1. Introduction
Molar pregnancy also named hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal human pregnancy arising from imbalance in or excess of paternal genetic material versus the maternal one resulting in abnormal embryonic development. Therefore, complete hydatidiform moles (CHM) develop following the loss of genetic material from the oocyte, which is then fertilized by two sperm cells or one sperm cell that reproduces its chromosomes. The CHMs (androgenetic diploid; monospermic-85% being the most common and dispermic androgeny-15%) consisting of only paternal DNA and are most commonly diploid with a 46XX karyotype (but 46XY also occurs) [
1]. Partial hydatidiform moles (PHM), which are diandric triploid with 69XXY or 69XYY (most common is dispermic of 98%, monospermic-2%) [
2] developing secondary to fertilization of an oocyte by two sperm cells resulting in triploid with a 2:1 paternal to maternal DNA content. Besides, reported are rare familial biparental hydatidiform moles explicited through the demonstration of
NLRP7 or
KHDC3L genes mutations sharing common imprinting alteration involved in the final development of two specific types of hydatidiform moles [
3,
4].
Histologically, both complete and partial hydatidiform moles exhibit hydropic degeneration of chorionic villi and somewhat exuberant trophoblastic cell proliferation. The defining histological features of each of two entities are quite different in most instances. Hence, complete hydatidiform displays diffuse hydropic villi along with circumferential trophoblastic hyperplasia and no fetal tissue whereas partial hydatidiform mole exhibiting partial trophoblastic proliferation along scalloped variably-sized villi with presence of fetal tissues.
While, the histomorphology analysis remains the basis for the diagnosis of hydatidiform mole in limited-resources settings inclusive of our country in addition to the molar pregnancies being nowadays evacuated earlier in the first trimester, the diagnosis and the classification have become a challenge over days following on the top of the lack of well-established classic morphological features. Further, the histomorphology alone suffers intra and inter-observer variability along with poor diagnostic reproducibility [
5].
Moreover, the distinction of PHMs and CHMs from abnormal non-molar villous lesions (NMs) is very crucial for evidenced-based clinical management as well as close follow-up with serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin (β hCG) levels monitoring together with contraceptive use for an earlier detection of possible persistent disease such as gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). As point of the fact, the latter two entities have demonstrated potential progression into this GTN [
6]. However, this special follow up is not required for a diagnosis of the non-molar villous lesions [
7].
More importantly, the genotyping studies or conventional cytogenetics make a distinction from CHMs, PHMs, and the abnormal non-molar villous lesions (NMs) more specifically in discerning the definitional ploidy status of the three entities including diploidy, diandric triploidy, and biparental diploidy respectively. Besides, the NMs share similar histologic features with PHMs and include hydropic01/08/2023 11:55:00 abortus, chromosomal abnormalities, digynic triploid conceptions, and placental mesenchymal dysplasia [
8].
Nonetheless, the complete hydatidiform moles (CHM) and partial hydatidiform moles (PHM) can be accurately distinguished from each other using immunohistochemistry that detects p57
KIP2 in trophoblastic tissue. p57
KIP2 gene on chromosome 11p15.5 encodes a strong inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/Cyclin dependent kinase complexes and is a negative regulator of cell proliferation. This gene is paternally imprinted and maternally expressed, and the presence of its protein product serves as a surrogate marker for the nuclear maternal genome [
9,
10]. The p57
KIP2 is an antibody that stains gestational tissue which has the maternal genome. Therefore, PHMs and normal trophoblastic tissues are positive to p57
KIP2 because they both have maternal and paternal genome. Therefore, p57
KIP2 can help in identifying CHM but not distinguish PHMs from normal trophoblastic tissues [
11]. A number of studies reported a perfect interobserver agreement of high sensitivity and specificity of p57 immunochemical staining when compared with genotyping tests such as PCR short tandem repeat. For instance, one recent study reported a sensitivity of 93% to 96% for individual pathologist and 96% by consensus of two gynecologic pathologists whereas a specificity ranging from 96% to 98% for individual pathologist in diagnosing both CHM and PHM respectively though the latter being problematic when it comes to distinguish it from non-molar lesions (NMs) [
12].
Problem statement and justification of the study
The accurate diagnosis of molar pregnancy is essential for both clinical follow-up and management of patients. However, in resource-limited settings like in our country Rwanda, only histopathogical diagnosis is rendered on hydatidiform moles although it is known to have considerable rates of inter/intra-observer variability and poor diagnostic reproducibility.
Moreover, with readily usage of ultrasound as first diagnostic modality, molar pregnancies are nowadays evacuated earlier, posing again a difficult diagnostic challenge with histomorphology alone. Together, these situations show that there is always a chance of misclassification of hydatidiform mole upon the single morphological diagnosis raising up to 20–30% [
6] in addition to near-miss diagnoses of clinical moles cases.
In resources constrained settings whereby cytogenetics studies are not available, the use of immunohistochemistry with p57
KIP2 may be a more affordable and best alternative in distinguishing both morphological types of hydatidiform moles mostly complete types from its mimics. Besides, the conventional karyotyping, which is also available in our clinical settings but not yet accessible for non-blood samples, can be utilized in definitive diagnosis of hydatidiform moles and it may be used for cases in which the IHC did not find to be CHMs. If these tests are performed as package, they will help in real classification, accurate risk stratification and proper prevention of potential malignancies such as choriocarcinoma which has high mortality rate [
13,
14].
