1. Introduction
Carbon (C) cycle in inland waters, including its dissolved and particulate concentrations and carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions are at the forefront of biogeochemical studies, especially in the regions most sensitive to on-going climate changes such as boreal and subarctic zones [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7] or the tropical/equatorial belt [
11,
12,
13,
14]. In contrast to these numerous works, the C storage, transport and emission in central continental, mountain and arid regions remain strongly understudied, either due to limited access and logistics, or still underestimated potential role of these remote territories in C cycling in inland waters. This is especially true for Central Asian mountain system encompassing Tibet, Himalaya, Pamir, Altai and Sayan regions. Exceptions are thorough works on DOC, DIC and POC fluxes in Himalayan Rivers [
15,
16,
17], and C concentrations and fluxes in thermokarst lakes of Tibetan Plateau [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. However, the northern part of the Central Asian Mountain System remains virtually unexplored from the view point of hydrochemistry and carbon balance in its rivers and lakes.
The Altai-Sayany Mountain system is a specific inland region of the northern part of Central Asia which covers the territory of four countries: Russia, Mongolia, China and Kazakhstan [
24]. In Russia, it is located within the Tyva Republic (Russian Federation). It is characterized by a high degree of continentally, aridity, as well as the highest level of endemicity under a huge variety of ecosystems and landscapes, many of which are vulnerable to climatic changes [
25]. The water bodies such as rivers and lakes are of particular importance for the sustainability, ecosystem services and conservation of the biodiversity of this arid region [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. Particulate interest of Altai-Sayan region is that the currently occurring climate changes in this territory contradict existing world models and forecasts. In particular, in the Tyva Republic, our group reported the first ever observed natural phenomenon, the “greening” or afforestation of steppes and bare sands [
32,
33]. This finding contrasts a number of prediction models which stipulated further progressive drying of the arid Altai- and Sayan regions (ASR), such as Khakassia, Tyva and Mongolia [
34,
35]. The other existing assessments of future climates in arid regions of Eurasia also predict an increase in aridity and even propose a propagation of desertification in the steppe regions [
36,
37,
38]. For instance, in the Tyva Republic, the areal extension of steppe ecosystems, including these of dry steppes, is predicted to increase by 20–65%, and the areas of semi-deserts the projected increase achieve several hundred percent compared to their current extent [
24].
In contrast to above-mentioned predictions, some other studies suggest an increase in the climatic instability, such as drastic transformation of the main atmospheric circulation in the South Siberia regions and at the border with Central Asia, which could lead to a decrease of the role of atmospheric transport from Atlantic regions hence resulting to blocking of anticyclones, and an increase in meridional atmospheric transport [
39,
40]. This process, in turn, causes many catastrophic weather events, such as dramatic appearance of rainstorms, hurricanes, water floods, altogether leading to progressive humidification of arid, previously dry, regions [
41]. Such catastrophic weather events have been observed over last few years in Khakassia, Tuva and Mongolia [
42,
43,
44].
It is clear that the ongoing climate changes can drastically impact the current hydrochemical, biogeochemical and hydrological status of inland rivers and lakes of the region. For example, it is known that lakes at high altitudes and cold climate are particularly sensitive to global change [
45,
46] and modifications in carbon biogeochemistry, including the status of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and C emission fluxes, may strongly alter the role of these lakes in the global C cycle [
47,
48,
49]. Among the consequences of progressive humification of Central Asian arid regions under on-going climate change, the treeline shift (greening of upland and advancement of treeline) can strongly affect the biogeochemical functioning of lakes, given that 15% of all lakes globally are located at elevations above 500 m above sea level [
50]. Further, existing paleo-reconstructions suggest that lake productivity [
51] and biogeochemistry [
52] are sensitive to changes in DOM input linked to treeline position. Therefore, thorough assessment of today’s status of C biogeochemical cycle (concentration, emission from the water surfaces) is necessary to be able to judge the possible future changes in Central Asian regions induced by climate instability.
Over past decade, a few studies in this area addressed hydrochemical [
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58], hydrological and hydrographic [
59,
60,
61] status of the water bodies, including balneological aspect of mineral springs [
62,
63,
64,
65]. There are also some studies of water bodies hydrochemistry conducted in adjacent regions of Mongolia [
66]. However, the status of aquatic C and CO
2 emissions from the water surfaces of Altai-Sayan region remain unknown. Towards filling this gap in the knowledge, here we assessed the concentration of dissolved organic and inorganics carbon and C emission in lakes and rivers of the Tyva region, via selecting large and small waterbodies, affected by permafrost in a different degree. Unprecedented physio-geographical and climatic transect of inland water bodies which we implemented in this study extends from the northwest (the highlands of the Western Sayan) to the southeast (the semi-deserts of the Ubsunur Depression on the border with Mongolia). This transect comprises large variety of natural ecosystems and landscapes of the region: from glacial-nival high mountain belts to foothill taiga forests, intermountain basins with mixed herbs and steppe ecosystems, and dry semi-deserts. As a working hypothesis, we anticipated strong environmental control on C biogeochemical parameters of lakes and rivers, including climate, altitude, permafrost extent and size of the watershed as main ‘external’ drivers of C concentration and emission. We also assessed the link between carbon parameters of the water bodies and possible ‘internal’ biogeochemical drivers (hydrochemical parameters) such as pH, mineralization, quality of dissolved organic matter and microbial abundance. We tested these controls across four main hydrological seasons (spring, summer, autumn and winter) in 5 lakes and 15 rivers of different size and landscape context.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water bodies of the Tyva Republic
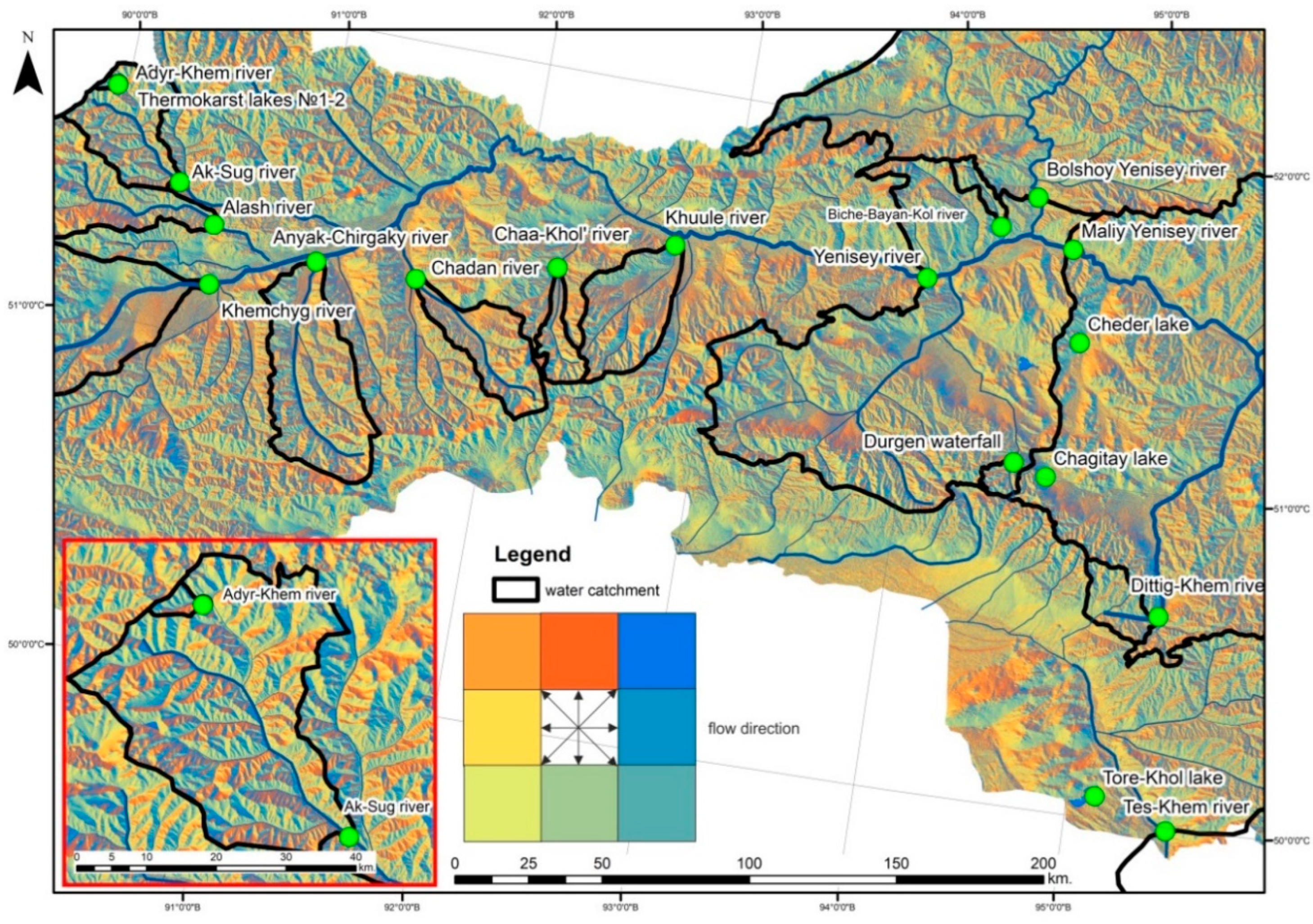
We visited 20 water bodies during four hydrological seasons (autumn 2021 - summer 2022) as shown in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. Main physio-geographical parameters of rivers and lakes are listed in
Table 1 and
Table 2 and described in details in the Appendix. The Republic of Tyva is located in the Sayan-Altai mountain region, between 50-53 °N and 88-99 °E; the elevations range from 2000 to 500 m, creating a large variety of landscapes, from high-altitude belts to basins with steppes and semi-deserts. The climate of the region is continental, with cold long winters and hot summers; mean monthly temperatures range from −41 in January to +35 °C in July; the precipitation is low (115 to 350 mm y
−1), and about 70 % of it falls during the warm season of the year [
67].
During the period of our study, the temperatures ranged from −28 °C to 21 °C, whereas the precipitation was equal to 322 and 144 m during 2021 and 2022, respectively. (
http://www.pogodaiklimat.ru/history/36096_2.htm). The water objects sampled in this work include numerous water bodies, mainly belonging to the Yenisei River basin, whereas only a small part belonged to the closed basin of the Ubsunur basin.
The largest river flowing through the region is the Yenisei River, formed at the confluence of the Maly and Bolshoy Yenisei rivers. Most of the rivers of the Yenisei basin are of mountain origin, that is, they mainly have snow and groundwater feeding. The studied lakes are mostly drainless, mainly fed by groundwater, with the exception of Lake Chagytai [
68,
69]. We collected the water samples during four hydrological seasons, in autumn (24.10.21–27.10.21), winter (07.03.22–11.03.22), spring (18.05.22–22.05.22) and summer (19.08.22–23.08.22). Altogether, we sampled 20 water bodies (15 rivers and five lakes). These were selected according to the criteria of proximity to the weather stations throughout the climate/landscape macro-transect of Tyva.
Figure 1.
Location of research objects within the Sayan-Altai Mountain system (Central Asia).
Figure 1.
Location of research objects within the Sayan-Altai Mountain system (Central Asia).
Figure 2.
