1. Introduction
Serious concerns have been raised regarding the environmental pollution caused by heavy metals and their detrimental effects on both human well-being and ecological systems. Multiple sources, including industrial waste, soil leaching, and petroleum products, contribute significantly to the presence of these heavy metals [
1]. Lead has garnered considerable interest, especially given its extensive application across multiple industrial domains [
2]. Drinking water is a primary source of Pb
2+ that enter the food web, and as a result, the World Health Organization has established a maximum allowable limit of 48 nmol/L for Pb
2+ in drinking water [
3]. Exceeding this limit can lead to severe health complications [
4].
Various physical and chemical techniques are at our disposal to eliminate contaminants, such as filtration, electrocoagulation, reverse osmosis, precipitation, biosorption, and adsorption. The costs associated with implementing and operating these techniques vary significantly, as does their efficacy in removing contaminants. Adsorption-based methods, in particular, often offer cost advantages in terms of infrastructure and operation, although the efficiency of eliminating the contaminants relies on the properties inherent to the utilized sorbent. Despite the numerous industrial adsorbents available for heavy metal removal in wastewater, there is a growing interest in the advancement of sustainable biosorbents. This interest stems from their renewable abundance and potential for incorporation into composite materials [
5].
The utilization of activated carbon (AC) has become popular due to its excellent adsorption performance. However, the effective reusability of AC poses challenges due to the complexity of recovery methods [
6]. In many instances, modifications are necessary to enhance the affinity of conventional AC towards specific pollutants. This is because common AC may exhibit limitations in adsorption capacity due to its small specific surface area, elevated ash content, inadequate adsorption selectivity, restricted surface functional groups, and electrochemical properties [
7,
8]. Additionally, powdered AC tends to disperse in water, resulting in poor recyclability, potential secondary contamination, and cost-intensive operational procedures, rendering it unsuitable for treating high flux effluents [
9].
Recognizing these challenges, extensive research has been performed using polyurethane (PU) in heavy metal treatment [
10]. PU foam is a promising and cost-effective material that exhibits favorable thermodynamics for sequestering and binding cations, thereby proving successful in the heavy metals and volatile compounds eradication from wastewater and aqueous systems [
11]. The manufacturing and shaping of PU adsorbents are relatively straightforward, adding to their appeal [
12]. The characteristics of the resulting foam are significantly influenced by the choice of polyol, the key starting material for PU [
13]. While petroleum-based polyols are commonly employed, their limited availability and environmental concerns have spurred investigations into alternative bio-based polyol sources.
In the present study, a novel coconut oil (CO)-based polyurethane foam-activated carbon composite (PACC) is formulated to address reusability, economic, environmental, and sustainability concerns. The process starts with the sequential glycerolysis and amidation of CO for the production of bio-based polyol [
14]. This polyol was then employed along with AC in a PU formulation to produce a PACC material. Moreover, the produced PACC is designed to exhibit excellent chemical and thermal stability, enhanced accessibility, and cost-effectiveness in production. To assess its performance, the dynamic adsorption behavior of these foams in relation was examined through experiments conducted in a fixed-bed column set-up, particularly for Pb
2+ sequestration.
In a controlled laboratory setting, a method involving a fixed-bed column was employed to systematically investigate the effects of various operational factors. These factors included bed height, pH levels, influent flow rate, and initial concentration. The aim of this study was to thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of using PACC as a medium for the process of adsorption [
15]. The patterns illustrating the breakthrough of Pb
2+ adsorption were additionally evaluated using the Bohart-Adams, Thomas, and Yoon-Nelson models.
This present investigation stands as the initial documented study on the incorporation of AC, derived from coconut shells, into an innovative CO-based PU matrix that possesses a remarkable Pb2+ adsorption efficiency. The results of the adsorption experiments demonstrate that PACC effectively adsorbs Pb2+ ions in water solutions, suggesting its potential for treating lead-contaminated industrial wastewater. This could be particularly beneficial in regions or industries where unregulated wastewater discharge is a major issue and where water quality monitoring plays a vital role in promoting sustainability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The activated carbon used in this research, sourced from Philippine Japan Active Carbon, was derived from coconut shells. To ensure uniform particle dimensions, the AC underwent comminution and passed through a 50-mesh sieve. The lead (II) nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) of analytical grade, surfactant (INV® 690), and catalyst (Polycat® 8) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals in the Philippines. The polyol part was created by blending a combination of polyol sourced from coconut oil and a portion of polyol derived from petroleum (namely, Voranol® 4701, categorized as a polyether polyol). To this mixture, a stabilizing agent and a dispersant in the shape of silicon oil were added, along with methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI, also known as PAPI 135 SH).
2.2. Polyol Synthesis
The polyol derived from coconut oil was synthesized through a sequential two-stage procedure. Initially, coconut triglycerides were disintegrated into individual acylglycerol constituents via glycerolysis (220°C, 2 hours) under constant stirring [
14]. This was followed by an amidation step (140°C, 3 hours). Following the synthesis process, the resultant polyol was given time to cool down to ambient room temperature and then carefully placed and stored within a glass container that was securely sealed to prevent any external contamination.
2.3. Preparation of the Adsorbate Solution
A standard solution containing Pb2+ at 1000 ppm was formulated by dissolving 1.598 g of Pb(NO3)2 in 1000 mL of distilled water. The resulting solution was then transferred into a glass container to ensure safe storage. The necessary concentrations for this study were achieved through sequential dilution of the initial stock solution (ranging from 0 to 150 ppm). The adsorption experiments were conducted using the resulting solutions with varying Pb2+ concentrations.
2.4. Polyurethane Foam-Activated Carbon Composite Formulation
The laboratory procedure for PU foams entailed combining the A-side component (MDI) with the B-side components (polyol and formulation additives). To achieve this, the appropriate quantities of polyols, INV 690, silicon oil, Polycat 8 (B-side), as well as activated carbon and abaca fiber (fillers), were vigorously mixed using a mechanical stirrer in a paper cup. Following this, MDI (A-side) was added to B-side with the fillers and agitated vigorously for 10 seconds. The obtained mixture was then left uninterrupted to allow the PU to expand in the open mold and rise vertically. After expansion, the foam was put in a preheated oven at 60°C for a duration of two hours. The detailed formulation for the preparation of the PU foam samples is provided in
Table 1. The quantities of each additive were determined based on a ratio of 100 parts by weight relative to the total polyol components. The isocyanate index for the foam is 100.
Following the curing procedure, the foam specimens were allowed to stand undisturbed overnight prior to being sectioned into cubes with 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 cm dimension for subsequent testing.
2.5. Characterization
The analysis of surface morphology for both the untreated polyurethane (PU) and polyurethane with activated carbon (PACC) samples was conducted by utilizing a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (JSM-6510LA Analytical Scanning Electron Microscope, Japan). The determination of the open-cell content (OCC) was carried out utilizing a nitrogen pycnometer (ULTRAPYC 1200e Automatic Density Analyzer, USA). The surface area and pore size of the composite material were measured with a surface area analyzer (Microtrac BELSORP MINI X, Japan). To discern the functional groups present in the composite, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was employed (Shimadzu FTIR-ATR IR Tracer-100, Japan) across a spectral range of 4000-400 cm−1. Thermal degradation analysis was executed through Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) in a nitrogen atmosphere, employing a Shimadzu DTG 60H instrument (Japan), with a constant flow rate of 20 mL min-1 and a temperature increment of 10°C per minute. The pH values were determined using a digital pH meter (KEM AT-710, Japan). X-ray Diffraction (XRD) patterns were captured using a Rigaku HR-XRD instrument (SMART Lab, 9 kW power type) equipped with a Cu K-α radiation source (40 kV and 30 mA). The measurements encompassed the range of 3–60 degrees 2θ, and the scanning speed was set at 0.02 degrees 2θ/0.60 seconds.
2.6. Column Adsorption Experiment
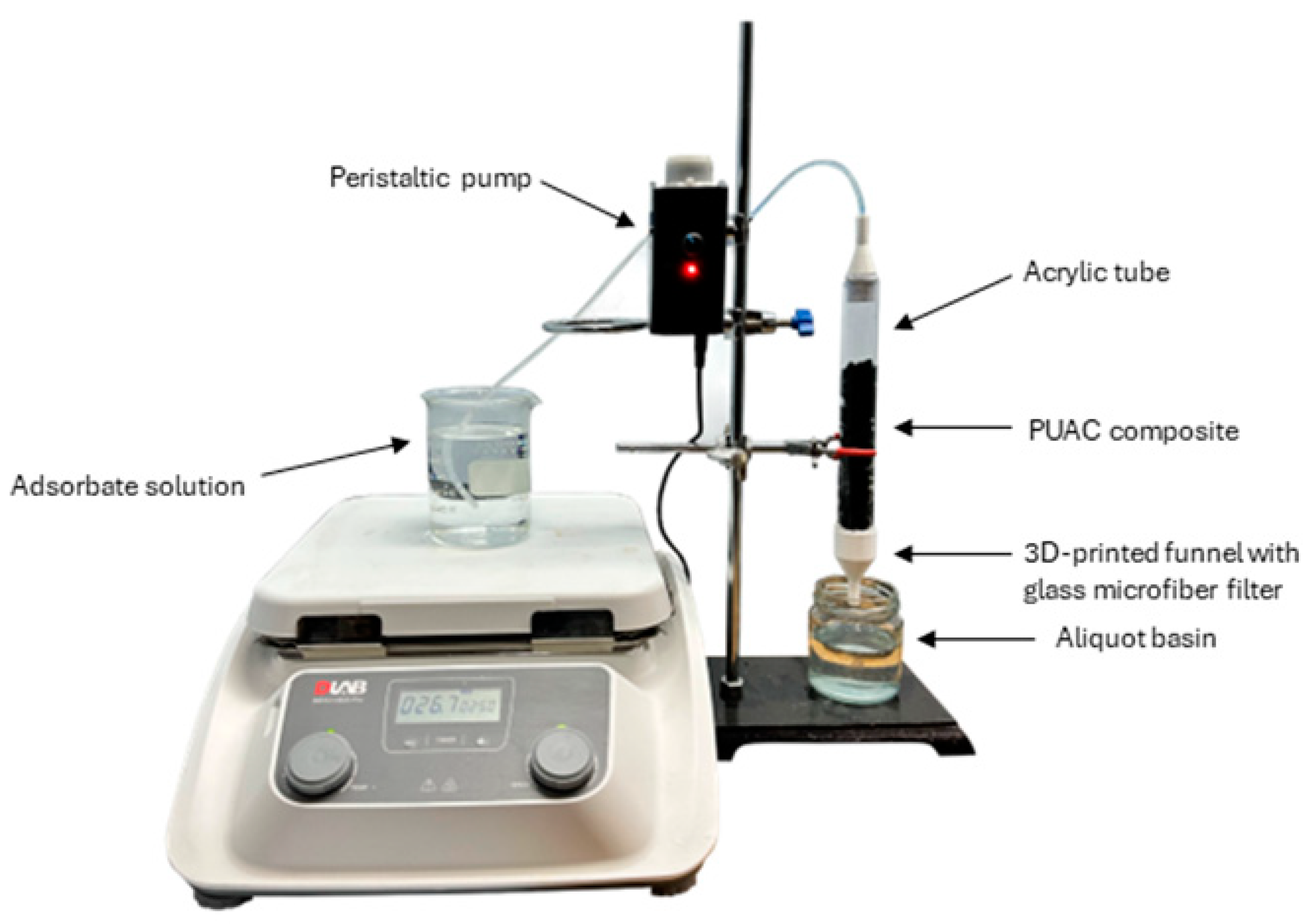
Figure 1 illustrates the actual fixed-bed column set-up. The adsorption trial employed a laboratory-scale continuous experimental arrangement comprising a transparent column measuring 2 cm by 20 cm. The complete procedure was conducted under conditions of ambient temperature. A mass of 1 g of the PACC per centimeter of the column was measured and compacted in alignment with the preferred column height. To guarantee the even distribution of the inlet solution and avert any potential seepage, a specially designed 3D-printed funnel was utilized to provide support for the column on both terminations, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
The solution, containing the intended concentration of Pb2+, underwent continuous stirring at a rate of 100 revolutions per minute (rpm) while being transported downward through the apparatus aided by a peristaltic pump. At various time intervals during this process, samples were methodically collected. Subsequent to this protocol, the concentration of the resultant solution was ascertained using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Genesys 10s, USA), operating within the wavelength range spanning from 190 nm to 300 nm [
16,
17].
The main objective of this investigation was to evaluate how altering flow rates and bed heights affect the adsorption of Pb2+ ions. This was accomplished through a sequence of experimental procedures. The experimental configuration was systematically investigated using a range of flow rates (4, 6, and 8 ml min-1), pH values (2, 4, 6), and bed heights (50, 100, and 150 mm), with the other factors were held steady. After determining the most suitable combination of flow rate, pH, and bed height, the impact of varying Pb2+ concentrations on adsorption efficiency was assessed at levels of 10, 50, and 100 mg L-1.
The fixed-bed experiment was conducted until saturation was attained, signifying the cessation of further adsorption of Pb
2+ ions. Generating breakthrough curves is a crucial aspect in assessing the efficiency of a fixed-bed column. These graphs are depicted by graphing the ratio of C
t/C
o against the elapsed time,
t [
18].