In this context, a number of studies have pointed out the usefulness of p57 expression which is mostly keeping with the results of universal gold standard test i.e., PCR short tandem repeats. Therefore, the latter serves as a reliable marker for diagnosis of complete hydatidiform moles, and identifying androgenetic cell lines in mosaic conception [
2]. Aside, p57 may be utilized in discerning all those cases of early first-trimester hydropic placentas and it has demonstrated concordant results with microsatellite DNA genotyping analysis in the latter cases [
15]. This study paved the way to refine our routine histological diagnosis of hydatidiform moles by p57
KIP2 immunohistochemistry while conventional karyotyping which are readily available in our clinical settings is to be exploited in coming age for establishment of algorithmic diagnosis of hydatidiform moles.
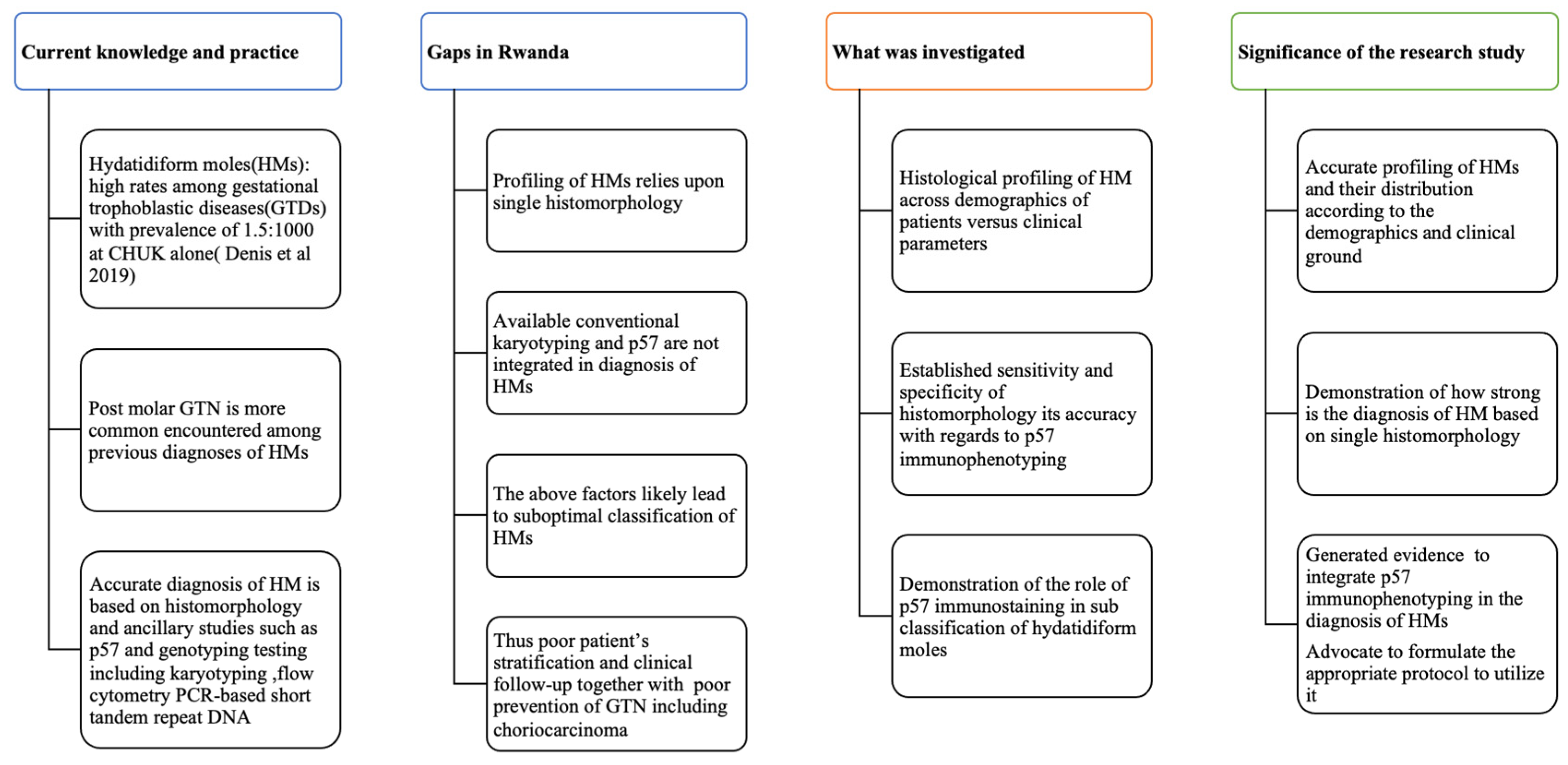
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework and its significance to the present research study.
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework and its significance to the present research study.
This figure summarises the current knowledge and standard practice in the diagnosis of HMs; then gaps in that field in Rwanda are highlighted, from which we show what has been investigated and the importance of performing such investigations, for the betterment of the patients.
Research questions
The present study aimed at answering the following questions:
What is the histological profile of hydatidiform moles at two university Teaching Hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB)?
What is the clinical outcome of hydatidiform moles at the university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB)?
What is the sensitivity and specificity of histomorphology with regard to p57KIP2immunophenotyping in the diagnosis and classification of hydatidiform moles?
