Submitted:
03 September 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
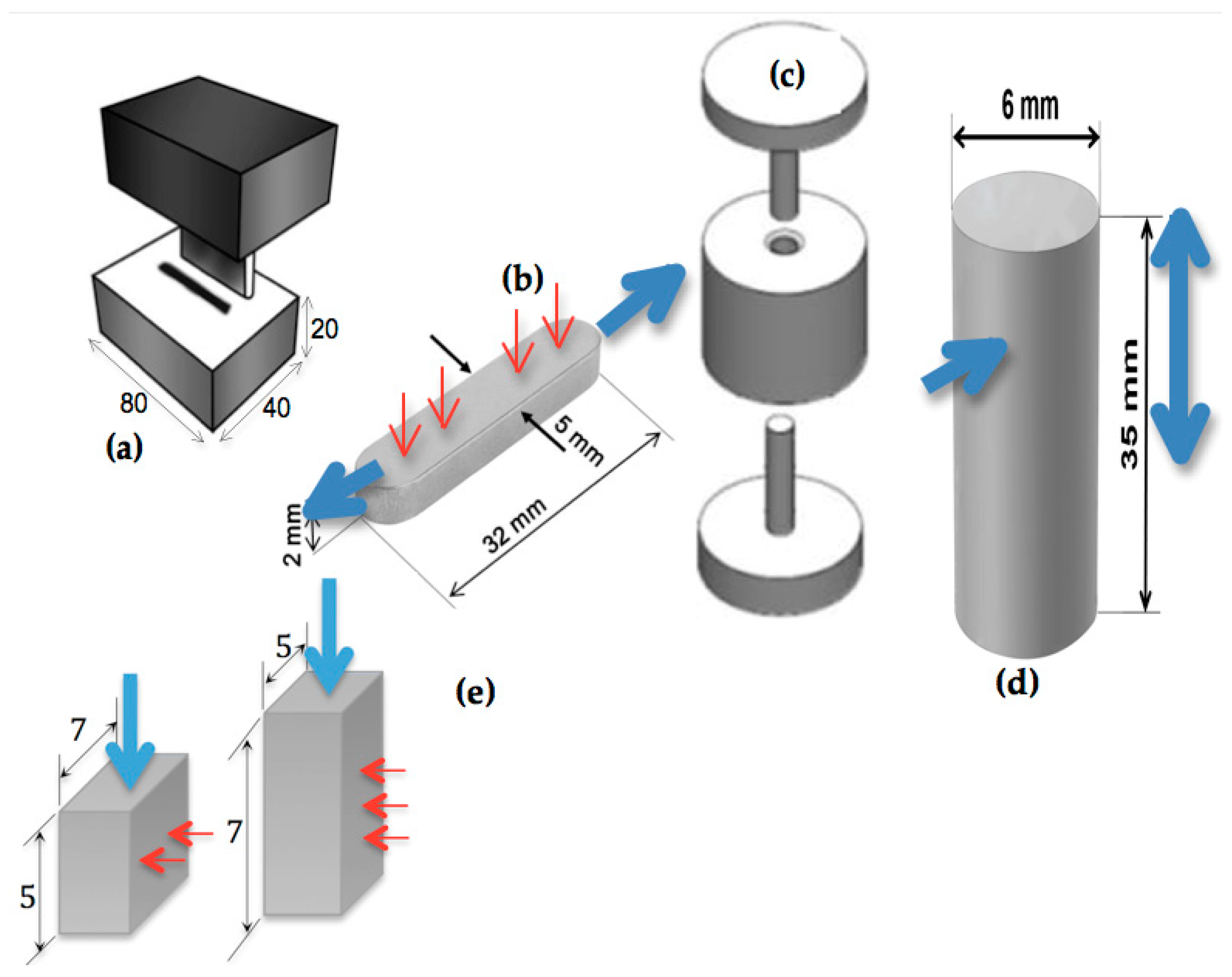
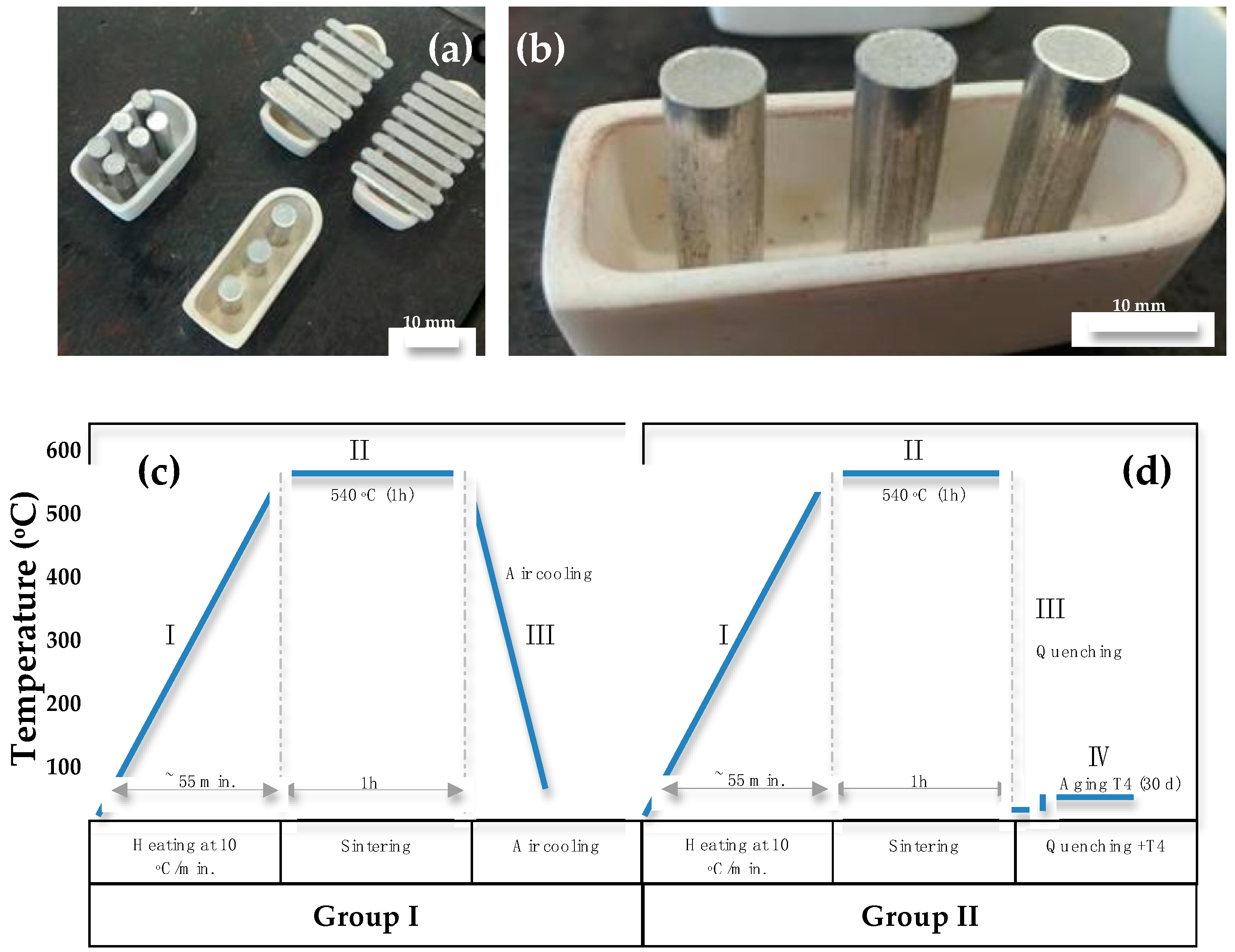
2.1. Initial Materials, Powder Production and Compaction
2.2. Densification Measurements and Heat Treatments
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
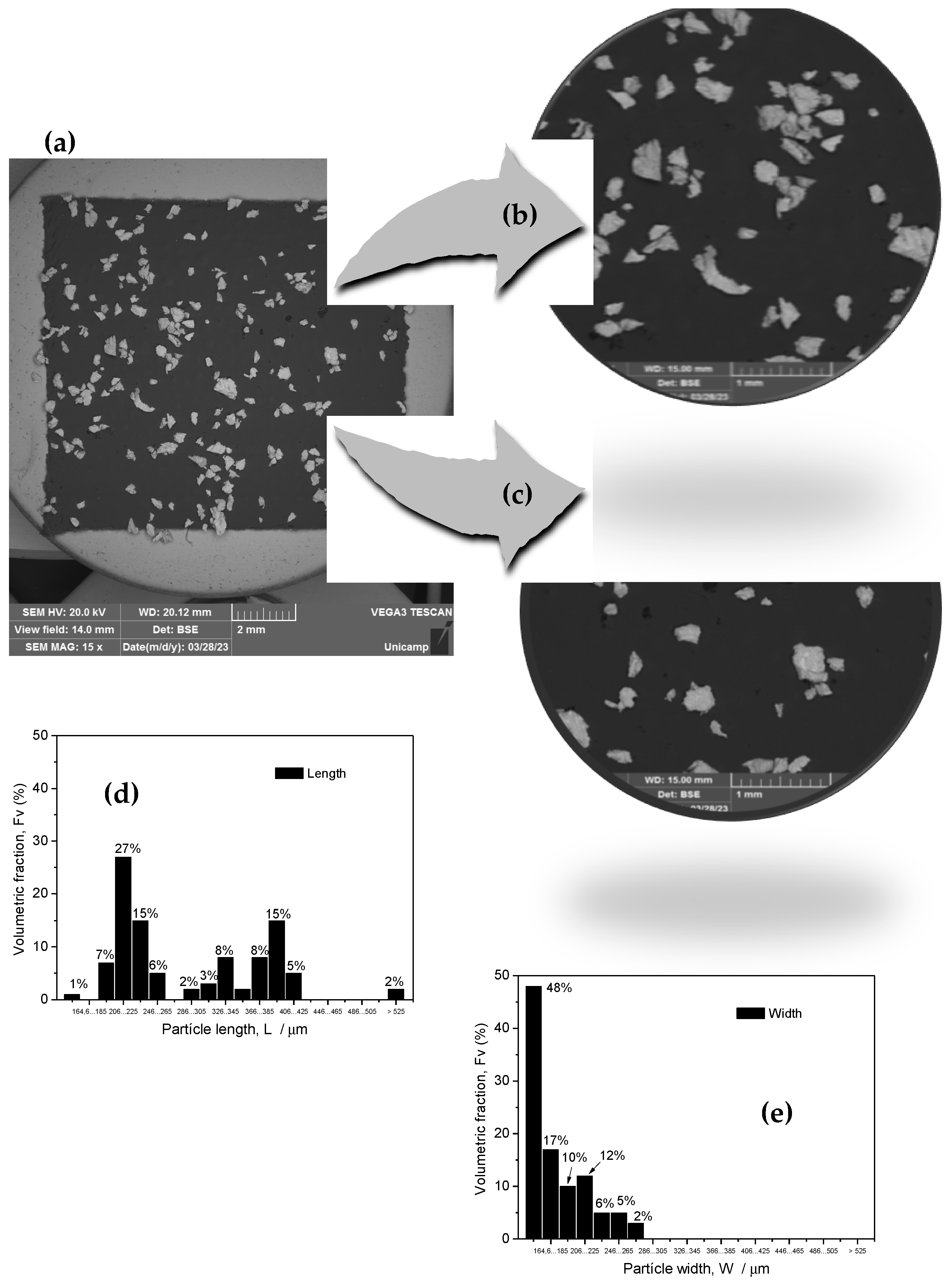
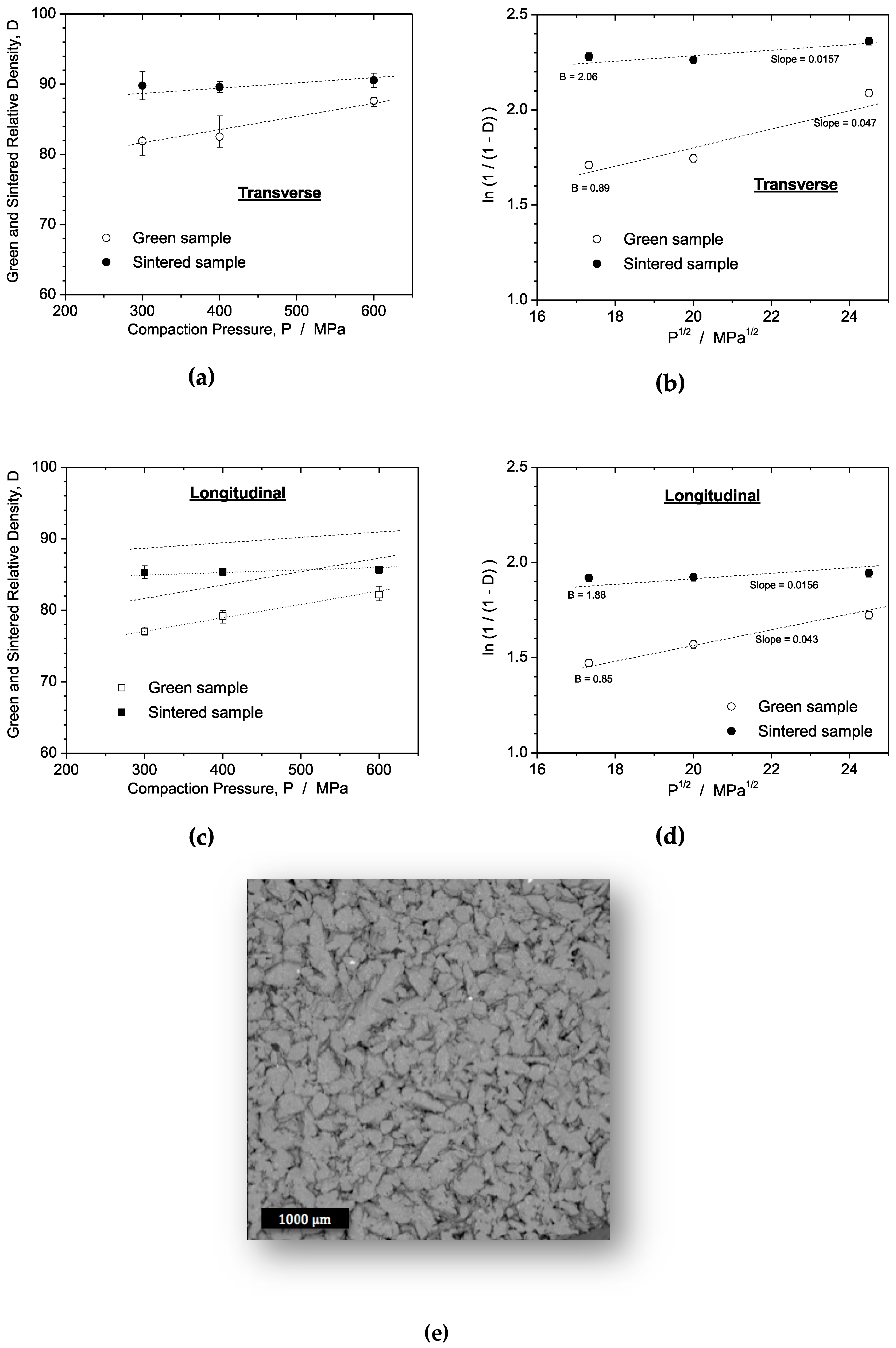
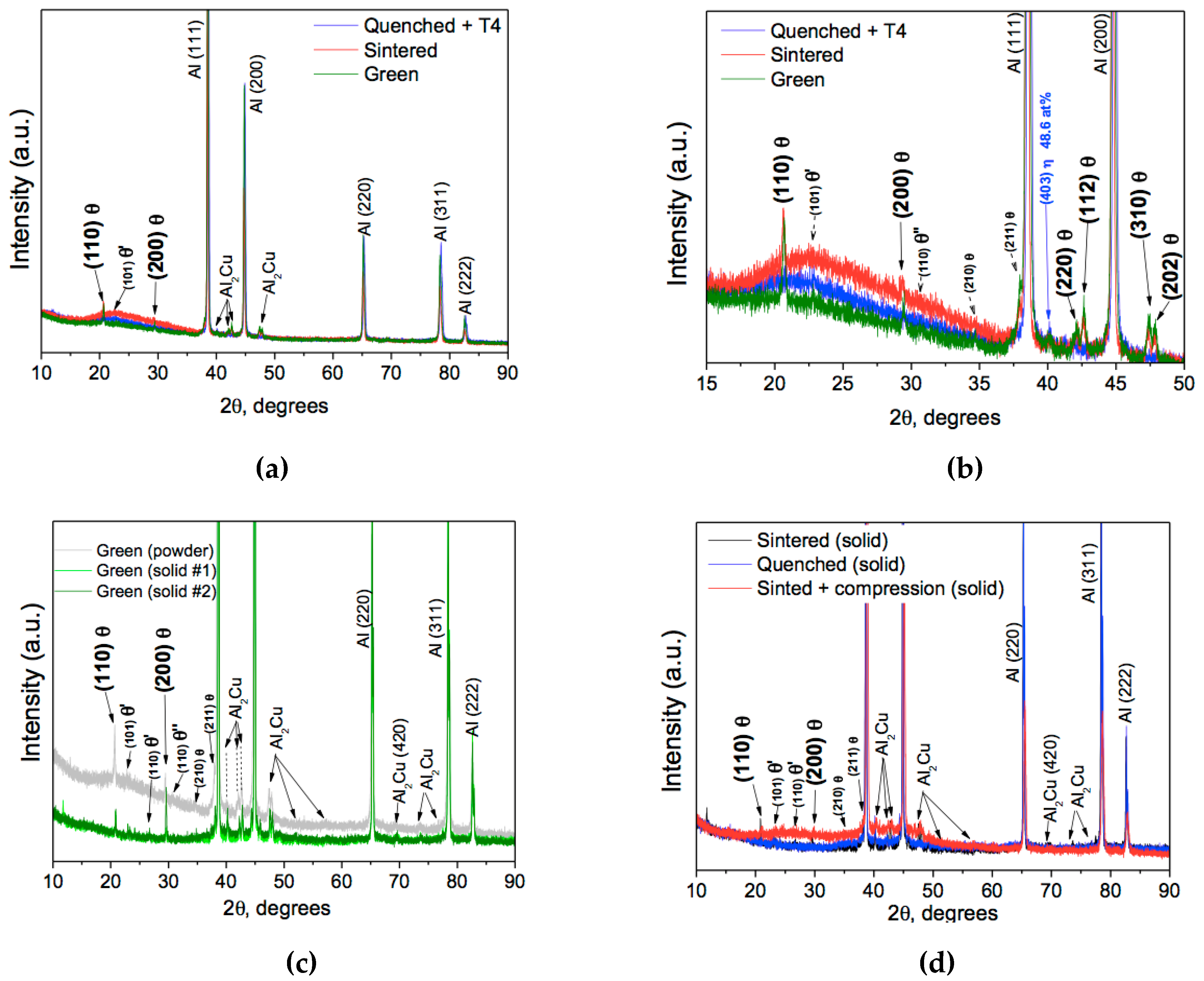