2.7. Analysis of Data from the Column
In fixed-bed column setups, a breakthrough curve is typically used to measure its effectiveness. Breakthrough curves indicate the total mass adsorbed by the adsorbent,
qtotal at specific conditions over time
t, as determined by Equation (1):
where
Q represents the flow rate (expressed in mL min
-1),
A signifies the area under the curve,
t denotes the total duration of the run (measured in minutes), and C
ad represents the amount of adsorbed concentration of Pb
2+ ions in milligrams per liter (mg L
-1).
Equation (2) was employed for the calculation of the maximum metal uptake, denoted as
qeq, within the continuous adsorption system. Additionally, Equation (3) was employed to calculate the total volume of effluent,
Veff, expressed as follows:
where
m represents the continuous system’s dry weight.
2.8. Breakthrough Curve Modeling
The behavior of the continuous sorption process can be assessed through breakthrough curves, which illustrate the variation in pollutant concentration in the effluent over time within a fixed bed column. Mathematical models that rely on these curves are employed to depict and forecast experimental data, serving as valuable tools for optimizing fixed bed column designs and scaling up the process [
19].
The Thomas model is commonly utilized to ascertain the parameters linked with breakthrough curves, and assessing the efficiency of adsorption often serves as an initial stage in the design of a removal system for a fixed-bed column [
20].
The determination of parameters, particularly the rate constant indicated as k
Th and the maximum adsorption capacity known as q
max, can be accomplished through the utilization of the linear approximation of the Thomas equation, represented by the following equation [
21]:
where
kTh represents the Thomas rate constant (measured in L mg
-1 min-1);
qTh signifies the adsorption capacity (measured in mg g
-1);
t represents the total flow time (measured in minutes);
m is the mass of the adsorbent (measured in grams); and
Q indicates the flow rate (measured in mL min-1).
According to the Bohart-Adams model, the adsorption efficiency relies on the properties of both the sorbent and the substance undergoing adsorption [
22]. This relationship is mathematically described by the following equation:
where
kAB signifies the Bohart-Adams rate constant (measured in L mg
-1 min
-1);
N0 represents the saturation concentration (measured in mg L
-1);
t signifies the flow time (measured in minutes);
Z denotes the bed height (measured in centimeters); and
U0 indicates the superficial velocity (measured in cm min-
1).
Conversely, the Yoon-Nelson model is based on the concept of diminishing adsorption probability[
23]. In prior research, the Yoon-Nelson model has been mathematically formulated in a linearized manner for the analysis of individual systems [
24,
25]:
where
kYN for the Yoon–Nelson rate constant (measured in min
-1); τ represents the time required for 50% breakthrough of the adsorbate (measured in minutes); and
t signifies the breakthrough time.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
3.1.1. SEM-EDX Analysis
This study involved the examination of the surface structure and morphology of the PACC adsorbent by utilizing scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
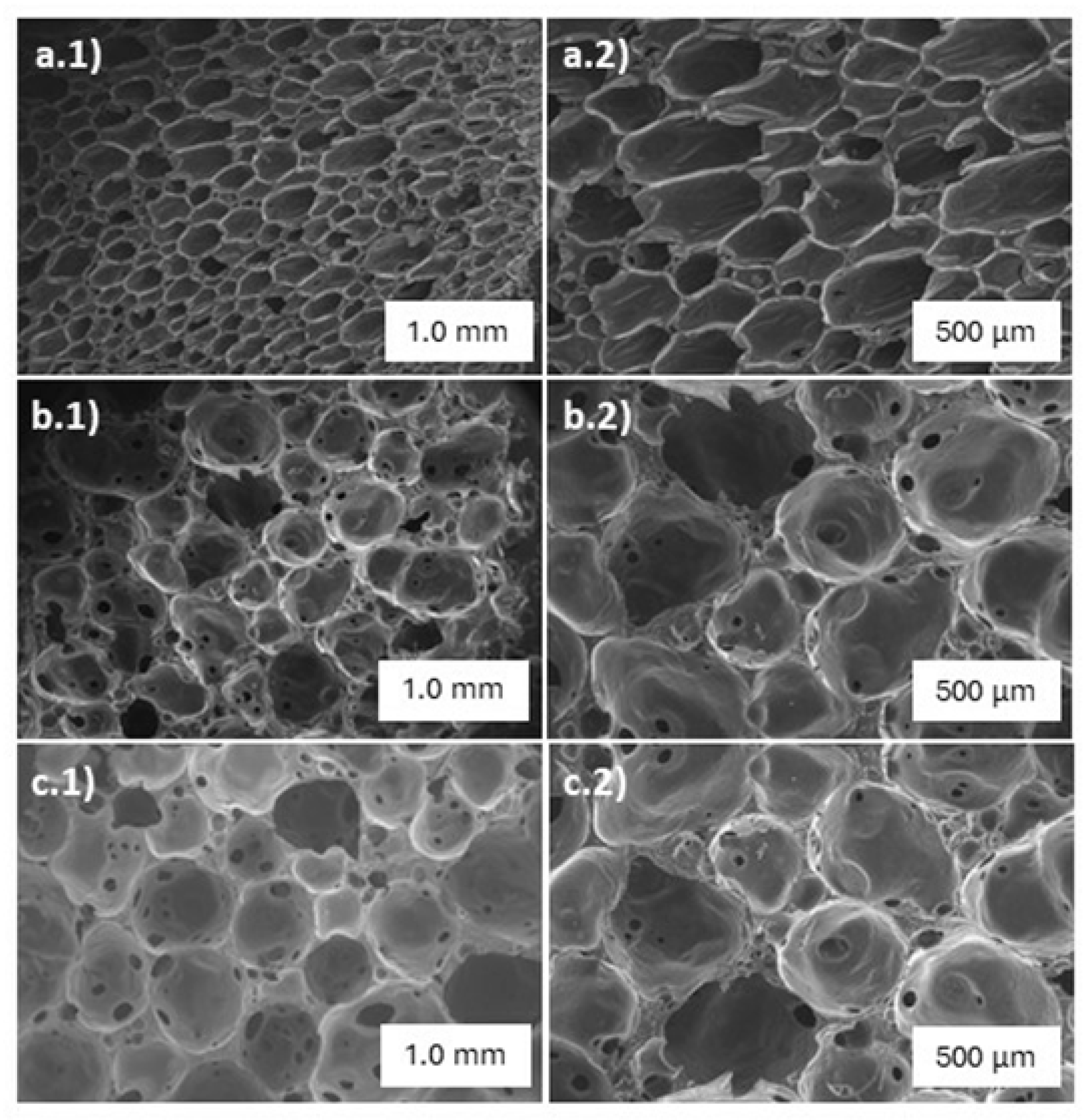
Figure 2 displays SEM images revealing the morphological structures of the blank PU foam and the PACC before and after subjecting to adsorption. It can be observed that the PACC exhibited a more distinct open-cell structure compared to the blank PU foam. This observation is verified with the pycnometric analysis that resulted to higher PACC open cell content of 88% compared to the 75% open cell content of blank PU. Moreover, the mircrophotographs of PACC as shown in
Figure 2(b.1,b.2) reveals larger cell sizes compared to the blank PU’s microphotograhps in
Figure 2(a.1,a.2). In the lens of PACC’s potential as Pb
2+ adsorbent, these observations could further translate to the enhancement of PACC’s ability for Pb
2+ sequestration [
26]. The inclusion of larger open-cell matrices in the composite foam enhances the accessibility of Pb
2+ to the PACC adsorbent [
27]. Furthermore, the presence of numerous small channels in the open-cell design of the PACC foam is advantageous, as it facilitates the rapid dispersion of Pb
2+ across the surface. Moreover, the substantial porosity of the material establishes an interconnected three-dimensional (3D) environment, providing accessibility and ample storage capacity for Pb
2+ [
28]. As shown in Figures 2(c.1,c.2), the mircrophotographs of PACC after subjecting to Pb
2+ adsorption revealed no significant physical changes as compared to the microphotographs of unused PACC in
Figure 2(b.1,b.2). These findings demonstrate the structural durability and stability of PACC during its employment for Pb
2+ adsorption.
Table 2 presents the elemental composition analysis of blank PU and PACC using EDX. After the integration of activated carbon (AC) into the polyurethane (PU) matrix, there was an observed rise in carbon content by 1.85% and oxygen content by 9.87%. Conversely, the nitrogen content displayed a relative decrease of 2.00%. Enhanced levels of an O/C and (O+N)/C values correspond to an increased degree of negative polarity in the material [
29]. As presented in
Table 2, PACC demonstrates notably elevated O/C ratio and (O+N)/C ratios of 35.55% and 17.65%, respectively, in comparison to the blank PU. This finding implies the creation of a higher number of sorption sites within PACC, which enhances its potential for the sequestration of Pb2+ ions. These observed variations in composition can be attributed to the intrinsic hydroxyl groups in AC, resulting to an enhanced oxygen concentrations in the PACC. PACC exhibits a significant presence of oxygen-containing functional groups, which have been previously reported to facilitate the adsorption of Pb
2+ [
30,
31]. Subsequent to the adsorption process, the O/C ratio and (O+N)/C ratios experienced a reduction of 37.70% and 31.25%, respectively. This is ascribed to the depolarization of the participating amino and oxygen-containing groups during their interaction with Pb
2+, thereby reducing the PACC’s negative polarity during the Pb
2+ adsorption process [
4]. Thus, this observation relates to the successful interaction of Pb
2+ to the PACC’s active sorption sites.
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
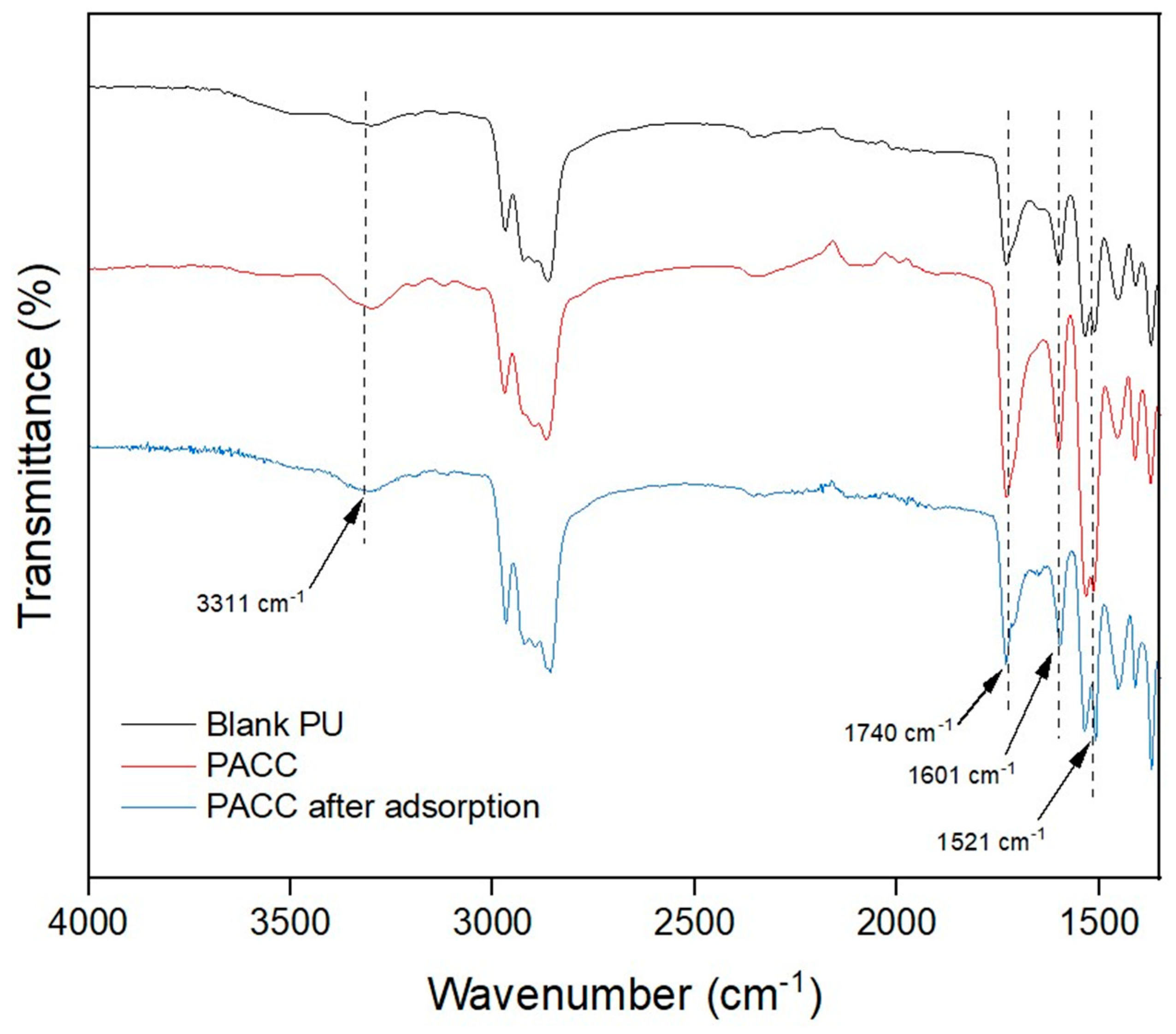
In addition to their physical characteristics, the adsorption capacity of PU and AC can also be influenced by their chemical composition. While the porous structure is important, the chemical structural attributes of these materials (i.e., their functional groups) can also have an impact on their adsorption capacities[
32]. FTIR spectroscopy was used to analyze the chemical characteristics of PU and PACC adsorbent foams, as illustrated in
Figure 3. The significant peak at 3311 cm
-1 is associated to the O-H bonds present in the foam samples. Additionally, the heightened intensity of the peak at 3311 cm-
1 in PACC is ascribed to the inherent OH (hydroxyl) groups existing in its AC constituent. This suggests that PACC harbors a greater abundance of OH groups compared to the blank PU, consequently manifesting a more negatively polar chemical structure. Furthermore, the identified peak at 1740 cm-1 is associated to the stretching vibrations of C=O, which are linked to the urethane component within the foam samples [
11]. The peaks at 1601 cm
-1 correspond to the bending vibrations of C=O, which can be linked to the urethane components, and the stretching vibrations of C-O in carboxylic acids present on the AC surfaces [
33]. The peaks at 1521 cm
-1 correspond to the bending of N-H and the stretching vibrations of C=O, which can be ascribed to the existence of urethane bonds and carboxyl groups within the PACC matrices. It is worth highlighting that the significant increase in the mentioned peaks found in PACC compared to the blank PU can be attributed to the presence of AC in the PACC matrix. Furthermore, the observed reduction of the oxygen- and nitrogen-related peaks on the FTIR spectrum of PACC after adsorption reveals the reduction of functional sites, as indicated by the peak intensity reductions found at 3311 cm
-1, 1740 cm
-1, 1601 cm-
1, 1521 cm
-1, due to the interaction of Pb
2+ ions. These observations are in agreement with other researches on the role of these peaks in the reaction with Pb
2+ [
2,
34].
