Submitted:
07 September 2023
Posted:
08 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Catalyst preparation
2.2. Catalyst characterization
2.3. Catalytic performance of MSR
3. Results and discussion
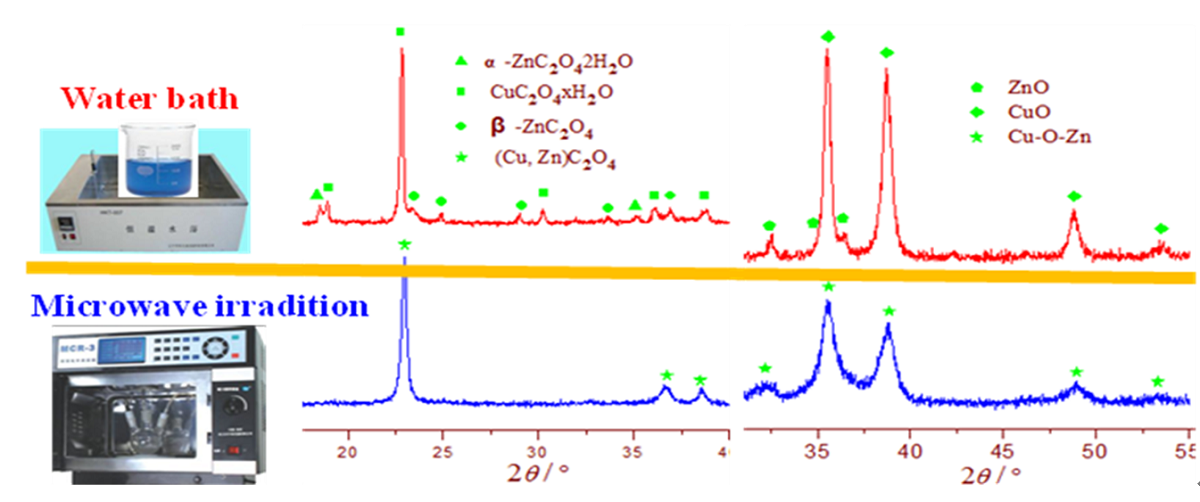
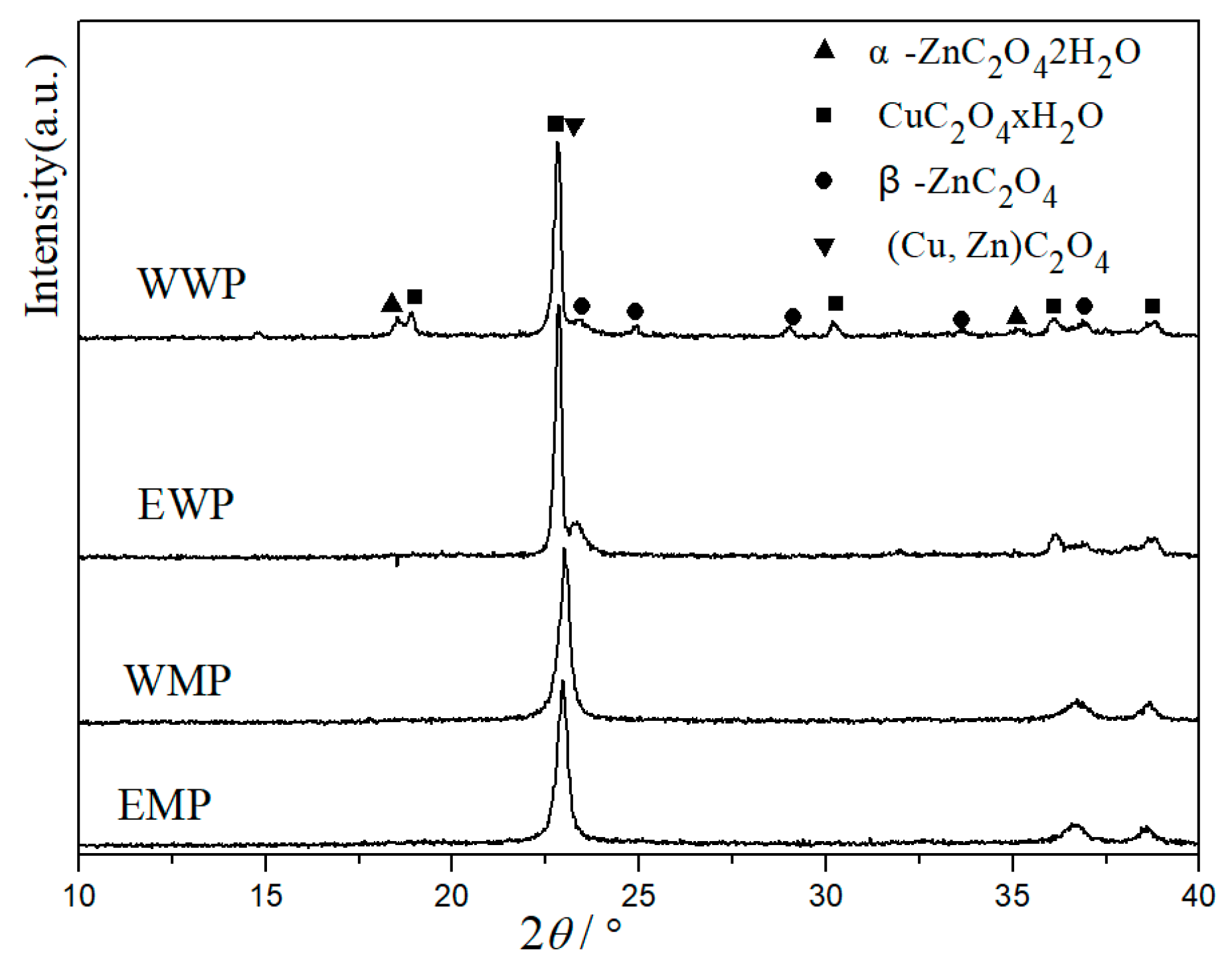
3.1. XRD characterization of precursors
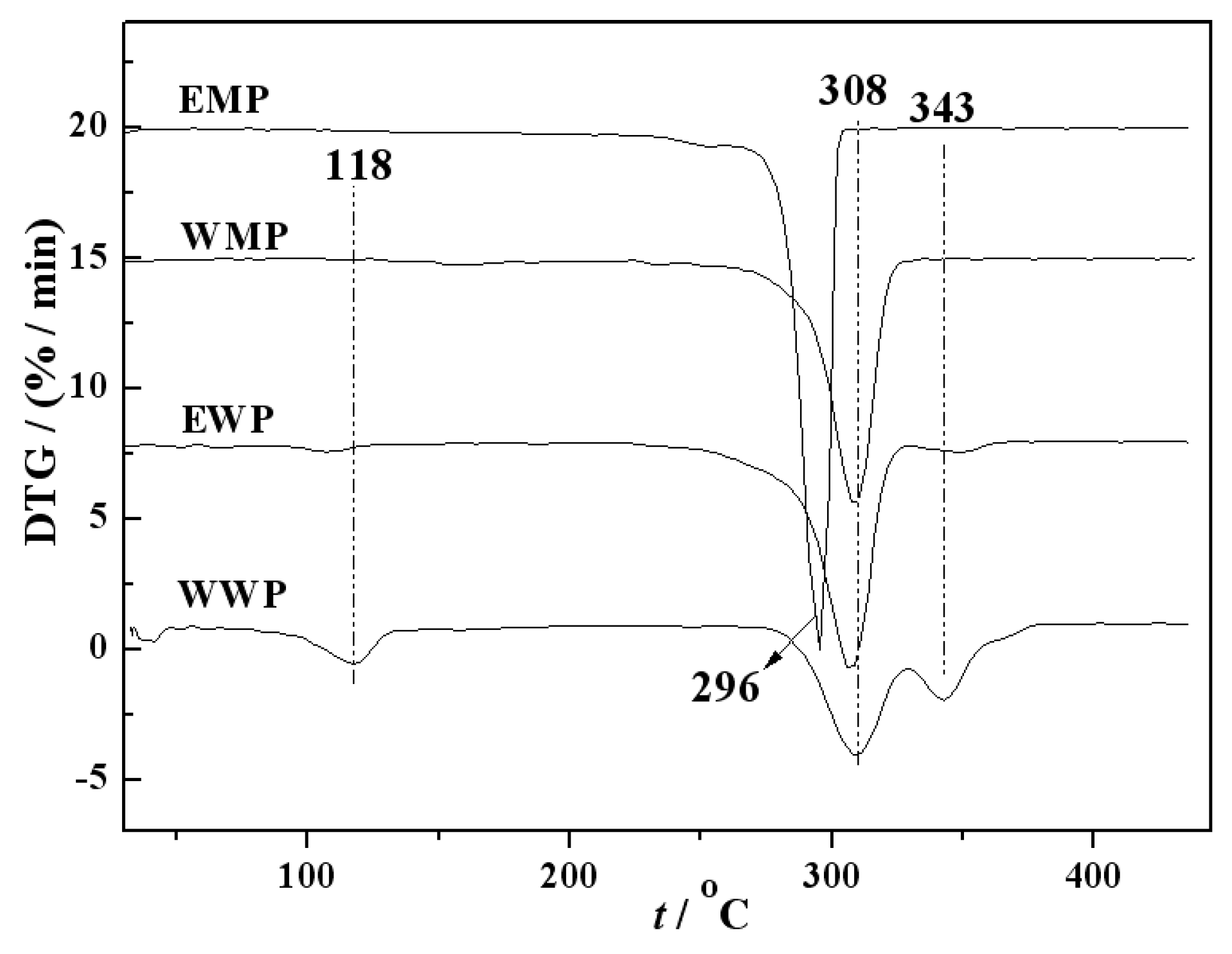
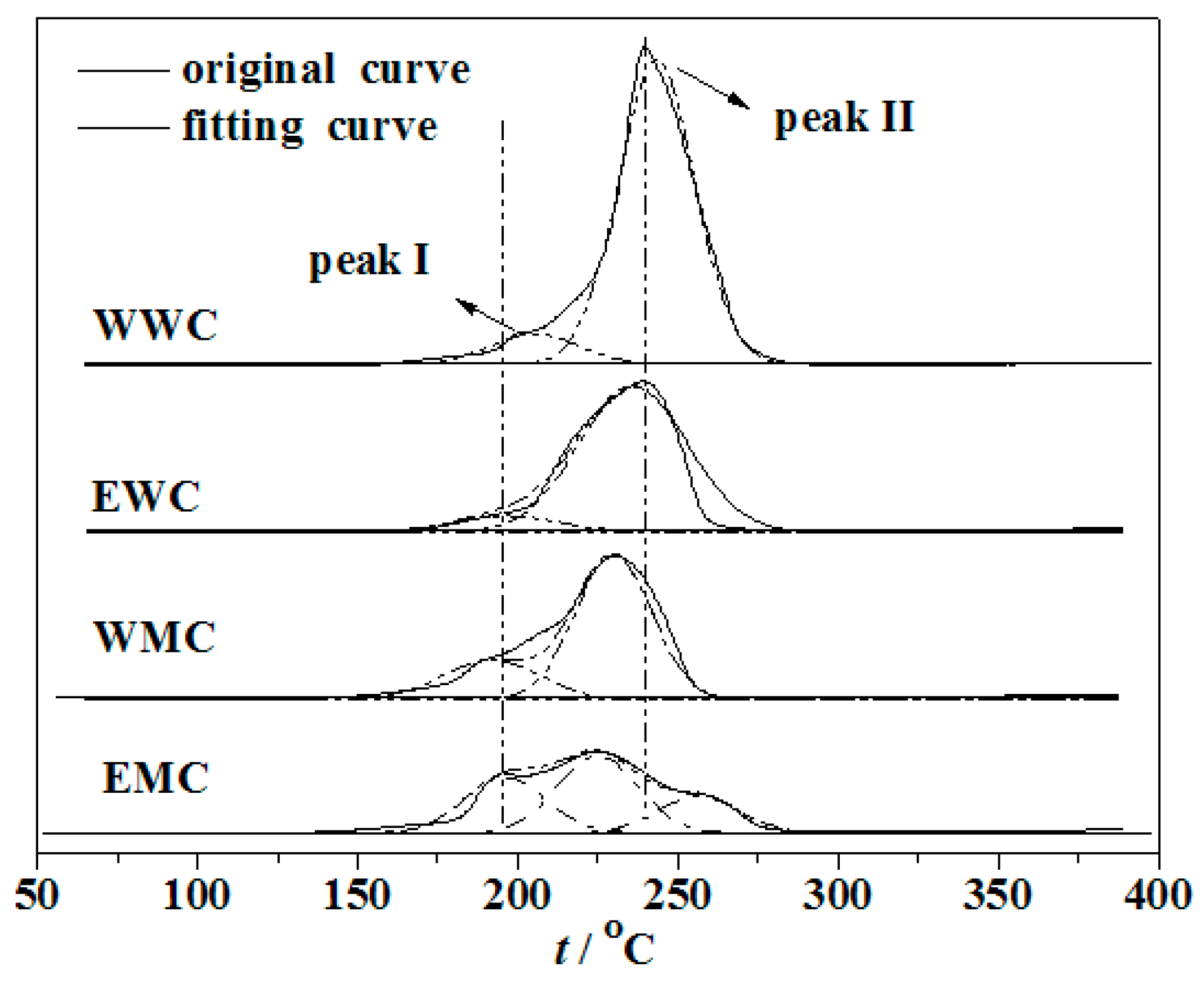
3.2. DTG characterization of precursors
3.3. SEM images of precursors and catalysts
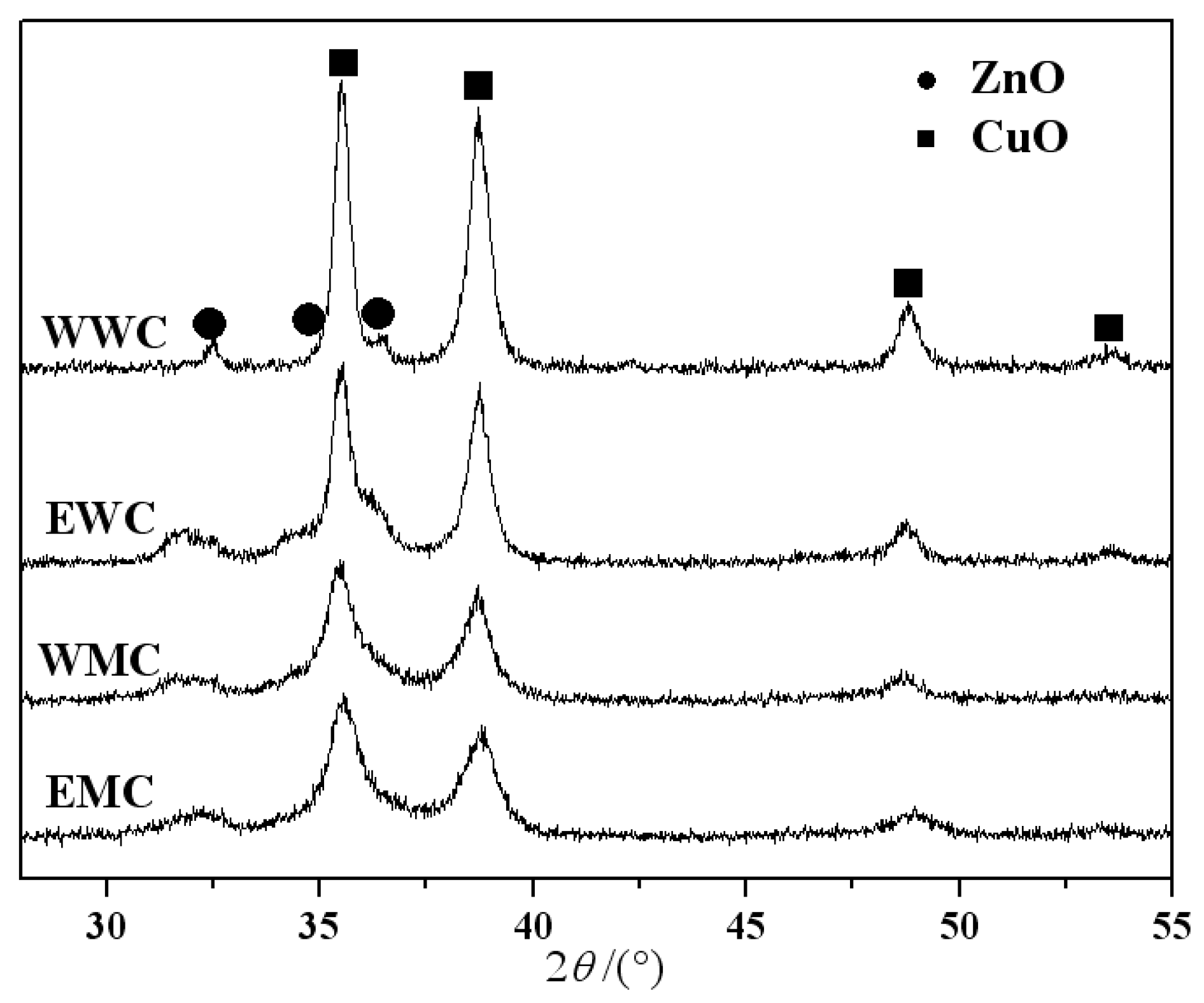
3.4. XRD characterization of catalysts
3.5. H2-TPR characterization of catalysts
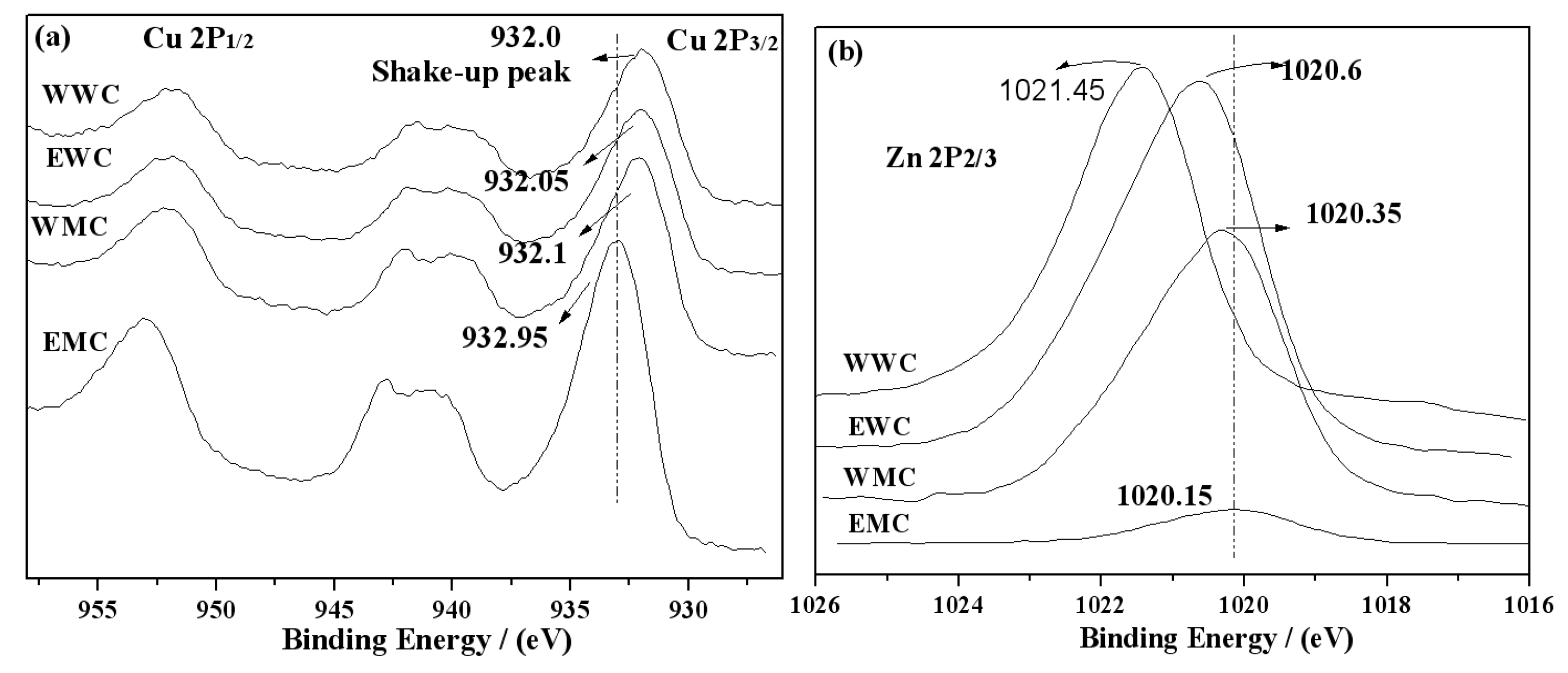
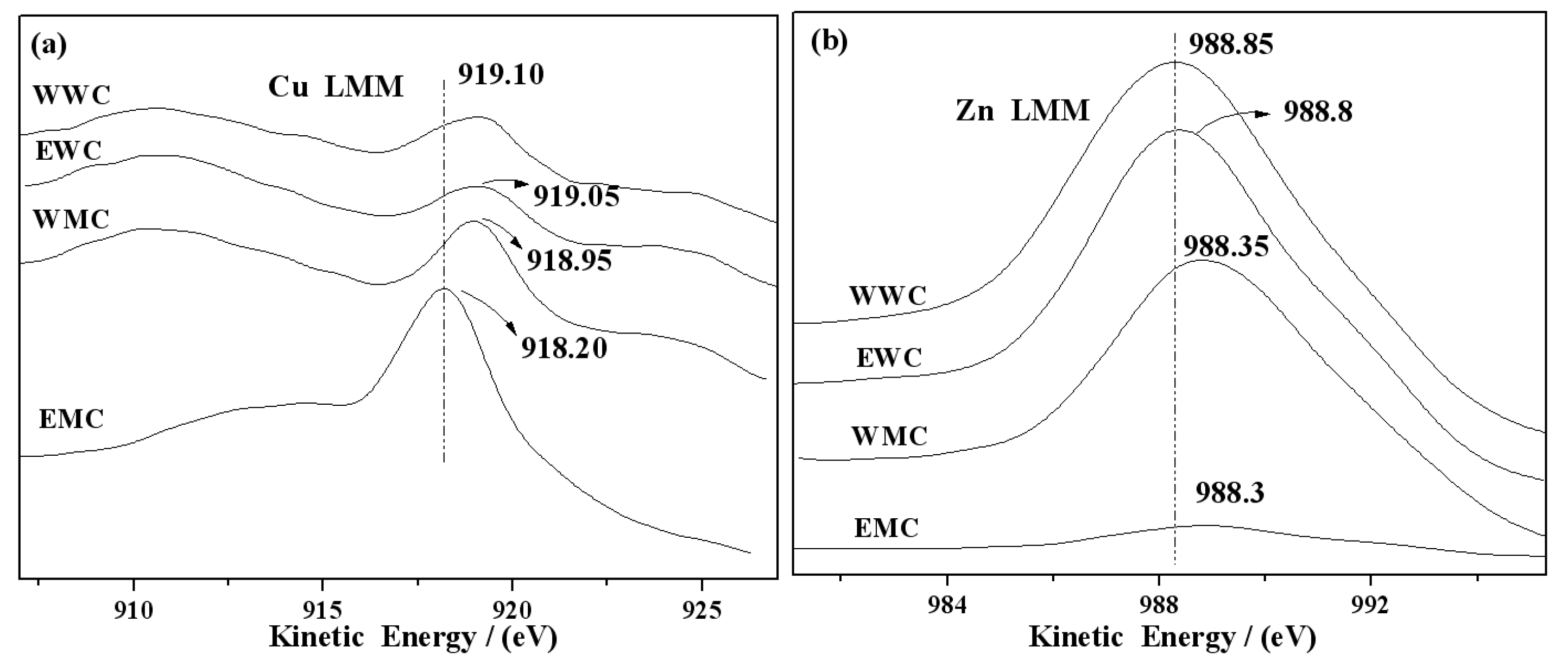
3.6. XPS and AES characterization of catalysts
3.7. Catalytic performance test for MSR reaction
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Kawamura Y, Ogura N, Igarashi A. Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming using microreactor. J Jpn Petrol Inst 2013, 56, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong ST, Ooi CW, Chai SP, Wu XS. Review of methanol reforming-Cu-based catalysts, surface reaction mechanisms, and