1. Introduction
According to the statistical yearbook published on the official website of the National Bureau of Statistics 2021, it is known that 1,659 cases of geologic hazards occurred in 2020 higher than in 2019, with 4,810 landslides occurring, 1,797 avalanches, 899 mudslides, and 183 ground collapses, which shows that about two-thirds of the geologic hazards originate from landslides. The location, time, scale, and mode of landslide occurrence possess uncertainty, and there is insufficient cognitive ability in terms of these uncertainties. With the development of InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) technology, it is possible to monitor surface deformation in real time to understand the stability of slopes.[
1] In 2005, Wasowski et al. successfully realized the monitoring of surface deformation in two areas of Umbria and Umbria, Italy, using PS-InSAR technology, thus accurately locating the spatial distribution of landslides.[
2,
3] Cheng Tao et al. Cheng Tao et al. identified the landslide deformation range in the loess area of northern Shaanxi by combining the results of field geological survey and remote sensing image interpretation with differential interference processing.[
4] Fabiana et al. successfully studied the Ivancich landslide in central Italy and accurately obtained its deformation characteristics by using a method combining PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR techniques.The results of GNSS, satellite InSAR and GB InSAR campaigns in the Northwestern Italian Alps by Tommaso Carlà et al. analyze and monitor the surface deformation at the landslide site[
5] The surface deformation at the landslide site was analyzed and monitored by Ge Daqing et al. Ge Daqing et al. used qualitative analysis to identify the location of hazard potentials, quantitative analysis to check the magnitude of changes in the hazardous body, and integrated remote sensing dynamic data to enhance the detection of potentials[
6] Xu et al. Xu Qiang et al. proposed the establishment of an early identification system for natural disaster hazards that integrates sky-space-earth and comprehensively utilizes a variety of disaster monitoring means to obtain more accurate landslide hazard information in real time.[
7] The system can be utilized in real time to obtain more accurate information about landslide hazards. After the in-depth study by Shi Xuguo et al, the deformation rate of the Three Gorges Lotus Root Pond landslide was effectively detected using time series InSAR technology, so as to effectively identify and monitor the landslide situation in the Three Gorges reservoir area and other areas.[
8] . Liu Bin and Cai Jiehua et al. processed the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and Jiuzhaigou data with InSAR technology, respectively, and identified the landslides through surface deformation, optical image data and field verification.[
9,
10]. Cong Dai and his team used the SBAS-InSAR method to identify 23 active landslides[
11] . Chenglong Zhang et al. used GACOS-assisted interferometric image stacking (InSAR Stacking) to monitor landslides in the Jinsha River Basin and demonstrated the reliability of this method.[
12] . By using two timing methods, Sentinel-1A/1B and SBAS-InSAR, Li Menghua et al. successfully identified 20 landslide hazards in the Minjiang River valley section of Maoxian County, and confirmed the accuracy of these findings through a field trip[
13]. Zhou Defin et al. used high-resolution imagery and elevated track shape variables to identify landslides in Dongchuan District, thus obtaining geohazard data for the area[
14] . He Jiayang et al. used five InSAR methods to identify landslides in the alpine valley area, and the results showed that SBAS-InSAR technology was effective in identifying landslides in the alpine valley area[
16] . The results show that SBAS-InSAR technology is effective in recognizing landslides in high mountain valley areas. Jiang Zhuo et al. proposed an improved InSAR-based procedure for mapping large landslides in loess hilly areas, which detects and maps a total of 50 potential loess landslides based on tropospheric delay correction by quadtree segmentation and automatic selection of interferograms based on minimum error boundaries.[
17] . Through the above scholars can find that the emergence of InSAR technology greatly improves the uncertainty of landslides, which can not only effectively help the government to detect, recognize, predict and prevent landslides in time, but also illustrates that the surface deformation has an extremely important role in landslide monitoring, and at the same time, it provides a scientific basis for the experiments in this paper.
Landslide susceptibility is mainly through the geological and environmental factors of landslide occurrence, statistically analyze the degree of landslide influence on the evaluation factors, calculate the relative probability value of landslide occurrence in each unit through the model, and classify the degree of susceptibility to the region. The landslide susceptibility model mainly includes two categories: statistical model and machine learning. Statistical models include information quantity model(I), logistic regression(LR), multiple linear regression(MLR), weight of evidence(WOE), index of entropy(IOE), frequency ratio(FR), certainty factor(CF) and other models[
18,
19,
20,
21,
22] . Machine learning has models such as random forest(RF), support vector machine(SVM), artificial neural network(ANN), convolutional neural network(CNN), deep learning, etc.[
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29] . With the development of computers, landslide susceptibility based on machine learning is widely used, for example, the Behnia Pouran et al. used random forest to predict landslide susceptibility probability maps, and the results showed that random forest has high performance in landslide susceptibility modeling[
30] The results show that random forests have high performance in modeling landslide susceptibility. Phong Tran Van et al. utilized 217 landslide datasets from Muong Lay area in Vietnam to evaluate landslide susceptibility using Support Vector Machines , Artificial Neural Networks , and Logistic Regression, which showed that the SVM model has a good prediction accuracy.[
31] . Wang Shibao et al. used Bayesian algorithm to optimize the hyperparameters of the random forest model, and then chose the optimal hyperparameters for landslide susceptibility, and the method improved the model accuracy by 4%[
32] . Yingbin Zhang et al. compared the prediction performance of LR, 5-CV-SVM, GA-SVM and PSO-SVM for landslide susceptibility in the Tibetan Plateau region, and PSO SVM has better performance in landslide susceptibility assessment.[
33] The PSO-SVM has better performance in landslide susceptibility assessment. The above machine learning has achieved certain results, but the phenomenon of insufficient accuracy and model overfitting may occur when facing the complex network structure and a large amount of sample data. Therefore, some scholars combine convolutional neural network and GIS landslide susceptibility research in order to reduce the overfitting phenomenon of the model by virtue of the powerful feature extraction ability and linear regression fitting ability, and further improve the prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility model. Based on the landslides in Wanzhou District, Chongqing, China, which is located in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, Wu Xueling et al. used the oversampling technique combined with CNN to evaluate landslide susceptibility, and the accuracy of the model was as high as 89.50%.[
34] The accuracy of the model is as high as 89.50%.
In summary, while considering a variety of environmental conditions and ensuring the prediction accuracy, the experiments in this paper combine InSAR technology for landslide identification, take the surface deformation rate as an evaluation factor for landslide susceptibility evaluation, and use the Pearson correlation coefficient to exclude the covariance factor, and then optimize the hyper-parameters through the BO algorithm on the basis of the CNN model, so as to make the model have a higher prediction accuracy. Comparative tests are conducted with BO-RF and PSO-SVM models to provide important scientific basis for major disaster prevention and prediction in the study area.