3.1.3. Surface Area Analysis
The textural characteristics of both blank PU and PACC, encompassing specific surface area and pore dimensions, were examined utilizing a surface area analyzer via nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms. The outcomes unveiled that the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of PU, quantified at 1.1817 m² g⁻¹, exhibited a notable disparity in comparison to PACC before adsorption, which demonstrated a measurement of 10.8949 m² g⁻¹. This discrepancy underscores that the integration of activated carbon into the PU matrix prompted a substantial upsurge in surface area, approximately tenfold, thereby yielding a plethora of binding sites for effective sequestration of Pb
2+. Furthermore, the average pore sizes for PU and PACC were determined as 2.3406 nm and 0.9825 nm, respectively. Reduced pore dimensions lead to an enlarged surface area and an increased surface-to-volume ratio. This phenomenon explains the observed augmentation in the PACC’s surface area [
35].
3.1.4. XRD Analysis
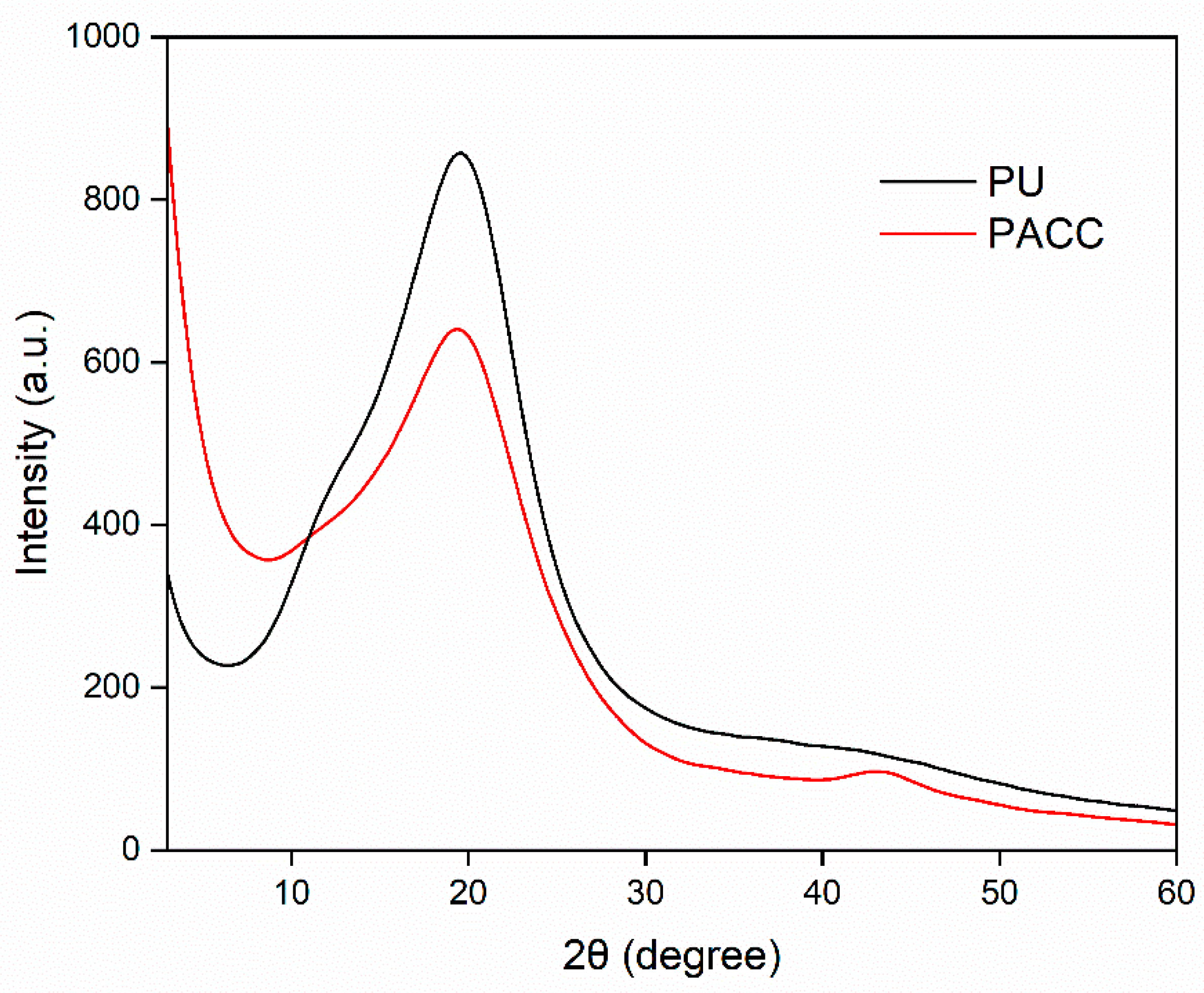
Figure 4 portrays the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of both the blank PU and PACC samples. The diffraction patterns exhibit a diffuse and subtle diffraction peak observed at approximately 19° and 43° 2θ angles. These angles correspond to the distinctive diffraction patterns associated with the amorphous carbon structure aligned with the (0 0 2) and (1 0 0) crystallographic planes, respectively [
36]. Furthermore, the presence of these peaks at a subdued intensity implies a limited extent of graphitization, thereby implying the presence of a carbonaceous structure with relatively low crystallinity [
37].
3.1.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
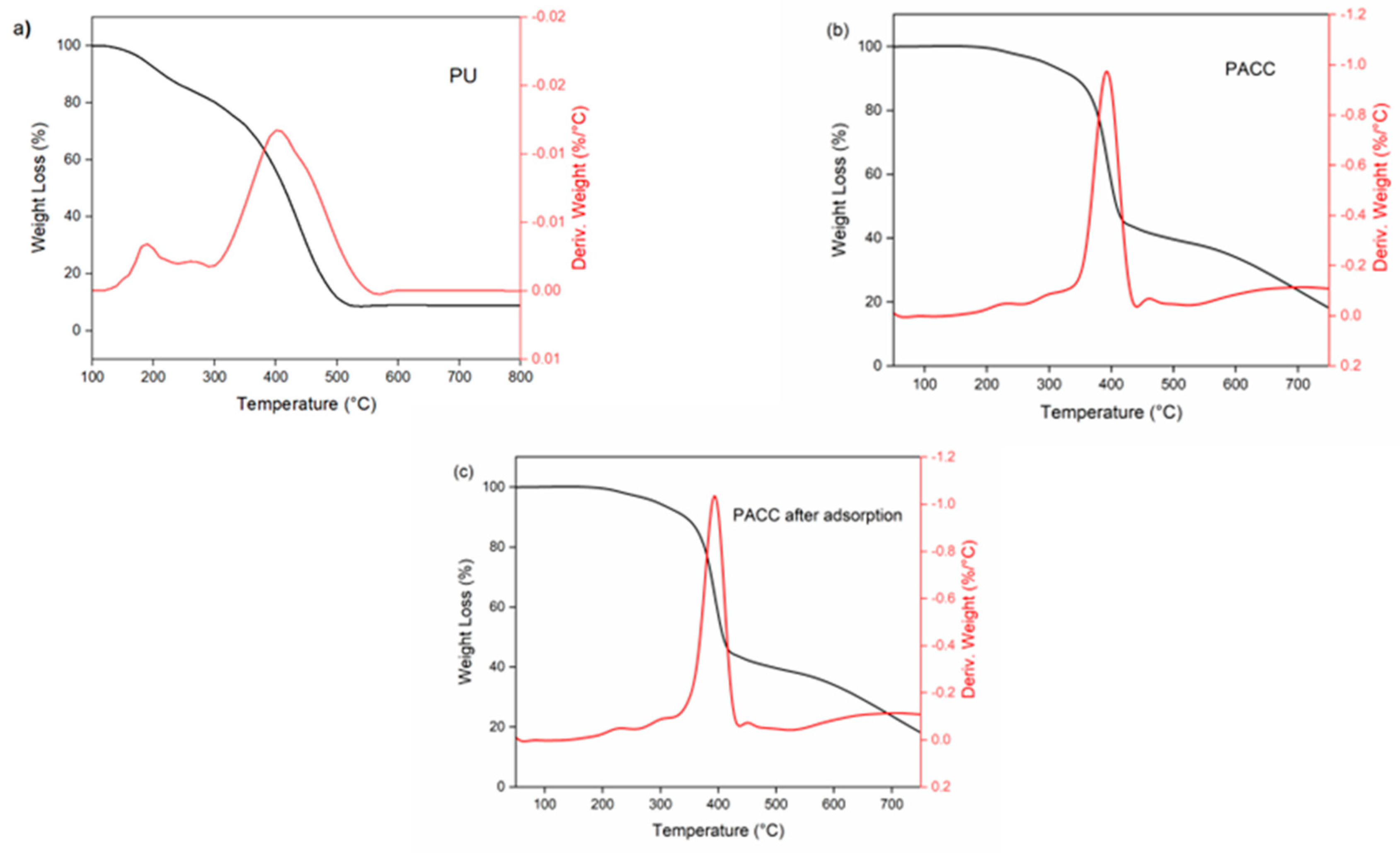
Figure 5 illustrates the thermal properties of blank PU, PACC, and PACC after adsorption. In
Figure 5a, the derivative thermogravimetry (DTG) graph of PU displays two notable endothermic peaks located at approximately 184°C and 406°C. The mentioned peaks suggest the thermal degradation of the unique rigid and flexible segments of PU. The rigid segments can be linked to the presence of urethane bonds, whereas the introduction of fatty acid chains into the PU matrix affects the flexible segments [
14]. In contrast, the DTG examination of PACC prior to and following adsorption discloses the presence of several peaks located at approximately 220°C, 310°C, 400°C, and 440°C, as displayed in
Figure 5b,c. Similar to pure PU, the peaks identified at 220°C and 400°C correspond to the thermal breakdown of the urethane segments and the fatty acid components within the PACC. Furthermore, the extra peak can be ascribed to the thermal disintegration of the activated carbon constituents incorporated into the composite [
38]. Additionally, the TGA-DTG curve of PACC following adsorption, as depicted in
Figure 5c, displays comparable thermal degradation peaks to those of PACC in
Figure 5b. This observation implies that the thermal stability of PACC was not compromised during the adsorption process.
3.2. Effect of Dynamic Adsorption Parameters
Table 3 displays the data parameters obtained from the column under varying Pb concentrations, bed heights, pH, and flow rates while maintaining a constant room temperature.
