Submitted:
30 August 2023
Posted:
31 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
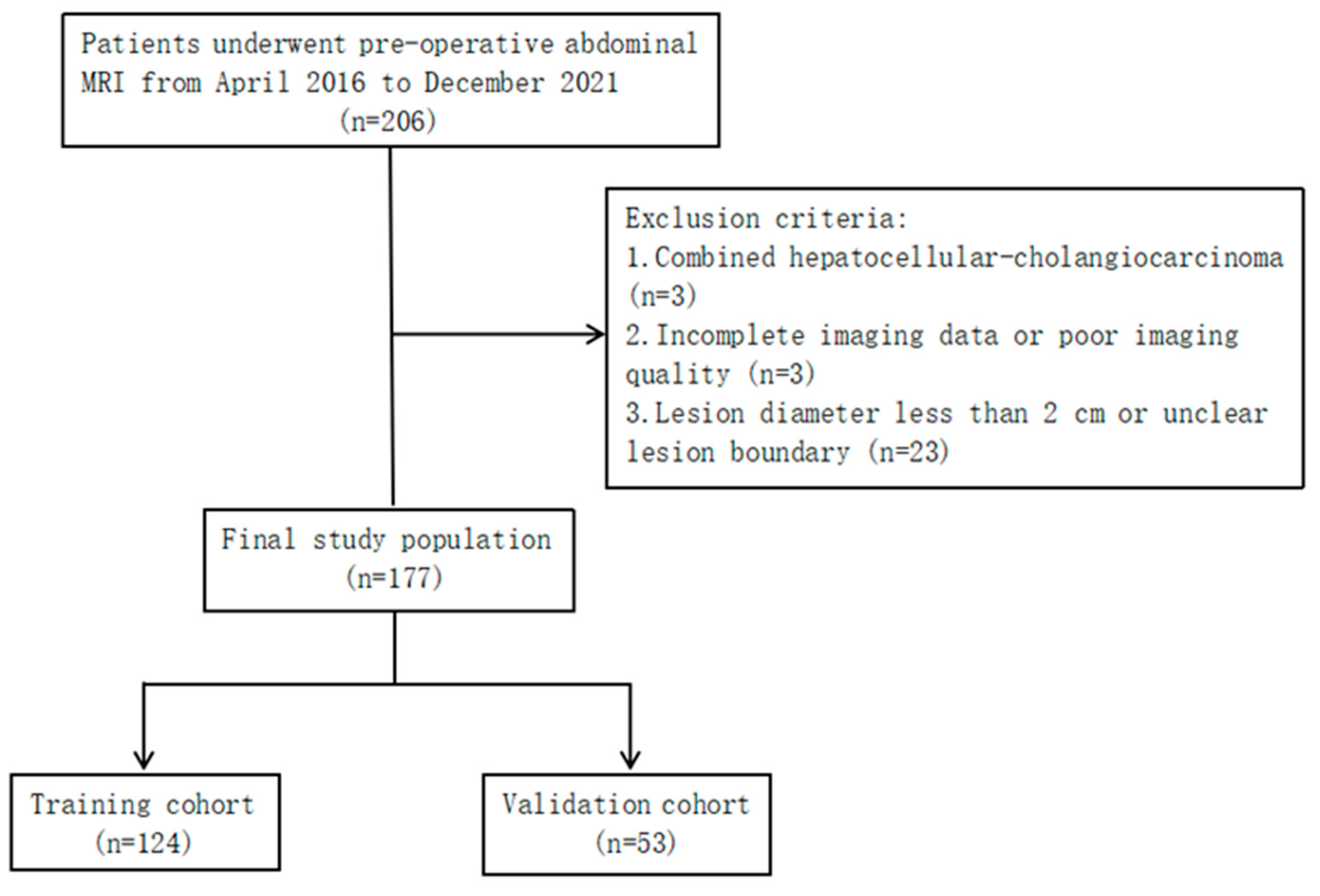
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Acquisition
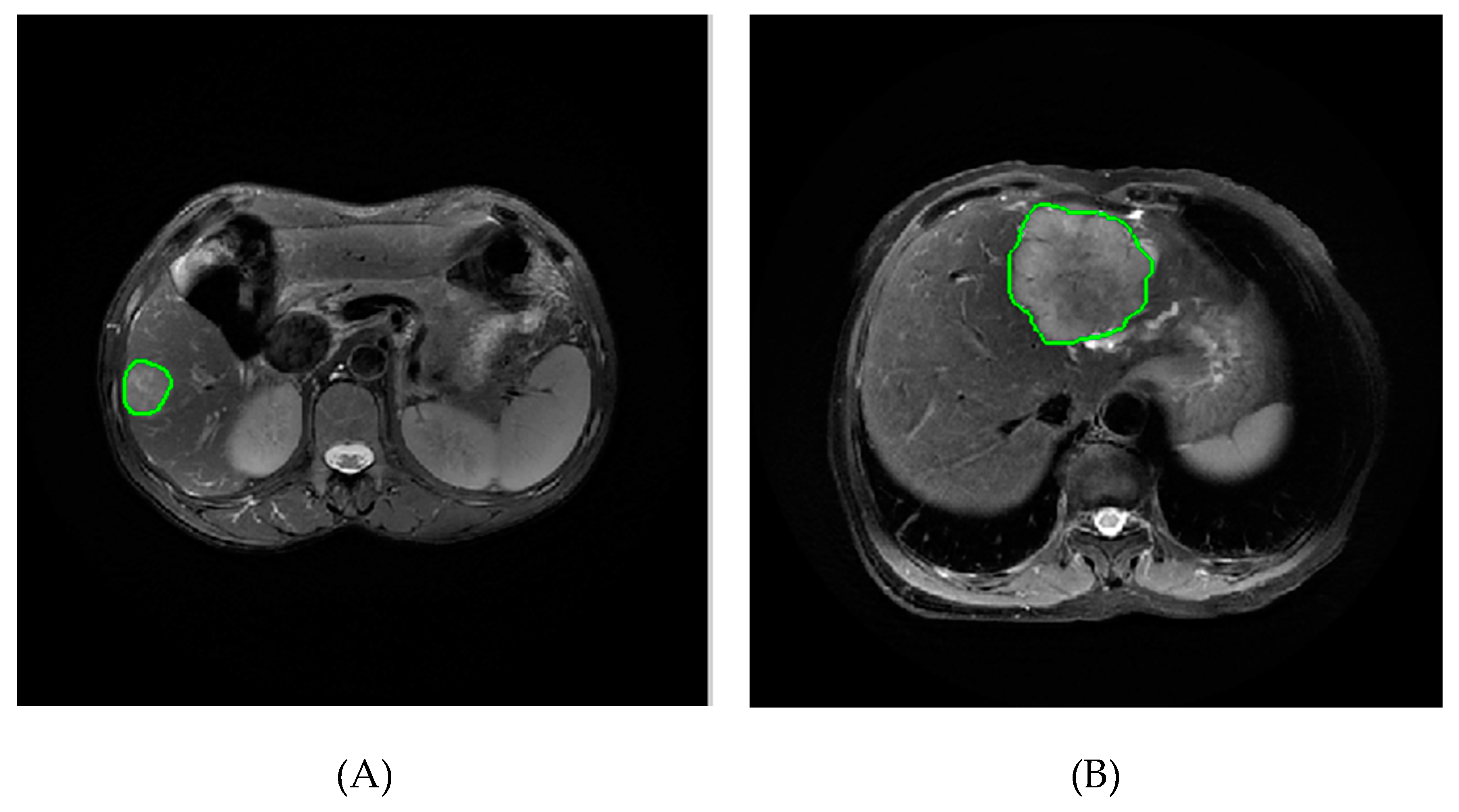
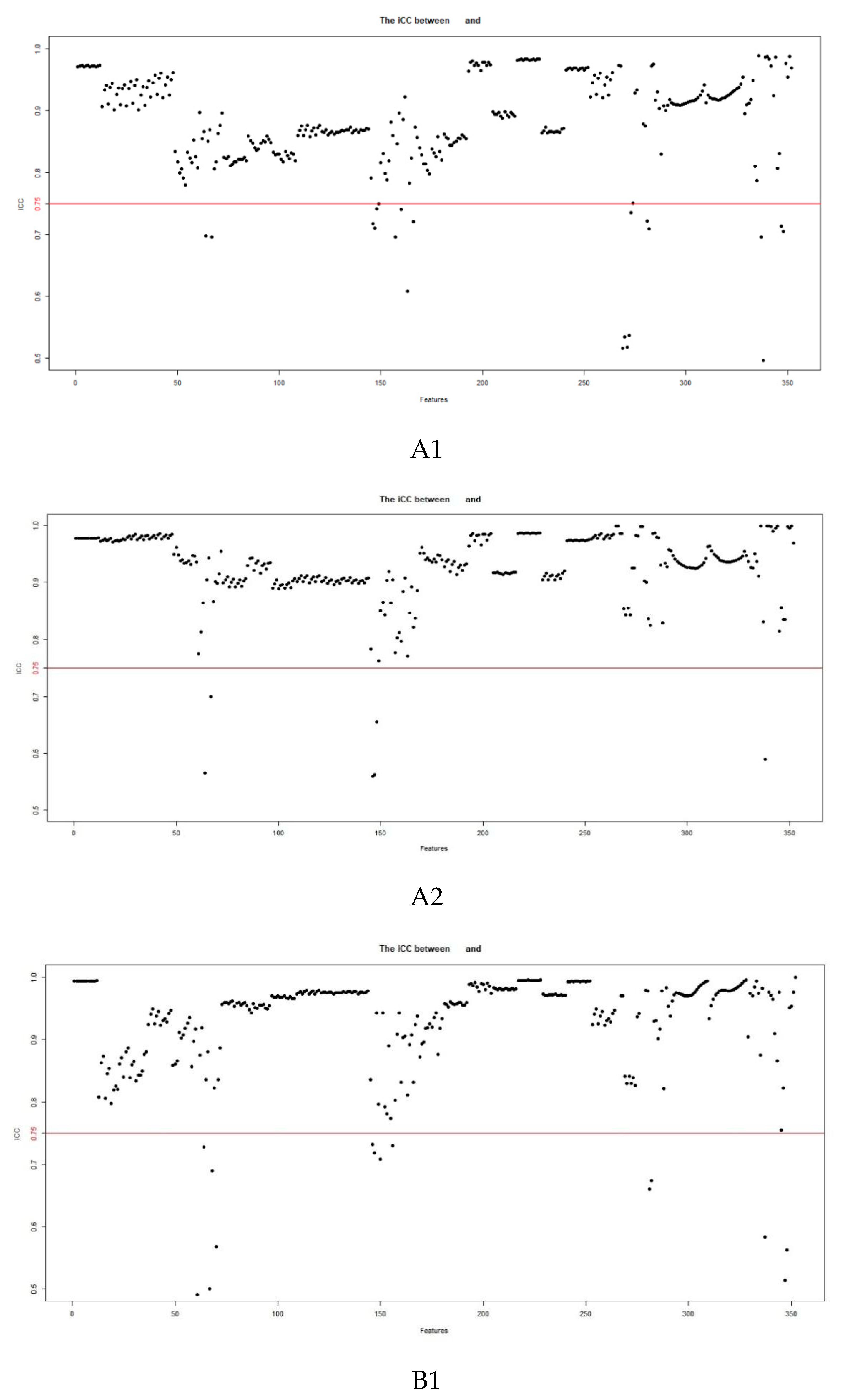
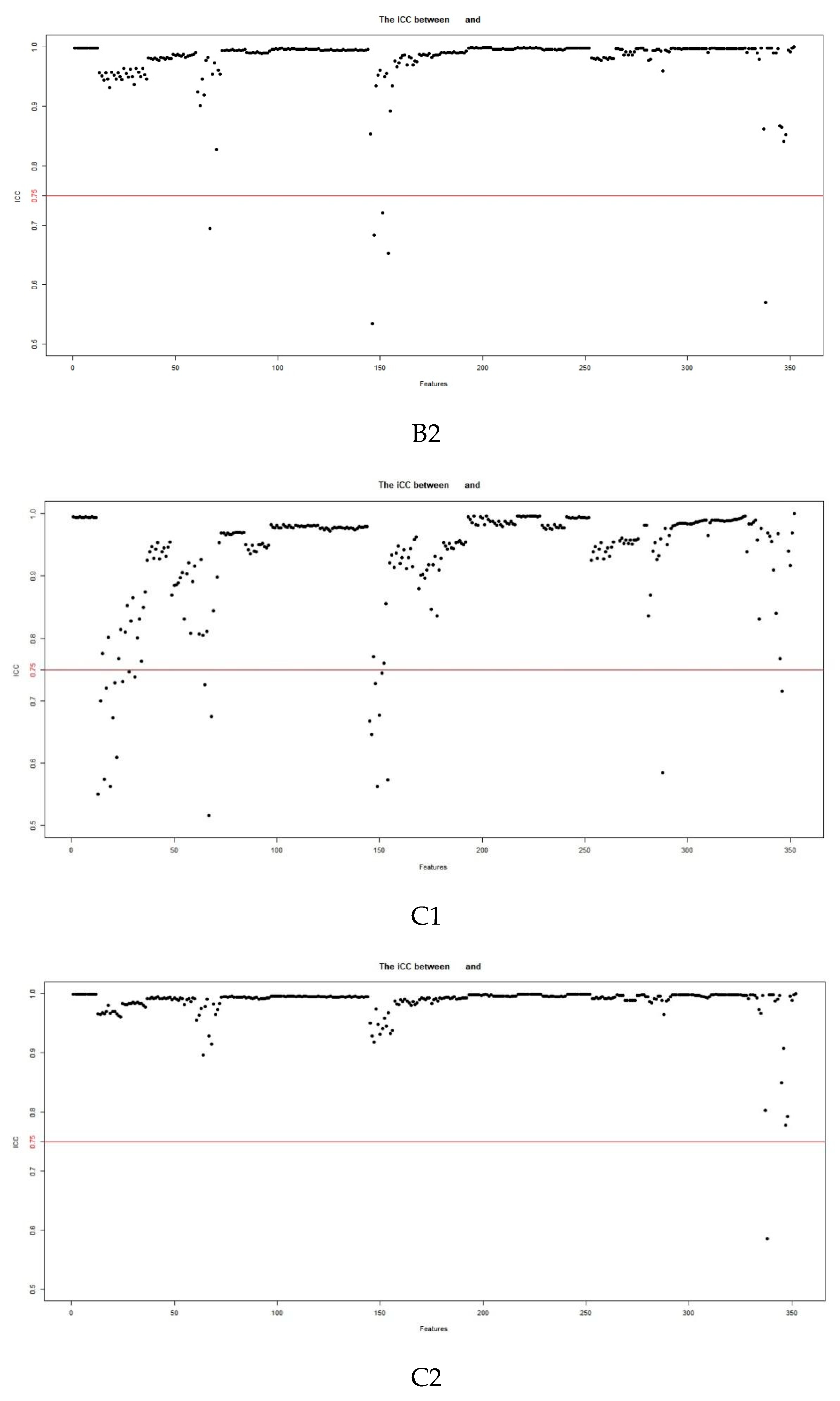
2.3. Image Segmentation and Feature Extraction