River catchments of the study region. The direction of water flow is shown by different colors.
Figure 2.
River catchments of the study region. The direction of water flow is shown by different colors.
Table 1.
General information about the rivers sampled in this work.
Table 1.
General information about the rivers sampled in this work.
|
Name
|
Flow velocity m/s
|
Depth (m)
|
Length (km)
|
Average discharge, m3/c |
Catchment area (km2)
|
Height at the sampling point, m |
Average catchment height (m) |
Slope of the riverbed (m/km) |
Location
|
| Yenisei |
0.25-2.6 |
2-3 |
3487 |
1020 |
102806 |
650 |
1196 |
16.8 |
Ulug-Khem basin |
| Big Yenisei |
1.4-2.4 |
1.5-4 |
605 |
594 |
57766 |
630 |
1448 |
3.1 |
Todzhin-skaya basin; Kyzyl basin |
| Small Yenisei |
1.8-2.3 |
1-2.4 |
563 |
411 |
36395 |
636 |
1555 |
2.8 |
Sangilen Highlands; Ulugh-Khem basin |
| Tes-Hem |
1.1-2.1 |
1-2.1 |
757 |
55.6 |
18430 |
1067 |
1842 |
7.9 |
East
Tannu-Ola |
| Hemchik |
- |
0.75-2 |
320 |
102 |
3268 |
850 |
1923 |
14.4 |
Shapshal ridge; Khemchik basin |
| Alash |
0.43 |
0.30-2 |
172 |
|
4741 |
920 |
2063 |
9.2 |
Alash Plateau |
| Ak-Sug |
0.31 |
0.25-1 |
160 |
14 |
997.4 |
1150 |
1966 |
26.8 |
Alash Plateau |
| Chadan |
- |
- |
98 |
- |
881.5 |
800 |
1567 |
28.8 |
West
Tannu-Ola |
| Durgen |
0.54 |
0.66-1 |
93 |
- |
121.7 |
1200 |
1751 |
42.3 |
The northern slope of East Tannu-Ola |
| Chaa-Hol |
0.28 |
0.5-2 |
90 |
- |
320.3 |
540 |
1694 |
43.1 |
The northern slope of the western
Tannu-Ola |
| Huule (Torgalyg) |
- |
0.4-2 |
53 |
- |
1090 |
535 |
1273 |
30.9 |
The northern slope of the Eastern Tannu-Ola; The Central Tuva basin |
| Anyyak-Chyrgaki |
0.173 |
0.2-2 |
52 |
- |
1859 |
800 |
1519 |
13.9 |
West Tannu-Ola |
| Dyttyg-Hem |
- |
0.2-0.8 |
34 |
- |
426.9 |
1250 |
1710 |
36.3 |
Southern slope of East
Tannu-Ola |
| Biche-Bayan-Kol |
0.34 |
0.3-0.8 |
32 |
- |
15.3 |
750 |
1222 |
26.0 |
Uyuk Ridge |
| Adyr-khem |
0.17 |
0.5-2 |
8.25 |
- |
8.25 |
1850 |
2076 |
66.2 |
Alash Plateau |
Table 2.
General information about the studied lakes [
15].
Table 2.
General information about the studied lakes [
15].
| Name |
Depth (m) |
Water mirror area, km2
|
Type |
Height (m) |
Location |
| Tore-Khol |
6-8
(max. 40 м) |
68.8 |
Freshwater |
1148 |
Ubsunur basin |
| Chagytai |
17 |
28.6 |
Freshwater lake |
1005 |
The foot of the northern slope of the Tannu-Ola ridge |
| Cheddar |
1.5-2 |
4.3 |
Salt Lake |
706 |
South of the Tuva basin,
a drainless depression |
| Thermokarst.1 |
4 |
0.3 |
Thermokarst Lake |
1850 |
Alash Plateau |
| Thermokarst.2 |
5 |
0.1 |
Thermokarst Lake |
1850 |
Alash Plateau |
2.2. Analytical methods
The list of measured parameters included temperature, pH, electrical conductivity and concentration of dissolved gases (CO
2 and O
2), dissolved organic (DOC) and inorganic carbon (DIC), isotopic composition of water, optical properties of organic matter, as well as CO
2 emission flux from the water surface. Dissolved oxygen, pH, electrical conductivity and temperature were measured in situ using an EXO2 multiparameter probe and a WTW Multi 3320 multimeter. The measurement of pCO
2 in water was carried out in situ using the GM70 data logger, Vaisala®. The pCO
2 was measured in-situ by an infrared gas analyzer (IRGA, GMT222, Vaisala, Finland) [
70]. The sensor was enclosed in a semi-permeable membrane and placed directly into the surface water (30-50 cm depth), where it was allowed to equilibrate for approximately 30 minutes. The sensors were calibrated against standard gas mixtures (0, 800, 3 000, 8 000 ppm) before and after the sampling. Following calibration, results were corrected using water temperature and barometric pressure.
Carbon dioxide emissions from the water surface were measured by direct floating chamber method using SensAir sensors. We used freely drifting chamber (30 cm diameter, covered with aluminum tape). The CO
2 accumulation rate inside the chamber was recorded continuously at 5 sec interval for 5-10 minutes and used to compute (by linear regression if R
2 > 0.75) CO
2 flux and k
CO2 following Kuhn et al., 2018 [
71]. For all calculations, the CO
2 air-water equilibrium was calculated assuming air concentration of 400 ppm. Further details of pCO
2 and fCO
2 measurements in rivers and lakes of adjacent regions are provided elsewhere [
1,
72,
73,
74,
75].
River and lake water was collected from the surface (depth 0.5 m) into a pre-cleaned polypropylene container with a capacity of 1 liter and immediately filtered through nitrate-cellulose filters (<0.45 microns Sartorius Minisart High Flow). DOC and DIC were measured in the BIO-GEO-CLIM Laboratory (TSU), using a total organic carbon analyzer of the TOC-LCSN series, Shimadzu, with an uncertainty of 2%. As indicator of the quality of DOM, we measured UV absorbance using spectrophotometry (Agilent Cary 300 spectrophotometer).
Total microbial cell concentration was measured after sample fixation in glutaraldehyde (in the field, immediately after collection), by a flow cytometry (Guava® EasyCyteTM systems, Merck). Cells were stained using 1 µL of 10 times diluted SYBR GREEN solution (10000×, Merck), added to 250 µL of each sample before analysis. Particles were identified as cells based on green fluorescence and forward scatter.
To build the maps, the DAICHI satellite (ALOS) survey with a resolution of 30 m
2 was used [
www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en] together with the 3D Analysis module in the ArcGIS environment. To delineate the catchments of the studied rivers, the Flow Direction module was used in the ArcGIS environment, which calculates flow lines based on data on the heights of nearby points.
3. Results
3.1. Major hydrochemical parameters
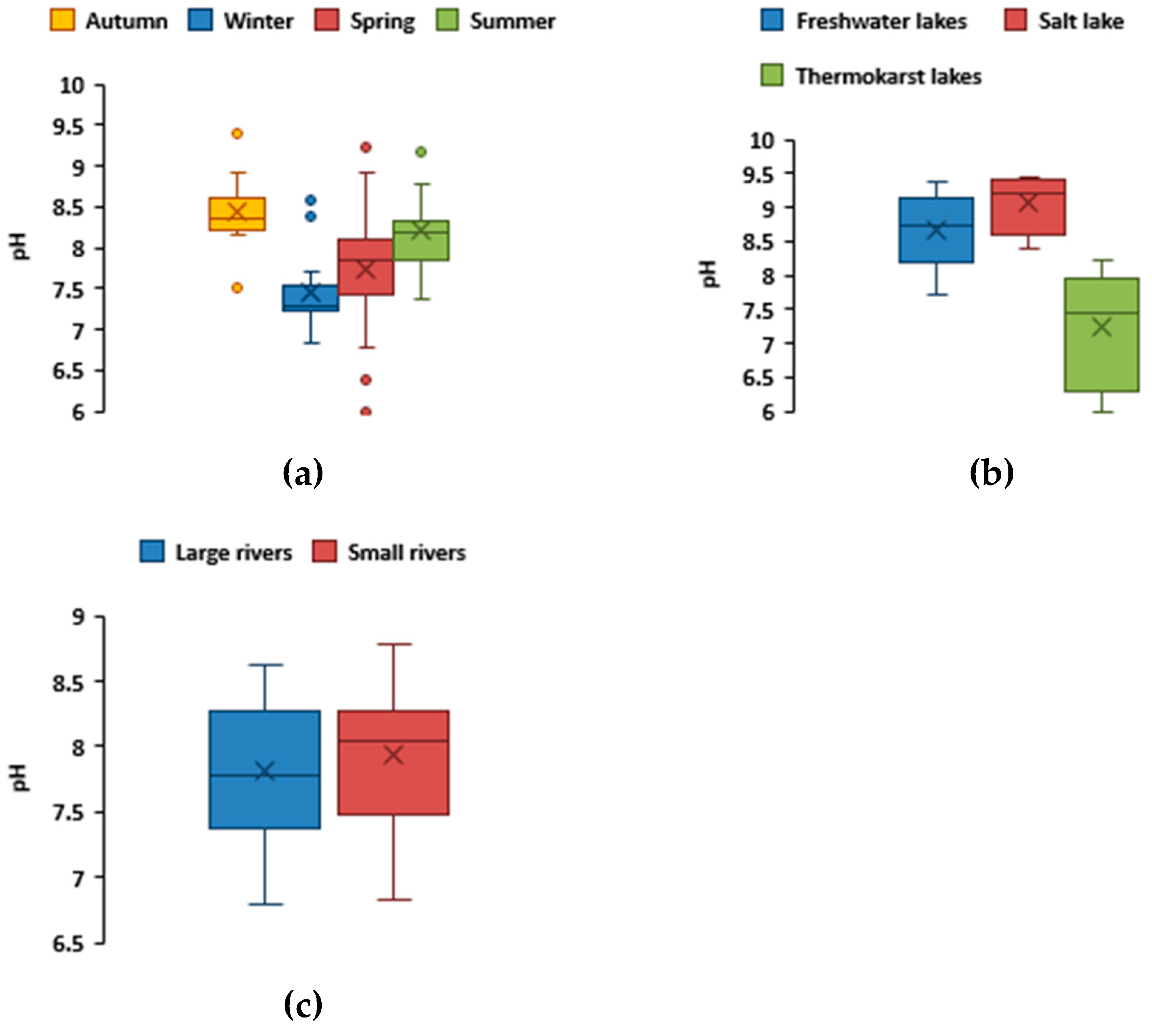
The values of pH varied significantly during different seasons of the year (F = 11.31, p = 0.00000,
Figure 3a) and between two major types of the water bodies–lakes and rivers (F = 10.667, p = 0.00000;
Figure 3b,c). The electrical conductivity (E.C.) in the studied water bodies varied widely, and increased in the order thermokarst lakes (29 ± 22) < large rivers (172 ± 97) < small rivers (207 ± 121) < freshwater lakes (534 ± 252) < salt lake (54600 ± 24380).