reaction schemes. Int J Hydrogen Energ 2013, 38, 9541–9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu XH, Shuai KP, Xu B. Review on copper and palladium based catalysts for methanol steam reforming to produce hydrogen. Catalysts 2017, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli A, Ribeirinha P, Mendes A, Basile A. Methanol steam reforming for hydrogen generation via conventional and membrane reactors: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 2014, 29, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa N, Masuda S, Ogawa N, Takezawa N. Steam reforming of methanol over Pd/ZnO: effect of the formation of PdZn alloys upon the reaction. Appl Catal A: Gen 1995, 125, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrani R, Haghighi M, Jodeiri N, Ajamein H, Abdollahifar M. Fuel cell grade hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming over CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 nanocatalyst with various oxide ratios synthesized via urea-nitrates combustion method. Int J Hydrogen Energ 2014, 39, 13141–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido T, Yamamoto Y, Morioka H, Takehira K. Production of hydrogen from methanol over Cu/ZnO and Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared by homogeneous precipitation: steam reforming and oxidative steam reforming. J Mol Catal A: Chem 2007, 268, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrell J, Birgersson H, Boutonnet M, Melián-Cabrera I, Navarro RM, Fierro JLG. Production of hydrogen from methanol over Cu/ZnO catalysts promoted by ZrO2 and Al2O3. J Catal 2003, 219, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, MS. Precursors of copper/zinc oxide catalysts. Catal Lett 2000, 66, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li JL, Inui T. Characterization of precursors of methanol synthesis catalysts copper/zinc/aluminum oxides precipitated at different pH and temperatures. Appl Catal A: Gen 1996, 137, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang DR, Ren WZ, Liu ZM, Xu XF, Xu L, Lv HY, et al. Synthesis and applications of mesoporous Cu-Zn-Al2O3 catalyst for dehydrogenation of 2-butanol. J Nat Gas Chem 2009, 18, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Sun Q, Wu D, Fan WH, Zhang