Submitted:
31 August 2023
Posted:
01 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Molecular Analysis
3. Results
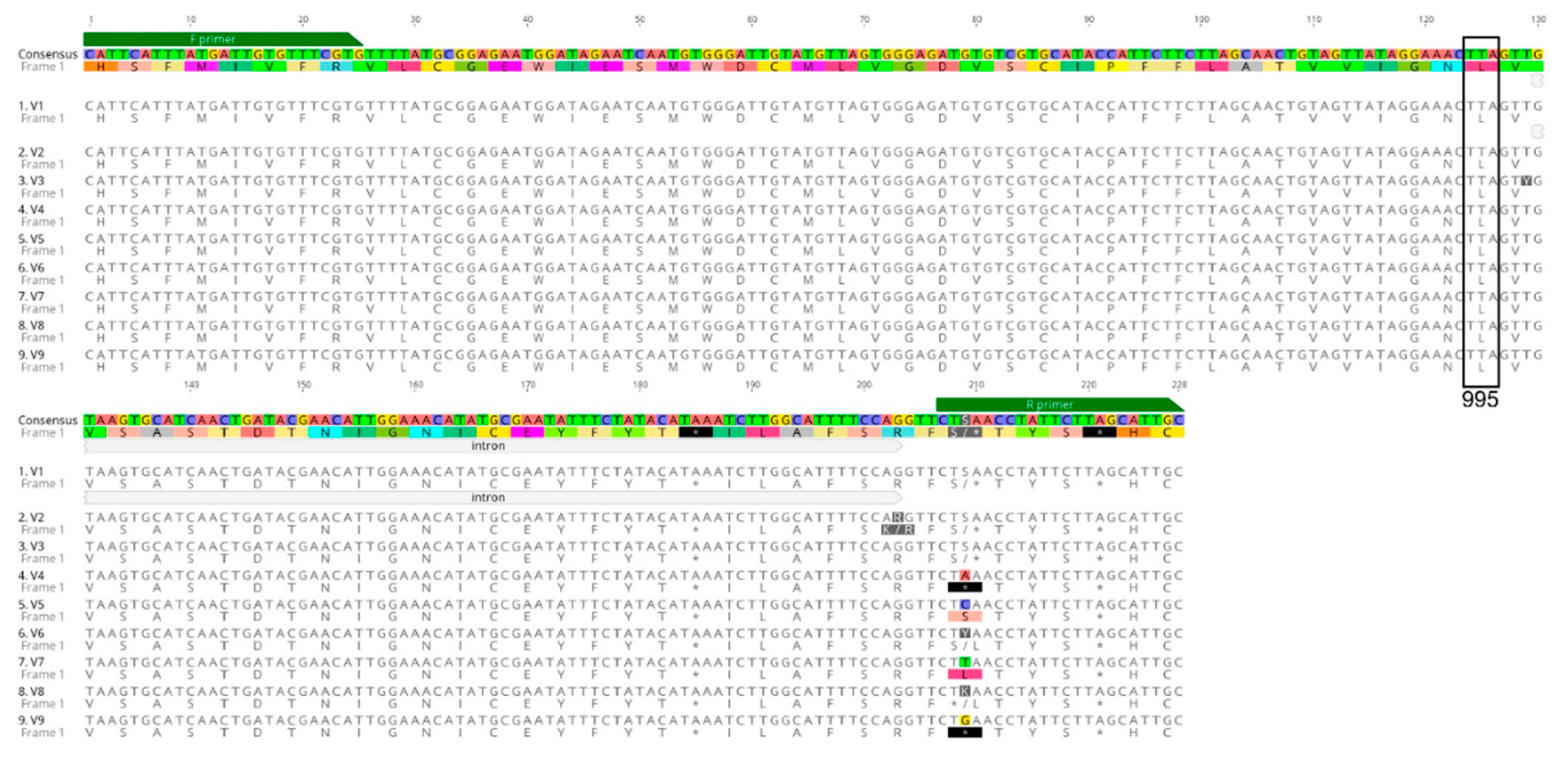
3.1. Detection of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel (VGSC) Mutations
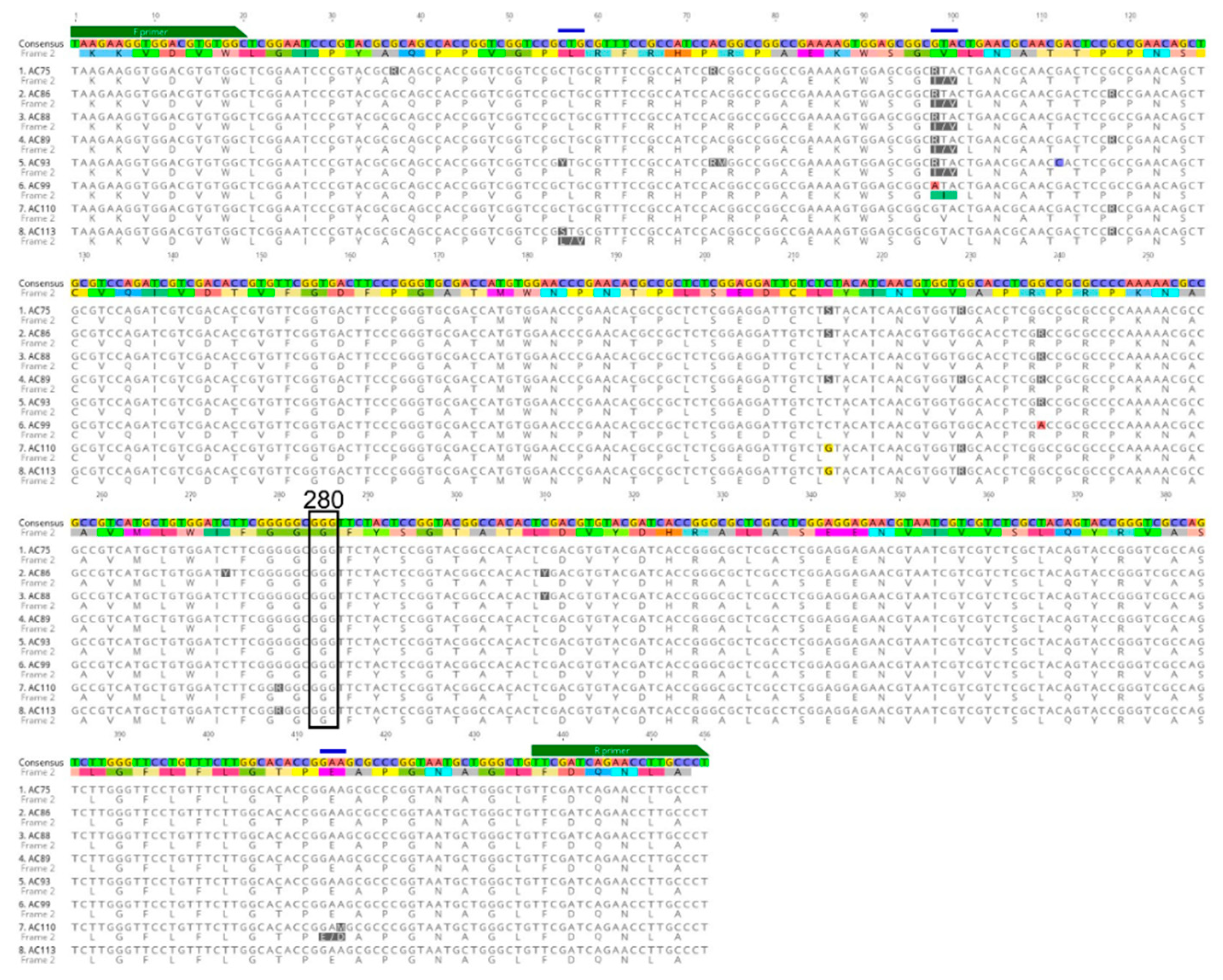
3.2. Detection of Acetylcholinesterase-1 (Ace-1) Mutations
3.3. Data Management
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Alexander, N.; Rodríguez, M.; Pérez, L.; Caicedo, J.C.; Cruz, J.; Prieto, G.; Arroyo, J.A.; Cotacio, M.C.; Suárez, M.; F, D.L.H.; et al. Case-control study of mosquito nets against malaria in the Amazon region of Colombia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrard-Smith, E.; Skarp, J.E.; Beale, A.D.; Fornadel, C.; Norris, L.C.; Moore, S.J.; Mihreteab, S.; Charlwood, J.D.; Bhatt, S.; Winskill, P.; et al. Mosquito feeding behavior and how it influences residual malaria transmission across Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2019, 116, 15086–15095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.S.; Paredes Olortegui, M.; Penataro Yori, P.; Escobedo, K.; Florin, D.; Rengifo Pinedo, S.; Cardenas Greffa, R.; Capcha Vega, L.; Rodriguez Ferrucci, H.; Pan, W.K.; et al. Hyperendemic malaria transmission in areas of occupation-related travel in the Peruvian Amazon. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Escobar, G.; Gamboa, D.; Castro, M.C.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Rodriguez, H.; Contreras-Mancilla, J.; Alava, F.; Speybroeck, N.; Lescano, A.G.; Vinetz, J.M.; et al. Micro-epidemiology and spatial heterogeneity of P. vivax parasitaemia in riverine communities of the Peruvian Amazon: A multilevel analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.E.; Rubio-Palis, Y.; Paez, E.; Perez, E.; Sanchez, V. Abundance, biting behaviour and parous rate of anopheline mosquito species in relation to malaria incidence in gold-mining areas of southern Venezuela. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2007, 21, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Saavedra, M.P.; Bickersmith, S.A.; Lainhart, W.; Tong, C.; Alava, F.; Vinetz, J.M.; Conn, J.E. Implications for changes in Anopheles darlingi biting behaviour in three communities in the peri-Iquitos region of Amazonian Peru. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durnez, L.; Coosemans, M. Residual transmission of malaria: an old issue for new approaches. In Anopheles mosquitoes—new insights into malaria vectors; Manguin, S., Ed.; Intech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 671–704. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, J.O.; de Albuquerque, B.C.; Coura, J.R.; Suárez-Mutis, M.C. Use and retention of long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) in a malaria risk area in the Brazilian Amazon: a 5-year follow-up intervention. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Calle, V.; Rosas-Aguirre, A.; Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Abatih, E.; DeDeken, R.; Rodriguez, H.; Rosanas-Urgell, A.; Gamboa, D.; Alessandro, U.D.; Erhart, A.; et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of malaria incidence in the Peruvian Amazon Region between 2002 and 2013. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World malaria report 2021. 2021, 322.
- Gabaldón-Figueira, J.C.; Villegas, L.; Grillet, M.E.; Lezaun, J.; Pocaterra, L.; Bevilacqua, M.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; González, O.N.; Chaccour, C. Malaria in Venezuela: Gabaldón’s legacy scattered to the winds. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e584–e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud. Documento technico: plan hacia la malaria en el Peru 2022-2030. 2022, 60.