2. Principles and Methods
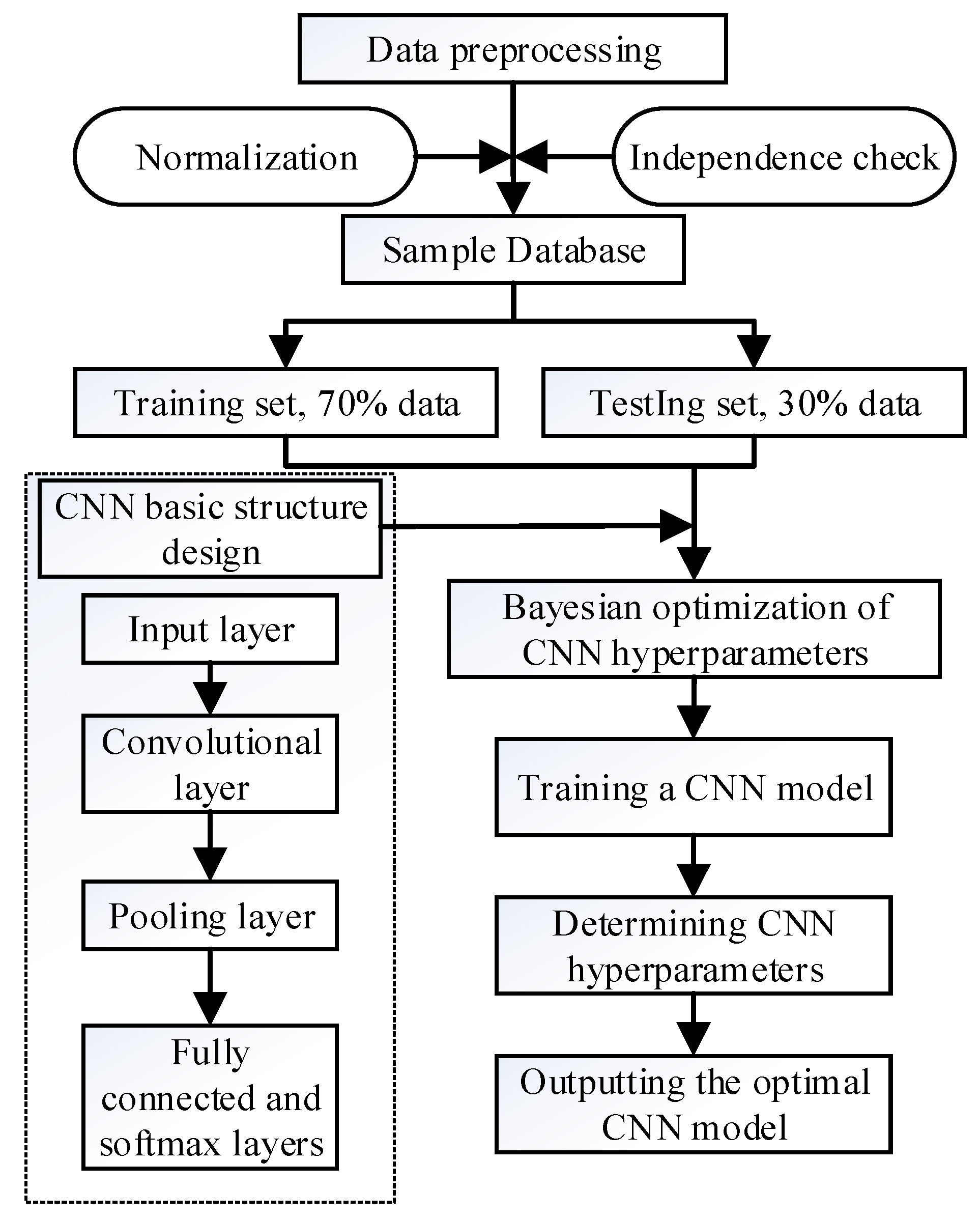
2.1 Convolutional Neural Networks for Bayesian Optimization
Convolutional Neural Networks are an important part of deep learning, which originated from Hunel and Wiesel's research in 1962[
35]. It originated from the research of Hunel and Wiesel in 1962, and has evolved on this basis to become the benchmark of deep learning today. Theoretically, convolutional neural network can be a good description of complex nonlinear relationships, and it is a feedforward neural network with better fault tolerance. Convolutional neural networks mainly include an input layer, a convolutional layer, a pooling layer, an activation layer and a fully connected layer.[
34] Based on the convolutional layer, a simple linear expression is formed by stacking the operational layers of convolution, pooling and upsampling, and the fully connected layer is activated using the Softmax function to realize the binary classification problem.
Bayesian optimization (BO) can quickly and accurately find the optimal solution of the model hyperparameters through multiple iterations and further optimize the model, so Bayesian optimization has an important role in parameter combination optimization. It is used to deal with the complex mapping relationship between the model fitting parameters and the objective function[
32] . As in equation (1)
where z* is the global optimum of f(z).
Landslide susceptibility is to predict the possibility of a landslide occurring in a certain place based on multiple environmental factors. Therefore, the construction of landslide susceptibility model should have a powerful feature extraction, probability prediction and linear regression fitting function, this paper adopts the deep learning method for model construction, in which the CNN has a better function in this regard, which can face the highly nonlinear landslide prediction to reduce the overfitting phenomenon of the model. In addition, there are many kinds of factors affecting the occurrence of landslides, and the direct processing of the original factor data will bring a lot of inconvenience to the model operation, thus wasting more computing power and leading to a reduction in the accuracy of the prediction model. For this reason, in this paper, by grading the factors and using the Pearson correlation coefficient for the initial screening of landslide factors, we obtain the dataset after screening, normalize the dataset to obtain the feature vectors, use the convolution kernel to extract the feature vectors, and then use the BO algorithm to search for optimization of the hyperparameters of the CNN, and finally obtain the prediction results through the calculation of the fully connected layer.
Figure 1.
Convolutional neural network with Bayesian optimization.
Figure 1.
Convolutional neural network with Bayesian optimization.
2.2 Random Forests
In 2001, BREIMAN L and CUTLER A introduced Random forest for the first time with decision trees, sampling, pruning techniques, stochastic subspaces and their related statistical principles.[
36] This intelligent combinatorial classification algorithm not only possesses good data mining, but also predicts complex problems more accurately.RF is a model that uses multiple decision trees as classifiers to carry out training and prediction.The model accuracy is necessary linked to the selection of model parameters.The manual tuning of the parameters is time consuming and unsatisfactory.Therefore, BO algorithm is chosen to perform hyper-parameter tuning to construct the BO RF model.
2.3 Support Vector Machines
Support vector machine classification method was completely proposed at the end of the 20th century[
37,
38] SVM classification. Due to the nonlinear transformation of the inner product function, the optimal hyperplane satisfying the classification is searched in the high-dimensional feature space. Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a computational method that has been used for optimization processing, with the advantages of fast computing speed and easy implementation.[
39] . In this way, the PSO algorithm can be applied to the support vector machine to find the optimal SVM parameters through the particle swarm, and each particle moves iteratively to find the potentially optimal particle swarm, using the constant updating of the particles to find the overall optimal position and to determine the direction of its movement and speed, in order to balance the global search and local search of the PSO algorithm, inertia weights are introduced, and the model optimization result is finally obtained.
2.4 Technical routes
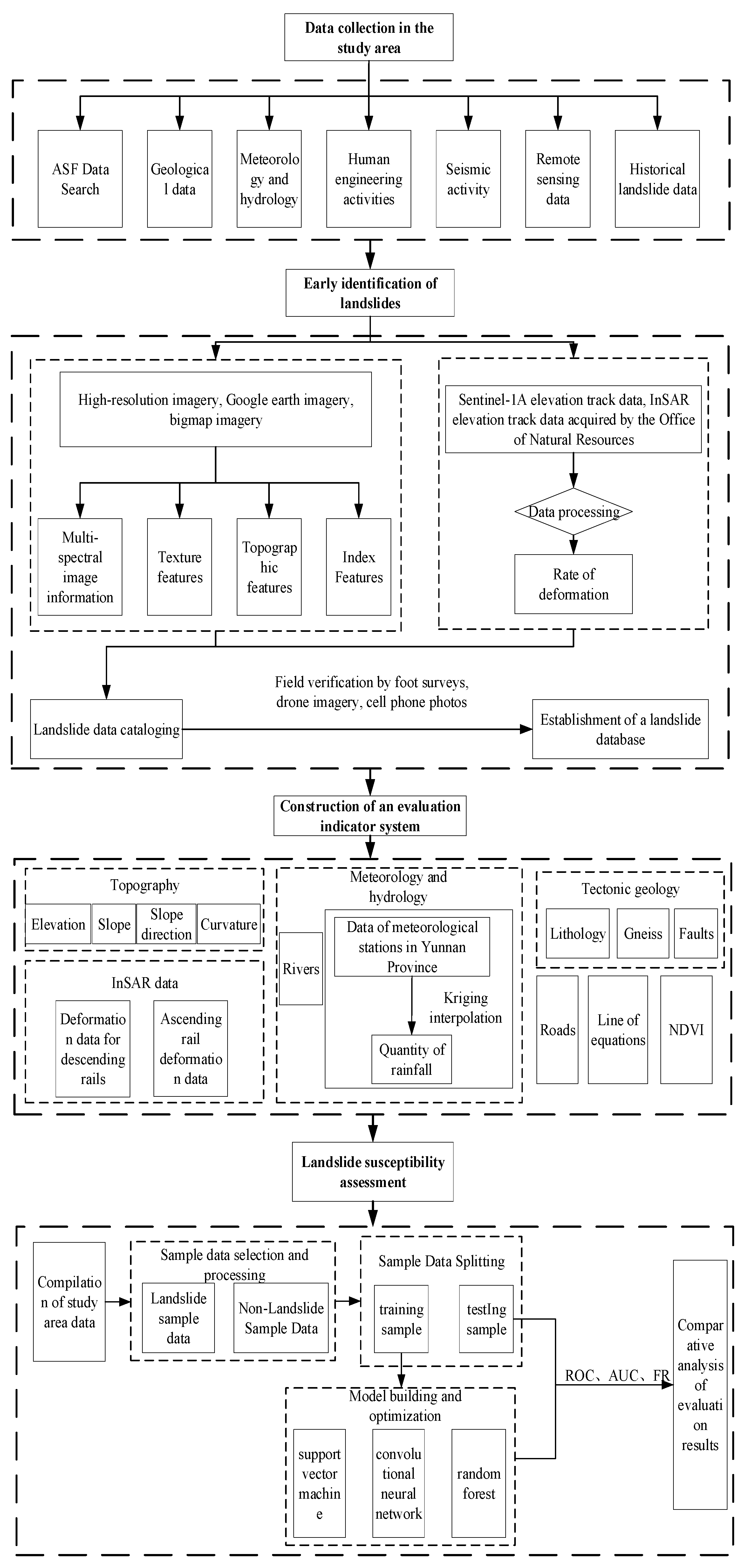
This paper adopts "3S" technology, InSAR radar technology and machine learning to study and design the program with the main line of landslide susceptibility evaluation in the study area. (1) data collection in the study area; (2) landslide cataloging; (3) construction of landslide susceptibility evaluation system; (4) construction of the model and accuracy evaluation. The research technical route of this paper is shown in
Figure 2.