Objectives
In order to improve the histomorphology of hydatidiform moles and better follow-up of patients to monitor and prevent the occurrence of choriocarcinoma, this study utilized the p57 immunohistochemistry, for the promotion of evidence-based medicine, in order:
General objective
To validate the histological diagnosis of hydatidiform moles with p57 immunophenotyping at university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB)
Specific objectives
- (1)
To determine the histological profile of hydatidiform moles at the university teachings of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB)
- (2)
To determine the clinical outcome of hydatidiform moles at the university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB)
- (3)
To determine the levels of sensitivity and specificity of histomorphology with regard to p57KIP2immunophenotyping in the diagnosis and classification of hydatidiform moles
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Period
This was a retrospective observational study carried out over a period of three years and six months (January 2017 through June 2020).
2.2. Study Sites
The study was embarked at two university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB) in Anatomical Pathology units.
2.3. Study Population
All women with clinical features of molar pregnancy and with confirmed histopathological diagnosis of hydatidiform mole were enrolled in the study.
2.4. The Primary Outcomes
Independent variable: histological data, demographic data (age, residency), clinical data (ultrasound findings, gravidity, gestational age, pre-treatment and follow up beta hCG levels)
Dependent variables: P57KIP2 immunostaining pattern, clinical outcome
2.5. Study Sample Selection
2.5.1. Inclusion Criteria
All clinically suspected cases of hydatidiform moles (i.e., clinical history and physical examination, ultrasound findings and beta hCG levels) were included for histopathological diagnosis and reviewed with subsequent validation by P57KIP2 immunostaining.
2.5.2. Exclusion Criteria
All Cases of non-molar lesions by histomorphology were excluded from the study.
2.6. Sample Size
The sample size was calculated using the formula as follows for cross-sectional studies:
n = the sample size, Z = the normal deviation P = the expected proportion, Q = l − P, d = required precision.
The expected proportion (P) of 6.1% the established prevalence of hydatidiform mole in our region [
16] since there is no known prevalence rate of hydatidiform mole in our settings. As P values are considered significant when below 5%, hence Z = 1.96 was used in this formula with precision of 5%, hence (d = 0.05).
Sample size for comparing the sensitivity (or specificity) of two diagnostic tests in diagnostic study [
17]
According to the above formula, almost the same sample size is calculated as follows:
P: 96%, Z
β: 0.84 Z
α: 1.96, P1 = 0.96, P2 = 81% and P ¼ 0:75, then
2.7. Study Procedure
For cases enrollment, the slides were reviewed for histological diagnosis of hydatidiform moles followed appropriate selection of FFPE block with subsequent immunostaining with p57KIP2.
Formalin fixed paraffin embedded blocks (FFPE) were obtained from archive for P57KIP2 immunostaining. A normal placenta has been collected for external positive control of p57KIP2 immunostaining together with maternal decidua and intermediate or extra/trophoblastic cells at the site of implantation that served as internal positive control.
The data collection sheet comprising patient clinical data, histomophological diagnosis, p57 IHC, clinical outcome and clinical follow-up time was pre-designed for this present study.
p57KIP2Immunohistochemistry and interpretation
In the present study, 96 cases corresponding formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded blocks depicting CHM, PHM, or HM, unspecified type were selected from the archives in the Department of Pathology, Anatomical Pathology unit at two university hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB) between January 2017 and June 2020. The original identification of CHM, PHM, and HM, unspecified type cases was based on previous histologic evaluation of H&E-stained sections from either product of dilation and evacuation or hysterectomy specimens.
Immunohistochemical staining with anti-p57
KIP2 mouse monoclonal antibody (clone KP10, 25% dilutions of 1.11 µg/Ml pure dose) was operated using an avidin-biotin immunoperoxidase complex (ABC) method (detailed full protocol). The immunostaining result was interpreted as positive for p57 with similar staining pattern in either decidual cells and/or extravillous trophoblastic cells, which served as an internal positive control and exhibited positive nuclear p57
KIP2 staining in both villous stromal cells and/or cytotrophoblasts. P57 was negative when there was lack of p57 expression in both villus cytotrophoblasts and villous stromal cells. The scoring of nuclear positivity and negativity for p57 IHC was established according to the study conducted by Karthi. P. Kumar, and P. S. Jayalakshmy [
18] as follows: 0, 1+ were interpreted as negative for p57 (no nuclear staining and 1–10% of positive cells) whereas 2+, 3+ (10–50% positive cells and >50% positive cells respectively) were considered as positive expression.
Of note, independent pathologist and I were blinded for previous histomophological diagnosis and signed out corresponding p57 immunostained slides for definitive recording of the diagnosis in the present study.
2.8. Enrollment and Data Collection
During the period of this study, we retrieved archived H&E slides of hydatidiform moles together with recorded information on the request form and in OPENCLINIC at both university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB). Demographic data (age, residency), clinical data (ultrasound findings, gravidity and gestational age, β-hCG levels prior to treatment and post-follow up levels) were recorded and 96 cases immunostained with p57 for which the FFPE Blocks were available.
2.9. Data Management and Statistical Analysis
A structured questionnaire served as main tool of data entry and together with Excel spreadsheet with password and the analysis performed using Statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 25 (IBM Corporation, New York 10504-1722, USA) and MedCalc (MedCalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium) v.10.2.0.0 from which the descriptive statistics were obtained including frequencies, percentiles. Also, computed were sensitivity, specificity, negative and positive likelihood ratios, negative and positive predictive values, odds ratio with confidence interval of 95%.