- World Health Organization. World malaria report 2020: 20 years of global progress and challenges. 2020, 247.
- Şengül Demirak, M.; Canpolat, E. Plant-based bioinsecticides for mosquito control: impact on insecticide resistance and disease transmission. Insects 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orjuela, L.I.; Álvarez-Diaz, D.A.; Morales, J.A.; Grisales, N.; Ahumada, M.L.; Venegas, H.J.; Quiñones, M.L.; Yasnot, M.F. Absence of knockdown mutations in pyrethroid and DDT resistant populations of the main malaria vectors in Colombia. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, M.L.; Norris, D.E.; Conn, J.E.; Moreno, M.; Burkot, T.R.; Bugoro, H.; Keven, J.B.; Cooper, R.; Yan, G.; Rosas, A.; et al. Insecticide resistance in areas under investigation by the International Centers of Excellence for Malaria Research: A challenge for malaria control and elimination. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lol, J.C.; Castañeda, D.; Mackenzie-Impoinvil, L.; Romero, C.G.; Lenhart, A.; Padilla, N.R. Development of molecular assays to detect target-site mechanisms associated with insecticide resistance in malaria vectors from Latin America. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baia-da-Silva, D.C.; Brito-Sousa, J.D.; Rodovalho, S.R.; Peterka, C.; Moresco, G.; Lapouble, O.M.M.; Melo, G.C.; Sampaio, V.S.; Alecrim, M.; Pimenta, P.; et al. Current vector control challenges in the fight against malaria in Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwat, H.; Bretas, G. Ecology of Anopheles darlingi Root with respect to vector importance: a review. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Test procedures for insecticide resistance monitoring in malaria vectors, bio-efficacy and persistence of insecticides on treated surfaces : report of the WHO informal consultation. 1998, 43.
