1. Introduction
Garlic (
Allium sativum), a bulbous plant well-known for its health benefits, has been widely used for treatment of diseases since ancient times [
1]. Despite the broad research available regarding its health benefits, little information is available on the functional properties of garlic components. In fact, to our knowledge, only our previous study [
2] —dealing with the emulsification properties of garlic extract—has focused on this matter. In this study it was proven that garlic aqueous extracts do include surface-active compounds which, even at low concentrations (0.48% wt/wt), can form relatively stable emulsions comprising sub-micron sized droplets (d
32=0.36 µm). However, droplet aggregation and accelerated creaming can be observed at higher extract concentrations (6.55% wt/wt) due to a combination of effects involving increasing emulsion droplet size formation (d
32=6.55 µm), depletion flocculation and bridging phenomena. The underpinning reason of these phenomena was related to the coexistence of compounds of different surface-active nature (
i.e. a combination of saponins, and proteins/peptides) and the interactions between them and with fructans present in garlic.
The effectiveness of an emulsifier can be affected by the media conditions—such as pH, ionic strength, heating and freezing [
3,
4,
5]. In fact, there is evidence on the interfacial behaviour of
Quillaja bark saponins being affected by pH, with the saponins becoming more surface active (reflected in a surface tension decrease) when pH was lowered from pH 7.0 to pH 3.0 [
6]. However, the thickness of the foam films formed with these solutions was lower at pH 3.0 compared to pH 7.0. Regarding proteins, no information on garlic protein is available, but there are many reports about the influence of environmental factors on the performance of other proteins, such as milk proteins [
7] or vegetal proteins (pea, soy, lentil and canola) [
8], among others. In the case of fructans, to the best of our knowledge there are only two studies that deal with their interfacial behaviour [
9], and no information about the effect of environmental stresses is available. Nevertheless, there are studies about the effect of acid hydrolysis [
10] or temperature [
11] on fructans structure.
The effect of environmental factors on the performance of garlic water-soluble extracts as emulsifiers has not been investigated. The ionic nature of the steroidal saponins detected in garlic [
2] as well as the presence of charged proteins and peptides make it likely that pH and temperature will have some impact on the emulsification properties. In addition, one of the causes for emulsion instability we have hypothesized was the possibility that proteins may be linked or complexed to the fructans and/or saponins in the native state in garlic. Therefore, the modification of various garlic aqueous extracts in order to try to modify/denature and remove larger aggregates involving the biopolymers present in the extract (proteins and polysaccharides)—visible in the transmission electron microscopy images of our previous research [
2], and likely to be involved in droplet aggregation— seems highly interesting to be able to control emulsion stability, as well as shedding light on the relative contributions of the surface-active species in garlic.
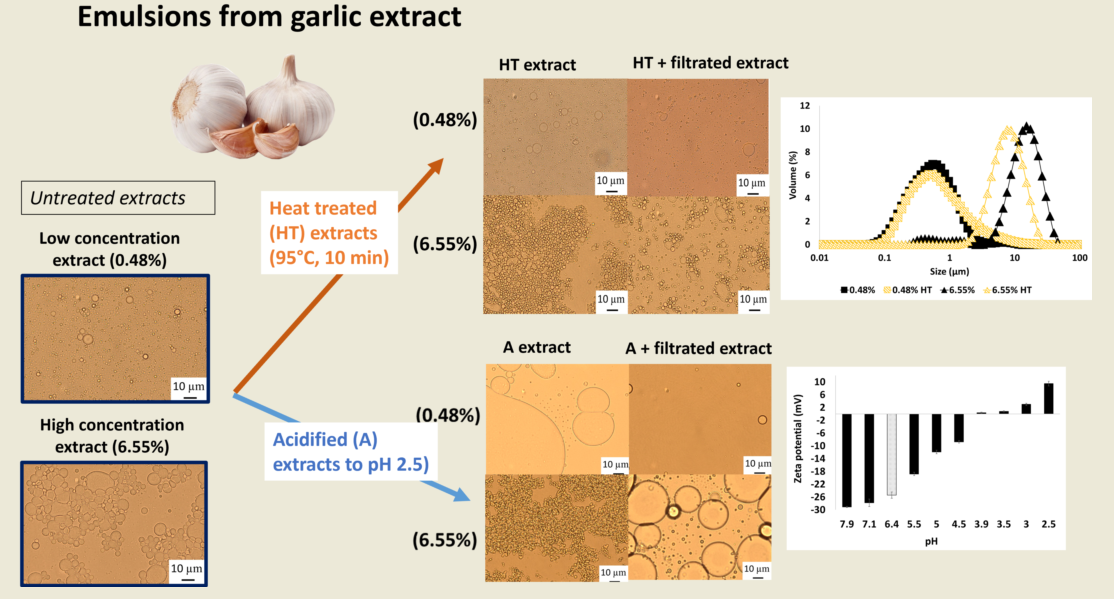
Given this background, the aim of the present work was to study the effect of pH and heat on the emulsification properties of garlic aqueous extracts—by the characterization of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with garlic extracts (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt) (previously modified by heat or pH treatments and filtrated through a 0.45 µm pore membrane, to remove the visible aggregates (likely formed by aggregated proteins and polysaccharides) [
2]. Microstructural analysis—droplet size by static light scattering, and light microscopy—along with phase separation measurements of the emulsions under storage were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fresh peeled garlic was purchased from Marlborough Garlic LTD (Marlborough, New Zealand) and frozen upon arrival (-18 ºC). Garlic was then defrosted overnight at 4 ºC before experiments. The total solids content of the garlic bulbs was 32.7 ± 0.75 (wt/wt %). Soya bean oil (containing antioxidant E-319) was purchased from Gilmours (Palmerston North, New Zealand). Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.1. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction of garlic water-soluble compounds (GWSC)
The aqueous extract was prepared as reported in our previous study [
2]. Firstly, defrosted garlic bulbs were blended with reverse osmosis (RO) water (1.78 or 28.44 g garlic/ 100 g RO water) with a Nutri Ninja
® slim blender (SharkNinja Operating LLC, Needham, Massachusetts, United States of America) for 1 min at room temperature (20ºC). The blended garlic + water mixtures were heated up to 50 ºC in a water bath during 2 h under continuous stirring to favour the extraction of the garlic water-soluble compounds (GWSC). Subsequently the mixtures were centrifuged for 30 min at 14,000 x g and at 20 ºC (Thermo Scientific Sorval RC 6+, USA). The supernatants were then filtered with Whatman® qualitative filter paper, Grade 1, under vacuum conditions at room temperature. Concentration of GWSC in the extracts (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt) was calculated as in Bravo-Núñez
et al. [
2]. Garlic extracts where subsequently used for the following experiments. Extracts were prepared and measured at least in duplicate.
2.2.2. Modification of garlic aqueous extract compounds
The extracts obtained as described before were modified either by a heat treatment (10 min at 95 °C in a water bath with temperature control under continuous stirring) or pH adjustment (pH’s 2.5, 3.5 and 7.8). using a solution of 0.1-1 M HCl (or 0.1-1 M NaOH). These extracts were then filtrated through 0.45 µm pore filters (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA, USA), in order to remove denatured biopolymers/big aggregates and some were used as controls (no filtration was carried out). Modification of garlic extracts was performed in duplicate.
2.2.3. ζ-Potential and isoelectric point of garlic aqueous extract compounds
The zeta potential (ζ) of unmodified GWSC (concentration of soluble compounds of 0.28% wt/wt) was measured using a Zetasizer Nano ZS (ZEN 169 3600) instrument (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, Worcestershire, UK) using a disposable, folded capillary cell (DTS 1060) at 25 °C. Z-potential was also measured at different pH’s to determine the isoelectric point of the extract. Solutions of 0.1-1 M HCl (or 0.1-1 M NaOH) were used to adjust the pH before measurements. Measurements were preformed in duplicate from two different batches.
2.2.4. Emulsion preparation
10% (wt/wt) oil-in-water emulsions were prepared by emulsifying soy bean oil and an aqueous phase containing the previously described modified GWSC, following the procedures earlier described in Bravo-Núñez
et al. [
2]. Oil + the modified garlic aqueous extract mixture was heated up to 50 ºC and subsequently pre-homogenized using a Silverson mixer (Silverson Machines Ltd., Chesham, U.K.). The coarse emulsions were immediately homogenised with three passes using a two-stage high-pressure homogenizer (APV 2000; Copenhagen, Denmark) operating at pressures: 25 MPa-first stage and 5 MPa-second stage. Sodium azide solution (0.02% v/v, 5 M) was added to the freshly homogenised emulsions as antimicrobial agent. Samples were kept under storage at 4 ºC. All emulsions were prepared and analysed in duplicate.
2.2.5. Droplet size measurement
The droplet size distribution of oil-in-water emulsions was determined by laser light scattering technique, using a Malvern Mastersizer MS 2000 (Malvern Instruments Ltd, Worcestershire, UK). Deionised water was used as a dispersant and the relative refractive index (N) of the emulsion was 1.105, i.e., the ratio of the refractive index of soy oil (1.470) to that of the aqueous medium (1.33). The droplet size distribution of the emulsion droplets was analysed the same day of preparation and on subsequent days (1st, 2nd, 3rd and 7th day)—when following emulsion stability over time. Samples were kept under storage at 4 ºC between measurements, and the emulsions were always homogenised before sampling to obtain representative measurements. The volume-mean droplet diameter (d43) and surface-mean droplet diameter (d32) were reported. Emulsions were prepared and measured in duplicate.
2.2.6. Light microscopy
A light microscope Olympus BX53 was used to visualise the microstructure of the emulsions. An aliquot portion of the emulsion sample was placed into a microscope slide. A cover slip was placed on top of the well ensuring that no air bubbles were trapped inside. The images were captured at 10x, 40x, and 100x magnifications. Emulsions were prepared and measured in duplicate (measurements were performed the same day of preparation and on subsequent days, 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 7th day). A total of ten pictures were taken per sample and representative images are presented here.
