Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
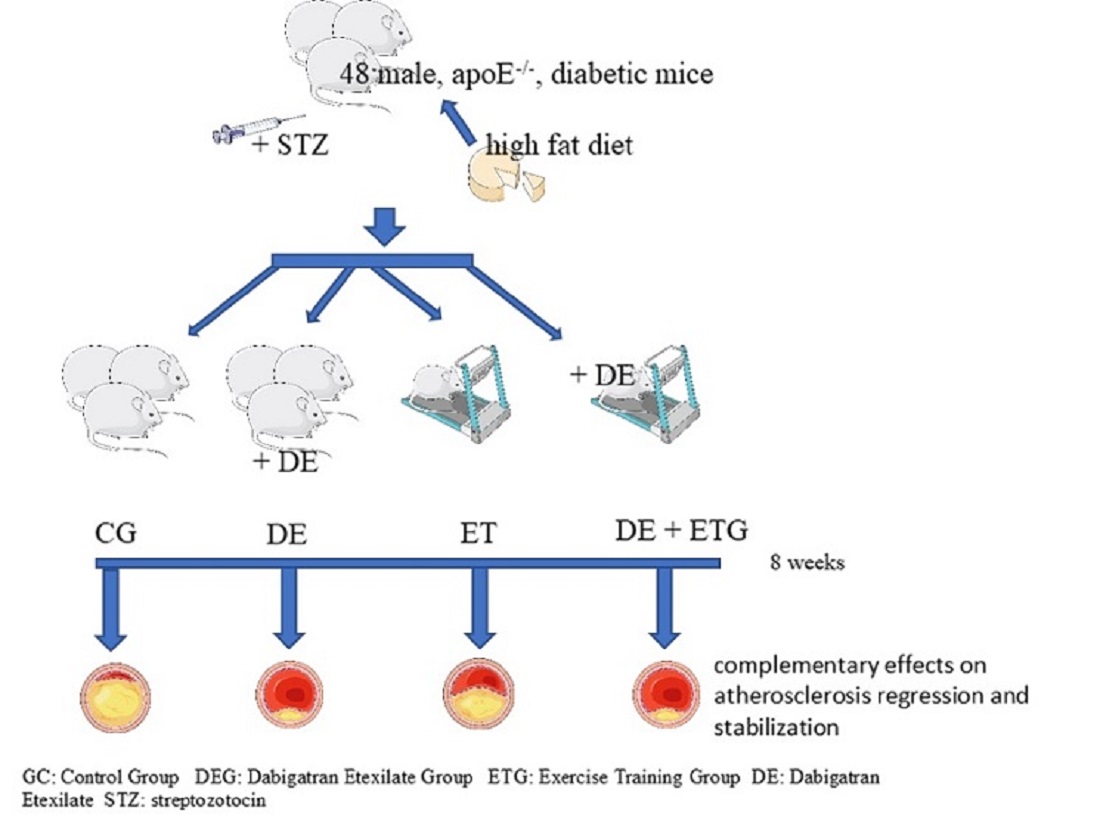
2.1. Mean plaque area and plaque stability
| CG (n=12) |
DEG (n=12) |
ETG (n=12) |
DE+ETG (n=12) |
p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plaque Area (x103 μm²) | 287.9±54.12 | 105.12±31.11a,c | 201.65±65.12a,b,d | 72.23±15.51 a,c | <0.001 |
| Lumen Area (x103 μm²) | 1323.56±265.3 | 1355.32±288.54 | 1222.1±243.51 | 1274.76±289.23 | 0.885 |
| Lumen Stenosis (%) | 23.3±5.5 | 7.9±2.2 a,c | 17.3±5.3a,b,d | 7.1±2.7a,c | <0.001 |
| Elastin (%) plaque | 9.79±2.92 | 21.62±6.52a,d | 18.91±5.07a,d | 30.24±7.72a,b,c | 0.002 |
| Collagen (%) plaque | 16.45±8.08 | 26.83±4.79 a,d | 21.44±3.1 a,d | 31.41±4.88 a,b,c | 0.001 |
| Fibrous cap thickness (μm) | 12.52±2.18 | 22.32±3.46 a,d | 19.63±3.02 a,d | 31.41±4.12 a,b,c | <0.001 |
| a-actin (VSMCs) (%) plaque | 15.91±4.98 | 23.79±5.54a | 18.51±4.31a,d | 25.22±6.18a,c | 0.039 |
| Mac-3 (macrophages) (%) plaque | 28.85±9.52 | 19.46±5.58a,d | 21.02±4.93a,d | 12.33±2.87a,b,c | <0.001 |
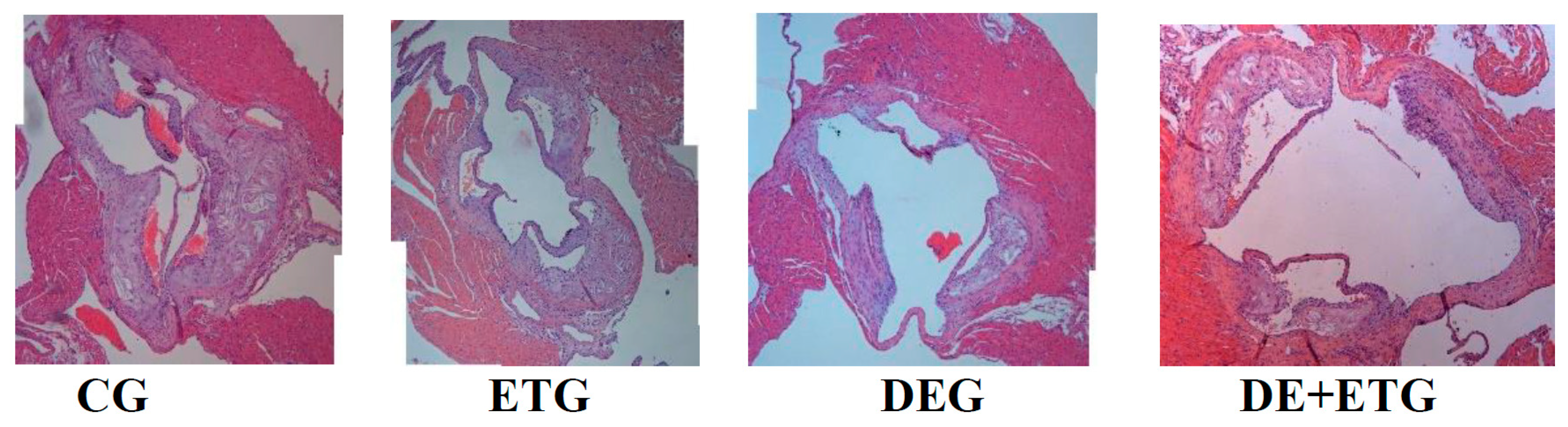

2.2. Inflammatory mediators
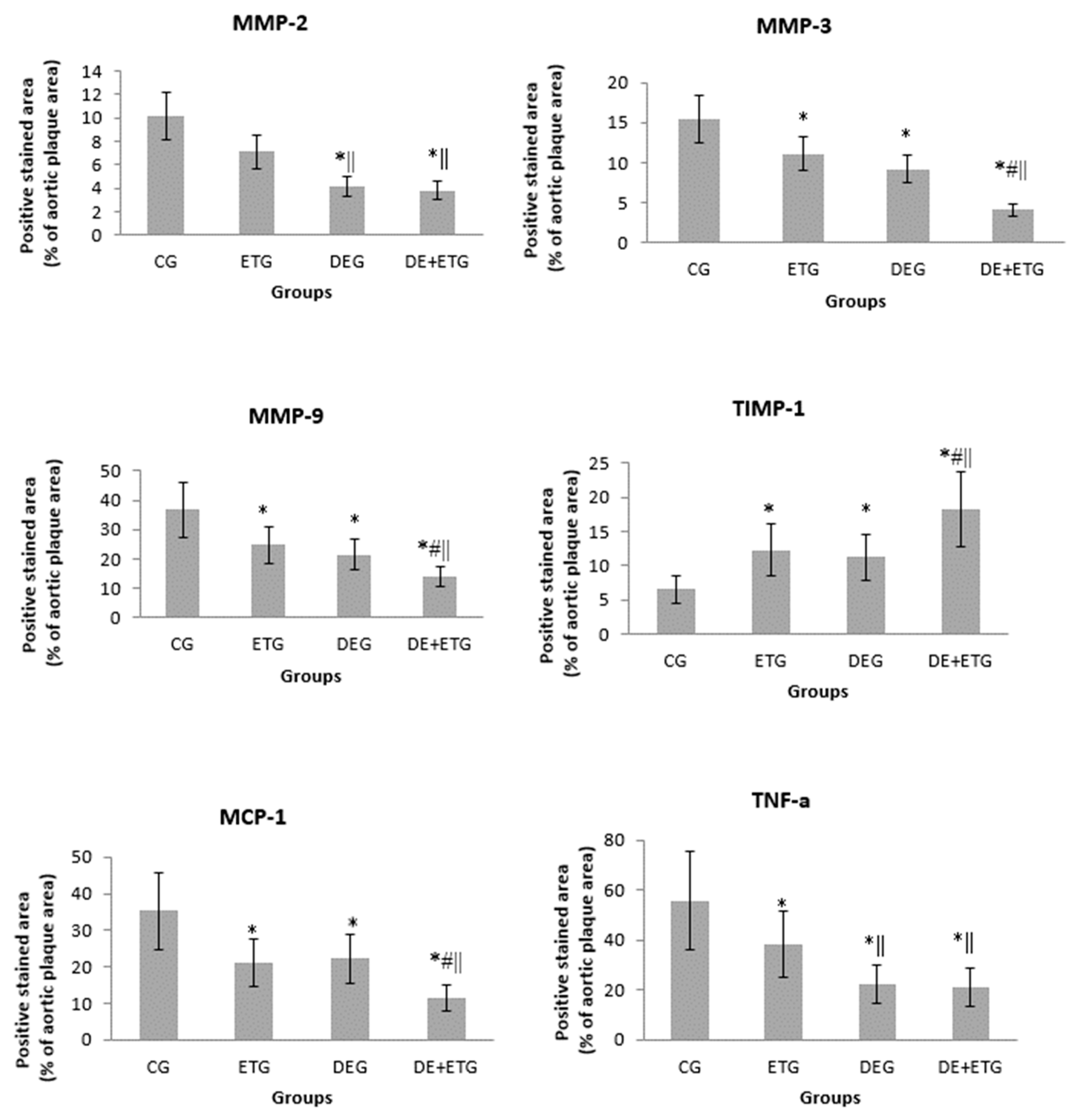
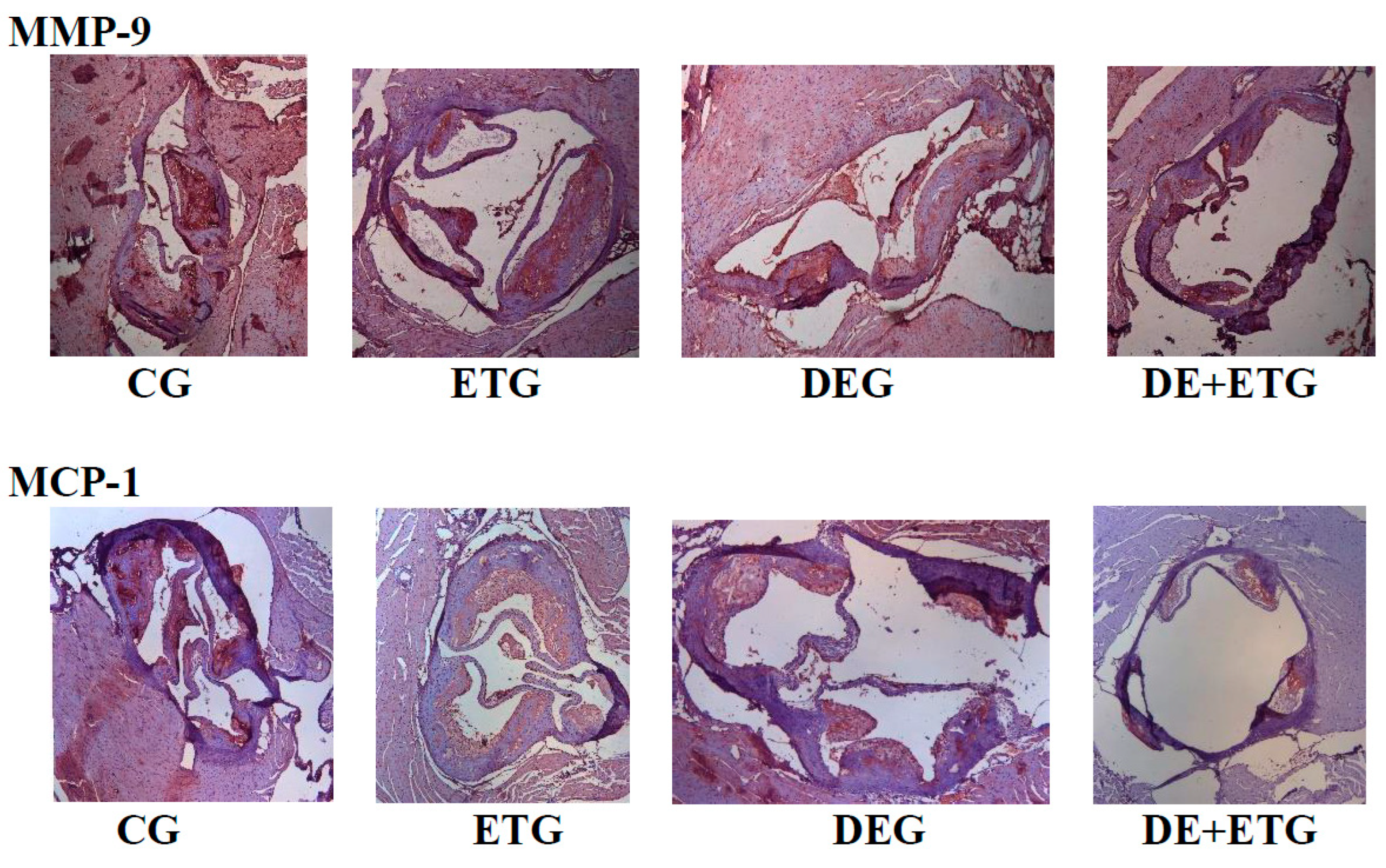
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study design
5.2. Glucose tolerance test
5.3. Histology
5.4. Digital processing -Histomorphometry
5.5. Blood analyses
5.6. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansson, G.K.; Hermansson, A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 2011, 12, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.R. Vulnerable plaque: Definition, diagnosis, and treatment. Cardiol Clin. 2010, 28, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Konstandi, O.A.; Kenoutis, C.; Kakazanis, Z.I.; Rizakou, A.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Crocus sativus L. aqueous extract reduces atherogenesis, increases atherosclerotic plaque stability and improves glucose control in diabetic atherosclerotic animals. Atherosclerosis. 2018, 268, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M. How to Use Statins in Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Diseases: From the Beneficial Early Initiation to the Potentially Unfavorable Discontinuation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023, 37, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Khattab, E.; Velidakis, N.; Patsourakos, N.; Lambadiari, V. A new approach of statin therapy in carotid atherosclerosis: Targeting indices of plaque vulnerability on the top of lipid-lowering. A narrative review. Kardiol Pol. 2022, 80, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Korakas, E.; Lampropoulos, S.; Maratou, E.; Kassimis, G.; Patsourakos, N.; Plotas, P.; Moutsatsou, P.; Lambadiari, V. Plasma