- Lenhart, A.; Chan, A.; Vizcaino, L.; Brogdon, W. Manual for evaluating insecticide resistance using the CDC bottle bioassay. 2023, 31.
- Brogdon, W.; Chan, A. Guideline for evaluating insecticide resistance in vectors using the CDC bottle bioassay. 2011, 28.
- World Health Organization. Global report on insecticide resistance in malaria vectors: 2010–2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, D.; Lefèvre, T.; Moiroux, N.; Pennetier, C.; Chandre, F.; Cohuet, A. Behavioural adaptations of mosquito vectors to insecticide control. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 34, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panini, M.; Manicardi, G.C.; Moores, G.D.; Mazzoni, E. An overview of the main pathways of metabolic resistance in insects. Invertebrate Surviv. J. 2016, 13, 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- Vontas, J.; Katsavou, E.; Mavridis, K. Cytochrome P450-based metabolic insecticide resistance in Anopheles and Aedes mosquito vectors: Muddying the waters. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 170, 104666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, M.; Lutfalla, G.; Mogensen, K.; Chandre, F.; Berthomieu, A.; Berticat, C.; Pasteur, N.; Philips, A.; Fort, P.; Raymond, M. Insecticide resistance in mosquito vectors. Nature 2003, 423, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.G.; Field, L.M.; Usherwood, P.N.; Williamson, M.S. DDT, pyrethrins, pyrethroids and insect sodium channels. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E.R.; Rockett, K.A.; Lynd, A.; Essandoh, J.; Grisales, N.; Kemei, B.; Njoroge, H.; Hubbart, C.; Rippon, E.J.; Morgan, J.; et al. A high throughput multi-locus insecticide resistance marker panel for tracking resistance emergence and spread in Anopheles gambiae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveron, J.M.; Tchouakui, M.; Mugenzi, L.; Menze, B.D.; Chiang, M.-C.; Wondji, C.S. Insecticide resistance in malaria vectors: an update at a global scale. In Towards Malaria Elimination; Sylvie, M., Vas, D., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.P.; Santos, J.M.; Martins, A.J. Mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channel gene of anophelines and their association with resistance to pyrethroids - a review. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridis, K.; Wipf, N.; Müller, P.; Traoré, M.M.; Muller, G.; Vontas, J. Detection and monitoring of insecticide resistance mutations in Anopheles gambiae: individual vs pooled specimens. Genes 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisinza, W.; Kabula, B.; Tungu, P.; Sindato, C.; Mweya, C.; Massue, D.; Emidi, B.; Kitau, J.; Chacha, M.; Batengana, B.; et al. Detection and monitoring of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors in Tanzania mainland; Technical Report of the National Institute for Medical Research, Tanzania: Muheza, Tanzania, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Malaria threats map. Available online: http://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/surveillance/malaria-threats-map (accessed on June 13).
- Berman, H.B. Stat Trek: random number generator. Available online: http://stattrek.com/statistics/random-number-generator.aspx (accessed on January 21).