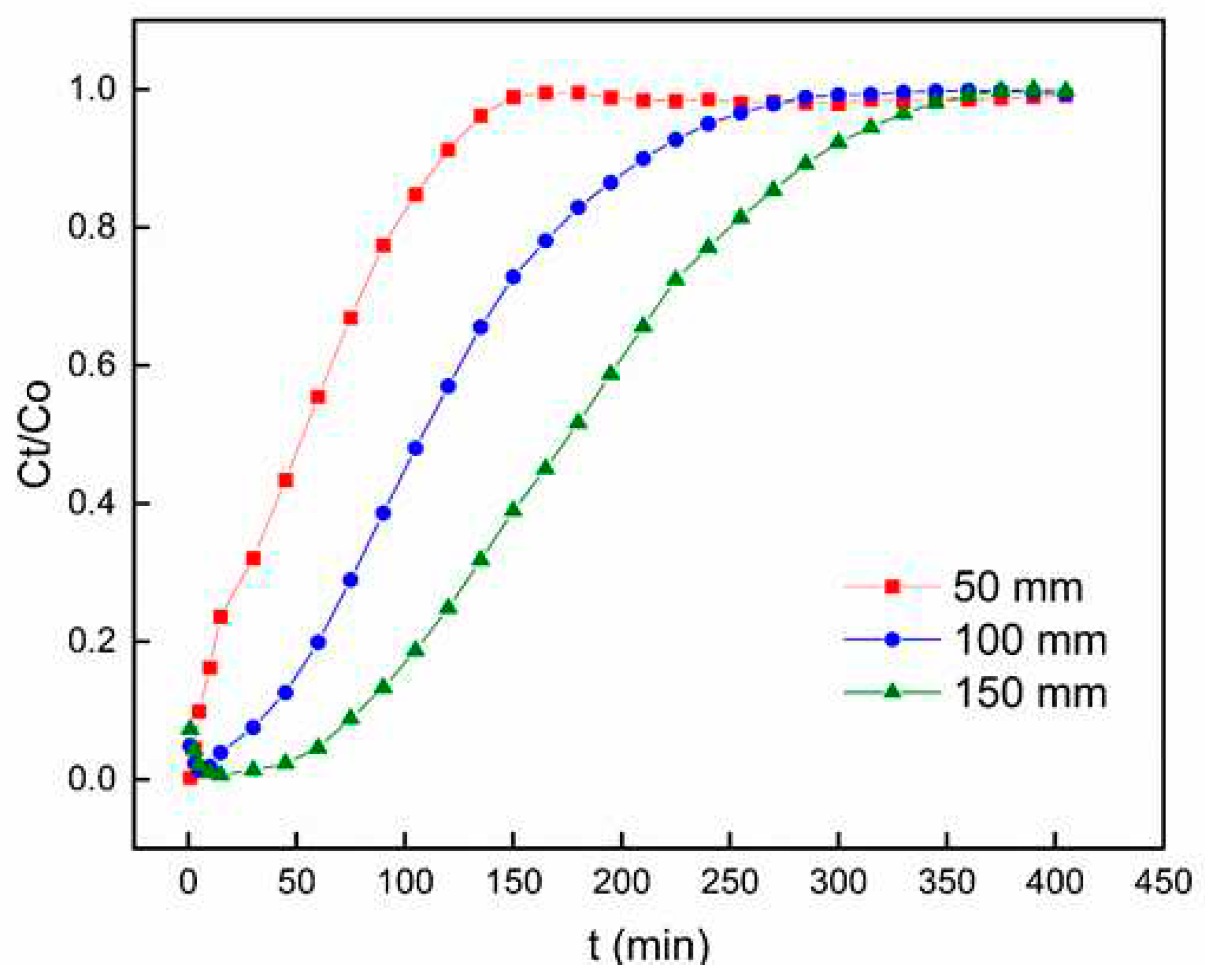
3.2.1. Effect of Bed Height
Figure 6 shows the breakthrough curve for Pb
2+ adsorption on PACC at three distinct bed heights (50 mm, 100 mm, and 150 mm). The flow rate was held steady at 6 mL min
-1, pH at 6, and the inlet concentration of Pb
2+ was kept constant at 50 mg L
-1. The experimental results show that elevating the bed height from 50 mm to 150 mm resulted in an extended time for the bed to achieve saturation. This observation implies a correlation between the breakthrough curve and the bed height, indicating an expansion in the zones of mass transfer [
39]. Additionally,
Figure 6 demonstrates that reducing the bed height resulted in a more rapid saturation. Meanwhile, increasing the bed height to 150 mm improved the removal efficiency. Similar studies have observed that these findings are influenced by the augmentation of active sorption sites and the prolongation of duration of contact between PACC and Pb
2+ [
40,
41].
3.2.2. Effect of Flow Rate
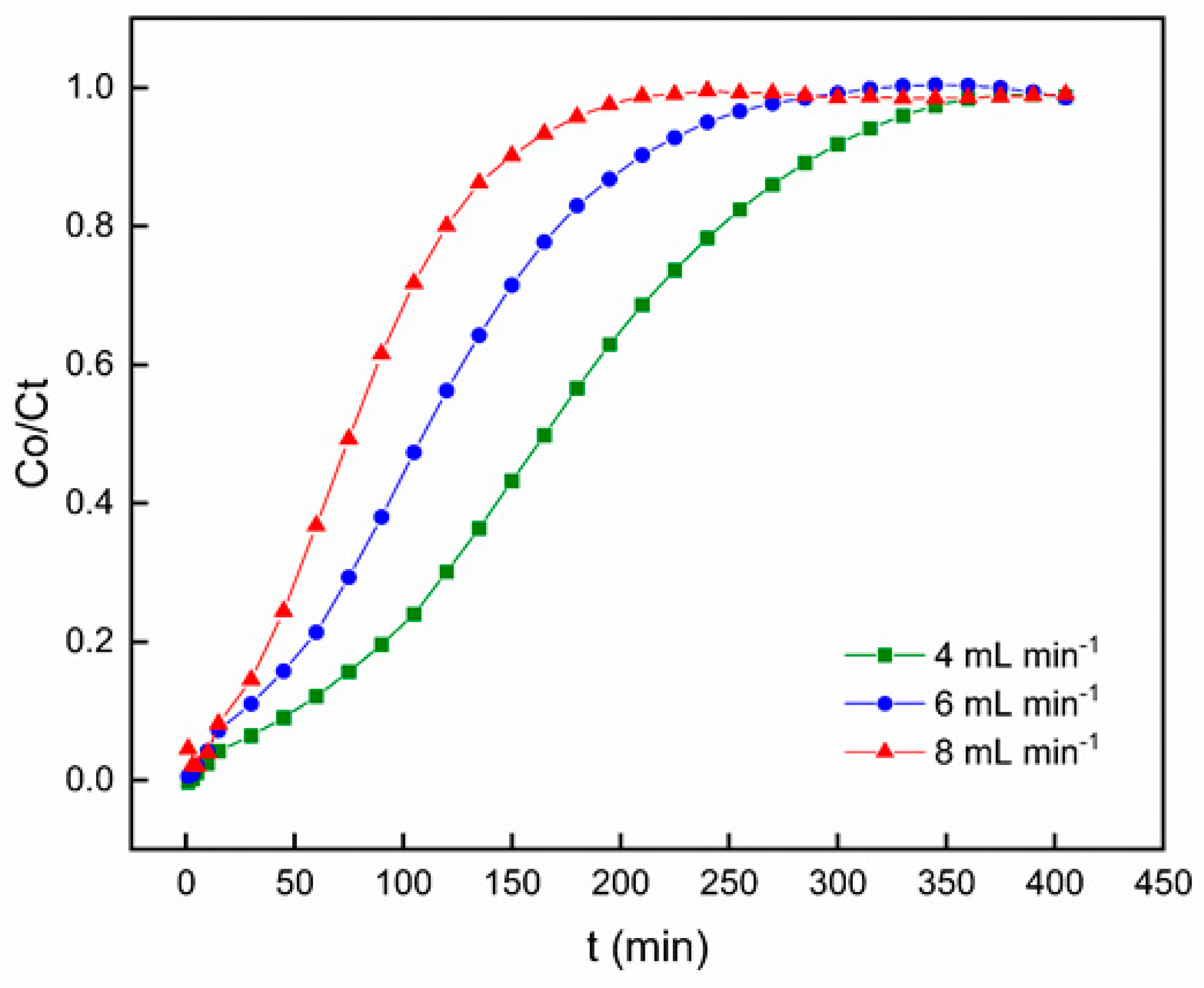
In order to examine the influence of flow rate on Pb
2+ adsorption using PACC, the flow rate was subjected to variation (4, 6, and 8 mL min-
1), keeping a consistent adsorbent bed height of 100 mm, a pH level of 6, and a constant inlet concentration of Pb
2+ at 50 mg L
-1. The outcomes of this investigation are presented in
Figure 7, where the breakthrough curve is depicted. The findings indicate a significant enhancement in breakthrough occurrence with the escalation of flow rate. Conversely, along with decreasing flow rate, there is a significant extension of the duration required to reach saturation. At lower flow rates, there was more time for the interaction between Pb and PACC, resulting in an augmented removal of Pb
2+ in the column.
The fundamental concepts of mass transfer clarify the variations noticed in the steepness of the breakthrough curve and the adsorption capacity. Increased flow rates induce a reduction in the hindrance to mass transfer posed by the external film at the surface of the adsorbent, leading to an escalated rate of mass transfer and a decreased residence time. As a consequence, saturation is achieved more quickly, leading to decreased removal efficiency. This implies that the amount of heavy metal adsorbed per unit of bed height, known as the mass transfer zone, enlarges with higher flow rates, resulting in a more rapid attainment of saturation capacity [
42,
43]. In contrast, inadequate solute residence time in the column results in the decline in the adsorption capacity, as the solute exits the column prior to reaching equilibrium. Similar patterns have been noted by other investigators [
44,
45,
46].
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Concentration
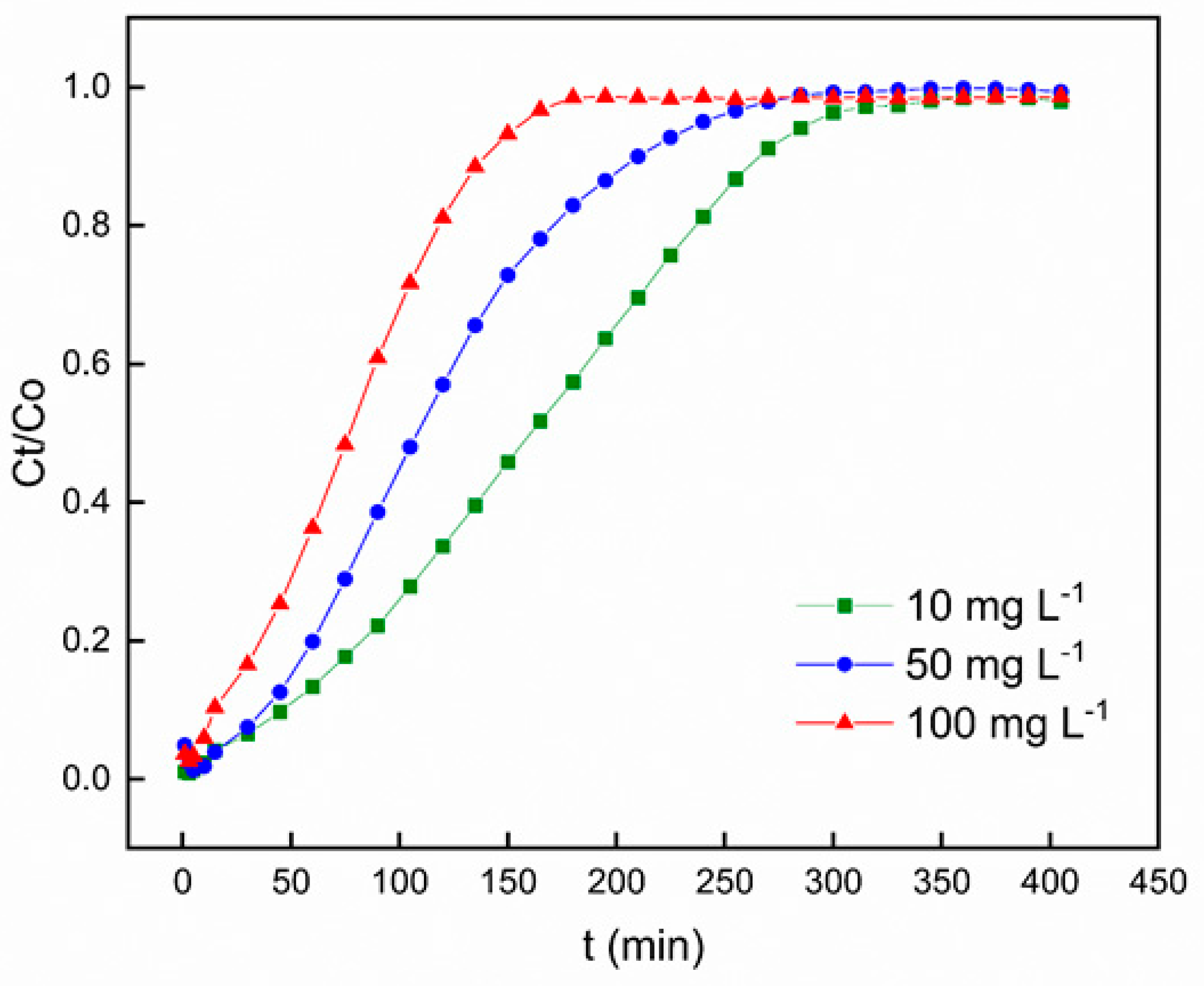
Figure 8 portrays the influence of varying the initial Pb
2+ concentration on the breakthrough curve, all the while sustaining a constant adsorbent bed height (100 mm), pH value of 6, and solution flow rate of 6 mL min
-1. The graphical representation clearly indicates that an elevation in the initial Pb
2+ influent concentration prompts a more rapid achievement of saturation in the adsorption process, subsequently leading to a reduction in breakthrough time. It is noteworthy that at lower Pb
2+ inlet concentrations, the breakthrough curves exhibited increased dispersion, resulting in a more gradual manifestation of breakthrough. Conversely, sharper breakthrough curves were observed upon increasing the influent concentration of Pb
2+. This phenomenon can be ascribed to the higher concentration gradient, which resulted to swifter movement attributed to mass transfer coefficient.
An elevated influent concentration results in a more pronounced incline of the breakthrough curve and a shorter breakthrough time, in accordance with findings from previous studies [
47,
48]. These results suggest that the concentration affect the level of saturation and breakthrough time, implying that the dispersion mechanism is influenced by the influent concentration. An increase in the influent concentration led to the increase in the driving force for mass transfer, leading to a decrease in the length of the adsorption zone [
49,
50]. These findings are congruent with prior studies conducted on numerous fixed-bed adsorption frameworks [
44,
46].
