1. Introduction
In contemporary microelectronics, there exists a compelling need to achieve enhanced functionality and superior properties within confined spatial constraints. For instance, consider today's smartphones, which have become substantially smaller yet capable of accommodating a myriad of functions compared to their predecessors. This phenomenon aligns with what is known as Moore's Law within the integrated circuits (ICs) industry, a theory postulating that the number of transistors on densely packed ICs doubles approximately every two years [
1]. In tandem with this progression, electronic packaging techniques have also advanced significantly. To meet the demands of modern electronics, characterized by a desire for slimmer, smaller, and lighter devices, Chip Size Package (CSP) technology was introduced [
2].
Among the various integrated chip package systems, Three-Dimensional Integrated Circuits (3D ICs) have emerged as a promising solution to address the imperative of integrating more functionalities while circumventing the limitations set by Moore's Law [
3]. 3D IC packaging stands as an innovative approach in semiconductor packaging, offering superior performance, energy efficiency, and spatial utilization. This technology involves the vertical stacking of multiple semiconductor dies, interconnected through Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs), culminating in a single compact package [
4]. Nevertheless, the manufacturing of 3D ICs poses formidable challenges. Concerns encompass issues such as heat dissipation within confined regions due to the misalignment of TSVs during chip stacking [
4]. These thermal issues necessitate effective heat dissipation strategies, demanding efficient thermal interfaces to ensure optimal performance.
In the realm of power modules, which encompass numerous power semiconductor dies, electronic packaging technologies play a pivotal role. These module packages facilitate electrical interconnections, thermal management, and mechanical support for semiconductor devices. Innovations have proliferated to enhance the thermal, electrical, and mechanical performance of power modules. Notably, these semiconductors are increasingly operated at elevated junction temperatures to achieve reductions in size and weight for converters. This shift is particularly pertinent when deploying wide-bandgap materials such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN), as they harness their unique material properties [
5]. Silicon-based power components, in comparison, can no longer fulfill these exacting requirements. SiC, for example, boasts a threefold greater energy gap, sixfold greater breakdown electric field strength, and triple the thermal conductivity compared to conventional silicon (Si) [
6]. Silicon carbide exhibits notable characteristics, including a high energy gap of 2.86 eV, excellent carrier mobility, thermal conductivity, and various other superior properties. Consequently, SiC power semiconductors have garnered substantial attention in both research and early mass production in recent years, positioning SiC as a promising semiconductor material for the future.
The deposition of thin films on the backside of SiC wafers necessitates careful consideration of thermal expansion coefficients, adhesion properties, and heat-dissipating materials. In this context, the choice of metal for the backside layer assumes critical importance, favoring metals with high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical properties, such as copper. An emerging aspect of importance relates to fabricating materials with unique microstructures that encompass smaller average grain sizes, higher yield strengths, hardness, and rapid diffusion paths, coupled with enhanced structural stability under elevated operating temperatures and reduced electrical resistance. The nanotwinned structure emerges as a compelling solution by virtue of its inherent attributes [
7,
8,
9]. Coherent twin boundaries (CTBs), in particular, are commonly perceived as inherently resistant to dislocation slip and tend to exhibit electrical resistivity approximately one order of magnitude lower than that observed in high-angle grain boundaries. Consequently, a copper structure characterized by a high density of nanotwins emerges as an apt choice owing to its commendable mechanical properties [
10,
11]. Additionally, it offers favorable electrical conductivity, along with proficient electromigration resistance and superior thermal stability [
8].
Fundamentally, the backside metallization (BSM) process functions as a versatile instrument for enhancing the performance of Silicon Carbide devices. BSM entails the deposition of a metal layer onto the backside of a semiconductor wafer. While the front side of the wafer houses active components, the backside, through the metallization process, transforms into a functionally vital element, significantly impacting overall device performance [
12]. Magnetron sputtering, notably, has emerged as a prominent technique for this purpose. It entails bombarding a metal target with high-energy ions, causing metal atoms to be ejected and deposited uniformly onto the wafer surface [
13]. This process ensures strong adhesion and uniformity of the metallization layer.
To further enhance the capabilities of this approach, researchers have explored the deposition of high-density (111)-textured Cu nanotwins onto SiC wafers. Zhang et al. conducted a series of studies involving the deposition of nanotwinned 330 stainless steels and copper (Cu) using magnetron sputtering [
14,
15,
16,
17]. They exercised precise control over twin thickness by modulating the deposition rate. These samples exhibited a robust <111> texture, and TEM images revealed an average columnar grain size of approximately 50 nm, accompanied by a high twin density. Furthermore, nanotwinned structures were successfully fabricated in materials characterized by high stacking fault energy, as demonstrated by Bufford et al., [
18]. In parallel research endeavors, Hodge et al. [
19,
20,
21] also employed magnetron sputtering to generate columnar nanotwinned Cu films. Subsequently, researchers conducted an in-depth examination of atomic-level structural features within these twin boundaries and grain boundaries, their findings unveiled a prominent <111> fiber texture in the samples, along with an appreciable fraction of low-angle grain boundaries, even though the columnar boundaries predominantly comprised random high-angle boundaries, as elucidated by Morris Wang et al., and Lagrange et al., [
22,
23]. Furthermore, the coherent twin boundaries exhibited inherent defects in the form of kink-like steps and curvature, which exerted discernible influences on the deformation mechanisms and mechanical behavior of nanotwinned Cu. These nanoscale structures exhibit a well-ordered crystalline arrangement predominantly oriented along the (111) crystallographic plane, endowing them with superior electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. Cu nanotwins hold great potential for revolutionizing the semiconductor industry, enabling the creation of more efficient interconnects, electrodes, and nano-electronic components. To achieve successful integration, in this research, a chromium (Cr) adhesive layer is utilized as an intermediary, facilitating Cu adhesion to SiC while preventing detrimental interfacial reactions. Its intermediate thermal expansion coefficient, which lies between that of copper and silicon carbide, makes it conducive for mitigating thermal stress-induced delamination at the substrate-interface interface [
24].