2.2.7. Statistical analysis
Data were analysed using one-way analysis of variance (simple ANOVA). When significant (p<0.05) differences were found, Fisher’s least significant differences (LSD) test was used to determine the differences among means. Statistical analyses were completed using Statgraphics Centurion XVI software (StatPoint Technologies Inc, Warrenton, Virginia, EE.UU).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of heat treatment on the emulsification properties of garlic aqueous extract compounds
3.1.1. Particle size distribution
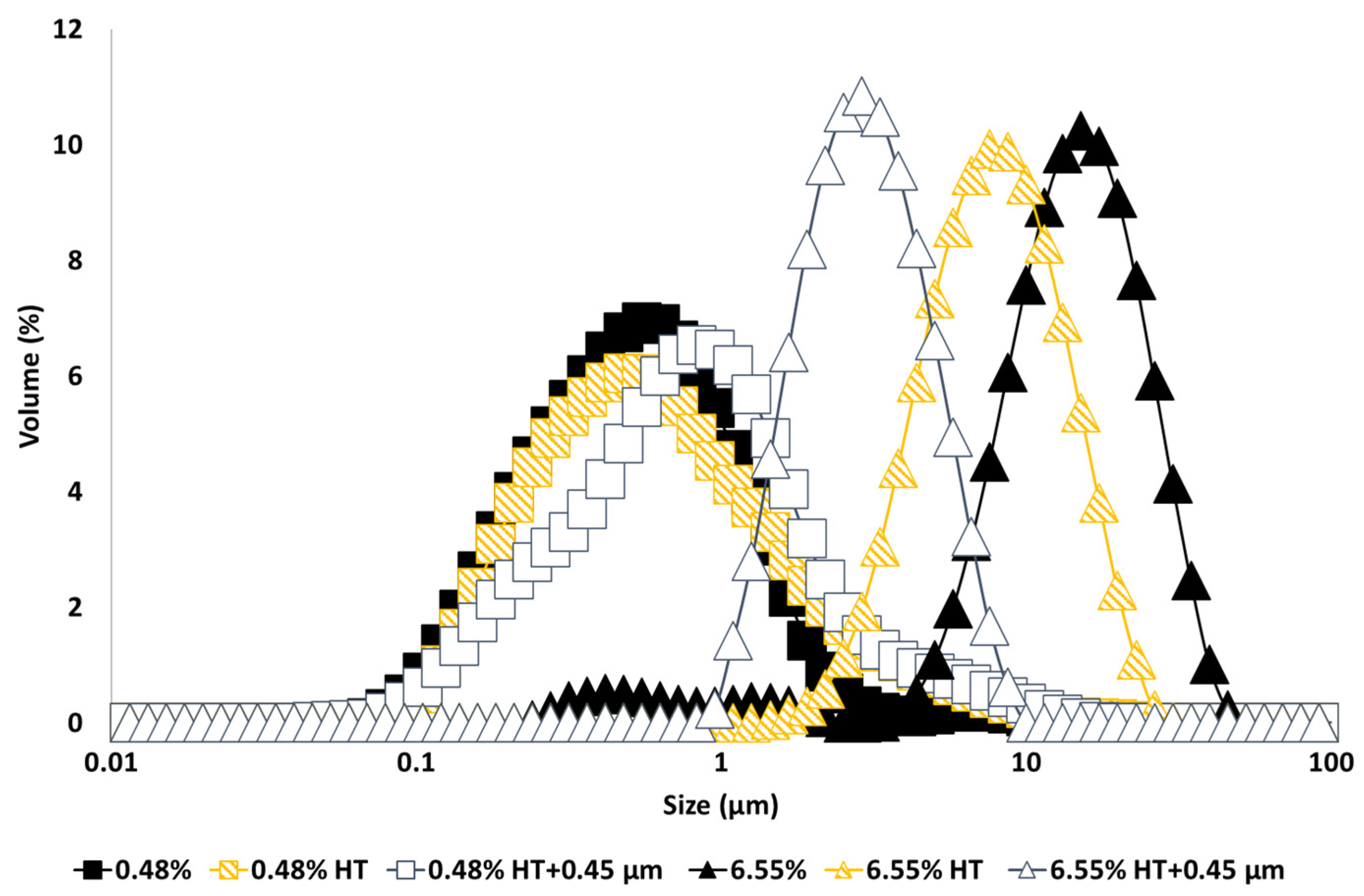
Droplet size distribution of emulsions made with untreated and heat-treated GWSC extracts (
Figure 1) shows that a smaller droplet size distribution was found for emulsions made at the lowest GWSC concentration, as opposed to using the highest GWSC concentration (6.55%), following the same trend as previously reported [
2]. Surface properties of water-soluble garlic extracts come from the various species previously identified which are likely to compete and/or interact at the interface (mainly proteins/peptides, saponins and fructans). The concentration of these compounds in the untreated extracts are shown in
Table 1. Recent work has demonstrated that pure native Agave fructans do not show any emulsifying capacity or surface activity (Ignot-Gutiérrez
et al.,[
12] therefore is unlikely that these compounds are responsible for any emulsification effect unless associated to proteins and/or saponins.
Interestingly, heat treatment of the extract and removal of the larger aggregates by filtration, had the opposite effect on the emulsification properties depending upon concentration; whereas at the lowest GWSC concentration (0.48% wt/wt), the emulsion droplet size slightly increased when using heat-treated + filtrated extract (d
32=0.48 µm) versus unmodified extract (d
32=0.36 µm), at the highest GWSC concentration (6.55% wt/wt), there was a reduction in the droplet size when the emulsions were made with heat-treated (d
43=8.18 µm; d
32=6.32 µm) and heat-treated + filtrated extracts (d
43=3.03 µm; d
32=2.46 µm) versus the unmodified one (d
43=12.46 µm; d
32=5.42 µm). The removal of the aggregates of the untreated GWSC also had a positive effect on droplet sizes (d
43=9.24 µm; d
32=7.21 µm) (size distribution shown in the supplementary information), although less pronounced than the removal of the aggregates after heat treatment of the GWSC. Clearly, the removal of the aggregated heat-sensitive compounds and previously existing aggregates (bigger than 0.45 µm) had a positive effect on the emulsifying properties of the GWSC extract at high concentration. This supports the hypothesis that the interface may be dominated by heat-sensitive biopolymers (likely proteins linked or not to fructans), when using the unmodified extracts at these concentrations. The denaturation of globular proteins and the removal of these aggregates (linked or not to polysaccharides) by heat and filtration may change the ratio of polymers to saponins rendering an overall positive effect on the droplet size achieved by allowing more preferential adsorption of the saponin fraction. On the other hand, at the lowest concentration (0.48% wt/wt), the removal of the heat-sensitive biopolymers results in a mild negative effect as slightly bigger droplets are formed, though overall, the droplet sizes are still much smaller than at high GWSC with or without treatment, showing that the interface is still potentially dominated by saponins over polymers as it has been shown earlier when these species are competing at low protein concentrations [
13,
14].