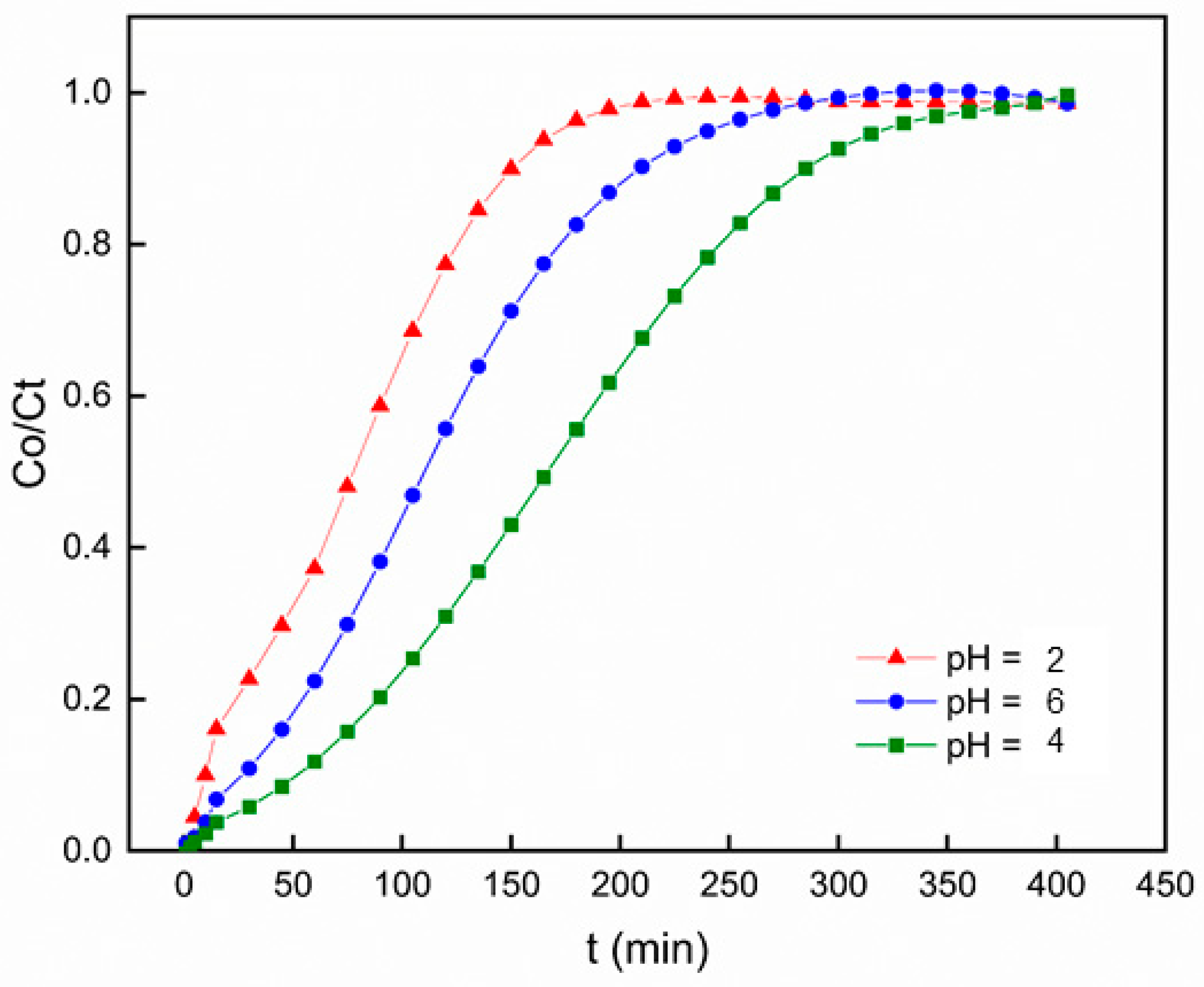
3.2.4. Effect of pH
The pH values exert a critical influence on various aspects of heavy metal behavior within the environment. Beyond its influence on the dissociation of heavy metal sites, pH exerts a substantial impact on solution chemistry by contributing to various processes, including redox reactions, hydrolysis, complexation with organic and/or inorganic ligands, and precipitation. The pH significantly governs these mechanisms and consequently has a notable effect on the availability of heavy metals for biosorption [
51]. To assess how pH levels affect the efficiency of Pb
2+ adsorption by PACC, a series of pH values ranging from 2 to 6 were utilized for investigation. Throughout this experimentation, the bed height (100 mm), flow rate (4 mL min-1), and initial concentration (50 mg L-
1) remained constant. As shown in
Figure 9, the breakthrough curve at pH = 2 shifted towards the left, indicating the shorter breakthrough time. This occurrence can be explained by the higher concentration of hydronium ions at lower pH levels, which competes effectively with Pb
2+ ions for interaction with the active sites of PACC [
52]. While at pH values greater than 6, Pb
2+ ions undergoes solvation, hydrolysis, and lead oxide precipitation [
53]. These precipitates are unable to be adsorbed by the PACC foam, leading to a decrease in the breakthrough time, which occurred at 240 minutes. Hence, at a moderate pH (pH = 4), these circumtances can be mitigated, resulting to the longest breakthrough time at 360 mins.
3.3. Modeling of Column Data
Mathematical modeling is of crucial importance in upscaling techniques from laboratory experiments to pilot plants and industrial scales. It acts as a valuable instrument for examining and explaining experimental information, recognizing significant process mechanisms, foreseeing the outcomes of different operational circumstances, and enhancing the total effectiveness of the process [
54].
3.3.1. Thomas Model
The theoretical framework suggested by the Thomas model suggests that the flow pattern inside the bed adheres to a plug flow configuration. Additionally, the model incorporates the Langmuir isotherm to describe the equilibrium behavior and second-order reversible reaction kinetics [
21]. This simulation is extensively accepted and commonly employed to characterize sorption processes in fixed-bed columns. It is especially applicable in situations where external and internal dispersion have minimal impact on the overall process.
Table 4 demonstrates that the Thomas model exhibited a remarkable fit, with
R2 values of 0.96 to 0.98. Based on the model, the total adsorption capacity (
qo) rises as the inlet concentration of Pb
2+ increases. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fundamental driving force of adsorption, which primarily originates from the difference in Pb
2+ concentration between the solution and the adsorbent composite[
55]. Furthermore, a surge in flow rate leads to a decreased total adsorption capacity (q
Th). Similar findings have been reported in other studies [
41,
45,
56].
3.3.2. Bohart-Adams Model
Bohart and Adams introduced an equation derived from surface reaction theory to establish a relationship relating to C
t/C
0 and
t in a continuous system [
22]. This equation can be used in illustrating the initial portion of the breakthrough curve, as it postulates that equilibrium is not immediately attained.
The data presented in
Table 5 reveals that higher effluent Pb
2+ concentration and flow rate are associated with decreased values of
kAB, while increased bed height corresponds to an increase in
kAB. These trends are consistent with findings from prior research[
45,
57], indicating that surface mass transfer plays a significant function in the kinetics of the overall system, particularly throughout the preliminary phase of column adsorption [
58].
Although the Bohart-Adams model is widely utilized and valuable for conducting and analyzing adsorption-column experiments, it is crucial to acknowledge that its applicability is limited to certain experimental conditions [
44,
51]. The model's correlation coefficient falling below 0.96 indicates that it is not sufficient for fully capturing the adsorption behavior of the column. Instead, it is exclusively suitable for depicting the initial portion of the breakthrough curve [
59].
3.3.3. Yoon-Nelson Model
Yoon-Nelson postulated that the decline in the likelihood of adsorbate molecule binding is intricately linked to both the probability of adsorbate adsorption and the occurrence of breakthrough phenomena within the adsorbent medium [
25].
Table 6.
Yoon-Nelson model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
Table 6.
Yoon-Nelson model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
| Parameter |
|
KYN
(mg-1 min-1) |
Tcalc
(min) |
R2 |
| Bed height (mm) |
5 |
0.02 |
175.63 |
0.98 |
| |
10 |
0.04 |
85.60 |
0.98 |
| |
15 |
0.05 |
57.86 |
0.98 |
| Flow Rate |
4 |
0.02 |
177.90 |
0.97 |
| (mL min-1) |
6 |
0.05 |
57.86 |
0.98 |
| |
8 |
0.04 |
85.60 |
0.98 |
| Initial metal |
10 |
0.02 |
159.22 |
0.96 |
| concentration |
50 |
0.03 |
122.35 |
0.97 |
| (mg L-1) |
100 |
0.04 |
79.38 |
0.97 |
| pH |
2 |
0.05 |
106.70 |
0.98 |
| 4 |
0.07 |
54.06 |
0.97 |
| 6 |
0.02 |
94.38 |
0.97 |
The Yoon-Nelson model demonstrated its applicability to the current system, as indicated by
R2 values surpassing 0.96. According to the model, the 50% breakthrough extended as the bed height increased, but decreased when higher concentrations and flow rates were employed. These observations align with earlier research findings [
41,
45].
The Thomas and Yoon-Nelson models proficiently described the adsorption patterns of Pb2+ within a fixed-bed column, as evidenced by high R2 values and well-matched breakthrough curves.
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Breakthrough Curves Fitting
It is worth emphasizing that despite their distinct assumptions, derivations, and simplifications, the Thomas, Bohart-Adams, and Yoon-Nelson models (Eqs. 5-7) may be expressed using the subsequent formula, where the 'lumped' variables a and b are defined in
Table 5:
Based on Equation (8), it can be concluded that the Thomas, Bohart-Adams, and Yoon-Nelson models are fundamentally equal. The breakthrough curve predictions obtained from Equation (8) depict the breakthrough curve that would be achieved through the use of any of the three previously mentioned models (Equations 5-7). The three sets of parameters (k
Th, q
Th; k
BA, N
0; and k
YN, t) can be determined from constants 'a' and 'b' (
Table 7) and are thus interchangeable [
60].
The effectiveness of the models employed in analyzing the breakthrough curves of Pb
2+ was assessed by evaluating the Sum of Squares Error (SSE) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) functions expressed as follows:
with
n being the number of experimental data points.
Previous literature already demonstrated that all the proposed mathematical models, namely Thomas, Bohart-Adams, and Yoon-Nelson, effectively represented the breakthrough curves of Pb
2+ [
60]. This portrayal was achieved with notable accuracy, as evidenced by the low values of Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Sum of Squared Errors (SSE). Furthermore, a high
R2 value indicated a strong relationship between the measured and computered removal performance. However, the calculated values marginally deviated from the experimental values as show in
Figure 10. As anticipated, the Bohart-Adams model exhibited improved suitability for defining the early portion of the experimental breakthrough curve. The favorable agreement derived from the analysis suggests that these models can be utilized to project breakthrough curves related to Pb
2+ adsorption by PACC [
61].
The merits and limitations of the models utilized in this study were assessed and summed up in
Table 8 based on the analysis and relationship of the experimental data. The results show that the three models were well-suited to describe the column data, especially in instances of columns with higher bed heights, where a consistent and even depletion process was observed[
62]. Hence, these models can be effectively used to forecast the performance of columns and aid in designing considerations and future enhancement endeavors. The applicability of the three utilized models in this study was observed for adsorption in distinct component systems. The utilization of the Thomas model offered valuable insights into the dynamics of mass transfer between the adsorbent material and metal solutions. This allowed for a better understanding of the driving forces behind these processes under various conditions. The experimental data collected from the Pb2+ columns showed a promising alignment with the theoretical predictions generated by the Thomas and Yoon-Nelson models. This alignment indicated the presence of hindrances to mass transfer within the columns. Each of the three models employed in this study necessitated distinct parameters for their respective theoretical calculations.
Among the three models utilized in this study, the Yoon-Nelson model stood out for its simplicity, requiring fewer parameters and theoretical calculations. It provided valuable information on the 50% breakthrough of the column, enabling the prediction of the saturation period without requiring extensive experimental duration [
62]. In contrast, the widely-used Bohart-Adams model has proven useful in predicting the sorption capacity of adsorbents in various studies, particularly for the design of large-scale effluent treatment systems. By analyzing experimental breakthrough data, the Bohart-Adams model can estimate breakthrough time and maximum adsorption capacity, which are crucial for efficient system design and operation [
63]. However, this model imposes additional parameters and computations to derive predicting data. It primarily focuses on adsorption through surface reactions, presence of sorption sites, and the starting portion of the breakthrough curve [
64]. In the case of removing Pb
2+ using PACC, involving an integration of ion-exchange and adsorption, the Bohart-Adams model is not an ideal fit for accurately and comprehensively representing column behaviors and mechanisms in this study. While the employed models exhibited a good fit for certain column parameters, there were certain parameters that were not accurately captured, likely due to the presence of mass transfer resistance and the intricate mechanisms involved in the removal process[
64].
The findings suggest that enhanced adsorption efficiency is attained through increased bed heights, reduced flow rates, and higher initial concentrations. Furthermore,
Table 9 offers a concise overview of how various adsorbents perform under similar circumstances. This investigation has affirmed that the adsorption capability of PACC is on par with, and conceivably superior to, the capacities of alternative adsorbents noted in contemporary scientific literature.
Given the absence of prior published research specifically focusing on fixed-bed column studies in relation to the biosorption of Pb2+ by PACC, this study can be compared to similar investigations that have examined either the same metal or biosorbents with similar characteristics.