The water bodies of the Alash plateau, both rivers and lakes, exhibited the lowest E.C. In winter and autumn during low water season, the electrical conductivity was significantly higher than in spring and summer (F = 3.3, p = 0.03),
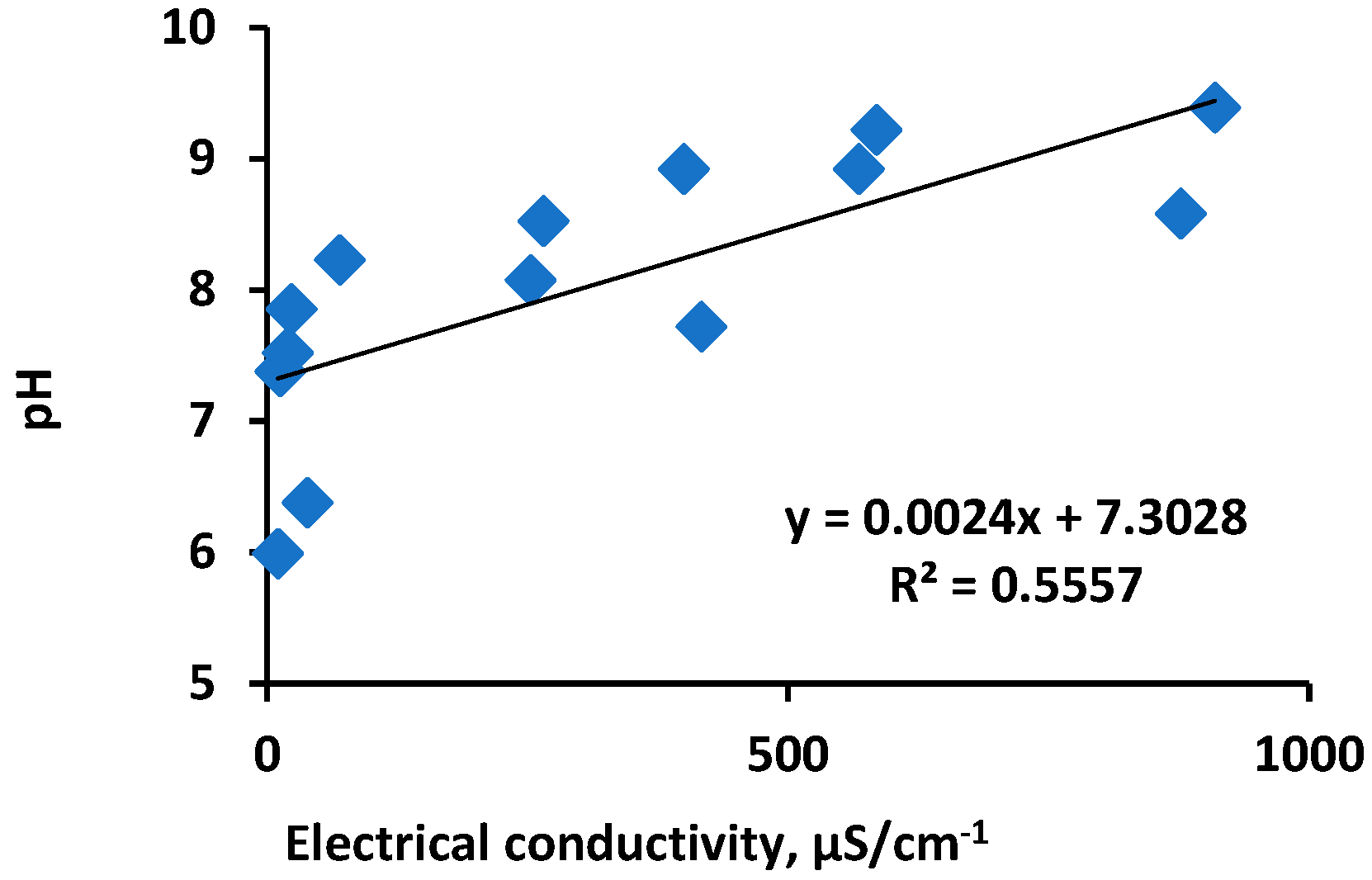
Supplementary Figures S1 and S2. For lakes, a significant relationship (p < 0.05) between electrical conductivity and the pH has been established (
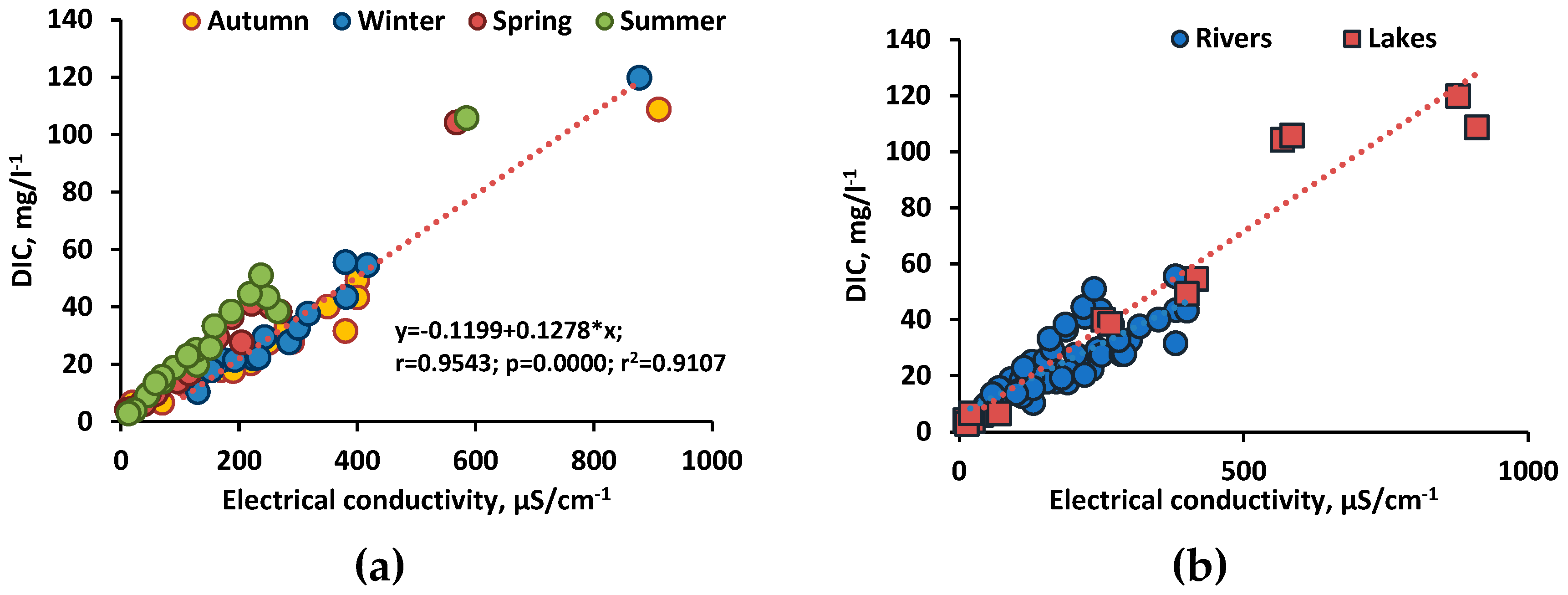
Figure 4). No such relationship has been revealed for rivers. A strong direct relationship between electrical conductivity and DIC content has been also established (
Figure 5), which reflected the dominance of bicarbonate ion in major salt composition of both rivers and lakes (
Supplementary Table S1).
Figure 3.
Box plot of median and IQR range (with outlies as dots) of pH values (a) during different seasons of the year (both rivers and lakes); (b) and separately in rivers; (c) and lakes.
Figure 3.
Box plot of median and IQR range (with outlies as dots) of pH values (a) during different seasons of the year (both rivers and lakes); (b) and separately in rivers; (c) and lakes.
Figure 4.
The relationship between electrical conductivity and DIC concentrations in the waters of the studied lakes (Salt Lake Cheder is excluded).
Figure 4.
The relationship between electrical conductivity and DIC concentrations in the waters of the studied lakes (Salt Lake Cheder is excluded).
Figure 5.
Linear relationship between DIC concentration and electrical conductivity in rivers and lakes of the Tyva region (a) and different seasons (lakes and rivers together); (b) in different types of objects (averaged across seasons).
Figure 5.
Linear relationship between DIC concentration and electrical conductivity in rivers and lakes of the Tyva region (a) and different seasons (lakes and rivers together); (b) in different types of objects (averaged across seasons).
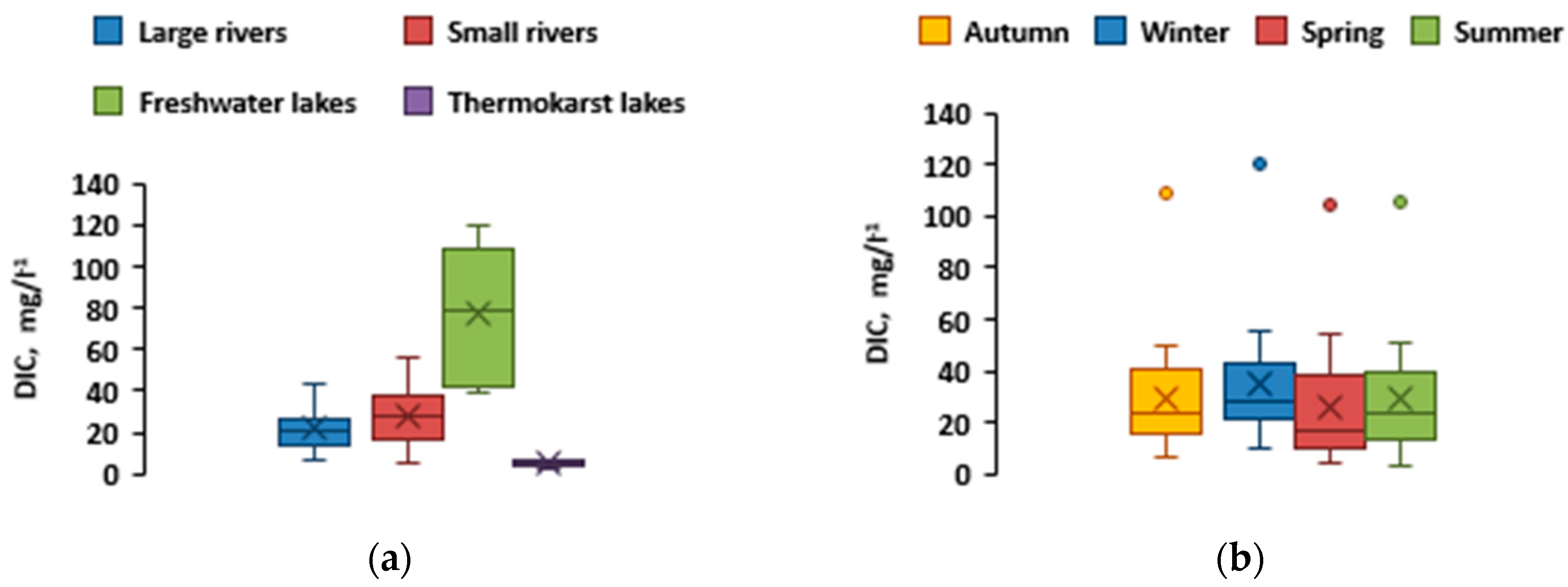
3.2. DIC и DOC concentrations
Elevated DIC concentrations were observed in freshwater lakes, especially in the Torehol Lake, where they reached 120 mg/L
−1, likely due to the impact of carbonate-rich groundwaters, which are reported to occur within the lake watershed (
Figure 6a). The minimal DIC values were recorded in the thermokarst lake waters, from 2.8 to 6.6 mg/L
−1. The seasonal dynamics of DIC demonstrated rather low variations (within 30 %) with minimal values observed in spring and maximal ones in winter
Figure 6b.