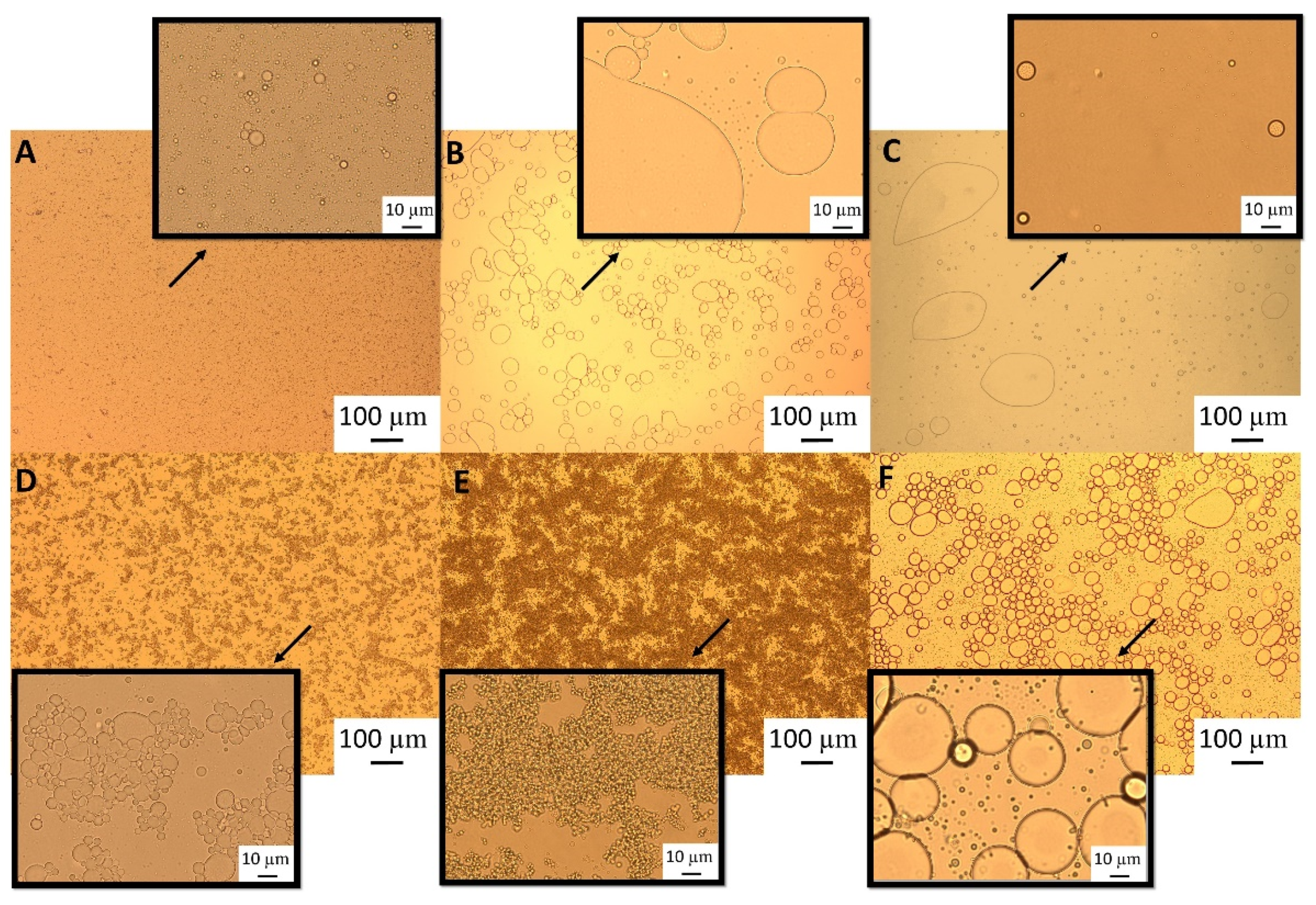
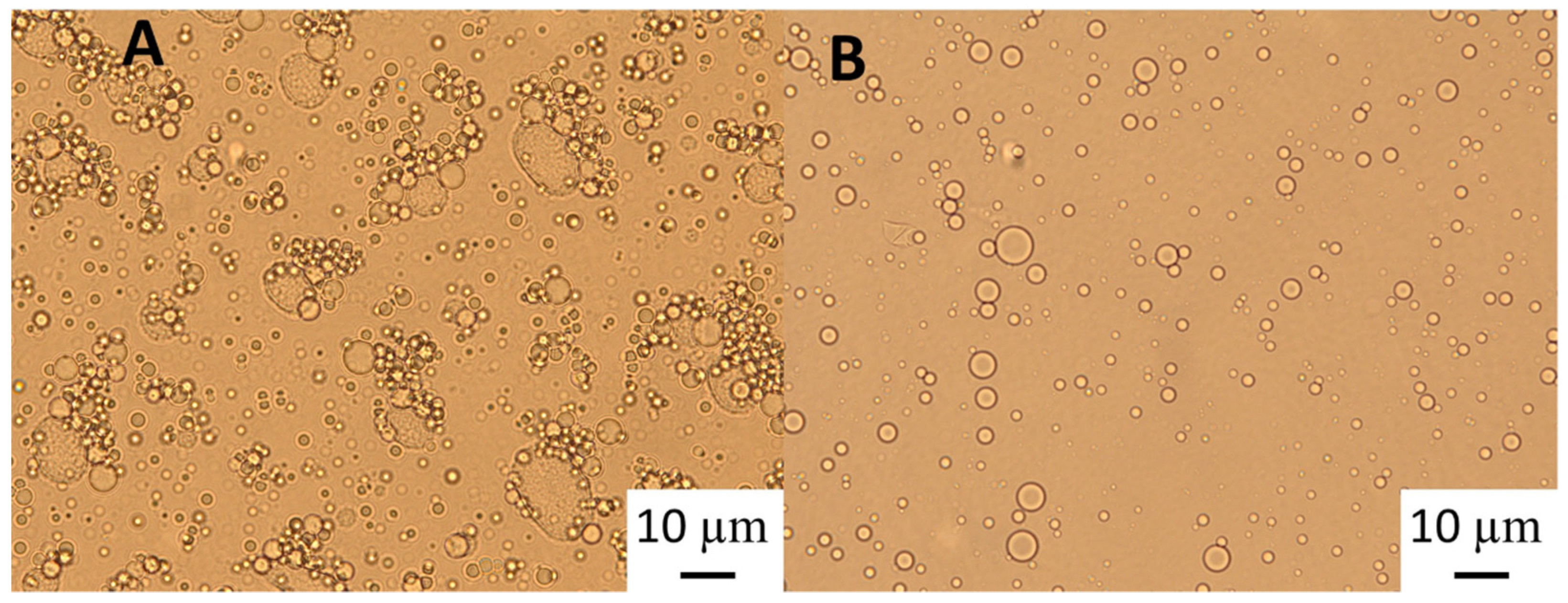
Light microscopy images (
Figure 2) show that although after heat treatment the droplet size of the emulsions formed with the highest GWSC was reduced (
Figure 2E), there is still strong flocculation phenomena being observed —attributed to depletion and bridging mechanisms —as reported in our previous research [
2]. Depletion phenomenon occurs when non-adsorbing biopolymers or surfactant micelles in the aqueous phase of an emulsion cause an increase in the attractive forces between the droplets, due to an osmotic effect associated with the exclusion of the non-adsorbing species from the narrow region between approaching droplets [
15,
16]. As previously observed with untreated extracts [
2], at very low concentrations of free polymers (0.48% wt/wt), the entropy loss linked to particle aggregation outweighs the depletion effect and the system remains stable even after heat treatment and filtration (
Figure 2B,C).
The polymers causing the aggregation phenomenon at high GWSC concentration (6.55% wt/wt) can be partially removed through filtration, considerably decreasing droplet aggregation (
Figure 2F). Nevertheless, some flocs could still be observed after removal of the denatured polymers through filtration, which suggest that not only depletion flocculation phenomena but also bridging flocculation phenomenon are taking place in these emulsions (
Figure 2E).
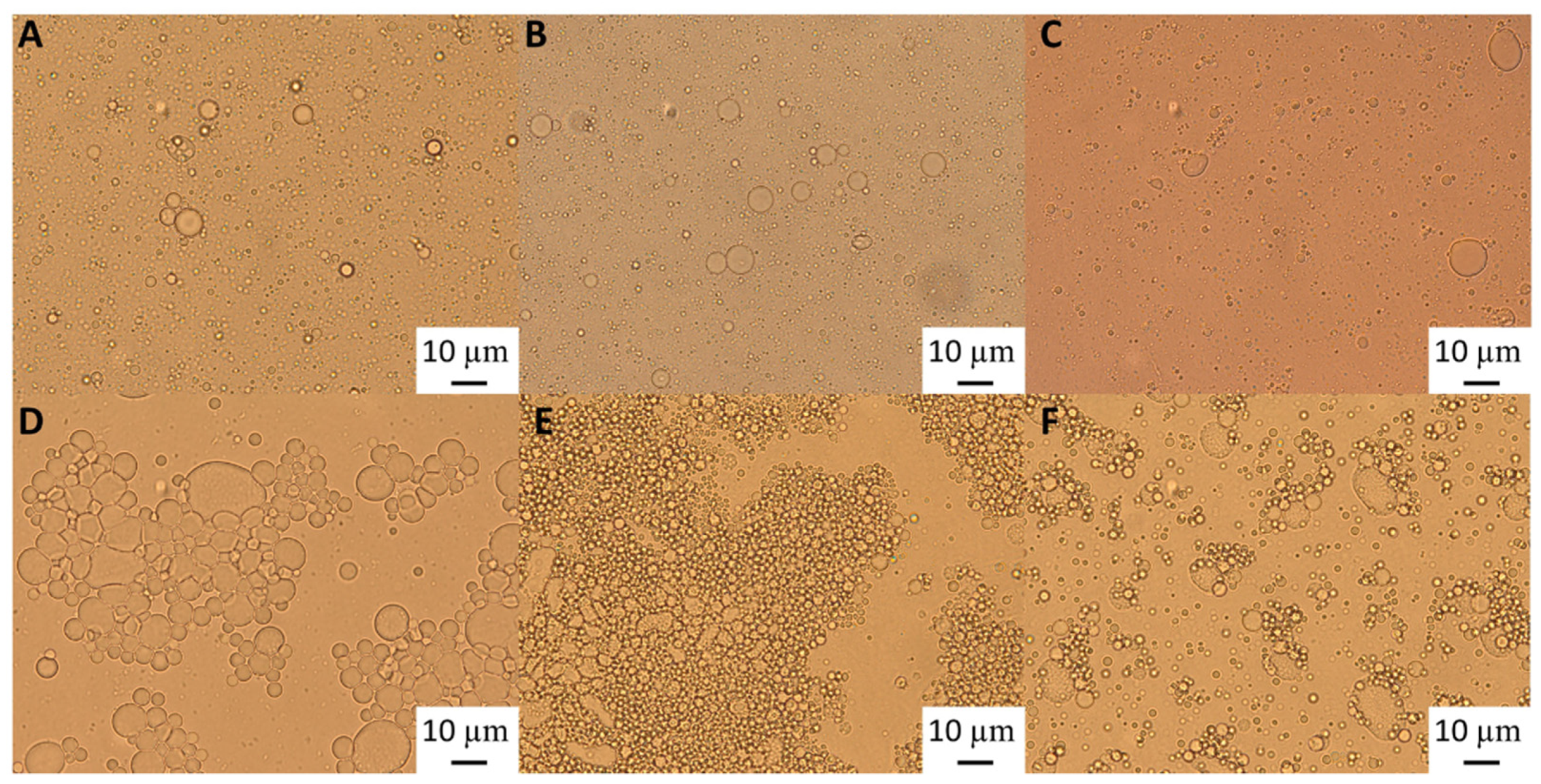
Figure 3 shows that when mixing the emulsion made with the heat-treated + filtrated extract at the highest concentration (6.55% wt/wt) with SDS, all the flocs disappeared. SDS is used to displace any protein/polysaccharide adsorbed at the interface, confirming the occurrence of bridging flocculation phenomena in both
Figure 2E,F as observed in emulsions where proteins and polysaccharides are involved in coating the droplets [
17].
This is interesting to note, as it shows that although heat treatment and filtration of the extracts can be applied to reduce droplet size distribution, there are still some surface active compounds remaining in the extracts after the filtration, responsible for the bridging and depletion flocculation phenomena. These compounds could be heat stable protein, fructans and saponin micelles—which are also proven to cause depletion flocculation effects, as high levels of non-adsorbed surfactant micelles are known to increase the osmotic pressure acting on oil droplets, thereby increasing their tendency to flocculate [
5]—or aggregates smaller than 0.45 µm. As previously stated, 0.45 µm was chosen as a cut off to remove big aggregates involving the biopolymers present in the extract and as demonstrated in this research, partially involved in droplet aggregation.