3. Data Preparation and Analysis
3.1 Overview of the Study Area
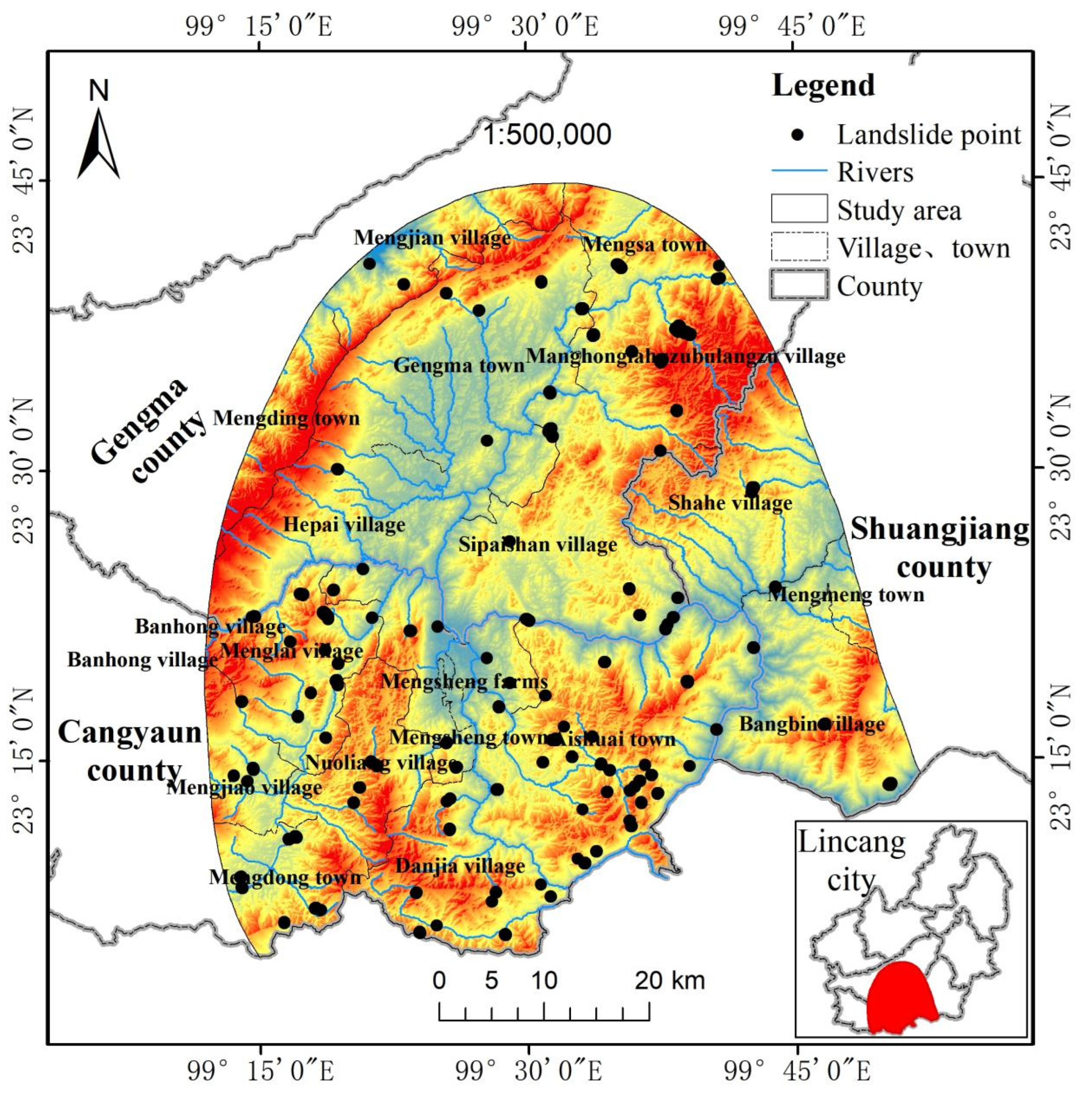
The study area is located in Gengma, Cangyuan, and Shuangjiang counties in the southwestern part of Lincang City, Yunnan Province, with geographic coordinates between 98°52′ and 99°43′ E longitude and 23°04′ and 24°01′ N latitude (
Figure 2). The study area was mainly selected in the region of the 1988 Lancang-Gengma earthquake, and the area extending 10 km outside the VII degree isobar of the Gengma earthquake was taken as the study area. There are many landslide geohazards in the study area, and the study mainly focuses on evaluating and analyzing the landslide geohazards in the area extending 10 km beyond the VII isoseismic line. The overall terrain of the study area is high on all sides and low in the middle, belonging to the Hengduan Mountain Range with high mountains and valleys. Most of the mountains were north-south or north-south direction, the northeast side of the mountain form high and steep, the highest elevation of 2931 m; southwest of the gullies and ravines, the lowest elevation of 676 m, the entire study area height difference of 2255 m, most of the terrain slope in 15 ° ~ 25 ° between. Local sections of the formation of cliffs, crustal uplift is strong, for the development of geological landslides provide favorable conditions[
40] The local areas form cliffs with strong crustal uplift, providing favorable conditions for the development of geological landslides.
Figure 3.
Geographic location of the study area.
Figure 3.
Geographic location of the study area.
3.2 Landslide Cataloging
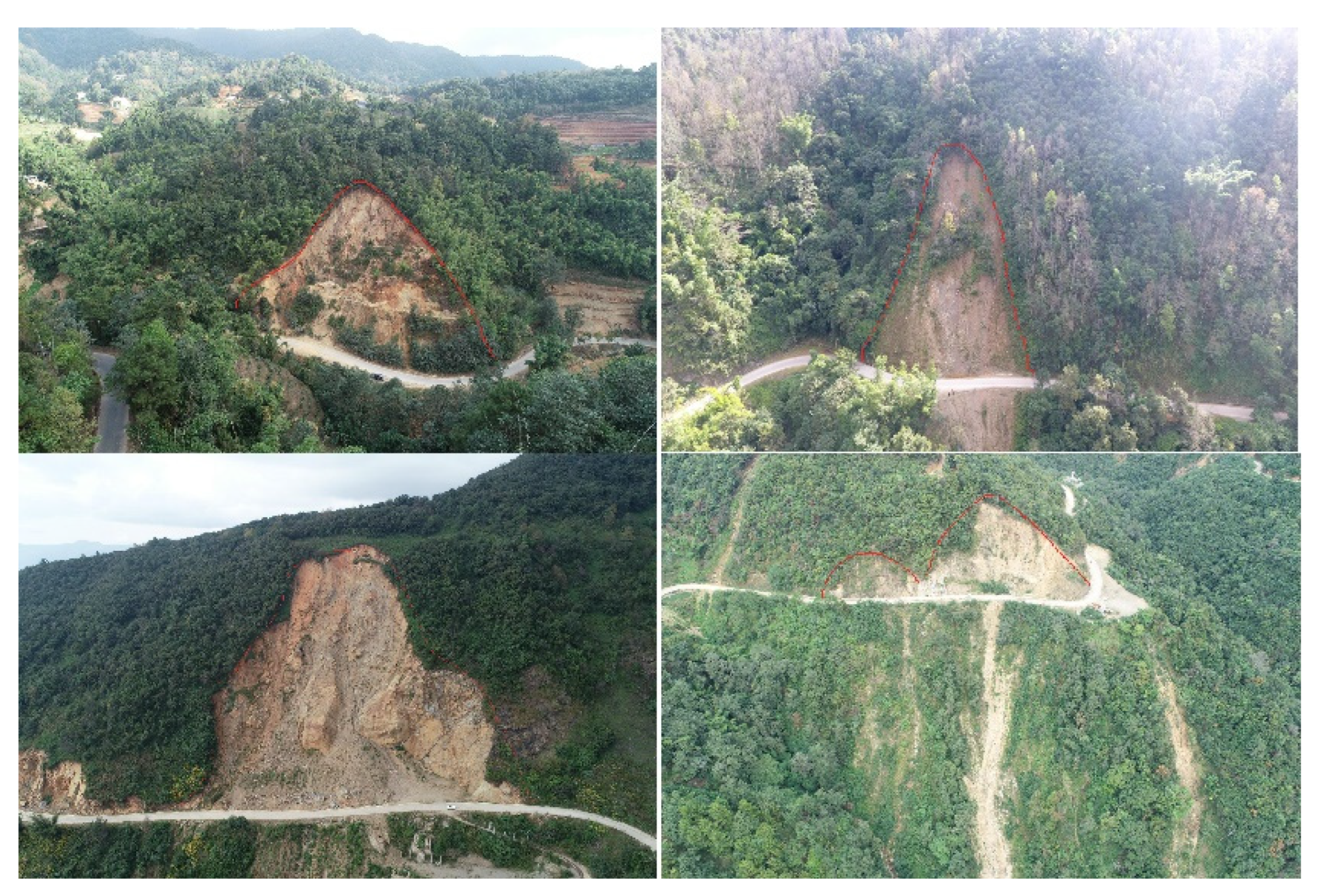
Landslide cataloging data is the prerequisite for landslide susceptibility evaluation, and the completeness and accuracy of its data is of great significance to landslide susceptibility evaluation. In this paper, based on the topography, geological structure and landslide ledger data of the study area, the landslide dataset was established through field validation by synthesizing a variety of new technological means, such as InSAR deformation rate, high-resolution satellite remote sensing, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing and airborne LIDAR measurements, and a total of 122 geologic landslides were identified(
Figure 4), of which 70 landslides, accounting for 57.38% of the total number of landslides, have obvious deformations.
