Russian J. Marine Biol. 2014, 40, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. The role of biophysical parameters in the antilipopolysaccharide activities of antimicrobial peptides from marine fish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1471–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.D.; Vergnes, A.; de Lorgeril, J.; Goncalves, P.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Sauné, L.; Romestand, B.; Fievet, J.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachère, E.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. Functional divergence in shrimp anti-lipopolysaccharide factors (ALFs): From recognition of cell wall components to antimicrobial activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, R.; Mohanram, H.; Joshi, M.; Domadia, P.N.; Torres, J.; Ruedl, C.; Bhattacharjya, S. Structure, activity and interactions of the cysteine deleted analog of tachyplesin-1 with lipopolysaccharide micelle: Mechanistic insights into outer-membrane permeabilization and endotoxin neutralization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1818, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, A.; Domadia, P.N.; Torres, J.; Hallock, K.J.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Bhattacharjya, S. NMR structure of pardaxin, a pore-forming antimicrobial peptide, in lipopolysaccharide micelles: Mechanism of outer membrane permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3883–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, Y.; Lev, N.; Shai, Y. Effect of the hydrophobicity to net positive charge ratio on antibacterial and anti-endotoxin activities of structurally similar antimicrobial peptides. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, D. Inhibitory effects of antimicrobial peptides on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 167572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domadia, P.N.; Bhunia, A.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Bhattacharjya, S. Structure, interactions, and antibacterial activities of MSI-594 derived mutant peptide MSI-594F5A in lipopolysaccharide micelles: Role of the helical hairpin conformation in outer-membrane permeabilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18417–18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rončević, T.; Puizina, J.; Tossi, A. Antimicrobial peptides as anti-infective agents in pre-post-antibiotic era? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximiano, M.R.; Rios, T.B.; Campos, M.L.; Prado, G.S.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Nanoparticles in association with antimicrobial peptides (NanoAMPs) as a promising combination for agriculture development. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 890654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, M.; Zahariev, S.; Pelillo, C.; Milan, A.; Gennaro, R.; Scocchi, M. PEGylation of the peptide Bac7 (1-35) reduces renal clearance while retaining antibacterial activity and bacterial cell penetration capacity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneev, K.V. Mouse Models of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Mol. Biol. (Mosk). 2019, 53, 799–814, Russian. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.C.; Pena, O.M.; Hancock, R.E.W. Host defense peptides: Front-line immunomodulators. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