In this portion of the research p57 IHC was considered as gold standard to assess the histomophological diagnostic modality and its accuracy by Youden J statistics method. The relationship between categorical variables were established using Chi-square and Chi-square for trend. P values were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
2.10. Ethical Considerations
2.10.1. Confidentiality
There were no risks to patient since this research did not engage the subjects, only operated in the laboratory settings whereby a retrieval of H&E slides for histological review and then appropriate FFPE block selection for P57KIP2 immunostaining. Every single case was assigned a research code corresponding to histopathology lab number and no identification appeared on data collection sheet. Besides, data were entered into password-protected excel spread sheet along with secured SPSS 25 version for analysis.
2.10.2. Ethical Approval
The Anatomical Pathology program of College of Medicine and Health Sciences (CMHS) at the University of Rwanda (UR) issued a scientist approval to our study, submitted into University Institutional review board (IRB) that granted its ethical approval (No 081/CMHS IRB/2020) and thereafter authorization letters (RC/UTHB/008/2020 and EC/CHUK/0134/2019) to conduct the study at two teaching hospitals were obtained from respective Research ethics committees of the above hospitals.
2.11. Strength, problems and limitation of the study
2.11.1. Strength of the Study
This was the first study of its kind in Rwanda to have generated pilot data on histological profile of hydatidiform moles with validation by p57 immunophenotyping. It has demonstrated a need to integrate p57 immunostaining in proper stratification of hydatidiform for evidenced-based treatment and clinical follow-up of affected patients.
2.11.2. Problems and Limitations of the Study
Being retrospective study in nature, we had incomplete data for evaluation of both clinical outcome and follow-up of all histologically diagnosed cases. It would have been useful to perform cytogenetics as gold standard diagnostic modality of hydatidiform moles but we did not do it due to financial constraints though these ones were pending from the university of Rwanda that postponed the grant.