3.3 Data Sources
The data used in the comprehensive remote sensing survey of geologic hazards in the study area are characterized by high precision, high current status and high authority, and the data sources mainly include:
Table 1.
Data sources.
| Data categories |
data scale |
data time phase |
data sources |
| DEM |
30m |
2021 |
ASTER GDEM V2 |
| Slope, slope direction, curvature |
30m |
2021 |
Elevation data acquisition |
| GF-2 remote sensing imagery |
1.0m |
2020, 2021 |
Yunnan Remote Sensing Center |
| Google Remote Sensing imagery |
-- |
2018-2021 |
Google Earth |
| Quantity of rainfall |
30m |
2016-2020 |
Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Statistics |
| Rivers and roads |
-- |
2020 |
Data from the Third National Land Survey |
| Stratigraphic lithology and faults |
1:50,000 |
2015 |
Natural Resources Bureau (NRB) |
| NDVI |
30m |
2020 |
Landsat 8 data |
| Sentinel data |
5m×20m |
2018.7-2021.5 |
European Space Agency (ESA) |
3.4. Selection of Evaluation Factors
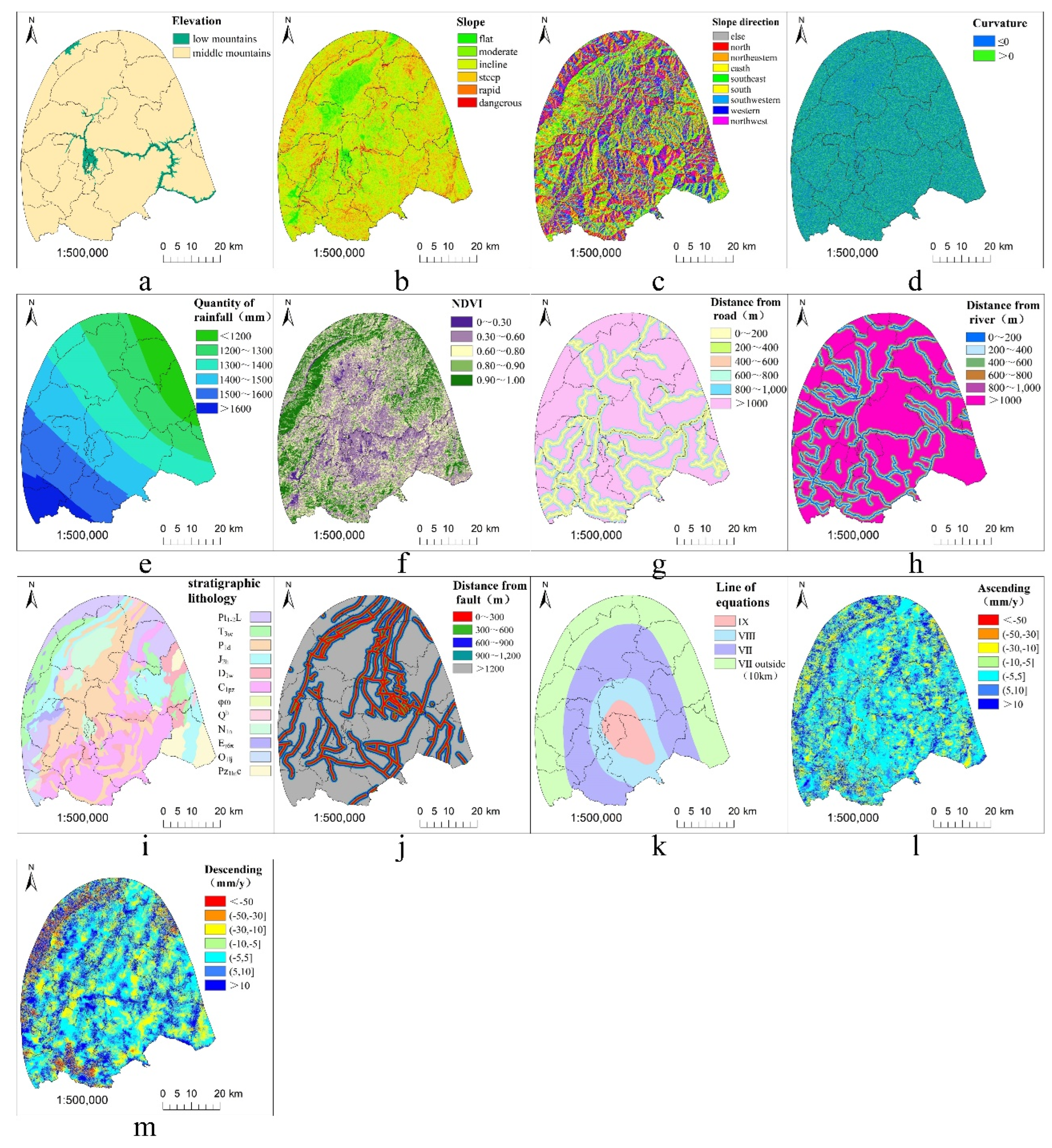
Environmental conditions such as strong neotectonic movements, development of fracture tectonics, structural fragility of geotechnical bodies, differential climate, and high seismic activity, which lead to geologic hazards such as landslides, avalanches, and mudslides. The main factors of geotechnical proximity conditions of landslides, vegetation cover, and the influence of human activities Elevation (
Figure 5a). Slope (
Figure 5b) is one of the important factors influencing landslides and also an important parameter for assessing landslide susceptibility[
41] , which reflects the degree of inclination of the surface and can be used to measure the efficiency of material flow and energy transfer at the surface. Slope orientation (
Figure 5c) has a greater role in mountain ecology[
42] . Different slope orientations cause differences in temperature, humidity, rainfall, sunshine hours and solar radiation intensity, which lead to differences in surface cover, which in turn cause differences in the effects of physical weathering and chemical differentiation, affecting the occurrence of landslides. Curvature (
Figure 5d) is a factor that measures the change in distortion of the terrain surface, which is used to characterize the change in surface curvature in the vertical direction and to better reflect the complexity of the ground surface[
43] . Large amount of precipitation (
Figure 5e) will cause severe damage in the valley, precipitation will destroy the structure and material in the valley and it may also change the landscape of the valley and it may also cause changes in the vegetation and water in the valley, which may ultimately result in the collapse, landslides and mudslides in the valley. Vegetation (
Figure 5f) is an important factor affecting the occurrence of landslides, which not only prevents soil erosion, but also improves the stability of slopes, and also regulates the climate and reduces the wind speed, thus playing the role of fixing slopes and preventing the loss of soil by scouring. The stability of mountain slopes is greatly affected by the large-scale construction of roads (
Figure 5g), which leads to more landslides on mountain slopes. Erosion, hollowing out, and wave impacts by rivers (
Figure 5h) will cause the rock layers at the bottom of valleys to be pushed away, resulting in cliffs at the bottom of valleys and creating a favorable environment for landslides to develop. Stratigraphic lithology (
Figure 5i) is the material basis for the occurrence of landslides. Fractures (
Figure 5j) play a significant role in the nurturing of landslides, and they are critical to the stability and security of the earth. As fractures continue to expand, they will severely destabilize the rock and soil on the upper and lower walls, as well as the entire surface, leading to more landslides. In the application of geohazard deformation monitoring, the displacement condition and spatial distribution of the deformation zone can be recognized by the InSAR deformation rate (
Figure 5l, 5m). Thirteen factors such as elevation, slope, slope direction, curvature, average annual rainfall, vegetation normalization index, stratigraphic lithology, distance from rupture, isokinetic line, distance from river, distance from road, deformation rate of descending rail and deformation rate of ascending rail are selected as the evaluation factors of landslide susceptibility, and the continuity data in the 13 evaluation factors are graded and processed; the discrete data are graded in accordance with the actual determination of the state, and the distribution map is shown in
Figure 5. The distribution diagram is shown in
Figure 5.