nesfatin-1 and DDP-4 levels in patients with coronary artery disease: Kozani study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021, 20, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Kapetanios, D.; Korakas, E.; Valsami, G.; Tentolouris, N.; Papanas, N.; Lambadiari, V.; Karkos, C. Association of serum levels of osteopontin and osteoprotegerin with adverse outcomes after endovascular revascularisation in peripheral artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022, 21, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, S.S.; McEver, R.P.; Weyrich, A.S.; Morrell, C.N.; Hoffman, M.R.; et al. Platelet Colloquium Participants. Platelet functions beyond hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2009, 7, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.A.; Philippou, H.; Huntington, J.A. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005, 106, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehaus, S.; Shahzad, K.; Kashif, M.; Vinnikov, I.A.; Schiller, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Hypercoagulability inhibits monocyte transendothelial migration through protease-activated receptor-1-, phospholipase-Cbeta-, phosphoinositide 3-kinase-, and nitric oxide-dependent signaling in monocytes and promotes plaque stability. Circulation. 2009, 120, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borissoff, J.I.; Spronk, H.M.; Heeneman, S.; ten Cate, H. Is thrombin a key player in the 'coagulation-atherogenesis' maze? Cardiovasc Res. 2009, 82, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienen, W.; Stassen, J.M.; Priepke, H.; Ries, U.J.; Hauel, N. In-vitro profile and ex-vivo anticoagulant activity of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran and its orally active prodrug, dabigatran etexilate. Thromb Haemost. 2007, 98, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, S.; Kearon, C.; Kakkar, A.K.; Mismetti, P.; Schellong, S.; RE-COVER Study Group; et al. (2009) Dabigatran versus warfarin in the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2009, 361, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, S.H.; Baumhäkel, M.; Neuberger, H.R.; Hohnloser, S.H.; van Gelder, I.C.; et al. Novel anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: Current clinical evidence and future developments. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010, 56, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldgren, J.; Budaj, A.; Granger, C.B.; Khder, Y.; Roberts, J.; RE-DEEM Investigators; et al. Dabigatran vs. placebo in patients with acute coronary syndromes on dual antiplatelet therapy: A randomized, double-blind, phase II trial. Eur Heart J. 2011, 32, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K.; Hernandez, A.V. Dabigatran association with higher risk of acute coronary events: Meta-analysis of noninferiority randomized Controlled Trials. Arch Intern Med. 2012, 172, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Moustardas, P.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Kapelouzou, A.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; et al. The beneficial effects of a direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran etexilate, on the development and stability of atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice: Dabigatran etexilate and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2012, 26, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.O.; Kratz, M.T.; Schirmer, S.H.; Baumhäkel, M.; Böhm, M. The effects of direct thrombin inhibition with dabigatran on plaque formation and endothelial function in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012, 343, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, D.L.; Lavie, C.J.; Johannsen, N.M.; Arena, R.; Earnest, C.P.; et al. Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and exercise training in primary and secondary coronary prevention. Circ J. 2013, 77, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Nunes, S.; Teixeira, F.; Reis, F. Regular physical exercise training assists in preventing type 2 diabetes development: Focus on its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2011, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Iliadis, F.; Liapis, C.D. Exercise and carotid atherosclerosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2008, 35, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Vrabas, I.S.; Kapelouzou, A.; Angelopoulou, N. The association of physical activity with novel adipokines in patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Intern Med. 2012, 23, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Valsami, G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N. Exercise training inhibits atherosclerosis progression and reduces VE-cadherin levels within atherosclerotic plaques in hypercholesterolemic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022, 623, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakos, I.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Gkeka, P.; Tzallas, A.T.