Submitted:
20 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
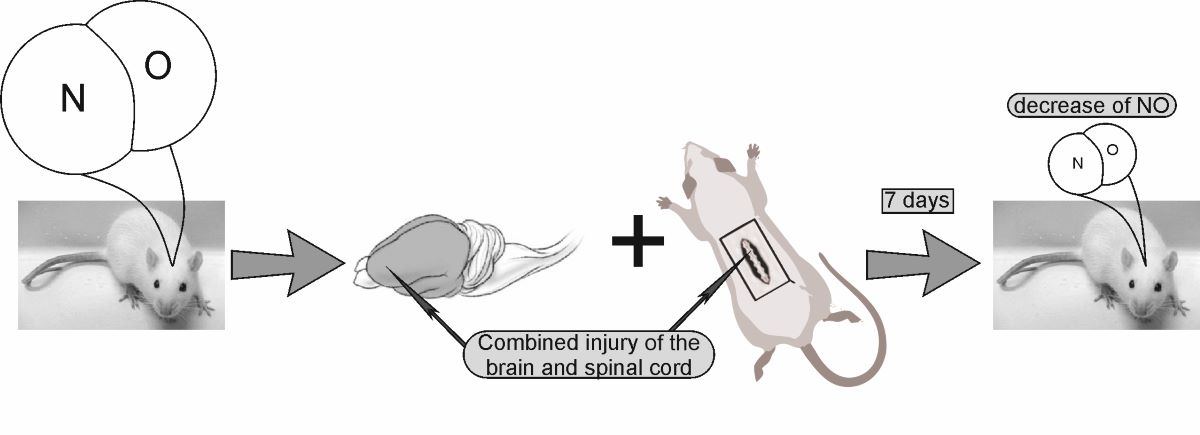
Keywords:
1. INTRODUCTION
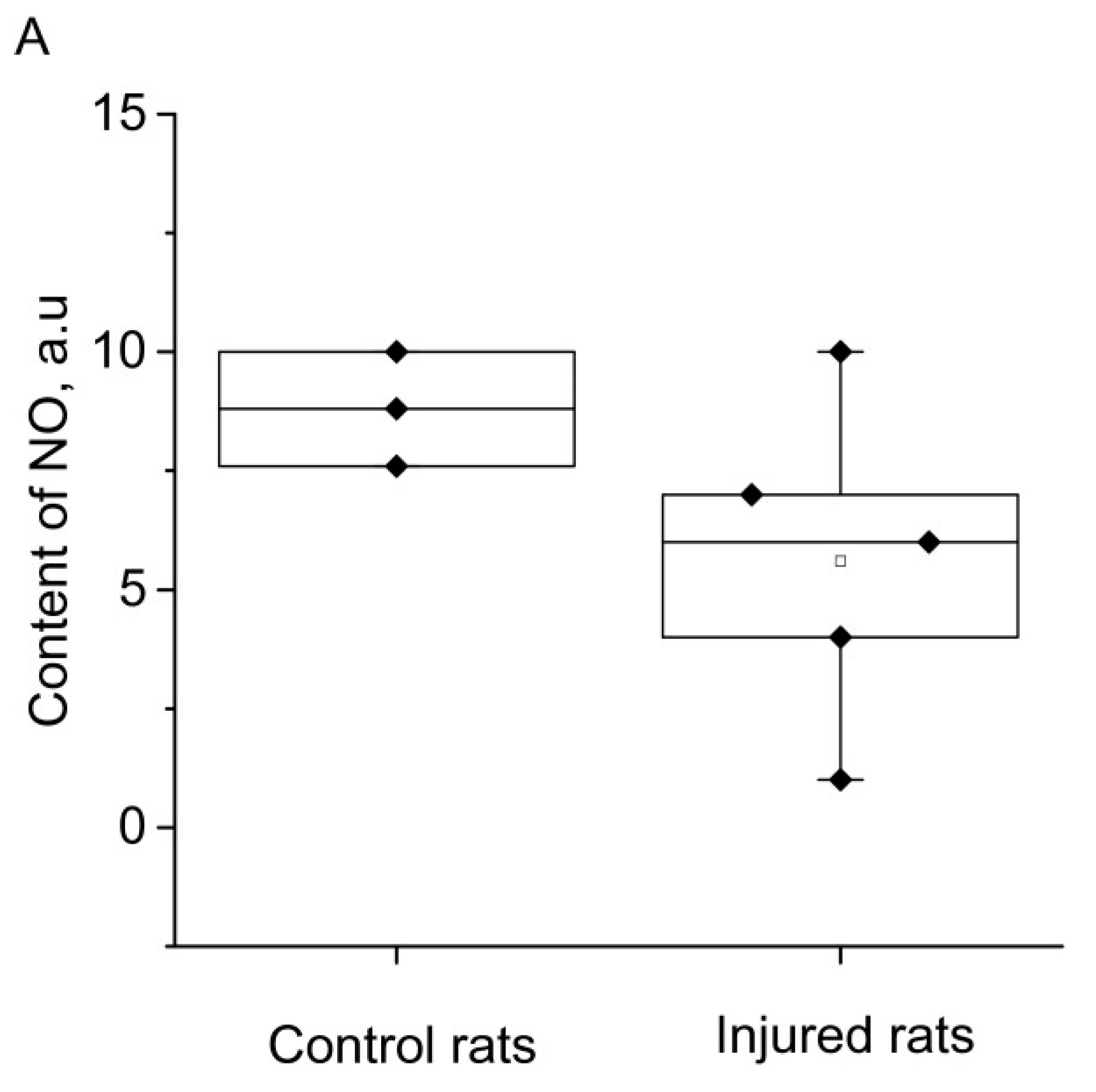
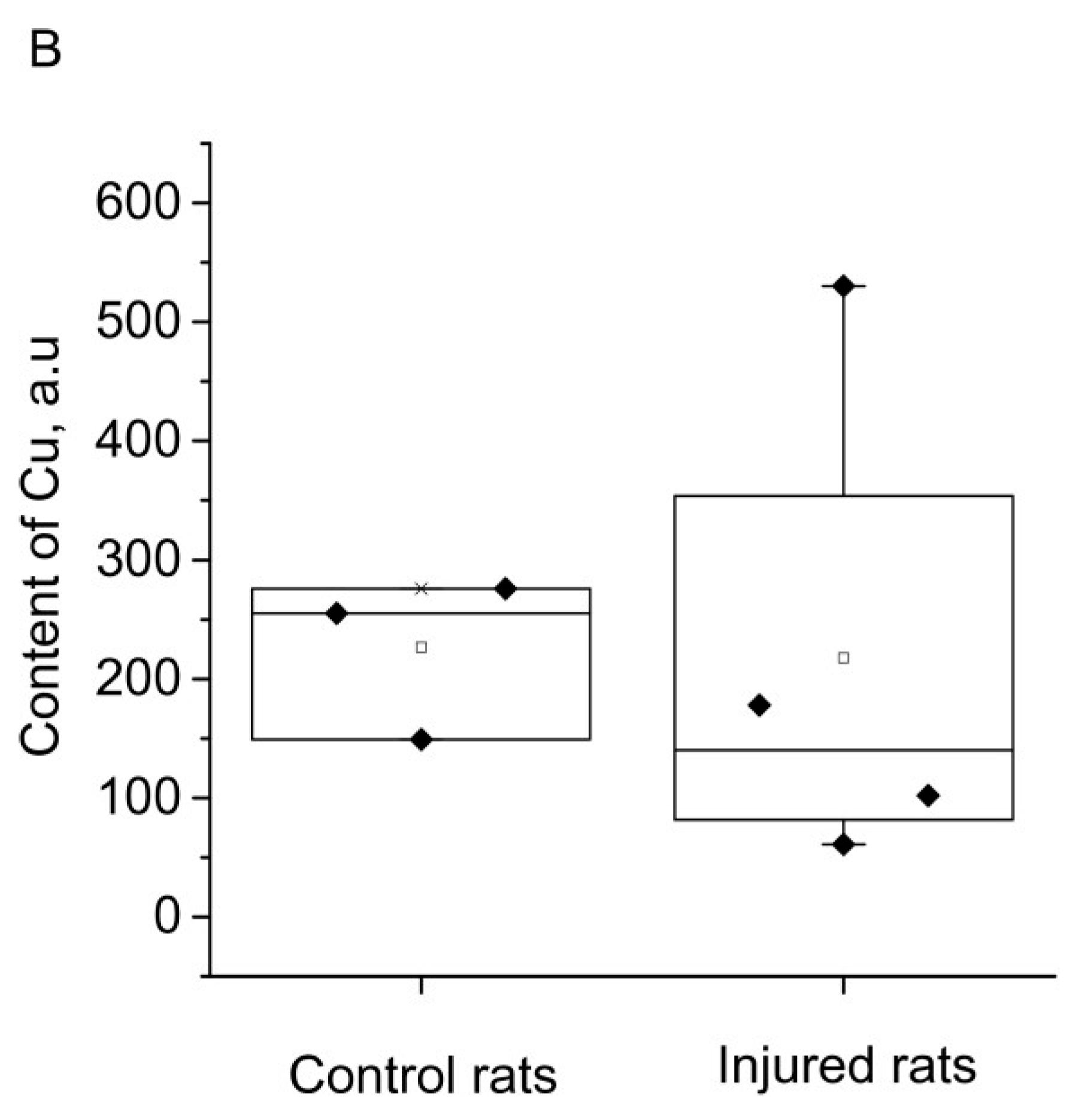
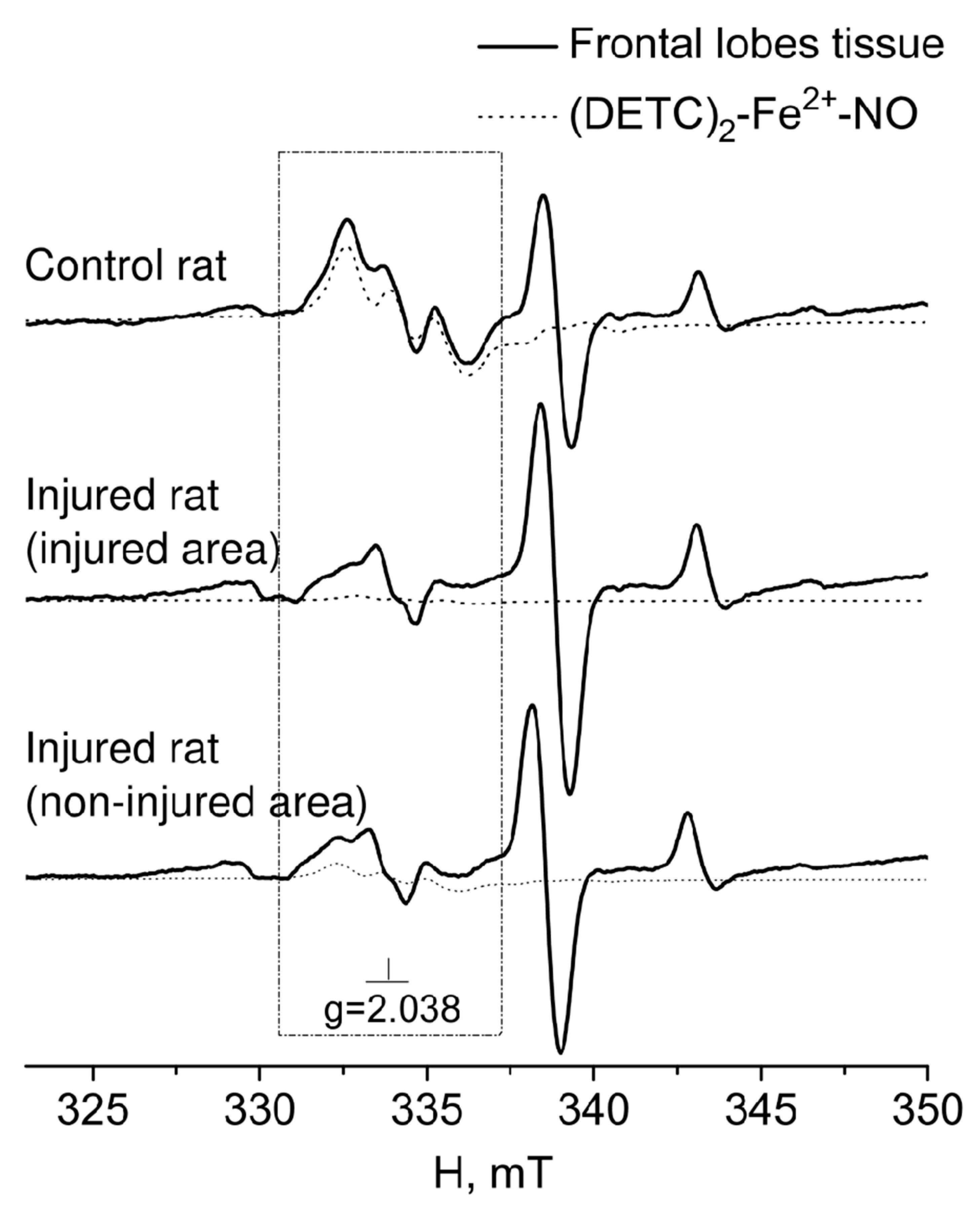
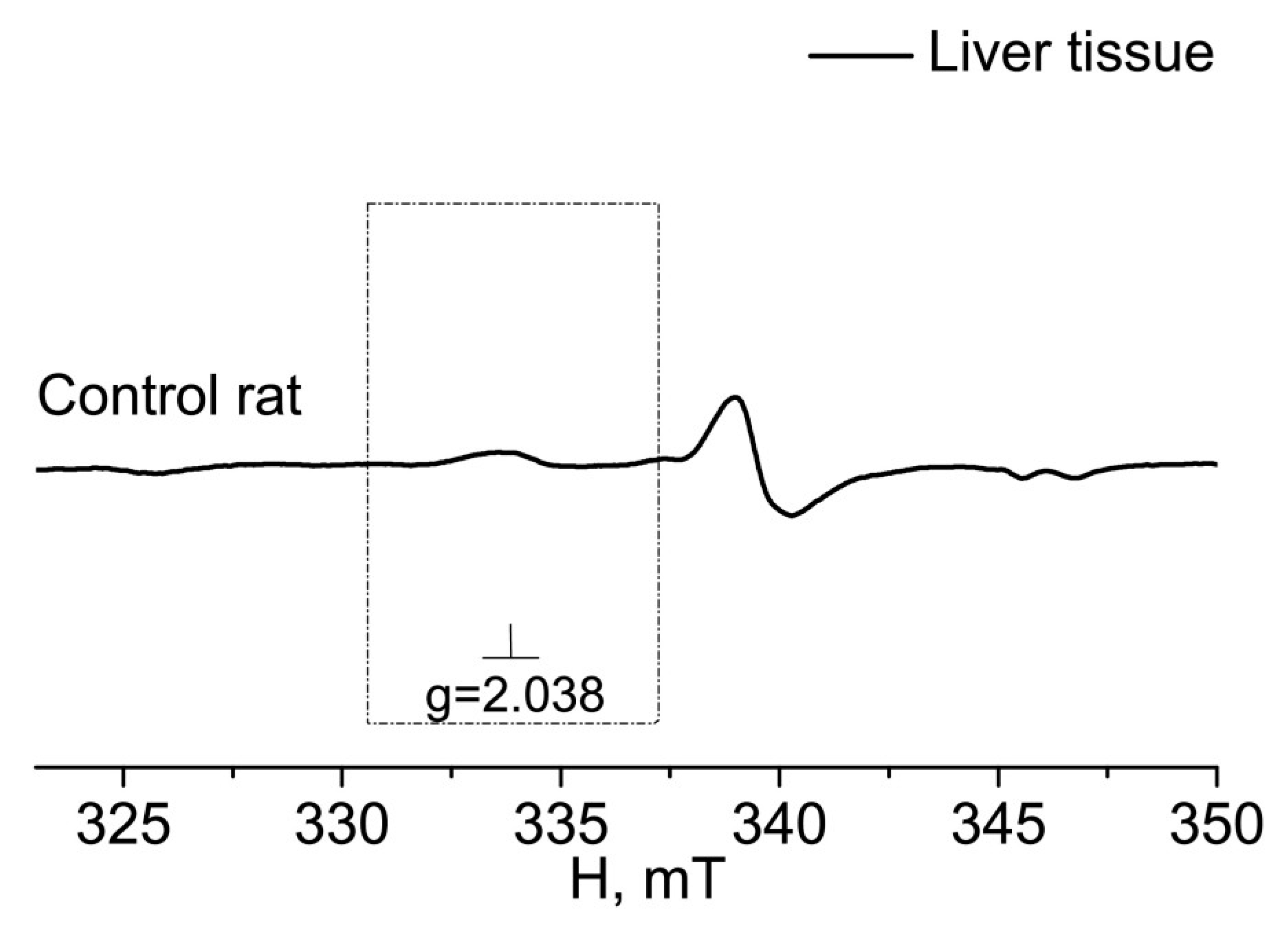
2. RESULTS
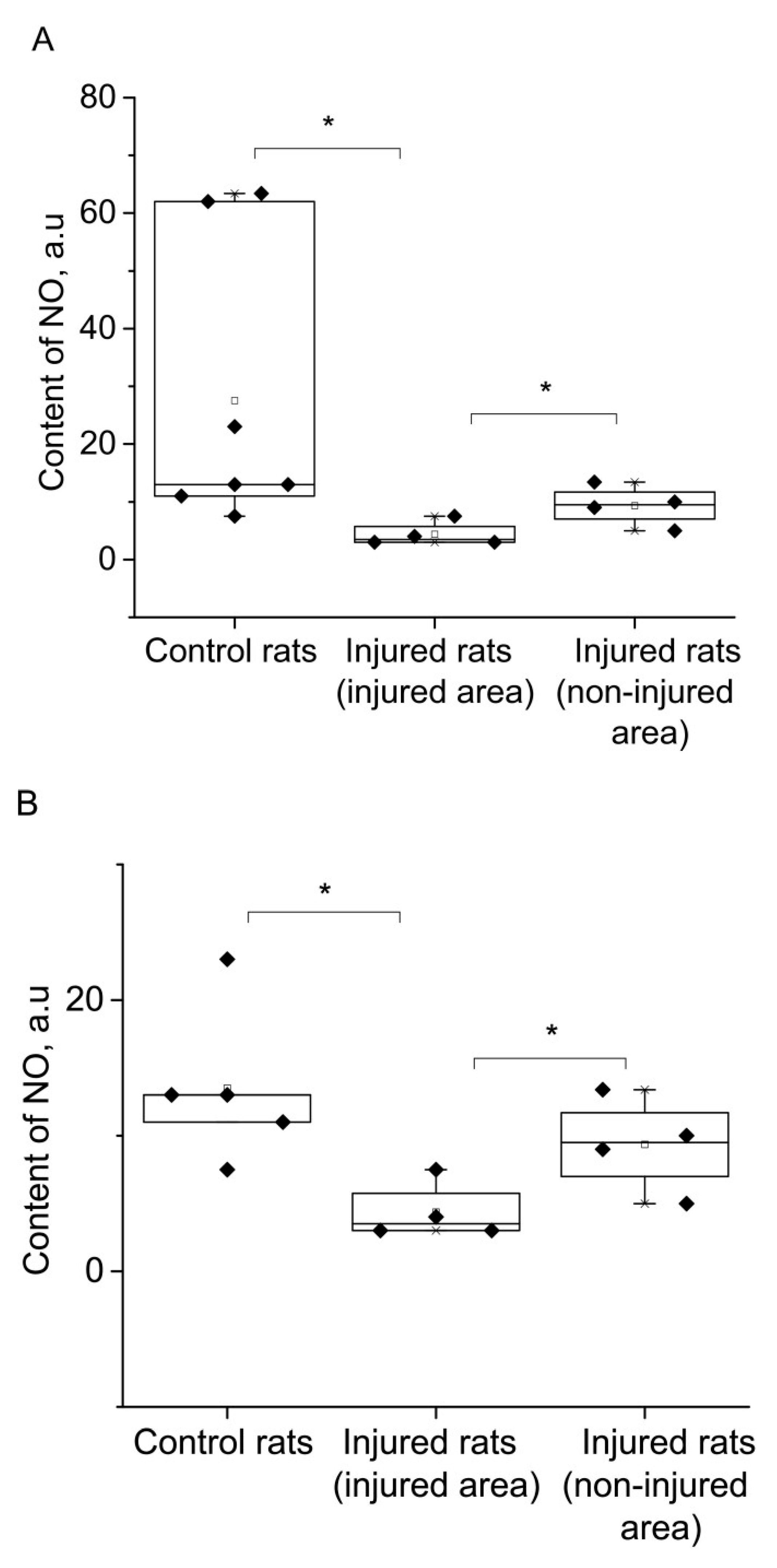
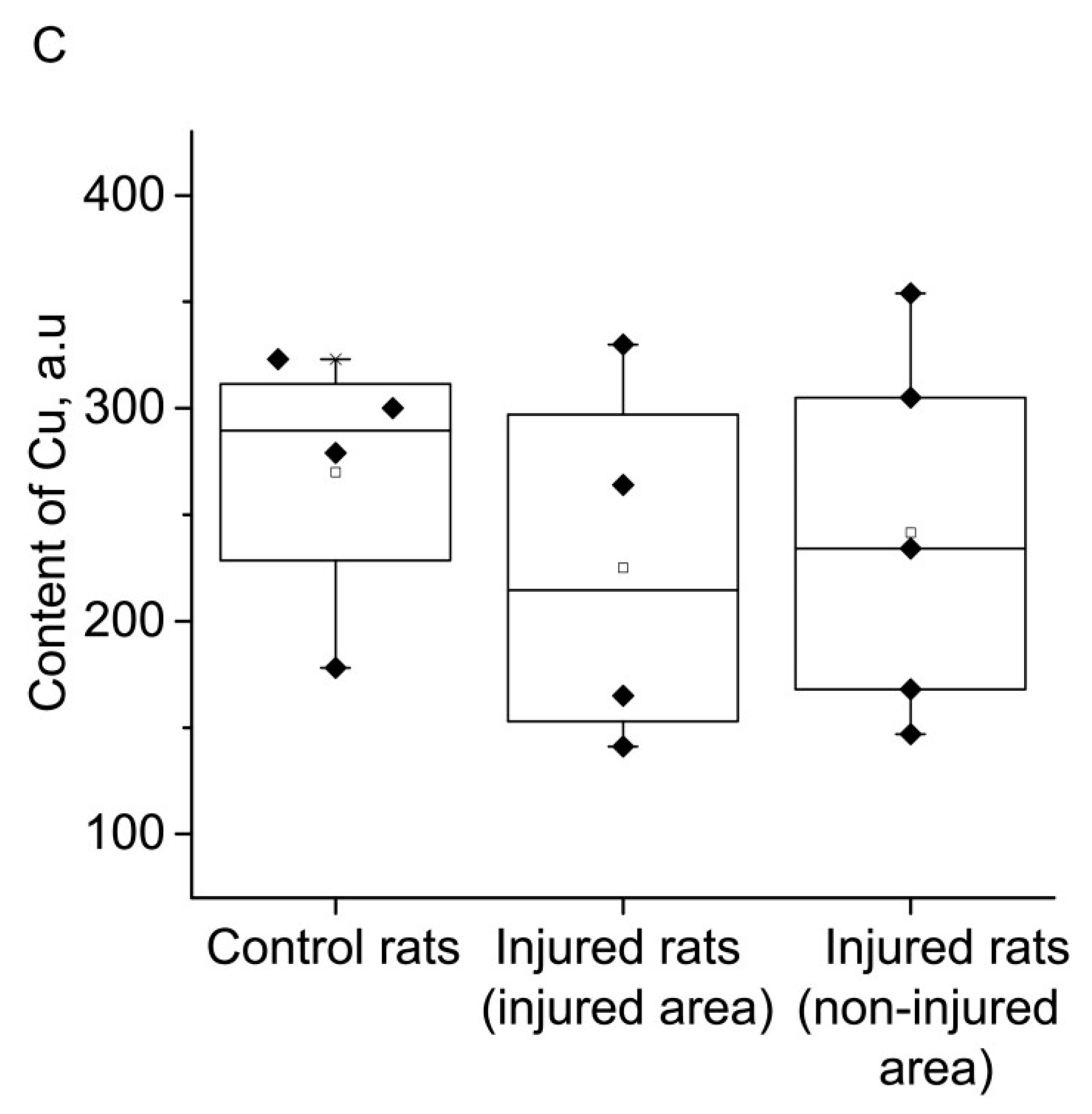
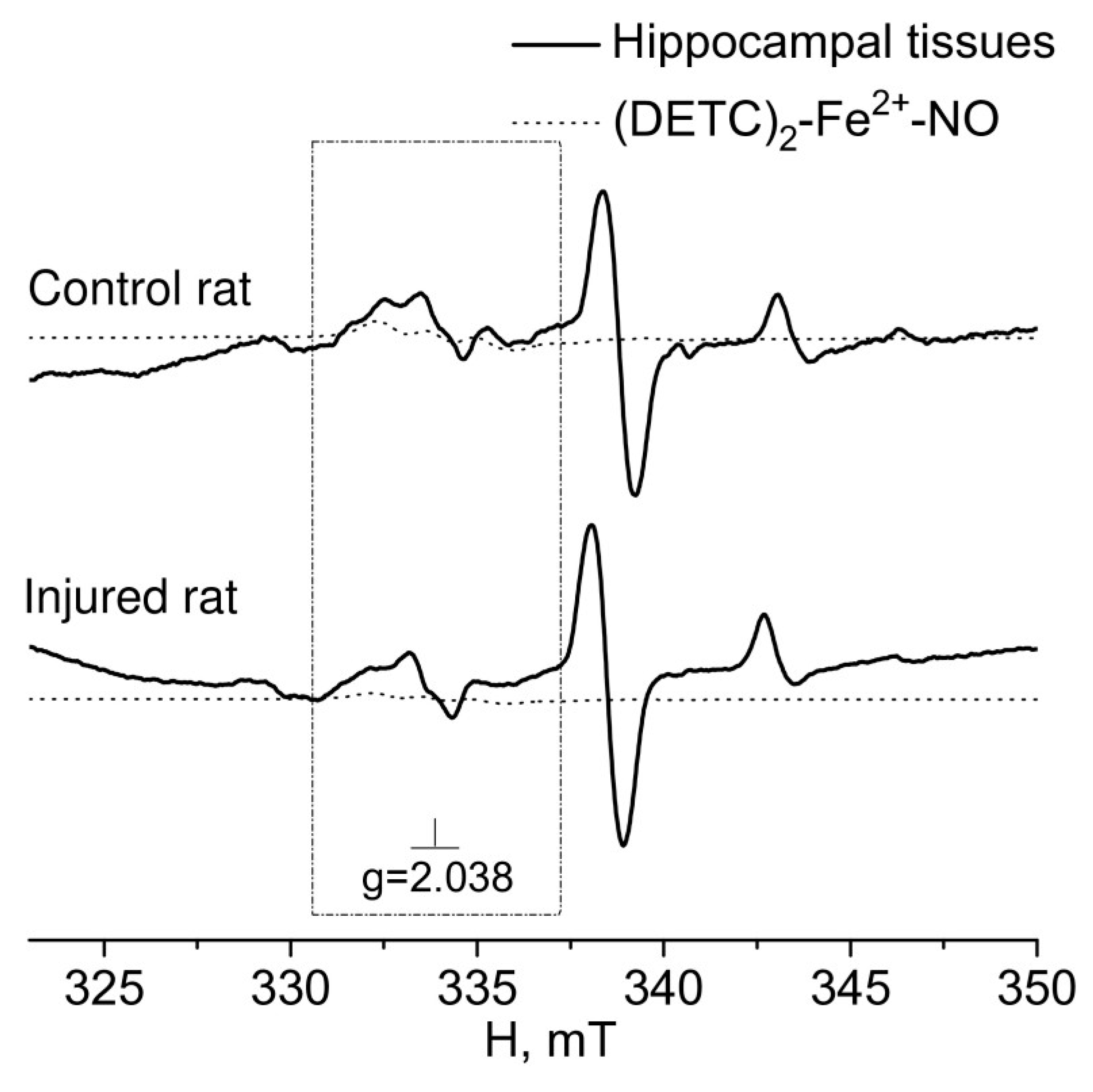
3. DISCUSSION
4. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
4.1. Animals
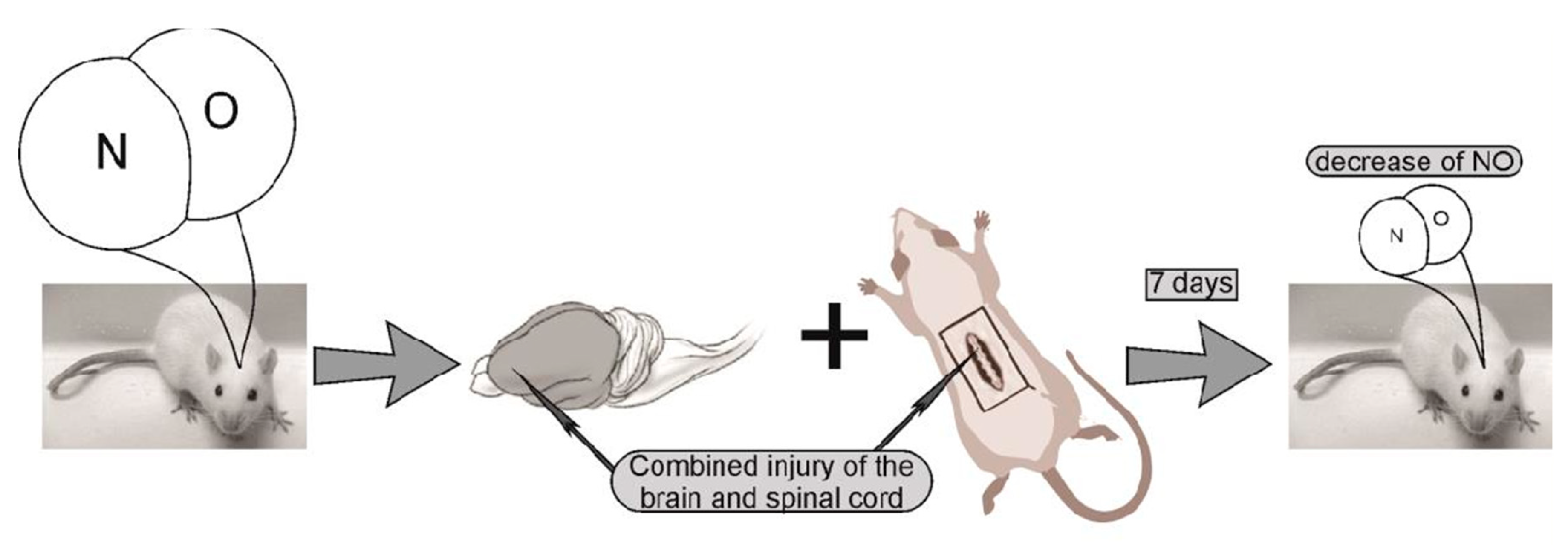