3.5 Independence Test
Considering the possible correlation between the indicator factors, it is necessary to select the indicator factors by multiple covariance analysis. In this paper, by obtaining the landslide data and its evaluation factors in the study area, the evaluation factors were tested for mutual independence using the band set statistical tool in ArcGIS software, and their correlation coefficients (ρ = covariance/standard deviation) were obtained, in order to ensure the accuracy of the evaluation model of landslide susceptibility. ρ<0.3 represents the uncorrelation between the factors; 0.3 ≤ ρ<0.5 is low correlation; 0.5 ≤ ρ<0.8 is medium correlation; ρ ≥ 0.8 is high correlation.
As shown in
Table 2, the correlation coefficients are all less than 0.3, indicating that the evaluation factors are independent of each other, and also indicating that all 13 evaluation factors can be included in the evaluation model.
3.6 Evaluation Factor Analysis
In this paper, 30m×30m resolution raster cells are selected for evaluation, totaling 3931814 rasters in the study area. The matrix arrangement of raster cells enables them to store, retrieve and recall information easily, and thus has been widely noticed and emphasized by academics. Frequency Ratio (FR) is a variable statistical analysis technique used to measure the probabilistic relationship of multiple influencing factors, which can better identify the key factors affecting landslides and can more accurately predict the trend of landslide development.The FR method is characterized by the fact that it can more accurately identify the correlation between the influencing factors, in which the value of the FR value depends on the the characteristics of multiple influencing factors, the FR value is greater than 1, it means that the correlation between the factors is strong, and the FR value is less than 1, it means that the correlation between the factors is weak[
44] The
Where: Nij is the number of landslide rasters occurring in the ith evaluation factor j class; N is the total number of rasters of landslides in the study area, Sij No. is the number of rasters in the interval of the ith evaluation factor j class; S is the total number of rasters in the study area.
As shown in
Table 3, the points of landslide distribution in the mid-mountain region are much higher than those in the low-mountain region, and the FR value in the low-mountain region is larger than that in the mid-mountain region, with a value of 1.35.According to the elevation of this class classification, the contribution to the landslide development is large in the low-mountain region.The FR value is positively correlated with the slope, and the larger the slope, the larger the FR value is. FR values were greater than 1 in southeast, south, southwest and west slopes, with southeast and southwest slopes contributing the most to landslide occurrence, with FR values of 1.40 and 1.78, respectively.FR values were greater than 1 in the Kv ≤ 0 region of the study area, with a value of 1.05, which illustrates that Kv ≤ 0 has an effect on landslide occurrence. The average annual rainfall in the areas of <1200 mm, 1200-1300 mm, 1400-1500 mm and >1600 mm had FR values greater than 1. The landslide FR decreased gradually with the increase of NDVI, and the landslide frequency ratios of NDVI in the area of 0-0.6 were greater than 1, with a higher FR in the area of 0-0.3 with a FR value of 2.54, the area of The area is mostly water bodies, bare land, cultivated land, and construction land, and human activities are relatively concentrated, which have a greater impact on the slope and are prone to landslides. As the distance from the road and the river increases, the FR value decreases gradually, in the distance from the road and the river 0-200 m, the FR value is the largest, the value is 3.24, 2.87 respectively, because of the influence of human engineering activities on both sides of the river, thus destroying the stability of the slope, resulting in the region prone to landslides. The FR values of P1d, C1pz and Eγδπ lithologies in the study area are all greater than 1, indicating that these lithologies have a certain role in landslide breeding, of which the Eγδπ lithology has the greatest influence, with an FR value of 7.10, and the formation is Old Tertiary quartz amphibole porphyritic. There is an obvious statistical relationship between the distance from the fracture and landslides, with the distance from the fracture becoming farther, the FR value becomes smaller gradually, and when the distance from the fracture is 300 m, the FR value is the largest, which is about 1.19, indicating that the closer the distance from the fracture, the more prone to landslides. The study area is mainly distributed in the (-5,5] mm/y area, accounting for 47.10%, and the FR value is greater than 1 in the areas of less than -50 mm/y, (5,10] mm/y and greater than 10 mm/y, among which the FR value of <-50 mm/y area is the largest, with the value of 12.50, because the area of the settlement zone occupies a very small area, however, the landslides partially distributed in its area, resulting in a large FR value.
4 Analysis of Evaluation Results
4.1 Results of the Vulnerability Assessment
After grading the evaluation factors, the graded information values corresponding to the 13 evaluation factors and the superimposed total information values are obtained. Since the evaluation factors have different scales, distribution spaces and values, the evaluation factors are normalized to unify the data in order to facilitate better data processing by the model. The commonly used method for normalization is min-max, which is calculated by the formula:
Where Xmax and Xmin represent the maximum and minimum values of the data set. In this study, 13 evaluation factors are selected to establish a sample data set, which includes landslide samples and non-landslide samples. A binary classification model was constructed to assign a value of "0" to the non-landslide unit and a value of "1" to the landslide unit. The sample data were divided into training data set and test data set according to 7:3, and the training data set was used for modeling operations, and the test data set was used for model accuracy testing.
In this paper, we use python3.8 software to train the random forest model, import the samples into the software, divide the training dataset and test dataset by using the random forest classifier, use the training dataset for modeling, and optimize the model before modeling, and search for the optimal hyper-parameter values by using the Bayesian optimization algorithm, which mainly focuses on the hyper-parameters such as n_estimators, max_depths, n_estimators, max_depths, min_samples_splits and max_features to get their optimal parameter values. The values of hyperparameters through 64 iterations are max_depth=18; min_samples_split=3; min_samples_leaf=1, max_features=1. The parameters are inputted into the model, and the modeling operation is carried out to get the landslide susceptibility results.
The accuracy of SVM, on the other hand, depends entirely on the chosen kernel function, and these variables contain linear function, radial basis function (RBF), sigmoid, and polynomial. Due to the better stability and robustness of the RBF radial basis function, the RBF radial basis function is chosen as the kernel function of the prediction model in this paper. Parameter selection is the most critical in the support vector machine model, and the parameter selection is directly related to the prediction performance of the model. In this paper, intelligent optimization search is carried out by PSO, which finds the potentially optimal particle swarm through each particle movement iteration, finds the overall optimal position by using the continuous updating of the particles and determines the direction of its movement and speed, and in order to balance the global and local searches of the PSO algorithm, inertia weight is introduced, and the final obtain the model optimization results. When initializing the particle swarm optimization calculation, the number of particle swarms in it is adjusted to 50, and the highest evolution frequency in it is adjusted to 200, and at the same time, the local search ability factor c1 is adjusted to 1.3, and the global search ability factor c2 is adjusted to 1.5, and the inertia weight ω is adjusted to 0.6, and furthermore, the initial coefficient wV is adjusted to 1, and the initial coefficient wP is adjusted to 1. After iteration, the SVM parameter optimization results are obtained as follows: penalty factor C=1 and kernel parameter gamma=0.02. Substituting the parameters into the model operation, the landslide susceptibility results are obtained.
In this paper, all the landslide evaluation factors are combined together, and each pixel can be regarded as a one-dimensional feature vector, and these vectors together constitute a one-dimensional array of the study area. Using the sample data randomly selected in the ratio of 7:3 to form the training set and test set for model training, and constructing a one-dimensional convolutional neural network based on keras. Firstly, the one-dimensional sample data consisting of 13 evaluation factors are input into the model, a convolutional layer of size 3 is constructed, and 32, 64, and 128 filters with kernel 3 are selected for feature extraction, respectively, and an average pooling layer of size 2 is defined behind each convolutional layer while keeping the output dimension unchanged to extract the salient features and at the same time reduce the parameters. According to Sigmoid, ReLU, Leaky ReLU, tanh activation function for comparison experiments, after comparison selected tanh activation function for experimental research in this paper, using Bayesian optimization algorithm to adjust the model hyper-parameters to optimize the performance of the model, get batch size = 128, epoch = 200 the best results, substitution of the parameters for the operation to get landslide The result of landslide susceptibility is obtained by substituting the parameters.