3. Results
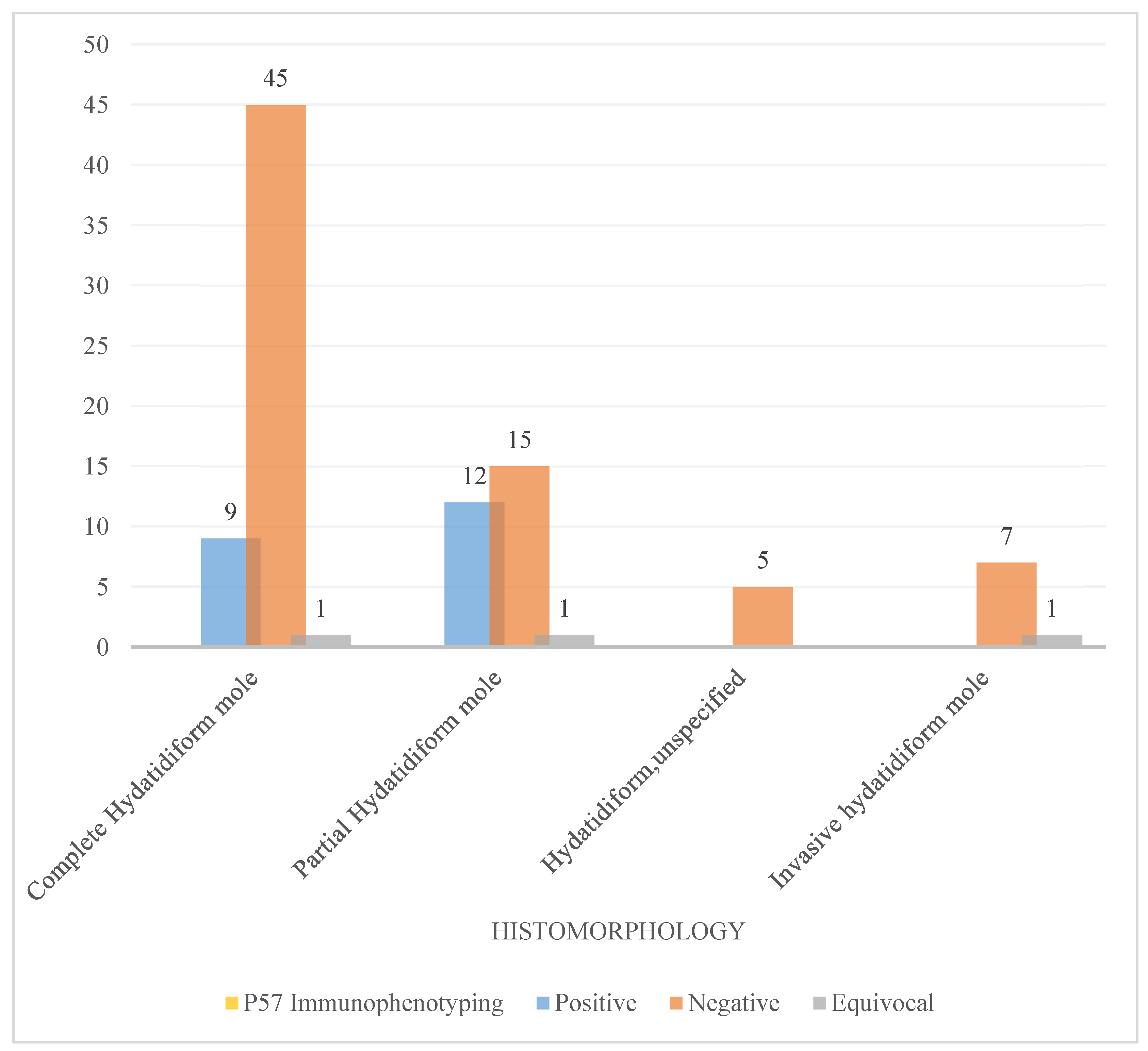
Over a period of three years and half, we recorded 211 cases of HM and of which Ninety-six (96) cases were subjected to p57 immunohistochemically staining at two teaching university hospitals, as shown in
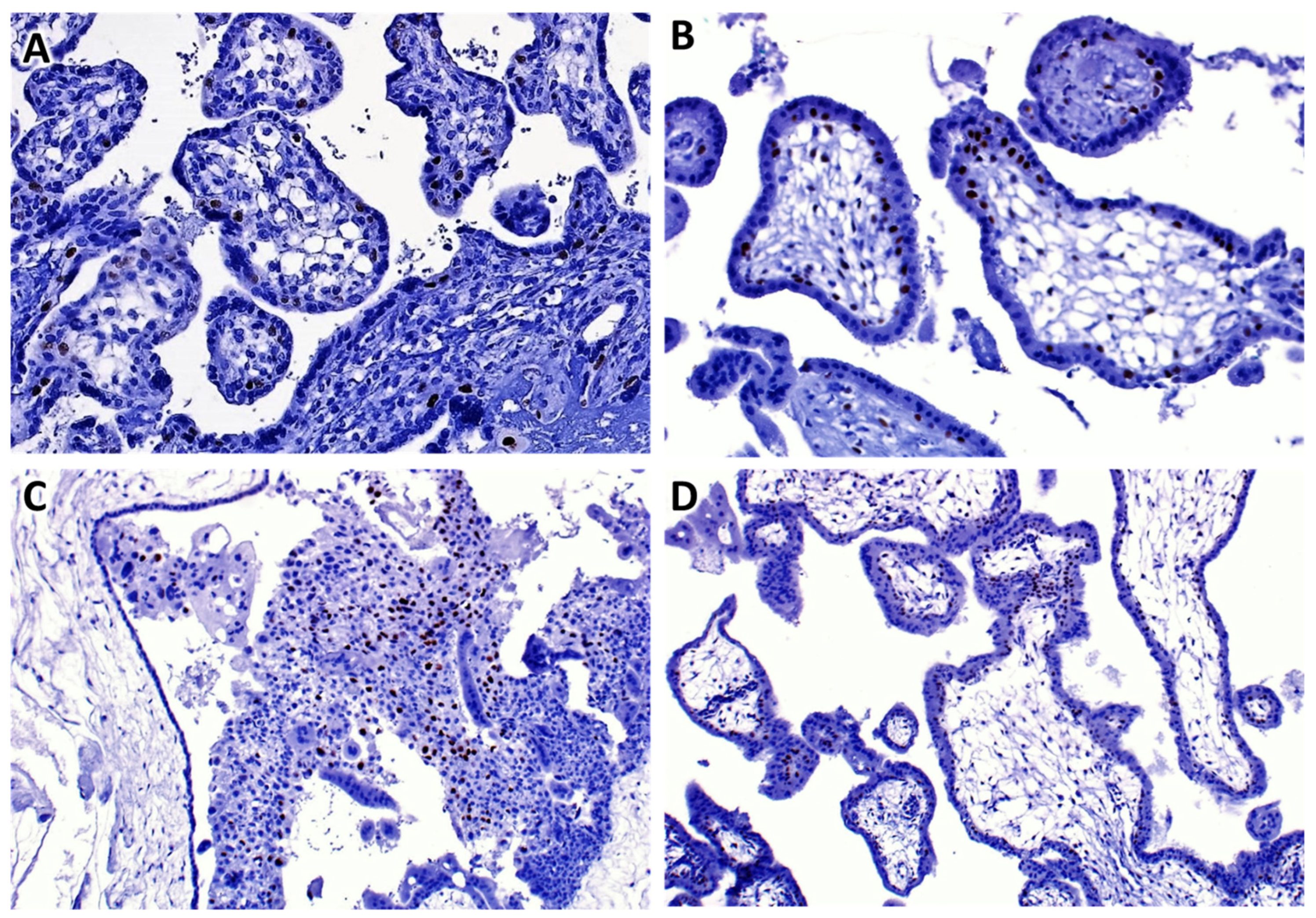
Table 1. The median age was 32 years old. The histopathology diagnosis of hydatidiform mole was more likely prevalent among women aged between 21 and 40 years old (55.5%) followed by those aged above 40 years old representing 42.2%. Complete hydatidiform mole was mostly occurring in this age range followed by partial hydatidiform moles. Most women were gravid one to three (G1–G3) between 11 weeks and 20 weeks of gestational age range (11W–20W) representing 27.7%. The p57 immunostaining was done on 96 cases and served to stratify five cases unspecified hydatidiform mole by histomorphology as complete hydatidiform mole (see
Figure 2 for photomicrographs of the typical staining pattern).
From this
Table 2 below, 96 cases were subjected to p57 immunostaining. Thus, the sensitivity and Specificity of the histomophological diagnosis to diagnose complete hydatidiform mole was 62.50% and 57.10% respectively whereas the positive and negative predictive value estimated at 81.8% and 29.30%. For partial hydatidiform mole, sensitivity and specificity of histomophological diagnosis was established at 57.10% and 79.20% respectively while the values of positive and negative predictive were computed at 42.90% and 83.80% respectively with statistical significance (p = 00.4). The accuracy of histomorphology to diagnose complete hydatidiform moles with Youden J statistics method is 19.6% (0.196) whereas for partial hydatidiform mole the accuracy goes up to 36.6% (0.366). Positive and negative likelihood ratios were computed at 1.45 and 0.54 meaning a very small value or rarely useful test alone.