Furthermore, in order to improve the viability of direct bonding, it is essential that the copper (Cu) nanotwinned films clearly favor the (111) crystallographic orientation, thereby optimizing atomic diffusivity. Nevertheless, a challenge arises from the presence of transition layers at the lower portion of nanotwinned films, characterized by numerous randomly-oriented grains. Unlike columnar grains hosting a high density of nanotwins, these randomly-oriented grains exhibit larger interfacial energy and lack structural regularity. Consequently, these irregularities introduce vulnerabilities in nanotwinned films, leading to a reduced proportion of (111) orientation and compromised thermal stability [
25]. To address this issue, the present study employed magnetron sputtering with negative substrate bias voltages. Substrate bias, achieved through the application of voltage to the substrate, significantly influences the energy, trajectory, and adhesion of sputtered Cu atoms as they impinge upon the SiC surface. This interplay between substrate bias and nanotwin growth mechanisms holds the potential to dictate the final film quality, texture, and crystallographic orientation. This approach was instrumental in reducing the thickness of the transition layers and promoting the desired (111) crystallographic orientation within the Cu nanotwinned films. The study delves into the underlying mechanisms responsible for the influence of substrate bias on the promotion of high-density nanotwinned structures.
2. Materials and Methods
The fabrication of copper (Cu) thin films in this experiment was conducted using a direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering system, specifically the JUBSUN TECH SGS-500 model. The deposition process was executed under controlled conditions, with a base pressure maintained at levels below 5 × 10−6 Torr (6 × 10−4 Pa). Argon gas, held at a consistent pressure of 5 milliTorr (0.67 Pa), was employed as the working gas throughout the deposition procedure. Prior to commencing each film deposition, a pre-sputtering step of 10 minutes duration was applied to all target surfaces to minimize potential contamination. Furthermore, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrates were subject to a thorough cleaning sequence involving acetone, ethanol, and deionized water to enhance adhesion during the deposition process. Preceding deposition, an argon discharge was administered to the substrate at a negative bias of -500 V for a duration of 5 minutes to