3.5. Regeneration Studies and Implications to Industrial Wastewater Treatment
In line with the comprehensive concept of sustainability, which encompasses economic, social, and environmental factors, the achievement of sustainable industrial development relies heavily on the adoption of viable technologies that generate positive socio-economic and environmental outcomes [
69]. This progress extends not only to novel strategies but also to the enhancement of protocols that offer optimal results while minimizing resource utilization, thus providing significant benefits such as environmental safety and yield improvement. In addition to possessing effective adsorption capability, the convenient reusability of the adsorbent without substantial reduction in adsorption capacity and its long-term reusability are crucial considerations for practical applications.
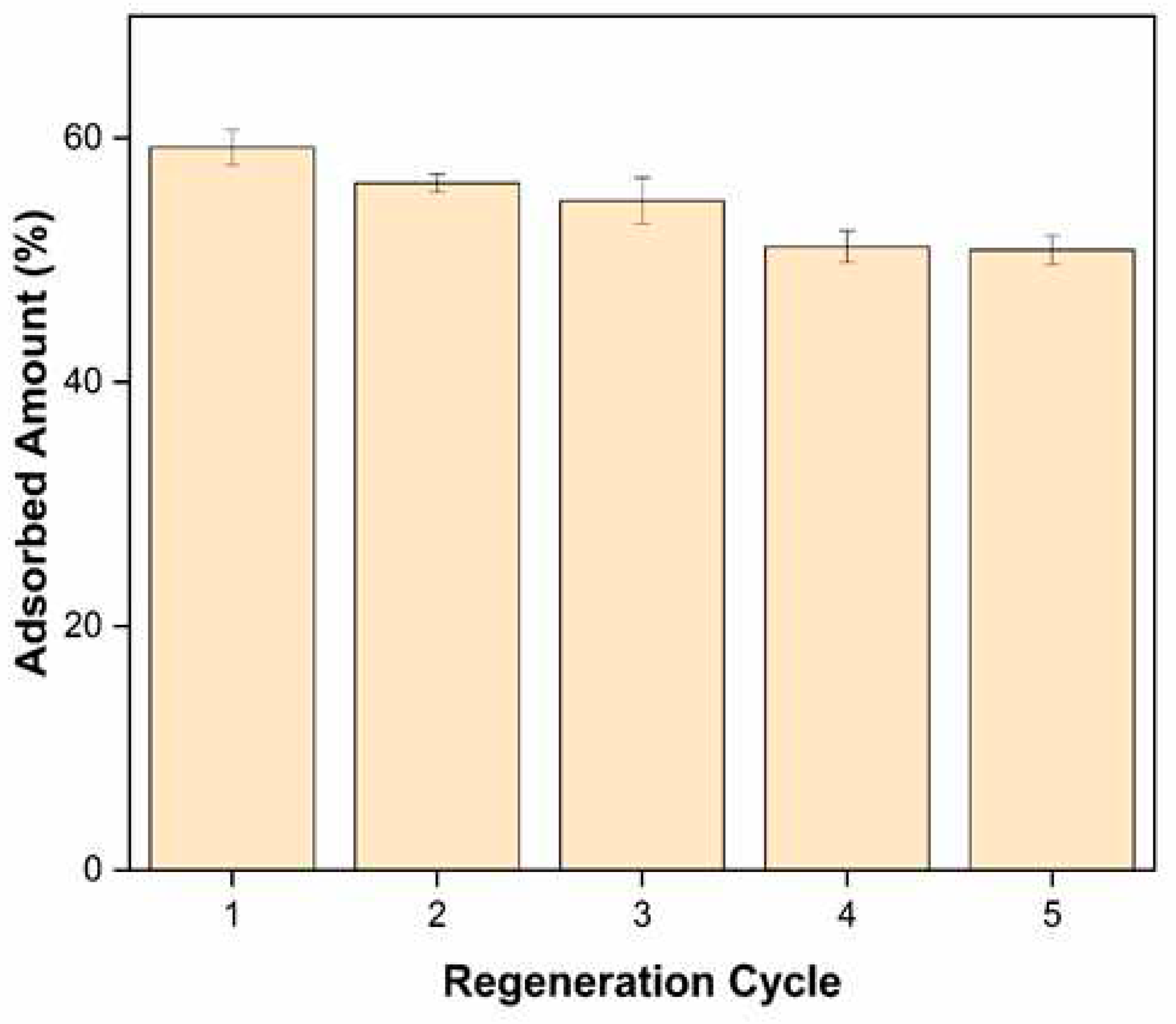
In this study, the PACC material, having undergone Pb2+ adsortption, was subjected to desorption experiments utilizing a 0.1M NaOH solution as the desorbing agent. The regeneration cycle encompassed the passage of the desorbing agent through the column at a flow rate of 2.5 mL min-1 for a duration of 30 minutes. Subsequently, a rinsing phase with deionized water was carried out for an additional 30 minutes before initiating a successive cycle of Pb2+ adsorption. Furthermore, following four (4) cycles of adsorption-desorption, the PACC exhibited a consistent removal efficiency surpassing 80% of its initial capacity. This observation signifies the potential of the composite material for repeated utilization in proficiently eliminating Pb2+ ions from wastewater streams.
Figure 11.
Regeneration performance of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) in sequestering Pb2+ in fixed-bed column.
Figure 11.
Regeneration performance of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) in sequestering Pb2+ in fixed-bed column.
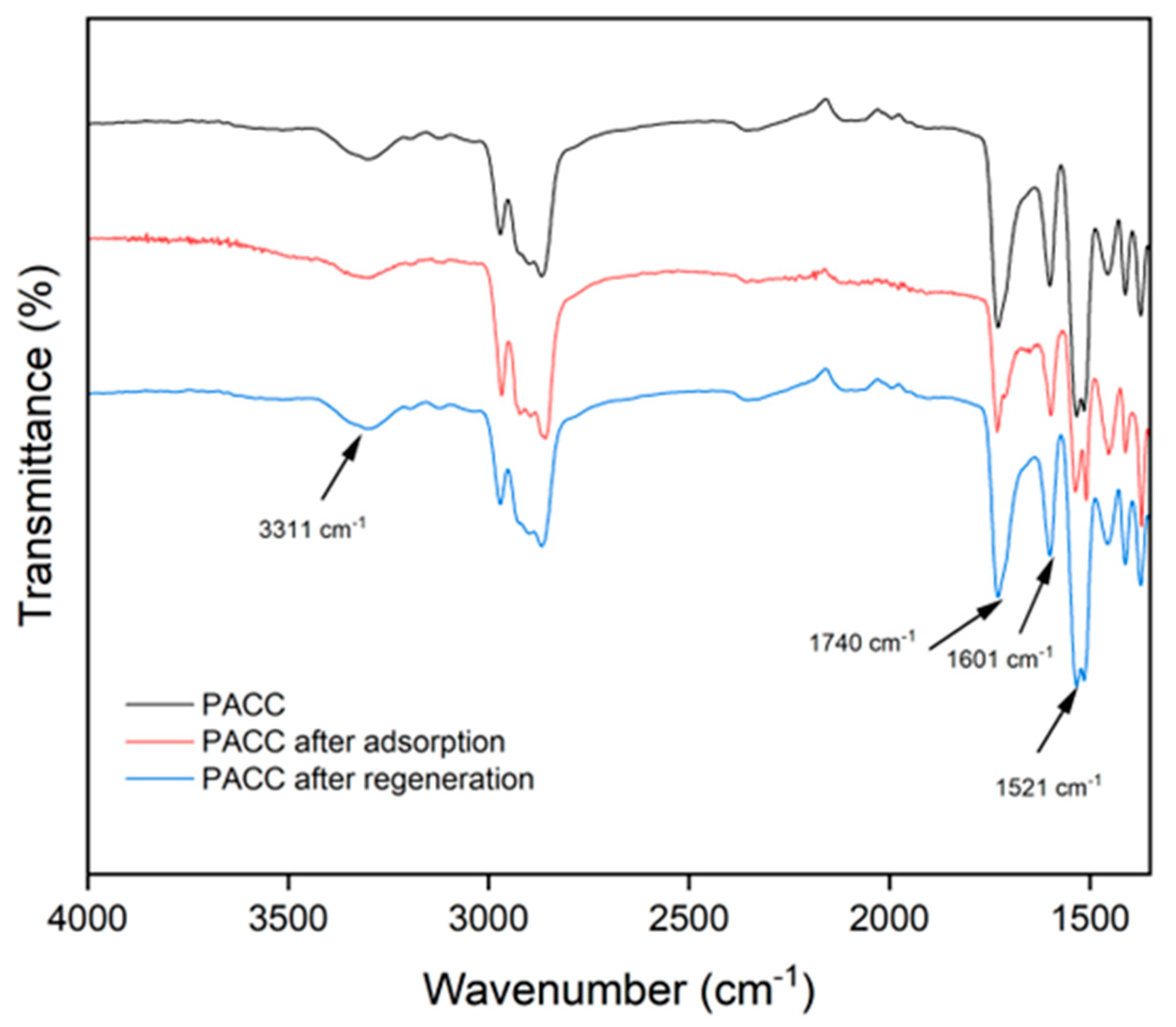
Figure 12 displays the FTIR spectra of PACC during distinct phases: pre-adsorption, post-adsorption, and after regeneration. In the pre-adsorption stage, the FTIR spectrum reveals pronounced and intense peaks associated with certain functional groups, specifically -OH, C=O, C-O, and N-H bonds. Upon regeneration, the FTIR spectrum of PACC displays comparable peak intensities to its pre-adsorption state, resembling the initial FTIR spectrum of PACC prior to exposure to Pb2+ adsorption. This observation demonstrates the successful regeneration of the adsorption sites showing PACC’s reusability feature.
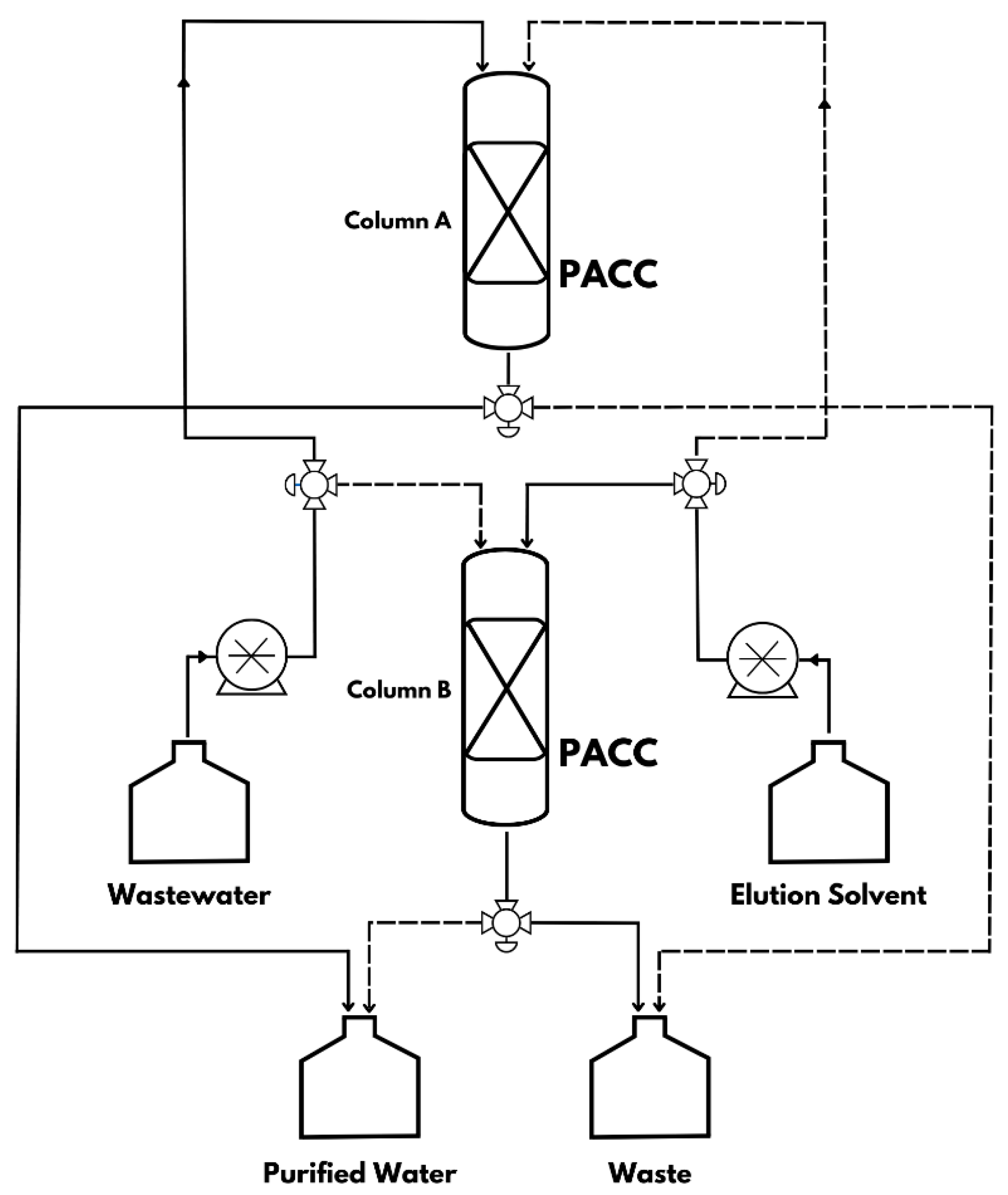
A proposed industrial setup for wastewater treatment is depicted in
Figure 8. To showcase the practicality of a continuous adsorptive water treatment method, a rotating pattern of two parallel columns can be utilized for wastewater treatment, as illustrated in
Figure 8. Each column can be filled with 50g of PACC adsorbent and utilized for uninterrupted processing. Once 2.5 L of wastewater has been treated in Column A, the wastewater feed will be directed to Column B, while Column A undergoes simultaneous regeneration using the elution solvent. This method offers the advantage of simultaneous adsorption-desorption processes, thereby circumventing the drawbacks associated with conventional adsorbents, which necessitate costly operating and manufacturing methods, resulting in potenrial secondary pollutions. The suggested approach is expected to mitigate environmental and health risks in comparison to alternative methods. A comprehensive life cycle assessment (LCA) can provide further evaluation and assessment of the environmental impact and sustainability aspects of this approach.