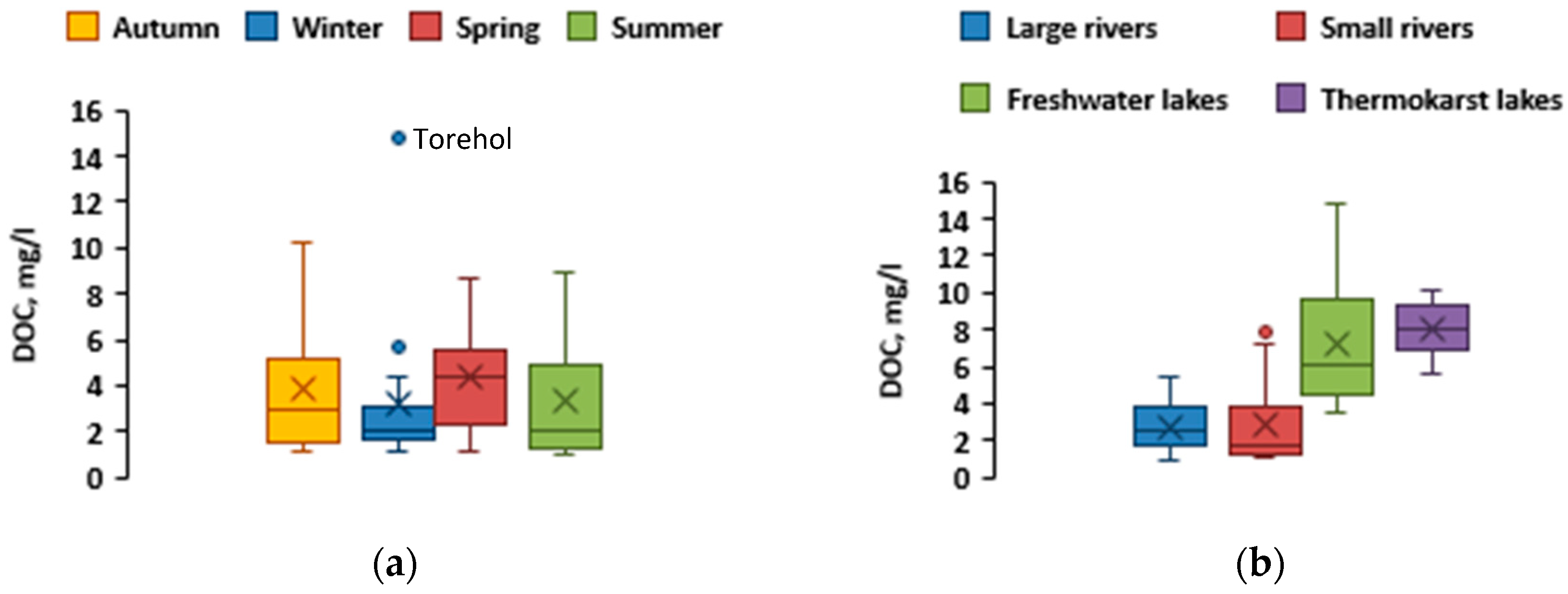
The maximal DOC values were measured for the waters of the Torehol Lake and thermokarst lakes. Of all the rivers studied, the Dyttyg-Khem, Durgen and Biche-Bayan-Kol waters are highly enriched in DOM whereas the majority of the waterbodies ranged from 2 to 6 mg L
−1 in DOC concentration. As in the case of DIC spatial and temporal pattern (
Figure 7a), the DOC concentrations demonstrated relative stability across seasons (
Figure 6b and
Figure 7b), with an exception of anomalously low value (14.8 mg L
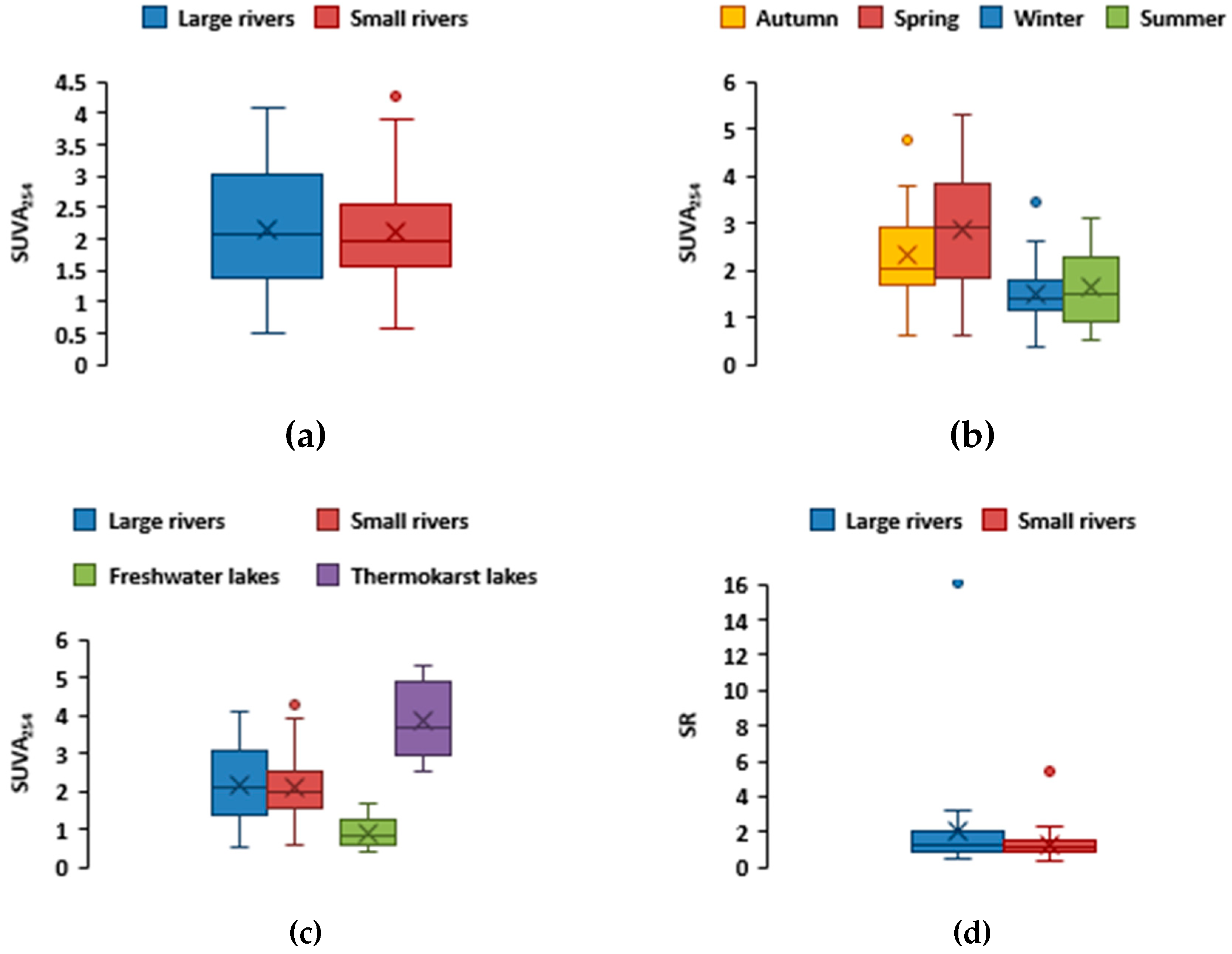
−1) in the Torehol Lake during winter. The highest SUVA
254 values, which reflect the DOM aromaticity, were observed in the waters of thermokarst lakes, followed by rivers, whereas the minimal values were recorded in freshwater lakes (
Figure 8a–c). The highest SUVA
254 was recorded in spring and the lowest in winter (
Figure 8b).
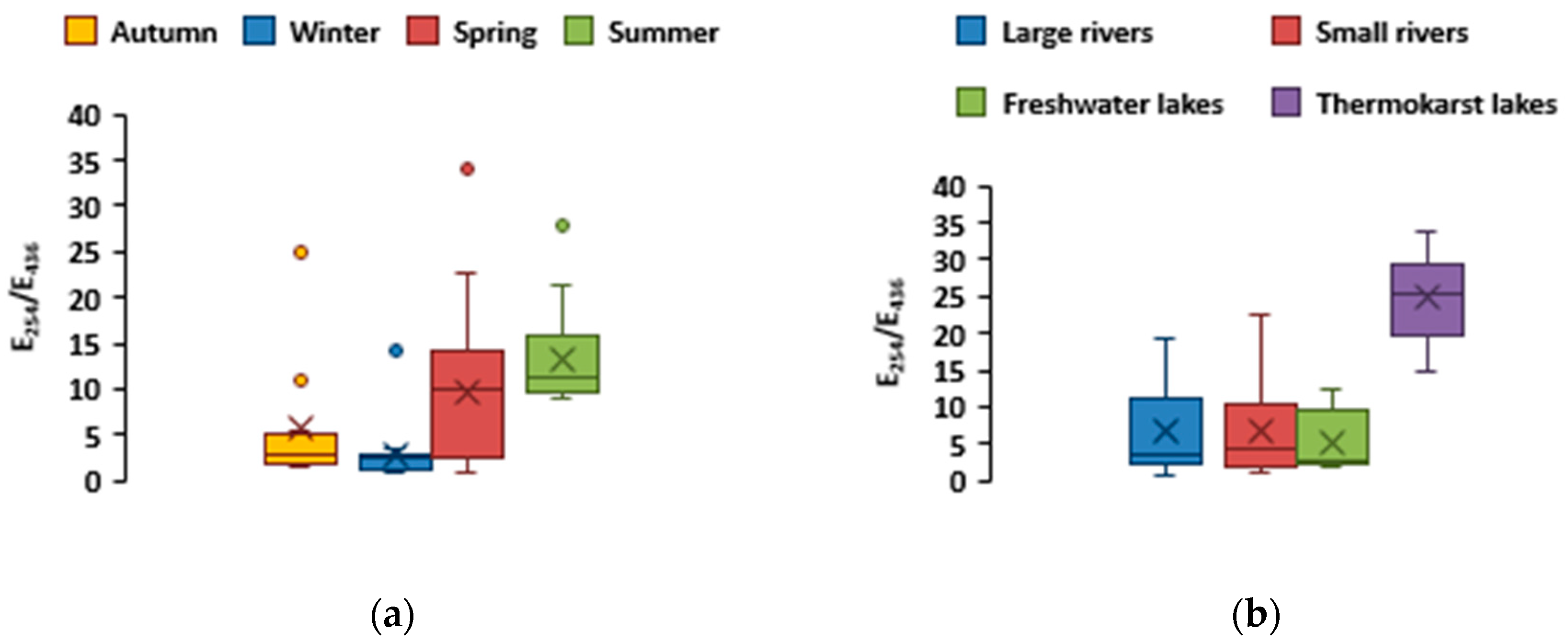
The ratio E
254:E
436 is known to indicate the relative role of allochthonous versus autochthonous organic substances in water bodies [
76,
77]. The DOM composition in the studied water objects was dominated by allochthonous substances, with the exception of the summer and partly spring period, when there was an increase in the E
254:E
436 ratio, indicating an active process of photosynthesis and destruction of detritus in the rivers and lakes themselves, leading to an increase in autochthonous organic matter [
78,
79].