According to literature, above a critical concentration, saponins are capable of forming micellar structures. This concentration varies among different studies—0.08-0.1%wt [
18], 0.013 and 0.198 g/L [
19], 0.1 %wt [
20], 02-0.7 g/L [
21], 0.5–0.7 g/L [
22] or 0.1-0.8 g/L [
23]— being the differences explained by the purity and variation in the saponin composition, as well as saponin source. The reported size of these micelles is relatively small (
i.e. Samal
et al. [
20] reported saponin micelles sizes in the range of 10-11.5 nm while Tippel
et al. [
24] reported saponin micelles of 6.5 nm). Because no research is available on the physicochemical properties of garlic saponins, the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of these saponins currently remains unknown. Nevertheless, knowing the saponin concentration of our extracts—0.06%/ 0.6g/L (0.48% wt/wt GWSC) and 0.9%/ 9g/L (6.55% wt/wt GWSC)—leads us to suspect that saponin micelles are likely present at the highest GWSC concentration after filtration, and therefore they could be partially responsible for the depletion flocculation effect observed after both heat treatment and filtration. Droplet bridging at relatively low saponin concentrations (0.1-1% w/v) has been previously reported in the literature in emulsions co-stabilized with proteins and saponins [
25]. Having said that, some of these micelles agglomerates initially present in the GWSC may equally be removed with filtration, as Samal
et al. [
20] reported saponin micelles sizes in the range of 10-11.5 nm, which can also form agglomerates of sizes ranging from 132-235 nm, 390-990 nm, and 5,155-8,520 nm, regardless the saponin concentration in the solution (up to 30 g/L).
3.1.2. Emulsion stability over time
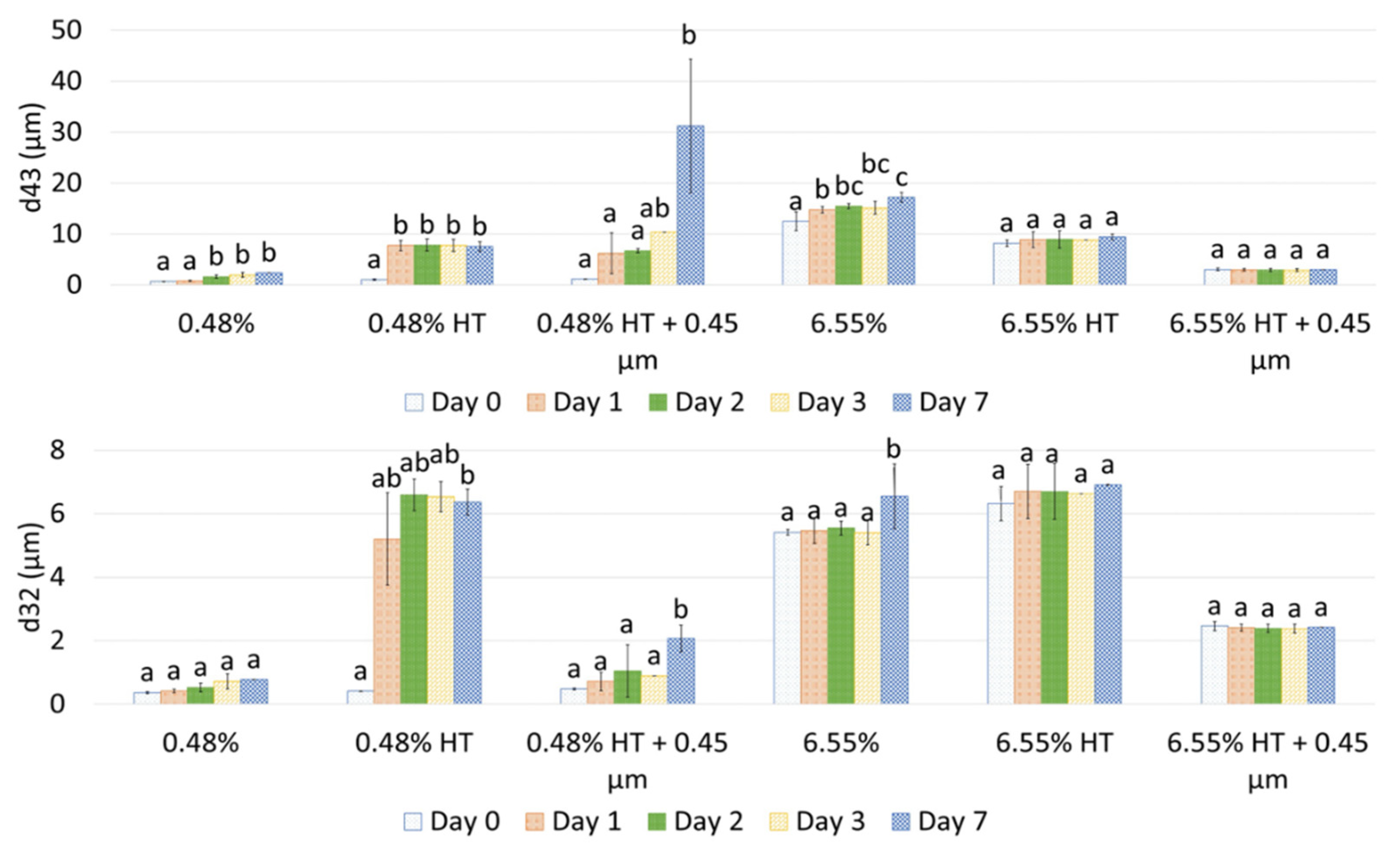
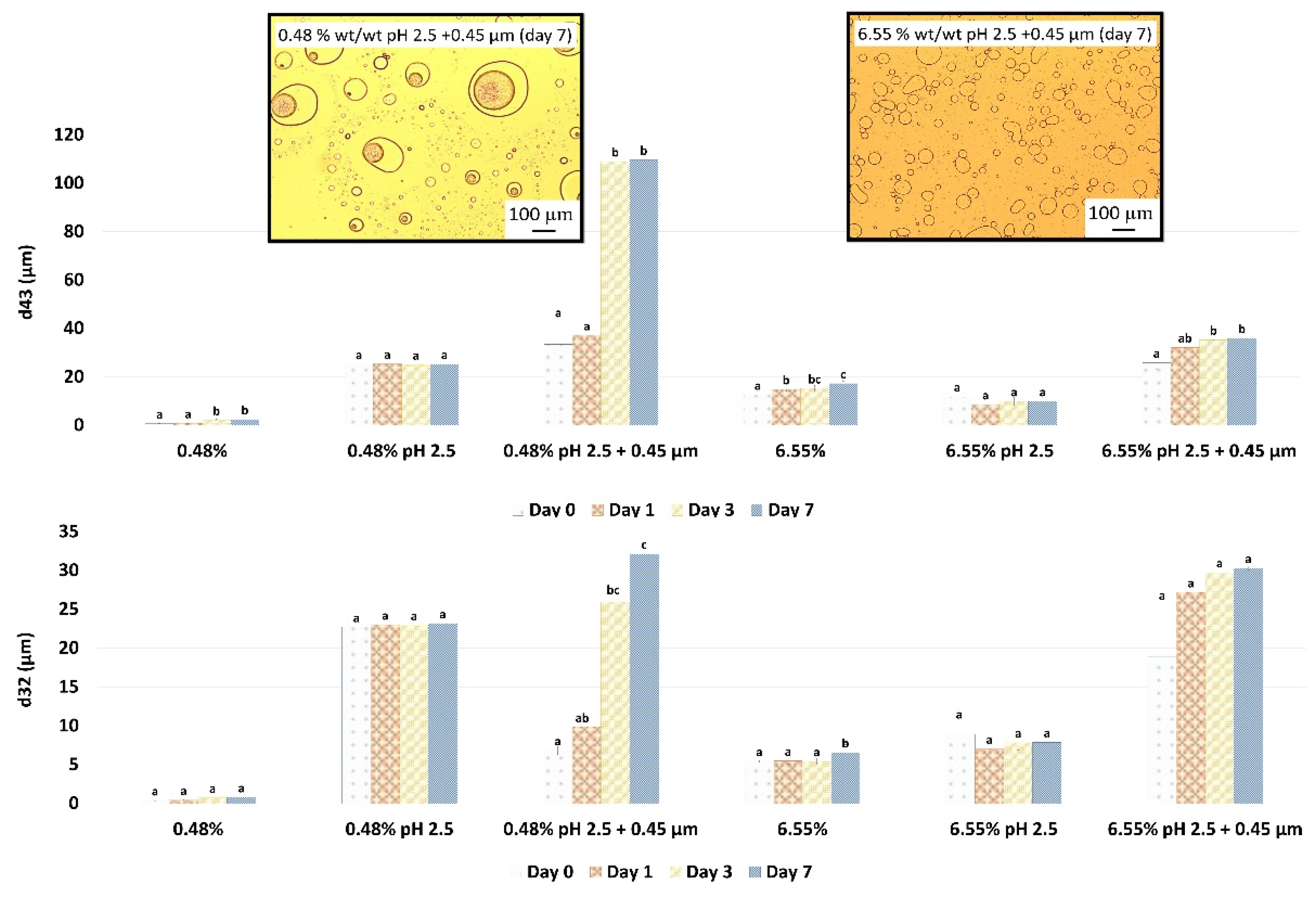
Droplet size changes with time of the garlic-based emulsions made with heat-treated extracts are shown in
Figure 4. It seems that the effect of heat treatment of the extracts on emulsion stability also depends on the concentration of the GWSC used. For the lowest concentration (0.48% wt/wt) stability was reduced, and flocculation (
Figure 5B) and coalescence (
Figure 5C) were observed, occurring more evidently before filtration, whereas for 0.48% HT + 0.45 µm emulsion, the drastic increase of d
43 at day 7 seems to be related to droplet aggregation, although coalescence was also observed (
Figure 5F). For the higher GWSC concentration (6.55% wt/wt), emulsion stability was improved after heat treatment + filtration. This is likely to be related to the increase of saponin content at the interface of the emulsions made at the highest GWSC after both heat treatment + filtration. Nonetheless these results are also affected by droplet aggregation (as already shown in
Figure 2D–F).