Figure 13.
Continuous adsorption unit process diagram using polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) as a sorbent material.
Figure 13.
Continuous adsorption unit process diagram using polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) as a sorbent material.
4. Conclusions
In summary, this study investigated the utilization of coconut oil-based PACC as a sustainable and economical substitute to other existing sorbents. The PACC material exhibited effective adsorption capabilities for removing Pb2+ from aqueous solutions as evidenced by fixed-bed column studies, which is consistent with the Thomas and Yoon-Nelson breakthrough curve modelling. This effective performance are collectively attributed to the PACC’s excellent physicochemical properties such as high porosity, large cell sizes, and enhanced negative polarity. Furthermore, PACC demonstrates exceptional reusability, characterized by its ability to maintain a considerable adsorption capacity while preserving both durability and structural stability. This assertion is substantiated through subsequent analysis of PACC's physicochemical and thermal characteristics. Consequently, the PACC’s remarkable attributes provides a compelling case for its viability as a comparable, and conceivably superior, alternative to other biosorbents. Hence, the successful synthesis of PACC realizes its potential application as an economical, eco-friendly, and sustainable biosorbent for large-scale removal of heavy metals, specifically Pb2+, from wastewater.
Authors contribution
Conceptualization, Rubie Mae Fernandez; Data curation, Renz John Estrada, Tomas Ralph Tomon and Alona Lubguban; Formal analysis, Roger Jr. Dingcong; Funding acquisition, Gerard Dumancas, Arnold Alguno and Arnold Lubguban; Methodology, Renz John Estrada and Tomas Ralph Tomon; Resources, Rubie Mae Fernandez; Software, Rubie Mae Fernandez, Renz John Estrada and Tomas Ralph Tomon; Supervision, Roberto Malaluan, Hernando P. Bacosa and Arnold Lubguban; Writing – review & editing, Ruben Amparado Jr., Rey Capangpangan, Roberto Malaluan, Arnold Alguno, Hernando P. Bacosa and Arnold Lubguban.
Funding
The Department of Science and Technology – Accelerated Science and Technology Human Resource Development Program provided support for this study as part of the primary author's scholarship program.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets utilized and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude for the financial assistance provided by the Department of Science and Technology through the Niche Centers in the Region (NICER) – R&D Center for Sustainable Polymers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- X. Zhao et al., “Assessment of residents’ total environmental exposure to heavy metals in China,” Sci Rep, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 16386, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Mohamed, I. A. Udoetok, M. Solgi, B. G. K. Steiger, Z. Zhou, and L. D. Wilson, “Design of Sustainable Biomaterial Composite Adsorbents for Point-of-Use Removal of Lead Ions From Water,” Frontiers in Water, vol. 4, no. February, pp. 1–12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang et al., “Electrochemical aptasensor based on gold modified graphene nanocomposite with different morphologies for ultrasensitive detection of Pb2+,” Sens Actuators B Chem, vol. 288, pp. 325–331, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. D. Vuković et al., “Removal of lead from water by amino modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 173, no. 3, pp. 855–865, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Basu, A. K. Guha, and L. Ray, “Adsorption of Lead on Lentil Husk in Fixed Bed Column Bioreactor,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 283, pp. 86–95, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Renu, K. Singh, S. Upadhyaya, and R. K. Dohare, “Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using modified agricultural adsorbents,” Mater Today Proc, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 10534–10538, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kuang, X. Zhang, and S. Zhou, “Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification,” Water (Basel), vol. 12, no. 2, p. 587, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Maulina and M. Iriansyah, “Characteristics of activated carbon resulted from pyrolysis of the oil palm fronds powder,” IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng, vol. 309, p. 012072, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- B. Wang, J. Lan, C. Bo, B. Gong, and J. Ou, “Adsorption of heavy metal onto biomass-derived activated carbon: review,” RSC Adv, vol. 13, no. 7, pp. 4275–4302, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Kalaivani, A. Muthukrishnaraj, S. Sivanesan, and L. Ravikumar, “Novel hyperbranched polyurethane resins for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution,” Process Safety and Environmental Protection, vol. 104, pp. 11–23, Nov. 2016. [CrossRef]
- H. Wang, Q. Wang, J. He, Z. Mao, and J. Sun, “Study on the Pyrolytic Behaviors and Kinetics of Rigid Polyurethane Foams,” Procedia Eng, vol. 52, pp. 377–385, 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. S. Carriço, T. Fraga, and V. M. D. Pasa, “Production and characterization of polyurethane foams from a simple mixture of castor oil, crude glycerol and untreated lignin as bio-based polyols,” Eur Polym J, vol. 85, pp. 53–61, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. S. Kaikade and A. S. Sabnis, “Polyurethane foams from vegetable oil-based polyols: a review,” Polymer Bulletin, vol. 80, no. 3, pp. 2239–2261, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. G. Dingcong et al., “A novel reaction mechanism for the synthesis of coconut oil-derived biopolyol for rigid poly(urethane-urea) hybrid foam application,” RSC Adv, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 1985–1994, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. A. E. de Franco, C. B. de Carvalho, M. M. Bonetto, R. de P. Soares, and L. A. Féris, “Removal of amoxicillin from water by adsorption onto activated carbon in batch process and fixed bed column: Kinetics, isotherms, experimental design and breakthrough curves modelling,” J Clean Prod, vol. 161, pp. 947–956, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Bo et al., “Efficiently selective adsorption of Pb(II) with functionalized alginate-based adsorbent in batch/column systems: Mechanism and application simulation,” J Clean Prod, vol. 250, p. 119585, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. G. Fouda-Mbanga, E. Prabakaran, and K. Pillay, “Synthesis and characterization of CDs/Al2O3 nanofibers nanocomposite for Pb2+ ions adsorption and reuse for latent fingerprint detection,” Arabian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 6762–6781, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, Q. Yue, B. Gao, Q. Li, X. Xu, and K. Fu, “Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by modified corn stalk: A fixed-bed column study,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 113, pp. 114–120, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. A. E. de Franco, C. B. de Carvalho, M. M. Bonetto, R. de Pelegrini Soares, and L. A. Féris, “Diclofenac removal from water by adsorption using activated carbon in batch mode and fixed-bed column: Isotherms, thermodynamic study and breakthrough curves modeling,” J Clean Prod, vol. 181, pp. 145–154, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. Bulgariu and L. Bulgariu, “Sorption of Pb(II) onto a mixture of algae waste biomass and anion exchanger resin in a packed-bed column,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 129, pp. 374–380, Feb. 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Thomas, “CHROMATOGRAPHY: A PROBLEM IN KINETICS,” Ann N Y Acad Sci, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 161–182, Feb. 1948. [CrossRef]
- G. S. Bohart and E. Q. Adams, “SOME ASPECTS OF THE BEHAVIOR OF CHARCOAL WITH RESPECT TO CHLORINE. 1,” J Am Chem Soc, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 523–544, Mar. 1920. [CrossRef]
- Y. K. Recepoğlu et al., “Packed bed column dynamic study for boron removal from geothermal brine by a chelating fiber and breakthrough curve analysis by using mathematical models,” Desalination, vol. 437, pp. 1–6, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Hoang, T. D. Pham, V. T. Nguyen, M. K. Nguyen, T. T. Pham, and B. Van der Bruggen, “Removal and recovery of lead from wastewater using an integrated system of adsorption and crystallization,” J Clean Prod, vol. 213, pp. 1204–1216, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. H. Yoon and J. H. Nelson, “Application of Gas Adsorption Kinetics I. A Theoretical Model for Respirator Cartridge Service Life,” Am Ind Hyg Assoc J, vol. 45, no. 8, pp. 509–516, Aug. 1984. [CrossRef]
- A. Keshavarz, H. Zilouei, A. Abdolmaleki, A. Asadinezhad, and A. A. Nikkhah, “Impregnation of polyurethane foam with activated carbon for enhancing oil removal from water,” International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 699–710, Feb. 2016. [CrossRef]
- W. Li and S. Liu, “Preparation and characterization of polyurethane foam/activated carbon composite adsorbents,” Journal of Porous Materials, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 567–572, Oct. 2012. [CrossRef]
- B. Li, G. Zhao, G. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Gong, and Z. Shi, “Biodegradable PLA/PBS open-cell foam fabricated by supercritical CO2 foaming for selective oil-adsorption,” Sep Purif Technol, vol. 257, p. 117949, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Qu et al., “Adsorption of lead (Ⅱ) from aqueous solution by modified Auricularia matrix waste: A fixed-bed column study,” Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, vol. 169, pp. 722–729, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Kılıç, M. E. Keskin, S. Mazlum, and N. Mazlum, “Hg(II) and Pb(II) adsorption on activated sludge biomass: Effective biosorption mechanism,” Int J Miner Process, vol. 87, no. 1–2, pp. 1–8, Apr. 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. X. Wang, C. C. Jin, and W. J. Qian, “Bi 2 O 3 with activated carbon composite as a supercapacitor electrode,” J Alloys Compd, vol. 615, pp. 12–17, Dec. 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. F. Hassan, A. M. Abdel-Mohsen, and H. Elhadidy, “Adsorption of arsenic by activated carbon, calcium alginate and their composite beads,” Int J Biol Macromol, vol. 68, pp. 125–130, Jul. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Xiong L. W. and K. H. Badri, “Preparation of polyurethane composites with activated carbon black as the reinforcing filler,” Journal of polymer science and technology, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 11–18, 2018.
- J. Mathivanan, H. Liu, J. Gan, A. R. Chandrasekaran, and J. Sheng, “Fluorescent Aptaswitch for Detection of Lead Ions,” ACS Appl Bio Mater, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Eichhorn and W. W. Sampson, “Relationships between specific surface area and pore size in electrospun polymer fibre networks,” J R Soc Interface, vol. 7, no. 45, pp. 641–649, Apr. 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. Nam, S. Choi, H. Byun, Y.-M. Rhym, and S. E. Shim, “Preparation of macroporous carbon foams using a polyurethane foam template replica method without curing step,” Macromol Res, vol. 21, no. 9, pp. 958–964, Sep. 2013. [CrossRef]
- W. El Malti, M. Hamieh, A. Noaman, R. Nasser El-Dine, A. Hijazi, and W. Al-Khatib, “Polyurethane Loaded with Vegetable Activated Carbon for Heavy Metals Removal from Water,” Journal of Ecological Engineering, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 99–110, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Udayakumar et al., “Synthesis of activated carbon foams with high specific surface area using polyurethane elastomer templates for effective removal of methylene blue,” Arabian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 14, no. 7, p. 103214, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Ahmad and B. H. Hameed, “Fixed-bed adsorption of reactive azo dye onto granular activated carbon prepared from waste,” J Hazard Mater, vol. 175, no. 1–3, pp. 298–303, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. B. Albadarin, C. Mangwandi, A. H. Al-Muhtaseb, G. M. Walker, S. J. Allen, and M. N. M. Ahmad, “Modelling and Fixed Bed Column Adsorption of Cr(VI) onto Orthophosphoric Acid-activated Lignin,” Chin J Chem Eng, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 469–477, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- V. Makrigianni, A. Giannakas, D. Hela, M. Papadaki, and I. Konstantinou, “Adsorption of methylene blue dye by pyrolytic tire char in fixed-bed column,” Desalination Water Treat, vol. 65, pp. 346–358, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Han et al., “Characterization and properties of iron oxide-coated zeolite as adsorbent for removal of copper(II) from solution in fixed bed column,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 149, no. 1–3, pp. 123–131, Jul. 2009. [CrossRef]
- D. C. K. Ko, J. F. Porter, and G. McKay, “Optimised correlations for the fixed-bed adsorption of metal ions on bone char,” Chem Eng Sci, vol. 55, no. 23, pp. 5819–5829, Dec. 2000. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Ahmad and B. H. Hameed, “Fixed-bed adsorption of reactive azo dye onto granular activated carbon prepared from waste,” J Hazard Mater, vol. 175, no. 1–3, pp. 298–303, Mar. 2010. [CrossRef]
- et al. Boucherdoud, A., “Fixed-bed adsorption dynamics of methylene blue from aqueous solution using alginate-activated carbon composites adsorbents,” Algerian Journal of Environmental Science and Technology Month Edition, 2021.