eliminate any surface oxide layer. Subsequent to this surface treatment, the Cu films were sputtered using a sputtering power of 300 W with the layer’s thickness is 2 µm. Additionally, a chromium (Cr) layer was pre-coated onto the substrate, utilizing a power of 150 W, with thickness 100 nm, to serve as an adhesive intermediary, promoting the adhesion between the Cu film and the substrate. To facilitate Ar ion bombardment during deposition, various negative substrate biases (-100, -150, -200, and -250 V) were applied. Following the deposition process, the samples were allowed to cool to room temperature within the deposition chamber.
Subsequently, the fabricated Cu film samples underwent in-depth analysis. Initially, a focused ion beam (FIB) instrument, specifically the Hitachi NX2000 model, was employed to scrutinize the microstructure of the thin films. For more detailed microscopic examination, an electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis was conducted to investigate the grain orientations on the surfaces of the Cu films. The crystallographic data from EBSD patterns were extracted using the Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) software developed by TSL in the United States. Finally, the crystal orientations and texture of the Cu films were determined through X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, utilizing the Rigaku TTRAX XRD instrument.
3. Results
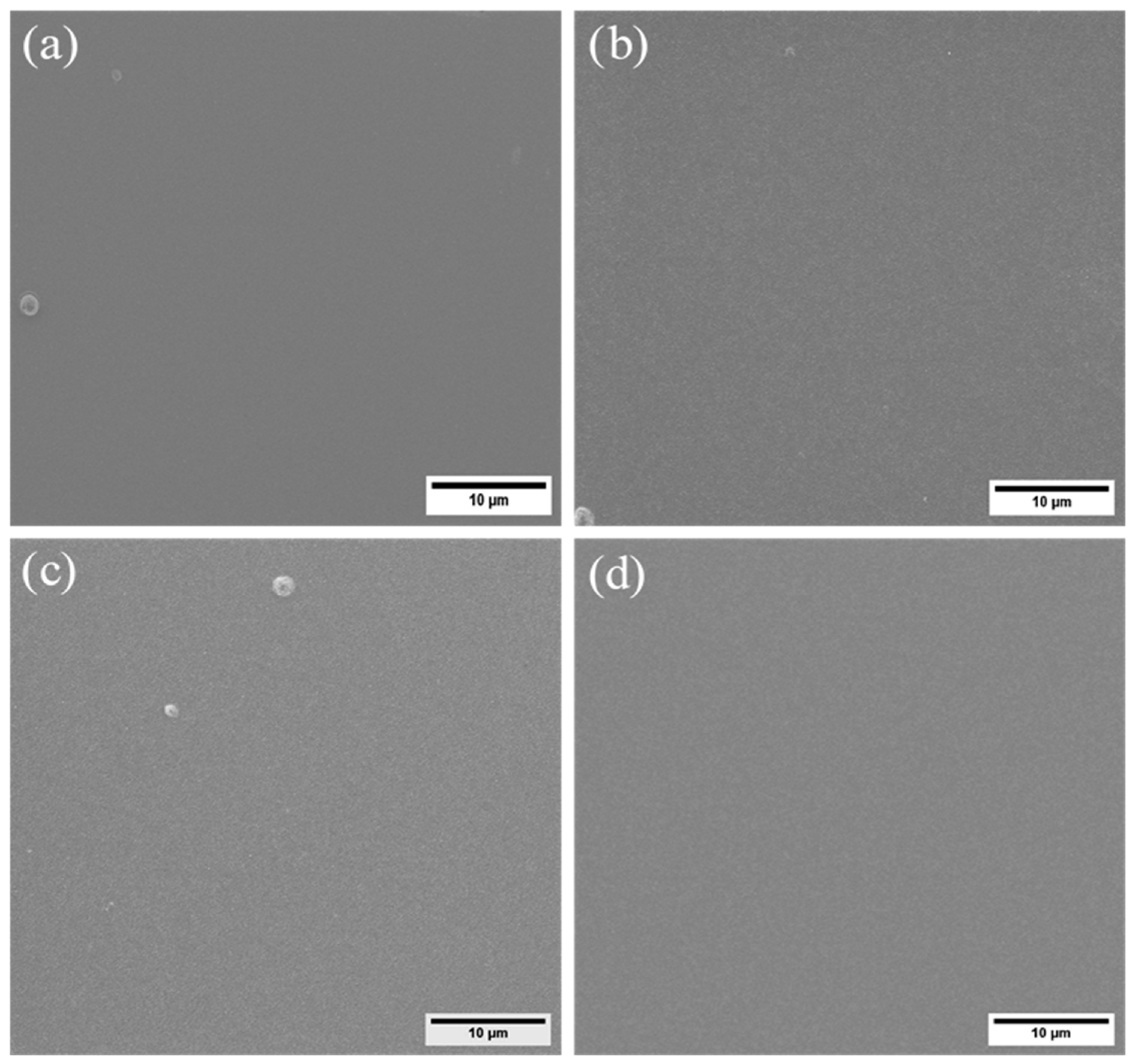
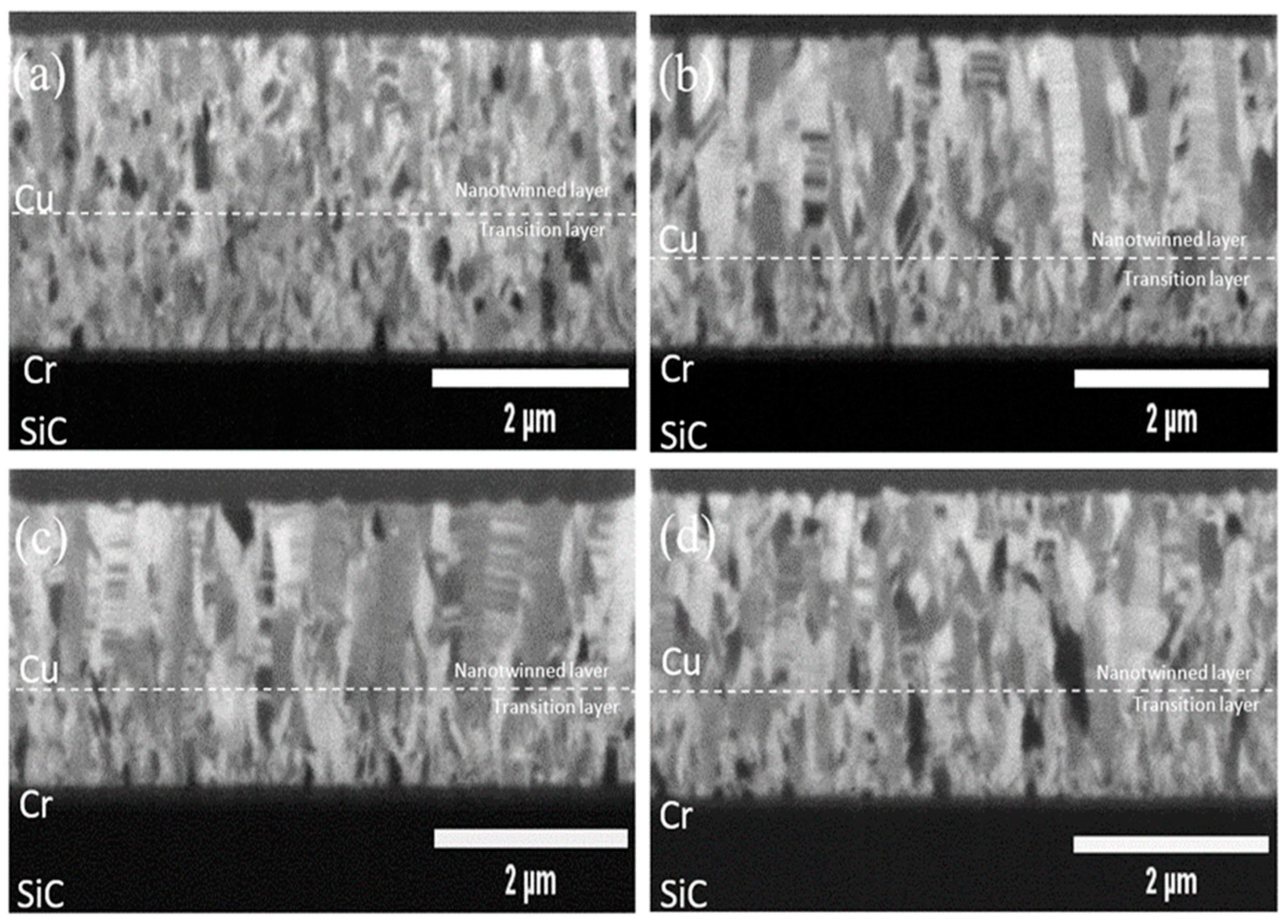
In
Figure 1 and
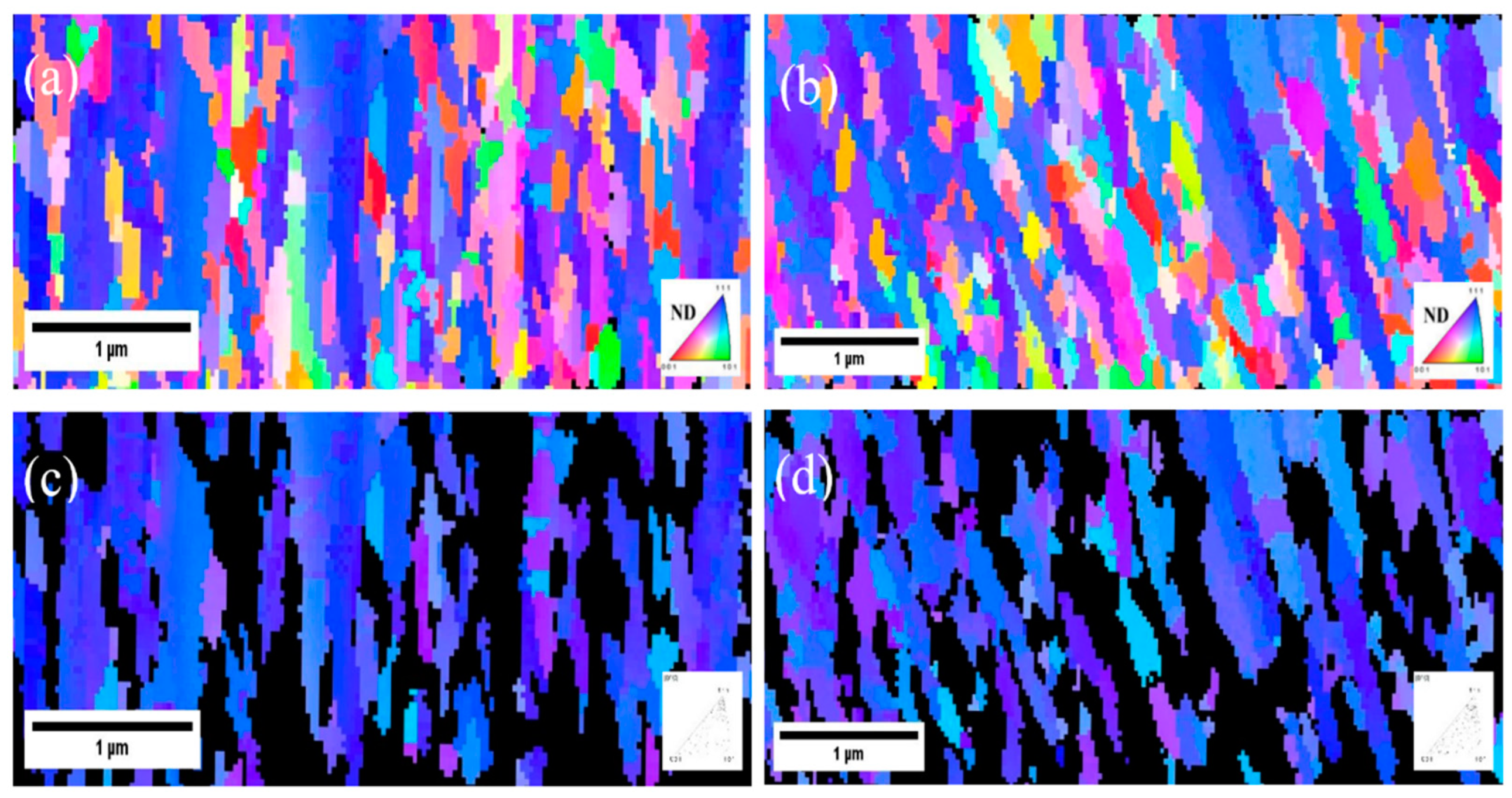
Figure 2, the focused ion beam (FIB) metallography images depict the top view and cross-section of nanotwinned copper (nt-Cu) films sputtered onto silicon carbide (SiC) substrates pre-coated with a chromium (Cr) layer. These films were subjected to varying substrate bias voltages during the deposition process. Notably, when a -100V substrate bias voltage was applied, the nt-Cu films exhibited a distinctive feature: the persistent presence of large-grain twin crystals, albeit in a significantly reduced proportion. This phenomenon was accompanied by a marked increase in the prevalence of columnar structures, concurrent with a substantial rise in the proportion of nanotwinned grains. Meanwhile, the sputtered Cu without substrate bias already investigated by [