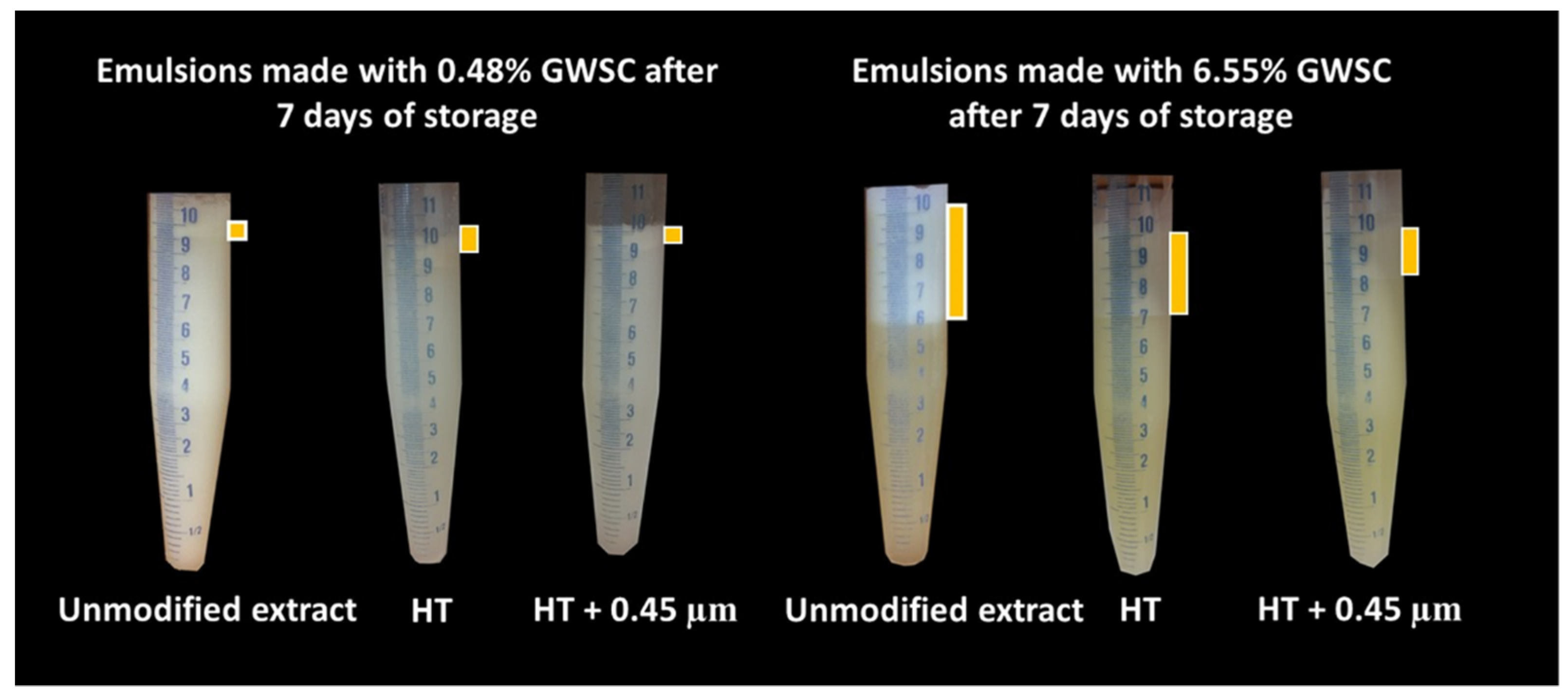
Visual phase separation of the emulsions after one week of storage can be observed in
Figure 6, showing the impact of GWSC concentration and its treatment on creaming stability. As expected an enhanced creaming due to bridging and depletion flocculation together with the greater droplet size occurring at higher GWSC was observed, as also reported in our previous research [
2]. At both, low (0.48% wt/wt) and high (6.55% wt/wt) GWSC, the filtration step in the extracts after heat treatment, reduced considerably the phase separation in the emulsions in agreement with the reduction in the extent of flocculation observed in the micrographs (
Figure 5). The underpinning reasons of these results were previously discussed in 3.1.1.
3.2. Effect of pH of the emulsification properties of garlic aqueous extracts compounds.
3.2.1. Particle size distribution
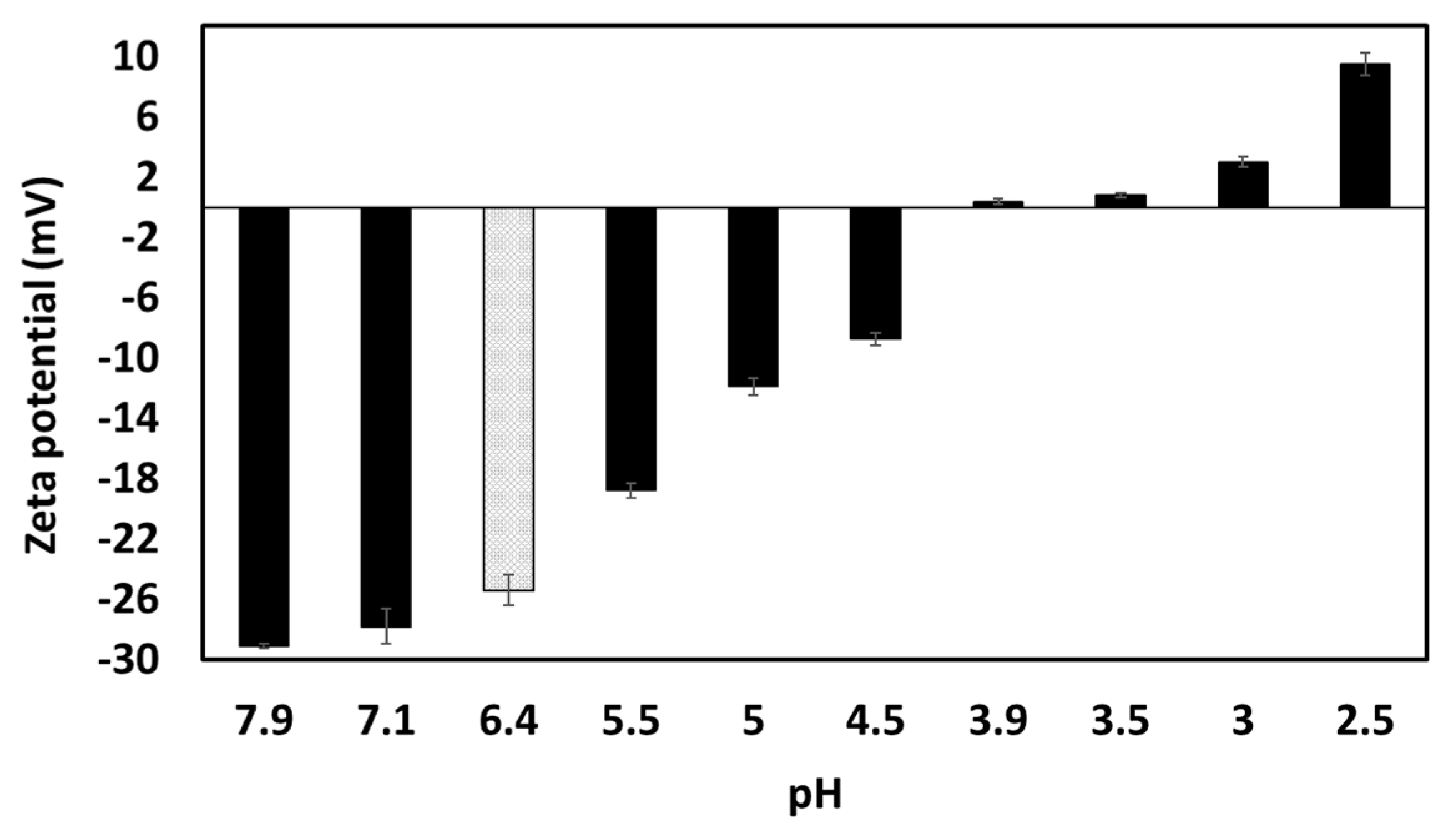
Unmodified garlic extract had a natural pH of 6.4, and neutral charge was achieved around pH 4 (
Figure 7). According to literature, the isoelectric point of garlic proteins is between 4.2-4.5 [
26,
27] and 5 [
28], while saponins remain negatively charged through the whole pH range evaluated here, being more negatively charged at more alkaline pHs [
29,
30]. The fact that the surface-active compounds found in the extract, lost negative charge while changing the pH towards acidic conditions, acquiring a positive zeta potential below pH 4.0, demonstrates that probably the proteins/peptides are dominating the overall charge of the species present in the extract; whereas saponins may lose charge towards low pH’s, the proteins start to regain positive charges below their isoelectric point.