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Mantziaras, G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Liapis, C.D.; Kakisis, J. Exercise Training Attenuates the Development of Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. In Vivo. 2018, 32, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagianni, G.; Panayiotou, C.; Vardas, M.; Balaskas, N.; Antonopoulos, C.; Tachmatzidis, D.; Didangelos, T.; Lambadiari, V.; Kadoglou, N.P.E. The anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine. 2023, 164, 156157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Fotiadis, G.; Kapelouzou, A.; Kostakis, A.; Liapis, C.D.; Vrabas, I.S. The differential anti-inflammatory effects of exercise modalities and their association with early carotid atherosclerosis progression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013, 30, e41–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Moustardas, P.; Kapelouzou, A.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Giagini, A.; Dede, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Karayannacos, P.E.; Kostakis, A.; Liapis, C.D. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training promote atherosclerotic plaque stabilization in apolipoprotein E knockout mice with diabetic atherosclerosis. Eur J Histochem. 2013, 57, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Vrabas, I.S.; Kapelouzou, A.; Angelopoulou, N. The association of physical activity with novel adipokines in patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Intern Med. 2012, 23, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockard, M.M.; Gopinathannair, R.; Paton, C.M.; Phares, D.A.; Hagberg, J.M. Exercise training-induced changes in coagulation factors in older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Kapelouzou, A.; Moustardas, P.; Katsimpoulas, M.; et al. Effects of exercise training on the severity and composition of atherosclerotic plaque in apoE-deficient mice. J Vasc Res. 2011, 48, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borissoff, J.I.; Otten, J.J.; Heeneman, S.; Leenders, P.; van Oerle, R.; Soehnlein, O.; et al. Genetic and pharmacological modifications of thrombin formation in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice determine atherosclerosis severity and atherothrombosis onset in a neutrophil-dependent manner. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e55784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Sobenin, I.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Vascular extracellular matrix in atherosclerosis. Cardiol Rev. 2013, 21, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D.; Kioufis, S.