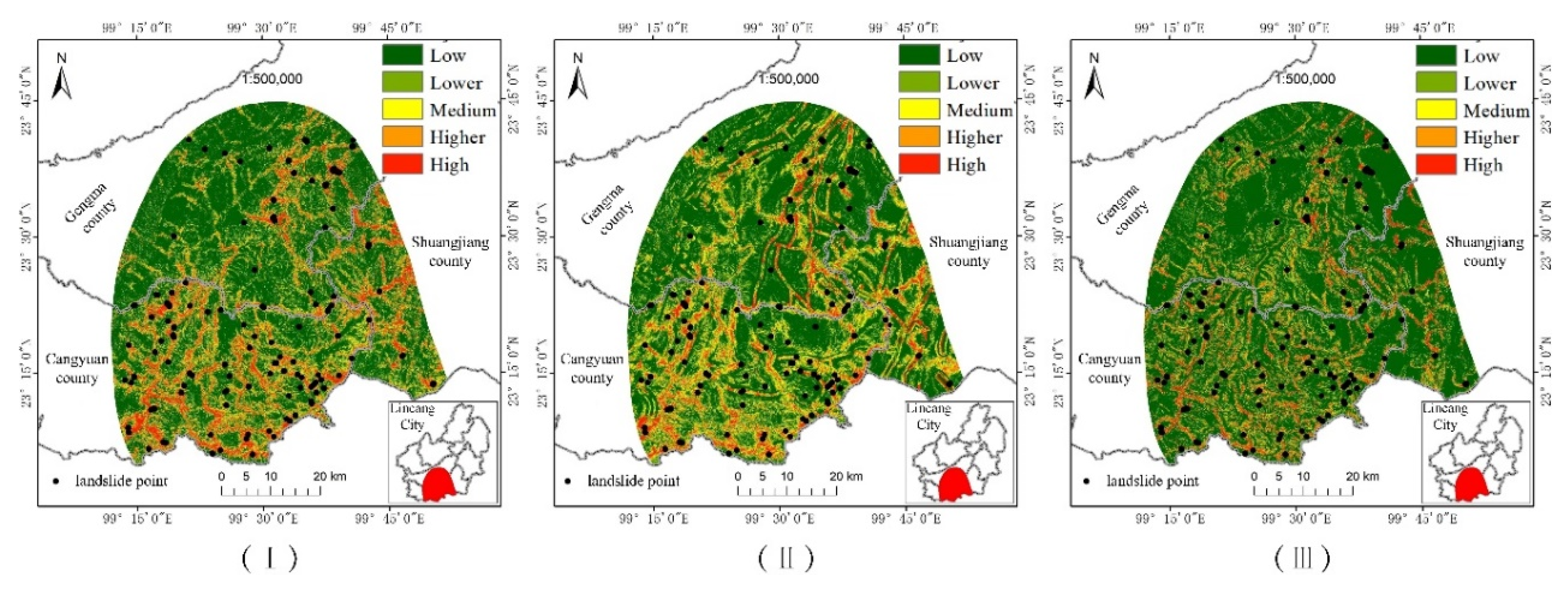
In order to realize the processing and visualization of the landslide susceptibility prediction results, ArcGIS10.2 software was used, combined with the resultant data obtained from the model, and the predicted values of the dataset were converted into raster image elements through the point to raster in the conversion tool of the software, and the landslide susceptibility assessment value of the whole study area was graded according to the natural segment point method of the software, and divided into five susceptibility grade intervals: low susceptibility zone , lower susceptibility zone, medium susceptibility zone, higher susceptibility zone, and high susceptibility zone.The landslide susceptibility maps of PSO-SVM, BO-RF, and BO-CNN models are shown as (Ⅰ), (Ⅱ), and (Ⅲ) in
Figure 6, respectively. By observing the landslide susceptibility maps predicted by the three models, all of them have similar spatial distributions, with high susceptibility zones mainly distributed in the southwestern part of the study area and low susceptibility zones mainly distributed in the northwestern part of the study area.
4.2 Evaluation Accuracy Analysis
The ROC curve shows that there is a close connection between sensitivity and specificity, and the relationship between them forms a complete network. By observing the performance of the ROC curve, we can better measure the performance of the model and thus make more accurate predictions. After previous practice, it is summarized that the value of the ROC curve closest to the inflection point in the upper left corner is the most appropriate value to be set as the threshold for classification[
45,
46,
47] The area under the curve (area under the curve) is the most appropriate threshold for classification. The area under curve (AUC) is the evaluation criterion for detecting the goodness of the model, and the size of the AUC value plays a decisive role in the prediction accuracy of the model, usually when the AUC value is lower than 0.5, the model has no prediction ability, when the AUC value is 0.5-0.7, the model has lower prediction ability, when the AUC value is 0.7-0.9, the model has higher prediction ability, and the AUC value is greater than 0.7, the model has lower prediction ability, and the AUC value is greater than 0.7, the model has lower prediction ability. predictive ability, and for AUC values greater than 0.9, the model has very high predictive ability.
Where: TPR is the true positive rate, FPR is the false positive rate.TP is the number of true positives, FP is the number of false positives, FR is the number of false negatives and TN is the number of true negatives.
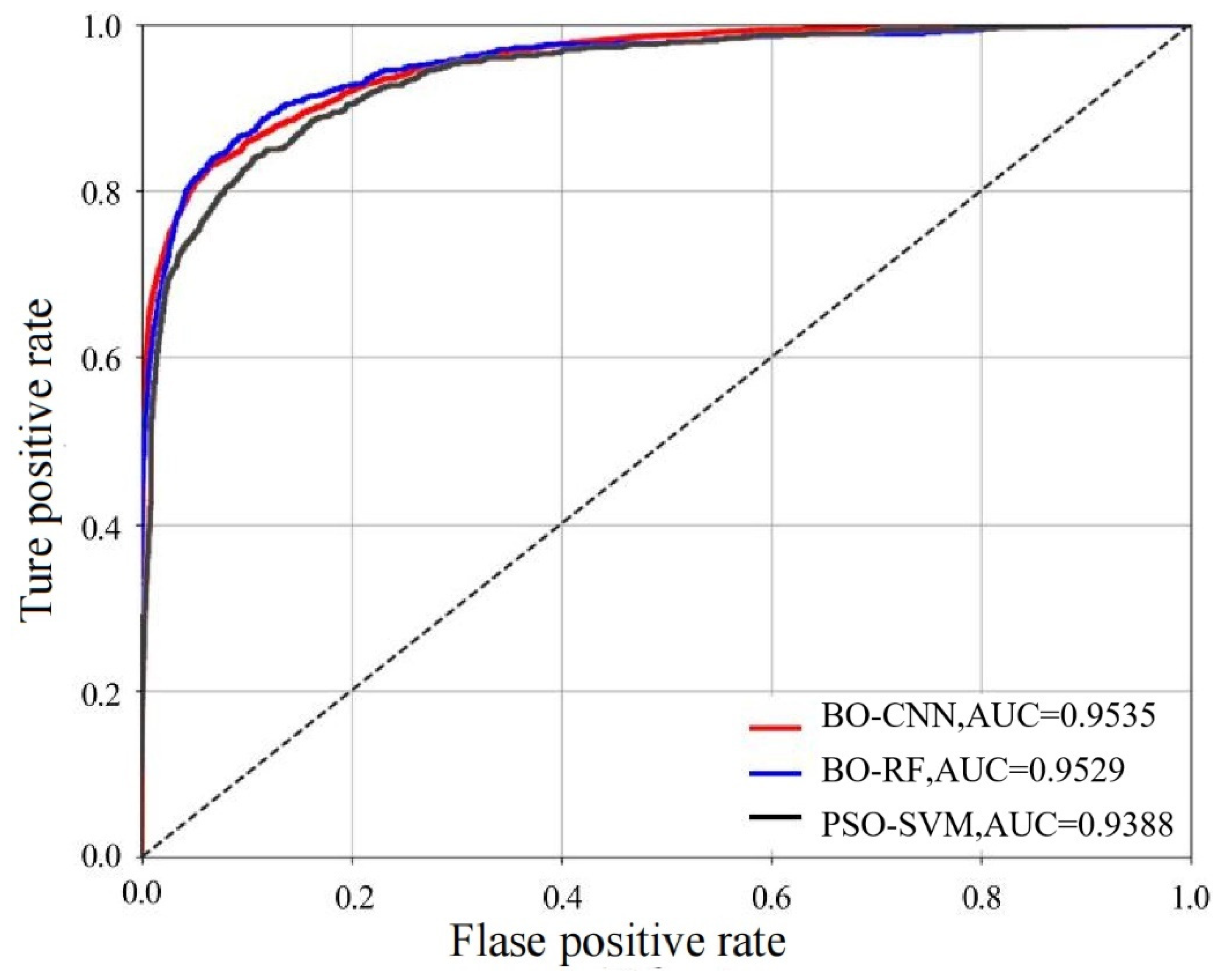
In this paper, the training set data are calculated by the optimization model, the ROC curve is plotted using the test data set, and the value of AUC is calculated. As shown in
Figure 7, the ROC curves drawn by PSO-SVM, BO-RF and BO-CNN models are all close to the inflection point at the upper left corner, indicating that all three models can effectively evaluate the landslide susceptibility, and the AUC values of PSO-SVM, BO RF and BO-CNN models are 0.9388, 0.9529 and 0.9535, respectively, which indicates that the prediction accuracies of the three models are high, and all of them can accurately evaluated the landslide susceptibility in the study area, among which the CNN model evaluated the best.