YL, Deng JF. A practical approach for the preparation of high activity Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalyst for methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation. Appl Catal A: Gen 1998, 171, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang YL, Sun Q, Deng JF, Wu D, Chen SY. A high activity Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for methanol synthesis: Preparation and catalytic properties. Appl Catal A: Gen 1997, 158, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang XR, Wang LC, Yao CZ, Cao Y, Dai WL, He HY, et al. A highly efficient Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst via gel-coprecipitation of oxalate precursors for low-temperature steam reforming of methanol. Catal Lett 2005, 102, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai WL, Sun Q, Deng JF, Wu D, Sun YH. XPS studies of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 ultra-fine catalysts derived by a novel gel oxalate co-precipitation for methanol synthesis by CO2+H2. Appl Surf Sci 2001, 177, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu ZJ, Ge SH, Zhang MH, Li W, Tao KY. Synthesis of a supported nickel boride catalyst under microwave irradiation. Catal Commun 2008, 9, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule EE, Sadik C, Siddik I. Conventional and microwave-assisted synthesis of ZnO nanorods and effects of PEG400 as a surfactant on the morphology. Inorg Chim Acta 2009, 362, 1855–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang XR, Wang LC, Cao Y, Dai WL, He HY, K. N. Fan. A unique microwave effect on the microstructural modification of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for steam reforming of methanol. Chem Commun 2005, 102, 4104–4106. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Y, Menéndez JA, Arenillas A, Fuente E, Peng JH, Zhang ZB, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of CuO/ZnO and CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 precursors using urea hydrolysis. Solid State Ionics 2009, 180, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura J, Choi Y, Fujitani T. On the issue of the active site and the role of ZnO in Cu/ZnO methanol synthesis catalysts. Top Catal 2003, 22, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasatkin I, Kurr P, Kniep B, Trunschke A, Schlögl R. Role of lattice strain and defects in copper particles on the activity of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol synthesis. Angew Chem Int Edit 2007, 46, 7324–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens M, Studt F, Kasatkin I, Kühl S, Hävecker M, Abild-Pedersen F, et al. The active site of methanol synthesis over Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 industrial catalysts. Science 2012, 336, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang LC, Liu YM, Chen M, Cao Y, He HY, Wu GS, et al. Production of hydrogen by steam reforming of methanol over Cu/ZnO catalysts prepared via a practical soft reactive grinding route based on dry oxalate-precursor synthesis. J Catal 2007, 246, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning WS, Shen HY, Liu HZ. Study of the effect of preparation method on CuO-ZnO-Al2O3 Catalyst. Appl Catal A: Gen 2001, 211, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An X, Li JL, Zuo YZ, Zhang Q, Wang DZ, Wang JF. A Cu/Zn/Al/Zr fibrous catalyst that is an improved CO2 hydrogenation to methanol catalyst. Catal Lett 2007, 118, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao J, Liu ZL, Zhang Y, Tsubaki N. Preparation of mesoporous Cu/ZnO catalyst and its application in low-temperature methanol synthesis. Catal Commun 2008, 9, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang RQ, Yu XC, Zhang Y, Li WZ, Tsubaki N. A new method of low-temperature methanol synthesis on Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts from CO/CO2/H2. Fuel 2008, 87, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae JW, Kang SH, Lee YJ, Jun KW. Synthesis of DME from syngas on the bifunctional Cu–ZnO–Al2O3/Zr-modified ferrierite: Effect of Zr content. Appl Catal B: Environ 2009, 90, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes C, Vukojevi´c S, Schüth F. Correlations between synthesis, precursor, and catalyst structure and activity of a large set of CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol synthesis. J Catal 2008, 258, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
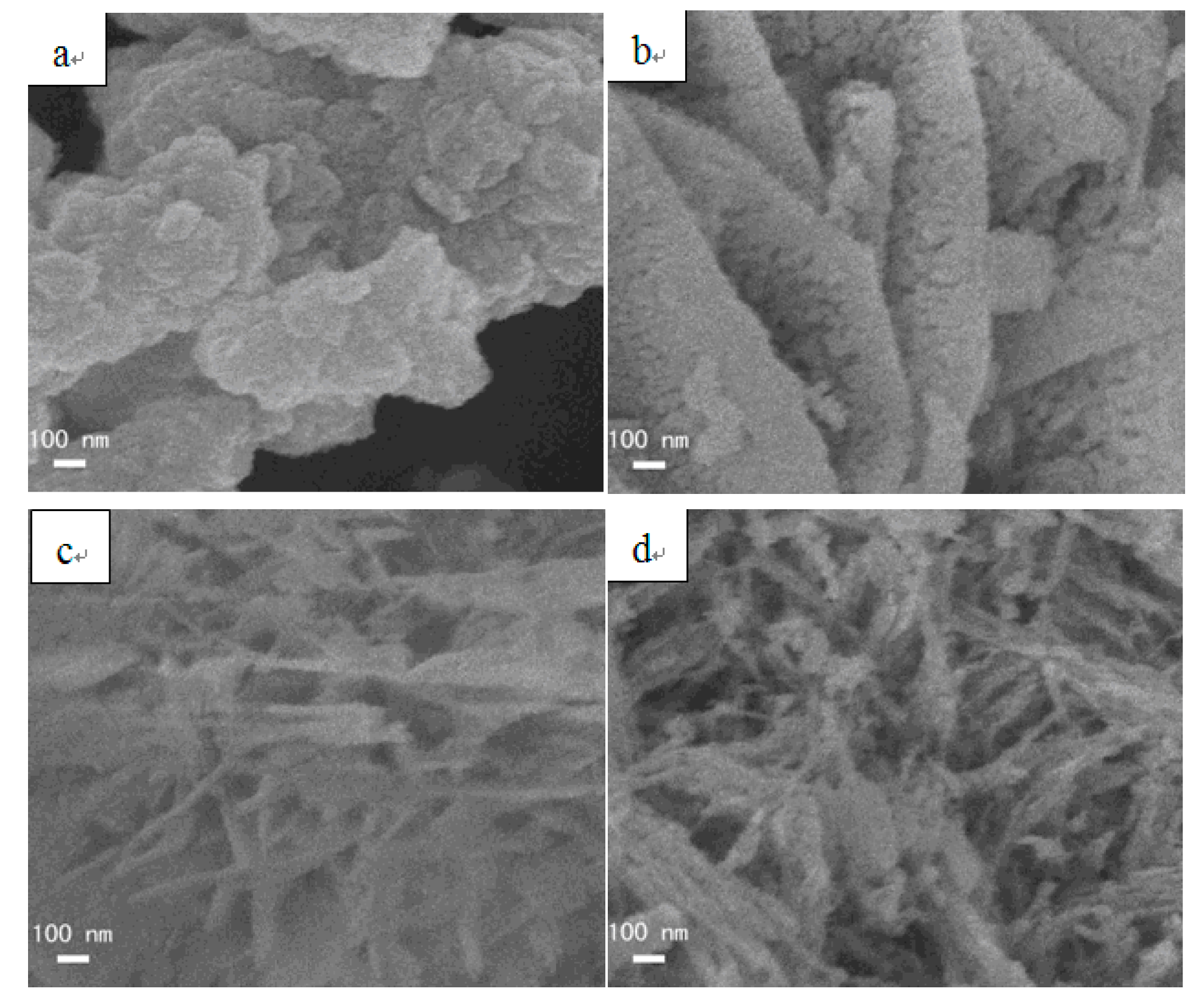


| Catalyst | Precursor | Solvent | Heating manner |