There were no strong variation in the value of SUVA
254 in the waters of both small and large rivers (
Figure 8a). However, small river waters had a lower SR value, which indicated an increased degree of aromaticity compared to large rivers (
Figure 8b). A high index of SUVA
254 (3.8 ± 1) and a low index of SR (0.9 ± 0.1) in the waters of thermokarst lakes indicated a presence of aromatic compounds. In contrast, freshwater lakes, poor in DOC, exhibited much lower SUVA
254 and higher SR values compared to thermokarst lakes. The ratio of optical densities E
254:E
436 in rivers followed the order “summer” > spring > autumn > winter (
Figure 9a).
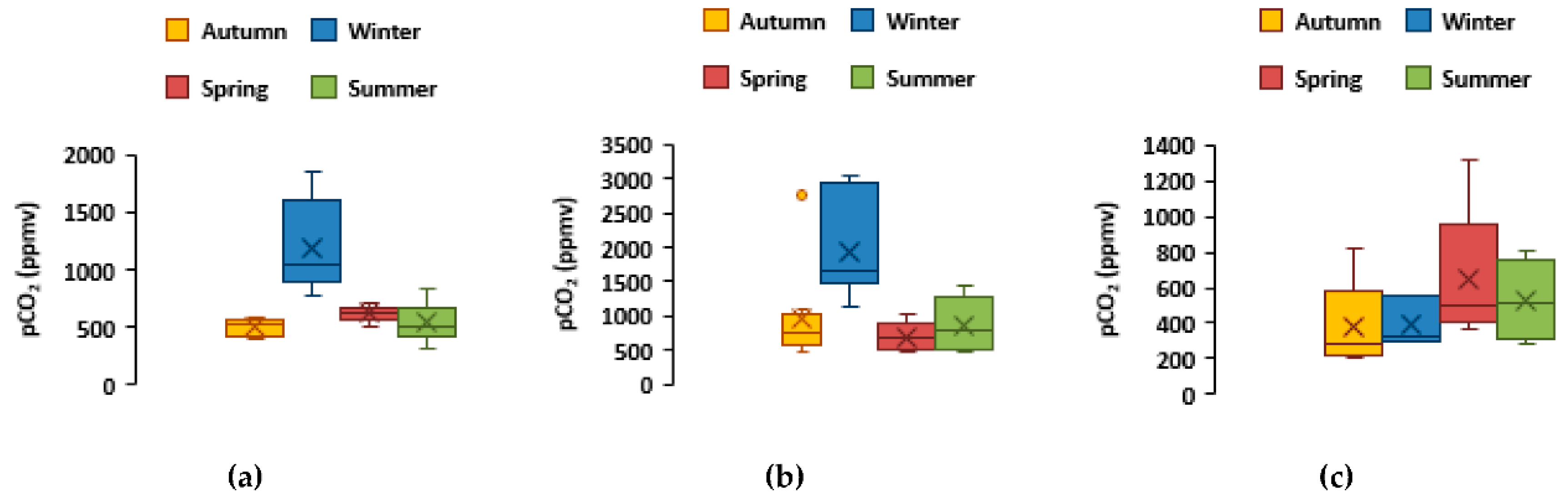
3.3. Spatial ad seasonal pattern of pCО2 and fCO2 in rivers and lakes
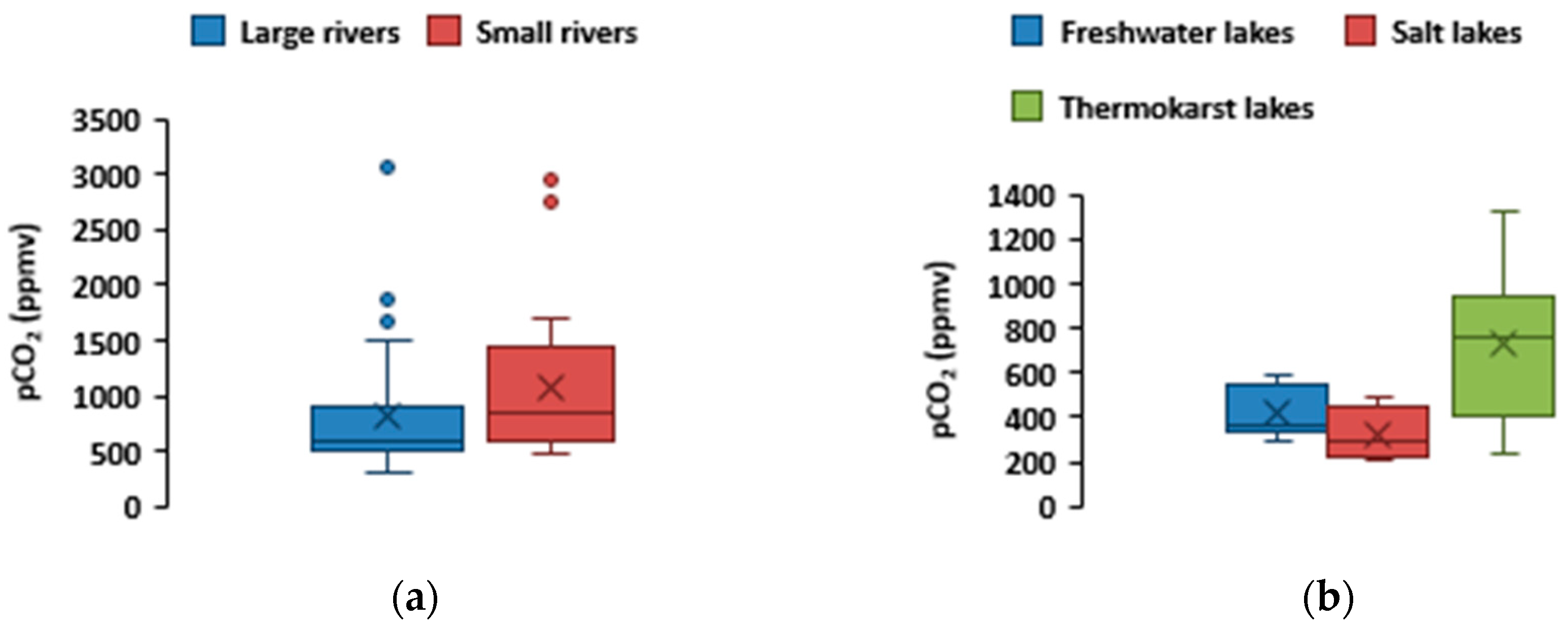
The highest values of pCO
2 were noted for a group of small rivers, with a maximum in the Adyr-Khem River, the smallest of the studied rivers draining the mound peat bog (
Table 3). A high content of dissolved CO
2 was also noted in the waters of the Chadan River, originating in the western Tannu-Ola and in the waters of the Khule River (Torgalyg), whose source is located on the Eastern Tannu-Ola. This region (Tannu-Ola) is known for its CO
2-rich underground discharges at the earth surface. The average values of pCO
2 in large rivers differ significantly from small ones; the minimum was marked for the Alash River (
Figure 10).
In lakes, the dissolved CO2 content was sizably lower than that in rivers; the minimum values were noted for the Cheder salt lake and the Tore-Khol Lake, located within a sandy substrate.
Table 3.
The values of pCO2 (ppmv) in rivers and lakes of the region.
Table 3.
The values of pCO2 (ppmv) in rivers and lakes of the region.
| Rivers |
Average |
Median |
| Large rivers |
| Yenisei |
689 |
578 |
| Big Yenisei |
860 |
587 |
| Small Yenisei |
790 |
571 |
| Tes-Khem |
672 |
609 |
| Khemchik |
705 |
715 |
| Alash |
563 |
502 |
| Small rivers |
| Ak-Sug |
809 |
552 |
| Chadan |
1470 |
1112 |
| Durgen |
739.5 |
493 |
| Chaa-Hol |
778 |
729 |
| Huule (Torgalyg) |
1133 |
1003 |
| Anyyak-Chyrgaki |
909 |
932 |
| Dyttyg-Hem |
840 |
660 |
| Biche-Bayan-Kol |
743 |
743 |
| Adyr-Khem |
2043 |
2105 |
| Lakes |
| Tore-Khol |
332,0 |
336,5 |
| Chagytai |
503,8 |
535,0 |
| Cheder |
320,5 |
292,0 |
| Thermokarst lake 1 |
754,0 |
705,0 |
| Thermokarst Lake 2 |
694,0 |
806,0 |
In terms of seasonal variations, both in rivers and lakes, the pCO
2 was significantly higher in winter due to CO
2 accumulation under ice (
Figure 11). Note that, because shallow thermokarst lakes freeze solid in winter, measurements of the water column during this period were not possible.
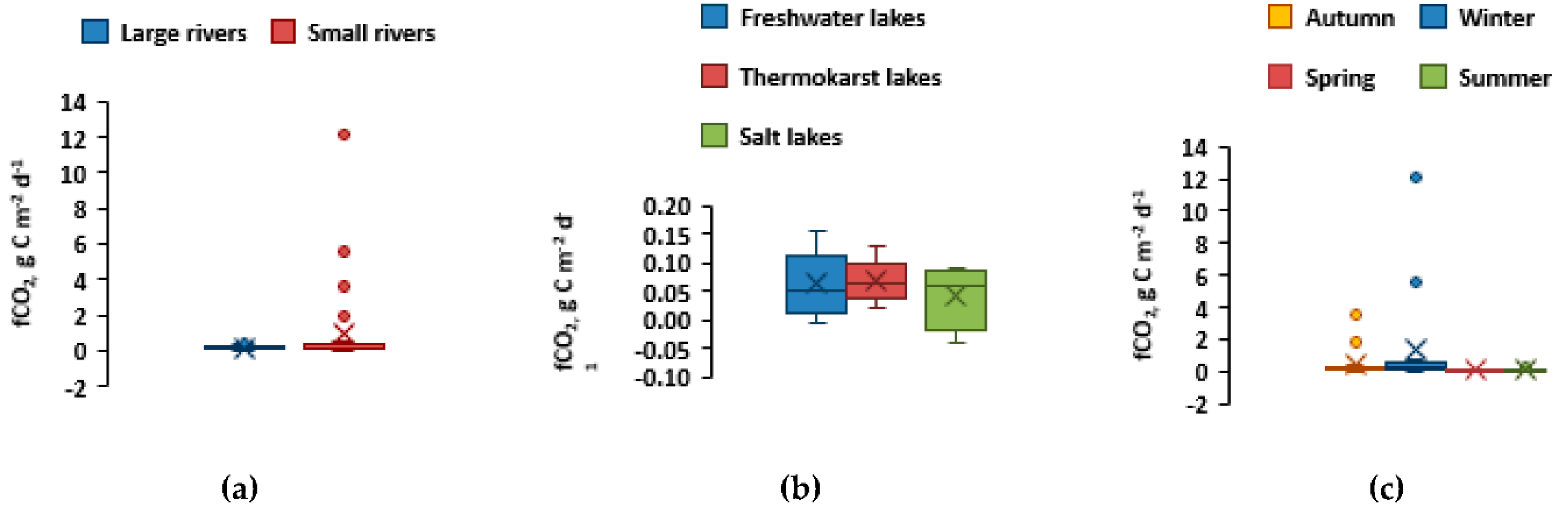
Overall, CO
2 emissions from the surface of rivers and lakes were quite low (median 0.05-0.15 g C m
−2 d
−1; Table 4) and did not differ significantly (p > 0.05) among different water bodies, including two main categories—rivers and lakes. There was no significant difference in fCO
2 between different seasons of the year (
Figure 12c). Exceptionally high CO
2 fluxes were encountered in the Chadan River and Ak-Sug River (12 and 5.6 g C m
−2 d
−1, respectively). Despite their small size, these rivers do not freeze solid during ice-on period, and they likely possess sizable bicarbonate/CO
2-rich underground sources that are mostly pronounced during winter baseflow.