3.1. Initial Powders and Anisotropic Effect on Densification
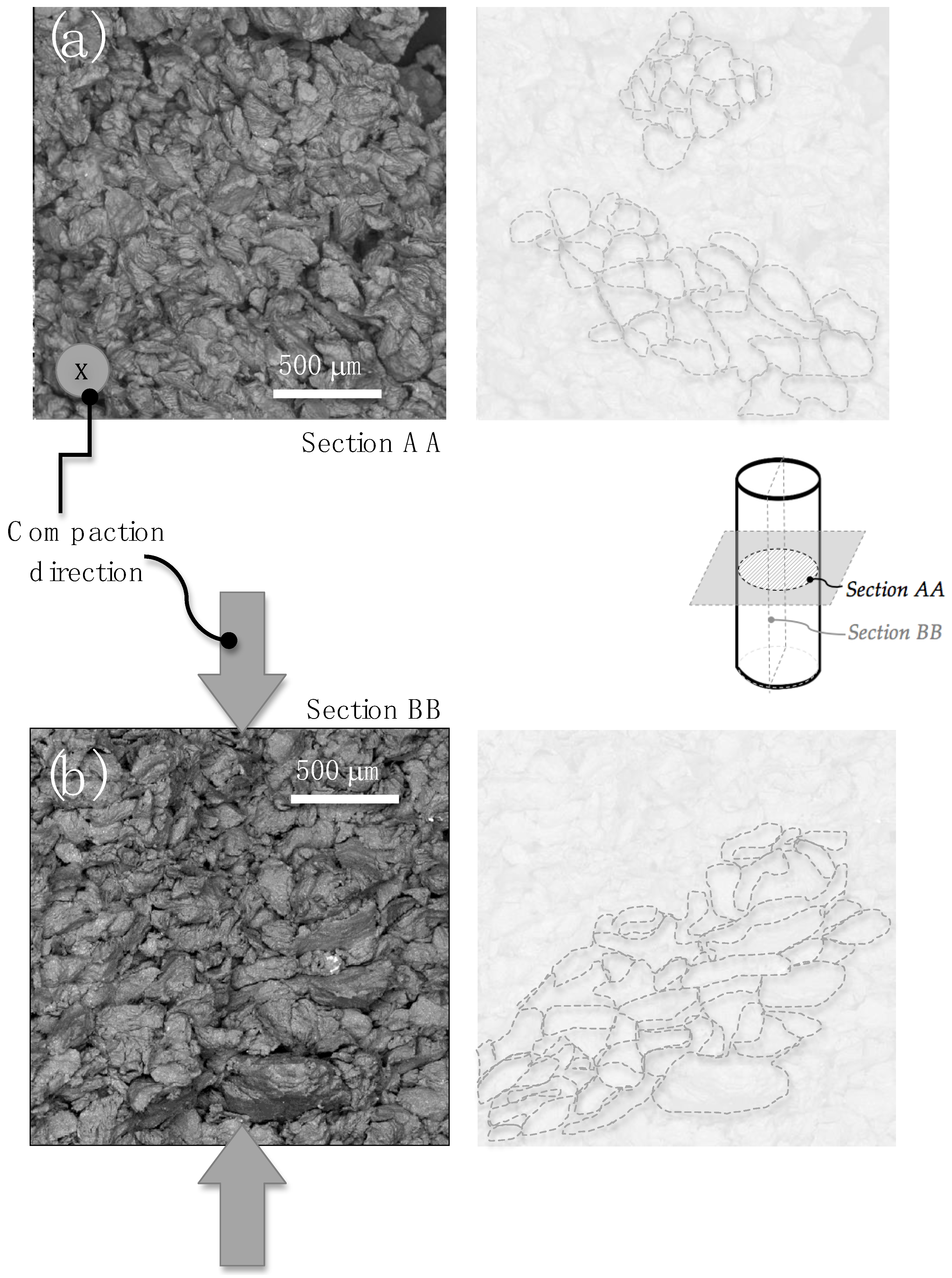
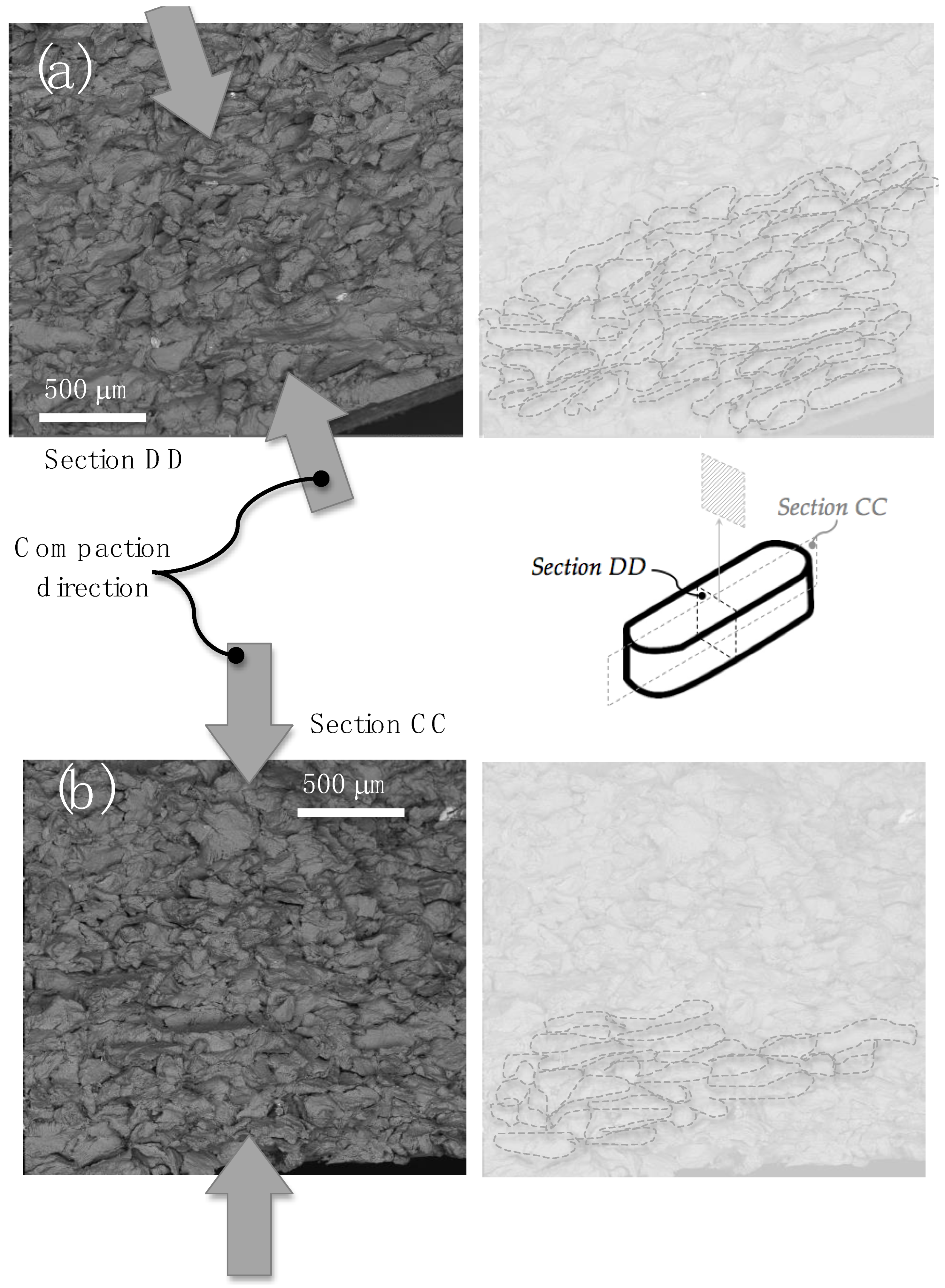
3.2. Anisotropic Effect on Morphology of Compacted Particles
3.3. Anisotropic and Mechanical Properties
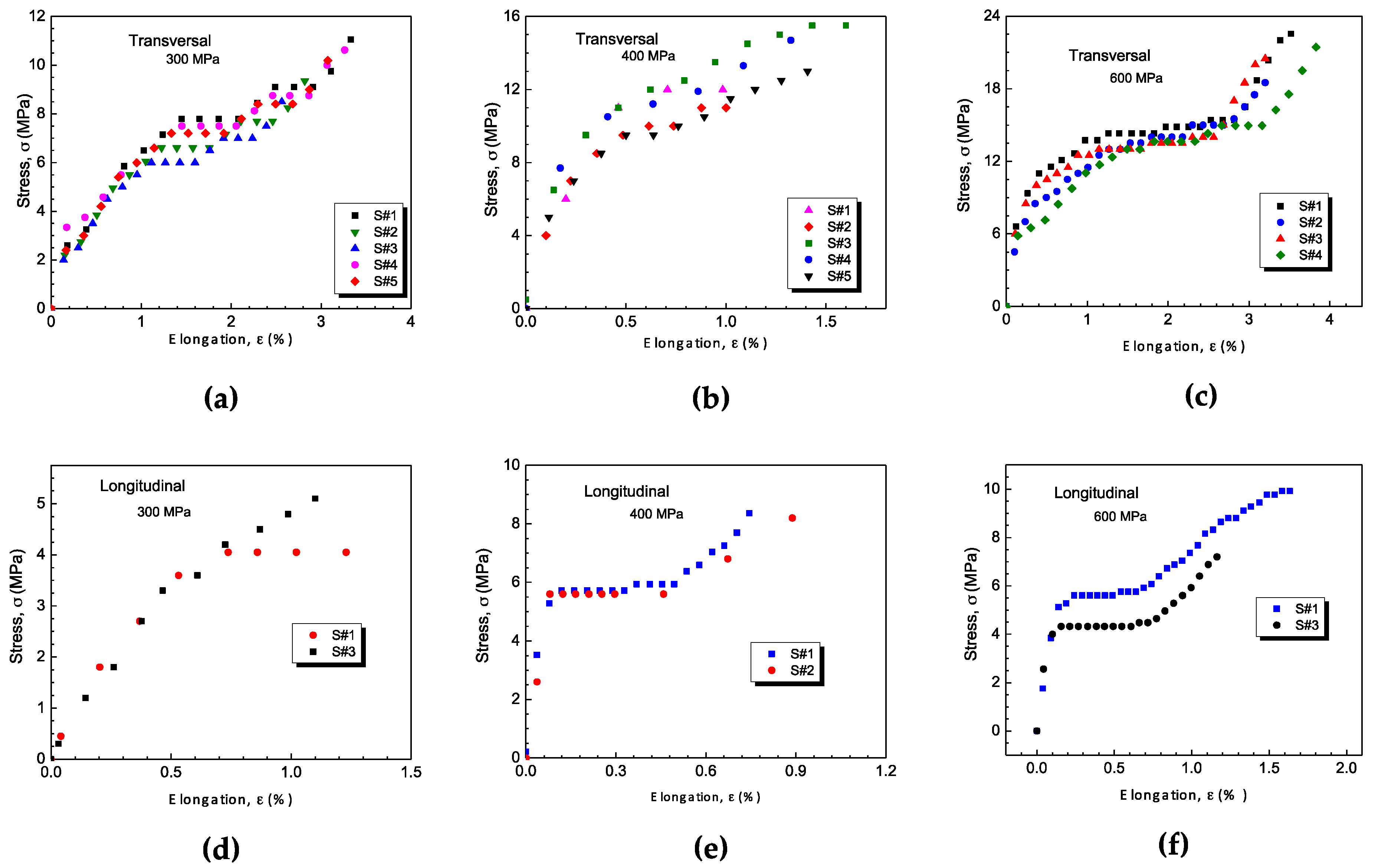
3.3.1. Tensile Strengths and Heat Treatments
3.3.2. Compressive Strengths and Heat Treatments
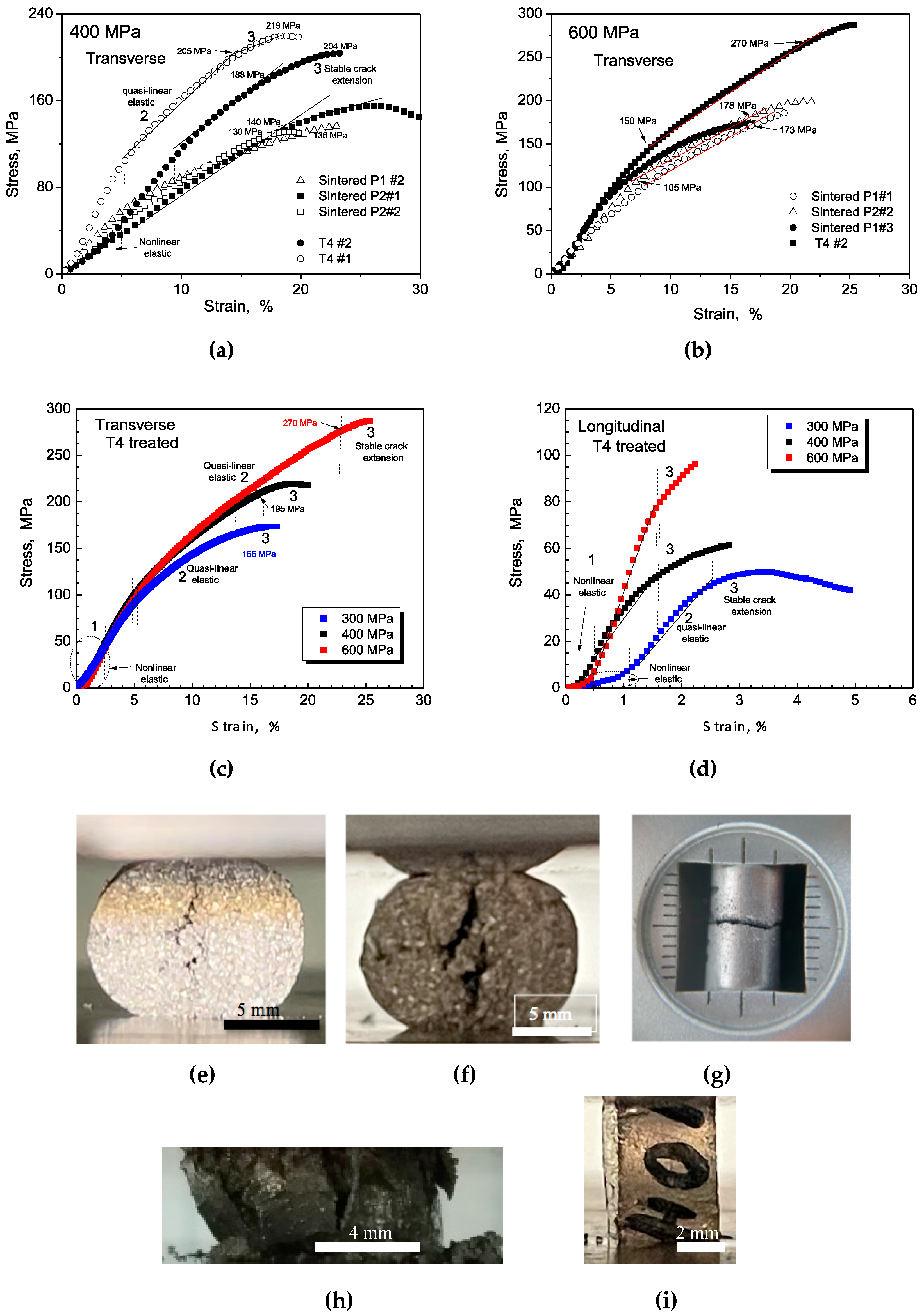