4.2. Experiment protocol. Modeling of combined trauma of the brain and spinal cord in rats
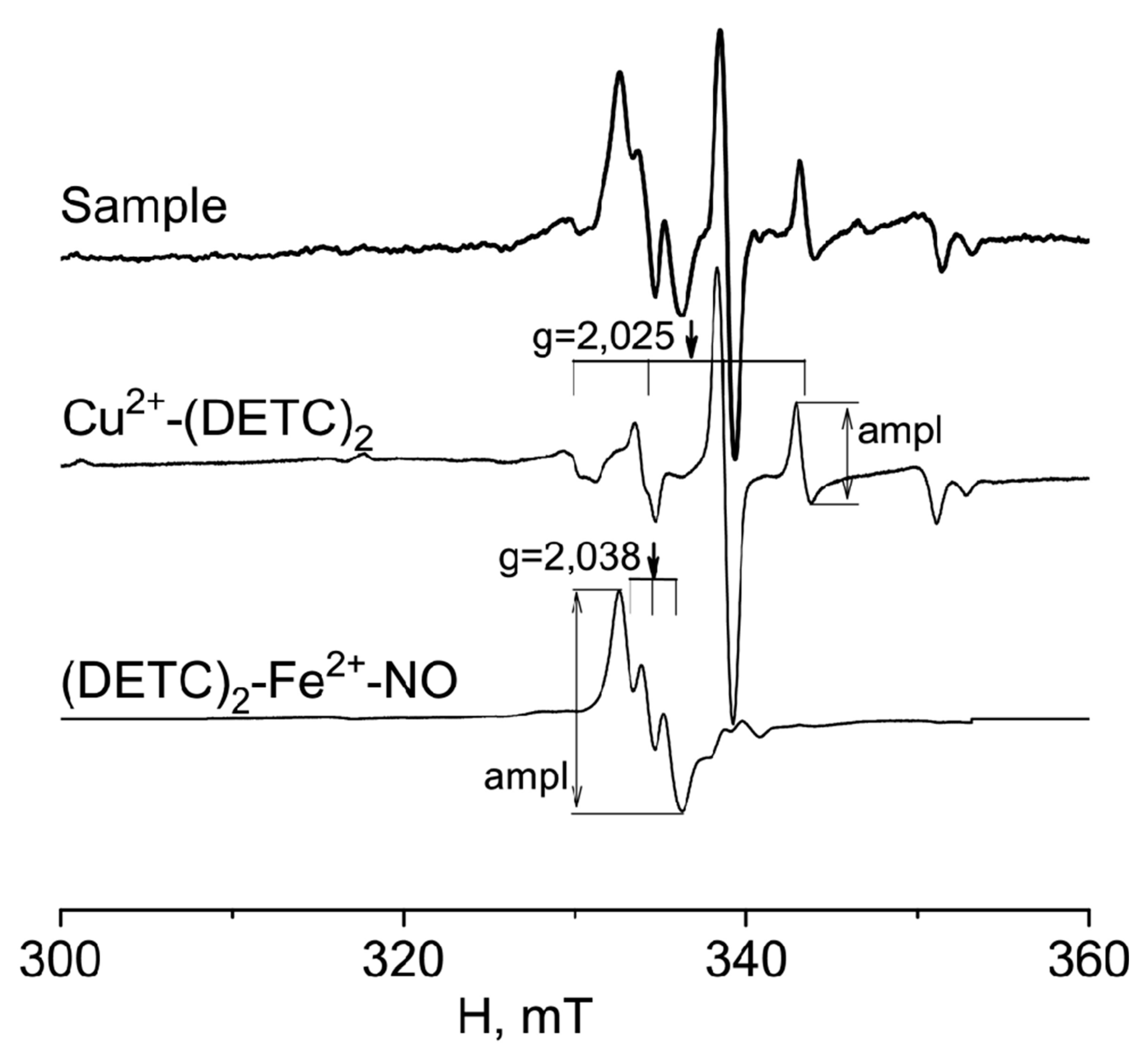
4.3. Formation of a (DETC)2-Fe2+-NO complex with a spin trap in rats tissues
4.4. Measurements of a (DETC)2-Fe2+-NO and Cu(DETC)2 complexes in rats tissues
4.5. Statistical processing of the result.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest
References
- Garthwaite, J. Concepts of neural nitric oxide-mediated transmission. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2783–2802. [CrossRef]