Analysis of correlations between O
2 and CO
2 concentrations of all objects across seasons did not show significant relationship (r = −0.13, p > 0.05); however, when considering solely large rivers and thermokarst lakes, a negative relationship (r = −0.47 and r = −0.95) was observed (
Table S1;
Figure S4). In freshwater lakes, pCO
2 also negatively correlated with O
2 level (r = −0.50). The water temperature exerted significant (r = 0.64, p < 0.05) impact on pCO
2 in large rivers (
Table S1).
Figure 11.
Median (and IQR) boxplots of CO2 partial pressure (ppmv) in (a) large and (b) small rivers across seasons, statistically different (Large rivers: F = 12.202, p = 0.001 and Small rivers: F = 7.8006, p = 0.001, accordingly.) (c): Median (and IQR) boxplots of CO2 partial pressure (ppmv) in lakes across seasons (F = 0.9223, p = 0.46).
Figure 11.
Median (and IQR) boxplots of CO2 partial pressure (ppmv) in (a) large and (b) small rivers across seasons, statistically different (Large rivers: F = 12.202, p = 0.001 and Small rivers: F = 7.8006, p = 0.001, accordingly.) (c): Median (and IQR) boxplots of CO2 partial pressure (ppmv) in lakes across seasons (F = 0.9223, p = 0.46).
Figure 12.
Boxplots (median and IQR range) of fCO2 (a) in rivers the difference is insignificant at (F = 2.30, p = 0.13); (b) in lakes (F = 0.30, p = 0.74356); (c) and all types of objects across (F = 2.5448, p = ,06369).
Figure 12.
Boxplots (median and IQR range) of fCO2 (a) in rivers the difference is insignificant at (F = 2.30, p = 0.13); (b) in lakes (F = 0.30, p = 0.74356); (c) and all types of objects across (F = 2.5448, p = ,06369).
3.4. Testing potential drivers of CO2 concentrations and fluxes
During summer period, the pCO
2 of the water column in lakes correlated with the lake water surface area (R
2 = 0.44, p < 0.05), whereas during other seasons, this relationship was not significant (R
2 = 0.1 to 0.2, p < 0.05);
Figure 13а. The flux of CO
2 positively correlated with lake surface area during the spring (R
2 = 0.53, p < 0.01) and winter periods (R
2 =0.79, p < 0.01) as illustrated in
Figure 13b. In thermokarst lakes, pCO
2 and fCO
2 increased with lake surface area in spring, but decreased with S
area in summer and autumn (
Figure S5), although these qualitative trends could not be statistically supported due to too low number of sampled lakes.
The river watershed area positively correlated with pCO
2 (R
2 = 0.38, p < 0.05) and fCO
2 (R
2 = 0.32, p < 0.05) in the autumn period whereas during other seasons, the correlation was absent (R
2 < 0.27; p > 0.05) as shown in
Figure S6.
Among the “internal” factors likely to control the CO
2 pattern (concentration and fluxes) in the water bodies we tested major hydrochemical parameters of the water column, including pH, conductivity, DIC, DOC, concentration, DOM quality and a microbiological parameter (i.e., total bacterial count) as presented in
Table 5. Considering all water objects together, neither pCO
2 nor fCO
2 correlated significantly (R
Pearson > 0.39 at p = 0.05) with any tested parameter. Note that this result does not contradict several significant relationships of pCO
2 with lake area or O
2, which were evidenced for individual seasons. Individual analyses of group of rivers and lakes demonstrated strong positive control (p < 0.05) of E.C. and pH on fCO
2 in large rivers (r = 0.5 and 0.64, respectively) and negative control of pH on pCO
2 in lakes (r = −0.99);
Table S1 of the Supplement.
4. Discussion
4.1. Major solutes, dissolved organic and inorganic carbon
It is known that inland water systems are sizable sources of CO
2, which is highly important prerequisite for retroactive link between the climate and C cycle in aquatic systems [
80,
81,
82]. Although at present, the climate changes in the territory of Tyva are already strongly pronounced (e.g., ref. [
83], it is not yet possible to quantify this impact on water bodies. However, the present study can provide a solid background for assessing current status of C cycle in order to be able to judge the future changes which are likely to occur over the next decades.
The level of DIC concentration was sizably higher than that of DOC, and hence the C export in studied rivers and C storage in lakes are dominated by inorganic carbon. Only during spring, the DOC concentration was higher than DIC, which could be linked to the snow melt. dilution of the groundwater signal and the dominance of surface flow.
Enhanced DOC delivery to lakes and rivers occurs during melt snow interaction with surface soil, organic-rich litter. This period contrasts shallow subsurface flow in summer and autumn, when the water hydrochemical signal essentially controlled by rock weathering at the watershed. In this regard, the present study corroborates the knowledge of processes controlling river and lake water chemical composition across seasons as established in the boreal, high latitude and subarctic rivers [
84,
85,
86] and subarctic lakes [
87]. Note here that the connection between the groundwaters and the lake, especially in permafrost-covered regions such Altai-Sayany Mountain system, is weaker than that for rivers. A co-mobilization of DIC and other ions from shallow subsurface/groundwaters, bearing the signal of chemical weathering, for all water objects is confirmed by the observation that the DIC values strongly correlated with the electrical conductivity index. In the Khemchik, Ak-Sug, Alash and Adyr-Khem mountain rivers flowing in the northwestern part of the Republic of Tyva, in the Western Sayans, the values ranged from 4 to 20, and in other rivers from 9~13 to 55. It is possible that a reason for such a reduced DIC values in mountain rivers is an increased precipitation in this area [
83], the presence of permafrost [
88] and high runoff [
89]. An opposite situation is observed in the water bodies of more arid Ubsu-Nur basin: the Tore-Khol Lake and the Tes-Khem River, where the DIC values are the highest. Here, evaporative concentration of major solutes, occurring both within the river watersheds and the lake water column, can be responsible for elevated DIC and S.C. values.
Increased DOC concentrations were observed in lakes, compared to rivers, which may be explained by higher water residence time and autochtonous production of OM. This was especially pronounced in thermokarst lakes, exhibiting the highest SUVA (
Figure 8b,c) and the humification index (E
254/E
436 ratio (
Figure 9b). According to the ratio of optical densities E
254/E
436, allochthonous (peat-originated) organic matter prevails in thermokarst lakes, and significantly exceeds the values of the ratios in other water bodies. A decrease of the optical index E
254/E
436 in rivers (
Figure 9a) demonstrated the highest allochthonous (terrestrial) source of DOM from forest litter during active period of the year. This likely corresponds to a decrease of the humification index [
90] due to biotically-driven degradation of humic-like aromatic components in streams and rivers [
91].
4.2. Dissolved C pattern and CO2 fluxes: driving factors and comparison with other regions
We identified the oxygen regime as one of the main controlling factors of pCO
2 level in both rivers and lakes across seasons. The highest CO
2 concentrations were observed in O
2-impoverished waters, likely due to important impact of partially anoxic sediment respiration on CO
2 regime of the water column. Similar effects are reported in many boreal and subarctic waters across the world, notably in lakes and channels of the Ob River floodplain (i.e., ref. [
73]).
The pCO
2 was generally lower in lakes of smaller surface area, which is well –known phenomenon in various lakes of the boreal and subarctic zone [
1,
75]. This can be linked to enhanced terrestrial input of CO
2-rich waters from the watershed in small lakes and sizable primary productivity of plankton and periphyton/macrophytes in large, mature lakes, as it is known in thermokarst water bodies in the neighboring territory of permafrost peatlands [
92].
The seasonal variations of CO
2 concentration were characterized by a maximum pCO
2 during winter in rivers and during spring in lakes. The former can be explained by enhanced underground discharge within the river main stem and CO
2 accumulation under ice, whereas the spring maximum of CO
2 in lakes in likely due to lack of phytoplankton activity and enhanced input of biologically labile terrestrial DOM from the watershed, during freshet. This DOM can be subjected to intensive bacterial processing leading to a maximum of CO
2 emissions [
93]. In summer period, lakes act as CO
2 sink due to biological production processes (macrophytes, cyanobacterial bloom) in the water column (e.g., ref. [
94]).
The results on carbon (DOC, DIC CO
2) concentrations and CO
2 fluxes in the Altai-Sayany mountain system were compared with data reported for the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau [
18,
95,
96], since this region has relatively similar climate and also impacted by the permafrost. To account for thermokarst lakes, we also chosen the largest compilation of lakes in sporadic to continuous permafrost zone of the Western Siberia reported in Serikova et al. (2019) [
1]. A synthesis of available information is provided in
Table 6. The DOC level of river and lakes of the Tuva Republic obtained in this study are quite similar. within the range of natural seasonal and spatial variations. to that in thermokarst lakes of the QTP as well as the Tibetan rivers. The DIC concentrations in lakes and rivers of the Sayan-Altai mountain system are also similar to the values of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. with the exception of saline lakes whose C cycle is strongly controlled by local evaporative processes.
In contrast to the DIC and DOC concentrations, for which the results of different regions are fairly comparable, the pCO
2 in Sayan-Altai Mountain region had generally lower values than those observed in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Western Siberia. It is possible that sizable autochthonous production and CO
2 uptake by plankton in lakes and macrophytes in rivers could be partially responsible for lower CO
2 level in the water bodies of studied region during summer period, when the water warms higher than that in the sub-Arctic western Siberia or high-altitude QTP. At the same time, our results on CO
2 flux are comparable to those Jia et al (2022) [
95] for the lakes and rivers of southwestern and northeastern regions of the QTP (0.3 ± 0.2 (g C m
−2 d
−1). However, unlike the maximal flux observed in this work during winter, the latter authors reported the lowest flux during ice-covered seasons. The lowest CO
2 emission is typically observed during cold periods, as also reported by other studies [
96,
97,
98,
99,
100]. In our case, this could indicate an existence of sizable underground sources of CO
2 (discharge of CO
2-rich fluids, especially pronounced during low water level period). These effects are visible for large rivers, which demonstrated strong positive impact of E.C., pH and DIC on fCO
2 (
Table S1).