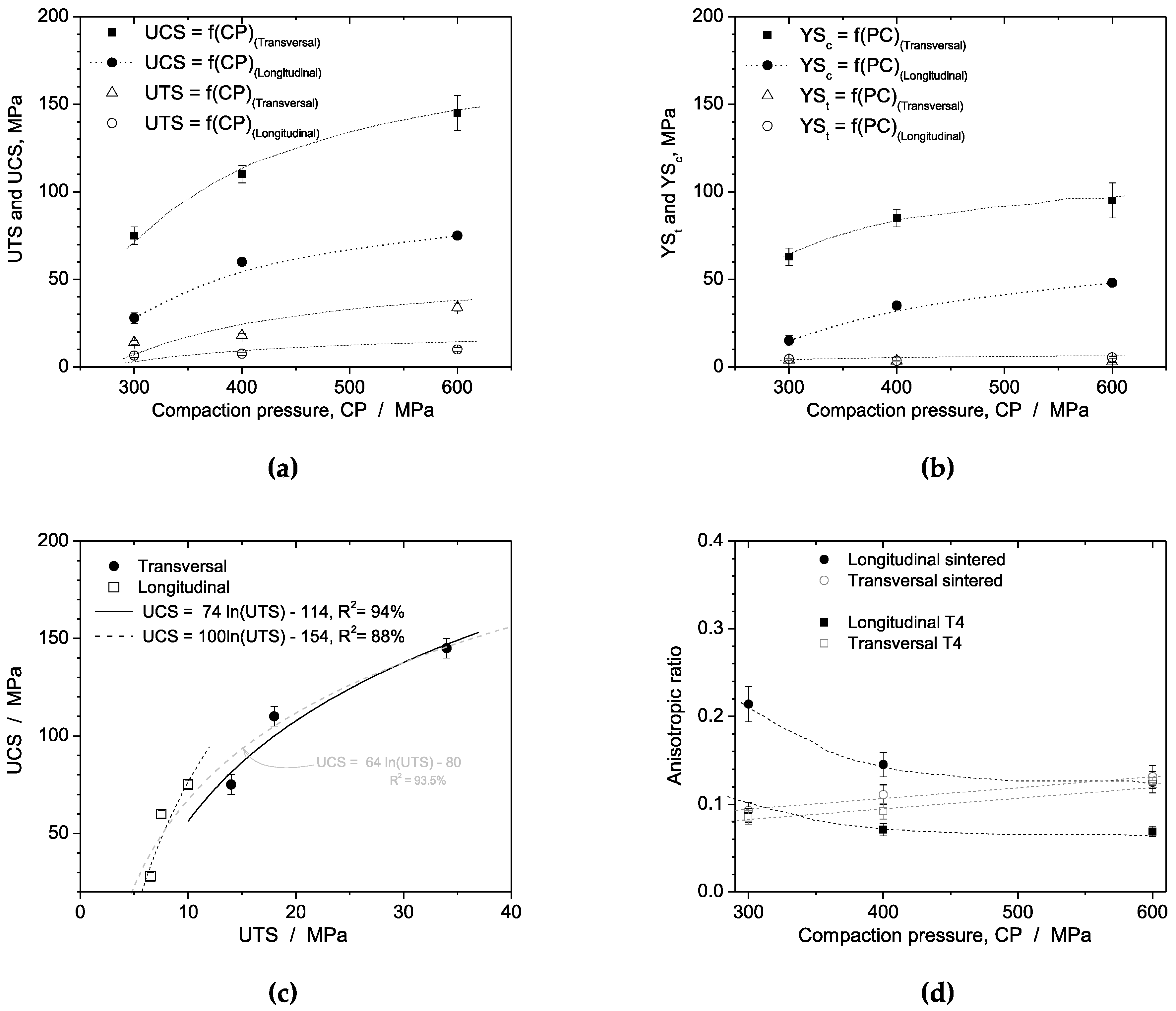
3.3.3. Mechanical Behavior Correlations
4. Conclusions
- Different compaction directions (longitudinal and transverse) result in distinctive morphologies of the compacted powders, with spheroidal-like and elongated-like shapes. These morphological differences contribute to a "bridging effect" among the powder particles, leading to different mechanical behaviors. The sintered transverse and longitudinal samples exhibit similar deformation capacity behavior based on Heckel's equation, but the sintered samples achieve higher densification (~90% compared to ~87% for longitudinal samples). Thus, compaction direction plays a significant role in densification and resulting mechanical behavior.
- T4 treated samples consistently exhibit the highest values of ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and ultimate compressive strength (UCS) compared to other experimental conditions. The UCS values are higher than the UTS values, as expected. Transverse samples generally demonstrate better mechanical performance than longitudinally compacted samples.
- Anisotropic ratios, which represent the degree of anisotropy, are determined by comparing the maximum values of UCS and UTS for each compaction direction and heat treatment condition. Transverse samples show similar anisotropic ratios with a slight increasing trend as the compaction pressure increases. In contrast, longitudinal samples exhibit non-linear decreasing trends in anisotropic ratios with increasing compaction pressure. The ratios for longitudinal samples are more dispersed compared to transverse samples. Therefore, sintered longitudinal samples are more isotropic or less anisotropic than T4 treated longitudinal samples.