2.4. Feature Selection
2.5. Model Establishment and Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
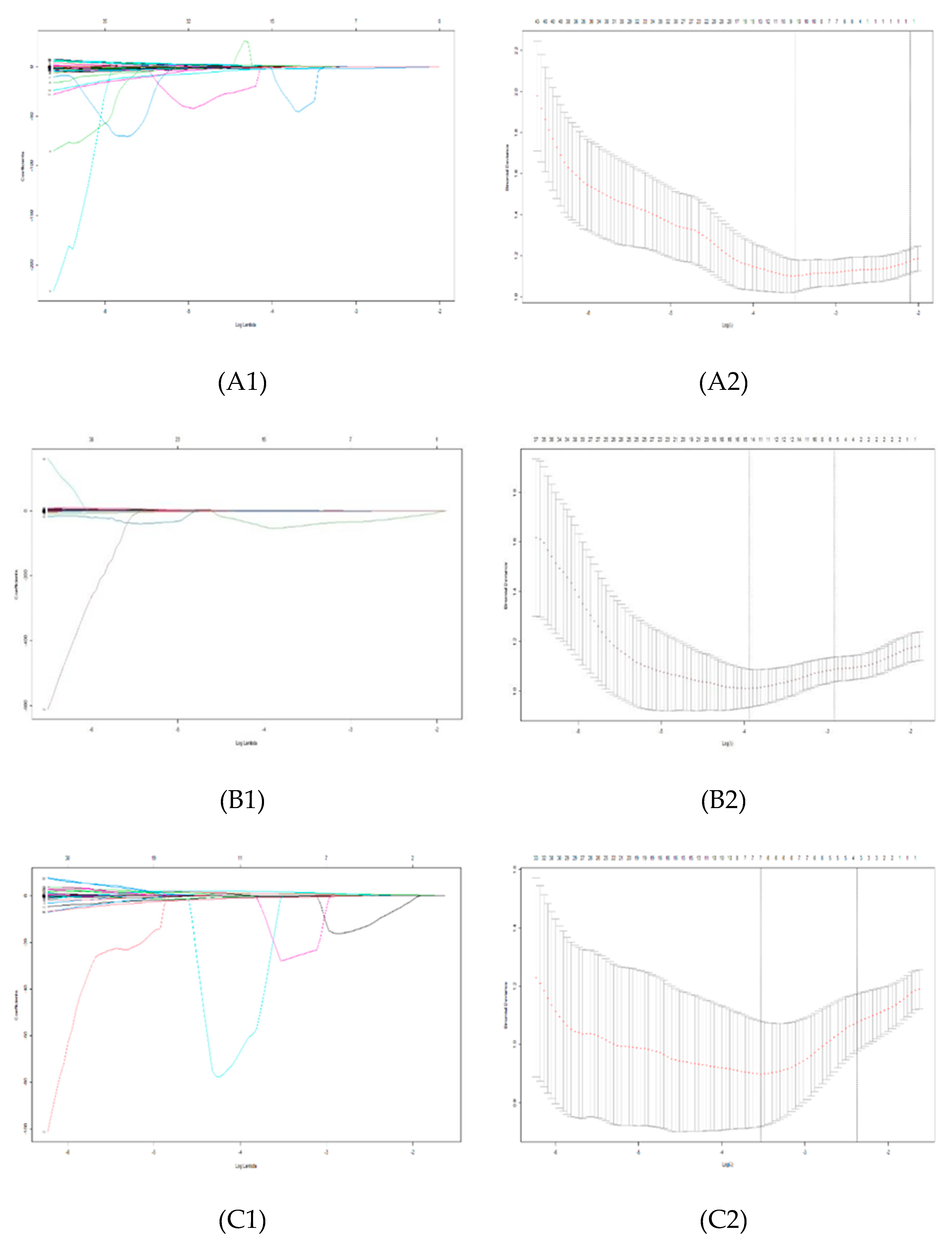
3.2. Feature Extraction and Selection
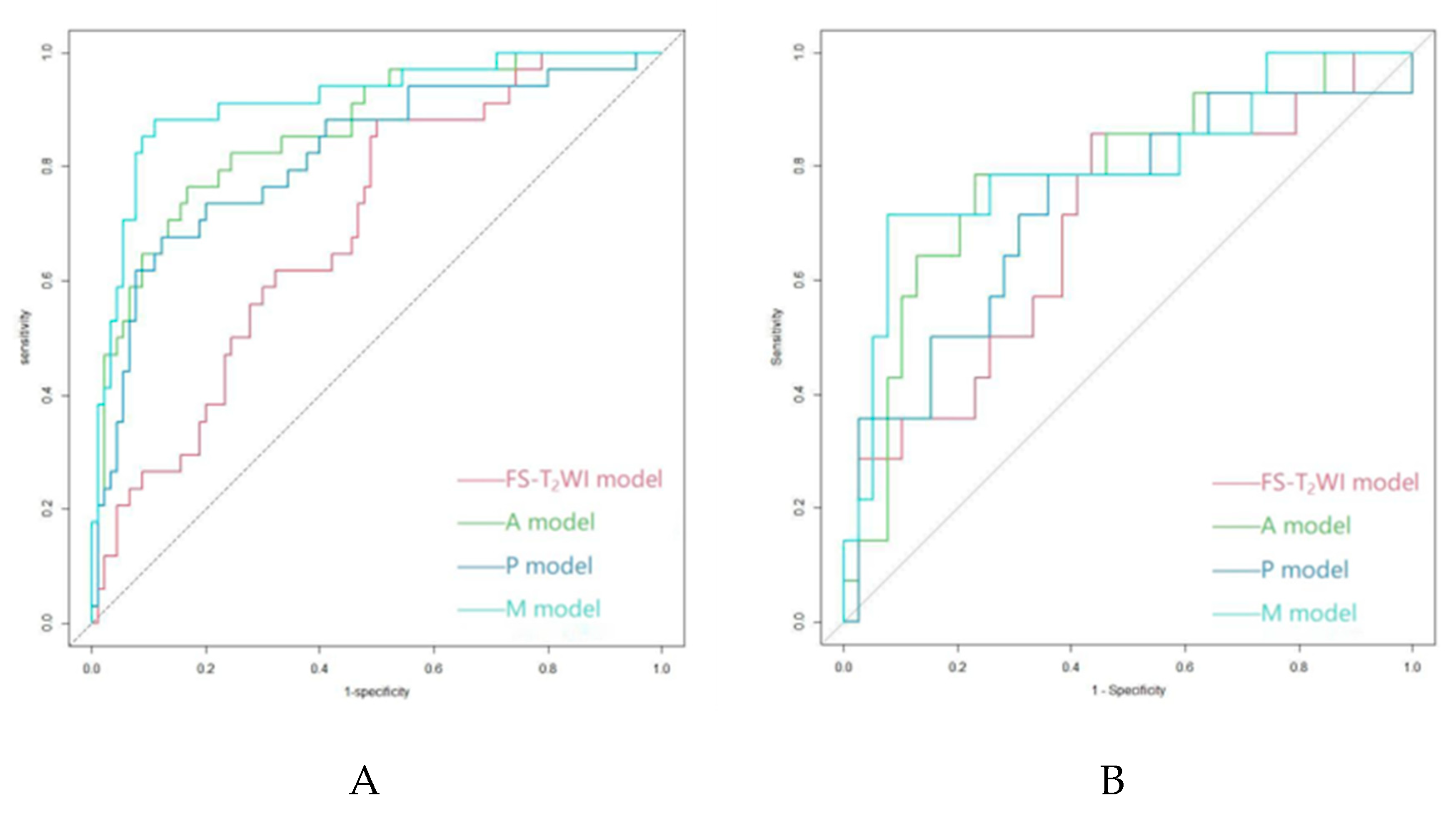
3.3. Model Establishment and Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2021,71(3):209-249. [CrossRef]
- Si Y, Wang X, Pan C, et al. An Efficient Nomogram for Discriminating Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma From Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Frontiers in oncology, 2022,12:833999. [CrossRef]
- Cheng N, Khoo N, Chung A Y F, et al. Pre-operative Imaging Characteristics in Histology-Proven Resected Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. World journal of surgery, 2020,44(11):3862-3867. [CrossRef]
- Florio A A, Ferlay J, Znaor A, et al. Global trends in intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma incidence from 1993 to 2012. Cancer, 2020,126(11):2666-2678. [CrossRef]
- Saha S K, Zhu A X, Fuchs C S, et al. Forty-Year Trends in Cholangiocarcinoma Incidence in the U.S.: Intrahepatic Disease on the Rise. The oncologist, 2016,21(5):594-599. [CrossRef]
- Valle J W, Borbath I, Khan S A, et al. Biliary cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of oncology: official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 2016,27(suppl 5):v28-v37.