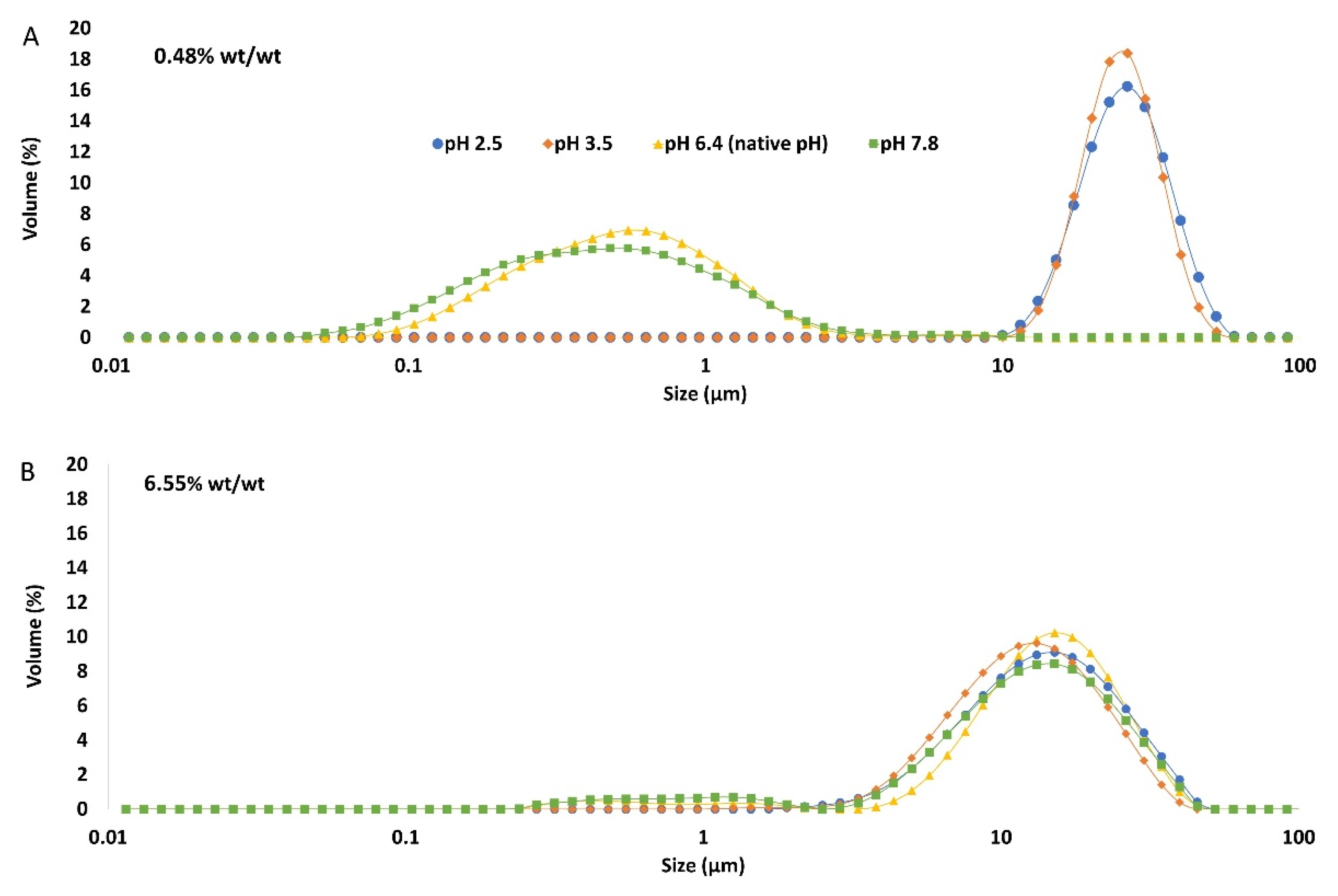
Particle size distribution of the emulsions comprising the pH-modified extracts (
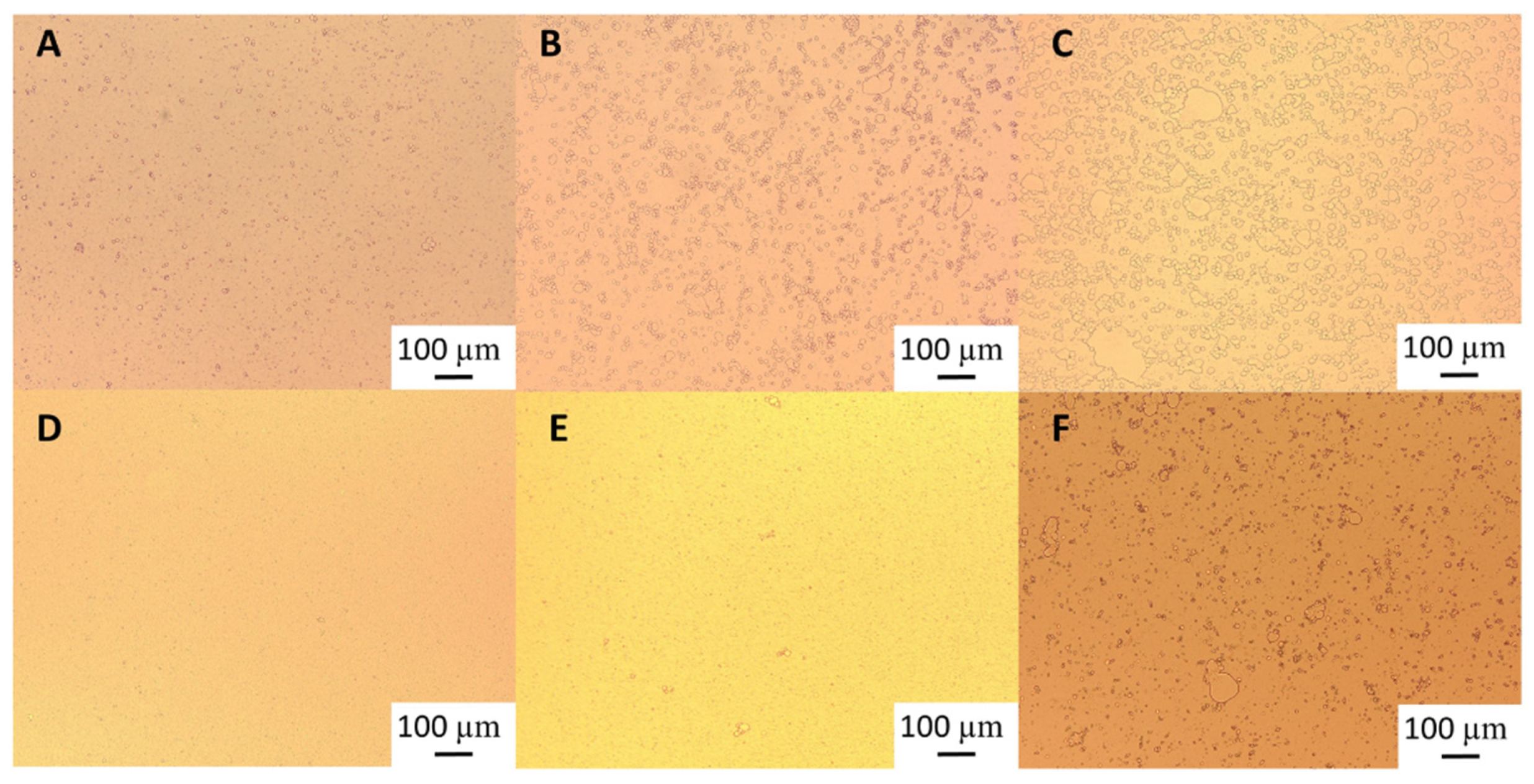
Figure 8) showed that for the lowest GWSC concentration (0.48% wt/wt), a more alkaline pH did not impact the droplet size distribution, while more acidic pH increased considerably the particle size in the range 10 to 80 µm as clearly shown in the micrographs of these emulsions (
Figure 10B). On the other hand, at the highest GWSC concentration (6.55% wt/wt), emulsions comprising the pH-treated extracts resulted in an overall particle size distribution slightly smaller than the untreated one, with the light microscopy images clearly revealing that when decreasing the pH of the extract, the extend of droplet flocculation is remarkably enhanced though the actual individual droplets appear smaller (
Figure 10F). Since no effect of alkaline pH was observed, and the effect of the two tested acid pHs was similar, it was decided to focus only on the pH modification at 2.5, and therefore only extracts with this pH were filtrated and emulsions followed over time.
The particle size distribution of emulsions made with GWSC extracts at pH 2.5, both before and after filtration (
Figure 9), showed that the removal of aggregates at the lowest concentration (0.48% wt/wt) resulted in a bimodal distribution of the droplets.
This bimodal distribution is composed by a first peak showing smaller droplet sizes— than when only changing the pH from 6.4 to 2.5, and a second peak showing bigger droplets in the 100 µm range, in agreement with the micrographs observed for this emulsion (
Figure 10 C), where also free oil was detected (non-spherical oil visualized on the left side of the mentioned figure). For the highest concentration (6.55% wt/wt), acidification to pH 2.5 resulted in smaller droplet size (d
32 = 8.91 µm) whereas the removal of the aggregates after pH adjustment to 2.5 led to greater droplet sizes (d
32 = 18.90 µm) also clearly observed in the micrographs (
Figure 10F). It is worthy to note that when measuring droplet size using static light scattering, the samples are diluted in water therefore any flocs derived from depletion flocculation are broken so mainly droplets flocculated via bridging will be detected. Larger individual droplets and clusters of bridged smaller droplets can generate very similar particle size distributions. This is clearly seen in
Figure 10E,F.
These microscopy images confirmed that changing pH (from 6.4 to 2.5) with or without the removal of large aggregates had a negative effect on the emulsification properties of small concentrations of GWSC. However, very small droplets were observed at high GWSC concentrations (6.55 % wt/wt) after only pH modification (from 6.4 to 2.5) (
Figure 10E), showing that this could improve the emulsification properties in terms of surface activity, although it came together with a stronger bridging/depletion flocculation phenomenon compared to the unmodified extract (
Figure 10D).