Overall, the differences on CO
2 emissions among different works may be due to the peculiarities inherent to our region, as well as due to differences in the methodologies used. It is interesting that the carbon uptake flux in the terrestrial Tyva steppe regions is estimated as 184 ± 41 g C m
−2 yr
−1 [
101]. This is fairly comparable with the CO
2 emission flux by the rivers of the region, assessed in the present study (213 g C m
−2 yr
−1). Such a comparison is consistent with the importance of inland water bodies (rivers and lakes) in overall C balance of the terrestrial biomes, as also demonstrated in Western Siberia [
102]. However, at the present status of research, straightforward comparison of the data on C pattern revealed in the Sayan-Altai region and that reported in the adjacent subarctic and mountain territories requires more thorough assessment of possible controlling factors such as local climate variation, productivity of the terrestrial compartments, underground influx, respiration of sediments and primary productivity in the river and lakes.
5. Conclusions
A thorough, first-time assessment of contemporary status of C biogeochemical cycle (concentration, emission from the water surfaces) was conducted in lakes and rivers of the Central Asian, Sayan-Altai mountain system in order to provide a background for judging possible future changes induced by a particulate climate instability in this region. Using a physio-geographical and climatic transect of inland water bodies, which comprised large variety of natural ecosystems and landscapes of the region, we found that permafrost exerts the largest impact on lake water hydrochemistry and C pattern including CO2 exchange with atmosphere, whereas the size of the river watershed had relatively little impact on CO2 pattern. In contrast, pCO2 decreased with an increase in lake size which could be linked to a combination of factors, notably i) enhanced input of terrestrial, biolabile DOM in small lakes which served as a source of CO2 production in the water column, ii) terrestrial input of CO2-rich shallow groundwater and soil waters, more pronounced in small lakes, and iii) CO2 uptake in large lakes due to macrophytes, periphyton and phytoplankton activity. Oxygen regime was found to be an important controlling factor of pCO2 level in both rivers and lakes during specific seasons, likely due to sediment respiration processes. However, despite these qualitative features of possible CO2 regime control in studied water bodies, a pairwise correlation analysis did not demonstrate statistically significant relationships between CO2 flux and physico-geographical parameters of river watersheds, river and lake size and internal parameters of the water column, including basic hydrochemical characteristic, DOM concentration and quality and bacterial concentration. A likely reason is the complexity of the ‘external’ and ‘internal’ factors controlling CO2 exchange between water surfaces and the atmosphere, and their often counter-action on CO2 production/uptake in the water column, sediments and the watershed.
We argue that further assessment of possible controlling factors such as local climate variation, productivity of the terrestrial compartments, underground influx, respiration of sediments and primary productivity in the river and lakes, are necessary for comparison of the aquatic C pattern revealed in the Sayan-Altai region in this study to that reported in the adjacent subarctic and mountain territories.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B., L.K., A.K., S.K.; methodology, I.K., T.R., A.P., I.L., Z.K., S.V.; software, I.K.; validation, S.V., O.P.; formal analysis, A.B., L.K.; investigation, A.B., L.K., I.K.; resources, A.K., S.K.; data curation, A.B., L.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B., L.K.; writing—review and editing, O.P.; visualization, A.B., L.K.; supervision, S.K.; project administration, A.K.; funding acquisition, S.K., A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
OP is grateful to partial support from TSU program “Priority 2030” and RSCF № 23-14-20015.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Serikova, S.; Pokrovsky, O.; Laudon, H.; Kritskov, I.; et al. High carbon emissions from thermokarst lakes of Western Siberia. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickov, I.; Lim, A.; Shirokova, L.; Korets, M.; Karlsson, J.; Pokrovsky, O. Environmental controllers for carbon emission and concentration patterns in Siberian rivers during different seasons. Sci Total Environ 2023, 859, 160202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotin, S.; Antoshkina, O.; Berezin, A.; Elshehawi, S.; Feurdean, A.; et al. Great Vasyugan Mire: How the world's largest peatland helps addressing the world's largest problems. Ambio 2021, 50, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupakov, A.; Pokrovsky, O.; Moreva, O.; Kotova, E.; et al. Export of organic carbon, nutrients and metals by the mid-sized Pechora River to the Arctic Ocean. Chemical Geology 2023, 632, 121524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackpoole, S.; Butman, D.; Clow, D.; Verdin, K.; et al. Inland waters and their role in the carbon cycle of Alaska. Ecol Appl 2017, 27, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.; Casas-Ruiz, J.; Prairie, Y.; Del Giorgio, P. Magnitude and drivers of integrated fluvial network greenhouse gas emissions across the boreal landscape in Québec. Water Res 2020, 173, 115556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.; Shirokova, L.; Manasypov, R.; et al. Thermokarst lakes of Western Siberia: A complex biogeochemical multidisciplinary approach. International J. Environmental Stud. 2014, 71, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dristi, A.; Xu, Y.J. Large Uncertainties in CO2 Water–Air Outgassing Estimation with Gas Exchange Coefficient KT for a Large Lowland River. Water 2023, 15, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ran, L. Total Organic Carbon Concentration and Export in a Human-Dominated Urban River: A Case Study in the Shenzhen River and Bay Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xv, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X. Interconnected River–Lake Project Decreased CO2 and CH4 Emission from Urban Rivers. Water 2023, 15, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, A.; Lauerwald, R.; Ciais, P.; Regnier, P. Aquatic carbon fluxes dampen the overall variation of net ecosystem productivity in the Amazon basin: An analysis of the interannual variability in the boundless carbon cycle. Glob Chang Biol. 2019, 25, 2094–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, R.; Powell, C.; Gordon, D.; Long, J.; Bliss, C. Abundance, distribution, and fluxes of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in four small sub-tropical rivers of the Tampa Bay Estuary (Florida, USA). Applied Geochemistry 2015, 63, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria Reinoso, I.; Alcocer, J.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; et al. The Seasonal Dynamics of Organic and Inorganic Carbon along the Tropical Usumacinta River Basin Mexico. Water 2022, 14, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting-Hsuan, H.; Yu-Han, F.; Pei-Yi, Pa.; Chen-Tung, A. Fluvial carbon fluxes in tropical rivers. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2012, 4, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, A.; Yang, Y.; Fang, X. Sequestration of carbon as carbonate in the critical zone: Insights from the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geochim 2017, 36, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emberson, R.; Galy, A.; Hovius, N. Weathering of Reactive Mineral Phases in Landslides Acts as a Source of Carbon Dioxide in Mountain Belts. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface 2018, 123, 2695–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Galy, A. On the significance of periglacial conditions in active mountain belts for chemical weathering processes: Insights from the Chayu area, SE Tibet. Chemical Geology 2021, 585, 120581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; et al. Net ecosystem carbon budget of a grassland ecosystem in central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Integrating terrestrial and aquatic carbon fluxes at catchment scale. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2020, 290, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, G.; Mao, T.; Huang, K.; et al. Spatiotemporal variability and sources of DIC in permafrost catchments of the Yangtze River source region: Insights from stable carbon isotope and water chemistry. Water Resources Research 2020, 55, e2019WR025343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Du, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Q.; et al. High methane emissions from thermokarst lakes on the Tibetan Plateau are largely attributed to ebullition fluxes. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 801, 149692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Shan, S.; et al. Sources and cycling of dissolved organic and inorganic carbon on the northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Radiocarbon results from Qinghai Lake. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 851, 158123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, S.L.; Zhu, X.; Jing, L.; et al. Dynamics and fluxes of dissolved carbon under short-term climate variabilities in headwaters of the Changjiang River, draining the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Hydrology 2021, 596, 126128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Du, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Du, J.; Jiang, R. Hotspots of riverine greenhouse gas (CH4, CO2, N2O) emissions from Qinghai Lake Basin on the northeast Tibetan Plateau. Sci Total Environ 2023, 857 Pt 1, 159373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorin, A. (Ed.) Assessment Report: Climate change and its impact on ecosystems, population and economy of the Russian portion of the Altai-Sayan Ecoregion. WWF Russia: Moscow, 2011; 152p. [Google Scholar]
- Golubeva, E.; Kerzhentsev, A.; Koropachinsky, I.; et al. Experiment "Ubsu-Nur". INTELLECT: Moscow, 1995; Volume 1, 336p, ISBN 5870470102. Part 1. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Anandhi, A.; Kannan, N. Vulnerability assessment of water resources—Translating a theoretical concept to an operational framework using systems thinking approach in a changing climate: Case study in Ogallala Aquifer. Journal of Hydrology 2018, 557, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Ghosh, S.; Pathak, A.; Sahai, A. Hydrologic impacts of climate change: Comparisons between hydrological parameter uncertainty and climate model uncertainty. Journal of Hydrology 2018, 566, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Pandey, B.; Yadav, A.; Saroj, S. Chapter 5—An overview of the potential impacts of global climate change on water resources. In Water Conservation in the Era of Global Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; et al. Water resource formation and conversion and water security in arid region of Northwest China. J. Geogr. Sci 2016, 26, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Meng, F.; et al. Identifying climate change impacts on water resources in Xinjiang, China. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 676, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Quantifying the effects of climate variability and human activities on runoff for Kaidu River Basin in arid region of northwest China. Theor Appl Climatol 2013, 111, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotin, S.; Callaghan, T.V.; Peregon, A.; et al. Impacts of environmental change on biodiversity and vegetation dynamics in Siberia. Ambio 2021, 50, 1926–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, T.; Shaduyko, O.; Kirpotin, S.; et al. Siberian environmental change: Synthesis of recent studies and opportunities for networking. Ambio 2021, 50, 2104–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Calvo Buendia, E.; et al. IPCC, 2019: Climate Change and Land: An IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019; 896p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Slade, R.; et al. IPCC, 2022: Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalibekov, Z.G. The arid regions of the world and their dynamics in conditions of modern climatic warming. Arid Ecosystems 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.I.; Ubugunov, L.L.; Mangataev, A.T. Global climate change and its impact on ecosystems. Arid Ecosystems 2014, 4, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo, M.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Soliveres, S.; et al. Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity. Science 2020, 367, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, D.; Dai, A.; Simmonds, I. Increased quasi stationarity and persistence of winter Ural blocking and Eurasian extreme cold events in response to Arctic warming. Part I: Insights from observational analyses. Journal of Climate 2017, 30, 3549–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhov, I.I.; Akperov, M.G.; Prokofyeva, M.A.; et al. Blockings in the Northern hemisphere and Euro-Atlantic region: Estimates of changes from reanalysis data and model simulations. Dokl. Earth Sc. 2013, 449, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Kuzhevskaia, I.; Nechepurenko, O.; Chursin, V.; Zemtsov, V. Long-Term Trends of Extreme Climate Indexes in the Southern Part of Siberia in Comparison with Those of Surrounding Regions. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattsov, V.M. (Ed.) The third assessment report on climate change and its consequences on the territory of the Russian Federation. In Roshydromet; Science-Intensive Technologies: St. Petersburg, 2022; 676p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuular, H.B.O.; Chuldum, A.F.; Hertek, S.B.O.; Namzin, S.A. Spatio-temporal distribution of the spring burnability of the vegetation cover of the Republic of Tyva in 2000-2020. Natural resources, environment and society 2021, 2, 18–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Risk Country Profile: Mongolia (2021): The World Bank Group and the Asian. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/709901/climate-risk-country-profile-mongolia.pdf.