- G. L. Dotto, J. M. N. dos Santos, R. Rosa, L. A. A. Pinto, F. A. Pavan, and E. C. Lima, “Fixed bed adsorption of Methylene Blue by ultrasonic surface modified chitin supported on sand,” Chemical Engineering Research and Design, vol. 100, pp. 302–310, Aug. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Chen and X. Wang, “Removing copper, zinc, and lead ion by granular activated carbon in pretreated fixed-bed columns,” Sep Purif Technol, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 157–167, Jul. 2000. [CrossRef]
- Z. Aksu and F. Gönen, “Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: prediction of breakthrough curves,” Process Biochemistry, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 599–613, Jan. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Baral, N. Das, T. S. Ramulu, S. K. Sahoo, S. N. Das, and G. R. Chaudhury, “Removal of Cr(VI) by thermally activated weed Salvinia cucullata in a fixed-bed column,” J Hazard Mater, vol. 161, no. 2–3, pp. 1427–1435, Jan. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zulfadhly, M. D. Mashitah, and S. Bhatia, “Heavy metals removal in fixed-bed column by the macro fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus,” Environmental Pollution, vol. 112, no. 3, pp. 463–470, May 2001. [CrossRef]
- R. HAN, J. ZHANG, W. ZOU, H. XIAO, J. SHI, and H. LIU, “Biosorption of copper(II) and lead(II) from aqueous solution by chaff in a fixed-bed column,” J Hazard Mater, vol. 133, no. 1–3, pp. 262–268, May 2006. [CrossRef]
- A. Özer, D. Özer, and A. Özer, “The adsorption of copper(II) ions on to dehydrated wheat bran (DWB): determination of the equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters,” Process Biochemistry, vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 2183–2191, Oct. 2004. [CrossRef]
- V. Choudhary, M. Patel, C. U. Pittman, and D. Mohan, “Batch and Continuous Fixed-Bed Lead Removal Using Himalayan Pine Needle Biochar: Isotherm and Kinetic Studies,” ACS Omega, vol. 5, no. 27, pp. 16366–16378, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. A. E. de Franco, C. B. de Carvalho, M. M. Bonetto, R. de P. Soares, and L. A. Féris, “Removal of amoxicillin from water by adsorption onto activated carbon in batch process and fixed bed column: Kinetics, isotherms, experimental design and breakthrough curves modelling,” J Clean Prod, vol. 161, pp. 947–956, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Lim and A. Z. Aris, “Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: Removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions in aqueous solution by dead calcareous skeletons,” Biochem Eng J, vol. 87, pp. 50–61, Jun. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, Q. Yue, B. Gao, Q. Li, X. Xu, and K. Fu, “Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by modified corn stalk: A fixed-bed column study,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 113, pp. 114–120, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu et al., “Carboxyl-functionalized lotus seedpod: A highly efficient and reusable agricultural waste-based adsorbent for removal of toxic Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution,” Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp, vol. 568, pp. 391–401, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Aksu and F. Gönen, “Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: prediction of breakthrough curves,” Process Biochemistry, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 599–613, Jan. 2004. [CrossRef]
- O. Ozdemir, M. Turan, A. Z. Turan, A. Faki, and A. B. Engin, “Feasibility analysis of color removal from textile dyeing wastewater in a fixed-bed column system by surfactant-modified zeolite (SMZ),” J Hazard Mater, vol. 166, no. 2–3, pp. 647–654, Jul. 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Chatterjee, S. Mondal, and S. De, “Design and scaling up of fixed bed adsorption columns for lead removal by treated laterite,” J Clean Prod, vol. 177, pp. 760–774, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. Khalfa, A. Sdiri, M. Bagane, and M. L. Cervera, “A calcined clay fixed bed adsorption studies for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions,” J Clean Prod, vol. 278, p. 123935, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Lim and A. Z. Aris, “Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: Removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions in aqueous solution by dead calcareous skeletons,” Biochem Eng J, vol. 87, pp. 50–61, Jun. 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. M. Sreenivas, M. B. Inarkar, S. V. Gokhale, and S. S. Lele, “Re-utilization of ash gourd (Benincasa hispida) peel waste for chromium (VI) biosorption: Equilibrium and column studies,” J Environ Chem Eng, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 455–462, Mar. 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. D. Dorado, X. Gamisans, C. Valderrama, M. Solé, and C. Lao, “Cr(III) removal from aqueous solutions: A straightforward model approaching of the adsorption in a fixed-bed column,” Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 179–186, Jan. 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Anwar, U. Shafique, Waheed-uz-Zaman, M. Salman, A. Dar, and S. Anwar, “Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water by adsorption on peels of banana,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 101, no. 6, pp. 1752–1755, Mar. 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. M. D. Zulkali, A. L. Ahmad, N. H. Norulakmal, and N. S. Sharifah, “Comparative studies ofOryza sativa L. husk and chitosan as lead adsorbent,” Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, vol. 81, no. 7, pp. 1324–1327, Jul. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. H. M. A. Kamal, W. M. K. W. K. Azira, M. Kasmawati, Z. Haslizaidi, and W. N. W. Saime, “Sequestration of toxic Pb(II) ions by chemically treated rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) leaf powder,” Journal of Environmental Sciences, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 248–256, Jan. 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. Donat, A. Akdogan, E. Erdem, and H. Cetisli, “Thermodynamics of Pb2+ and Ni2+ adsorption onto natural bentonite from aqueous solutions,” J Colloid Interface Sci, vol. 286, no. 1, pp. 43–52, Jun. 2005. [CrossRef]
- B. Purvis, Y. Mao, and D. Robinson, “Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins,” Sustain Sci, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 681–695, May 2019. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Laboratory-scale fixed-bed column set-up using polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) as a sorbent material.
Figure 1.
Laboratory-scale fixed-bed column set-up using polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) as a sorbent material.
Figure 2.
SEM images of blank polyurethane foam (a.1and a.2), polyurethane-activated carbon composite (b.1 and b.2), polyurethane-activated carbon composite after lead adsorption (c.1 and c.2).
Figure 2.
SEM images of blank polyurethane foam (a.1and a.2), polyurethane-activated carbon composite (b.1 and b.2), polyurethane-activated carbon composite after lead adsorption (c.1 and c.2).
Figure 3.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of blank polyurethane foam, polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), and PACC after Pb adsorption.
Figure 3.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of blank polyurethane foam, polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), and PACC after Pb adsorption.
Figure 4.
XRD profile of a blank polyurethane (PU) and polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC).
Figure 4.
XRD profile of a blank polyurethane (PU) and polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC).
Figure 5.
TGA- DTG curves of (a) polyurethane (PU), (b) polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), and (c) PACC composite after adsorption.
Figure 5.
TGA- DTG curves of (a) polyurethane (PU), (b) polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), and (c) PACC composite after adsorption.
Figure 6.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different bed heights.
Figure 6.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different bed heights.
Figure 7.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different flow rates.
Figure 7.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different flow rates.
Figure 8.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different initial concentrations.
Figure 8.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different initial concentrations.
Figure 9.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different pH values.
Figure 9.
Breakthrough curves for Pb2+ adsorption on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) at different pH values.
Figure 10.
Prediction of the breakthrough curves of Pb2+ on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) material.
Figure 10.
Prediction of the breakthrough curves of Pb2+ on polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) material.
Figure 12.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), PACC after Pb adsorption, and PACC after regeneration.
Figure 12.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC), PACC after Pb adsorption, and PACC after regeneration.
Table 1.
Integration of A-side component, B-side components, and filler in the formulation of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) material.
Table 1.
Integration of A-side component, B-side components, and filler in the formulation of polyurethane-activated carbon composite (PACC) material.
| Ingredients |
Concentration(based on 100 parts polyol) |
| B-side Components |
|
| VORANOL® 4701 (petroleum-based polyol) |
80.00 |
| Coconut-based polyol |
20.00 |
| Polycat® 8 (gelling catalyst) |
0.50 |
| INV® 690 (surfactant) |
1.75 |
| Silicon oil |
5.00 |
| Fillers |
|
| Coconut activated carbon |
40.00 |
| |
|
| A-side Component |
|
| Isocyanate index of PAPI® 27 |
100.0 |
Table 2.
Elemental composition comparison of blank PU (a), PACC (b), and PACC after lead adsorption (c).
Table 2.
Elemental composition comparison of blank PU (a), PACC (b), and PACC after lead adsorption (c).
| Element |
Wt% |
|
|
| |
a |
b |
c |
Difference (b-a) |
Difference (c-b) |
| CK |
53.28 ± 1.13 |
55.13 ± 1.05 |
56.11 ± 1.03 |
1.85 |
-4.02 |
| NK |
12.58 ± 1.00 |
10.58 ± 0.81 |
9.56 ± 0.79 |
-2.00 |
3.98 |
| OK |
23.73 ± 1.19 |
33.60 ± 1.22 |
21.27 ± 1.20 |
9.87 |
-4.33 |
| SiK |
1.31 ± 0.01 |
0.60 ± 0.01 |
0.51 ± 0.01 |
|
|
| PtK |
3.10 ± 0.80 |
0.09 ± 0.11 |
0.18 ± 0.09 |
|
|
| PbK |
0.00 |
0.00 |
12.37 ± 0.16 |
|
|
| O/C |
0.45 |
0.61 |
0.38 |
35.55% |
-37.70% |
| (O+N)/C |
0.68 |
0.80 |
0.55 |
17.65% |
-31.25% |
Table 3.
Data parameters attained at different bed heights, pH, flow rates, and inlet Pb concentrations (T=28±1 ◦C).
Table 3.
Data parameters attained at different bed heights, pH, flow rates, and inlet Pb concentrations (T=28±1 ◦C).
Initial Concentration
(mg L-1) |
Bed height
(mm) |
Flow rate
(mL min-1) |
pH |
Total time
(min) |
Total mass adsorbed
(mg) |
Equilibrium uptake
(mg g-1) |
Effluent volume
(mL) |
| 50 |
50 |
4 |
6 |
230 |
70 |
7.08 |
770 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
290 |
94 |
8.28 |
1010 |
| 50 |
150 |
4 |
6 |
350 |
118 |
10.50 |
1250 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
290 |
94 |
10.56 |
1010 |
| 50 |
100 |
6 |
6 |
245 |
115 |
10.46 |
1220 |
| 50 |
100 |
8 |
6 |
200 |
118 |
8.56 |
1250 |
| 10 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
350 |
58 |
9.38 |
1250 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
290 |
94 |
10.56 |
1010 |
| 100 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
230 |
142 |
13.44 |
770 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
2 |
290 |
100 |
12.00 |
1070 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
4 |
305 |
118 |
27.31 |
1250 |
| 50 |
100 |
4 |
6 |
350 |
94 |
10.56 |
1010 |
Table 4.
Thomas model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
Table 4.
Thomas model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
| Parameter |
|
kTh
(L mg-1 min-1) x 10-4
|
qTh
(mg g-1) |
R2 |
| Bed height (mm) |
50 |
4.60 |
0.75 |
0.98 |
| |
100 |
2.62 |
0.86 |
0.97 |
| |
150 |
2.14 |
0.64 |
0.98 |
| Flow Rate |
4 |
2.11 |
0.79 |
0.97 |
| (mL min-1) |
6 |
4.60 |
0.75 |
0.98 |
| |
8 |
3.60 |
0.64 |
0.98 |
| Initial metal |
10 |
4.40 |
0.47 |
0.96 |
| concentration |
50 |
2.71 |
0.70 |
0.97 |
| (mg L-1) |
100 |
2.62 |
0.86 |
0.97 |
| pH |
2 |
2.50 |
0.82 |
0.97 |
| 4 |
2.80 |
0.99 |
0.96 |
| 6 |
2.10 |
0.37 |
0.97 |
| |
|
|
|
|
Table 5.
Bohart-Adams model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
Table 5.
Bohart-Adams model parameters at different conditions using linear regression analysis.
| Parameter |
|
KAB
(L mg-1 min-1) x 10-5
|
N0
(mg L-1) |
R2 |
| Bed height (mm) |
50 |
2.25 |
61.91 |
0.78 |
| |
100 |
1.64 |
92.79 |
0.77 |
| |
150 |
1.13 |
125.55 |
0.80 |
| Flow Rate |
4 |
1.15 |
99.75 |
0.82 |
| (mL min-1)
|
6 |
1.13 |
125.55 |
0.80 |
| |
8 |
1.64 |
92.79 |
0.77 |
| Initial metal |
10 |
2.25 |
61.91 |
0.78 |
| concentration |
50 |
1.28 |
97.67 |
0.77 |
| (mg L-1) |
100 |
1.13 |
125.55 |
0.80 |
| |
2 |
3.00 |
70.42 |
0.89 |
| pH |
4 |
2.89 |
82.77 |
0.69 |
| |
6 |
2.39 |
60.25 |
0.70 |
Table 7.
Parameters of “a” and “b” of generic model (Eq. 7) formulated using variables of different models.
Table 7.
Parameters of “a” and “b” of generic model (Eq. 7) formulated using variables of different models.
| |
Thomas |
Bohart-Adams |
Yoon-Nelson |
| a |
kThCo
|
kBACo
|
kYN
|
| b |
kThqThM/Q |
kBANoZ/u |
kYNτ |
Table 8.
Merits and limitations of column models employed in this study in relation to PACC.
Table 8.
Merits and limitations of column models employed in this study in relation to PACC.
| |
Merits |
Limitations |
| Thomas model |
|
|
| Bohart-Adams |
|
Require additional parameters for the model to be utilized Insufficiently described the behaviors of the metal columns Only applicable to adsorption processes involving surface reactions |
| Yoon-Nelson model |
|
|
Table 9.
Summary of capacity uptake of other adsorbents used for Pb2+ adsorption.
Table 9.
Summary of capacity uptake of other adsorbents used for Pb2+ adsorption.
| Adsorbent |
qeq (mg g-1) |
Reference |
| PACC |
27.31 |
Present study |
| Banana peel |
2.18 |
[65] |
| Rice husk |
5.69 |
[66] |
| Activated carbon |
26.5 |
[67] |
| Bentonite |
12.6 |
[68] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).