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasou, Z.; Limperi, M.; et al. Inflammatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis: The impact of matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012, 12, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Perrea, D.; Liapis, C.D. Matrix metalloproteinases and diabetic vascular complications. Angiology 2005, 56, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogita, M.; Miyauchi, K.; Morimoto, T.; Daida, H.; Kimura, T.; Hiro, T.; et al. Association between circulating matrix metalloproteinase levels and coronary plaque regression after acute coronary syndrome--subanalysis of the JAPAN-ACS study. Atherosclerosis. 2013, 226, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Li, K.; Festenstein, S.; Karegli, J.; Wilkinson, H.; Leonard, H.; Wei, L.L.; Ma, N.; Xia, M.; Tam, H.; Wang, J.A.; Xu, Q.; McVey, J.H.; Smith, R.A.G.; Dorling, A. Regression of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice Via Modulation of Monocyte Recruitment and Phenotype, Induced by Weekly Dosing of a Novel "Cytotopic" Anti-Thrombin Without Prolonged Anticoagulation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma, J.J.; Posma, J.J.N.; van Oerle, R.; Leenders, P.; van Gorp, R.H.; Jaminon, A.M.G.; Mackman, N.; Heitmeier, S.; Schurgers, L.J.; Ten Cate, H.; Spronk, H.M.H. Targeting Coagulation Factor Xa Promotes Regression of Advanced Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein-E Deficient Mice. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Otsuka, K.; Kono, Y.; Hojo, K.; Yamaura, H.; Hirata, K.; Kasayuki, N.; Izumiya, Y.; Fukuda, D. Extent of coronary atherosclerosis is associated with deterioration of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in patients with preserved ejection fraction undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2023, 44, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wei, M.; Huang, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, Z.; Xia, J. The atherogenic index of plasma and carotid atherosclerosis in a community population: A population-based cohort study in China. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023, 22, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Pavlidis, G.; Kadoglou, N.; Makavos, G.; Katogiannis, K.; Kountouri, A.; Thymis, J.; Kostelli, G.; Kapniari, I.; Theodoropoulos, K.; Parissis, J.; Katsimbri, P.; Papadavid, E.; Lambadiari, V. Apremilast Improves Endothelial Glycocalyx Integrity, Vascular and Left Ventricular Myocardial Function in Psoriasis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Sailer, N.; Moumtzouoglou, A.; Kapelouzou, A.; Gerasimidis, T.; Kostakis, A.; Liapis, C.D. Adipokines: A novel link between adiposity and carotid plaque vulnerability. Eur J Clin Invest. 2012, 42, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.K. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2009, 23, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsis, A.