25] showing the polycrystalline copper (Cu) grains exhibited a uniform distribution across the entirety of the thin film, and no discernible presence of copper nanotwins was detected within the cross-sectional analysis. Upon intensifying the substrate bias voltage to -150V (Fig. 2b), a conspicuous absence of large-grain annealed twin crystals was observed in the copper film. It becomes evident that as the negative substrate bias increased, there was a tendency for the densely-stacked nanotwinned columnar grain structures to become more dominant. Consequently, a distinct dual-layered architecture emerged, comprising a lower transition layer and an upper nanotwin layer. The transition layer, characterized by disordered small grains, exhibited relatively greater prominence than the nanotwin layer. This structural configuration remained consistent as the substrate bias voltage was further increased to -200V, with minimal deviation from the -150V configuration. This structural trend persisted until the substrate bias voltage reached -250V. Remarkably, the transition layer notably diminished, while the proportion of columnar grains underwent a discernible increase. However, the nanotwin structures experienced a significant reduction, giving way to larger twin crystals.
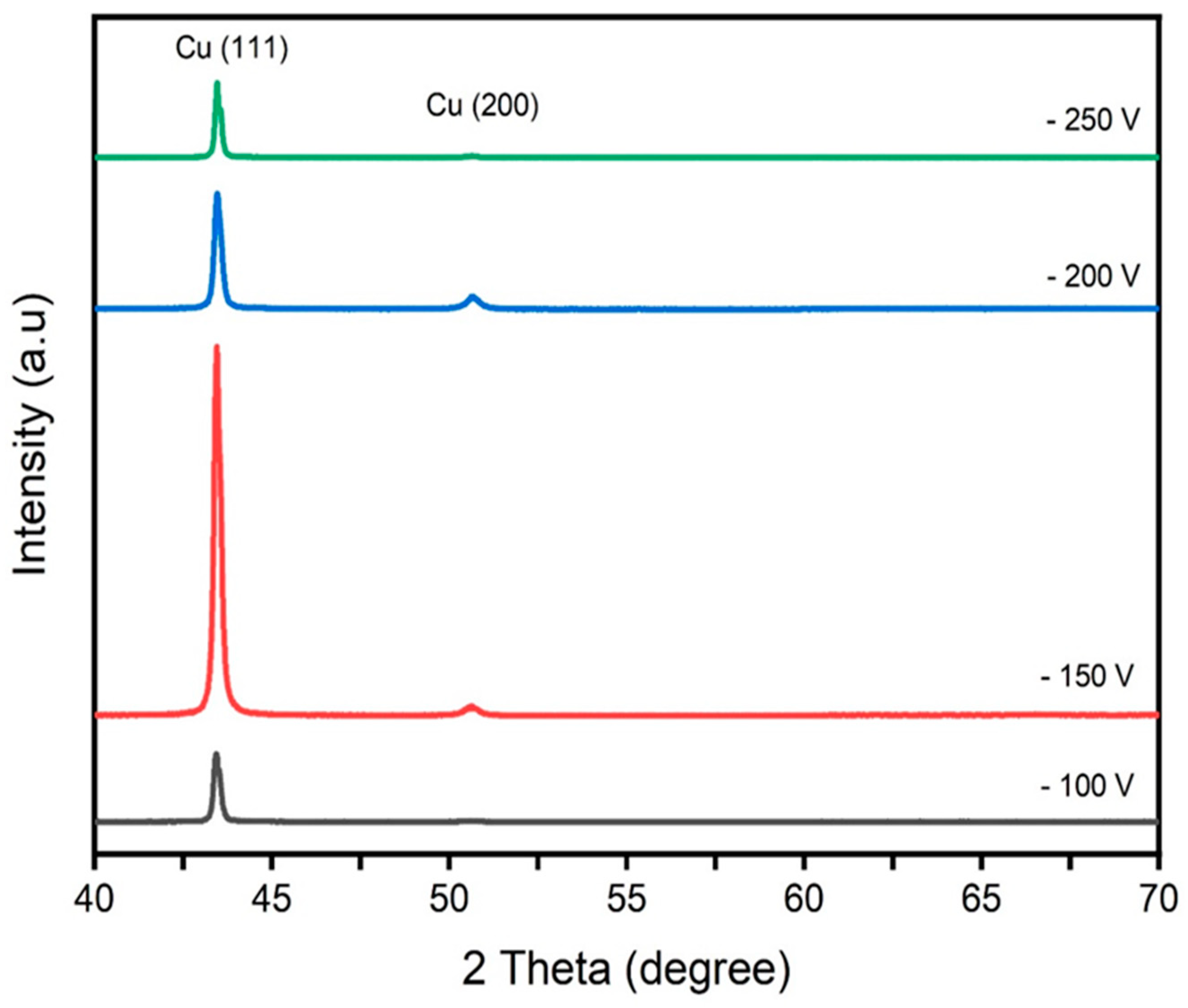
Crystallographic orientation analysis through X-ray diffraction highlighted that copper films deposited across the spectrum of bias voltages predominantly favored a (111) crystal orientation, albeit with significant signal intensity fluctuations. This is illustrated in
Figure 3, which underscores the profound influence of applied bias voltage on the signal intensity of the (111) orientation. Crucially, copper films deposited under -150V exhibited the most robust (111) crystal orientation signal. As bias voltage surpassed -150V, the intensity exhibited a gradual decline. However, even in comparison to copper films lacking substrate bias voltage, the (111) orientation signal remained substantially amplified. Supplementary quantitative analysis was performed using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) techniques (
Figure 4). Furthermore, the application of negative bias voltage to the substrate attracted a multitude of positive ions, precipitating ion bombardment effects. During the process of film deposition, atoms with weak bonding in the film layer experienced sputtering due to the positive ions drawn by the negative bias voltage. This process engendered re-sputtering effects. The escalation of substrate bias voltage corresponded to an augmentation in the energy of incident positive ions, which intensified re-sputtering and consequently led to diminished deposition rates.