- The resulting morphology of the longitudinal samples, which is more spheroidal compared to transverse samples, is associated with the compaction direction. This finding indicates that the initial morphology, compaction load, and heat treatment affect the strength anisotropy. Recycled powder particles from conventional machining processes can potentially be used, allowing for the production of components with specific mechanical requirements through careful compaction planning and treatments. These approaches offer environmental benefits by eliminating metallic fumes and reducing electrical energy consumption associated with melting processes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, M.X.; Wang, M.P. Effects of particle size, volume fraction, orientation and distribution on the high temperature compression and dynamic recrystallization behaviors of particle-contaning alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 546, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loidolt, P.; Ulz, M.H.; Khinast, J. Prediction of the anisotropic mechanical properties of compacted powders. Powder Technology 2019, 345, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akisanya, A.R.; Cocks, A.C.F.; Fleck, N.A. The yield behavior of metal powders. Int J Mech Sci 1997, 39, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vityaz, P.A.; Sheleg, V.K.; Kaptsevich, V.M.; Kusin, R.A.; Gurevich, A.A. Plasticity condition of anisotropic high-porosity powder materials. Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya 1984, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, J.E. Origin of strength anisotropy in hot-pressed silicon nitride. J Mater Sci 1980, 15, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavaliangos, A.; Bouvard, D. Numerial simulation of anisotropy in sintering due to prior compaction. Metal Powder Rerpot 2002, 57, 39–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galen, S.; Zavaliangos, A. Strength anisotropy in cold compacted ductile and brittle powders. Acta Materialia 2005, 53, 4801–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zeng, W.; Xie, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D. Effect of powder oxidation on the anisotropy in tensile mechanical properties of bulk Al samples fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater Sci Eng A 2019, 764, 138246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; He, C.; Su, A.; Chen, Z. Experimental investigation of the anisotropic mechanical behavior of phyllite under triaxial compression. Int. J Rock Mech and Mining Sci 2018, 104, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.A.P.; Couto, A.A.; Domingues Jr, N.I.; Hirschmann, A.C.O.; Zepka, S.; Moura Neto, C. Effect of artificial aging on the mechanical properties of an aerospace aluminum alloy 2024. Defect and Diffusion Forum 326- 2012, 328, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.B.; Karthik, P.; Krishna, G. Mechanical behavior of Al-Cu binary alloy system/ Cu particulates reinforced metal-metal composites. Results in Eng 2019, 4, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswanto, P.T.; Pambekti, A. Heat treatment T4 and T6 effects on mechanical properties in Al-Cu alloy after remelt with different pouring temperatures. Metalurgija 2020, 59, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos, N.D.; Velonaki, Z.; Stergiou, C.I.; Kour-koulis, S.K. Effect of ageing on precipitation kinetics, tensile and work hardening behavior of Al-Cu-Mg (2024) alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 2017, 700, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Gutiérrez, R.; Sket, F.; Maire, E.; Wilde, F.; Boller, E.; Requena, G. Effect of solution heat treatment on microstructure and damage accumulation in cast Al-Cu alloys. J Alloys Compd 2017, 697, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Cerezo, H.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Bautista-Margulis, R.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Maldonado-Bandal, E.; Estupiñan_lopez, F.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Effect of heat treatment on the electrochemical behavior of AA2055 and AA2024 alloys for aeronautical applications. Metals 2023, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satizabal, L.M.; Caurin, H.F.N.; Meyer, Y.A.; Padilha, G.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. Distinct heat treatments and powder size ratios affecting mechanical responses of Al/Si/Cu composites. J Comp Mater. 2021, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Y.A.; Bonatti, R.S.; Costa, D.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. Compaction pressure and Si contente effects on compressive strengths of Al/Si/Cu composites. Mater Sci Eng A 2020, 770, 13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, R.S.; Siqueira, R.R.; Padilha, G.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. Distinct Alp/Sip composites affecting its densification and mechanical behavior. J Alloys Compd 2018, 757, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Y.A.; Bonatti, R.S.; Costa, D.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. Compaction pressure and Si contente effects in compressive strengths of Al/Si/Cu alloy composites. Mater Sci Eng A 2020, 770, 13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogagnolo, J.B.; Robert, M.H.; Torralba, J.M. Mechanically alloyed AlN particle-reinforced Al-6061 matrix composites: Powder processing, consolidation and mechanical strength and hardness of the as-extruded materials. Mater Sci Eng A 2006, 426, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Méndez, C.; Maquieira, C.P.; Arias, J.T. The impact of ESG performance on the value of family firms: The moderating role of financial constrainsts and agency problems. Sustainab 2023, 15, 6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D.J. Fundamentals of Solidification, Trans. Tech. Public, Switzerland, 1992.