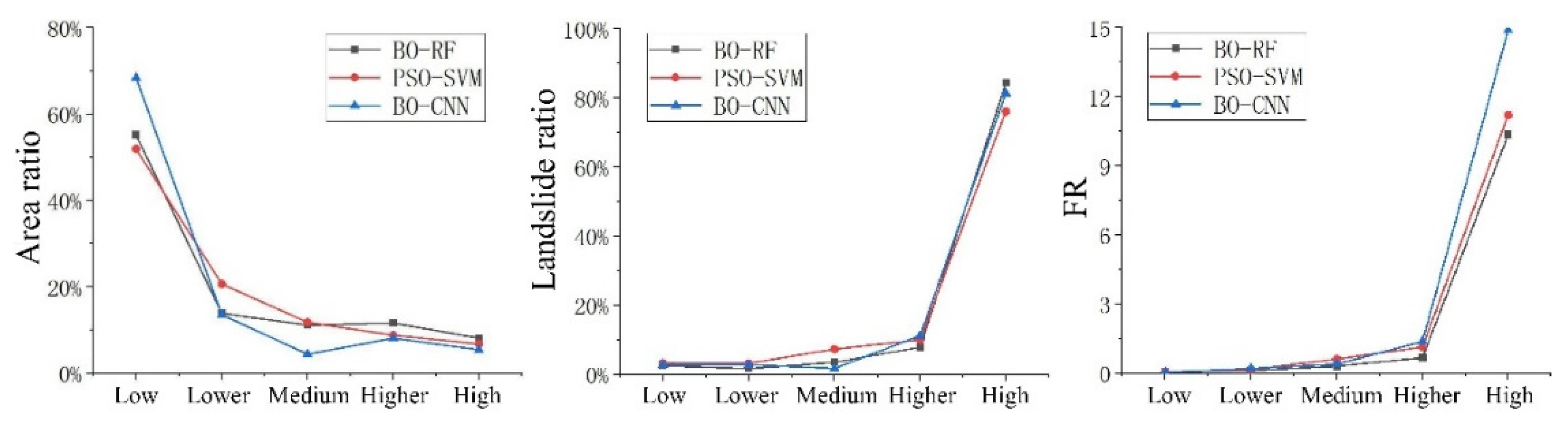
Through reclassification in the Spatial Analyst tool in ArcGIS 10.2 software, the raster image elements and the number of landslides in the geologic landslide susceptibility zones of the study area were counted, and the results of landslide hazard susceptibility in the study area were analyzed using the FR method. As can be seen in
Figure 8, the prediction results of PSO-SVM, BO-RF and BO-CNN models were classified into five categories of susceptibility zones, namely, high, high, medium, low and low, using the natural breakpoint method.The area of landslide susceptibility in low susceptibility zones of BO-CNN model accounted for 68.43% of the total area, and the area of low susceptibility zones was larger than that of BO-RF and PSO-SVM, and the area of high susceptibility zones accounted for 5.46% of the total area, and the area of high susceptibility zones accounted for 5.46% of the total area. and the area of high susceptibility zone is smaller than that of BO-RF and PSO-SVM; the distribution of landslides in each susceptibility zone is relatively the same in each model, and the proportion of landslides in high susceptibility zones is 76.10%, 84.39%, and 81.37%, respectively; the frequency ratios of BO-CNN in the high susceptibility zones and higher susceptibility zones are greater than 1, and those in the middle susceptibility zones, lower susceptibility zones, and lower susceptibility zones are less than 1, with the highest value of frequency ratio and the value of frequency ratio in the high susceptibility zone being the highest. The frequency ratio of BO-CNN in the high susceptibility zone and higher susceptibility zone is greater than 1. The frequency ratio of BO-CNN in the middle susceptibility zone and lower susceptibility zone and low susceptibility zone is less than 1, in which the frequency ratio of the high susceptibility zone is the highest, with a value of 14.90 and higher than that of BO-RF and PSO-SVM, whose frequency ratios in the high susceptibility zone are 10.35 and 11.21, respectively, which indicates that BO-CNN model has a high accuracy in the prediction of landslide susceptibility.
5 Conclusion
Aiming at the problems of limited data sources of traditional landslide monitoring means and the lack of effective methods to excavate the spatial distribution characteristics of landslide disasters and their triggering factors, this paper provides a landslide susceptibility evaluation method taking into account InSAR deformation, utilizing the historical landslide data, high-resolution satellite remote sensing, unmanned aircraft remote sensing, airborne LIDAR measurements, and surface deformation information of the study area by inverting the InSAR technology, combining the engineering geology principles and landslide interpretation signs to carry out early identification of regional landslides, and 122 landslide databases were established after field verification. In this paper, after screening, we finally selected 13 evaluation factors, including elevation, slope, slope direction, curvature, average annual rainfall, vegetation normalization index, stratigraphic lithology, distance from faults, Line of equations, distance from rivers, distance from roads, rate of descending and ascending deformation, and constructed an evaluation index system by using the factors to build a data set of landslides in the study area, and then adopted BO-CNN model to evaluate the susceptibility of landslides in the study area from the point of view of disaster prevention and mitigation. model to evaluate the landslide susceptibility of the study area from the perspective of disaster prevention and mitigation.
The screened evaluation factors were tested for independence, and the 13 evaluation factors were independent of each other to ensure the accuracy of the susceptibility model. The relationship between landslides and indicator factors was analyzed based on the frequency ratio method by grading each evaluation factor. The results showed that the categories of the impact factors identified by the frequency-ratio model included elevation of low mountains, slope gradient of sharp, steep and dangerous slopes, slope direction of south-east and south-west slopes, topographic curvature less than or equal to 0, average annual rainfall of less than 1300 mm, 1400-1500 mm and more than 1600 mm, NDVI 0-0.6, distance from roads 0-400 m, distance from rivers 0-400 m and 600-800 m, the stratigraphic lithology is P, C, Eγδπ , the distance from the fault is 0-300 m and more than 1200 m, the isoseismic line is Ⅶ and Ⅶ outside (10km), the rate of deformation of the descending rail is more than -5 mm/y, and the rate of deformation of the ascending rail is less than -50 mm/y and more than 5 mm/y, which has an indirect or direct contribution to the occurrence of landslides.
PSO-SVM, BO-RF and BO-CNN landslide susceptibility models were implemented using Python programming language and susceptibility evaluation was performed. In order to determine the accuracy of the models, ROC and AUC are selected as the model accuracy indicators in this paper. The calculation results show that the ROC curves of the three models are close to the upper left corner, and the AUC values of the three models are 0.9388, 0.9529, and 0.9535, respectively, among which the BO-CNN model obtains the most effective ROC curve and AUC value. The distribution of susceptible zones in the study area was analyzed, and the feasibility of the models was tested with the percentage of the number of landslides in the susceptible zones predicted by the three models and the FR. The experimental results show that the proportion of landslides in the high susceptibility zone of PSO-SVM, BO-RF and BO-CNN are 76.10%, 84.39% and 81.37%, respectively, which indicates that the majority of landslides in the study area of landslides are distributed in the high susceptibility zone in line with the actual situation, and the FR value of landslides in the high susceptibility zone of BO-CNN is as high as 14.9, and the FR value is much higher than 1, which demonstrates a stronger correlation . The combination of the two situations shows that the BO-CNN model is used for landslide susceptibility evaluation with high accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D. and Y.L.; methodology, Y.D.; software, Y.D.; validation, X.Z. and Y.D.; formal analysis, Y.D.; investigation, Y.D.and X.Z.; resources, X.Z.; data curation, Y.D. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D.; writing—review and editing, Y.D., X.Z. and Y.L.; visualization, Y.D.; supervision, X.Z.; project administration, X.Z.; funding acquisition, X.Z . All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42161067.