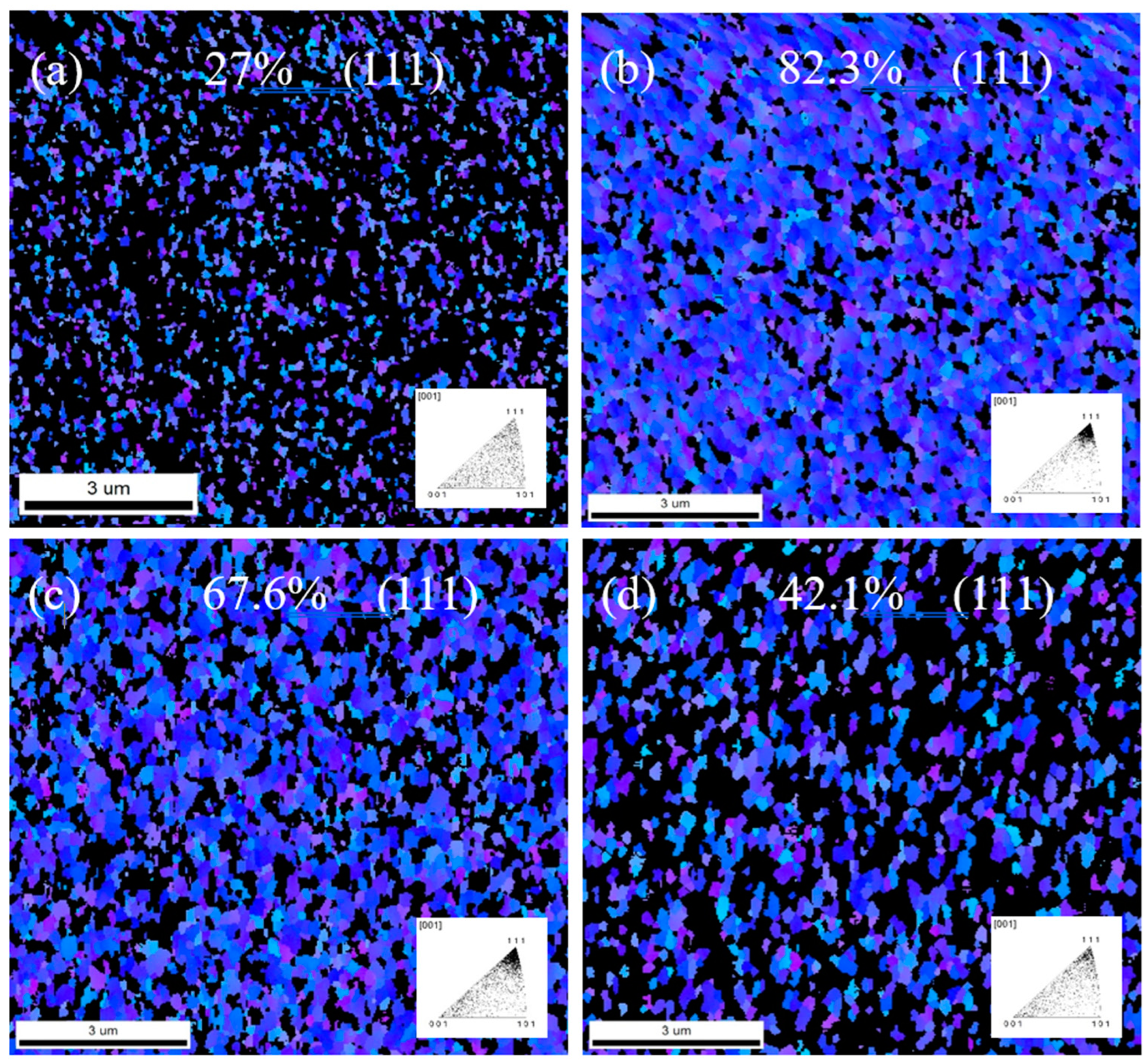
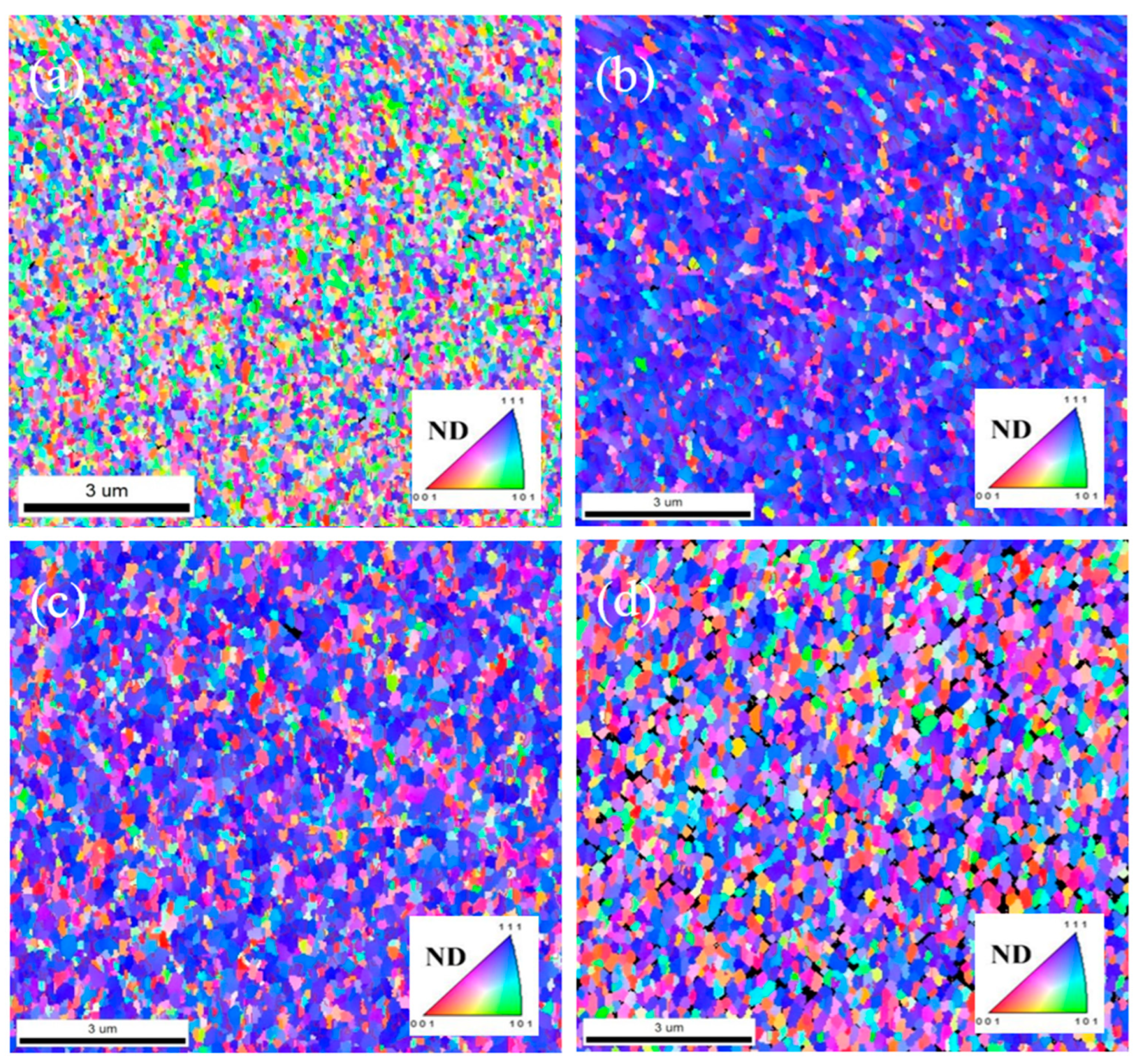
Based on the cross-sectional ion images obtained from FIB, it can be observed that under lower negative substrate bias, the copper film exhibits a polycrystalline structure. The surfaces of nanotwinned Cu films must meet a crucial criterion for further bonding applications, that is the percentage of (111)-orientation. To further characterize the grain orientations of the Cu thin films, a top-viewEBSD measurements were conducted and shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5.
Figure 4a shows the (111) proportion is only 27% for bias -100 V. Correspondingly, some nanocrystalline structures begin to emerge on the surface in the cross-sectional ion images. Increasing the bias to -150V (Fig.4b) leads to a significant increase in the proportion of (111) orientation on the surface, reaching 82.3%. Compared to -100V, the overall structure now contains more high-density nanocrystalline structures, with a higher (111) orientation and the copper film exhibits highly ordered columnar nanocrystalline structures. From plan-view EBSD images, it can be observed that the copper film surface displays a high (111) orientation with bias -150 V. This orientation improvement is highly beneficial for future low-temperature bonding. As the substrate bias increases to -200V, the (111) orientation decreases to 67.6% of the total surface area. However, at -250 V bias, the nanocrystalline structures become less organized compared to -200 V, and the nanocrystalline density significantly decreases. EBSD images reveal that the (111) proportion drops substantially to 42.1%. Based on these results, the quantity of nanocrystalline structures directly affects the proportion of surface (111) orientation. From the current experimental findings, -150V is the optimal sputtering parameter, resulting in the highest density of nanocrystalline structures on the overall copper film, along with a highly preferred (111) orientation. This suggests that substrate bias not only influences the generation and development of sputter deposition structures but also has a significant impact on crystal orientation.
Furthermore, an analysis of the grain boundaries within the Cu films presented in