- Banales J M, Cardinale V, Carpino G, et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016,13(5):261-280. [CrossRef]
- Gupta A, Dixon E. Epidemiology and risk factors: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary surgery and nutrition, 2017,6(2):101-104. [CrossRef]
- Nart D, Ertan Y, Pala E E, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma arising in chronic viral hepatitis-associated cirrhosis: two transplant cases. Transplant Proc, 2008,40(10):3813-3815. [CrossRef]
- Kelley R K, Bridgewater J, Gores G J, et al. Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Journal of hepatology, 2020,72(2):353-363. [CrossRef]
- Banales J M, Iñarrairaegui M, Arbelaiz A, et al. Serum Metabolites as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 2019,70(2):547-562. [CrossRef]
- Buettner S, van Vugt J L, IJzermans J N, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: current perspectives. OncoTargets and therapy, 2017,10:1131-1142. [CrossRef]
- Liu W, Wang K, Bao Q, et al. Hepatic resection provided long-term survival for patients with intermediate and advanced-stage resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World journal of surgical oncology, 2016,14:62. [CrossRef]
- Weber S M, Ribero D, O'Reilly E M, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: expert consensus statement. HPB : the official journal of the International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association, 2015,17(8):669-680. [CrossRef]
- Spolverato G, Kim Y, Alexandrescu S, et al. Is Hepatic Resection for Large or Multifocal Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Justified? Results from a Multi-Institutional Collaboration. Annals of surgical oncology, 2015,22(7):2218-2225. [CrossRef]
- Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-Based Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Gastroenterology, 2016,150(4):835-853. [CrossRef]
- Huang D, Lin Q, Song J, et al. Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Serum CA199 in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Treated with CRT Followed by TME with Normal Pretreatment Carcinoembryonic Antigen Levels. Digestive surgery, 2021,38(1):24-29. [CrossRef]
- Qi F, Zhou A, Yan L, et al. The diagnostic value of PIVKA-II, AFP, AFP-L3, CEA, and their combinations in primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020,34(5):e23158. [CrossRef]
- Afshar M, Fletcher P, Bardoli A D, et al. Non-secretion of AFP and neutrophil lymphocyte ratio as predictors for survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib: a large UK cohort. Oncotarget, 2018,9(24):16988-16995. [CrossRef]
- Teng D, Wu K, Sun Y, et al. Significant increased CA199 levels in acute pancreatitis patients predicts the presence of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget, 2018,9(16):12745-12753. [CrossRef]
- Marrero J A, Kulik L M, Sirlin C B, et al. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 2018,68(2):723-750. [CrossRef]
- Lafaro K J, Cosgrove D, Geschwind J H, et al. Multidisciplinary Care of Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Updates in Management. Gastroenterology research and practice, 2015,2015:860861. [CrossRef]
- Hennedige T P, Neo W T, Venkatesh S K. Imaging of malignancies of the biliary tract- an update. Cancer imaging : the official publication of the International Cancer Imaging Society, 2014,14(1):14. [CrossRef]
- Liver E A F T, Cancer E O F R. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatology, 2012,56(4):908-943.
- Li R, Cai P, Ma K, et al. Dynamic enhancement patterns of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in cirrhosis on contrast-enhanced computed tomography: risk of misdiagnosis as hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep, 2016,6:26772. [CrossRef]
- Huang B, Wu L, Lu X, et al. Small Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers May Share Similar Enhancement Patterns at Multiphase Dynamic MR Imaging. Radiology, 2016,281(1):150-157. [CrossRef]
- Galassi M, Iavarone M, Rossi S, et al. Patterns of appearance and risk of misdiagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in cirrhosis at contrast enhanced ultrasound. Liver Int, 2013,33(5):771-779. [CrossRef]
- Iavarone M, Piscaglia F, Vavassori S, et al. Contrast enhanced CT-scan to diagnose intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Journal of hepatology, 2013,58(6):1188-1193. [CrossRef]
- Kim S J, Lee J M, Han J K, et al. Peripheral mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma in cirrhotic liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2007,189(6):1428-1434. [CrossRef]
- Hanna R F, Aguirre D A, Kased N, et al. Cirrhosis-associated hepatocellular nodules: correlation of histopathologic and MR imaging features. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc, 2008,28(3):747-769. [CrossRef]
- Choi S, Kim Y K, Min J H, et al. Added value of ancillary imaging features for differentiating scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. European radiology, 2018,28(6):2549-2560. [CrossRef]
- Chong Y S, Kim Y K, Lee M W, et al. Differentiating mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from atypical hepatocellular carcinoma using gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Clinical radiology, 2012,67(8):766-773. [CrossRef]
- Potretzke T A, Tan B R, Doyle M B, et al. Imaging Features of Biphenotypic Primary Liver Carcinoma (Hepatocholangiocarcinoma) and the Potential to Mimic Hepatocellular Carcinoma: LI-RADS Analysis of CT and MRI Features in 61 Cases American Journal of Roentgenology, 2016,207(1):25-31. [CrossRef]
- Losic B, Craig A J, Villacorta-Martin C, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity and clonal evolution in liver cancer. Nature communications, 2020,11(1):291. [CrossRef]
- Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis Eur J Cancer, 2012,48(4):441-446. [CrossRef]
- Tao Y, Shi Y, Gong X, et al. Radiomic Analysis Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Predicting PD-L2 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 2023,15(2). [CrossRef]
- Mao Q, Zhou M, Zhao Z, et al. Role of radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. World journal of gastroenterology, 2022,28(42):6002-6016. [CrossRef]
- Huang F, Liu X, Liu P, et al. The Application Value of MRI T2∗ WI Radiomics Nomogram in Discriminating Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022,2022:1-13. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Zhou G, Zhang J, et al. DCE-MRI based radiomics nomogram for preoperatively differentiating combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma from mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. European radiology, 2022,32(7):5004-5015. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Khalvati F, Namdar K, et al. Can machine learning radiomics provide pre-operative differentiation of combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma from hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma to inform optimal treatment planning? European Radiology, 2021,31(1):244-255. [CrossRef]
- Wang W, Gu D, Wei J, et al. A radiomics-based biomarker for cytokeratin 19 status of hepatocellular carcinoma with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. European radiology, 2020,30(5):3004-3014. [CrossRef]
- Mokrane F, Lu L, Vavasseur A, et al. Radiomics machine-learning signature for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with indeterminate liver nodules. European radiology, 2020,30(1):558-570. [CrossRef]
- Jeong W K, Jamshidi N, Felker E R, et al. Radiomics and radiogenomics of primary liver cancers Clinical and Molecular Hepatology, 2019,25(1):21-29. [CrossRef]
- Jiang H, Liu X, Chen J, et al. Man or machine? Prospective comparison of the version 2018 EASL, LI-RADS criteria and a radiomic odel to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Imaging, 2019,19(1):84.