- Steinert, J.R.; Chernova, T.; Forsythe, I.D. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Brain Function, Dysfunction, and Dementia. Neurosci. 2010, 16, 435–452. [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.; Lourenço, C.F.; Ledo, A.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Nitric Oxide Inactivation Mechanisms in the Brain: Role in Bioenergetics and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Maggio, D.M.; Singh, A.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; Bleicher, D.H.; Ghosh, M.; Lopez, M.M.; Tuesta, L.M.; Flora, G.; Dietrich, W.D.; Pearse, D.D. Identifying the Long-Term Role of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase after Contusive Spinal Cord Injury Using a Transgenic Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 245. [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 2853–2878. [CrossRef]
- Boehning, D.; Snyder, S.H. Novel neural modulators Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 26, 105-131. [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.; Cornelius, C.; Rizzarelli, E.; Owen, J.B.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Butterfield, D.A. Nitric Oxide in Cell Survival: A Janus Molecule. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2717–2739. [CrossRef]
- Balaban, P.M.; Roshchin, M.; Timoshenko, A.K.; Gainutdinov, K.L.; Bogodvid, T.K.; Muranova, L.N.; Zuzina, A.B.; Korshunova, T.A. Nitric oxide is necessary for labilization of a consolidated context memory during reconsolidation in terrestrial snails. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 2963–2970. [CrossRef]
- Moroz, L.L. Gaseous transmission across time and species. Am Zool. 2015, 41, 304-320.