- Hamza, H.M.; Deen, K.M.; Haider, W. Microstructural examination and corrosion behavior of selective laser melted and conventionally manufactured Ti6Al4V for dental applications. Mater Sci Eng C 2020, 113, 110980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Materials Project. Available online: https://next-gen.materialsproject.org.
- Alam, S.N.; Shrivastava, P.; Panda, D.; Gunale, B.; Susmitha, K.; Pola, P. Synthesis of Al2Cu intermetallic compound by mechanical alloying. Mater Today Communications 2022, 31, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Duszczyk, J. Preparation of Al-20Si-4.5Cu alloy and its composite from elemental powders. J Mater Sci 1999, 34, 5067–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramberger, R.; Burger, A. On the application of the Heckel and Kawakita equation to powder compaction. Powder Technol 1985, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; An, Z.H.; Wang, D.; Fu, H.; Yang, X.H.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Z. MPFEM simulation of compaction densification behavior of Fe-Al composite powders with different size ratios. J Alloys Compds 2018, 741, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, R.S.; Meyer, Y.A.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Costa, D.; Osório, W.R. Morphology and size effects on densification and mechanical behavior of sintered powders from Al-Si and Al-Cu casting alloys. J Alloys Compds 2019, 786, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, D. Densification behaviour of mixtures of hard and soft powders under pressure. Powder Technol. 2000, 111, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizpour, H.R.; Simchi, A. Investigation on compressibility of Al–SiC composite powders. Powder Metall. 2008, 51, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokçe, A.; Findik, F. Mechancial and physical properties of sintered aluminum powders. J Achiev Mater Manufact Eng 2008, 30, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sweet, G.A.; Brochu, M.; Hexemer Jr, R.L.; Donaldson, I.W.; Bishop, D.P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of air atomized aluminum powder consolidated via spark plasma sintering. Mater Scie Eng A 2014, 608, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsén, P.; Haggblad, H.A.; Sommer, K. Tensile strength and fracture energy of pressed metal powder by diametral compression test. Powder Technol. 2007, 176, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, A.; Zavaliangos, A.; Cunningham, J.C. Analysis of the diametrical compression test and the applicability to plastically deforming materials. J Mater Sci 2003, 38, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguechari, N.; Boudiaf, A.; Ouali, M.O. Effect of artificial aging treatment on microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture behavior of 2017A alloy. Metall Mater Eng 2022, 28, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Martínez, J.; Estela-García Suárez, O.M.; Vega, C.A. Fabrication of a porous metal via selective phase dissolution in Al-Cu alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Microstructural evolution of Al2Cu phase and mechanical properties of the large-scale Al alloy components under different consecutive manufacturing processes. J Alloys Compds 2019, 808, 151634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
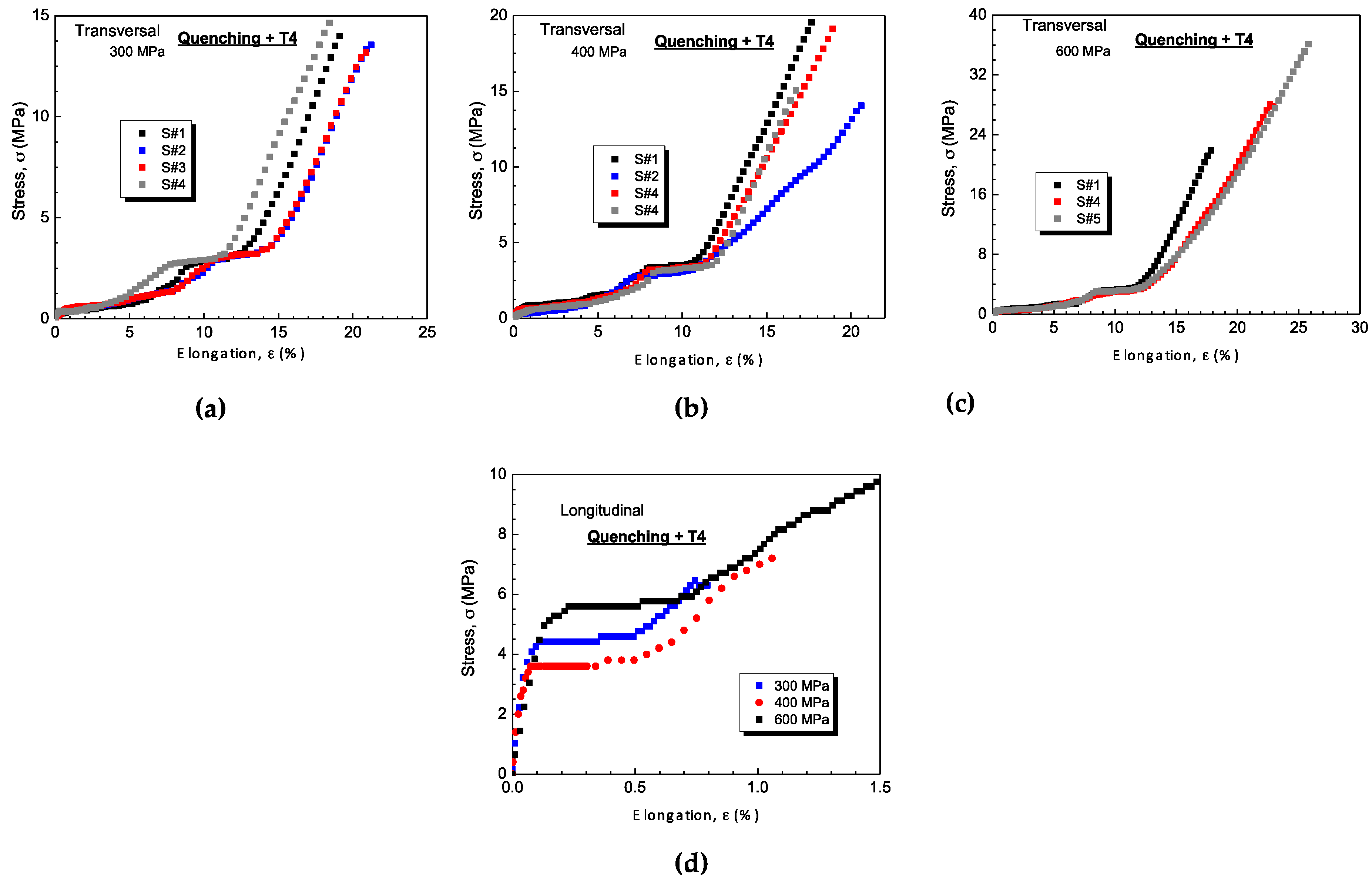
| Samples | Sintered | Quenched + T4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transversal | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | ε, % | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | ε, % |
| 300 MPa | 7 (± 1) | 11 (± 1) | 3.5 (± 0.2) | 4 (± 0.5) | 14 (± 1) | 18 (± 0.2) |
| 400 MPa | 10 (± 0.5) | 15 (± 1) | 1.5 (± 0.2) | 3.5 (± 0.5) | 18 (± 1) | 19 (± 0.2) |
| 600 MPa | 14 (± 0.5) | 23 (± 1) | 3.6 (± 0.2) | 3.0 (± 0.5) | 34 (± 2) | 23 (± 0.2) |
| Longitudinal | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | ε, % | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | ε, % |
| 300 MPa | 4.0 (± 0.5) | 6 (± 1.0) | 0.9 (± 0.2) | 4.5 (± 0.5) | 6.5 (± 0.5) | 0.8 (± 0.1) |
| 400 MPa | 4.5 (± 0.5) | 8 (± 0.5) | 0.8 (± 0.2) | 3.5 (± 0.5) | 7.5 (± 0.5) | 1.2 (± 0.1) |
| 600 MPa | 4.5 (± 0.5) | 10 (± 0.5) | 1.3 (± 0.3) | 4.5 (± 0.5) | 10 (± 0.5) | 1.5 (± 0.2) |
| Samples | Sintered | Quenched + T4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSVERSAL | YS, MPa | UCS, MPa | YS, MPa | UCS, MPa | F, N | DC* |
| 300 MPa | 65 (± 5) | 118 (± 6) | 92 (± 5) | 165(± 10) | --- | --- |
| 400 MPa | 80 (± 10) | 135 (± 10) | 118 (± 5) | 195 (± 10) | --- | --- |
| 600 MPa | 105 (± 8) | 175 (± 8) | 150(± 10) | 270 (± 10) | --- | --- |
| LONGITUDINAL | YS, MPa | UCS, MPa | YS, MPa | UCS, MPa | F, N | DC* |
| 300 MPa | 15 (± 2) | 28 (± 5) | 63 (± 5) | 75 (± 6) | 0.9 (± 0.2) | 8.6 (± 3) |
| 400 MPa | 35 (± 2) | 55 (± 5) | 85 (± 5) | 110 (± 8) | 1.2 (± 0.2) | 11.6 (± 3) |
| 600 MPa | 48 (± 4) | 80 (± 8) | 95 (± 10) | 145 (± 10) | 2.3 (± 0.1) | 23.2 (± 0.8) |
| Sintered | Longitudinal | Transversal |
|---|---|---|
| 300 MPa | 0.214 | 0.093 |
| 400 MPa | 0.145 | 0.111 |
| 600 MPa | 0.125 | 0.131 |
| Quenched + T4 | Longitudinal | Transversal |
| 300 MPa | 0.087 | 0.085 |
| 400 MPa | 0.071 | 0.092 |
| 600 MPa | 0.069 | 0.126 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