Figure 5a–d. The distribution of misorientation angles is used to quantify the proportion of general grain boundaries and CSL-Σ3 twin boundaries.
Figure 5a revealed that they comprised 9% Columnar Symmetric Low-Angle Tilt (CSL-Σ3) boundaries and 2% CSL-Σ9 boundaries in relation to the total grain boundaries, which is the lowest propotion obtained by substrate bias -100 V. In contrast, the Cu films depicted in
Figure 5b with substrate bias -150 V exhibited a higher fraction of CSL-Σ3 boundaries, accounting for 33.7% of the total grain boundaries, with only 3.2% attributed to CSL-Σ9 boundaries. These findings underscore the significant influence of substrate bias in facilitating the formation of nanotwins and promoting a <111> crystallographic texture in Cu films. It is worth noting that the high diffusivity characteristic of the Cu (111) plane, in comparison to the (111), (110), and (100) planes, suggests that the application of substrate bias is particularly effective in enhancing bonding quality, leveraging the advantageous properties of the Cu (111) plane.
The insights provided in
Figure 6 offer a compelling visualization of the predominant growth pattern of columnar copper (Cu) grains, which intriguingly align along the (111) crystallographic direction. This alignment of grain growth along the (111) direction is indicative of a well-defined crystalline orientation preference. Further examination of the data yields noteworthy proportions of certain boundaries within the copper films. Specifically, for the Cu films fabricated on chromium (Cr) pre-coated substrates with substrate biases of -150 V and -200 V, the proportions of Σ3 coincident twin boundaries - a specific type of grain boundary structure - relative to the total grain boundaries are observed to be 49.9% and 42%, respectively. Additionally, the proportions of CSL-Σ9 near twin boundaries - another distinct type of grain boundary configuration - for the substrate biases of -150 V and -200 V amount to 3.1% and 2.6%, respectively. These findings imply that the Cu film cultivated under the bias of -150 V exhibits the highest twin density in terms of these specific boundaries. This result corroborates the earlier observations from the cross-sectional metallography depicted in
Figure 4 and
Figure 6a,b.