The
Table 3 below demonstrates that women above 40 years of age were 2.85 times more likely to have complete histomorphology compared to women of 40 years old and (below OR = 2.85; 95% CI: 0.94–8.64; p = 0.063). Women with βhCG count >200,000 were 2.64 times more likely to have complete histomorphology as those with βhCG count ≤ 200,000 (OR = 2.64; 95% CI: 0.50–13.8; 0.251). There was no difference in histomorphology according to the ultrasound findings.
Women below 40 years of age were 3.81 times more likely to have positive P57 Immunophenotyping compared to women of above 40 years of age (OR = 3.81; 95% CI: 1.02–14.2; p = 0.045). Women who had not suggestive ultrasound findings were 1.72 times more likely to have positive P57 Immunophenotyping as those with suggestive ultrasound findings (OR = 1.72; 95% CI: 0.32–9.09; 0.637) and women with βhCG count of ≤200,000 were 1.43 times more likely to have positive p57 Immunophenotyping as those with βhCG count of >200,000 (OR = 1.43; 95% CI: 0.51–3.96; p = 0.493)
Figure 3 is a diagram illustrating the role of p57 immunostaining in classifying the morphological challenging cases of hydatidiform whereby in our study five cases of unspecified type were classified as complete hydatidiform by p57 and seven cases of invasive hydatidiform moles were stratified as complete type by p57 immunostaining.
4. Discussion
Hydatidiform moles include a form of abnormal human pregnancy displaying characteristic hydropic chorionic villi along trophoblastic proliferation. It is stipulated that genomic imprinting is implicated in the formation of hydatidiform moles although their pathogenesis remains ununderstood [
3]. In this study, we aimed at validation of histological diagnosis by immunostaining with anti-p57 monoclonal antibody that is labelling nuclear maternal genome. Besides, we attempted to have a look at clinical outcome and distribution of two histomophological forms of hydatidiform moles.
Histological profile of hydatidiform moles and age at presentation
Over three years and six months period, 211 histological cases of hydatidiform moles were recorded inclusive of complete hydatidiform mole representing 56.4% followed by partial hydatidiform moles (23.2%). The same distribution of hydatidiform moles was confirmed when 96 cases were subsequently subjected to p57 immunostaining; the complete hydatidiform moles being the predominant type and followed by partial hydatidiform moles. Our findings are supported by what reported by Yassemine Khawajkie et al. [
1] wherein they even performed more ancillary studies on their cohort cases studies including ploidy studies (Flow cytometry and SNP) and genotyping test such as PCR short tandem repeats (STR).Further, this trends reflects the utility of integrating ancillary tests in proper classification of hydatidiform moles and definitive stratification of patients for best clinical follow-up and management of post-molar gestational neoplasia.
Nonetheless, Nawras Najah Mubarak et al. reported different single-based histopathological distribution to what we found as similarly recorded in a number other reports such that partial hydatidiform moles was the most common subtype followed complete hydatidiform moles [
19]. Although, no highlighted explanation in their report for this different histological profile, it can be justified by utilizing ancillary tests.
The majority of cases were encountered in women aged between 21–40 years with median age of 32.0 (28.0–43.0) and followed by those aged above 40 years against women aged below 20 years in whom the hydatidiform moles were less represented. These findings are in line with the results obtained by Yassemine Khawajkie et al. (204 cases of HM) and they reported almost the same age range of 21–30 versus 31–40 years and those above 40. Thus, androgenetic monospermic and dispermic CHM were the most common subtype of HM (45) (39.4% were in between 21 and 30, 43 (37.7%) were in between 31 and 40, and 20 (17.5%) were older than 40 years of age) concurring with what we found in our study while triploid dispermic PHM represented in the same age range of 21–30, 31–40 years of age, 37.6% and 60.9% is higher than what we found.
In our study, we found cases of complete and partial hydatidiform moles above 40 years old whereas Yassemine et al. did find few cases above 40 when genotyping testing was performed on their study cases and the latter ancillary test would have made such a difference in different numbers of CHM eventually highlighting the role cytogenetics studies in diagnosing the hydatidiform moles. The median age at the diagnosis of HM in our study was 32.0 years, almost similar mean age of 32.5 years reported in the study conducted by Abimbola O. Kolawole et al. [
20] lower age than what is reported by Yassemine et al. of 33 and 36 years, higher than one reported by Ahmed et al. of 26.22 years [
4] while median age 22 years reported by Madi et al. [
3,
20]. Our obtained age range translates a positive association of hydatidiform moles with increasing maternal age reported in many other studies [
1,
16] and complete hydatidiform mole subtype being more represented as reported in other studies [
16,
21].
In our present study, women aged above 40 years of age were 2.85 times more likely to have complete mole histomorphology compared to women aged 40 years and below (below OR = 2.85; 95% CI: 0.94–8.64; p = 0.063). These findings are in agreement with what other authors reported the extreme maternal age being independently associated with hydatidiform moles and explained by possible unnatural fertilization of an oocytes [
16,
22].
Gravidity and gestational age at the diagnosis of hydatidiform moles
Our study showed that most affected women by hydatidiform were multigravida (G1–G3) in their late first trimester through second trimester (11–20 WA) and similar findings were reported in other studies [
20,
23] and these data also translate a possibility to encounter many cases of early hydatidiform moles which pose a diagnostic difficulty on single histomorphology with eventual of misclassification.