- Reutov, V.P.; Okhotin, V.E.; Shuklin, A.V.; Sorokina, E.G.; Kosicin, N.S.; Gurin, Nitric oxide and the cycle in the myocardium: molecular, biochemical and physiological aspects. V.N. Uspehi fiziologicheskih nauk 2007, 38, 39-58. (in Russian).
- Andrianov, V.V.; Sitdikov, F.G.; Gainutdinov, Kh.L.; Yurtaeva, S.V.; Muranova, L.N.; Obynochnyi, A.A.; Karimov, F.K.; Chiglintsev, V.M.; Iyudin, V.S. Changes in nitric oxide in heart of intact and sympathectomized rats of different age. Russ. J. Develop. Biol. 2008, 38 (6), 352-356.
- Baider, L.M.; Reutov, V.P.; Krushinsky, A.L.; Kuzenkov, V.S.; Sorokina, E.G.; Koshelev, V.B.; Fadyukova, O.E.; Djumbaeva, T.T.; Komissarova, L.Kh.; Pinelis, V.G. et al Investigation by method of EPR of influence of hypoxia on nitric oxide (NO) production in blood of rats Krushinskii-Molodkina. Biofizika 2009, 54(5), 894-899. (in Russian).
- Tennyson, A.G.; Lippard, S.J. Generation, Translocation, and Action of Nitric Oxide in Living Systems. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1211–1220. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Qu, Y.; Mu, D. Nitric oxide synthase in hypoxic or ischemic brain injury. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 26, 105–17. [CrossRef]
- Garry, P.S.; Ezra, M.; Rowland, M.J.; Westbrook, J.; Pattinson, K.T. The role of the nitric oxide pathway in brain injury and its treatment - from bench to bedside. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 263, 235-243. [CrossRef]
- Sukmanskiy, O.I.; Reutov, V.P. Gasotransmitters: physiological role and involvement in the pathogenesis of diseases. Uspekhi fiziol. nauk 2016, 47(3), 30-58. (In Rus).
- Sobrevia, L.; Ooi, L.; Ryan, S.; Steinert, J.R. Nitric Oxide: A Regulator of Cellular Function in Health and Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2016, 1–2. [CrossRef]
- Balez, R.; Ooi, L. Getting to NO Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroprotection versus Neurotoxicity Mediated by Nitric Oxide. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2016, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, H.; Gulati, K.; Ray, A. Effects of Nitric Oxide (NO) Modulators on Cognitive Function and Brain Oxidative Stress in Experimental Model of Alzheimers Disease in Rats. J Pharmacol Rep. 2017, 2, 2.
- Vanin, A.F. Dinitrosyl iron complexes and S-nitrosothiols are two possible forms of stabilization and transport of nitric oxide in biosystems. Biohimia 1998, 63, 924-938. (in Russian).
- Ignarro, L.J.; Cirino, G.; Casini, A.; Napoli, C. Nitric Oxide as a Signaling Molecule in the Vascular System: An Overview. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 34, 879–886. [CrossRef]
- Manukhina, E.B.; Malyshev, I.Y. Stress-limiting nitric oxide system. Rossijskii fiziologicheskii zhurnal im. I. M. Sechenova 2000, 86, 1283-1292. (in Russian).
- Luiking, Y.C.; Engelen, M.P.; Deutz, N.E. Regulation of nitric oxide production in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 97–104. [CrossRef]
- A Heinrich, T.; da Silva, R.S.; Miranda, K.M.; Switzer, C.H.; A Wink, D.; Fukuto, J.M. Biological nitric oxide signalling: chemistry and terminology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1417–1429. [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Fernández, A.P.; Martínez-Murillo, R.; Alonso, D.; Rodrigo, J.; Salas, E.; Mourelle, M.; Martínez, A. The nitric oxide donor LA 419 decreases ischemic brain damage.. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 229–236. [CrossRef]
- Wierońska, J.; Cieślik, P.; Kalinowski, L. Nitric Oxide-Dependent Pathways as Critical Factors in the Consequences and Recovery after Brain Ischemic Hypoxia. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1097. [CrossRef]
- Godecke, A.; Schrader, J. The Janus faces of NO Circ. Res. 2004, 94, e55-e57.
- Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Calvani, M.; Rizzarelli, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Stella, A.M.G. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 766–775. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F. What is the Mechanism of Nitric Oxide Conversion into Nitrosonium Ions Ensuring S-Nitrosating Processes in Living Organisms. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 77, 279–292. [CrossRef]
- Samdani, A.F.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Nitricoxide synthase in models of focal ischemia. Stroke 1997, 28, 1283.
- Vanin, A.F. What is the Mechanism of Nitric Oxide Conversion into Nitrosonium Ions Ensuring S-Nitrosating Processes in Living Organisms. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 77, 279–292. [CrossRef]
- Malyshev, I.Y.; Zenina, T.A.; Golubeva, L.Y.; Saltykova, V.A.; Manukhina, E.B.; Mikoyan, V.D.; Kubrina, L.N.; Vanin, A.F. NO-Dependent Mechanisms of Adaptation to Hypoxia. Nitric Oxide 1999, 3, 105–113. [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Tominaga, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Ohnishi, S.T. Electron paramagnetic resonance study on nitric oxide production during brain focal ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. Brain Res. 1994, 647, 91–96. [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, T.; Sato, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Ohnishi, S.T. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Detection of Nitric Oxide Produced during Forebrain Ischemia of the Rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 715–722. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Irie, Y.; Keung, W.M.; Maret, W. S-Nitrosothiols React Preferentially with Zinc Thiolate Clusters of Metallothionein III through Transnitrosation. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 8360–8367. [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.; Kusumoto, K.; Graham, D.; McCulloch, J.; Macrae, I. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis does not reduce infarct volume in a rat model of focal cerebral ischaemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 142, 151–154. [CrossRef]
- Sancesario, G.; Iannone, M.; Morello, M.; Nisticò, G.; Bernardi, G. Nitric oxide inhibition aggravates ischemic damage of hippocampal but not of NADPH neurons in gerbils.. Stroke 1994, 25, 436–443. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Golanov, E.V.; Berger, S.B.; Reis, D.J. Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Synthesis Increases Focal Ischemic Infarction in Rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1992, 12, 717–726. [CrossRef]
- Willmot, M.; Gray, L.; Gibson, C.; Murphy, S.; Bath, P.M. A systematic review of nitric oxide donors and l-arginine in experimental stroke; effects on infarct size and cerebral blood flow. Nitric Oxide 2005, 12, 141–149. [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-H.; Chu, K.; Ko, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-T.; Sinn, D.-I.; Park, D.-K.; Kim, J.-M.; Song, E.-C.; Kim, M.; Roh, J.-K. Early Intravenous Infusion of Sodium Nitrite Protects Brain Against In Vivo Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Stroke 2006, 37, 2744–2750. [CrossRef]
- Evgenov, O.V.; Pacher, P.; Schmidt, P.M.; Haskó, G.; Schmidt, H.H.H.W.; Stasch, J.-P. NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase: discovery and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 755–768. [CrossRef]
- Godínez-Rubí, M.; Rojas-Mayorquín, A.E.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. Nitric Oxide Donors as Neuroprotective Agents after an Ischemic Stroke-Related Inflammatory Reaction. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Kuzenkov, V.S.; Krushinskiy, A.L. Protective effect of magnesium nitrate on cerebral ischemia. Vestnik Mosk.universiteta. Biologiya 2014, 4, 9-14. (In Rus).