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Lambadiari, V.; Alexiou, S.; Theodoropoulos, K.C.; Avraamides, P.; Kassimis, G. Prognostic role of inflammatory cytokines and novel adipokines in acute myocardial infarction: An updated and comprehensive review. Cytokine. 2022, 153, 155848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Korakas, E.; Karkos, C.; Maratou, E.; Kanonidis, I.; Plotas, P.; Papanas, N.; Moutsatsou, P.; Ikonomidis, I.; Lambadiari, V. The prognostic role of RBP-4 and adiponectin in patients with peripheral arterial disease undergoing lower limb endovascular revascularization. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, I.; Sciangula, A.; Perrotta, E.; Donato, G.; Cassese, M. Ultrastructural analysis and electron microscopic localization of Nox4 in healthy and atherosclerotic human aorta. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2011, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Johnson, J.A.; Fulp, A.; Sutton, M.A.; Lessner, S.M. Adhesive strength of atherosclerotic plaque in a mouse model depends on local collagen content and elastin fragmentation. J Biomech. 2013, 46, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalz, J.; Ten Cate, H.; Spronk, H.M. Thrombin generation and atherosclerosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014, 37, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, D.; Sanchez, A.; Yin, X.; Luo, J.; Martinez, J.; Grammas, P. Thrombin, a mediator of cerebrovascular inflammation in AD and hypoxia. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina-Canseco Mdel, S.; Páez-Arenas, A.; Massó, F.; Pérez-Campos, E.; Martínez-Cruz, R.; Hernández-Cruz, P.; Majluf-Cruz, A.; et al. Protein C activation peptide inhibits the expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and interleukin-8 induced by TNF-α in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasinski, F.; Bacurau, R.F.; Moraes, M.R.; Haro, A.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Estrela, G.R.; et al. Exercise and caloric restriction alter the immune system of mice submitted to a high-fat diet. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 395672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, V.; Yin, J.; Mirza, A.M.; Phan, D.; Vanegas, S.; Issafras, H.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-1 beta reduce biomarkers of atherosclerosis in vitro and inhibit atherosclerotic plaque formation in Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 2011, 216, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.H.