Moreover, the study ventures further to analyze the distribution of other grains within the Cu film that deviate from the [111] direction by more than 15°. These distinct grains are represented as black regions in
Figure 6c,d. This analysis underlines the selective prevalence of the (111) orientation across the nanotwinned Cu film surface. Specifically, it becomes apparent that 61.4% of the nanotwinned Cu film surface maintains the (111) orientation when grown under the -150 V bias condition. In comparison, the bias condition of -200 V yields a slightly reduced prevalence of the (111) orientation, with only 60.4% of the surface adhering to this crystallographic orientation.
These nuanced observations accentuate the intricate interplay between substrate bias, crystalline orientations, and grain boundary structures within the fabricated copper films. The high twin density exhibited by the Cu film grown under -150 V bias further substantiates the influence of bias conditions on crystallographic orientations and the associated grain boundary configurations. This understanding is pivotal in optimizing the synthesis of materials with desired microstructural attributes, which subsequently impact their mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties for various applications.
4. Discussion
The bias voltage applied to the substrate has a direct impact on the energy of ions during their bombardment of the surface where thin film growth takes place as the results above. Consequently, this deposition parameter is expected to exert a substantial influence on the microstructure of the thin film as it is initially deposited. Higher substrate bias voltages lead to increased levels of compressive stress, enhanced surface mobilities, greater implantation of impinging particles, and increased displacement of lattice atoms. These factors collectively facilitate the introduction of additional stacking faults, which then accumulate and evolve into twin boundaries within the material. A thermodynamic model predicts that a higher deposition rate, often achieved through elevated target power, enhances the likelihood of the formation and growth of these twinned nuclei in the thin film [
15].
Nonetheless, the present investigation does not exhibit this phenomenon; instead, a greater prevalence of nanotwin structures is evident in the coating deposited at a lower deposition rate. While the precise underlying factors for this observation remain ambiguous, it is hypothesized that the mechanisms governing film growth and twin formation during magnetron sputtering are subject to kinetic control. Consequently, the applicability of the thermodynamic model in comprehensively elucidating this behavior is constrained [
26]. In practical terms, the process of film growth during magnetron sputtering is primarily governed by kinetics, rendering it challenging to provide a comprehensive description solely through thermodynamic models. While the thermodynamic model mentioned in the preceding section suggests that elevated deposition rates should result in increased twin density, multiple experimental studies have contradicted this prediction. Moreover, alterations in twin spacing are often concurrent with shifts in grain size. These challenges arise from the interdependence of adatom kinetic energy and flux, both of which significantly influence the film growth process and rates of twin formation. Unfortunately, these factors are inherently linked to the same tunable sputtering parameters, rendering independent control challenging [
27].
Additionally, The Cr interlayer can reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between Cu-SiC substrate and can smooth the difference in lattice parameters at the interface by effectively absorbs some of this differential expansion, acting as a buffer zone. Zi Hong and coworkers have reported that the Cu nanotwinned thin film produced through sputtering and subjected to surface activation displayed a thinner transition layer. This layer consisted of randomly oriented grains, potentially serving as a structural weak point that could compromise the uniformity of the nanotwinned films. In contrast, the Cu nanotwinned thin film sputtered without surface activation exhibited a thicker transition layer [
28].
Chromium can create strong chemical bonds with both the Cu layer and the SiC film as an adhesion layer [
29]. This characteristic enhances the adhesion between the Cu layer and the SiC substrate, preventing the Cu film from delaminating or peeling. It acts as a barrier layer, preventing atoms from diffusing between the Cu layer and the SiC substrate. At elevated temperatures, copper has a tendency to diffuse into silicon-based materials such as SiC, which can cause material degradation and device failure. Thus, Cr adhesion layer inhibiting diffusion and preserving the structure's integrity. As a result, the Cr interlayer creates a transitional region where the lattice parameters gradually change from those of SiC to those of Cu. This gradual transition reduces abrupt changes at the Cu-SiC interface, minimizing stress and defects.
The application of a suitably biased substrate is also recognized for its capacity to enhance the adhesive properties of magnetron-sputtered coatings. This improvement stems from the additional energy made available to the growing film, as high-energy atoms tend to migrate towards low-energy sites on the surface to optimize their adhesion characteristics. This phenomenon was prominently observed in the samples subjected to substrate bias due to the multifaceted advantages it confers. When a negative substrate bias voltage was employed during deposition, it led to the attraction of Ar+ ions for the bombardment of the films. As the magnitude of the applied negative substrate bias increased, a greater number of Ar+ ions possessing higher energy levels were drawn in to bombard the films, thereby altering the translational kinetic energy of the adatoms. As these high-energy Ar+ ions collided with the surface atoms of the films, the mobility of the atoms was augmented, resulting in a reduction in the formation of voids and the development of finer faceted columns.
It is evident that the film deposited with substrate bias, as depicted in
Figure 2b, exhibited finer and more densely packed faceted columns, with a concurrent reduction in the thickness of the transition region. This refinement and densification of the grains typically correlates with an increase in the hardness of the coatings. Furthermore, as the grains were refined to the nanoscale, a greater number of grain boundaries and free surfaces characterized by higher energy levels were generated, creating more nucleation sites for the formation of nanotwins. From the aforementioned discussion, it can be deduced that the addition of substrate bias, when appropriately applied, results in the densification and improved lattice arrangement of the crystal structure. This, in turn, promotes the nucleation of nanotwins, characterized by a higher proportion of (111)-crystal orientation, as depicted in
Figure 4b. In essence, this process swiftly transforms copper thin films into a nanotwinned columnar layer, thereby enhancing overall film quality.
5. Conclusions
In this investigation, the influence of varying substrate biases on the microstructural and crystallographic characteristics of copper (Cu) films was systematically examined. The observed augmentation in nanotwin formation is believed to be attributed to ion bombardment and the presence of a chromium (Cr) adhesive layer. Notably, the Cu film sputtered with a substrate bias of -150 V demonstrated better properties, with thinner transition layer and higher twin density. These were characterized by a high-density of Cu nanotwinned structures predominantly oriented along the (111) crystallographic plane. This particular nanotwinned film exhibits the potential to enhance the performance of backside metallization processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.-H.C., and M.-T.C.; data curation, D.I.S., M.-T.C., and T.-H.C.; investigation, T.-H.C., and M.-T.C.; methodology, M.-T.C., and T.-H.C.; writing—original draft, D.I.S.; writing—review and editing, D.I.S.; supervision, T.-H.C.; project administration, T.-H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was sponsored by the Emerging Technology Application Program of the Hsinchu Science Park R & D program of Ag Materials Technology Co., LTD under Grant No. 112AO03A.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in any capacity, competing or financial.