- Prussing, C.; Moreno, M.; Saavedra, M.P.; Bickersmith, S.A.; Gamboa, D.; Alava, F.; Schlichting, C.D.; Emerson, K.J.; Vinetz, J.M.; Conn, J.E. Decreasing proportion of Anopheles darlingi biting outdoors between long-lasting insecticidal net distributions in peri-Iquitos, Amazonian Peru. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporta, G.Z.; Ilacqua, R.C.; Bergo, E.S.; Chaves, L.S.M.; Rodovalho, S.R.; Moresco, G.G.; Figueira, E.A.G.; Massad, E.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Bickersmith, S.A.; et al. Malaria transmission in landscapes with varying deforestation levels and timelines in the Amazon: a longitudinal spatiotemporal study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallum, M.A.M.; Conn, J.E.; Bergo, E.S.; Laporta, G.Z.; Chaves, L.S.M.; Bickersmith, S.A.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Figueira, E.A.G.; Moresco, G.; Olívêr, L.; et al. Vector competence, vectorial capacity of Nyssorhynchus darlingi and the basic reproduction number of Plasmodium vivax in agricultural settlements in the Amazonian Region of Brazil. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, A.C.; Araki, A.S.; Bruno, R.V.; Lima, J.B.P.; Ladeia-Andrade, S.; Santacoloma, L.; Martins, A.J. Molecular diversity of genes related to biological rhythms (period and timeless) and insecticide resistance (Na V and ace-1) in Anopheles darlingi. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2023, 118, e220159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lol, J.C.; Castellanos, M.E.; Liebman, K.A.; Lenhart, A.; Pennington, P.M.; Padilla, N.R. Molecular evidence for historical presence of knock-down resistance in Anopheles albimanus, a key malaria vector in Latin America. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie-Impoinvil, L.; Weedall, G.D.; Lol, J.C.; Pinto, J.; Vizcaino, L.; Dzuris, N.; Riveron, J.; Padilla, N.; Wondji, C.; Lenhart, A. Contrasting patterns of gene expression indicate differing pyrethroid resistance mechanisms across the range of the New World malaria vector Anopheles albimanus. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0210586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, T.A.; Loureiro, A.C.; Lima, J.B.P.; Martins, A.J. Insecticide resistance in Anopheles albitarsis s.s. from a rice production field, with the first record of Kdr mutation. Research Square 2021 preprint. [CrossRef]
- Alimi, T.O.; Fuller, D.O.; Quinones, M.L.; Xue, R.D.; Herrera, S.V.; Arevalo-Herrera, M.; Ulrich, J.N.; Qualls, W.A.; Beier, J.C. Prospects and recommendations for risk mapping to improve strategies for effective malaria vector control interventions in Latin America. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floch, H. [Antimalarial campaign in French Guiana. III. DDT campaigns and their results]. Riv. Malariol. 1955, 34, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angella, A.F.; Gil, L.H.; Silva, L.H.; Ribolla, P.E. Population structure of the malaria vector Anopheles darlingi in Rondonia, Brazilian Amazon, based on mitochondrial DNA. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2007, 102, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, H. Current and future prospects for preventing malaria transmission via the use of insecticides. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souris, M.; Marcombe, S.; Laforet, J.; Brey, P.T.; Corbel, V.; Overgaard, H.J. Modeling spatial variation in risk of presence and insecticide resistance for malaria vectors in Laos. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0177274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelo-Matubi, E.; Zanga, J.; Binene, G.; Mvuama, N.; Ngamukie, S.; Nkey, J.; Schopp, P.; Bamba, M.; Irish, S.; Nguya-Kalemba-Maniania, J.; et al. The effect of a mass distribution of insecticide-treated nets on insecticide resistance and entomological inoculation rates of Anopheles gambiae s.l. in Bandundu City, Democratic Repub`lic of Congo. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 40, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanou, A.; Nelli, L.; Guelbéogo, W.M.; Cissé, F.; Tapsoba, M.; Ouédraogo, P.; Sagnon, N.; Ranson, H.; Matthiopoulos, J.; Ferguson, H.M. Insecticide resistance and behavioural adaptation as a response to long-lasting insecticidal net deployment in malaria vectors in the Cascades region of Burkina Faso. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangbakembi-Ngounou, C.; Costantini, C.; Longo-Pendy, N.M.; Ngoagouni, C.; Akone-Ella, O.; Rahola, N.; Cornelie, S.; Kengne, P.; Nakouné, E.R.; Komas, N.P.; et al. Diurnal biting of malaria mosquitoes in the Central African Republic indicates residual transmission may be “out of control”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2022, 119, e2104282119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezenegho, S.B.; Adde, A.; Pommier de Santi, V.; Issaly, J.; Carinci, R.; Gaborit, P.; Dusfour, I.; Girod, R.; Briolant, S. High malaria transmission in a forested malaria focus in French Guiana: How can exophagic Anopheles darlingi thwart vector control and prevention measures? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.; Skelton, J.; de Wildt, G.; Meza, G. A qualitative study on the use of long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) for the prevention of malaria in the Peruvian Amazon. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, L.S.M.; Bergo, E.S.; Conn, J.E.; Laporta, G.Z.; Prist, P.R.; Sallum, M.A.M. Anthropogenic landscape decreases mosquito biodiversity and drives malaria vector proliferation in the Amazon rainforest. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0245087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, D.; Ascencio, K.; Ortiz, A.; Palma, A.; Fontecha, G. Distribution and phylogenetic diversity of Anopheles species in malaria endemic areas of Honduras in an elimination setting. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, E.; Dusfour, I.; Lacour, G.; Saldanha, R.; Guidez, A.; Gomes, M.S.; Sanna, A.; Epelboin, Y.; Restrepo, J.; Davy, D.; et al. Resurgence risk for malaria, and the characterization of a recent outbreak in an Amazonian border area between French Guiana and Brazil. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusfour, I.; Carinci, R.; Issaly, J.; Gaborit, P.; Girod, R. A survey of adult anophelines in French Guiana: enhanced descriptions of species distribution and biting responses. J. Vector Ecol. 2013, 38, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier de Santi, V.; Dusfour, I.; de Parseval, E.; Lespinet, B.; Nguyen, C.; Gaborit, P.; Carinci, R.; Hyvert, G.; Girod, R.; Briolant, S. Risk of daytime transmission of malaria in the French Guiana rain forest. Medecine et sante tropicales 2017, 27, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwat, H.; Issaly, J.; Gaborit, P.; Somai, A.; Samjhawan, A.; Sardjoe, P.; Soekhoe, T.; Girod, R. Behavioral heterogeneity of Anopheles darlingi (Diptera: Culicidae) and malaria transmission dynamics along the Maroni River, Suriname, French Guiana. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, K.A.; Pinto, J.; Valle, J.; Palomino, M.; Vizcaino, L.; Brogdon, W.; Lenhart, A. Novel mutations on the ace-1 gene of the malaria vector Anopheles albimanus provide evidence for balancing selection in an area of high insecticide resistance in Peru. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.C.; McKenzie, F.E. The contribution of agricultural insecticide use to increasing insecticide resistance in African malaria vectors. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaïbou, M.S.; Fodjo, B.K.; Fokou, G.; Allassane, O.F.; Koudou, B.G.; David, J.P.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Ranson, H.; Bonfoh, B. Influence of the agrochemicals used for rice and vegetable cultivation on insecticide resistance in malaria vectors in southern Côte d’Ivoire. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.W.; Tren, R. Implications of public-health insecticide resistance and replacement costs for malaria control: challenges and policy options for endemic countries and donors. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2012, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, K.B.; Martins, A.J.; Rodovalho, C.M.; Bellinato, D.F.; Dias, L.D.S.; Macoris, M.; Andrighetti, M.T.M.; Lima, J.B.P.; Obara, M.T. Assessment of the susceptibility status of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) populations to pyriproxyfen and malathion in a nation-wide monitoring of insecticide resistance performed in Brazil from 2017 to 2018. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.P.; Lima, J.B.P.; Martins, A.J. Insecticide resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus Say, 1823 in Brazil: a review. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.L.; Fayal Ada, S.; Aguiar, A.E.; Vieira, D.B.; Póvoa, M.M. [Evaluation of the residual effect of pyrethroids on Anopheles in the Brazilian Amazon]. Rev. Saude Publica 2007, 41, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, A.; Galardo, A.K.R.; Lima, L.A.; Câmara, D.C.P.; Müller, J.N.; Barroso, J.F.S.; Lapouble, O.M.M.; Rodovalho, C.M.; Ribeiro, K.A.N.; Lima, J.B.P. Efficacy of insecticides used in indoor residual spraying for malaria control: an experimental trial on various surfaces in a “test house”. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamareddine, L. The biological control of the malaria vector. Toxins (Basel) 2012, 4, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
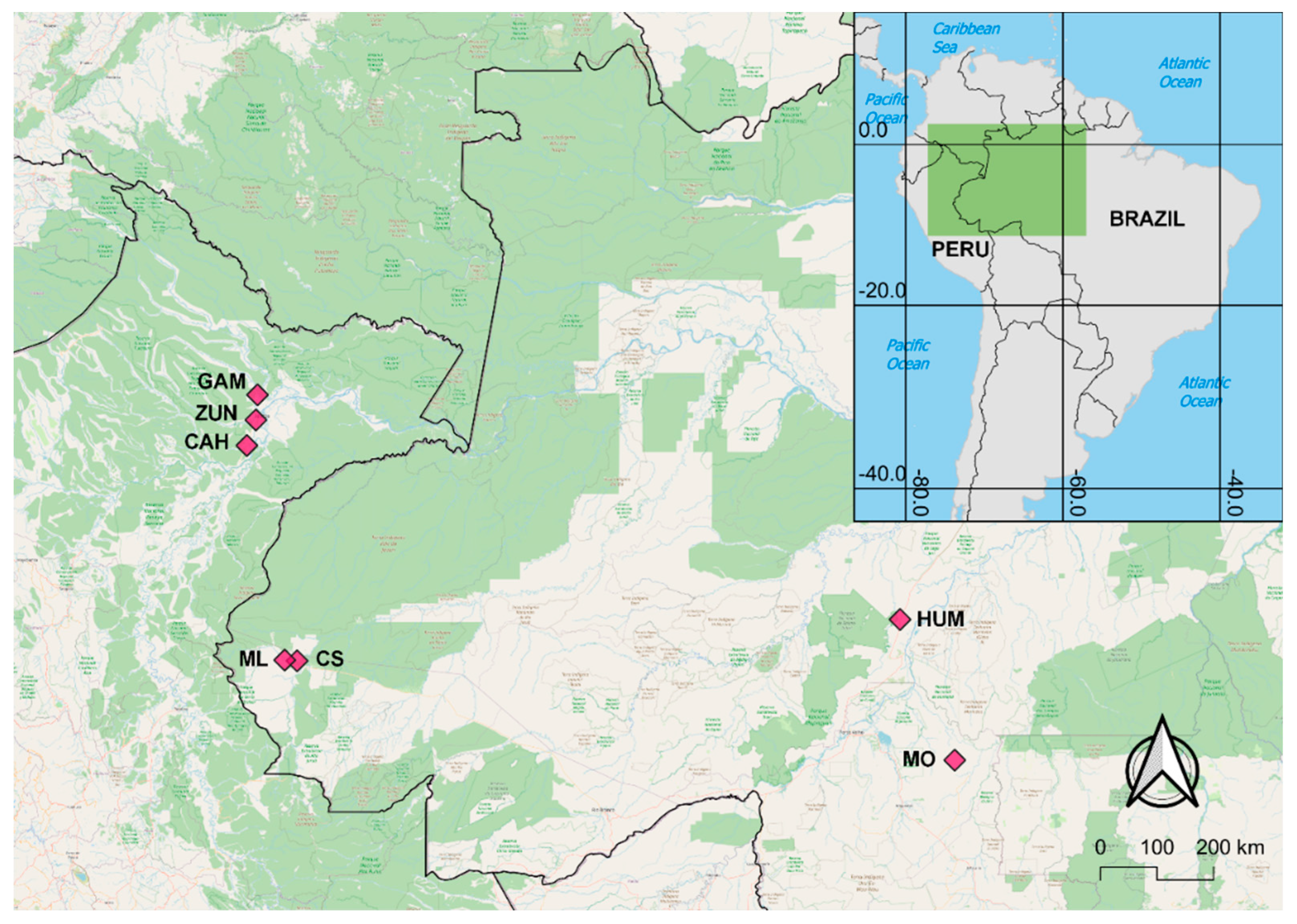
| Locality | State/Dept | Country | Latitude | Longitude | Collection year | Ace-1 N | VGSC N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cruzeiro do Sul (CS) | Acre | Brazil | -7.631889 | -72.688722 | 2015 | 49 | 50 |
| Humaitá (HUM) | Amazonas | Brazil | -6.980687 | -63.100031 | 2016 | 49 | 49 |
| Machadinho d’Oeste (MO) | Rondônia | Brazil | -9.193528 | -62.230107 | 2015 | 50 | 50 |
| Mâncio Lima (ML) | Acre | Brazil | -7.620124 | -72.885559 | 2015 | 50 | 50 |
| Gamitanacocha (GAM) | Loreto | Peru | -3.426000 | -73.318000 | 2018 | 50 | 50 |
| Zungarococha (ZUN) | Loreto | Peru | -3.824560 | -73.343880 | 2019; 2021 | 106 | 107 |
| Cahuide (CAH) | Loreto | Peru | -4.230350 | -73.487833 | 2014; 2019 | 139 | 139 |
| TOTAL | 493 | 495 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