- Yang, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, T.-T.; Cao, H.-L. Recent advances in the neuroprotective effects of medical gases. Med Gas Res. 2019, 9, 80–87. [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Han, X.; Xie, H.; Liao, H.; Xiao, X.; Huang, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W. Protective role of nitric oxide donors on endothelium in ischemia-reperfusion injury: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.; Ha, E.; Zhang, M.; Fall, C.; Hwang, M.; Taylor, E.; Stetkevich, S.; Bhanot, A.; Wilson, C.G.; Figueroa, J.D.; et al. Neuroprotective role of nitric oxide inhalation and nitrite in a Neonatal Rat Model of Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0268282. [CrossRef]
- Gainutdinov, K.L.; Gavrilova, S.A.; Iyudin, V.S.; Golubeva, A.V.; Davydova, M.P.; Jafarova, G.G.; Andrianov, V.V.; Koshelev, V.B. EPR Study of the Intensity of the Nitric Oxide Production in Rat Brain After Ischemic Stroke. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2011, 40, 267–278. [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, V.V.; Pashkevich, S.G.; Yafarova, G.G.; Denisov, A.A.; Iyudin, V.S.; Bogodvid, T.K.; Dosina, M.O.; Kulchitsky, V.A.; Gainutdinov, K.L. Changes of Nitric Oxide Content in the Rat Hippocampus, Heart and Liver in Acute Phase of Ischemia. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2016, 47, 965–976. [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, V.V.; Yafarova, G.G.; Pashkevich, S.G.; Tokalchik, Y.P.; Dosina, M.O.; Zamaro, A.S.; Bogodvid, T.K.; Iyudin, V.S.; Bazan, L.V.; Kulchitsky, V.A.; et al. Changes of the Nitric Oxide and Copper Content in the Olfactory Bulbs of Rat Brain After Modeling of Brain Stroke and Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2020, 51, 375–387. [CrossRef]
- Deryagin, O.G.; Gavrilova, S.A.; Buravkov, S.V.; Andrianov, V.V.; Yafarova, G.G.; Gainutdinov, K.L.; Koshelev, V.B. The Role of ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels and Nitric Oxide in the Protective Effect of Preconditioning of the Brain. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 48, 58–63. [CrossRef]
- Deryagin, O.G.; Gavrilova, S.A.; Gainutdinov, K.L.; Golubeva, A.V.; Andrianov, V.V.; Yafarova, G.G.; Buravkov, S.V.; Koshelev, V.B. Molecular Bases of Brain Preconditioning. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 427–427. [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, K.D.; Devarakonda, C.B.; Joshi, A.R.; Sharma, S.S.; Roy, N. Role of nitric oxide synthases in cerebral ischemia. Current Res. and Information on Pharmaceut. Sci. 2011, 11(3), 50-56.
- Chen, Z.Q.; Mou, R.T.; Feng, D.X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. The role of nitric oxide in stroke. Med Gas Res. 2017, 7(3), 194-203. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y.; Hong F.; Yang S. Role of nitric oxide in brain ischemia and reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4243. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.-J. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces brain damage by promoting collateral recruitment in a cerebral hypoxia-ischemia mice model. 2018, 22, 3166–3172.
- Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Bonnin, P.; Gharib, A.; Leger, P-L.; Villapol, S.; Pocard, M.; Gressens, P.; Renolleau, S.; Baud, Ol. Inhaled nitric oxide reduces brain dDamage by collateral recruitment in a neonatal stroke model. Stroke 2012, 43, 3078-3084.
- A Terpolilli, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Thal, S.C.; Kuebler, W.M.; Plesnila, N. Inhaled Nitric Oxide Reduces Secondary Brain Damage after Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 33, 311–318. [CrossRef]
- A Terpolilli, N.; Feiler, S.; Dienel, A.; Müller, F.; Heumos, N.; Friedrich, B.; Stover, J.; Thal, S.; Schöller, K.; Plesnila, N. Nitric oxide inhalation reduces brain damage, prevents mortality, and improves neurological outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage by resolving early pial microvasospasms. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 2096–2107. [CrossRef]
- Remizova, M.I.; Kochetygov, N.I.; Gerbout, K.A.; Lakomkin, V.L.; Timoshin, A.A.; Burgova, E.N.; Vanin, A.F. Effect of dinitrosyl iron complexes with glutathione on hemorrhagic shock followed by saline treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 662, 40–46. [CrossRef]
- A Terpolilli, N.; A Moskowitz, M.; Plesnila, N. Nitric Oxide: Considerations for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1332–1346. [CrossRef]
- Manukhina, E.B.; Malyshev, I.Y.; Smirin, B.V.; Mashina, S.Y.; Saltykova, V.A.; Vanin, A.F. Production and Storage of Nitric Oxide in Adaptation to Hypoxia. Nitric Oxide 1999, 3, 393–401. [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, J.P.; Almeida, A. Roles of nitric oxide in brain hypoxia-ischemia. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Bioenerg. 1999, 1411, 415–436. [CrossRef]
- Capizzi, A.; Woo, J.; Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic Brain Injury. Med Clin. North Am. 2020, 104, 213–238. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, E.V.; Gavrilova, S.A.; Koshelev, V.B. Brain acute ischemia mechanisms: implications to experimental and clinical treatment. Reg. blood Circ. Microcirc. 2021, 20, 5-19. [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Misra, H.; Li, Y. Oxidative stress in spinal cord injury and antioxidant-based intervention. Spinal Cord 2011, 50, 264–274. [CrossRef]
- Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Ciofi-Baffoni, S.; Kozyreva, T.; Zovo, K.; Palumaa, P. Affinity gradients drive copper to cellular destinations. Nature 2010, 465, 645–648. [CrossRef]
- Festa, R.A.; Thiele, D.J. Copper: An essential metal in biology. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R877–R883. [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.-F. Superoxide dismutases: Ancient enzymes and new insights. FEBS Lett. 2011, 586, 585–595. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Abreu, I.A.; Cabelli, D.E.; Maroney, M.J.; Miller, A.-F.; Teixeira, M.; Valentine, J.S. Superoxide Dismutases and Superoxide Reductases. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3854–3918. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Capri, J.; Waring, A.; Valentine, J.S.; Whitelegge, J. Exposure of Solvent-Inaccessible Regions in the Amyloidogenic Protein Human SOD1 Determined by Hydroxyl Radical Footprinting. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 30, 218–226. [CrossRef]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.-R.; Hong, Y.-C.; Choquet, H.; Trapani, E.; Goitre, L.; Trabalzini, L.; Akers, A.; et al. Superoxide Dismutases: Role in Redox Signaling, Vascular Function, and Diseases. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [CrossRef]
- Sehba, F.A.; Bederson, J.B. Mechanisms of acute brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol. Res. 2006, 28, 381–398. [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.M.; Jones, G.M.; Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Mailloux, P.; McLaughlin, D.; Papangelou, A.; Samuel, S.; Tokumaru, S.; Venkatasubramanian, C.; Zacko, C.; et al. Guidelines for the Acute Treatment of Cerebral Edema in Neurocritical Care Patients. Neurocritical Care 2020, 32, 647–666. [CrossRef]
- Everitt, A.; Root, B.; Calnan, D.; Manwaring, P.; Bauer, D.; Halter, R. A bioimpedance-based monitor for real-time detection and identification of secondary brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Murthy, T.; Bhatia, P.; Sandhu, K.; Prabhakar, T.; Gogna, R. Secondary brain injury: Prevention and intensive care management. Indian J. Neurotrauma 2005, 2, 7–12. [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Fang, Y.; Si, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Reis, C.; Chen, S. The Role of Gaseous Molecules in Traumatic Brain Injury: An Updated Review. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 392. [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, V.V.; Kulchitsky, V.A.; Yafarova, G.G.; Zamaro, A.S.; Tokalchik, Y.P.; Bazan, L.V.; Bogodvid, T.K.; Iyudin, V.S.; Pashkevich, S.G.; Dosina, M.O.; et al. Comparative Study of the Intensity of Nitric Oxide Production and Copper Content in Hippocampus of Rats After Modeling of Hemorrhagic Stroke and Brain Injury. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2021, 52, 1657–1669. [CrossRef]
- Crobeddu, E.; Pilloni, G.; Tardivo, V.; Fontanella, M.M.; Panciani, P.P.; Spena, G.; Fornaro, R.; Altieri, R.; Agnoletti, A.; Ajello, M. et al Role of nitric oxide and mechanisms involved in cerebral injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: is nitric oxide a possible answer to cerebral vasospasm? J Neurosurg Sci. 2016,60(3), 385-91. Epub 2015 Jan 20.