Clinical outcome of hydatidiform moles at two university teachings of Kigali and Butare
Looking at clinical outcome measured by decrease β-hCG levels with median value 35650 m.I.U/mL (8225–195203 m.i.u/ml), we did not find a significant association across different types of hydatidiform moles with regard to their progression to GTN (p = 0.402 with chi-square for trend of 0.6339) and similar findings were reported by Ahmed Zakaria et al. in their prospective study [
4] whereby mean pre-evacuation β-hCG levels were higher than what we found in our study. Besides, our study showed that complete hydatidiform moles subtypes together with those stratified by p57 IHC were the most likely to progress into post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia as opposed to partial hydatidiform mole subtype. These findings were in line with the same results obtained in other studies [
1]. Women with β hCG count >200,000 were 1.43 times more likely to have complete mole histomorphology as those with β hCG count ≤200,000 (OR = 2.64; 95% CI: 0.50–13.8; 0.251) and this supports the usual higher β hCG levels associated with complete moles types. In addition, p57 immunophenotyping was likely positive in the latter cases and more positive in cases where ultrasound was not suggestive. These findings point out the positivity of p57 in partial hydatidiform cases than complete hydatidiform cases (OR = 1.43; 95% CI: 0.51–3.96; p = 0.493).
Sensitivity and specificity of histomorphology with regard to p57KIP2 immunophenotyping in the diagnosis and classification of hydatidiform moles
The p57 immunostaining served to accurately stratify the cases of hydatidiform moles. In our study, the most common histological subtype was complete hydatidiform mole representing 56.4% what is different from Nawras Najah Mubarak et al. that reported partial HM, the most common followed by CHM [
19], such a trend is explained by the fact the latter is purely descriptive study and the results of histological profile are of single-based histomorphology findings hence recalling for interobserver variability and poor diagnostic reproducibility among pathologists when it comes to histomophological diagnosis of hydatidiform in absence of ancillary tests. Likewise, our findings were reduplicated in the report of Kumar et al. [
18].
The sensitivity and specificity of histomophological diagnosis were calculated at 62.5% and 57.1% for complete hydatidiform whereas for partial hydatidiform moles, they were estimated at 57.1% and 79.2%.The above estimated levels of sensitivity and specificity concur with those established in a study conducted by Madi et al. 2018 in which they improved values of sensitivity and specificity using p57 that is 59% to 100% of sensitivity for histomorphology of complete hydatidiform mole and 91% to 96% of specificity whilst for partial hydatidiform mole (PHM), the sensitivity 56% to 93% with specificity of 58% to 92% [
24]. Thus, our results demonstrate gaps to bridge by initiating p57 IHC adjunct the diagnosis of hydatidiform moles as it has been proven to highly sensitive and specific in discerning complete hydatidiform from its mimics in various studies [
25]. The accuracy of the histomophological diagnosis was low 0.196 and 0.366 for both complete and partial hydatidiform moles respectively. The latter similar low accuracy of single histomophological diagnosis was also highlighted by other studies that quoted interobserver variability and suboptimal reproducibility amongst even experts of the field of gynecologic pathology [
15,
26] with a rate of 20–30% of misclassified hydatidiform moles by single-based histomophology alone. Hence, p57 immunostaining would be opted as adjunct to histomorphology of HM at least in settings of challenging cases.
5. Conclusions
Our study established relatively low levels of sensitivity and specificity for histomophological diagnosis of hydatidiform moles at both university teaching hospitals of Kigali and Butare (CHUK, CHUB) when compared to the estimated levels in other high resourced settings. Thus, a need to incorporate p57 immunostaining in diagnosis of hydatidiform moles as way to refine and support the histomophological diagnosis of molar pregnancy in a subset of cases that might pose a diagnostic challenge. The obtained profile highlighted challenges in classification of hydatidiform moles based on single histomorphology as reported in many other studies.
Author Contributions
HT, IJ, ND, UA and RB helped with the conceptualization, methodology, and formal analysis, HT wrote the first draft of this manuscript and obtained ethical approval. TH contributed to data acquisition, BR, UA and HC for critical review of the manuscript. HT, MF and BR contributed to data analysis and critical reviewing of the manuscript. All authors reviewed, edited, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly funded by the university teaching hospital of Kigali (CHUK, French acronym), through CHUK small grants 2019 and Dr. Chris Hansen.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the IRB of the University of Rwanda, CMHS (approval notice No 081/CMHS IRB/2020) and the Ethics Committees of two University Teaching Hospitals of Kigali and Butare (Review Approval Notice No: EC/CHUK/0134/2019 and RC/UTHB/008/2020 respectively).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the financial support of p57IHC given by Dr. Chris Hansen along with the Special IHC pen provided by Dr. Manirakiza Felix to facilitate the entire work of immunostaining of enrolled cases for our study. Special acknowledgements go to the university teaching hospital of Kigali (CHUK, French acronym) for financing part of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khawajkie Y, Mechtouf N, Nguyen NMP, Rahimi K, Breguet M, Arseneau J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of 204 sporadic hydatidiform moles: revisiting risk factors and their correlations with the molar genotypes. Mod Pathol. 2020, 33, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banet, N.; DeScipio, C.; Murphy, K.M.; Beierl, K.; Adams, E.; Vang, R.; Ronnett, B.M. Characteristics of hydatidiform moles: analysis of a prospective series with p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, P.; Buza, N.; Murphy, K.M.; Ronnett, B.M. Hydatidiform Moles: Genetic Basis and Precision Diagnosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 449–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, A.; Hemida, R.; Elrefaie, W.; Refaie, E. Incidence and outcome of gestational trophoblastic disease in lower Egypt. Afr. Heal. Sci. 2020, 20, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi, J.M.; Braga, A.; Paganella, M.P.; Litvin, I.E.; Wendland, E.M. Accuracy of p57KIP 2 compared with genotyping to diagnose complete hydatidiform mole: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG: Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 125, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo US, Lai CYL, Sc MM, Chan KYK, Ph D, Xue W cheng, et al. Metastatic Trophoblastic Disease after an Initial Diagnosis of Partial Hydatidiform Mole Genotyping and Chromosome In Situ Hybridization Analysis. Cancer. 2004, 100, 1411–1417.