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, H.O.; Jo, Y.H.; Yoon, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Plaque rupture is a determinant of vascular events in carotid artery atherosclerotic disease: Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. J Clin Neurol. 2011, 7, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Valsami, G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N. Exercise training inhibits atherosclerosis progression and reduces VE-cadherin levels within atherosclerotic plaques in hypercholesterolemic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022, 623, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, M.R.; Niessen, H.W.; Löwik, C.W.; Hamming, J.F.; Jukema, J.W.; Quax, P.H. (2012) Plaque rupture complications in murine atherosclerotic vein grafts can be prevented by TIMP-1 overexpression. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e47134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Sailer, N.; Fotiadis, G.; Kapelouzou, A.; Liapis, C.D. The impact of type 2 diabetes and atorvastatin treatment on serum levels of MMP-7 and MMP-8. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2014, 122, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagtzidis, I.T.; Kadoglou, N.P.; Mantas, G.; Spathis, A.; Papazoglou, K.O.; Karakitsos, P.; Liapis, C.D.; Karkos, C.D. The Profile of Circulating Matrix Metalloproteinases in Patients Undergoing Lower Limb Endovascular Interventions for Peripheral Arterial Disease. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017, 43, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasinopoulou, M.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Christodoulou, E.; Paronis, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Valsami, G.; Liapis, C.D.; Kakisis, J. Statins' Withdrawal Induces Atherosclerotic Plaque Destabilization in Animal Model-A "Rebound" Stimulation of Inflammation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019, 24, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CG (n=12) |
DEG (n=12) |
ETG (n=12) |
DE+ETG (n=12) |
p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | |||||
| Baseline | 27.8±4.6 | 28.5±7 | 28.3±5.1 | 27.2±4 | 0.881 |
| End | 31.1±4.1 | 32.23±6.3 | 29.8±2.7 | 29.7±5 | 0.321 |
| FPG (mg/dl) | |||||
| Baseline | 113±28 | 108±31 | 103±21 | 120±41 | 0.773 |
| End | 165±44* | 189±45* | 165±52* | 182±49* | 0.654 |
| TC (mg/dl) | |||||
| Baseline | 358±145 | 398±103 | 404±198 | 387±134 | 0.298 |
| End | 684±169* | 612±223* | 556±110* | 579±311* | 0.112 |
| TG (mg/dl) | |||||
| Baseline | 82±13 | 84±21 | 89±28 | 94±31 | 0.498 |
| End | 125±29* | 115±24* | 126±31* | 116±32* | 0.687 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