Data Availability Statement
No applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chi T H, Su Y F. Integrated System for Remote Sensing Monitoring and Assessment of Major Natural Disasters [M]. China Science and Technology Press, 1995.
- Wasowski, J, Bovenga, F, Casarano, D, et al. Application of PSI techniques to landslide investigations in the Caramanico area (Italy): lessons learnt[C Application of PSI techniques to landslide investigations in the Caramanico area (Italy): lessons learnt[C]//Fringe 2005 Workshop. 2006, 610.
- Guzzetti, F, Reichenbach, P, Ardizzone, F, et al. Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models[J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 81(1/2):166-184. [CrossRef]
- Cheng T, San X J, Dong W T, et al. A study of landslide distribution in loess area with InSAR [J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2008, (1): 4. [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T, Tofani, V, Lombardi, L, et al. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment[J]. Geomorphology, 2019, 335: 62-75. [CrossRef]
- Ge D Q, Dai K R, Guo Z C et al. Early Identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies:thoughts and recommendations[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2019, 44(07): 949-956. [CrossRef]
- Xu Q, Dong X J, Li W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,Monitoring and warming system for potentianl catastrophic geohazards[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2019, 44(07):957-966. [CrossRef]
- Shi X G, Xu J H, Jiang H J, et al. Slope stability state monitoringandn updating of the outang landslide,Three gorges area with time series InSAR analysis[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(12): 4284-4292. [CrossRef]
- Liu B, Ge D Q, Wang S S, et al. Combining application of TOPS and scanSAR InSAR in large-scale geohazards identification[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2020, 45(11): 1756-1762. [CrossRef]
- Cai J H, Zhang L, Dong J, et al. Detection and monitoring of post-earthquake landslides in jiuzhaigou using radar remote sensing[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2020, 45(11): 1707-1716. [CrossRef]
- Dai, C, Li, W L, Lu, H Y, et al. Active landslides detection in Zhouqu county,gansu province using InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science), 2021,46(07): 994-1002. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C L, Li Z H, Yu C, et al. Landslide detection of the jinsha river region using GACOS assisted InSAR stacking[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2021, 46(11): 1649-1657. [CrossRef]
- Li M H, Zhang L, Dong J, et al. Detection and monitoring of potential landslides along Minjiang river valley in maoxian county,sichuan using radar remote sensing[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science), 2021 ,46(10): 1529-1537. [CrossRef]
- Zhou D Y, Zuo X Q, Xi W F, et al. Early identification of landslide hazards in deep-cut alpine canyon using SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2022, 33(02): 16-24. [CrossRef]
- Xu Q, Lu H Y, Li W L, et al. Types of potential landslide and corresponding identification technologies[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science), 2022, 47(03): 377-387. [CrossRef]
- He J Y, Ju N P, Xie M L, et al. Comparison of InSAR technology for identification of hidden dangers of geological hazards in alpine and canyon areas[J/OL]. Earth Science: 1-20[2023-02-16].
- Jiang, Z, Zhao, C, Yan, M, et al. The Early Identification and Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Loess Landslides with SENTINEL-1A Datasets: A Case of Dingbian County, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(23): 6009. [CrossRef]
- Zhou P, Deng H, Zhang W J et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on information value model and machine learning method: A case study of lixian county, sichuan province[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 42(09): 1665-1675.
- Luo L G, Pei X J, Cui S H, et al. Combined selection of susceptibility assessment factors for Jiuzhaigou earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(11): 2306-2319 .
- Zhang Z Y, Dang M G, Xu S G, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(01): 157-171 . [CrossRef]
- Li Y W, Xu L R, Zhang L L,et al. Study on development patterns and susceptibility evaluation of coseismic landslides within mountainous regions Influenced by strong earthquakes[J/OL]. Earth Science, 2022, : 1-14. [CrossRef]
- S. B, T. F, B. A H. Landslide susceptibility mapping using maximum entropy (MaxEnt) and geographically weighted logistic regression (GWLR) models in the Río Aguas catchment (Almería, SE Spain)[J]. Natural Hazards, 2023, 117(1). [CrossRef]
- Wubiao H,Mingtao D,Zhenhong L, et al. An Efficient User-Friendly Integration Tool for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Based on Support Vector Machines: SVM-LSM Toolbox[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(14). [CrossRef]
- Huang W B, Ding M T, Wang D et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment along the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor based on layer adaptive weighted convolutional neural network[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(06): 2015-2030. [CrossRef]
- Yuke H,Lei S,Umair K, et al. Stacking ensemble of machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility mapping in Zhangjiajie City, Hunan Province, China[J]. China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2022,82(1). [CrossRef]
- Kong J X, Zhong J Q, Peng J B et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in chinese loess plateau based on IV-RF and IV-CNN coupling models[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(05): 1711-1729. [CrossRef]
- Hidayatul M U,Rohmaneo M D. Landslide Susceptibility Spatial Modelling Using Random Forest Algorithm: a Case Study of Malang Regency[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2023,1127(1). [CrossRef]
- Jingyun G,Rafael L A,Miao Y, et al. GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Modeling: a Comparison between Best-First Decision Tree and Its Two Ensembles ( BagBFT and RFBFT)[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(4). [CrossRef]
- Teruyuki K,Koki S,Satoshi N, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using automatically constructed CNN architectures with pre-slide topographic DEM of deep-seated catastrophic landslides caused by Typhoon Talas[J]. Natural Hazards,2023,117(1). [CrossRef]
- Behnia P, Blais-Stevens A. Landslide susceptibility modelling using the quantitative random forest method along the northern portion of the Yukon Alaska Highway Corridor, Canada[J]. Natural hazards, 2018, 90(3): 1407-1426. [CrossRef]
- Phong T V, Phan T T, Prakash I, et al. Landslide susceptibility modeling using different artificial intelligence methods: a case study at Muong Lay district, Vietnam[J]. Geocarto International, 2021, 36(15): 1685-1708. [CrossRef]
- Shibao W, Jianqi Z, Jia Z, et al. Application of Bayesian Hyperparameter Optimized Random Forest and XGBoost Model for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9. [CrossRef]
- Bin Y Z,Yi P X,Jing L, et al. Comparison of LR, 5-CV SVM, GA SVM, and PSO SVM for landslide susceptibility assessment in Tibetan Plateau area, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2023,20(4). [CrossRef]
- Wu X L,Yang J Y,Niu R Q. A Landslide susceptibility assessment method using SMOTE and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition),2020,45(08):1223-1232. [CrossRef]
- Hubel D H, Wiesel T N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex[J]. The Journal of physiology, 1962, 160(1): 106. [CrossRef]
- Breiman L. Random forests [J]. Machine learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. [CrossRef]
- Vapnik V, Lerner A. Pattern recognition using generalized portrait method[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 1963, 24:774-780.
- Vapnik V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory[M]. Springer. 2000. [CrossRef]
- Sunil S,Anik S,Bishnu R, et al. Correction to: integrating the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) with machine learning methods for improving the accuracy of the landslide susceptibility model[J]. Earth Science Informatics,2022,15(4). [CrossRef]
- Zou S L, Duan H C. Study on the distribution pattern of geologic hazards in Gengma County, Yunnan Province[J]. Sichuan Journal of Geology, 2016, 36(S1): 38-41+46. [CrossRef]
- Gorokhovich Y, Machado E A, Melgar L I G, et al. Improving landslide hazard and risk mapping in Guatemala using terrain aspect [J]. Nat Hazards, 2016, 81(2): 869-886. [CrossRef]
- Qi W J, Yang X M, Li Z, et al. Study on the correlation between topographic features and distribution of land use types in Jinggang Mountain[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2018, 33(04): 64-71. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y G, Li Z F, Liu M Y, et al. Analysis of topographic differences of yongshou county based on different resolutions of DEM[J]. Research on Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(06): 131-136.
- Guo Z Z, Yin K L, Huang F M, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(02): 287-300. [CrossRef]
- Khouz A, Trindade J, Oliveira S C, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the rocky coast subsystem of Essaouira, Morocco[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2022, 22(11): 3793-3814. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal N, Dixit J. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping of the Meghalaya-Shillong Plateau region using machine learning algorithms[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2023, 82(5): 170. [CrossRef]
- Sun D L, Chen D L, Mi C L et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in the gentle hill-valley areas based on the interpretable random forest-recursive feature elimination model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2023, 29(02): 202-219. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
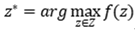 ,
,
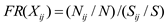
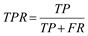 ,
,
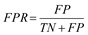 ,
,