- Hectors S J, Lewis S, Besa C, et al. MRI radiomics features predict immuno-oncological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. European radiology, 2020,30(7):3759-3769. [CrossRef]
- Chen S, Feng S, Wei J, et al. Pretreatment prediction of immunoscore in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics-based clinical model based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI imaging European Radiology, 2019,29(8):4177-4187.
- Yang L, Gu D, Wei J, et al. A Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver cancer, 2019,8(5):373-386. [CrossRef]
- Nebbia G, Zhang Q, Arefan D, et al. Pre-operative Microvascular Invasion Prediction Using Multi-parametric Liver MRI Radiomics. Journal of digital imaging, 2020,33(6):1376-1386. [CrossRef]
- Ji G, Zhu F, Xu Q, et al. Machine-learning analysis of contrast-enhanced CT radiomics predicts recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: A multi-institutional study. EBioMedicine, 2019,50:156-165. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Long L, Cui Y, et al. MRI-based radiomic odel for preoperative prediction of 5-year survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. British journal of cancer, 2020,122(7):978-985. [CrossRef]
- Lubner M G, Smith A D, Sandrasegaran K, et al. CT Texture Analysis: Definitions, Applications, Biologic Correlates, and Challenges. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc, 2017,37(5):1483-1503.
- Lambin P, Leijenaar R T H, Deist T M, et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 2017,14(12):749-762. [CrossRef]
- Eu E A F T, Live E A F T. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatology, 2018,69(1):182-236.
- Management consensus guideline for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2016 updated by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan yi zhi, 2018,117(5):381-403.
- Lee Y J, Lee J M, Lee J S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology, 2015,275(1):97-109.
- Liu X, Jiang H, Chen J, et al. Gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging outperformed multidetector computed tomography in diagnosing small hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Liver Transpl, 2017,23(12):1505-1518. [CrossRef]
- Choi S H, Lee S S, Kim S Y, et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis: Differentiation from Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Using Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR Imaging and Dynamic CT. Radiology, 2017,282(3):771-781. [CrossRef]
- Wei Y, Gao F, Zheng D, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the setting of HBV-related cirrhosis: Differentiation with hepatocellular carcinoma by using Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Oncotarget, 2018,9(8):7975-7983. [CrossRef]
- Lewis S, Peti S, Hectors S J, et al. Volumetric quantitative histogram analysis using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate HCC from other primary liver cancers. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2019,44(3):912-922. [CrossRef]
- Wei M, Lü L, Lin P, et al. Multiple cellular origins and molecular evolution of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer letters, 2016,379(2):253-261. [CrossRef]
- Peng J, Zheng J, Yang C, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging to differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Scientific reports, 2020,10(1):7717. [CrossRef]
- Choi I Y, Lee S S, Sung Y S, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging for characterizing focal hepatic lesions: Correlation with lesion enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2017,45(6):1589-1598. [CrossRef]
- Shao S, Shan Q, Zheng N, et al. Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion in Discriminating Hepatitis B Virus-Related Intrahepatic Mass-Forming Cholangiocarcinoma from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System v2018. Cancer biotherapy & radiopharmaceuticals, 2019,34(8):511-518. [CrossRef]
- Çelebi F, Yaghouti K, Cindil E, et al. The Role of 18F-FDG PET/MRI in the Assessment of Primary Intrahepatic Neoplasms. Academic radiology, 2021,28(2):189-198. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Wang S, Yin X, et al. MRI-based radiomics distinguish different pathological types of hepatocellular carcinoma. Computers in biology and medicine, 2022,141:105058. [CrossRef]
- Han X, Sun M, Wang M, et al. The enhanced T(2) star weighted angiography (ESWAN) value for differentiating borderline from malignant epithelial ovarian tumors. European journal of radiology, 2019,118:187-193. [CrossRef]
- Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith R D. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Preventive veterinary medicine, 2000,45(1-2):23-41. [CrossRef]
- Fahmy D, Alksas A, Elnakib A, et al. The Role of Radiomics and AI Technologies in the Segmentation, Detection, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cancers, 2022,14(24):6123. [CrossRef]
- Jiang C, Zhao L, Xin B, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomic analysis for classifying and predicting microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 2022,12(8):4135-4150. [CrossRef]
- Xu X, Mao Y, Tang Y, et al. Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Based on Radiomic Analysis Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022,2022:1-9.