At pH 2.5, GWSC had a net positive charge (see
Figure 7), based on the relative balance between negatively and positively charged components (saponins and proteins respectively). Böttcher & Drisch [
18] reported a decrease in the surface tension of saponins solutions from different sources when decreasing the pH of the media, which makes us believe that the same occurred with the garlic saponins present in our GWSC, adsorbing faster to the interface, although they also reported different foaming stability depending on the saponin’s botanical origin, which shows that not only pH but also molecular structure of saponins is important. Schreiner
et al. [
23] also reported that acidifying the pH of saponin solutions from different sources was also beneficial for the capacity of the extracts to form emulsions. The improvement of the adsorption of saponins to the interface is probably allowing them to rapidly stabilize oil droplets against re-coalescence explaining the really small droplets observed in
Figure 10E. However, this means that other compounds (proteins and fructans) are likely to stay in the aqueous phase, thereby contributing to the strong droplet aggregation. This droplet aggregation is probably also related to the lower CMC of saponins at acid pH [
22].
Figure 10.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with 0.48% wt/wt GWSC concentration: A) unmodified, B) pH treated (pH 2.5), and C) pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm), and emulsions made with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC concentration: D) unmodified, E) pH treated (pH 2.5), and F) pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm).
Figure 10.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with 0.48% wt/wt GWSC concentration: A) unmodified, B) pH treated (pH 2.5), and C) pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm), and emulsions made with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC concentration: D) unmodified, E) pH treated (pH 2.5), and F) pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm).
There is no literature on the effect of pH on the emulsification properties of garlic proteins, however, based on other food proteins, we know that these tend to be more aggregated close to their p
I in many occasions leading to greater droplet sizes or even droplet flocculation due to the loss of electrostatic stabilization [
31]. Overall, the fact that these small droplets were not observed with the lowest GWSC compound concentration suggest that the emulsification properties of garlic proteins become worse when decreasing the pH of the aqueous media, and although an acidic pH may improve the emulsification properties of saponins, their concentration at the lowest GWSC content (048% wt/wt) is not high enough to stabilize properly the oil droplets, resulting in significantly bigger oil droplets. The fact that after lowering the pH and removing the big aggregates, 6.55 % wt/wt GWSC extract resulted in bigger droplet sizes than after only changing the pH suggest that saponins micelles were removed after filtration. However, to better understand the underpinning reasons, separating the different biopolymers/surfactants and testing their emulsification capacity individually would be needed.
3.2.2. Emulsion stability over time
Droplet size changes with time of the garlic-based emulsions made with pH treated extracts (pH 2.5) are shown in
Figure 11. When adjusting only pH to 2.5 for both GWSC concentrations, the emulsions did not change droplet size over time. This is also supported by light microscopy images taken after 7 days of storage (images not shown
). However, storage had a strong negative effect on the droplet size of emulsions made with the acidified GWSC extracts after the removal of larger aggregates, and coalescence occurred, more evidently at the lowest GWSC concentration. This is likely due to the decrease of biopolymers at the interface which protects emulsions against close contact between coated droplets via steric stabilization [
3].
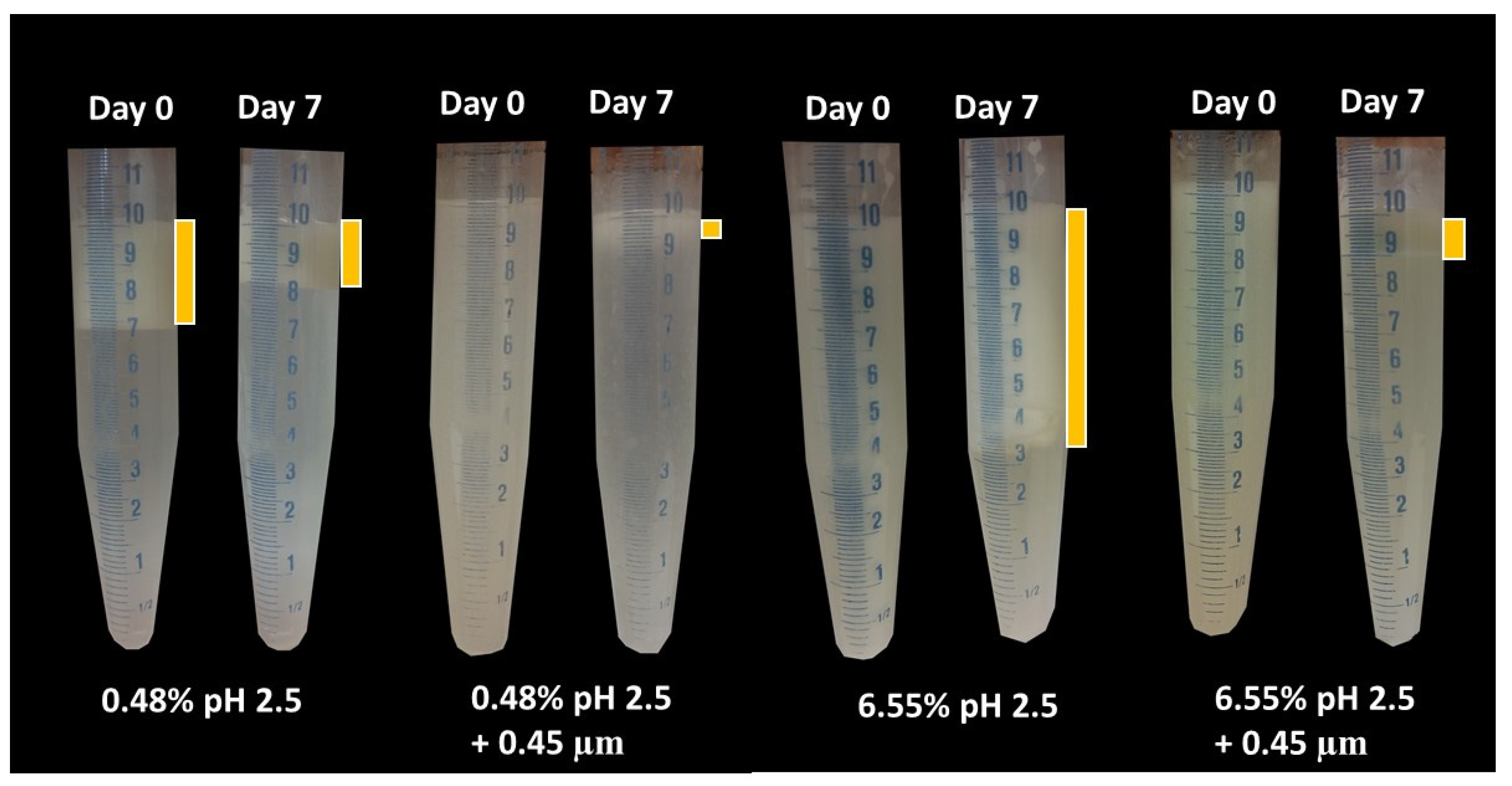
Visual phase separation of these emulsions can be observed in
Figure 12. For the lowest GWSC concentration (0.48% wt/wt), strong phase separation was observed after pH modification of the extract (from 6.4 to 2.5). Interestingly, this strong phase separation was not observed after both pH modification and removal of aggregates of the extract. This is probably affected by both the presence of free oil and the removal of the big aggregates producing droplet aggregation. For the highest GWSC concentration (6.55% wt/wt), phase separation after pH modification or after both pH modification and removal of aggregates of the extract did not occur at day 0, but was observed after 7 days of storage. At day 7, same trend as with the lower GWSC concentration was observed, probably having the same underpinning reasons.
4. Conclusions
The emulsification properties of GWSC are affected by both heat treatment and acidification. However, the effects were dependent on the overall concentration of the GWSC in the garlic extract. For 0.48% wt/wt GWSC concentration, extract treatments had a negative effect on droplet size, as it was increased. This is highly likely related to their low saponin concentration, not able to overcome the reduction of the emulsifying capacity of the other surface-active compounds (proteins and peptides) after heat treatment/acidification.
At 6.55% wt/wt GWSC concentration, both heat treatment and pH modification (from 6.4 to 2.5) had a positive effect on droplet size, as it was significantly reduced. However, strong flocculation was also observed. In the case of the emulsions made with heat-treated GWSC, flocculation was reduced after the removal of biopolymer aggregates bigger than 0.45 µm. The same cannot be said for the emulsions made with acidified GWSC, as the removal of these aggregates resulted in a large reduction of surface-active compounds, that led to bigger droplets in the final emulsion.
The underpinning reason of these results are related to the coexistence of different surface-active compounds and their interactions after GWSC modifications. To better understand their individual emulsifying properties of these novel compounds after heat treatment or pH reduction, more research needs to be done regarding the emulsifying capacity of each water-soluble compound after the fractionation of individual components.