- Mikoyan, V.D.; Kubrina, L.N.; Serezhenkov, V.A.; Stukan, R.A.; Vanin, A.F. Complexes of Fe2+ with diethyldithiocarbamate or N-methyl-D-glucamine dithiocarbamate as traps of nitric oxide in animal tissues Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1336, 225-234.
- van Faassen, E.E.; Koeners, M.P.; Joles, J.A.; Vanin, A.F. Detection of basal NO production in rat tissues using iron–dithiocarbamate complexes. Nitric Oxide 2008, 18, 279–286. [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, M.A.; Pyka, J.; Michalczyk-Wetula, D.; Baczyński, K.; Cieśla, M.; Susz, A.; Ferdek, P.E.; Płonka, B.K.; Fiedor, L.; Płonka, P.M. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals alterations in the redox state of endogenous copper and iron complexes in photodynamic stress-induced ischemic mouse liver. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101566. [CrossRef]
- Gainutdinov, K.L.; Kulchitsky, V.A.; Andrianov, V.V.; Yafarova, G.G.; Tokalchik, Y.P.; Zamaro, A.S.; Bazan, L.V.; Bogodvid, T.K.; Iyudin, V.S.; Pashkevich, S.G.; et al. Application of EPR Spectroscopy to Study the Content of NO and Copper in the Frontal Lobes, Hippocampus, and Liver of Rats after Cerebral Ischemia. Tech. Phys. 2022, 67, 311–316. [CrossRef]
- Ismailova, A.I.; Gnezdilov, O.I.; Obynochny, A.A.; Muranova, L.N.; Andrianov, V.V.; Gainutdinov, K.L.; Nasyrova, A.G.; Nigmatullina, R.R.; Rakhmatullina, F.F.; Zefirov, A.L. ESR study of the nitric oxide production in tissues of animals under an external influence on the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2005, 28, 421–430. [CrossRef]
- AlRuwaili, R.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Alruwaili, M.; Khalifa, A.K.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. The potential therapeutic effect of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors in the acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiol-containing ligands as a “working form” of endogenous nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 2016, 54, 15–29. [CrossRef]
- Maiese, K. The dynamics of cellular injury: transformation into neuronal and vascular protection. Histol. Histopathol. 2001, 16(2), 633-644. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-N.; Shao, A.; Tong, L.-S.; Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. The Role of Nitric Oxide and Sympathetic Control in Cerebral Autoregulation in the Setting of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 53, 3606–3615. [CrossRef]
- A Donnan, G.; Fisher, M.; Macleod, M.; Davis, S.M. Stroke. Lancet 2008, 371, 1612–1623. [CrossRef]
- Reutov, V.P.; Samosudova, N.V.; Sorokina, E.G. A Model of Glutamate Neurotoxicity and Mechanisms of the Development of the Typical Pathological Process. Biophysics 2019, 64, 233–250. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Targeting nitric oxide in the subacute restorative treatment of ischemic stroke. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 843–851. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F.; Huisman, A.; Van Faassen, E.E. Iron Dithiocarbamate as Spin Trap for Nitric Oxide Detection: Methods in Enzymology. Pitfalls and Successes 2003, 359, 27-42.
- Hogg, N. Detection of nitric oxide by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 122–129. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F.; Mordvintcev, P.I.; Kleshchev, A.L. Appearance of nitrogen oxide in animal tissues in vivo. Studia Biophys. 1984, 102, 135-143.
- Shanko, Y.; Zamaro, A.; Takalchik, S.Y.; Koulchitsky, S.; Pashkevich, S.; Panahova, E.; Navitskaya, V.; Dosina, M.; Denisov, A.; Bushuk, S.; Kulchitsky, V. Mechanisms of neural network structures recovery in brain trauma. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 7(5), MS.ID.001567.
- Bogodvid, T.; Pashkevich, S.; Dosina, M.; Zamaro, A.; Takalchik, Y.; Yafarova, G.; Andrianov, V.; Denisov, A.; Loiko, D.; Gainutdinov, K.; Kulchitsky, V. Effect of intranasal administration of mesenchymal stem cells on the approximate motor activity of rats after simulation of ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49(Suppl 1, P146-T), 161. [CrossRef]
- Shanko, Y.; Navitskaya, V.; Zamaro, A.; Krivenko, S.; Zafranskaya, M.; Pashkevich, S.; Koulchitsky, S.; Takalchik–Stukach, Y.; Denisov, A.; Kulchitsky, V. Prospects of perineural administration of autologous mesenchymal stem cells of adipose tissue in patients with cerebral infarction. Biomed J Sci&Tech Res. 2018, 10(1), 1-3. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.; Poltorakov, A. NO spin trapping in biological systems. Front. Biosci. 2009, ume, 4427–35. [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F.; Mordvintcev, P.I.; Kleshchev, A.L. Appearance of nitric oxide in animal tissue in vivo. Studia Biophysica 1984, 107, 135-142.
- Plonka, P.M.; Chlopicki, S.; Wisniewska, M.; Plonka, B.K. Kinetics of increased generation of (.)NO in endotoxaemic rats as measured by EPR.. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 807–813. [CrossRef]
- Kleschyov, A.L.; Wenzel, P.; Munzel, T. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin trapping of biological nitric oxide. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 851, 12–20. [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, T.; Sato, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Ohnishi, S.T. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Detection of Nitric Oxide Produced during Forebrain Ischemia of the Rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 715–722. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Fujii, S.; Tominaga, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Kamada, H. The origin of an EPR signal observed in dithiocarmate-loaded tissues Copper (II)- dithiocarmate complexes account for the narrow hyperfine lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1335, 242-245.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