References
- S. Thompson and S. Parthasarathy. Moore’s Law: the future of Si microelectronics. Mater today 2006. 9, 5–20. [CrossRef]
- P. Garrou. Wafer Level Chip Scale Packaging (WL-CSP): An Overview. Fellow IEEE 2000. 23, 198-205. [CrossRef]
- S. Kumar. Fundamental Limits to Moore’s Law. ArXiv 2015.
- Haji-Sheikh, M. A. Amaya, R. Raihan, Z. Celik-Butler, and F. Mirza. Reliability Enhancement of Heterogeneous 3D Integrated Circuit And Characterization of Thermal Interface Material. 2020.
- Z. Liang, P. Ning, and F. Wang. Development of advanced all-sic power modules. IEEE Trans Power Electron 2014. 29, 2289–2295.
- Neeb, L. Boettcher, M. Conrad, and R. W. de Doncker. Innovative and reliable power modules: A future trend and evolution of technologies. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine 2014. 8, 6–16. [CrossRef]
- L. Lu, X. Chen, X. Huang, and K. Lu. Revealing the Maximum Strengthin Nanotwinned Copper. Science 2009. 323, 603–607.
- X. Zhang and A. Misra. Superior thermal stability of coherent twin boundaries in nanotwinned metals. Scr Mater 2012. 66, 860–865. [CrossRef]
- Anderoglu, A. Misra, H. Wang, F. Ronning, M. F. Hundley, and X. Zhang. Epitaxial nanotwinned Cu films with high strength and high conductivity. Appl Phys Lett 2008. 93, 8. [CrossRef]
- Detavernier, D. Deduytsche, R. L. Van Meirhaeghe, J. De Baerdemaeker, and C. Dauwe. Room-temperature grain growth in sputter-deposited Cu films. Appl Phys Lett 2003. 1863–1865. [CrossRef]
- X. Tong, G. You, Y. Ding, H. Xue, Y. Wang, and W. Guo. Effect of grain size on low-temperature electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of pure magnesium. Mater Lett 2018. 229, 261–264. [CrossRef]
- K. H. Yeap, H. Nisar, and V. Dakulagi. Warpage reduction for power mosfet wafers. Electrica 2021. 21, 173–179. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xie, Q. Wang, L. Han, and D. Wu. Study on Ion Bombardment Semiconductor Shaped Self-Assembled Nanostructures. Academic Journal of Materials & Chemistry 2023. 4, 4. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, A. Misrah, H. Wang, M. Nastasi, J.Embury, T.Mitchell, R.Hongland, J.Hirth. Nanoscale-twirming-induced strengthening in austenitic stainless steel thin films. Appl Phys Lett 2004. 84, 1096–1098.
- X. Zhang, A. Misrah, H. Wang, T.D. Shen, M. Nastasi, T. Mitchell, J.Hirth, R.Hongland, J.Embury. Enhanced hardening in Cu/330 stainless steel multilayers by nanoscale twinning. Acta Mater 2004. 52, 995–1002. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, H. Wang, H.X Chen, L. Lu, K. Lu, R.G Hoagland, A. Misra. High-strength sputter-deposited Cu foils with preferred orientation of nanoscale growth twins. Appl Phys Lett 2006. 88, 17. [CrossRef]
- Anderoglu, A. Misra, H. Wang, F. Ronning, M. F. Hundley, and X. Zhang. Epitaxial nanotwinned Cu films with high strength and high conductivity. Appl Phys Lett 2008. 93, 8. [CrossRef]
- Bufford, Z. Bi, Q. X. Jia, H. Wang, and X. Zhang. Nanotwins and stacking faults in high-strength epitaxial Ag/Al multilayer films. Appl Phys Lett 2012. 101, 22. [CrossRef]
- M. Hodge, Y. M. Wang, and T. W. Barbee. Mechanical deformation of high-purity sputter-deposited nano-twinned copper. Scr Mater 2008. 59, 163–166. [CrossRef]
- M. Hodge, Y. M. Wang, and T. W. Barbee. Large-scale production of nano-twinned, ultrafine-grained copper. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2006. 429, 272–276.
- J. Shute et al. Detwinning, damage and crack initiation during cyclic loading of Cu samples containing aligned nanotwins. Acta Mater 2011. 59, 4569–4577. [CrossRef]
- Y. Morris Wang, F. Sansoz, T. Lagrange, R.T. Ott, J. Marian. T.W Barbee. A.V. Hamza. Defective twin boundaries in nanotwinned metals. Nat Mater 2013. 12, 697–702. [CrossRef]
- T. Lagrange, B. W. Reed, M. Wall, J. Mason, T. Barbee, and M. Kumar. Topological view of the thermal stability of nanotwinned copper. Appl Phys Lett 2013. 102, 1. [CrossRef]
- V. K. Khanna. Adhesion-delamination phenomena at the surfaces and interfaces in microelectronics and MEMS structures and packaged devices. J Phys D Appl Phys 2011. 44, 3. [CrossRef]
- Z. H. Yang, P. C. Wu, and T. H. Chuang. Effects of substrate bias on the sputtering of high density (111)-nanotwinned Cu films on SiC chips. Sci Rep 2022. 12, 1. [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z. Zhou, Z. Xie, and P. Munroe. High entropy alloy FeMnNiCoCr coatings: Enhanced hardness and damage-tolerance through a dual-phase structure and nanotwins. Surf Coat Technol 2020. 385. [CrossRef]
- C. Bufford, Y. M. Wang, Y. Liu, and L. Lu. Synthesis and microstructure of electrodeposited and sputtered nanotwinned face-centered-cubic metals. MRS Bull 2016. 41, 286–291. [CrossRef]
- Z. H. Yang, Y. T. Chen, and T. H. Chuang. Growth of Cu nanotwinned films on surface activated SiC chips. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2023. 34, 23. [CrossRef]
- C. H. Vu, D. W. Seo, H. J. Kim, and J. K. Lim. Surface Wetting Properties of Si3N4/SiC Ceramics by Cu Alloys. Key Eng Mater 2006. 306–308, 423–428.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).