Author Contributions
Ángela Bravo-Núñez: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing; Matt Golding: Validation, Supervision, Writing - review & editing; Manuel Gómez: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing Lara Matía-Merino: Conceptualization, Project administration, Methodology, Supervision, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing - review & editing.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Ángela Bravo-Núñez would like to acknowledge the University of Valladolid for her scholarship and for traveling funding that made possible a temporal mobility to Massey University (New Zealand).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rivlin RS. Historical perspective on the use of garlic. J Nutr. 2001 Mar 1;131(3s):951S-4S. [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Núñez Á, Golding M, McGhie TK, Gómez M, Matía-Merino L. Emulsification properties of garlic aqueous extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2019 Aug;93:111–9. [CrossRef]
- Dickinson E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003 Jan;17(1):25–39. [CrossRef]
- Garti N, Reichman D. Hydrocolloids as food emulsifiers and stabilizers. Food Microstruct. 1993;12:411–26. [CrossRef]
- McClements DJ. Food Emulsions: Principles, practice and techniques. 3rd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan V, Del Castillo L, Webber JL, Ho TTM, Ferri JK, Krasowska M; et al. The influence of pH on the interfacial behaviour of Quillaja bark saponin at the air-solution interface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;176(May 2018):412–9. [CrossRef]
- Singh H, Ye A. Interactions and functionality of milk proteins in food emulsions. In: Boland M, Singh H, editors. Milk Proteins From Expression to Food. Third edit. Academic Press; 2020. p. 467–97. [CrossRef]
- Chang C, Tu S, Ghosh S, Nickerson MT. Effect of pH on the inter-relationships between the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties for pea, soy, lentil and canola protein isolates. Food Res Int. 2015 Nov;77:360–7. [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Herrera MG, Martínez-Padilla LP, Delgado-Reyes VA, Torres-Robledo A. Effect of agave fructans on bulk and surface properties of sodium caseinate in aqueous media. Food Hydrocoll. 2016;60:199–205. [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Fernández Á, Galicia-Lagunas N, Rodríguez-Alegría ME, Olvera C, López-Munguía A. Production of functional oligosaccharides through limited acid hydrolysis of agave fructans. Food Chem. 2011 Nov;129(2):380–6. [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Andrews H, Urias-Silvas JE. Thermal properties of agave fructans (Agave tequilana Weber var. Azul). Carbohydr Polym. 2012;87(4):2671–6. [CrossRef]
- Ignot-Gutiérrez A, Ortiz-Basurto RI, García-Barradas O, Díaz-Ramos DI, Jiménez-Fernández M. Physicochemical and functional properties of native and modified agave fructans by acylation. Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Oct;245. [CrossRef]
- Mackie AR, Gunning AP, Wilde PJ, Morris VJ. Competitive displacement of β-lactoglobulin from the air/water interface by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Langmuir. 2000;16(21):8176–81. [CrossRef]
- Miller R, Fainerman VB, Makievski A V., Krägel J, Grigoriev DO, Kazakov VN; et al. Dynamics of protein and mixed protein/surfactant adsorption layers at the water/fluid interface. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;86(1):39–82. [CrossRef]
- McClements DJ. Comments on viscosity enhancement and depletion flocculation by polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2000;14(2):173–7. [CrossRef]
- Walstra P. Physical Chemestry of Foods. New York: Decker, Marcel; 2003.
- Dickinson E, Pawlowsky K. Influence of k-carrageenan on the properties of a protein-stabilized emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 1998;12:417–23. [CrossRef]
- Böttcher S, Drusch S. Interfacial properties of saponin extracts and their impact on foam characteristics. Food Biophys. 2016;11(1):91–100. [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski K. Surface activity of saponin from Quillaja bark at the air/water and oil/water interfaces. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;108:95–102. [CrossRef]
- Samal K, Das C, Mohanty K. Eco-friendly biosurfactant saponin for the solubilization of cationic and anionic dyes in aqueous system. Dyes Pigments. 2017;140:100–8. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro BD, Alviano DS, Barreto DW, Coelho MAZ. Functional properties of saponins from sisal (Agave sisalana) and juá (Ziziphus joazeiro): Critical micellar concentration, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp. 2013;436:736–43. [CrossRef]
- Mitra S, Dungan SR. Micellar properties of quillaja saponin. 1. Effects of temperature, salt, and pH on solution properties. J Agric Food Chem. 1997;45(5):1587–95. [CrossRef]
- Schreiner TB, Colucci G, Santamaria-echart A, Fernandes IP, Pinho P, Filomena M; et al. Evaluation of saponin-rich extracts as natural alternative emulsifiers : A comparative study with pure Quillaja Bark saponin. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp. 2021;623(February). [CrossRef]
- Tippel J, Lehmann M, Von Klitzing R, Drusch S. Interfacial properties of Quillaja saponins and its use for micellisation of lutein esters. Food Chem. 2016;212:35–42. [CrossRef]
- Yan S, Xu J, Liu G, Du X, Hu M, Zhang S; et al. Emulsions co-stabilized by soy protein nanoparticles and tea saponin: Physical stability, rheological properties, oxidative stability, and lipid digestion. Food Chem. 2022 Sep;387:132891. [CrossRef]
- Gao X, Chen Y, Chen Z, Xue Z, Jia Y, Guo Q; et al. Identification and antimicrobial activity evaluation of three peptides from laba garlic and the related mechanism. Food Funct. 2019;10(8):4486–96. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi M, Hassan ZM, Mostafaie A, Mehrjardi NZ, Ghazanfari T. Purified protein fraction of garlic extract modulates cellular immune response against breast transplanted tumors in BALB/c mice model. Cell J. 2013;15(1):65–74.
- Hadji I, Marzouki MN, Ferraro D, Fasano E, Majdoub H, Pani G; et al. Purification and characterization of a Cu,Zn-SOD from garlic (Allium sativum L.). Antioxidant effect on tumoral cell lines. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007;143(2):129–41. [CrossRef]
- Maier C, Zeeb B, Weiss J. Investigations into aggregate formation with oppositely charged oil-in-water emulsions at different pH values. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;117:368–75. [CrossRef]
- Ozturk B, Argin S, Ozilgen M, McClements DJ. Formation and stabilization of nanoemulsion-based vitamin e delivery systems using natural surfactants: Quillaja saponin and lecithin. J Food Eng. 2014;142:57–63. [CrossRef]
- Dickinson E. Flocculation of protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;81(1):130–40. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified (0.48% and 6.55%), heat-treated (HT), and heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts.
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified (0.48% and 6.55%), heat-treated (HT), and heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts.
Figure 2.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with 0.48% wt/wt GWSC: A) unmodified, B) heat-treated (HT), and C) heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm), and emulsions made with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC: D) unmodified, E) heat-treated (HT), and F) heat-treated+ filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm).
Figure 2.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with 0.48% wt/wt GWSC: A) unmodified, B) heat-treated (HT), and C) heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm), and emulsions made with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC: D) unmodified, E) heat-treated (HT), and F) heat-treated+ filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm).
Figure 3.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions of an emulsion stabilised with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC: A) heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm), and B) heat-treated + filtrated (HT +0.45 μm) mixed with 2% SDS solution (1:1 ratio).
Figure 3.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions of an emulsion stabilised with 6.55% wt/wt GWSC: A) heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm), and B) heat-treated + filtrated (HT +0.45 μm) mixed with 2% SDS solution (1:1 ratio).
Figure 4.
(A) and d32 (B) evolution during 7 days storage of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, heat-treated (HT), and heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts (0.48% and 6.55% wt/wt). A different statistical analysis was applied for each concentration. Samples within the concentration and treatment with the same letter(s) did not present significant differences (p > 0.05).
Figure 4.
(A) and d32 (B) evolution during 7 days storage of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, heat-treated (HT), and heat-treated + filtrated (HT + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts (0.48% and 6.55% wt/wt). A different statistical analysis was applied for each concentration. Samples within the concentration and treatment with the same letter(s) did not present significant differences (p > 0.05).
Figure 5.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions of an emulsion stabilised with: 0.48% wt/wt heat-treated (HT) GWSC A) day 0, B) day 1, and C) day 7 and 0.48% wt/wt heat-treated + filtrated (HT +0.45 μm) GWSC D) day 0, E) day 1, and F) day 7.
Figure 5.
Light microscopy of 10% oil-in-water emulsions of an emulsion stabilised with: 0.48% wt/wt heat-treated (HT) GWSC A) day 0, B) day 1, and C) day 7 and 0.48% wt/wt heat-treated + filtrated (HT +0.45 μm) GWSC D) day 0, E) day 1, and F) day 7.
Figure 6.
Visual phase separation after 7 days of storage of emulsions made with heat-treated (HT) and heat-treated + filtrated (HT+0.45 μm) GWSC (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt).
Figure 6.
Visual phase separation after 7 days of storage of emulsions made with heat-treated (HT) and heat-treated + filtrated (HT+0.45 μm) GWSC (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt).
Figure 7.
The zeta potential (ζ) of garlic aqueous extract (0.28% GWSC wt/wt concentration) at different pHs. Grey column corresponds to the ζ -potential of the unmodified aqueous extract at native pH.
Figure 7.
The zeta potential (ζ) of garlic aqueous extract (0.28% GWSC wt/wt concentration) at different pHs. Grey column corresponds to the ζ -potential of the unmodified aqueous extract at native pH.
Figure 8.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with pH treated GWSC extracts at: A) 0.48% wt/wt and B) 6.55% wt/wt.
Figure 8.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with pH treated GWSC extracts at: A) 0.48% wt/wt and B) 6.55% wt/wt.
Figure 9.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, pH treated (pH 2.5), and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts at two different concentrations.
Figure 9.
Particle size distribution of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, pH treated (pH 2.5), and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts at two different concentrations.
Figure 11.
d43 (A) and d32 (B) changes during 7 days storage of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, pH treated (pH 2.5), and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC at two different concentrations. A different statistical analysis was applied for each concentration. Samples within the concentration and treatment with the same letter(s) did not present significant differences (p > 0.05).
Figure 11.
d43 (A) and d32 (B) changes during 7 days storage of 10% oil-in-water emulsions made with unmodified, pH treated (pH 2.5), and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC at two different concentrations. A different statistical analysis was applied for each concentration. Samples within the concentration and treatment with the same letter(s) did not present significant differences (p > 0.05).
Figure 12.
Visual phase separation over time of emulsions made with pH treated (pH 2.5) and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt).
Figure 12.
Visual phase separation over time of emulsions made with pH treated (pH 2.5) and pH treated + filtrated (pH 2.5 + 0.45 μm) GWSC extracts (0.48 and 6.55% wt/wt).
Table 1.
Approximate composition of various garlic aqueous extracts*.
Table 1.
Approximate composition of various garlic aqueous extracts*.
| GWSC (%) |
Water (%) |
Proteins (%) |
Carbohydrates (%) |
Saponins (%) |
Other components (%) |
| 0.48 |
99.52 |
0.1 ± 0.01 |
0.21 ± 0.03 |
0.06 ± 0.01 |
No data |
| 6.55 |
93.45 |
1.06 |
3.45 ± 0.75 |
0.9 ± 0.12 |
1.14 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).