- Ren S, Li Q, Liu S, et al. Clinical Value of Machine Learning-Based Ultrasomics in Preoperative Differentiation Between Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Multicenter Study. Frontiers in oncology, 2021,11:749137. [CrossRef]
- Peng Y, Lin P, Wu L, et al. Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Analysis for Preoperatively Predicting Different Histopathological Subtypes of Primary Liver Cancer. Frontiers in oncology, 2020,10:1646. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Huang Z, Cao L, et al. Differentiation combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma based on radiomics machine learning. Annals of translational medicine, 2020,8(4):119. [CrossRef]
- Gao R, Zhao S, Aishanjiang K, et al. Deep learning for differential diagnosis of malignant hepatic tumors based on multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT and clinical data. J Hematol Oncol, 2021,14(1):154. [CrossRef]
- Just, N. Improving tumour heterogeneity MRI assessment with histograms. British journal of cancer, 2014,111(12):2205-2213. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Chen W, Wu D, et al. Differentiation of mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from poorly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma: based on the multivariate analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography findings. Abdominal radiology (New York), 2016,41(5):978-989. [CrossRef]
| Sequence | TR/TE (ms) | FA (°) | Matrix (mm2) | FOV (mm2) | ST (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BH Ax LAVA-Flex | 4/2 | 12 | 260×192 | 320×320–360×360 | 2.6 |
| RTr Ax fs T2WI | 2,609/97 | 110 | 384×384 | 320×320–380×380 | 5 |
| BH Ax LAVA-Flex+C | 4/2 | 12 | 224×192 | 320×320–360×360 | 5 |
| Parameter | Training cohort (n=124) |
Validation cohort (n=53) |
P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex Male Female |
94 30 |
38 15 |
0.565 |
| Age ≤60 >60 |
78 46 |
32 21 |
0.751 |
| Satellite nodules Yes No |
47 77 |
18 35 |
0.618 |
| Diameter ≤5 >5 |
41 83 |
25 28 |
0.076 |
| Intrahepatic bile duct dilation Yes No |
31 93 |
14 39 |
0.843 |
| Ascites Yes No |
36 88 |
18 35 |
0.514 |
| Hemorrhagic necrosis Yes No Pseudocapsule Yes No |
86 38 26 98 |
31 22 11 42 |
0.162 0.975 |
| Extrahepatic metastases Yes No |
23 101 |
6 47 |
0.234 |
| Portal vein tumor thrombus Yes No |
35 89 |
18 35 |
0.445 |
| Cirrhosis Yes No |
83 41 |
38 15 |
0.533 |
| Hepatitis B or C Yes No |
90 34 |
39 14 |
0.891 |
| AFP (ng/mL) <20 20~400 >400 |
54 21 49 |
30 8 15 |
0.259 |
| DCP (mAU/mL) ≤27.8 >27.8 |
11 113 |
5 48 |
0.905 |
| CA19-9 (U/mL) ≤37 >37 |
68 56 |
24 29 |
0.244 |
| CEA (µg/L) ≤5 >5 |
80 44 |
32 21 |
0.601 |
| Histologic result HCC ICC |
90 34 |
39 14 |
0.891 |
| Cohort | Feature type | Feature name |
|---|---|---|
| FS-T2WI | Shape features (n=1) | Roundness |
| Arterial phase | Texture features (n=3) | |
| GLCM (n=1) | 45-7InverseDiffMomentNorm | |
| GLRLM (n=2) | 0LongRunEmphasis | |
| 90ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmpha | ||
| Intensity histogram features (n=1) | InterQuartileRange | |
| Shape features (n=2) | Mass | |
| Roundness | ||
| Portal vein phase | Texture features (n=2) | |
| GLCM (n=2) | 90-1Contrast | |
| 45-7InverseDiffMomentNorm | ||
| Intensity histogram features (n=2) | InterQuartileRange | |
| MeanAbsoluteDeviation |
| Cohort | Model | AUC | Sen | Spe | PPV | NPV | ACC | F1-score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | FS-T2WI model | 0.693 | 0.147 | 0.956 | 0.556 | 0.748 | 0.734 | 0.233 | ||
| A model | 0.863 | 0.588 | 0.933 | 0.769 | 0.857 | 0.839 | 0.667 | |||
| P model | 0.818 | 0.588 | 0.922 | 0.741 | 0.856 | 0.831 | 0.656 | |||
| M model | 0.914 | 0.706 | 0.922 | 0.774 | 0.892 | 0.863 | 0.738 | |||
| Validation | FS-T2WI model | 0.690 | 0.071 | 0.974 | 0.5 | 0.745 | 0.736 | 0.125 | ||
| A model | 0.784 | 0.571 | 0.897 | 0.667 | 0.854 | 0.811 | 0.615 | |||
| P model | 0.727 | 0.357 | 0.897 | 0.556 | 0.795 | 0.756 | 0.435 | |||
| M model | 0.802 | 0.571 | 0.923 | 0.727 | 0.857 | 0.83 | 0.640 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