| WWC | WWP | Water | Water bath (WB) |
| EWC | EWP | Ethanol | Water bath (WB) |
| WMC | WMP | Water | Microwave irradiation (MI) |
| EMC | EMP | Ethanol | Microwave irradiation (MI) |
| Catalyst | Grain size /nm | Textural properties | ||
| 2θ≈35.5° | 2θ≈38.7° | Surface area (m2/g) | Pore volume (cm3/g) | |
| WWC | 18.8 | 14.4 | 43.9 | 0.27 |
| EWC | 12.0 | 13.9 | 56.4 | 0.31 |
| WMC | 8.9 | 11.2 | 59.5 | 0.29 |
| EMC | 8.4 | 9.5 | 77.2 | 0.36 |
| Catalyst | Surface atom/% | BE(Cu 2p3/2) /eV |
BE(Zn 2p3/2) /eV |
KE(Cu LMM) /eV |
KE(Zn LMM) /eV |
||
| Cu | Zn | XCu/XZn | |||||
| WWC | 6.56 | 15.61 | 0.42 | 932.00 | 1021.45 | 919.10 | 988.30 |
| EWC | 4.96 | 9.17 | 0.54 | 932.05 | 1020.60 | 919.05 | 988.35 |
| WMC | 5.49 | 8.7 | 0.63 | 932.10 | 1020.35 | 918.95 | 988.80 |
| EMC | 10.77 | 1.2 | 8.98 | 932.95 | 1020.15 | 918.20 | 988.85 |
| Catalyst | Solvent |
aHeating Manner |
XMeOH /% |
STYH2 /mL·g-1·h-1 |
bSCO /% |
| WWC | Water | WB | 53.6 | 300.0 | 1.53 |
| EWC | Ethanol | WB | 59.1 | 333.9 | 0.39 |
| WMC | Water | MI | 85.0 | 479.5 | 0.82 |
| EMC | Ethanol | MI | 91.2 | 516.7 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