- Soper; J. T. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Current Evaluation and Management. Obstet. Anesthesia Dig. 2021, 41, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, C. Simon RHYKRJMLC. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of female Reproductive Organs. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer(IARC); 2014. 156–167 p.
- Popiolek, D.; Yee, H.; Mittal, K.; Chiriboga, L.; Prinz, M.; Caragine, T.; Budimlija, Z. Multiplex short tandem repeat DNA analysis confirms the accuracy of p57KIP2 immunostaining in the diagnosis of complete hydatidiform mole. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi, J.M.; Braga, A.; Paganella, M.P.; Litvin, I.E.; Wendland, E.M. Accuracy of p57KIP 2 compared with genotyping to diagnose complete hydatidiform mole: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG: Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 125, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillon, Diego H. M.D., Ph.D.; Sun, Deqin M.S.; Weremowicz, Stanislawa Ph.D.; Fisher, Rosemary A. Ph.D.; Crum, Christopher P. M.D.; Genest DRMD. Discrimination of complete hydatidiform mole from its mimics by immunohistochemistry of the paternally imprinted gene product p57KIP2. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001, 25, 1225–1230.
- Gupta M, Vang R, Yemelyanova AV, Kurman RJ, Li FR, Maambo EC, et al. Diagnostic reproducibility of hydatidiform moles: Ancillary techniques (p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping) improve morphologic diagnosis for both recently trained and experienced gynecologic pathologists. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012, 36, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzayisenga, I.; Segal, R.; Pritchett, N.; Xu, M.J.; Park, P.H.; Mpanumusingo, E.V.; Umuhizi, D.G.; Goldstein, D.P.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Hategekimana, V.; et al. Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia Treatment at the Butaro Cancer Center of Excellence in Rwanda. J. Glob. Oncol. 2016, 2, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillon, Diego H. M.D., Ph.D.; Sun, Deqin M.S.; Weremowicz, Stanislawa Ph.D.; Fisher, Rosemary A. Ph.D.; Crum, Christopher P. M.D.; Genest DRMD. Hydatidiform moles: Ancillary techniques to refine diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018, 142, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, S.H.; Amin, M.B.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Malhotra, R.K.; Moehlenkamp, C.; Joste, N.E. p57KIP2 immunohistochemistry in early molar pregnancies: emphasis on its complementary role in the differential diagnosis of hydropic abortuses. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, H.; Vyberg, M.; Eriksen, H.H.; Grove, A.; Jensen, A. .; Sunde, L. Decreasing incidence of registered hydatidiform moles in Denmark 1999–2014. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwabizi D, Rulisa S, Ghebre R, Ntasumbumuyange D, Nkubito V, Small M. The “ honeycomb sign ”: gestational trophoblastic disease in the largest tertiary center in Rwanda. Int J Pregnancy Child Birth. 2019, 5, 45–46.
- Jagtap, S.V. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - Clinicopathological Study at Tertiary Care Hospital. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, EC27–EC30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaballa, A.; García, Y.; Herrero, A.; Laínez, N.; Fuentes, J.; De Juan, A.; Freixinós, V.R.; Aparicio, J.; Casado, A.; García-Martinez, E. SEOM clinical guidelines in gestational trophoblastic disease (2017). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 20, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.K.; Mandal, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Panda, U.K.; Ray, A.; Ali, S.M. Expression of p57 immunomarker in the classification and differential diagnosis of partial and complete hydatidiform moles. J. Lab. Physicians 2019, 11, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurain, JR. Gestational trophoblastic disease I: Epidemiology, pathology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic disease, and management of hydatidiform mole. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010, 203, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipata, F.; Parkash, V.; Talmor, M.; Bell, S.; Chen, S.; Maric, V.; Hui, P. Precise DNA Genotyping Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Mole. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2010, 115, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulisya, O.; Roberts, D.J.; Sengupta, E.S.; Agaba, E.; Laffita, D.; Tobias, T.; Mpiima, D.P.; Henry, L.; Augustine, S.; Abraham, M.; et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Hydatidiform Mole among Patients Undergoing Uterine Evacuation at Mbarara Regional Referral Hospital. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckl, M.J.; Sebire, N.J.; Fisher, R.A.; Golfier, F.; Massuger, L.; Sessa, C. Gestational trophoblastic disease: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, vi39–vi50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics. J. Biomed. Informatics 2014, 48, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawras Najah Mubark, Abduladheem Turki Jalil SHD. Descriptive study of hydatidiform mole according to type and age among patients in wasit province. Glob J Public Health Med. 2020, 2, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).