- Adrian, R.; O'Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; et al. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnology and oceanography 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenov, N.; Sommaruga, R.; Morales-Baquero, R.; et al. Dust inputs and bacteria influence dissolved organic matter in clear alpine lakes. Nat Commun 2011, 2, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.A.; Baron, J.S.; Brahney, J.; Oleksy, I.A.; Saros, J.E.; et al. Mountain lakes: Eyes on global environmental change. Global and Planetary Change 2019, 178, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogora, M.; Frate, L.; Carranza, M.L.; et al. Assessment of climate change effects on mountain ecosystems through a cross-site analysis in the Alps and Apennines. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; et al. Lakes and Reservoirs as Regulators of Carbon Cycling and Climate. Limnology and Oceanography 2009, 54, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Doll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrology 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G.; Edwards, T.; Moser, K.; et al. Rapid response of treeline vegetation and lakes to past climate warming. Nature 1993, 361, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, L.; Leavitt, P.R.; Weidman, R.P.; Vinebrooke, R.D. Regulation of the Nitrogen Biogeochemistry of Mountain Lakes by Subsidies of Terrestrial Dissolved Organic Matter and the Implications for Climate Studies. Limnology and Oceanography 2010, 55, 333–345. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/20622883. [CrossRef]
- Oidup, C.K. Lithium-uranium mineralization of salt lakes and underground springs of Central Tuva. Geospheric Research 2018, 3, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzyl, O.M. Hydrogeochemistry of mineral water sources of the Republic of Tyva. Bulletin of the Kurgan State University 2015, 4, 2222–3371. (In Russian). Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/gidrogeohimiya-mineralnyh-istochnikov-vod-respubliki-tyva.
- Ivanova, K.Yu.; Khvashchevskaya, A.A. Features of the chemical composition of groundwater springs of Western Tuva. Resort base and natural health-improving areas of Tuva and adjacent regions 2015, 2, 167–173. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kalnaya, O.I.; Rychkova, O.I.; et al. Ecological and hydrochemical state of watercourses in the area of Kyzyl (Republic of Tyva). Natural resources, environment and society 2020, 4, 52–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kalnaya, O.I.; Ainova, O.D. Retrospective analysis of the ecological and hydrochemical state of two-dimensional and auxiliary means in the region of Lake Duskhol (Svatikovo), central Tuva. Natural resources, environment and society 2022, 1, 37–47. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kirova, N.A.; Kalnaya, O.I.; Ayunova, O.D. On the issue of hydrochemistry and biology of Lake Duskhol (Tuva). Izvestiya AO RGO 2018, 4, 82–88. (In Russian). Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/k-voprosu-o-gidrohimii-i-biologii-ozera-dus-hol-tuva.
- Sambuu, A.; Ayunova, O.; Chupikova, S.; Dugerzhaa, Ch.Sh.; Biche-ool, O.E. Water resources of the republic of Tuva and their current state. International Journal of Hydrology Science and Technology 2020, 7, 60–66. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State report "On the state and environmental protection of the Republic of Tyva in 2019".—Text: Electronic//Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Republic of Tyva: Official website 2019. (In Russian). Available online: https://mpr.rtyva.ru/upload/files/f992a01d-bc33-488f-8f71-ea266cfa02ec.pdf.
- Chupikova, S.A.; Prudnikov, S.D.; Chuldum, A.F. Morphometric analysis of the water intake of relig-Hem (Tuva) using GIS and DDZ. Bulletin of SGUGiT (Siberian State Geosystem University and Technological University) 2023, 28, 76–88. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineeva, L.A.; Arakchaa, K.K.D.; Kyzyl, O.M. Physical and chemical characteristics of mineral waters from the Shumak and Choigan deposits. Bulletin of the Irkutsk State University. Series: Earth Sciences 2016, 17, 115–134. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kopylova, Yu.G.; Guseva, N.V.; Arakchaa, K.D.; Khvashchevskaya, A.A. Geochemistry of carbon dioxide mineral waters of the Choigan natural complex (northeastern Tuva). Russian Geology and Geophysics 2014, 55, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodnam, N.I.; et al. Physico-chemical review of arzhanov Ovyursky district. Bulletin of Tuva State University. No. 2 Natural and agricultural sciences 2019, 2, 52–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Klopotova, N.G. The current state and study of therapeutic hydromineral resources of Tuva. Resort base and natural health-improving areas of Tuva and adjacent regions 2013, 1, 16–19. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Szopińska, M.; Szumińska, D.; et al. The chemistry of river–lake systems in the context of permafrost occurrence (Mongolia, Valley of the Lakes). Part I. Analysis of ion and trace metal concentrations, Sedimentary Geology 2016, 340, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuular, H.B. Climate warming in the Republic of Tyva according to ground observations. Natural Resources, Environment and Society 2021, 1, 62–67. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakchaa, K.D. Prospects for the development of balneoresources of lake Cheder. Natural Resources, Environment and Society 2021, 1, 21–29. (In Russian). Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/perspektivy-osvoeniya-balneoresursov-ozera-cheder.
- Dubovik, D.S.; Yakutin, M.V. The use of Earth remote sensing data in monitoring of small lakes of the Ubsunur basin (Tyva). Interexpo Geo-Siberia 2016, 4, 74–78. (In Russian). Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ispolzovanie-dannyh-distantsionnogo-zondirovaniya-zemli-v-monitoringe-malyh-ozer-ubsunurskoy-kotloviny-tyva.
- Johnson, M.S.; Billett, M.F.; Dinsmore, K.J.; Wallin, M.B.; Dyson, K.E.; Jassal, R.S. Direct and continuous measurement of dissolved carbon dioxide in freshwater aquatic systems—Method and applications. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Lundin, E.J.; Giesler, R.; et al. Emissions from thaw ponds largely offset the carbon sink of northern permafrost wetlands. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.; Kritskov, I.; Vorobyev, S.; Korets, M.; et al. Carbon emission and export from the Ket River, western Siberia. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 5859–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickov, I.; Serikova, S.; Pokrovsky, O.; et al. Sizable carbon emission from the floodplain of Ob River. Ecological Indicators 2021, 131, 108164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, S.N.; Karlsson, J.; Kolesnichenko, Y.Y.; et al. Fluvial carbon dioxide emission from the Lena River basin during the spring flood. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 4919–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabelina, S.; Shirokova, L.; Klimov, S.; Chupakov, A.; Lim, A.; et al. Carbon emission from thermokarst lakes in NE European tundra. Limnology and Oceanography 2020, 66, S216–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdova, O.Y.; et al. Organic Matter Transformation in the Conjugate Series of Surface Water in Northern Karelia. Water Resources 2019, 46, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, S.M.; Drozdova, O.Y.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; et al. Size fractionation and optical properties of dissolved organic matter in the continuum soil solution-bog-river and terminal lake of a boreal watershed. Organic Geochemistry 2014, 66, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, R.; Boyer, J.N.; Lu, X.; et al. Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Marine Chemistry 2004, 84, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J. Dissolved organic materials and its optical properties in a blackwater tributary of the upper Orinoco River, Venezuela. Organic Geochemistry 1998, 28, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, C.; Wang, M.; Xue, W.; et al. The carbon flux of global rivers: A re-evaluation of amount and spatial patterns. Ecological Indicators 2017, 80, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; et al. Plumbing the Global Carbon Cycle: Integrating Inland Waters into the Terrestrial Carbon Budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotin, S.N.; Kvasnikova, Z.N.; Potapova, S.A.; et al. Pilot Studies of the Unique Highland Palsa Mire in Western Sayan (Tuva Republic, Russian Federation). Atmosphere 2022, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.S.; Viers, J.; Dupre, B.; et al. Biogeochemistry of carbon, major and trace elements in watersheds of Northern Eurasia drained to the Arctic Ocean: The change of fluxes, sources and mechanisms under the climate warming prospective. Comptes Rendus Geoscience 2012, 344, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickov, I.; Lim, A.G.; Loiko, S.V.; et al. Major and trace elements in suspended matter of western Siberian rivers: First assessment across permafrost zones and landscape parameters of watersheds. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2020, 269, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagard, M.L.; Chabaux, F.; Stille, P.; et al. Seasonal variability of element fluxes in two Central Siberian rivers draining high latitude permafrost dominated areas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2011, 75, 3335–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasypov, R.M.; Vorobyev, S.N.; Loiko, S.V.; Kritzkov; et al. Seasonal dynamics of organic carbon and metals in thermokarst lakes from the discontinuous permafrost zone of western Siberia. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 3009–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.E.; McClelland, J.W. Impacts of permafrost degradation on arctic river biogeochemistry. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, S.; Parolari, A.J.; Porporato, A. Hydrologic Transport of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon and Its Control on Chemical Weathering. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface 2017, 122, 2016–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Joe, K.S.; Han, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Characteristics of dissolved organic carbon in the leachate from Moonam Sanitary Landfill. Environmental Technology 1999, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.H.S.; Aukes, P.; Schiff, S.L.; et al. The optical, chemical, and molecular dissolved organic matter succession along a boreal soil-stream-river continuum. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2017, 122, 2892–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirokova, L.S.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Kirpotin, S.N.; et al. Biogeochemistry of organic carbon, CO2, CH4, and trace elements in thermokarst water bodies in discontinuous permafrost zones of Western Siberia. Biogeochemistry 2013, 113, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payandi-Rolland, D.; Shirokova, L.S.; Nakhle, P.; et al. Aerobic release and biodegradation of dissolved organic matter from frozen peat: Effects of temperature and heterotrophic bacteria. Chemical Geology 2020, 536, 119448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payandi-Rolland, D.; Shirokova, L.S.; Lariux, J.; et al. Laboratory growth capacity of an invasive cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) on organic substrates from surface waters of permafrost peatlands. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts 2023, 25, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; et al. Determining whether Qinghai–Tibet Plateau waterbodies have acted like carbon sinks or sources over the past 20 years. Science Bulletin 2022, 67, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. In-situ measurement on air–water flux of CH4, CO2 and their carbon stable isotope in lakes of northeast Tibetan Plateau. Advances in Climate Change Research 2022, 13, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; et al. Organic versus Inorganic Carbon Exports from Glacier and Permafrost Watersheds in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Aquat Geochem 2021, 27, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurischat, P.; Lehnert, L.; Zerres, H.D.V.; et al. The glacial–terrestrial–fluvial pathway: A multiparametrical analysis of spatiotemporal dissolved organic matter variation in three catchments of Lake Nam Co, Tibetan Plateau. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 838, 156542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.D.; You, C.F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Hydrological and solute budgets of Lake Qinghai, the largest lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary International 2010, 218, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.X.; Li, Y.; Zhai, C.X.; et al. CO2 absorption by alkaline soils and its implication to the global carbon cycle. Environmental Geology 2009, 56, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubyatnikov, L.; Kurganova, I.N.; lopes de Gerenyu, V. Estimation of C-CO2 balance of natural steppe ecosystems: Khakassia and Tuva (Eastern Siberia, Russia) case studies. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2020, 606, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Serikova, S.; Rocher-Ros, G.; Denfeld, B.; Voorbyev, S.N.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Carbon emission from Western Siberian inland waters. Nature Communication 2021, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).